History of Christianity
| Part of a series of articles on Christianity | ||||||

| ||||||
|
Foundations Bible Christian theology History and traditions
Topics in Christianity Important figures | ||||||
The history of Christianity concerns the history of the Christian religion and the Church, from Jesus and his Twelve Apostles and Seventy Disciples to contemporary times. Christianity is the monotheistic religion which considers itself based on the revelation of Jesus Christ. In many Christian denominations "The Church" is understood theologically as the institution founded by Jesus for the salvation of humankind. This understanding is sometimes called High Church. In contrast, Low Church denominations generally emphasize the personal relationship between a believer and Jesus Christ.
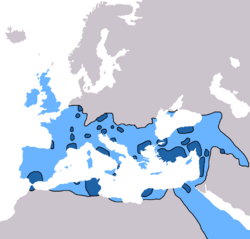
Christianity began in first century C.E. Jerusalem as a Jewish sect, but quickly spread throughout the Roman Empire and beyond to countries such as Ethiopia, Armenia, Georgia, Assyria, Iran, India, and China. Although it was originally persecuted, it would ultimately become the state religion of the Roman Empire in 380 C.E. During the Age of Exploration, Christianity expanded throughout the world, becoming the world's largest religion.[1]
Throughout its history, the religion has weathered schisms and theological disputes that have resulted in many distinct Churches. The two largest Churches are the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church, but the various other Eastern Churches (such as Oriental Orthodoxy), Protestant Churches (such as Lutheranism) and others represent a large portion of the Christian community as well.
As Christianity moves into the twenty-first century significant efforts have been made to reconcile the schism between the Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Churches, between Catholicism and Protestantism and between all the Protestant denominations.
Life of Jesus (2–8 B.C.E. to 29–36 C.E.)
Though the life of Jesus is a matter of academic debate, scholars[2] generally agree on the following basic points: Jesus was born ca. 4 B.C.E. and grew up in Nazareth in Galilee; his ministry included recruiting disciples, who regarded him as a miracleworker, exorcist, and healer; he was executed by crucifixion in Jerusalem ca. 33 C.E. on orders of the Roman Governor of Iudaea Province, Pontius Pilate;[3] and after his crucifixion,[4] Jesus was buried in a tomb.[5] Some have argued for the historicity of the empty tomb story[6] and Jesus' resurrection appearances.[7] The resurrection of Jesus formed the basis and impetus of the Christian faith.[8] It is claimed in the Bible that after Christ's resurrection, he appeared to the disciples in Galilee and Jerusalem and was on the earth for 40 days before his Ascension to heaven.[9]
The main sources of information regarding Jesus' life and teachings are the four canonical Gospels and to a lesser extent the writings of Paul.
Early Christianity (33 – 325 C.E.)
Early Christianity refers to the period when the religion spread in the Greco-Roman world and beyond, from its beginnings as a first century Jewish sect,[10] to the end of the imperial persecution of Christians after the ascension of Constantine the Great in 313 C.E., to the First Council of Nicaea in 325. It may be divided into two distinct phases: the apostolic period, when the first apostles were alive and organizing the Church, and the post-apostolic period, when an early episcopal structure developed, whereby bishoprics were governed by bishops (overseers) via apostolic succession.
Apostolic Church
The Apostolic Church, or Primitive Church, was the community led by Jesus' apostles and his relatives.[11] According to the Great Commission, the resurrected Jesus commanded the apostles to spread his teachings to all the world. The principal source of information for this period is the Acts of the Apostles, which gives a history of the Church from the Great Commission (Acts 1:3-11) and Pentecost (Acts 2) and the establishment of the Jerusalem Church to the spread of the religion among the gentiles (Acts 10) and Paul's conversion (Acts 9) and eventual imprisonment (house arrest: Acts 28:30–31) in Rome in the mid-first century. However, the accuracy of Acts is also disputed and may conflict with accounts in the Epistles of Paul.[12]
The first Christians were essentially all ethnically Jewish or Jewish Proselytes. Jesus preached to the Jewish people and called from them his first disciples, though the earliest documented "group" of appointed evangelizers, called the Seventy Disciples, was not specifically ethnically Jewish. An early difficulty arose concerning Gentile (non-Jewish) converts. Some argued that they had to "become Jewish" (usually referring to circumcision and adherence to dietary law) before becoming Christian. The decision of Peter, as evidenced by conversion of the Centurion Cornelius,[13] was that they did not. The matter was further addressed with the Council of Jerusalem.
The doctrines of the apostles brought the Early Church into conflict with some Jewish religious authorities, and this eventually led to the martyrdom of Stephen and James the Great and expulsion from the synagogues. Thus, Christianity acquired an identity distinct from Rabbinic Judaism. The name "Christian" (Greek Χριστιανός) was first applied to the disciples in Antioch, as recorded in Acts 11:26.
Worship of Jesus

The sources for the beliefs of the apostolic community include the Gospels and New Testament Epistles. The very earliest accounts are contained in these texts, such as early Christian creeds and hymns, as well as accounts of the Passion, the empty tomb, and Resurrection appearances; often these are dated to within a decade or so of the crucifixion of Jesus, originating within the Jerusalem Church. The earliest Christian creeds and hymns express belief in the risen Jesus, e.g., that preserved in 1Corinthians 15:3–4 quoted by Paul: "For what I received I passed on to you as of first importance: that Christ died for our sins according to the Scriptures, that he was buried, that he was raised on the third day according to the Scriptures."[15] The antiquity of the creed has been located by many scholars to less than a decade after Jesus' death, originating from the Jerusalem apostolic community,[16] No scholar dates it later than the 40s.[17] Other relevant and very early creeds include 1John 4:2,[18] 2Timothy 2:8,[19] Romans 1:3–4,[20] and 1Timothy 3:16, an early creedal hymn.[21]
Jewish continuity
Early Christianity retained many of the doctrines and practices of Judaism. They held the Jewish scriptures to be authoritative and sacred, employing mostly the Septuagint translation as the Old Testament, and added other texts as the New Testament canon developed. Christianity also continued other Judaic practices: liturgical worship, including the use of [incense]], an altar, a set of scriptural readings adapted from synagogue practice, use of sacred music in hymns and prayer, and a religious calendar, as well as other distinctive features such as an exclusively male priesthood, and ascetic practices (fasting, etc.).
The early Christians in first century believed Jehovah to be the Only true God, the God of Israel, and considered Jesus to be the Messiah (Christ) prophesied in the Old Testament.
Post-Apostolic Church
- See also: Apostolic Fathers
The post-apostolic period encompasses the time roughly after the death of the apostles when bishops emerged as overseers of urban Christian populations, and continues during the time of persecutions until the legalization of Christian worship during the reign of Constantine the Great. The earliest recorded use of the terms Christianity (Greek Χριστιανισμός) and Catholic (Greek καθολικός), dates to this period, attributed to Ignatius of Antioch c. 107.[22]
Persecutions
From the beginning, Christians were subject to various persecutions. This involved even death for Christians such as Stephen (Acts 7:59) and James, son of Zebedee (Acts 12:2). Larger-scale persecutions followed at the hands of the authorities of the Roman Empire, beginning in the year 64, when, as reported by the Roman historian Tacitus, the Emperor Nero blamed Christians for that year's great Fire of Rome.
According to Church tradition, it was under Nero's persecution that Peter and Paul were each martyred in Rome. Similarly, several of the New Testament writings mention persecutions and stress the importance of endurance through them. For 250 years Christians suffered from sporadic persecutions for their refusal to worship the Roman emperor, which Rome considered treasonous and punishable by execution. In spite of these periodic persecutions, the Christian religion continued its spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin.
Ecclesiastical structure
By the late first and early second century, a hierarchical and episcopal structure became clearly visible; early bishops of importance were Clement of Rome, Ignatius of Antioch, Polycarp of Smyrna, and Irenaeus of Lyons. This structure was based on the doctrine of Apostolic Succession in which, by the ritual of the laying on of hands, a bishop becomes the spiritual successor of the previous bishop in a line tracing back to the apostles themselves. Each Christian community also had presbyters, as was the case with Jewish communities, who were also ordained and assisted the bishop; as Christianity spread, especially in rural areas, the presbyters exercised more responsibilities and took distinctive shape as priests. Lastly, deacons also performed certain duties, such as tending to the poor and sick.
Early Christian writings
As Christianity spread, its converts included members from well-educated circles of the Hellenistic world, some of whom became bishops. They produced two sorts of works: theological and "apologetic;" the latter were works aimed at defending the faith by using reason to refute arguments against the veracity of Christianity. These authors are known as the Church Fathers, and study of them is called Patristics. Notable early Fathers include Ignatius of Antioch, Polycarp, Justin Martyr, Irenaeus, Tertullian, and Clement of Alexandria, Origen among others.
Early iconography

Christian art emerged relatively late; the first known Christian images appeared from about 200 C.E. This early rejection of images, although never proclaimed by theologians, leaves us with little archaeological records regarding early Christianity and its development. The oldest Christian paintings are from the Roman Catacombs, dated to about 200, and the oldest Christian sculptures are from sarcophagi, dating to the beginning of the third century.[23]
Early heresies
The New Testament itself speaks of the importance of maintaining orthodox doctrine and refuting heresies, showing the antiquity of the concern.[24] Because of the biblical proscription against false prophets (notably the Gospels of Matthew and Mark) Christianity has always been preoccupied with the "correct," or orthodox, interpretation of the faith. Indeed, one of the main roles of the bishops in the early Church was to determine the correct interpretations and refute contrarian opinions (referred to as heresy). As there were differing opinions among the bishops, defining orthodoxy would consume the Church through the centuries (and still does, hence, "denominations").
In his book Orthodoxy, Christian Apologist and writer G. K. Chesterton asserts that there have been substantial disagreements about faith from the time of the New Testament and Jesus. He pointed out that the Apostles all argued against changing the teachings of Christ as did the earliest church fathers including Ignatius of Antioch, Irenaeus, Justin Martyr and Polycarp (see false prophet, the antichrist, the gnostic Nicolaitanes from the Book of Revelations and Man of Sin). Jesus also refers to false prophets (Mark 13:21–23) and the "darnel" (Matthew 13:25–30, Matthew 13:36–43) of the flock, warning that their distortion of the Christian faith should be rejected.
The earliest controversies were generally Christological in nature; that is, they were related to Jesus' (eternal) divinity or humanity. Docetism held that Jesus' humanity was merely an illusion, thus denying the incarnation. Arianism held that Jesus, while not merely mortal, was not eternally divine and was, therefore, separate from God, the Father. Trinitarianism held that God the Father, Jesus the Son, and the Holy Spirit were all strictly one being with three aspects. Many groups held dualistic beliefs, maintaining that reality was composed of two radically opposing parts: matter, usually seen as evil, and spirit, seen as good. Others held that both the material and spiritual worlds were created by God and were therefore both good, and that this was represented in the unified divine and human natures of Christ.[25]
The development of doctrine, the position of orthodoxy, and the relationship between the various opinions is a matter of continuing academic debate. Since most Christians today subscribe to the doctrines established by the Nicene Creed, modern Christian theologians tend to regard the early debates as a unified orthodox position against a minority of heretics. Other scholars, drawing upon, among other things, distinctions between Jewish Christians, Pauline Christians, and other groups such as Gnostics and Marcionites, argue that early Christianity was fragmented, with contemporaneous competing orthodoxies.[26]
Biblical canon
- See also: Deuterocanonical books , Apocrypha , and Antilegomena
The Biblical canon is the set of books Christians regard as divinely inspired and thus constituting the Christian Bible. Though the Early Church used the Old Testament according to the canon of the Septuagint (LXX), the apostles did not otherwise leave a defined set of new scriptures; instead the New Testament developed over time.
The writings attributed to the apostles circulated among the earliest Christian communities. The Pauline epistles were circulating in collected form by the end of the first century C.E. In the early second century, Justin Martyr mentions the "memoirs of the apostles," which Christians called "gospels" and which were regarded as on par with the Old Testament.[27] A four gospel canon (the Tetramorph) was in place by the time of Irenaeus, c. 160, who refers to it directly.[28] By the early third century, Origen may have been using the same 27 books as in the modern New Testament, though there were still disputes over the canonicity of Hebrews, James, II Peter, II and III John, and Revelation.[29] Likewise by 200 C.E. the Muratorian fragment shows that there existed a set of Christian writings somewhat similar to what is now the New Testament, which included the four gospels and argued against objections to them.[30] Thus, while there was a good measure of debate in the Early Church over the New Testament canon, the major writings were accepted by almost all Christians by the middle of the second century.[31]
In his Easter letter of 367, Athanasius, Bishop of Alexandria, gave a list of exactly the same books as what would become the New Testament canon,[32] and he used the word "canonized" (kanonizomena) in referring to them.[33] The African Synod of Hippo, in 393, approved the New Testament, as it stands today, together with the Septuagint books, a decision that was repeated by Councils of Carthage in 397 and 419. These councils were under the authority of St. Augustine, who regarded the canon as already closed.[34] Damasus's commissioning of the Latin Vulgate edition of the Bible, c. 383, was instrumental in the fixation of the canon in the West.[35] In 405, Pope Innocent I sent a list of the sacred books to a Gallic bishop, Exsuperius of Toulouse. When these bishops and councils spoke on the matter, however, they were not defining something new, but instead "were ratifying what had already become the mind of the Church."[36] Thus, from the fourth century, there existed unanimity in the West concerning the New Testament canon (as it is today), and by the fifth century the East, with a few exceptions, had come to accept the Book of Revelation and thus had come into harmony on the matter of the canon.[37] Nonetheless, a full dogmatic articulation of the canon was not made until the Council of Trent of 1546 for Roman Catholicism,[38] the Thirty-Nine Articles of 1563 for the Church of England, the Westminster Confession of Faith of 1647 for Calvinism, and the Synod of Jerusalem of 1672 for the Greek Orthodox.
Church of the Roman Empire (313–476)
Christianity in the period of Late Antiquity begins with the ascension of Constantine to the Emperorship of Rome in the early fourth century, and continues until the advent of the Middle Ages. The terminus of this period is variable because the transformation to the sub-Roman period was gradual and occurred at different times in different areas. It may generally be dated as lasting to the late sixth century and the reconquests of Justinian, though a more traditional date is 476, the year that Romulus Augustus, traditionally considered the last western emperor, was deposed.
Christianity legalized
Galerius issued an edict permitting the practice of the Christian religion under his rule in April of 311.[39] In 313 Constantine I and Licinius announced toleration of Christianity in the Edict of Milan. Constantine would become the first Christian emperor. By 391, under the reign of Theodosius I, Christianity had become the state religion. Constantine I, the first emperor to embrace Christianity, was also the first emperor to openly promote the newly legalized religion.
Constantine the Great
The Emperor Constantine I was exposed to Christianity by his mother, Helena. There is scholarly controversy, however, as to whether Constantine adopted his mother's humble Christianity in his youth, or whether he adopted it gradually over the course of his life.[40]
Christian sources record that Constantine experienced a dramatic event in 312 at the Battle of Milvian Bridge, after which Constantine would claim the emperorship in the West. According to these sources, Constantine looked up to the sun before the battle and saw a cross of light above it, and with it the Greek words "Εν Τουτω Νικα" ("by this, conquer!," often rendered in the Latin "in hoc signo vinces"; Constantine commanded his troops to adorn their shields with a Christian symbol (the Chi-Ro). Under this banner they were victorious.[41] How much Christianity Constantine adopted at this point is difficult to discern; most influential people in the empire, especially high military officials, were still pagan, and Constantine's rule exhibited at least a willingness to appease these factions. The Roman coins minted up to eight years subsequent to the battle still bore the images of Roman gods. Nonetheless, the accession of Constantine was a turning point for the Christian Church. After his victory, Constantine supported the Church financially, built various basilicas, granted privileges (for example, exemption from certain taxes) to clergy, promoted Christians to high ranking offices, and returned property confiscated during the Great Persecution of Diocletian.[40] Between 324 and 330, Constantine built, virtually from scratch, a new imperial capital at Byzantium on the Bosphorus (it came to be named for him: Constantinople); the city employed overtly Christian architecture, contained churches within the city walls (unlike "old" Rome), and had no pagan temples. In accordance with the prevailing customs, Constantine was baptized on his deathbed.
Constantine also played an active role in the leadership of the Church. In 313, he issued the Edict of Milan, legalizing Christian worship. In 316, he acted as a judge in a North African dispute concerning the Donatist controversy. More significantly, in 325 he summoned the Council of Nicaea, effectively the first Ecumenical Council (unless the Council of Jerusalem is so classified), to deal with the Arian controversy. The Council would become more famous for their issue of the Nicene Creed, which, among other things, professed a belief in One Holy Catholic Apostolic Church, the start of Christendom. The reign of Constantine established a precedent for the position of the Christian Emperor in the Church. Emperors considered themselves responsible to God for the spiritual health of their subjects, and thus they had a duty of maintain orthodoxy.[42] The emperor did not decide doctrine—that was the responsibility of the bishops—rather his role was to enforce doctrine, root out heresy, and uphold ecclesiastical unity. The emperor ensured that God was properly worshiped in his empire; the exact nature of proper worship was left for the Church to determine. This precedent would continue until certain emperors of the fifth and six centuries sought to alter doctrine by imperial edict without recourse to councils, though Constantine's precedent generally remained the norm.[42]
The reign of Constantine did not represent a complete acceptance for Christianity in the empire, nor an end of persecution. His successor in the East, Constantius II, kept Arian bishops at his court and installed them in various sees, expelling the orthodox bishops.
Constantius's successor, Julian, known in the Christian world as Julian the Apostate, was a philosopher who upon becoming emperor renounced Christianity and embraced a Neo-platonic and mystical form of paganism, shocking the Christian establishment. Intent on re-establishing the prestige of the old pagan beliefs, he modified them to resemble Christian traditions such as the episcopal structure and public charity (hitherto unknown in Roman paganism). Julian eliminated most of the privileges and prestige previously afforded to the Christian Church as the official state religion. His reforms attempted to create a form of religious heterogeneity by, among other things, reopening pagan temples, accepting Christian bishops previously exiled as heretics, promoting Judaism, and returning Church lands to their original owners. However, Julian's short reign ended when he died while campaigning in the East.
Christianity came to dominance during the reign of Julian's successors, Jovian, Valentinian I, and Valens. On Feb. 27, 380, Theodosius I issued the edict De Fide Catolica establishing "Catholic Christianity"[43] as the exclusive official state religion, outlawed other faiths, and closed pagan temples.[44] Additional prohibitions were passed by Theodosius I in 391 further proscribing remaining pagan practices.
Diocesan structure
After legalization, the Church adopted the same organizational boundaries as the Empire: geographical provinces, called dioceses, corresponding to imperial governmental territorial division. The bishops, who were located in major urban centers as per the pre-legalization tradition, oversaw each diocese. The bishop's location was his "seat," or "see"; among the sees, five held special eminence: Rome, Constantinople, Jerusalem, Antioch, and Alexandria. The prestige of these sees depended in part on their apostolic founders, from whom the bishops were thus considered spiritual successors, e.g., St. Mark as founder of the See of Alexandria, St. Peter of the See of Rome, etc. There were other significant reasons for their priority. Jerusalem was the location of Christ's death and resurrection and the site of a first century council, among other things. Antioch was where Jesus' followers were first called Christians. Rome was where Saints Peter and Paul were martyred. Constantinople was the "New Rome" where Constantine had moved his capital c. 330. In addition, all these cities had important relics.
Papacy and primacy
- See also: History of the Papacy
The Pope is the Bishop of Rome and the office is the "papacy." As a bishopric, its origin is consistent with the development of an episcopal structure in the first century. The papacy, however, also carries the notion of primacy: that the See of Rome is preeminent amongst all other sees. The origins of this concept are historically obscure; theologically, it is based on three ancient Christian traditions: (1) that the apostle Peter was preeminent among the apostles, see Primacy of Simon Peter, (2) that Peter ordained his successors for the Roman See, and (3) that the bishops are the successors of the apostles (Apostolic Succession). As long as the Papal See also happened to be the capital of the Western Empire, the prestige of the Bishop of Rome could be taken for granted without the need of sophisticated theological argumentation beyond these points; after its shift to Milan and then Ravenna, however, more detailed arguments were developed based on Matthew 16:18–19 etc.[45] Nonetheless, in antiquity the Petrine and Apostolic quality, as well as a "primacy of respect," concerning the Roman See went unchallenged by emperors, eastern patriarchs, and the Eastern Church alike.[46] The Ecumenical Council of Constantinople in 381 affirmed the primacy of Rome. Though the appellate jurisdiction of the Pope, and the position of Constantinople, would require further doctrinal clarification, by the close of Antiquity the primacy of Rome and the sophisticated theological arguments supporting it were fully developed. Just what exactly was entailed in this primacy, and its being exercised, would become a matter of controversy at certain later times.
Ecumenical Councils
During this era, several Ecumenical Councils were convened. These were mostly concerned with Christological disputes. The two Councils of Nicaea (325, 382) condemned Arian teachings as heresy and produced a creed (see Nicene Creed). The Council of Ephesus condemned Nestorianism and affirmed the Blessed Virgin Mary to be Theotokos ("God-bearer" or "Mother of God"). Perhaps the most significant council was the Council of Chalcedon that affirmed that Christ had two natures, fully God and fully man, distinct yet always in perfect union. This was based largely on Pope Leo the Great's Tome. Thus, it condemned Monophysitism and would be influential in refuting Monothelitism. However, not all denominations accepted all the councils, for example Nestorianism and the Assyrian Church of the East split over the Council of Ephesus of 431, Oriental Orthodoxy split over the Council of Chalcedon of 451, Pope Sergius I rejected the Quinisext Council of 692, and the Fourth Council of Constantinople of 869-870 and 879-880 is disputed by Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy.
Nicene and Post-Nicene Fathers
The early Church Fathers have already been mentioned above; however, Late Antique Christianity produced a great many renowned Fathers who wrote volumes of theological texts, including Saints Augustine, Gregory Nazianzus, Cyril of Jerusalem, Ambrose of Milan, Jerome, and others. What resulted was a golden age of literary and scholarly activity unmatched since the days of Virgil and Horace. Some of these fathers, such as John Chrysostom and Athanasius, suffered exile, persecution, or martyrdom from heretical Byzantine Emperors. Many of their writings are translated into English in the compilations of Nicene and Post-Nicene Fathers.
The Pentarchy
By the fifth century, the ecclesiastical had evolved a hierarchical "pentarchy" or system of five sees (patriarchates), with a settled order of precedence, had been established. Rome, as the ancient center and largest city of the empire, was understandably given the presidency or primacy of honor within the pentarchy into which Christendom was now divided; though it was and still held that the patriarch of Rome was the first among equals.
The list below are the five Pentarchs of the original Pentarchy of the Roman Empire.
- Rome (Sts. Peter and Paul), i.e., the Pope, the only Pentarch in the Western Roman Empire.
- Alexandria (St. Mark), currently in Egypt
- Antioch (St. Peter), currently in Turkey
- Jerusalem (St. James), currently in Israel/Palestine
- Constantinople (St. Andrew), currently in Turkey
Monasticism
Monasticism is a form of asceticism whereby one renounces worldly pursuits (in contempu mundi) and concentrates solely on heavenly and spiritual pursuits, especially by the virtues humility, poverty, and chastity. It began early in the Church as a family of similar traditions, modeled upon Scriptural examples and ideals, and with roots in certain strands of Judaism. St. John the Baptist is seen as the archetypical monk, and monasticism was also inspired by the organization of the Apostolic community as recorded in Acts of the Apostles.
There are two forms of monasticism: eremetic and cenobitic. Eremetic monks, or hermits, live in solitude, whereas cenobitic monks live in communities, generally in a monastery, under a rule (or code of practice) and are governed by an abbot. Originally, all Christian monks were hermits, following the example of Anthony the Great. However, the need for some form of organized spiritual guidance lead Saint Pachomius in 318 to organize his many followers in what was to become the first monastery. Soon, similar institutions were established throughout the Egyptian desert as well as the rest of the eastern half of the Roman Empire. Central figures in the development of monasticism were, in the East, St. Basil the Great, and Saint Benedict in the West, who created the famous Benedictine Rule, which would become the most common rule throughout the Middle Ages.
Growing tensions between East and West
The cracks and fissures in Christian unity which led to the Great Schism started to become evident as early as the fourth century. Although 1054 is the date usually given for the beginning of the Great Schism, there is, in fact, no specific date on which the schism occurred. What really happened was a complex chain of events whose climax culminated with the sacking of Constantinople by the Fourth Crusade in 1204.
The events leading to schism were not exclusively theological in nature. Cultural, political, and linguistic differences were often mixed with the theological. Any narrative of the schism which emphasizes one at the expense of the other will be fragmentary. Unlike the Copts or Armenians who broke from the Church in the fifth century, the eastern and western parts of the Church remained loyal to the faith and authority of the seven ecumenical councils. They were united, by virtue of their common faith and tradition, in one Church.
Nonetheless, the transfer of the Roman capital to Constantinople inevitably brought mistrust, rivalry, and even jealousy to the relations of the two great sees, Rome and Constantinople. It was easy for Rome to be jealous of Constantinople at a time when it was rapidly losing its political prominence. In fact, Rome refused to recognize the conciliar legislation which promoted Constantinople to second rank. But the estrangement was also helped along by the German invasions in the West, which effectively weakened contacts. The rise of Islam with its conquest of most of the Mediterranean coastline (not to mention the arrival of the pagan Slavs in the Balkans at the same time) further intensified this separation by driving a physical wedge between the two worlds. The once homogeneous unified world of the Mediterranean was fast vanishing. Communication between the Greek East and the Latin West by the 600s had become dangerous and practically ceased.[47]
Two basic problems—the primacy of the bishop of Rome and the procession of the Holy Spirit—were involved. These doctrinal novelties were first openly discussed in Photius's patriarchate.
By the fifth century, Christendom was divided into a pentarchy of five sees with Rome holding the primacy. This was determined by canonical decision and did not entail hegemony of any one local church or patriarchate over the others. However, Rome began to interpret her primacy in terms of sovereignty, as a God-given right involving universal jurisdiction in the Church. The collegial and conciliar nature of the Church, in effect, was gradually abandoned in favor of supremacy of unlimited papal power over the entire Church. These ideas were finally given systematic expression in the West during the Gregorian Reform movement of the eleventh century. The Eastern churches viewed Rome's understanding of the nature of episcopal power as being in direct opposition to the Church's essentially conciliar structure and thus saw the two ecclesiologies as mutually antithetical.
This fundamental difference in ecclesiology would cause all attempts to heal the schism and bridge the divisions to fail. Characteristically, Rome insisted on basing her monarchical claims to "true and proper jurisdiction" (as the Vatican Council of 1870 put it) on Saint Peter. This "Roman" exegesis of Matthew 16:18, however, was unknown to the patriarchs of Eastern Orthodoxy. For them, specifically, Saint Peter's primacy could never be the exclusive prerogative of any one bishop. All bishops must, like Saint Peter, confess Jesus as the Christ and, as such, all are Saint Peter's successors. The churches of the East gave the Roman See primacy but not supremacy. The Pope being the first among equals, but not infallible and not with absolute authority.[48]
The other major irritant to Eastern Orthodoxy was the Western interpretation of the procession of the Holy Spirit. Like the primacy, this too developed gradually and entered the Creed in the West almost unnoticed. This theologically complex issue involved the addition by the West of the Latin phrase filioque ("and from the Son") to the Creed. The original Creed sanctioned by the councils and still used today by the Orthodox Church did not contain this phrase; the text simply states "the Holy Spirit, the Lord and Giver of Life, who proceeds from the Father." Theologically, the Latin interpolation was unacceptable to Eastern Orthodoxy since it implied that the Spirit now had two sources of origin and procession, the Father and the Son, rather than the Father alone.[49] In short, the balance between the three persons of the Trinity was altered and the understanding of the Trinity and God confused.
The result, the Orthodox Church believed, then and now, was theologically indefensible. But in addition to the dogmatic issue raised by the filioque, the Byzantines argued that the phrase had been added unilaterally and, therefore, illegitimately, since the East had never been consulted.[50] In the final analysis, only another ecumenical council could introduce such an alteration. Indeed the councils, which drew up the original Creed, had expressly forbidden any subtraction or addition to the text.
Church of the Early Middle Ages (476–800)
The Church in the Early Middle Ages covers the time from the deposition of the last Western Emperor in 476 and his replacement with a barbarian king, Odoacer, to the coronation of Charlemagne as "Emperor of the Romans" by Pope Leo III in Rome on Christmas Day, 800. The year 476, however, is a rather artificial division.[51] In the East, Roman imperial rule continued through the period historians now call the Byzantine Empire. Even in the West, where imperial political control gradually declined, distinctly Roman culture continued long afterwards; thus historians today prefer to speak of a "transformation of the Roman world" rather than a "fall of the Roman Empire." The advent of the Early Middle Ages was a gradual and often localized process whereby, in the West, rural areas became power centers whilst urban areas declined. With the Muslim invasions of the seventh century, the Western (Latin) and Eastern (Greek) areas of Christianity began to take on distinctive shapes. Whereas in the East the Church maintained its structure and character and evolved more slowly, in the West the Bishops of Rome (i.e., the Popes) were forced to adapt more quickly and flexibly to drastically changing circumstances. In particular whereas the bishops of the East maintained clear allegiance to the Eastern Roman Emperor, the Bishop of Rome, while maintaining nominal allegiance to the Eastern Emperor, was forced to negotiate delicate balances with the "barbarian rulers" of the former Western provinces. Although the greater number of Christians remained in the East, the developments in the West would set the stage for major developments in the Christian world during the later Middle Ages.
Conversion of barbarian hinterland
As the political boundaries of the Western Roman Empire diminished and then collapsed, Christianity spread beyond the old borders of the Empire and into lands that had never been Romanized.
Ireland and Irish missionaries
Beginning in the fifth century, a unique culture developed around the Irish Sea consisting of what today would be called Wales and Ireland. In this environment, Christianity spread from Roman Britain to Ireland, especially aided by the missionary activity of St. Patrick. Patrick had been captured into slavery in Ireland and, following his escape and later consecration as bishop, he returned to the isle that had enslaved him so that he could bring them the Gospel. Soon, Irish missionaries such as Saints Columba and Columbanus spread this Christianity, with its distinctively Irish features, to Scotland and the Continent. One such feature was the system of private penitence, which replaced the former practice of penance as a public rite.[52]
Anglo-Saxons (English)
Although Britain had been a Roman province, in 407 the imperial legions left the isle, and the Roman elite followed. Some time later that century, various barbarian tribes went from raiding and pillaging the island to settling and invading. These tribes are referred to as the "Anglo-Saxons," predecessors of the English. They were entirely pagan, having never been part of the Empire, and although they experienced Christian influence from the surrounding peoples, they were converted by the mission of Saint Augustine sent by Pope Gregory the Great. Later, under Archbishop Theodore, the Anglo-Saxons enjoyed a golden age of culture and scholarship. Soon, important English missionaries such as Saints Wilfrid, Willibrord, Lullus and Boniface would begin evangelizing their Saxon relatives in Germany.
Franks
The largely Christian Gallo-Roman inhabitants of Gaul (modern France) were overrun by Germanic Franks in the early fifth century. The native inhabitants were persecuted until the Frankish King, Clovis I converted from paganism to Roman Catholicism in 496. Clovis insisted that his fellow nobles follow suit, strengthening his newly-established kingdom by uniting the faith of the rulers with that of the ruled.
Netherlands and non-Frankish Germany
In 698 the Northumbrian Benedictine monk, Saint Willibrord was commissioned by Pope Sergius I as bishop of the Frisians in what is now the Netherlands. Willibrord established a church in Utrecht.
Much of Willibrord's work was wiped out when the pagan Radbod, king of the Frisians destroyed many Christian centers between 716 and 719. In 717, the English missionary Boniface was sent to aid Willibrord, re-establishing churches in Frisia and continuing to preach throughout the pagan lands of Germany. Boniface was killed by pagans in 754.
Early evangelization in Scandinavia was begun by Ansgar, Archbishop of Bremen, "Apostle of the North." Ansgar, a native of Amiens, was sent with a group of monks to Jutland, Denmark around 820 at the time of the pro-Christian Jutish king Harald Klak. The mission was only partially successful, and Ansgar returned two years later to Germany, after Harald had been driven out of his kingdom. In 829 Ansgar went to Birka on Lake Mälaren, Sweden, with his aide friar Witmar, and a small congregation was formed in 831 which included the king's own steward Hergeir. Conversion was slow, however, and most Scandinavian lands were only completely Christianized at the time of rulers such as Saint Canute IV of Denmark and Olaf I of Norway in the years following 1000 C.E.
Early Medieval Papacy
The city of Rome was embroiled in the turmoil and devastation of Italian peninsular warfare during the Early Middle Ages. Emperor Justinian I attempted to reassert imperial dominion in Italy against the Gothic aristocracy. The subsequent campaigns were more or less successful, and the Imperial Exarchate was established in Ravenna to oversee Italy, though actually imperial influence was often limited. However, the weakened peninsula then experienced the invasion of the Lombards, and the resulting warfare essentially left Rome to fend for itself. Thus the popes, out of necessity, found themselves feeding the city with grain from papal estates, negotiating treaties, paying protection money to Lombard warlords, and, failing that, hiring soldiers to defend the city.[53]Eventually, the failure of the Empire to send aid resulted in the popes turning for support from other sources, especially the Franks.
Carolingian Renaissance
The Carolingian Renaissance was a period of intellectual and cultural revival during the late eighth and ninth centuries, mostly during the reigns of Charlemagne and Louis the Pious. There was an increase of literature, the arts, architecture, jurisprudence, liturgical and scriptural studies. The period also saw the development of Carolingian minuscule, the ancestor of modern lower-case script, and the standardization of Latin which had hitherto become varied and irregular. To address the problems of illiteracy among clergy and court scribes, Charlemagne founded schools and attracted the most learned men from all of Europe to his court, such as Theodulf, Paul the Deacon, Angilbert, Paulinus of Aquileia, and Alcuin of York.
Church of the High Middle Ages (800–1499)
The High Middle Ages is the period from the coronation of Charlemagne in 800 to the close of the fifteenth century, which saw the fall of Constantinople (1453), the end of the Hundred Years War (1453), the discovery of the New World (1492), and thereafter the Protestant Reformation (1515).
Conversion of East and South Slavs
Though by 800 Western Europe was ruled entirely by Christian kings, Eastern Europe remained an area of missionary activity. For example, in the ninth century Saints Cyril and Methodius had extensive missionary success in Eastern Europe among the Slavic peoples, translating the Bible and liturgy into Slavonic. The Baptism of Kiev in 988 spread Christianity throughout Kievan Rus', establishing Christianity among the Ukraine, Belarus and Russia.
In the ninth and tenth centuries, Christianity made great inroads into Eastern Europe, including Kievan Rus'. The evangelization, or Christianization, of the Slavs was initiated by one of Byzantium's most learned churchmen—the Patriarch Photius. The Byzantine emperor Michael III chose Cyril and Methodius in response to a request from Rastislav, the king of Moravia who wanted missionaries that could minister to the Moravians in their own language. The two brothers spoke the local Slavonic vernacular and translated the Bible and many of the prayer books. As the translations prepared by them were copied by speakers of other dialects, the hybrid literary language Old Church Slavonic was created.
Bulgaria was officially recognized as a patriarchate by Constantinople in 945, Serbia in 1346, and Russia in 1589. All these nations, however, had been converted long before these dates.
The missionaries to the East and South Slavs had great success in part because they used the people's native language rather than Latin as the Roman priests did, or Greek.
Conversion of the Serbs and Bulgarians
Methodius later went on to convert the Serbs. Some of the disciples, namely Saint Kliment, Saint Naum who were of noble Bulgarian descent and Saint Angelaruis, returned to Bulgaria where they were welcomed by the Bulgarian Tsar Boris I who viewed the Slavonic liturgy as a way to counteract Greek influence in the country. In a short time the disciples of Cyril and Methodius managed to prepare and instruct the future Slav Bulgarian clergy into the Glagolitic alphabet and the biblical texts and in AD 893, Bulgaria expelled its Greek clergy and proclaimed the Slavonic language as the official language of the church and the state.
Conversion of the Rus'
The success of the conversion of the Bulgarians facilitated the conversion of other East Slavic peoples, most notably the Rus', predecessors of Belarusians, Russians, and Ukrainians, as well as Rusyns. By the beginning of the eleventh century most of the pagan Slavic world, including Russia, Bulgaria and Serbia, had been converted to Byzantine Christianity.
The traditional event associated with the conversion of Russia is the baptism of Vladimir of Kiev in 989, on which occasion he was also married to the Byzantine princess Anna, the sister of the Byzantine Emperor Basil II. However, Christianity is documented to have predated this event in the city of Kiev and in Georgia.
Today the Russian Orthodox Church is the largest of the Orthodox Churches.
Iconoclasm
Iconoclasm as a movement began within the Eastern Christian Byzantine church in the early 8th Century, following a series of heavy military reverses against the Muslims. Sometime between 726-730 the Byzantine Emperor Leo III the Isaurian ordered the removal of an image of Jesus prominently placed over the Chalke gate, the ceremonial entrance to the Great Palace of Constantinople, and its replacement with a cross. This was followed by orders banning the pictorial representation of the family of Christ, subsequent Christian saints, and biblical scenes. In the West, Pope Gregory III held two synods at Rome and condemned Leo's actions. In Leo's realms, the Iconoclast Council at Hieria, 754 ruled that the culture of holy portraits was not of a Christian origin and therefore heretical[54]. The movement destroyed much of the Christian church's early artistic history, to the great loss of subsequent art and religious historians. The iconoclastic movement itself was later defined as heretical in 787 under the Seventh Ecumenical Council, but enjoyed a brief resurgence between 815 and 842.
Monastic Reform Movement
From the 6th century onward most of the monasteries in the West were of the Benedictine Order. Owing to the stricter adherence to a reformed Benedictine rule, the abbey of Cluny became the acknowledged leader of western monasticism from the later 10th century. A sequence of highly competent abbots of Cluny were statesmen on an international level. The monastery of Cluny itself became the grandest, most prestigious and best endowed monastic institution in Europe. Cluny created a large, federated order in which the administrators of subsidiary houses served as deputies of the abbot of Cluny and answered to him. Free of lay and episcopal interference, responsible only to the papacy, the Cluniac spirit was a revitalizing influence on the Norman church. The height of Cluniac influence was from the second half of the tenth century through the early twelfth.
The next wave of monastic reform came with the Cistercian Movement. The first Cistercian abbey was founded by Robert of Molesme in 1098, at Cîteaux Abbey. The keynote of Cistercian life was a return to a literal observance of the rule of Saint Benedict. Rejecting the developments that the Benedictines had undergone, they tried to reproduce the life exactly as it had been in Saint Benedict's time, indeed in various points they went beyond it in austerity. The most striking feature in the reform was the return to manual labor, and especially to field-work, which became a special characteristic of Cistercian life.
Inspired by Saint Bernard of Clairvaux, the Cistercians became the main force of technological diffusion in medieval Europe. By the end of the twelfth century the Cistercian houses numbered 500; in the thirteenth a hundred more were added; and at its height in the fifteenth century, the order claimed to have close to 750 houses. Most of these were built in wilderness areas, and played a major part in bringing such isolated parts of Europe into economic cultivation.
Mendicant orders
A third level of monastic reform was provided by the establishment of the Mendicant orders. Commonly known as Friars, mendicants are members of religious communities that live under a monastic rule but, rather than residing in the seclusion of a monastery, they emphasize public evangelism and are thus known for preaching, missionary activity, and education, as well as the traditional vows of poverty, chastity and obedience. Beginning in the twelfth century, the Franciscan order was instituted by the followers of Francis of Assisi, and thereafter the Dominican Order was begun by Saint Dominic.
Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy, or Lay investiture controversy, was the most significant conflict between secular and religious powers in medieval Europe. It began as a dispute in the 11th century between the Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV, and Pope Gregory VII concerning who would appoint bishops (investiture). The end of lay investiture threatened to undercut imperial power, for the benefit of Church reform, as the pope intended, and for ambitious noblemen as well.
Bishops collected revenues from estates attached to their bishopric. Noblemen who held lands (fiefdoms) passed those lands on within their family. However, because bishops had no legitimate children, when a bishop died it was the king's right to appoint a successor. So, while a king had little recourse in preventing noblemen from acquiring powerful domains via inheritance and dynastic marriages, a king could keep careful control of lands under the domain of his bishops. Kings would bestow bishoprics to members of noble families whose friendship he wished to secure. Furthermore, if a king left a bishopric vacant, then he collected the estates' revenues until a bishop was appointed, when in theory he was to repay the earnings. The infrequence of this repayment was an obvious source of dispute. The Church wanted to end this lay investiture because of the potential corruption, not only from vacant sees but also from other practices such as simony. Thus, the Investiture Contest was part of the Church's attempt to reform the episcopate and provide better pastoral care.
Pope Gregory VII issued the Dictatus Papae, which declared that the pope alone could appoint or depose bishops, or translate them to other sees. Henry VI's rejection of the decree led to his excommunication and a ducal revolt; eventually Henry received absolution after dramatic public penance barefoot in Alpine snow and cloaked in a hairshirt, though the revolt and conflict of investiture continued. Likewise, a similar controversy occurred in England between King Henry I and St. Anselm, Archbishop of Canterbury, over investiture and ecclesiastical revenues collected by the king during an episcopal vacancy. The English dispute was resolved by the Concordat of London, 1107, where the king renounced his claim to invest bishops but continued to require an oath of fealty from them upon their election. This was a partial model for the Concordat of Worms (Pactum Calixtinum), which resolved the Imperial investiture controversy with a compromise that allowed secular authorities some measure of control but granted the selection of bishops to their cathedral canons. As a symbol of the compromise, lay authorities invested bishops with their secular authority symbolized by the lance, and ecclesiastical authorities invested bishops with their spiritual authority symbolized by the ring and the staff.
Sanctification of knighthood

The nobility of the Middle Ages was a military class; in the Early Medieval period a king (rex) attracted a band of loyal warriors (comes) and provided for them from his conquests. As the Middle Ages progressed, this system developed into a complex set of feudal ties and obligations. As Christianity had been accepted by barbarian nobility, the Church sought to prevent ecclesiastical land and clergymen, both of which came from the nobility, from embroilment in martial conflicts. By the early eleventh century, clergymen and peasants were granted immunity from violence—the Peace of God (Pax Dei). Soon the warrior elite itself became "sanctified," for example fighting was banned on holy days—the Truce of God (Treuga Dei). The concept of chivalry developed, emphasizing honor and loyalty amongst knights, and, with the advent of Crusades, holy orders of knights were established who perceived themselves as called by God to defend Christendom against Muslim advances in Spain, Italy, and the Holy Land, and pagan strongholds in Eastern Europe.
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of military conflicts conducted by Christian knights for the defense of Christians and for the expansion of Christian domains. Generally, the crusades refer to the campaigns in the Holy Land against Muslim forces sponsored by the Papacy. There were other crusades against Islamic forces in southern Spain, southern Italy, and Sicily, as well as the campaigns of Teutonic Knights against pagan strongholds in Eastern Europe. A few crusades such as the Fourth Crusade were waged within Christendom against groups that were considered heretical and schismatic (also see the Battle of the Ice and the Northern Crusades).
The Holy Land had been part of the Roman Empire, and thus Byzantine Empire, until the Islamic conquests of the seventh and eighth centuries. Thereafter, Christians had generally been permitted to visit the sacred places in the Holy Land until 1071, when the Seljuk Turks closed Christian pilgrimages and assailed the Byzantines, defeating them at the Battle of Manzikert. Emperor Alexius I asked for aid from Pope Urban II (1088–1099) for help against Islamic aggression. He probably expected money from the pope for the hiring of mercenaries. Instead, Urban II called upon the knights of Christendom in a speech made at the Council of Clermont in November 1095, combining the idea of pilgrimage to the Holy Land with that of waging a holy war against infidels.
The First Crusade captured Antioch in 1099 and then Jerusalem. The Second Crusade occurred in 1145 when Edessa was retaken by Islamic forces. Jerusalem would be held until 1187 and the Third Crusade, famous for the battles between Richard the Lionheart and Saladin. The Fourth Crusade, begun by Innocent III in 1202, intended to retake the Holy Land but was soon subverted by Venetians who used the forces to sack the Christian city of Zara. Innocent excommunicated the Venetians and crusaders. Eventually the crusaders arrived in Constantinople, but due to strife which arose between them and the Byzantines, rather than proceed to the Holy Land the crusaders instead sacked Constantinople and other parts of Asia Minor effectively establishing the Latin Empire of Constantinople in Greece and Asia Minor. This was effectively the last crusade sponsored by the papacy; later crusades were sponsored by individuals. Thus, though Jerusalem was held for nearly a century and other strongholds in the Near East would remain in Christian possession much longer, the crusades in the Holy Land ultimately failed to establish permanent Christian kingdoms. Islamic expansion into Europe would renew and remain a threat for centuries culminating in the campaigns of Suleiman the Magnificent in the sixteenth century. On the other hand, the crusades in southern Spain, southern Italy, and Sicily eventually lead to the demise of Islamic power in the regions; the Teutonic knights expanded Christian domains in Eastern Europe, and the much less frequent crusades within Christendom, such as the Albigensian Crusade, achieved their goal of maintaining doctrinal unity.[55]
Medieval Inquisition
The Medieval Inquisition is a series of Inquisitions (Roman Catholic Church bodies charged with suppressing heresy) from around 1184, including the Episcopal Inquisition (1184-1230s) and later the Papal Inquisition (1230s). It was in response to large popular movements throughout Europe considered apostate or heretical to Western Catholicism, in particular the Cathars and the Waldensians in southern France and northern Italy. These were the first inquisition movements of many that would follow.
The inquisitions in combination with the brutal Albigensian Crusade were fairly successful in eliminating mass heresy. When they started, the heretical sects were quite strong and growing, but by the fourtenth century the Waldensians had been driven underground and the Cathars had been slaughtered en masse or forced to recant.
Rise of universities
Modern western universities have their origins directly in the Medieval Church. They began as cathedral schools, and all students were considered clerics. This was a benefit as it placed the students under ecclesiastical jurisdiction and thus imparted certain legal immunities and protections. The cathedral schools eventually became partially detached from the cathedrals and formed their own institutions, the earliest being the University of Paris (c. 1150), the University of Bologna (1088), and the University of Oxford (1096).
Photian schism
In the ninth century C.E., a controversy arose between Eastern (Byzantine, later Orthodox) and Western (Latin, Roman Catholic) Christianity that was precipitated by the opposition of the Roman Pope John VII to the appointment by the Byzantine emperor Michael III of Photius I to the position of patriarch of Constantinople. Photius was refused an apology by the pope for previous points of dispute between the East and West. Photius refused to accept the supremacy of the pope in Eastern matters or accept the filioque clause. The Latin delegation at the council of his consecration pressed him to accept the clause in order to secure their support.
The controversy also involved Eastern and Western ecclesiastical jurisdictional rights in the Bulgarian church, as well as a doctrinal dispute over the Filioque ("and from the Son") clause. That had been added to the Nicene Creed by the Latin church, which was later the theological breaking point in the ultimate Great East-West Schism in the eleventh century.
Photius did provide concession on the issue of jurisdictional rights concerning Bulgaria and the papal legates made do with his return of Bulgaria to Rome. This concession, however, was purely nominal, as Bulgaria's return to the Byzantine rite in 870 had already secured it an autocephalous church. Without the consent of Boris I of Bulgaria, the papacy was unable to enforce any its claims.
East-West Schism
In the 11th century the Great Schism took place between Rome and Constantinople, which led to separation of the Church of the West, the Roman Catholic Church, and the Eastern Orthodox Church. There were doctrinal issues like the filioque clause and the authority of the Pope involved in the split, but these were exacerbated by cultural and linguistic differences between Latins and Greeks. Prior to that, the Eastern and Western halves of the Church had frequently been in conflict, particularly during periods of iconoclasm and the Photian schism.[47]
The East-West Schism, or Great Schism, separated the Church into Western (Latin) and Eastern (Greek) branches, i.e., Western Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy. It was the first major division since certain groups in the East rejected the decrees of the Council of Chalcedon, and was far more significant. Though normally dated to 1054, the East-West Schism was actually the result of an extended period of estrangement between Latin and Greek Christendom over the nature of papal primacy and certain doctrinal matters like the filioque clause, but intensified by cultural and linguistic differences.
The "official" schism in 1054 was the excommunication of Patriarch Michael Cerularius of Constantinople, followed by his excommunication of papal legates. Attempts at reconciliation were made in 1274 (by the Second Council of Lyon) and in 1439 (by the Council of Basel), but in each case the eastern hierarchs who consented to the unions were repudiated by the Orthodox as a whole, though reconciliation was achieved between the West and what are now called the "Eastern Rite Catholic Churches." More recently, in 1965 the mutual excommunications were rescinded by the Pope and the Patriarch of Constantinople, though schism remains.
Both groups are descended from the Early Church, both acknowledge the apostolic succession of each other's bishops, and the validity of each other's sacraments. Though both acknowledge the primacy of the Bishop of Rome, Eastern Orthodoxy understands this as a primacy of honor with limited or no ecclesiastical authority in other dioceses.
The Orthodox East perceived the Papacy as taking on monarch type characteristics that where not in line with the church's tradition.
The final breach is often considered to have arisen after the capture and sacking of Constantinople by the Fourth Crusade in 1204. Crusades against Christians in the East by Roman Catholic crusaders was not exclusive to the Mediterranean though (see also the Northern Crusades and the Battle of the Ice). The sacking of Constantinople and the Church of Holy Wisdom and establishment of the Latin Empire as a seeming attempt to supplant the Orthodox Byzantine Empire in 1204 is viewed with some rancor to the present day. Many in the East saw the actions of the West as a prime determining factor in the weakening of Byzantium. This led to the Empire's eventual conquest and fall to Islam.
In 2004, Pope John Paul II extended a formal apology for the sacking of Constantinople in 1204; the apology was formally accepted by Patriarch Bartholomew of Constantinople. Many things that were stolen during this time: holy relics, riches, and many other items, are still held in various Western European cities, particularly Venice.
Papal Primacy
In 1294, Benedetto Caetani was elected pope and took the name Boniface VIII. Boniface was elected on Celestine's abdication, and during his first years he was opposed by those who had suffered from Celestine's retirement—the Neapolitans, the Colonna family, and the extreme Franciscans, among them Jacopone da Todi. To preclude schism, Boniface kept Celestine imprisoned for the rest of his life. Boniface reigned in a time of crisis in Europe.
His contest with Philip IV The Fair of France was the principal feature of his career. The pope tried to stop Philip from his illegal levies on the clergy by the bull Clericis laicos (1296), enunciating the principle that laymen could not tax clerics without the consent of the Holy See. Philip retaliated by cutting off the contributions of the French church to Rome. In England the Pope faced an equally resistant Edward I, and in a subsequent bull (1297) Boniface relaxed the ruling.
Two of his statements in the controversy are famous—the bull Ausculta fili (1301), which summoned a French synod to meet at Rome to discuss the reformation of French affairs, and the bull Unam sanctam (1302), an extreme statement (not naming Philip) of the principle that Catholic princes as well as others are subject to the pope in temporal (moral) and religious matters. The Unam sanctam is a landmark in the history of the doctrine of Papal Primacy.
Hesychast Controversy
About the year 1337 Hesychasm attracted the attention of a learned member of the Orthodox Church, Barlaam of Calabria who at that time held the office of abbot in theMonastery of St. Saviour's in Constantinople and who had visited Mount Athos. Mount Athos was then at the height of its fame and influence under the reign of Andronicus III Palaeologus and under the 'first-ship' of the Protos Symeon. On Mount Athos, Barlaam encountered Hesychasts and heard descriptions of their practices, also reading the writings of the teacher in Hesychasm of Saint Gregory Palamas, himself an Athonite monk. Trained in Western Scholastic theology, Barlaam was scandalized by Hesychasm and began to combat it both orally and in his writings. As a private teacher of theology in the Western Scholastic mode, Barlaam propounded a more intellectual and propositional approach to the knowledge of God than the Hesychasts taught. Hesychasm is a form of constant purposeful prayer or experiential prayer, explicitly referred to as contemplation. Descriptions of the Hesychast practices can be found in the Philokalia, The Way of a Pilgrim, and St. John Climacus' The Ladder of Divine Ascent.
Barlaam took exception to the doctrine entertained by the Hesychasts as to the nature of the uncreated light, the experience of which was said to be the goal of Hesychast practice. It was maintained by the Hesychasts to be of divine origin and to be identical to that light which had been manifested to Jesus' disciples on Mount Tabor at the Transfiguration. This Barlaam held to be polytheistic, inasmuch as it postulated two eternal substances, a visible and an invisible God.
On the Hesychast side, the controversy was taken up by Saint Gregory Palamas, afterwards Archbishop of Thessalonica, who was asked by his fellow monks on Mount Athos to defend Hesychasm from the attacks of Barlaam. Saint Gregory himself, was well-educated in Greek philosophy. Gregory defended Hesychasm in the 1340s at three different synods in Constantinople, and he also wrote a number of works in its defense.
In 1341 the dispute came before a synod held at Constantinople and was presided over by the Emperor Andronicus; the synod, taking into account the regard in which the writings of the pseudo-Dionysius were held, condemned Barlaam, who recanted and returned to Calabria, afterwards becoming a bishop in the Roman Catholic Church.
One of Barlaam's friends, Gregory Akindynos, who originally was also a friend of Saint Gregory Palamas, took up the controversy, and three other synods on the subject were held, at the second of which the followers of Barlaam gained a brief victory. But in 1351 at a synod under the presidency of the Emperor John VI Cantacuzenus, Hesychast doctrine was established as the doctrine of the Orthodox Church.
Up to this day, the Roman Catholic Church has never fully accepted Hesychasm, especially the distinction between the energies or operations of God and the essence of God, and the notion that those energies or operations of God are uncreated. In Roman Catholic theology as it has developed since the Scholastic period ca. 1100–1500, the essence of God can be known, but only in the next life; the grace of God is always created; and the essence of God is pure act, so that there can be no distinction between the energies or operations and the essence of God (see, e.g., the Summa Theologiae of Thomas Aquinas). Some of these positions depend on Aristotelian metaphysics.
The contemporary historians Cantacuzenus and Nicephorus Gregoras deal very copiously with this subject, taking the Hesychast and Barlaamite sides respectively. Respected fathers of the church have held that these councils which agree that experiential prayer is Orthodox, refer to these councils as Ecumenical Councils Eight and Nine.[56]
Age of Captivity
In 1453, the Byzantine Empire fell to the Ottoman Empire. By this time Egypt had been under Muslim control for some seven centuries, but Orthodoxy was very strong in Russia which had recently acquired an autocephalous status; and thus Moscow called itself the Third Rome, as the cultural heir of Constantinople.
Under Ottoman rule, the Greek Orthodox Church acquired substantial power as an autonomous millet. The ecumenical patriarch was the religious and administrative ruler of the entire "Greek Orthodox nation" (Ottoman administrative unit), which encompassed all the Eastern Orthodox subjects of the Empire.
Isolation from the West
As a result of the Ottoman conquest of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, and the Fall of Constantinople, the entire Orthodox communion of the Balkans and the Near East became suddenly isolated from the West. For the next four hundred years, it would be confined within a hostile Islamic world, with which it had little in common religiously or culturally. Only the Russian Orthodox Church was the only part of the Orthodox communion which remained outside the control of the Ottoman Empire. It is, in part, due to this geographical and intellectual confinement that the voice of Eastern Orthodoxy was not heard during the Reformation in sixteenth century Europe. As a result, this important theological debate often seems strange and distorted to the Orthodox; after all, they never took part in it and thus neither Reformation nor Counter-Reformation is part of their theological framework.
Religious rights under the Ottoman Empire
The new Ottoman government that arose from the ashes of Byzantine civilization was neither primitive nor barbaric. Islam not only recognized Jesus as a great prophet, but tolerated Christians as another People of the Book. As such, the Church was not extinguished nor was its canonical and hierarchical organization significantly disrupted. Its administration continued to function. One of the first things that Mehmet the Conqueror did was to allow the Church to elect a new patriarch, Gennadius Scholarius. The Hagia Sophia and the Parthenon, which had been Christian churches for nearly a millennium were, admittedly, converted into mosques, yet countless other churches, both in Constantinople and elsewhere, remained in Christian hands. Moreover, it is striking that the patriarch's and the hierarchy's position was considerably strengthened and their power increased. They were endowed with civil as well as ecclesiastical power over all Christians in Ottoman territories. Because Islamic law makes no distinction between nationality and religion, all Christians, regardless of their language or nationality, were considered a single millet, or nation. The patriarch, as the highest ranking hierarch, was thus invested with civil and religious authority and made ethnarch, head of the entire Christian Orthodox population. Practically, this meant that all Orthodox Churches within Ottoman territory were under the control of Constantinople. Thus, the authority and jurisdictional frontiers of the patriarch were enormously enlarged.
However, these rights and privileges, including freedom of worship and religious organization, were often established in principle but seldom corresponded to reality. The legal privileges of the patriarch and the Church depended, in fact, on the whim and mercy of the Sultan and the Sublime Porte, while all Christians were viewed as little more than second-class citizens. Moreover, Turkish corruption and brutality were not a myth. That it was the "infidel" Christian who experienced this more than anyone else is not in doubt. Nor were pogroms of Christians in these centuries unknown.[57] Devastating, too, for the Church was the fact that it could not bear witness to Christ. Missionary work among Moslems was dangerous and indeed impossible, whereas conversion to Islam was entirely legal and permissible. Converts to Islam who returned to Orthodoxy were put to death as apostates. No new churches could be built and even the ringing of church bells was prohibited. Education of the clergy and the Christian population either ceased altogether or was reduced to the most rudimentary elements.
Corruption
The Orthodox Church found itself subject to the Turkish system of corruption. The patriarchal throne was frequently sold to the highest bidder, while new patriarchal investiture was accompanied by heavy payment to the government. In order to recoup their losses, patriarchs and bishops taxed the local parishes and their clergy. Nor was the patriarchal throne ever secure. Few patriarchs between the fifteenth and the nineteenth centuries died a natural death while in office. The forced abdications, exiles, hangings, drowning, and poisonings of patriarchs are well documented. But if the patriarch's position was precarious so was the hierarchy's. The hanging of patriarch Gregory V from the gate of the patriarchate on Easter Sunday 1821 was accompanied by the execution of two metropolitans and twelve bishops.
Devshirmeh
Devshirmeh was the system of the collection of young boys from conquered Christian lands by the Ottoman sultans as a form of regular taxation in order to build a loyal army (formerly largely composed of war captives) and the class of (military) administrators called the "Janissaries," or other servants such as tellak in hamams. The word devşirme means "collecting, gathering" in Ottoman Turkish. Boys delivered to the Ottomans in this way were called ghilmán or acemi oglanlar ("novice boys").
Western Schism
The Western Schism, or Papal Schism, was a prolonged period of crisis in Latin Christendom from 1378 to 1416, when there were two or more claimants to the See of Rome and there was conflict concerning the rightful holder of the papacy. The conflict was political, rather than doctrinal, in nature.
In 1309, Pope Clement V, due to political considerations, moved to Avignon in southern France and exercised his pontificate there. For sixty-nine years popes resided in Avignon rather than Rome. This was not only an obvious source of not only confusion but of political animosity as the prestige and influence of city of Rome waned without a resident pontiff. Though Pope Gregory XI, a Frenchman, returned to Rome in 1378, the strife between Italian and French factions intensified, especially following his subsequent death. In 1378 the conclave elected an Italian from Naples, Pope Urban VI; his intransigence in office soon alienated the French cardinals, who withdrew to a conclave of their own, asserting the previous election was invalid since its decision had been made under the duress of a riotous mob. They elected one of their own, Robert of Geneva, who took the name Pope Clement VII. By 1379, he was back in the palace of popes in Avignon, while Urban VI remained in Rome.
For nearly forty years, there were two papal curias and two sets of cardinals, each electing a new pope for Rome or Avignon when death created a vacancy. Each pope lobbied for support among kings and princes who played them off against each other, changing allegiance according to political advantage. In 1409, a council was convened at Pisa to resolve the issue. The council declared both existing popes to be schismatic (Gregory XII from Rome, Benedict XIII from Avignon) and appointed a new one, Alexander V. But the existing popes refused to resign and thus there were three papal claimants. Another council was convened in 1414, the Council of Constance. In March 1415 the Pisan pope, John XXIII, fled from Constance in disguise; he was brought back a prisoner and deposed in May. The Roman pope, Gregory XII, resigned voluntarily in July. The Avignon pope, Benedict XIII, refused to come to Constance; nor would he consider resignation. The council finally deposed him in July 1417. The council in Constance, having finally cleared the field of popes and antipopes, elected Pope Martin V as pope in November.
Church and the Italian Renaissance (1399–1599)
- See also: Italian Renaissance and Christian Humanism
The Renaissance was a period of great cultural change and achievement, marked in Italy by a classical orientation and an increase of wealth through mercantile trade. The City of Rome, the Papacy, and the Papal States were all affected by the Renaissance. On the one hand, it was a time of great artistic patronage and architectural magnificence, where the Church pardoned such artists as Michelangelo, Brunelleschi, Bramante, Raphael, Fra Angelico, Donatello, and da Vinci. On the other hand, wealthy Italian families often secured episcopal offices, including the papacy, for their own members, some of whom were known for immorality, such as Alexander VI and Sixtus IV.
In addition to being the head of the Church, the Pope became one of Italy's most important secular rulers, and pontiffs such as Julius II often waged campaigns to protect and expand their temporal domains. Furthermore, the popes, in a spirit of refined competition with other Italian lords, spent lavishly both on private luxuries but also on public works, repairing or building churches, bridges, and a magnificent system of aqueducts in Rome that still function today. It was during this time that St. Peter's Basilica, perhaps the most recognized Christian church, was built on the site of the old Constantinian basilica. It was also a time of increased contact with Greek culture, opening up new avenues of learning, especially in the fields of philosophy, poetry, classics, rhetoric, and political science, fostering a spirit of humanism–all of which would influence the Church.
Protestant Reformation (1521–1579)
In the early sixteenth century, movements were begun by two theologians, Martin Luther and Huldrych Zwingli, that aimed to reform the Church; these reformers are distinguished from previous ones in that they considered the root of corruptions to be doctrinal (rather than simply a matter of moral weakness or lack of ecclesiastical discipline) and thus they aimed to change contemporary doctrines to accord with what they perceived to be the "true gospel." The word protestant is derived from the Latin protestatio meaning declaration which refers to the letter of protestation by Lutheran princes against the decision of the Diet of Speyer in 1529, which reaffirmed the edict of the Diet of Worms against the Reformation.[58] Since that time, the term has been used in many different senses, but most often as a general term refers to Western Christianity that is not subject to papal authority. The term "Protestant" was not originally used by Reformation era leaders; instead, they called themselves evangelical," emphasizing the "return to the true gospel (Greek: euangelion)."[59]
The beginning of the Protestant Reformation is generally identified with Martin Luther and the posting of the 95 Theses on the castle church in Wittenberg, Germany. Early protest was against corruptions such as simony, episcopal vacancies, and the sale of indulgences. The Protestant position, however, would come to incorporate doctrinal changes such as sola scriptura and sola fide. The three most important traditions to emerge directly from the Protestant Reformation were the Lutheran, Reformed (Calvinist, Presbyterian, etc.), and Anglican traditions, though the latter group identifies as both "Reformed" and "Catholic," and some subgroups reject the classification as "Protestant."
The Protestant Reformation may be divided into two distinct but basically simultaneous movements, the Magisterial Reformation and the Radical Reformation. The Magisterial Reformation involved the alliance of certain theological teachers (Latin: magistri) such as Luther, Zwingli, Calvin, Cramner, etc. with secular magistrates who cooperated in the reformation of Christendom. Radical Reformers, besides forming communities outside state sanction, often employed more extreme doctrinal change, such as the rejection of tenants of the Councils of Nicaea and Chalcedon. Often the division between magisterial and radical reformers was as violent as the general Catholic and Protestant hostilities.
The Protestant Reformation spread almost entirely within the confines of Northern Europe, but did not take hold in certain northern areas such as Ireland and parts of Germany. By far the magisterial reformers were more successful and their changes more widespread than the radical reformers. The Catholic response to the Protestant Reformation is known as the Counter Reformation, or Catholic Reformation, which resulted in a reassertion of traditional doctrines and the emergence of new religious orders aimed at both moral reform and new missionary activity. The Counter Reformation reconverted approximately 33% of Northern Europe to Catholicism and initiated missions in South and Central America, Africa, Asia, and even China and Japan. Protestant expansion outside of Europe occurred on a smaller scale through colonization of North America and areas of Africa.
Martin Luther
Martin Luther was an Augustinian friar and professor at the University of Wittenberg. In 1517, he published a list of 95 Theses, or points to be debated, concerning the illicitness of selling indulgences. Luther had a particular disdain for Aristotelian philosophy, and as he began developing his own theology, he increasingly came into conflict with Thomistic scholars, most notably Cardinal Cajetan.[60] Soon, Luther had begun to develop his theology of justification, or process by which one is "made right" (righteous) in the eyes of God. In Catholic theology, one is made righteous by a progressive infusion of grace accepted through faith and cooperated with through good works. Luther's doctrine of justification differed from Catholic theology in that justification rather meant "the declaring of one to be righteous," where God imputes the merits of Christ upon one who remains without inherent merit.[61] In this process, good works are more of an unessential byproduct that contribute nothing to one's own state of righteousness. Conflict between Luther and leading theologians lead to his gradual rejection of authority of the Church hierarchy. In 1520, he was condemned for heresy by the papal bull Exsurge Domine, which he burned at Wittenberg along with books of canon law.
Ulrich Zwingli
Ulrich Zwingli was a Swiss scholar and parish priest who was likewise influential in the beginnings of the Protestant Reformation. Zwingli claimed that his theology owed nothing to Luther, and that he had developed it in 1516, before Luther's famous protest, though his doctrine of justification was remarkably similar to that of the German friar.[62] In 1518, Zwingli was given a post at the wealthy collegiate church of the Grossmünster in Zürich, where he would remain until his death at a relatively young age. Soon he had risen to prominence in the city, and when political tension developed between most of Switzerland and the Catholic Habsburg Emperor Charles V. In this environment, Zwingli began preaching his version of reform, with certain points as the aforementioned doctrine of justification, but others (with which Luther vehemently disagreed) such as the position that veneration of icons was actually idolatry and thus a violation of the first commandment, and the denial of the real presence in the Eucharist.[63] Soon the city council had accepted Zwingli's doctrines and Zürich became a focal point of more radical reforming movements, and certain admirers and followers of Zwingli pushed his message and reforms far further than even he had intended, such as rejecting infant baptism.[64] This split between Luther and Zwingli formed the essence of the Protestant division between Lutheran and Reformed theology. Meanwhile, political tensions increased; Zwingli and the Zürich leadership imposed an economic blockade on the inner Catholic states of Switzerland, which lead to a battle in which Zwingli, in full armor, was slain along with his troops.
John Calvin
John Calvin was a French cleric and doctor of law turned Protestant reformer. He belonged to the second generation of the Reformation, publishing his theological tome, the Institutes of the Christian Religion, in 1536 (later revised), and establishing himself as a leader of the Reformed church in Geneva, which became an "unofficial capital" of Reformed Christianity in the second half of the sixteenth century. He exerted a remarkable amount of authority in the city and over the city council, such that he has (rather ignominiously) been called a "Protestant pope." Calvin established an eldership together with a "consistory," where pastors and the elders established matters of religious discipline for the Genevan population.[65] Calvin's theology is best known for his doctrine of (double) predestination, which held that God had, from all eternity, providentially foreordained who would be saved (the elect) and likewise who would be damned (the reprobate). Predestination was not the dominant idea in Calvin's works, but it would seemingly become so for many of his Reformed successors.[66]
English Reformation
- See also: English Civil War

Unlike other reform movements, the English Reformation began by royal influence. Henry VIII considered himself a thoroughly Catholic King, and in 1521 he defended the papacy against Luther in a book he commissioned entitled, The Defense of the Seven Sacraments, for which Pope Leo X awarded him the title Fidei Defensor (Defender of the Faith). However, the king came into conflict with the papacy when he wished to annul his marriage with Catherine of Aragon, for which he needed papal sanction. Catherine, among many other noble relations, was the aunt of Emperor Charles V, the papacy's most significant secular supporter. The ensuing dispute eventually lead to a break from Rome and the declaration of the King of England as head of the English Church. England would later experience periods of frenetic and eclectic reforms contrasted by periods led by staunch conservatives. Monarchs such as Edward VI, Mary I, Elizabeth I, and Archbishops of Canterbury such as Thomas Cranmer and William Laud pushed the Church of England in many directions over the course of only a few generations. What emerged was a state church that considered itself both "Reformed" and "Catholic" but not "Roman" (and hesitated from the title "Protestant"), and other "unofficial" more radical movements such as the Puritans.
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation, or Catholic Reformation, was the response of the Catholic Church to the Protestant Reformation. The essence of the Counter-Reformation was a renewed conviction in traditional practices and the upholding of Catholic doctrine as the source of ecclesiastic and moral reform, and the answer to halting the spread of Protestantism. Thus it experienced the founding of new religious orders, such as the Jesuits, the establishment of seminaries for the proper training of priests, renewed worldwide missionary activity, and the development of new yet orthodox forms of spirituality, such as that of the Spanish mystics and the French school of spirituality. The entire process was spearheaded by the Council of Trent, which clarified and reasserted doctrine, issued dogmatic definitions, and produced the Roman Catechism.
Though Ireland, Spain, France, and elsewhere featured significantly in the Counter-Reformation, its heart was Italy and the various popes of the time, who established the Index Librorum Prohibitorum (the list of prohibited books) and the Roman Inquisition, a system of juridical tribunals that prosecuted heresy and related offenses. The Papacy of St. Pius V (1566-1572) was known not only for its focus on halting heresy and worldly abuses within the Church, but also for its focus on improving popular piety in a determined effort to stem the appeal of Protestantism. Pius began his pontificate by giving large alms to the poor, charity, and hospitals, and the pontiff was known for consoling the poor and sick, and supporting missionaries. The activities of these pontiffs coincided with a rediscovery of the ancient Christian catacombs in Rome. As Diarmaid MacCulloch stated, "Just as these ancient martyrs were revealed once more, Catholics were beginning to be martyred afresh, both in mission fields overseas and in the struggle to win back Protestant northern Europe: the catacombs proved to be an inspiration for many to action and to heroism."[67]
The Council of Trent
The Council of Trent (1545–1563), initiated by Pope Paul III (1534–1549) addressed issues of certain ecclesiastical corruptions such as simony, absenteeism, nepotism, and other abuses, as well as the reassertion of traditional practices and the dogmatic articulation of the traditional doctrines of the Church, such as the episcopal structure, clerical celibacy, the seven Sacraments, transubstantiation (the belief that during mass the consecrated bread and wine truly become the body and blood of Christ), the veneration of relics, icons, and saints (especially the Blessed Virgin Mary), the necessity of both faith and good works for salvation, the existence of purgatory and the issuance (but not the sale) of indulgences, etc. In other words, all Protestant doctrinal objections and changes were uncompromisingly rejected. The Council also fostered an interest in education for parish priests to increase pastoral care. Milan's Archbishop Saint Charles Borromeo (1538-1584) set an example by visiting the remotest parishes and instilling high standards.
Age of Discovery (1492–1769)
The Age of Discovery began with the voyage of Christopher Columbus c. 1492. It is characterized by European colonization of missionary activity.
Catholic missions
During the Age of Discovery, the Roman Catholic Church established a number of Missions in the Americas and other colonies in order to spread Christianity in the New World and to convert the indigenous peoples. At the same time, missionaries such as Francis Xavier as well as other Jesuits, Augustinians, Franciscans and Dominicans were moving into Asia and the Far East. The Portuguese sent missions into Africa. While some of these missions were associated with imperialism and oppression, others (notably Matteo Ricci's Jesuit mission to China) were relatively peaceful and focused on integration rather than cultural imperialism.
Protestant colonization
The most famous colonization by Protestants in the New World was that of English Puritans in North America. Unlike the Spanish or French, the English colonists made surprisingly little effort to evangelize the native peoples.[68] The Puritans, or pilgrims, left England so that they could live in an area with Puritanism established as the exclusive civic religion. Though they had left England because of the suppression of their religious practice, most Puritans had thereafter originally settled in the Low Countries but found the licentiousness there, where the state hesitated from enforcing religious practice, as unacceptable, and thus they set out for the New World and the hopes of a Puritan utopia.
Church and the Enlightenment (1580–1800)
The Galileo affair, in which Galileo Galilei came into conflict with the Roman Catholic Church over his support of Copernican astronomy, is often considered a defining moment in the history of the relationship between religion and science.
In 1610, Galileo published his Sidereus Nuncius (Starry Messenger), describing the surprising observations that he had made with the new telescope. These and other discoveries exposed major difficulties with the understanding of the heavens that had been held since antiquity, and raised new interest in radical teachings such as the heliocentric theory of Copernicus.
In reaction, many scholars maintained that the motion of the Earth and immobility of the Sun were heretical, as they contradicted some accounts given in the Bible as understood at that time. Galileo's part in the controversies over theology, astronomy. and philosophy culminated in his trial and sentencing in 1633, on a grave suspicion of heresy.
Revivalism (1720–1906)
Revivalism refers to the Calvinist and Wesleyan revival, called the Great Awakening, in North America which saw the development of evangelical Congregationalist, Presbyterian, Baptist, and new Methodist churches. When the movement eventually waned, it gave rise to new Restorationist movements.
Great Awakenings
The First Great Awakening was a wave of religious enthusiasm among Protestants in the American colonies, 1730–1740, emphasizing the traditional Reformed virtues of Godly preaching, rudimentary liturgy, and a deep sense of personal guilt and redemption by Christ Jesus. Historian Sydney E. Ahlstrom saw it as part of a "great international Protestant upheaval" that also created Pietism in Germany, the Evangelical Revival, and Methodism in England.[69] It centered on reviving the spirituality of established congregations, and mostly affected Congregational, Presbyterian, Dutch Reformed, German Reformed, Baptist, and Methodist churches, while also spreading within the slave population. The Second Great Awakening (1800–1830s), unlike the first, focused on the unchurched and sought to instill in them a deep sense of personal salvation as experienced in revival meetings. It also sparked the beginnings of Restorationist groups such Joseph Smith's Mormons, and the Holiness movement. The Third Great Awakening began from 1857 and was most notable for taking the movement throughout the world, especially in English speaking countries. The final group to emerge from the "great awakenings" in North America was Pentecostalism, which had its roots in the Methodist, Wesleyan, and Holiness movements, and began in 1906 on Azusa Street, in Los Angeles. Pentecostalism would later lead to the Charismatic movement.
Restorationism
Restorationism refers to various unaffiliated movements that considered contemporary Christianity, in all its forms, to be a deviation from the true, original Christianity, which these groups then attempted to "Reconstruct," often using the Book of Acts as a "guidebook" of sorts. Restorationism developed out of the Second Great Awakening and is historically connected to the Protestant Reformation,[70] but differs in that Restorationists do not usually describe themselves as "reforming" a Christian Church continuously existing from the time of Jesus, but as restoring the Church that they believe was lost at some point. The name Restoration is also used to describe the Mormons and the Jehovah's Witness Movement.
Contemporary history (1848-present)
The history of the Church in contemporary times covers the period from the revolutions of 1848 to today.
Russian Orthodox Church in the Russian Empire
The Russian Orthodox Church held a privileged position in the Russian Empire, expressed in the motto, Orthodoxy, Autocracy, and Populism, of the late Russian Empire. At the same time, it was placed under the control of the Tsar by the Church reform of Peter I in eighteenth century. Its governing body was Most Holy Synod, which was run by an official (titled Ober-Procurator) appointed by the Tsar himself.
The church was involved in the various campaigns of Russification,[71] and accused of the involvement in anti-Jewish pogroms.[72] In the case of anti-Semitism and the anti-Jewish pogroms, no evidence is given of the direct participation of the church, and many Russian Orthodox clerics, including senior hierarchs, openly defended persecuted Jews, at least from the second half of the nineteenth century. Also, the Church has no official position on Judaism as such.[73]
The Church, like the Tsarist state was seen as an enemy of the people by the Bolsheviks and other Russian revolutionaries.
Russian Orthodox Church in the Soviet Union
The Russian Orthodox Church collaborated with the White Army in the Russian Civil War (see White movement) after the October Revolution. This may have further strengthened the Bolshevik animus against the church. According to Lenin, a communist regime cannot remain neutral on the question of religion but must show itself to be merciless towards it. There was no place for the church in Lenin's classless society.[74] Before and after the October Revolution of November 7, 1917, (October 25 Old Calendar) there was a movement within the Soviet Union to unite all of the people of the world under Communist rule. This included the Eastern European bloc countries as well as the Balkan States. Since some of these Slavic states tied their ethnic heritage to their ethnic churches, both the peoples and their church where targeted by the Soviets.[75][76]
The Soviet Union was the first state to have as an ideological objective the elimination of religion. Toward that end, the Communist regime confiscated church property, ridiculed religion, harassed believers, and propagated atheism in the schools. Criticism of atheism was strictly forbidden and sometimes lead to imprisonment.[77] Actions toward particular religions, however, were determined by State interests, and most organized religions were never outlawed. Some actions against Orthodox priests and believers along with execution included torture being sent to prison camps, labor camps or mental hospitals.[78][79] The result of this militant atheism was to transform the Church into a persecuted and martyred Church. In the first five years after the Bolshevik revolution, 28 bishops and 1200 priests were executed. This included people like the Grand Duchess Elizabeth Fyodorovna who was at this point a monastic. Along with her murder was Grand Duke Sergei Mikhailovich Romanov; the Princess Ioann Konstantinovich, Konstantin Konstantinovich, Igor Konstantinovich and Vladimir Pavlovich Paley; Grand Duke Sergei's secretary, Fyodor Remez; and Varvara Yakovleva, a sister from the Grand Duchess Elizabeth's convent. They were herded into the forest, pushed into an abandoned mineshaft and grenades were then hurled into the mineshaft. Her remains were buried in Jerusalem, in the Church of Maria Magdalene.

The main target of the anti-religious campaign in the 1920s and 1930s was the Russian Orthodox Church, which had the largest number of faithful. Nearly its entire clergy, and many of its believers, were shot or sent to labor camps. Theological schools were closed, and church publications were prohibited. In the period between 1927 and 1940, the number of Orthodox Churches in the Russian Republic fell from 29,584 to less than 500. Between 1917 and 1940, 130,000 Orthodox priests were arrested. Father Pavel Florensky was one of the New-martyrs of this particular period.
After Nazi Germany's attack on the Soviet Union in 1941, Joseph Stalin revived the Russian Orthodox Church to intensify patriotic support for the war effort. By 1957 about 22,000 Russian Orthodox churches had become active. But in 1959 Nikita Khrushchev initiated his own campaign against the Russian Orthodox Church and forced the closure of about 12,000 churches. By 1985 fewer than 7000 churches remained active.
In the Soviet Union, in addition to the methodical closing and destruction of churches, the charitable and social work formerly done by ecclesiastical authorities was taken over by the state. As with all private property, Church owned property was confiscated into public use. The few places of worship left to the Church were legally viewed as state property which the government permitted the church to use. After the advent of state funded universal education, the Church was not permitted to carry on educational, instructional activity for children. For adults, only training for church-related occupations was allowed. Outside of sermons during the celebration of the divine liturgy it could not instruct or evangelize to the faithful or its youth. Catechism classes, religious schools, study groups, Sunday schools and religious publications were all illegal and or banned. This persecution continued, even after the death of Stalin until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. This caused many religious tracts to be circulated as illegal literature or samizdat.[80]Since the fall of the Soviet Union there have been many New-martyrs added as Saints from the yoke of atheism.
Fascism
Fascism describes certain related political regimes in twentieth century Europe, especially the Nazi Germany of Adolf Hitler. The position of Christians in Nazi Fascism is highly complex.
Regarding the matter, historian Derek Holmes wrote, “There is no doubt that the Catholic districts, resisted the lure of National Socialism (Nazism) far better than the Protestant ones.”[81] Pope Pius XI declared that Fascist governments had hidden "pagan intentions" and expressed the irreconcilability of the Catholic position and Fascism, which placed the nation above God and fundamental human rights and dignity. His declaration that “Spiritually, [Christians] are all Semites” prompted the Nazis to give him the title “Chief Rabbi of the Christian World.”[82]
Catholic priests were executed in concentration camps alongside Jews; for example, 2600 Catholic Priests were imprisoned in Dachau, and 2000 of them were executed. A further 2700 Polish priests were executed (a quarter of all Polish priests), and 5350 Polish nuns were either displaced, imprisoned, or executed.[83] Many Catholic laypeople and clergy played notable roles in sheltering Jews during the Holocaust, including Pope Pius XII (1876-1958). The head rabbi of Rome became a Catholic in 1945 in honor of the actions the Pope undertook to save Jewish lives; he took the name Eugenio (the pope’s first name).[84] A former Israeli consul in Italy claimed: “The Catholic Church saved more Jewish lives during the war than all the other churches, religious institutions, and rescue organizations put together.”[85]
The relationship between Nazism and Protestantism, especially the German Lutheran Church, was complex. Though the majority of Protestant church leaders in Germany supported the Nazis' growing anti-Jewish activities, some, such as Dietrich Bonhoeffer (a Lutheran pastor) were strongly opposed to the Nazis. Bonhoeffer was later found guilty in the conspiracy to assassinate Hitler and executed.
Diaspora emigration to the West
One of the most striking developments in modern historical Orthodoxy is the dispersion of Orthodox Christians to the West. Emigration from Greece and the Near East in the last hundred years has created a sizable Orthodox diaspora in Western Europe, North and South America, and Australia. In addition, the Bolshevik Revolution forced thousands of Russian exiles westward. As a result, Orthodoxy's traditional frontiers have been profoundly modified. Millions of Orthodox are no longer geographically "eastern" since they live permanently in their newly adopted countries in the West. Nonetheless, they remain Eastern Orthodox in their faith and practice. Virtually all the Orthodox nationalities—Greek, Arab, Russian, Serbian, Albanian, Ukrainian, Romanian, and Bulgarian—are represented in the United States.
Modern trends in Christian theology
Modernism and liberal Christianity
Liberal Christianity, sometimes called liberal theology, is an umbrella term covering diverse, philosophically-informed religious movements and moods within late eighteenth, nineteenth, and twentieth century Christianity. The word "liberal" in liberal Christianity does not refer to a leftist political agenda or set of beliefs, but rather to the freedom of dialectic process associated with continental philosophy and other philosophical and religious paradigms developed during the Age of Enlightenment.
Fundamentalism
Fundamentalist Christianity, is a movement that arose mainly within British and American Protestantism in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries in reaction to modernism and certain liberal Protestant groups that denied doctrines considered fundamental to Christianity yet still called themselves "Christian." Thus, fundamentalism sought to reestablish tenets that could not be denied without relinquishing a Christian identity, the "fundamentals": inerrancy of the Bible, Sola Scriptura, the Virgin Birth of Jesus, the doctrine of substitutionary atonement, the bodily resurrection of Jesus, and the imminent return of Jesus Christ.
Second Vatican Council
On October 11, 1962 Pope John XXIII opened the Second Vatican Council, the 21st Ecumenical Xouncil of the Catholic Church. The council was "pastoral" in nature, emphasizing and clarifying already defined dogma, revising liturgical practices, and providing guidance for articulating traditional Church teachings in contemporary times. The council is perhaps best known for its instructions that the Mass may be celebrated in the vernacular as well as in Latin.
Ecumenism
Ecumenism broadly refers to movements between Christian groups to establish a degree of unity through dialogue. "Ecumenism" is derived from Greek οἰκουμένη (oikoumene), which means "the inhabited world," but more figuratively something like "universal oneness." The movement can be distinguished into Catholic and Protestant movements, with the latter characterized by a redefined ecclesiology of "denominationalism" (which the Catholic Church, among others, rejects).
Catholic ecumenism
Over the last century, a number of moves have been made to reconcile the schism between the Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox churches. Although progress has been made, concerns over papal primacy and the independence of the smaller Orthodox churches has blocked a final resolution of the schism.
On November 30, 1894, Pope Leo XIII published the Apostolic Letter Orientalium Dignitas (On the Churches of the East) safeguarding the importance and continuance of the Eastern traditions for the whole Church. On December 7, 1965, a Joint Catholic-Orthodox Declaration of His Holiness Pope Paul VI and the Ecumenical Patriarch Athenagoras I was issued lifting the mutual excommunications of 1054.
Some of the most difficult questions in relations with the ancient Eastern Churches concern some doctrine (i.e., Filioque, Scholasticism, functional purposes of asceticism, the essence of God, Hesychasm, Fourth Crusade, establishment of the Latin Empire, Uniatism to note but a few) as well as practical matters such as the concrete exercise of the claim to papal primacy and how to ensure that ecclesiastical union would not mean mere absorption of the smaller Churches by the Latin component of the much larger Catholic Church (the most numerous single religious denomination in the world), and the stifling or abandonment of their own rich theological, liturgical and cultural heritage.
With respect to Catholic relations with Protestant communities, certain commissions were established to foster dialog and documents have been produced aimed at identifying points of doctrinal unity, such as the Joint Declaration on the Doctrine of Justification produced with the Lutheran World Federation in 1999.
Ecumenism within Protestantism
Ecumenical movements within Protestantism have focused on determining a list of doctrines and practices essential to being Christian and thus extending to all groups which fulfill these basic criteria a (more or less) co-equal status, with perhaps one's own group still retaining a "first among equal" standing. This process involved a redefinition of the idea of "the Church" from traditional theology. This ecclesiology, known as denominationalism, contends that each group (which fulfills the essential criteria of "being Christian") is a sub-group of a greater "Christian Church," itself a purely abstract concept with no direct representation, i.e., no group, or "denomination," claims to be "the Church." Obviously, this ecclesiology is at variance with other groups that indeed consider themselves to be "the Church." But moreover, because the "essential criteria" generally consist of belief in the Trinity, it has resulted in strife between these Protestant ecumenical movements and non-Trinitarian groups such as Latter-day Saints (Mormons) and Jehovah's Witnesses, which are not often regarded as Christian by these ecumenical groups.
International Christianity and future developments
At the beginning of the twenty-first century China is estimated to be the third largest Christian nation on earth, with the future prospect of Christianity eventually becoming a Sino-centric religion:
I suspect that even the most enthusiastic accounts err on the downside, and that Christianity will have become a Sino-centric religion two generations from now. China may be for the 21st century what Europe was during the 8th-11th centuries, and America has been during the past 200 years: the natural ground for mass evangelization. If this occurs, the world will change beyond our capacity to recognize it. Islam might defeat the western Europeans, simply by replacing their diminishing numbers with immigrants, but it will crumble beneath the challenge from the East. -Oswald Spengler[86]
Notes
- ↑ Number of Adherents. Adherents.com. Retrieved November 24, 2019.
- ↑ Robert E. Van Voorst, Jesus Outside the New Testament: An Introduction to the Ancient Evidence (Grand Rapids: Wm. B. Eerdmans, ISBN 978-0802843685), 16.
- ↑ R.E. Brown, The Death of the Messiah: From Gethsemane to the Grave (New York: Doubleday, Anchor Bible Reference Library, 1994), 964; S.J.D. Cohen, From the Maccabees to the Mishnah (Westminster Press, 1987), 78, 93, 105, 108; Michael Grant, Jesus, An Historian's View of the Gospels (New York: Scribner's, 1977), 34–35, 78, 166, 200; Paula Fredriksen, Jesus of Nazareth, King of the Jews (Pan Books, 2000, ISBN 0333783131), 6–7, 105–110, 232–234, 266; John P. Meier, A Marginal Jew: Rethinking the Historical Jesus vol. 1 The Roots of the Problem and the Person (Doubleday, 1991), 68, 146, 199, 278, 386, and vol. 2, 726; Geza Vermes, Jesus the Jew (Philadelphia: Fortress Press, 1973), 37; P. L. Maier, In the Fullness of Time (Kregel, 1991), 1, 99, 121, 171; N.T. Wright, The Meaning of Jesus: Two Visions (HarperCollins, 1998), 32, 83, 100–102, 222; L.T. Johnson, The Real Jesus (San Francisco: Harper San Francisco, 1996), 123; Rudolf Bultmann, Jesus (Berlin: Deutsche Bibliothek, 1926), 159.
- ↑ on death by crucifixion, see L.T. Johnson, The Real Jesus (San Francisco: Harper San Francisco, 1996); John P. Meier, "The Circle of the Twelve: Did It Exist during Jesus' Public Ministry?" in Journal of Biblical Literature 116 (1997): 664–665.
- ↑ R.E. Brown, Death of the Messiah vol. 2 (Garden City, NY: Doubleday, 1994), 1240–1241; J.A.T. Robinson, The Human Face of God (Philadelphia: Westminster, 1973), 131; Bart Ehrman, From Jesus to Constantine: A History of Early Christianity (The Teaching Company, 2003), lecture 4, "Oral and Written Traditions About Jesus" (audiotape); M. J. Borg and N. T. Wright, The Meaning of Jesus (San Francisco: Harper Collins, 1999), 12; G. Habermas, The Historical Jesus (College Press, 1996), 128.
- ↑ Michael Grant, Jesus: An Historian's Review of the Gospels (New York: Scribner's 1977), 176; P.L. Maier, "The Empty Tomb as History" in Christianity Today (March 1975): 5; William Craig, "The Guard at the Tomb," in New Testament Studies 30 (1984): 273–281; W. Craig, "The Historicity of the Empty Tomb of Jesus," in New Testament Studies 31 (1985): 39–67.
- ↑ Robert H. Gundry, Soma in Biblical Theology: With Emphasis on Pauline Anthropology (Society for New Testament Studies Monograph Series) (Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 1976).
- ↑ Johnson, 1996, 136; Gerd Ludemann, What Really Happened to Jesus? trans. J. Bowden (Louisville, Kentucky: Westminster John Knox Press, 1995), 80; N.T. Wright, "The New Unimproved Jesus," in Christianity Today (September 13, 1993): 26.
- ↑ J.W. McGarvey, Jesus Christ's Life: Key Events christianity.com. Retrieved November 24, 2019.
- ↑ Acts 3:1; Acts 5:27–42; Acts 21:18–26; Acts 24:5; Acts 24:14; Acts 28:22; Romans 1:16; Tacitus, Annales xv 44; Josephus. Antiquities xviii 3; Mortimer Chambers, et al. The Western Experience Volume II. chapter 5 (McGraw-Hill, 2006) ; The Oxford Dictionary of the Jewish Religion (Oxford University Press, USA, 1997, ISBN 0195086058), 158.
- ↑ Richard Gerberding and J. H. Moran Cruz, Medieval Worlds (New York: Houghton Mifflin Company, 2004), 51.
- ↑ "Nevertheless this well-proved truth has been contradicted. Baur, Schwanbeck, De Wette, Davidson, Mayerhoff, Schleiermacher, Bleek, Krenkel, and others have opposed the authenticity of the Acts. An objection is drawn from the discrepancy between Acts ix, 19-28 and Gal., i, 17, 19. In the Epistle to the Galatians, i, 17, 18, Paul declares that, immediately after his conversion, he went away into Arabia, and again returned to Damascus. "Then after three years, I went up to Jerusalem to visit Cephas." In Acts no mention is made of Paul's journey into Arabia; and the journey to Jerusalem is placed immediately after the notice of Paul's preaching in the synagogues. Hilgenfeld, Wendt, Weizäcker, Weiss, and others allege here a contradiction between the writer of the Acts and Paul." Acts of the Apostles Catholic Encyclopedia. Retrieved November 25, 2019.
- ↑ "The baptism of Cornelius is an important event in the history of the Early Church. The gates of the Church, within which thus far only those who were circumcised and observed the Law of Moses had been admitted, were now thrown open to the uncircumcised Gentiles without the obligation of submitting to the Jewish ceremonial laws." Catholic Encyclopedia: Cornelius. Retrieved November 25, 2019.
- ↑ "The figure (…) is an allegory of Christ as the shepherd" Andre Grabar, Christian iconography: a study of its origins (Princeton University Press, 1981, ISBN 0691018308).
- ↑ Vernon H. Neufeld, The Earliest Christian Confessions (Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1963), 47; Oscar Cullmann, The Earlychurch: Studies in Early Christian History and Theology, ed. A. J. B. Higgins (Philadelphia: Westminster, 1966), 64; Bultmann, Theology of the New Testament vol. 1, 45, 80–82, 293; R. E. Brown, The Virginal Conception and Bodily Resurrection of Jesus (New York: Paulist Press, 1973), 81, 92.
- ↑ Wolfhart Pannenberg, Jesus–God and Man, translated Lewis Wilkins and Duane Pribe, (Philadelphia: Westminster, 1968), 90; Oscar Cullmann, The Early church: Studies in Early Christian History and Theology, ed. A. J. B. Higgins, (Philadelphia: Westminster, 1966), 66–66.
- ↑ Gerald O'Collins, What are They Saying About the Resurrection? (New York: Paulist Press, 1978), 112; on historical importance, cf. Hans von Campenhausen, "The Events of Easter and the Empty Tomb," in Tradition and Life in the Church (Philadelphia: Fortress, 1968), 44.
- ↑ Cullmann, 32.
- ↑ Bultmann, Theology of the New Testament vol 1, 49, 81; Joachim Jeremias, The Eucharistic Words of Jesus, translated Norman Perrin (London: SCM Press, 1966), 102.
- ↑ Pannenberg, 118, 283, 367; Neufeld, 1964, 7, 50.
- ↑ Reginald H. Fuller, The Foundations of New Testament Christology (New York: Scribner's, 1965), 214, 216, 227, 239; Neufeld, 1964, 7, 9, 128.
- ↑ Walter Bauer, Greek-English Lexicon; Ignatius of Antioch, Letter to the Magnesians 10, Letter to the Romans, Greek text) Retrieved November 25, 2019.
- ↑ Grabar, 7
- ↑ for example, 2Corinthians 11:13–15; 2Peter 2:1–17; 2John 7–11; Jude 4–13, and the Epistle of James in general.
- ↑ Gerberding and Moran Cruz, 58
- ↑ Walter Bauer, Orthodoxy and Heresy in Earliest Christianity (Fortress Press, 1979, ISBN 0800613635); Elaine Pagels, The Gnostic Gospels (Vintage; Reissue edition, 1989, ISBN 0679724532); Bart D. Ehrman, Lost Christianities: The Battles for Scripture and the Faiths We Never Knew (New York: Oxford University Press, 2003, ISBN 0195141830).
- ↑ Everett Ferguson, "Factors leading to the Selection and Closure of the New Testament Canon," in The Canon Debate, eds. L. M. McDonald & J. A. Sanders (Hendrickson, 2002), 302–303; cf. Justin Martyr, First Apology 67.3.
- ↑ Ferguson, 301; cf. Irenaeus, Adversus Haereses 3.11.8
- ↑ Both points taken from Mark A. Noll's Turning Points (Grand Rapids: Baker Academic, 1997), 36–37.
- ↑ H. J. De Jonge, "The New Testament Canon," in The Biblical Canons, eds. de Jonge & J. M. Auwers, (Leuven University Press, 2003), 315.
- ↑ The Cambridge History of the Bible, Volume 1, eds. P. R. Ackroyd and C. F. Evans, (Cambridge University Press, 1970), 308.
- ↑ Carter Lindberg, A Brief History of Christianity (Blackwell Publishing, 2006, ISBN 1405110783), 15.
- ↑ David Brakke, "Canon Formation and Social Conflict in Fourth Century Egypt: Athanasius of Alexandria's Thirty Ninth Festal Letter," in Harvard Theological Review 87 (1994): 395–419.
- ↑ Everett Ferguson, "Factors leading to the Selection and Closure of the New Testament Canon," in The Canon Debate, eds. L. M. McDonald & J. A. Sanders, (Hendrickson, 2002), 320; Frederick Fyvie Bruce, The Canon of Scripture (Intervarsity Press, 1988), 230; cf. Augustine, De Civitate Dei 22.8.
- ↑ Bruce, 1988, 225.
- ↑ Ferguson, 2002, 320.
- ↑ The Cambridge History of the Bible (volume 1), 1970, 305; Canon of the New Testament Catholic Encyclopedia. Retrieved November 25, 2019.
- ↑ Canon of the New Testament Catholic Encyclopedia. Retrieved November 25, 2019.
- ↑ Lactantius, De Mortibus Persecutorum ("On the Deaths of the Persecutors"), ch. 35–34. University of Calgary. Retrieved November 25, 2019.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 Richard Gerberding and J. H. Moran Cruz, Medieval Worlds (New York: Houghton Mifflin Company, 2004), 55-56.
- ↑ Gerberding and Moran Cruz, 55; cf. Eusebius, Life of Constantine.
- ↑ 42.0 42.1 Jeffrey Richards, The Popes and the Papacy in the Early Middle Ages 476–752. (London: Routledge & Kegan Paul, 1979), 14–15.
- ↑ Theodosian Code XVI.i.2, Medieval Sourcebook: Banning of Other Religions by Paul Halsall, June 1997. Retrieved November 25, 2019.
- ↑ Gerberding and Moran Cruz, 57.
- ↑ Richards, 9
- ↑ Richards, 10, 12
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 The Great Schism: The Estrangement of Eastern and Western Christendom. Orthodoxinfo.com. Retrieved November 25, 2019.
- ↑ Kallistos Ware, The Orthodox Church (London: St. Vladimir's Seminary Press, 1995, ISBN 978–0913836583).
- ↑ Vladimir Lossky, The Mystical Theology of the Eastern Church ((1991) reprint ed. SVS Press, 1997, ISBN 0913836311).
- ↑ Nikolai O. Lossky, History of Russian Philosophy (International Universities Press, 1951) Quoting Aleksey Khomyakov, 87: The legal formalism and logical rationalism of the Roman Catholic Church have their roots in the Roman State. These features developed in it more strongly than ever when the Western Church without consent of the Eastern introduced into the Nicene Creed the filioque clause. Such arbitrary change of the creed is an expression of pride and lack of love for one's brethren in the faith. "In order not to be regarded as a schism by the Church, Romanism was forced to ascribe to the bishop of Rome absolute infallibility." In this way Catholicism broke away from the Church as a whole and became an organization based upon external authority. Its unity is similar to the unity of the state: it is not necessarily rational but is rationalistic and legally formal. Rationalism has led to the doctrine of the works of supererogation, established a balance of duties and merits between God and man, weighing in the scales sins and prayers, trespasses and deeds of expiation; it adopted the idea of transferring one person's debts or credits to another and legalized the exchange of assumed merits; in short, it introduced into the sanctuary of faith the mechanism of a banking house.
- ↑ Gerberding and Moran Cruz, 33.
- ↑ On the development of penitential practice, see John T. McNeill and Helena M. Gamer, (translators), Medieval Handbooks of Penance (1938) reprint ed. (Columbia University Press, 1990, ISBN 0231096291), 9–54.
- ↑ Richards, 36.
- ↑ Epitome, Iconoclast Council at Hieria, 754
- ↑ Brian Tierney and Sidney Painter, Western Europe in the Middle Ages 300–1475 (McGraw-Hill, 1998).
- ↑ Father John S. Romanides. Retrieved November 29, 2019.
- ↑ Black Book" The tragedy of Pontus. Retrieved November 29, 2019.
- ↑ Definition of Protestantism at the Episcopal Church website. Retrieved November 29, 2019.
- ↑ Diarmaid MacCulloch, The Reformation: A History (New York: Penguin Books, 2004. ISBN 014303538X), xx.
- ↑ MacCulloch, 124–125.
- ↑ MacCulloch, 119.
- ↑ MacCulloch, 137–138.
- ↑ MacCulloch, 146–148.
- ↑ MacCulloch, 148–149.
- ↑ MacCulloch, 238.
- ↑ MacCulloch, 243.
- ↑ MacCulloch, 404
- ↑ MacCulloch, 540
- ↑ Sydney E. Ahlstrom, A Religious History of the American People (New Haven and London: Yale University Press, 1972), 263.
- ↑ Ahlstrom's summary is as follows: Restorationism has its genesis with Thomas and Alexander Campbell, whose movement is connected to the German Reformed Church through Otterbein, Albright, and Winebrenner, 212; American Millennialism and Adventism, which arose from Evangelical Protestantism, produced certain groups such as The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, 387, 501–509; the Jehovah's Witness movement, 807; and, as a reaction specifically to William Miller, Seventh Day Adventism, 381.
- ↑ Natalia Shlikhta, "'Greek Catholic'-'Orthodox'-'Soviet': a symbiosis or a conflict of identities?" Religion, State & Society 32(3) (2004).
- ↑ Shlomo Lambroza and John D. Klier, Pogroms: Anti-Jewish Violence in Modern Russian History (Cambridge University Press, 2003).
- ↑ It is no coincidence that in the entry on 'Orthodoxy' in the seventh volume of the Kratkaya Evreiskaya Entsyklopedia, devoted to the Russian Orthodox Church, 733–743, where numerous examples are given of persecution of the Jews in Russia, including religious persecution, no evidence is given of the direct participation of the church, either in legislative terms or in the conduct of policy. Although the authors of the article state that the active role of the Church in inciting the government to conduct anti-Jewish acts (for example in the case of Ivan the Terrible's policy in the defeated territories) is 'obvious', no facts are given in their article to support this.
- ↑ V.I. Lenin, Socialism and Religion. Marxists.org. Retrieved November 29, 2019.
- ↑ Afonsas Eidintas, President of Lithuania: Prisoner of the Gulag: a Biography of Aleksandras Stulginskis (Vilnius: Genocide and Resistance Research Center of Lithuania, 2001, ISBN 998675741X), 23. quote: "As early as August 1920 Lenin wrote to E. M. Skliansky, President of the Revolutionary War Soviet: "We are surrounded by the greens (we pack it to them), we will move only about 10–20 versty and we will choke by hand the bourgeoisie, the clergy, and the landowners. There will be an award of 100,000 rubles for each one hanged." He was speaking about the future actions in the countries neighboring Russia.
- ↑ Father George Calciu, Christ Is Calling You: A Course in Catacomb Pastorship (Spruce Island, AK: Saint Herman Press, 1997, ISBN 9781887904520).
- ↑ Father George Calciu-Dumitreasa, Christ is Calling You! Sermons to young people, given at the Chapel of the Romanian Orthodox Church Seminary. Retrieved November 29, 2019.
- ↑ Alexander, (ed.), and Vera Bouteneff, (transl.), Father Arseny 1893–1973: Priest, Prisoner, Spiritual Father (St Vladimir's Seminary Press, 1998, ISBN 0881411809), Introduction vi—1.
- ↑ Patricia Sullivan, Anti-Communist Priest Gheorghe Calciu-Dumitreasa. The Washington Post, November 26, 2006. Retrieved November 29, 2019.
- ↑ Alexander, Father Arseny 1893–1973: Priest, Prisoner, Spiritual Father : Being the Narratives Compiled by the Servant of God Alexander Concerning His Spiritual Father (Crestwood, NY: St. Vladimir's Seminary Press, ISBN 0881411809), Introduction, vi—1.
- ↑ Derek Holmes, History of the Papacy, 102.
- ↑ Holmes, 116.
- ↑ John Vidmar, The Catholic Church Through the Ages: A History (New York: Paulist Press, 2005), 332 & n. 37.
- ↑ Vidmar, 332.
- ↑ Holmes, 158.
- ↑ Christianity finds a fulcrum in Asia. Asia Times Online, August 7, 2007. Retrieved November 29, 2019.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Ahlstrom, Sydney E. A Religious History of the American People. New Haven and London: Yale University Press, 1972.
- Bauer, Walter. Orthodoxy and Heresy in Earliest Christianity. Sigler Press, 1971. ISBN 0800613635
- Brown, R. E. The Death of the Messiah: From Gethsemane to the Grave. New York: Doubleday, Anchor Bible Reference Library, 1994.
- Bruce, Frederick Fyvie. The Canon of Scripture. Intervarsity Press, 1988. ISBN 083081258X
- Bultmann, Rudolf. Jesus. Berlin: Deutsche Bibliothek, 1926.
- Cambridge History of the Bible, The Volume 1, eds. P. R. Ackroyd and C. F. Evans. Cambridge University Press, 1970.
- Chambers, Mortimer. The Western Experience. Volume II: Since the Sixteenth Century, chapter 5. McGraw-Hill.
- Cohen, S.J.D. From the Maccabees to the Mishnah. Westminster Press, 1987.
- Craig, William Lane. "The Guard at the Tomb," in New Testament Studies 30 (1984): 273–281.
- Craig, William Lane. "The Historicity of the Empty Tomb of Jesus," in New Testament Studies 31 (1985): 39–67.
- Cullmann, Oscar. The Early Church: Studies in Early Christian History and Theology, ed. A. J. B. Higgins. Philadelphia: Westminster, 1966.
- De Jonge, H. J., "The New Testament Canon," in The Biblical Canons, eds. de Jonge & J. M. Auwers. Leuven University Press, 2003. ISBN-10: 905867309X
- Dowley, Tim. 1977. Eerdmans' Handbook to the History of Christianity. Grand Rapids: Eerdmans. ISBN 0802834507
- Ehrman, Bart. From Jesus to Constantine: A History of Early Christianity. The Teaching Company, 2003, lecture 4, "Oral and Written Traditions About Jesus." (audiotape)
- Ehrman, Bart. Lost Christianities: The Battles for Scripture and the Faiths We Never Knew. New York: Oxford Univ. Press, 2003. ISBN 0195141830
- Eidintas, Alfonsas. President of Lithuania: Prisoner of the Gulag: a Biography of Aleksandras Stulginskis. (Vilnius: Genocide and Resistance Research Center of Lithuania, 2001. ISBN 998675741X
- Ferguson, Everett, "Factors leading to the Selection and Closure of the New Testament Canon," in The Canon Debate, eds. L. M. McDonald & J. A. Sanders. Hendrickson, 2002. ISBN 1565635175
- Fuller, Reginald Horace. The Foundations of New Testament Christology. New York: Scribner, 1978. ISBN 068415532X
- Gerberding, Richard, and J. H. Moran Cruz. Medieval Worlds. New York: Houghton Mifflin Company, 2004. ISBN 039556087X
- Gonzalez, Justo L. The Story of Christianity. San Francisco: Harper & Row, 1984. ISBN 0060633158
- Grabar, Andre. Christian iconography: a study of its origins. Princeton University Press, 1981. ISBN 0691018308
- Grant, Michael. Jesus: An Historian's Review of the Gospels. New York: Scribner's, (1977) reprint 1995. ISBN 0684818671.
- Guericke, Heinrich Ernst Ferdinand. A Manual of Church History. (1874) reprint ed. General Books, 2009. ISBN 0217664970
- Gundry, Robert H. Soma in Biblical Theology: With Emphasis on Pauline Anthropology. (Society for New Testament Studies Monograph Series) Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, (1976) reprint 2005. ISBN 0521018706.
- Hastings, Adrian. A World History of Christianity. Grand Rapids, MI: W.B. Eerdmans, 1999. ISBN 0802824420
- Herring, George. Introduction to the History of Christianity. Washington Square, NY: New York University Press, 2006. ISBN 0814736998
- Jeremias, Joachim. The Eucharistic Words of Jesus, translated Norman Perrin. London: SCM Press, 1966.
- Johnson, L. T. The Real Jesus. San Francisco: Harper San Francisco, 1996.
- Johnson, Paul. A History of Christianity. New York: Atheneum, 1976. ISBN 0689107285
- Latourette, Kenneth Scott. A History of Christianity. Peabody, MA: Prince Press, 1975. ISBN 1565633288
- Lindberg, Carter. A Brief History of Christianity. Blackwell Publishing, 2006. ISBN 1405110783
- Lossky, Vladimir. The Mystical Theology of the Eastern Church. (1991) reprint ed. SVS Press, 1997. ISBN 0913836311
- MacCulloch, Diarmaid. The Reformation: A History. New York: Penguin Books, 2004. ISBN 014303538X
- Meier, John P. A Marginal Jew. Doubleday, 1991. vol. 1 ‘’The Roots of the Problem and the Person’’; and vol. 2 ‘’Mentor, Message, and Miracles.’’
- Meier, John P. "The Circle of the Twelve: Did It Exist during Jesus' Public Ministry?," in Journal of Biblical Literature 116 (1997): 664–665.
- Neufeld, Vernon H. The Earliest Christian Confessions. Grand Rapids: Eerdmans, 1963.
- Noll, Mark A. Turning Points: Decisive Moments in the History of Christianity. Grand Rapids: Baker Academic, 1997. ISBN 080106211X
- Pagels, Elaine. The Gnostic Gospels. New York: Vintage, (1979) 1989. ISBN 0679724532
- Pannenberg, Wolfhart. Jesus–God and Man, translated Lewis Wilkins and Duane Pribe Philadelphia: Westminster, 1968.
- Richards, Jeffrey. The Popes and the Papacy in the Early Middle Ages 476–752. London: Routledge & Kegan Paul, 1979
- Robinson, J.A.T. The Human Face of God. Philadelphia: Westminster, 1973.
- Shelley, Bruce L. 1995. Church History in Plain Language. Dallas, TX: Word Pub. ISBN 0849938619
- Tierney, Brian, and Sidney Painter. Western Europe in the Middle Ages 300–1475, 6th ed. McGraw-Hill, 1998.
- Van Voorst, Robert E. Jesus Outside the New Testament: An Introduction to the Ancient Evidence. (Studying the Historical Jesus). Grand Rapids: Wm. B. Eerdmans. ISBN 978-0802843685
- Vermes, Geza. Jesus the Jew. Philadelphia: Fortress Press, (1973) 1981. ISBN 0800614437
- Vidmar, John. The Catholic Church Through the Ages: A History. New York: Paulist Press, 2005. ISBN 0809142341
- Wright, N. T. The Meaning of Jesus: Two Visions. HarperCollins, 1998.
External links
All links retrieved July 18, 2024.
- Aristeides Papadakis, Ph.D., History of the Orthodox Church
- Reformation Timeline, A short timeline of the Protestant Reformation.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.