Difference between revisions of "Spain" - New World Encyclopedia
Mike Butler (talk | contribs) |
Mike Butler (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
Spain is a [[democracy]] which is organised as a [[parliamentary monarchy]]. It is a [[developed country]] with the ninth-largest economy in the world. It is the largest of the three sovereign nations that make up the [[Iberian Peninsula]]—the others are [[Portugal]] and the [[microstate]] of [[Andorra]]. | Spain is a [[democracy]] which is organised as a [[parliamentary monarchy]]. It is a [[developed country]] with the ninth-largest economy in the world. It is the largest of the three sovereign nations that make up the [[Iberian Peninsula]]—the others are [[Portugal]] and the [[microstate]] of [[Andorra]]. | ||
| + | ==Geography== | ||
| + | [[Image:Sp-map.png|left|thumb|300px|Map of Spain.]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Spain topo.jpg |left|thumb|300px|Topography of Spain.]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Rural Basque Country.jpg|right|thumb|200px|Rural Basque country.]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Berria3 lou.JPG|left|thumb|300px|Coast of [[Cantabria]], in the so called ''Green Spain''.]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Düne4.jpg|left|thumb|300px|The [[Maspalomas]] dunes of the Canary Islands.]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Central pyrenees.jpg|left|thumb|300px|The Pyrenees.]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
The name ''Spain'' (''España'' in Spanish) comes from the Latin name [[Hispania]]. | The name ''Spain'' (''España'' in Spanish) comes from the Latin name [[Hispania]]. | ||
| Line 81: | Line 86: | ||
At 194,884 square miles (504,782 square kilometers), Spain is the world's 51st-largest country (after [[Thailand]]). It is comparable in size to [[Turkmenistan]], and somewhat larger than the US state of [[California]]. | At 194,884 square miles (504,782 square kilometers), Spain is the world's 51st-largest country (after [[Thailand]]). It is comparable in size to [[Turkmenistan]], and somewhat larger than the US state of [[California]]. | ||
| − | Mainland Spain is dominated by | + | Spain takes up more than 80 percent of the Iberian Peninsula. Mainland Spain is dominated by a large plateau, the Meseta Central, which is divided by the roughly west-east Sistema Central mountain range. The Cordillera Cantábrica mountains border the Meseta to the north, the Iberian Cordillera to the northeast and east, the Sierra Morena to the south, while the lower mountains of the Portuguese frontier and Spanish Galicia are located to the northwest. The [[Pyrenees]] form Spain's border with France. In the southeast, the Sistema Penibético runs parallel to the coast to merge with the Iberian Cordillera. Along the Mediterranean seaboard there are coastal plains, some with lagoons (e.g., Albufera, south of Valencia). The Balearic Islands in the Mediterraneanare are a portion of the Baetic Cordillera. The Canary Islands are of volcanic origin and contain Spain's highest point, Teide Peak, which rises to 12,198 feet (3718 metres) on the island of Tenerife. |
| − | + | Except for the subtropical [[Canary Islands]], Spain can be divided into areas experiencing, respectively, a Mediterranean climate; a climate dominated by the [[Atlantic Ocean]]; and (in the inner areas) a rather extreme climate with hotter summers and colder winters than nearer the coasts. A continental climate covers the majority of peninsular Spain. It is characterized by wide diurnal and seasonal variations in temperature and by low, irregular rainfall with high rates of evaporation that leave the land arid. Annual rainfall generally is 300mm to 640mm. Continental winters are cold (-1[[Celsius|°C]]), with strong winds. Summers are warm and cloudless, producing average daytime temperatures that reach 21[[Celsius|°C]] in the northern Meseta and 24 to 27°C in the southern Meseta; nighttime temperatures range from 7 to 10°C. The Ebro Basin, at a lower altitude, is extremely hot during the summer, and temperatures can exceed 40°C. | |
| − | + | An [[oceanic climate]] prevails in the northern part of the country, often called "[[Green Spain]]", from the Pyrenees to the northwest region, characterized by relatively mild winters, warm but not hot summers, and generally abundant rainfall spread out over the year. Temperatures vary only slightly, both on a diurnal and a seasonal basis. The moderating effects of the sea, however, abate in the inland areas, where temperatures are 9 to 18°C more extreme than temperatures on the coast. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The [[Mediterranean climate]] region roughly extends from the Andalusian Plain along the southern and eastern coasts up to the Pyrenees, on the seaward side of the mountain ranges that parallel the coast. Total rainfall in this region is lower than in the rest of Spain, and it is concentrated in the late autumn-winter period. Temperatures in January normally average 10 to 13°C in most of the Mediterranean region, and they are 9°C colder in the northeastern coastal area near Barcelona. Temperatures in July and August average 22 to 27°C on the coast and 29 to 31°C farther inland, with low humidity. The Mediterranean region is marked by Leveche winds: hot, dry, easterly or southeasterly air currents that originate over North Africa. | ||
| − | - | + | The generally warm and relatively dry summers have led to a culture in which a lot of life is lived outdoors, whether on a [[patio]] in the courtyard of a building or on a public plaza. In Madrid, many of the most popular nightclubs move for several months in the summer to an outdoor ''terraza'' much farther from the city centre than their indoor winter location, continuing in a way the older tradition of the ''[[verbena (fair)]]''. In the Mediterranean areas (and in the Canary Islands), outdoor meals can be a nearly year-round phenomenon. |
| − | + | ||
| + | Despite apparent aridity, the Iberian Peninsula has a dense network of roughly 1800 rivers and streams, all of which, except the Ebro, drain into the Atlantic Ocean. Three rank among Europe's longest. The Tagus is 626 miles (1007km), the Ebro is 565 miles (909 km), and the Douro at 556 miles (895km). The Guadiana and the Guadalquivir are 508 miles (818 km) and 408 miles (657 km) long, respectively. The Tagus, the Douro, and the Guadiana, reach the Atlantic Ocean in Portugal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Natural resources include [[coal]], [[lignite]], [[iron]] ore, [[uranium]], [[mercury (element)|mercury]], [[pyrite]]s, [[fluorspar]], [[gypsum]], [[zinc]], [[lead]], [[tungsten]], [[copper]], [[kaolin]], [[potash]], [[hydropower]], as well as arable land. | ||
| − | + | Natural hazards include periodic droughts, and wildfires. Environmental issues include pollution of the Mediterranean Sea from raw sewage and effluents from the offshore production of oil and gas, water quality and quantity, air pollution, deforestation, and desertification. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Most populous metropolitan regions are: | Most populous metropolitan regions are: | ||
| Line 572: | Line 570: | ||
Image:Santuario Novelda.jpg|Vista del Santuario de Santa María Magdalena de Novelda, Spain | Image:Santuario Novelda.jpg|Vista del Santuario de Santa María Magdalena de Novelda, Spain | ||
Image:Guggenheim-bilbao-jan05.jpg|[[Guggenheim Museum Bilbao|Guggenheim Museum]], [[Bilbao]] | Image:Guggenheim-bilbao-jan05.jpg|[[Guggenheim Museum Bilbao|Guggenheim Museum]], [[Bilbao]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
Image:Spain Cabo Trafalgar.jpg|Cabo Trafalgar in Cádiz (Spain) | Image:Spain Cabo Trafalgar.jpg|Cabo Trafalgar in Cádiz (Spain) | ||
Image:Cadaqués.jpg|Port of [[Cadaqués]], [[Catalonia]] | Image:Cadaqués.jpg|Port of [[Cadaqués]], [[Catalonia]] | ||
Image:Antequera pena de los enamorados.JPG|Antequera, in Málaga (Spain) | Image:Antequera pena de los enamorados.JPG|Antequera, in Málaga (Spain) | ||
| − | + | ||
Image:javea.jpg|Jávea, [[Xàbia]] | Image:javea.jpg|Jávea, [[Xàbia]] | ||
Image:llanes.JPG|Llanes, [[Asturias]] | Image:llanes.JPG|Llanes, [[Asturias]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
</gallery></center> | </gallery></center> | ||
Revision as of 21:59, 5 November 2007
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN CLAIMED FOR MIKE BUTLER BY MARY ANGLIN. THANK YOU!
| Reino de España Kingdom of Spain |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: Plus Ultra (motto) (Latin: "Further Beyond") |
||||||
| Anthem: Marcha Real 1 (Spanish lanuguage: "Royal March") |
||||||
| Capital (and largest city) | Madrid 40°26′N 3°42′W | |||||
| Official languages | Spanish. In some autonomous communities of Spain, Aranese, Basque, Catalan and Galician are co-official. | |||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | |||||
| Formation | 15th century | |||||
| - | Dynastic union | Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in 1516 | ||||
| - | Unification | |||||
| - | De facto | Nueva Planta Decrees of 1716 | ||||
| - | De jure | Spanish Constitution of 1812 | ||||
| EU accession | January 1 1986 | |||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 505,992 km² (51st) 195,364 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 1.04 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 1 January 2006 estimate | 44,395,286 (29th) | ||||
| - | 2005 census | 44,108,530 | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2005 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $1.029 trillion (12th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $26,320 (25th) | ||||
| Currency | Euro (€)2 (EUR) |
|||||
| Time zone | CET3 (UTC+1) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | Central European Summer Time (UTC+2) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .es4 | |||||
| Calling code | +34 | |||||
| 1 Also serves as the Royal anthem. 2 Prior to 1999: Spanish Peseta. |
||||||
Spain, officially the Kingdom of Spain (Spanish: Reino de España, is a country located in Southern Europe, with two small exclaves in North Africa (both bordering Morocco).
Spain is a democracy which is organised as a parliamentary monarchy. It is a developed country with the ninth-largest economy in the world. It is the largest of the three sovereign nations that make up the Iberian Peninsula—the others are Portugal and the microstate of Andorra.
Geography
The name Spain (España in Spanish) comes from the Latin name Hispania.
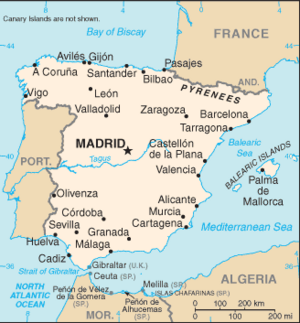
Spain is located southwest of France, with the Bay of Biscay to the north, North Atlantic Oceanand Portugal to the west, Gibraltar to the south, the Mediterranean Sea to the south-east. The Pyrenees Mountains form the border with France. The tiny principality of Andorra is located on the French border.
Spain includes two autonomous cities - Ceuta and Melillathe - in North Africa, the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean Sea, the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean and a number of uninhabited islands on the Mediterranean side of the strait of Gibraltar, known as Plazas de soberanía, such as the Chafarine islands, the isle of Alborán, the "rocks" (peñones) of Vélez and Alhucemas, and the tiny Isla Perejil. In the northeast along the Pyrenees, a small exclave town called Llívia in Catalonia is surrounded by French territory.
At 194,884 square miles (504,782 square kilometers), Spain is the world's 51st-largest country (after Thailand). It is comparable in size to Turkmenistan, and somewhat larger than the US state of California.
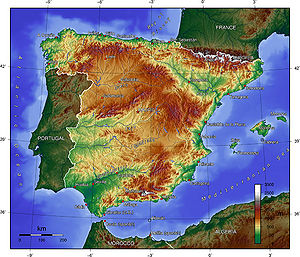
Spain takes up more than 80 percent of the Iberian Peninsula. Mainland Spain is dominated by a large plateau, the Meseta Central, which is divided by the roughly west-east Sistema Central mountain range. The Cordillera Cantábrica mountains border the Meseta to the north, the Iberian Cordillera to the northeast and east, the Sierra Morena to the south, while the lower mountains of the Portuguese frontier and Spanish Galicia are located to the northwest. The Pyrenees form Spain's border with France. In the southeast, the Sistema Penibético runs parallel to the coast to merge with the Iberian Cordillera. Along the Mediterranean seaboard there are coastal plains, some with lagoons (e.g., Albufera, south of Valencia). The Balearic Islands in the Mediterraneanare are a portion of the Baetic Cordillera. The Canary Islands are of volcanic origin and contain Spain's highest point, Teide Peak, which rises to 12,198 feet (3718 metres) on the island of Tenerife.
Except for the subtropical Canary Islands, Spain can be divided into areas experiencing, respectively, a Mediterranean climate; a climate dominated by the Atlantic Ocean; and (in the inner areas) a rather extreme climate with hotter summers and colder winters than nearer the coasts. A continental climate covers the majority of peninsular Spain. It is characterized by wide diurnal and seasonal variations in temperature and by low, irregular rainfall with high rates of evaporation that leave the land arid. Annual rainfall generally is 300mm to 640mm. Continental winters are cold (-1°C), with strong winds. Summers are warm and cloudless, producing average daytime temperatures that reach 21°C in the northern Meseta and 24 to 27°C in the southern Meseta; nighttime temperatures range from 7 to 10°C. The Ebro Basin, at a lower altitude, is extremely hot during the summer, and temperatures can exceed 40°C.
An oceanic climate prevails in the northern part of the country, often called "Green Spain", from the Pyrenees to the northwest region, characterized by relatively mild winters, warm but not hot summers, and generally abundant rainfall spread out over the year. Temperatures vary only slightly, both on a diurnal and a seasonal basis. The moderating effects of the sea, however, abate in the inland areas, where temperatures are 9 to 18°C more extreme than temperatures on the coast.
The Mediterranean climate region roughly extends from the Andalusian Plain along the southern and eastern coasts up to the Pyrenees, on the seaward side of the mountain ranges that parallel the coast. Total rainfall in this region is lower than in the rest of Spain, and it is concentrated in the late autumn-winter period. Temperatures in January normally average 10 to 13°C in most of the Mediterranean region, and they are 9°C colder in the northeastern coastal area near Barcelona. Temperatures in July and August average 22 to 27°C on the coast and 29 to 31°C farther inland, with low humidity. The Mediterranean region is marked by Leveche winds: hot, dry, easterly or southeasterly air currents that originate over North Africa.
The generally warm and relatively dry summers have led to a culture in which a lot of life is lived outdoors, whether on a patio in the courtyard of a building or on a public plaza. In Madrid, many of the most popular nightclubs move for several months in the summer to an outdoor terraza much farther from the city centre than their indoor winter location, continuing in a way the older tradition of the verbena (fair). In the Mediterranean areas (and in the Canary Islands), outdoor meals can be a nearly year-round phenomenon.
Despite apparent aridity, the Iberian Peninsula has a dense network of roughly 1800 rivers and streams, all of which, except the Ebro, drain into the Atlantic Ocean. Three rank among Europe's longest. The Tagus is 626 miles (1007km), the Ebro is 565 miles (909 km), and the Douro at 556 miles (895km). The Guadiana and the Guadalquivir are 508 miles (818 km) and 408 miles (657 km) long, respectively. The Tagus, the Douro, and the Guadiana, reach the Atlantic Ocean in Portugal.
Natural resources include coal, lignite, iron ore, uranium, mercury, pyrites, fluorspar, gypsum, zinc, lead, tungsten, copper, kaolin, potash, hydropower, as well as arable land.
Natural hazards include periodic droughts, and wildfires. Environmental issues include pollution of the Mediterranean Sea from raw sewage and effluents from the offshore production of oil and gas, water quality and quantity, air pollution, deforestation, and desertification.
Most populous metropolitan regions are:
- Madrid 5,904,041
- Barcelona 5,300,701
- Valencia 1,623,724
- Sevilla 1,317,098
- Málaga 1,074,074
- Bilbao 946,829
History
Prehistory and Pre-Roman peoples in the Iberian Peninsula
The earliest records of hominids living in Europe to date has been found in the Spanish cave of Atapuerca which has become a key site for world Paleontology due to the importance of the fossils found there, dated roughly 1,000,000 years ago.
Modern humans in the form of Cro-Magnons began arriving in the Iberian peninsula from north of the Pyrenees some 35,000 years ago. The more conspicuous sign of prehistoric human settlements are the famous paintings in the northern Spanish Altamira (cave), which were done ca. 15,000 B.C.E. and are regarded, along with those in Lascaux, France, as paramount instances of cave art.
The earliest urban culture documented is that of the semi-mythical southern city of Tartessos, pre- 1100 B.C.E. The seafaring Phoenicians, Greeks and Carthaginians successively settled along the Mediterranean coast and founded trading colonies there over a period of several centuries. Around 1100 B.C.E., Phoenician merchants founded the trading colony of Gadir or Gades (modern day Cádiz) near Tartessos. In the 9th century B.C.E. the first Greek colonies, such as Emporion (modern Empúries), were founded along the Mediterranean coast on the East, leaving the south coast to the Phoenicians. The Greeks are responsible for the name Iberia, apparently after the river Iber (Ebro in Spanish). In the 6th century B.C.E. the Carthaginians arrived in Iberia while struggling first with the Greeks and shortly after with the Romans for control of the Western Mediterranean. Their most important colony was Carthago Nova (Latin name of modern day Cartagena).
The native peoples which the Romans met at the time of their invasion in what is now known as Spain were the Iberians, inhabiting from the Southwest part of the Peninsula through the Northeast part of it, and then the Celts, mostly inhabiting the north and northwest part of the Peninsula. In the inner part of the peninsula, where both groups were in contact, a mixed, distinctive, culture was present, the one known as Celtiberian.
Roman Empire and Germanic Invasions
The Romans arrived in the Iberian peninsula during the Second Punic war in the 2nd century B.C.E., and annexed it under Augustus after two centuries of war with the tenacious Celtic and Iberian tribes (from whom they copied the short sword known as falcata). These, along with the Phoenician, Greek and Carthaginian coastal colonies, became the province of Hispania. It was divided into Hispania Ulterior and Hispania Citerior during the late Roman Republic; and, during the Roman Empire, Hispania Taraconensis in the northeast, Hispania Baetica in the south and Lusitania (province with capital in the city of Emerita Augusta) in the southwest.
Hispania supplied Rome with food, olive oil, wine and metal. The emperors Trajan, Hadrian, Marcus Aurelius and Theodosius I, the philosopher Seneca and the poets Martial, Quintilian and Lucan were born in Spain. The Spanish Bishops held the Council at Elvira in 306. The collapse of the Western Roman empire did not lead to the same wholesale destruction of Western classical society as happened in areas like Britain, Gaul and Germania Inferior during the Dark Ages, even if the institutions, infrastructure and economy did suffer considerable degradation. Spain's present languages, its religion, and the basis of its laws originate from this period. The centuries of uninterrupted Roman rule and settlement left a deep and enduring imprint upon the culture of Spain.
The first hordes of Barbarians to invade Hispania arrived in the 5th century, as the Roman empire decayed. The tribes of Goths, Visigoths, Swebians (Suebi), Alans, Asdings and Vandals, arrived to Spain by crossing the Pyrenees mountain range. They were all of Germanic origin. This led to the establishment of the Swebian Kingdom in Gallaecia, in the northwest, and the Visigothic Kingdom elsewhere. (For a while, the Germans lived under their law while the much more numerous Spaniards continued more or less to live under Roman law.) The Visigothic Kingdom eventually encompassed the entire Iberian Peninsula with the Catholic conversion of the Goth monarchs. The famous horseshoe arch, which was adapted and perfected by the later Muslim era builders was in fact originally an example of Visigothic art.
Muslim Iberia
In the 8th century, nearly all the Iberian peninsula, which had been under Visigothic rule, was quickly conquered (711–718), by mainly Berber Muslims (see Moors), who had crossed over from North Africa, led by Tariq ibn Ziyad. Visigothic Spain was the last of a series of lands conquered in a great westward charge by the Islamically inspired armies of the Umayyad empire. Indeed they continued northwards until they were defeated in central France at the Battle of Tours in 732. Astonishingly the invasion started off as an invitation from a Visigoth faction within Spain for support. But instead the Moorish army, having defeated King Roderic proceeded to conquer the peninsula for itself. The Roman Catholic populace, unimpressed with the constant internal feuding of the Visigothic leaders, often stood apart from the fighting, often welcoming the new rulers, thereby forging the basis of the distinctly Spanish-Muslim culture of Al-Andalus. Only three small counties in the mountains of the north of Spain managed to cling to their independence: Asturias, Navarra and Aragon, which eventually became kingdoms.
The Muslim emirate proved strong in its first three centuries; stopping Charlemagne's massive forces at Saragossa and, after a serious Viking attack, established effective defences. Indeed it became a terror in its own right to Christian neighbours, with its "al-jihad fil-bahr" (holy war at sea). Christian Spain struck back from its mountain redoubts by seizing the lands north of the Duero river, and the Franks were able to seize Barcelona (801) and the Spanish Marches), but save for these and some other small incursions in the north, the Christians were unable to make headway against the superior forces of Al-Andalus for several centuries. It was only in the 11th century that the break up of Al-Andalus led to the creation of the Taifa kingdoms, who attempted to outshine each other in art and culture and were often at war, became vulnerable to the consolidating power of Spain's Christian kingdoms.
The Moorish capital was Córdoba, in southern Spain. During this time large populations of Jews, Christians and Muslims lived in close quarters, and at its peak some non-Muslims were appointed to high offices under the some of the more lenient Muslim rulers. At its best it produced exquisite architecture and art, and Muslim and Jewish scholars played a major part in reviving the tradition of classical Greek philosophy, mathematics and science in western Europe, whilst making their own contributions to it. However, there were restrictions on non-Muslims that grew after the death of Al-Hakam II in 976. Later invasions of stricter Muslim groups led to persecutions of non-Muslims, forcing some (including Muslim scholars) to seek safety in the then still relatively tolerant city of Toledo after its Christian reconquest in 1085.

Spanish society under Muslim rule became increasingly complex, partly because Islamic conquest did not involve the systematic conversion of the much larger conquered population to Islam. At the same time, Christians and Jews were recognized under Islam as "peoples of the book", and so given dhimmi status. Most importantly, the Islamic Berber and Arab invaders were a small minority, ruling over several million Christians. Thus, Christians and Jews were free to practise their religion, but faced certain restrictions and financial burdens. Conversion to Islam proceeded at a steadily increasing pace, as it offered social and economic and political advantages. Merchants, nobles, large landowners, and other local elites were usually among the first to convert. By the 11th century Muslims are believed to have outnumbered Christians in Al-Andalus.
The Muslim community in Spain was itself diverse and beset by social tensions. From the beginning, the Berber people of North Africa had provided the bulk of the armies, clashed with the Arab leadership from the Middle East. The Berbers, who were comparatively recent converts to Islam, resented the aristocratic pretensions of the Arab elite. They soon gave up attempting to settle the harsh lands of the north of the Meseta Central handed to them by the Arab rulers, and many returned to Africa during a Berber uprising against Arab rule. However, the Berbers later took over power and Muslim Spain fell under the rule of the Almoravid and then the Almohad dynasties, amongst others. Over time the relatively tiny number of Moors gradually increased with immigration and cross marriages. Large Moorish populations grew, most notably in the south in the Guadalquivir river valley, and in the east, along the fertile Mediterranean coastal plain and in the Ebro river valley.
Muslim Spain was wealthy and sophisticated under Islamic rule. Cordoba was the richest and most sophisticated city in all of western Europe. It was not until the 12th century that western medieval Christiandom began to reach comparable levels of sophistication, and this was due in part to the stimulus coming from Muslim Spain. Mediterranean trade and cultural exchange flourished. Muslims imported a rich intellectual tradition from the Middle East and North Africa, including knowledge of mathematics and science, that they helped revive. Crops and farming techniques introduced by the Arabs, led to a remarkable expansion of agriculture, which had been in decline since Roman times. In towns and cities magnificent mosques, palaces, and other monuments were constructed. Outside the cities, the mixture of large estates and small farms that existed in Roman times remained largely intact because Muslim leaders rarely dispossessed landowners. The Muslim conquerors were relatively few in number and so they tried to maintain good relations with their subjects. This relative social peace, which was already deteriorating from the late 10th century, broke down with the later, stricter, Muslim sects.
Roman, Jewish, and Muslim culture interacted in complex ways. A large part of the population gradually adopted Arabic. Arabic was the official language of government. Even Jews and Christians often spoke Arabic, while Hebrew and Latin were frequently written in Arabic script. These diverse traditions interchanged in ways that gave Spanish culture — religion, literature, music, art and architecture, and writing systems — a rich and distinctive heritage. However, as the 11th century drew to a close most of the north and centre of Spain was back under Christian control.
Fall of Muslim rule and Unification
The long period of expansion of the Christian kingdoms, beginning in 722 with the Muslim defeat in the battle of Covadonga and the creation of the Christian kingdom of Asturias, only eleven years after the Moorish invasion, is called the Reconquista. As early as 739 Muslim forces were driven out of Galicia, which came to host one of Christianity's holiest sites, Santiago de Compostela. Areas in the northern mountains and around Barcelona were soon captured by Frankish and local forces, providing a base for Spain's Christians. The 1085 conquest of the central city of Toledo largely completed the reconquest of the northern half of Spain.
In 1086 the Almoravids, an ascetic Islamic sect from North Africa, conquered the divided small Moorish states in the south and launched an invasion in which they captured the east coast as far north as Saragossa. By the middle of the 12th century the Almoravid empire had disintegrated. The Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212 heralded the collapse of the great Moorish strongholds in the south, most notably Córdoba in 1236 and Seville in 1248. Within a few years of this nearly the whole of the Iberian peninsula had been reconquered, leaving only the Muslim enclave of Granada as a small tributary state in the south. Surrounded by Christian Castile but afraid of another invasion from Muslim northern Africa, it clung tenaciously to its isolated mountain splendour for two and half centuries. It came to an end in 1492 when Isabella and Ferdinand captured the southern city of Granada, the last Moorish city in Spain. The Treaty of Granada[1] guaranteed religious tolerance toward Muslims while Spain's Jewish population of over 200,000 people was expelled that year. At Ferdinand's urging the Spanish Inquisition had been established in 1478. With a history of no less than the invasions of three Islamic empires (Ummayad, Almoravid and Almohad), there was a fear that Muslims might assist yet another invasion. Also, Aragonese labourers were angered by landlords' use of Moorish workers to undercut them. A 1499 Muslim uprising, triggered by forced conversions, was crushed and was followed by the first of the expulsions of Muslims, in 1502. The year 1492 was also marked by the discovery of the New World. Isabella I funded the voyages of Christopher Columbus. Ferdinand and Isabella, as exemplars of the Renaissance New Monarchs, consolidated the modernization of their respective economies that had been pursued by their predecessors and enforced reforms that weakened the position of the great magnates against the new centralized crowns. In their contests with the French army in the Italian Wars, Spanish forces under Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba eventually achieved success, against the French knights, thereby revolutionizing warfare. The combined Spanish kingdoms of Castile and Aragon, long vibrant and expansive, emerged as a European great power.
The reconquest from the Muslims is one of the most significant events in Spanish history since the fall of the Roman Empire. Arabic quickly lost its place in southern Spain's life, and was replaced by Castilian. The process of religious conversion which started with the arrival of the moors was reversed from the mid 13th century as the Reconquista was advancing south: as this happened the Muslim population either fled or forcefully converted into Catholicism, mosques and synagogues were converted into churches.
With the union of Castile and Aragón in 1479 and the subsequent conquest of Granada in 1492 and Navarre in 1512, the word Spain (España, in Spanish) began being used only to refer to the new unified kingdom and not to the whole of Hispania (the term Hispania (from which España was originally derived) is Latin and the term Iberia Greek).
From the Renaissance to the nineteenth century
Until the late fifteenth century, Castile and León, Aragón and Navarre were independent states, with independent languages, monarchs, armies and, in the case of Aragon and Castile, two empires: the former with one in the Mediterranean and the latter with a new, rapidly growing, one in the Americas. The process of political unification continued into the early 16th century. It was the unification of these separate Iberian empires that became the base of what is now referred to as the Spanish Empire.
Holy Roman Emperor Charles V
By 1512, most of the kingdoms of present-day Spain were politically unified by the crown, although not as a modern, centralized state. In contemporary minds, "Spain" was a geographic term that was more or less synonymous with Iberia, not the present-day state called Spain, although today's more restricted notion of it was beginning to gain in currency. As the old states continued to exist and function with their own laws, assemblies and administrations under one monarch, the title of the reigning Habsburgs was "The King of the Spaniards", not "Spain". The grandson of Isabella and Ferdinand, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor was called Carlos I of Castille and Aragon, extended his crown to other places in Europe and the rest of the world. The short-lived unification of Iberia was complete when Charles V's son, Philip II, became King of Portugal in 1580.
During the 16th century, early Habsburg Spain (i.e. the reigns of Charles V and Philip II) became the most powerful state in Europe. The Spanish Empire covered most territories of South and Central America, Mexico, the south of North America, some of Eastern Asia (including the Philippines), the Iberian peninsula (including the Portuguese empire invaded by the Kingdom of Spain and the Duke of Alba in 1580), southern Italy, Sicily, Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands. It was the first empire about which it was said that the sun did not set. It was a time of daring explorations by sea and by land, the opening up of new trade routes across oceans, conquests and the beginning of European colonization. Not only did this lead to the arrival of ever increasing quantities of precious metals, spices and luxuries, and new agricultural plants, that had a great influence on the development of Europe, but the explorers, soldiers, sailors, traders and missionaries also brought back with them a flood of knowledge that radically transformed the European understanding of the world, ending conceptions inherited from medieval times. This Renaissance intellectual transformation is best seen in the influential School of Salamanca.
In 1640, under Philip IV, the centralist policy of the Count-Duke of Olivares provoked wars in Portugal and Catalonia. Portugal became an independent kingdom again, taking with it its empire, and Catalonia achieved some years of French-supported independence but was quickly returned to the Spanish Crown after a bad experience under the French, except Roussillon.
A series of long and costly wars and revolts followed in the early 17th century, and began a gradual decline of Spanish power in Europe from the 1640s.
Of note during the 16th and 17th centuries was the cultural efflorescence now known as the Spanish Golden Age.
Spain had vast colonies in America (the continent), stretching from Chile and Argentina to Central America and Mexico, to some states in the present-day United States. These included all of Florida, California (see, in this regard, the Spanish missions in California), Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas. Then also parts of Oklahoma, Colorado and Wyoming. Thus, the Spanish founded cities like Los Angeles, California; Santa Fe, New Mexico; and San Antonio, Texas.
The middle and latter 17th century saw a grim decline and stagnation under the drifting leadership of the last Spanish Habsburgs. The lingering, "decline of Spain" after a long period of considerable growth since the Black Death in the 14th century, was partly due to its successes in the 15th and 16th centuries that gave rise to the treasure fleets across the Atlantic and the Manila galleons across the Pacific, which, combined with the earlier political, social and military adaptations, made Spain the most powerful nation in Europe from the beginning of the 16th century until the middle of the 17th century.
The rapid growth of these silver shipments in the second half of the 16th century, after the opening of the American mines, engendered inflation that undermined Spanish trades and commerce (never very large in the Iberian Peninsula, which wasn't highly populated, thus much of the manufactures and finance were diverted to peripheral parts of the Empire - when related to the Peninsula, that is to say - like Flanders or third countries like The Netherlands, northern Italy and other nearby countries like England or the German speaking States).
Worsening matters were the wars defending the global empire against envious European rivals, internal successions and the European wars (Eighty Years' War and Thirty Years' War) in fighting for the Habsburg's dynastic and religious interests (Counter Reformation).
Particularly the Thirty Years' War must be accounted as an on and off but almost continuous conflict which drained Spanish resources into war in Central Europe thus heavily burdening the Empire's economy. During this vast war, the Spanish Crown attempted to meet its needs by tampering with the silver content of the currency, leading to severe bouts of inflation and deflation. A steep economic and demographic decline in the Empire's overly burdened and plague ridden lynchpin (Castile), vast grants of land to the Church and the Habsburg's restoration of power to an increasingly self-serving nobility, also undermined the empire.
Reasons for this war were both dynastic and religious. It should be stressed at this point, for a better understanding of the phenomenon, that the moral commitment of the Spanish Empire to the Catholic Church by that time was total and the Spanish Kings often waged war more in terms of genuine faith against the rising Protestantism rather than based in any national interest.
A fog of officially sanctioned orthodoxy gradually smothered a once vibrant and diverse intellectual life. The resentment of ordinary peasants and labourers found expression in implicating the nobility of Moorish ancestry and the churchmen of hypocrisy. The growing beggary forced many to live by their wits, increasing the popularity of picaresque literature. This 17th century stagnation was mirrored throughout Europe, as the growing global oceanic trade that had been pioneered by the Iberian countries, was increasingly diverted to North-Western Europe.
Controversy over succession to the throne consumed what had become an essentially leaderless country with a vast empire, and much of Europe, during the first years of the 18th century.
- Further information: War of the Spanish Succession
It was only after this war ended and a new dynasty—the French Bourbons—was installed that a true Spanish state was established when the absolutist first Bourbon king Philip V of Spain in 1707 (declared in 1714) dissolved the parliamentarist Aragon court and unified the kingdoms of Castile and Aragon into a single, unified Kingdom of Spain, abolishing many of the regional privileges and autonomies (fueros) that had hampered Habsburg rule. The British abandoned the conflict after Utrecht (1713), which led to Barcelona's easy defeat by the "absolutists" in 1714. The National Day of Catalonia still commemorates this defeat.
Following the wars at its commencement the 18th century saw a long, slow recovery, with an expansion of the iron and steel industries in the Basque Country, a growth in ship building, some increase in trade and a recovery in food production and a gradual recovery of population in Castile. The new Bourbon monarchy drew on the French system in trying to modernize the administration and economy, in which it was more successful in the former than the latter. In the last two decades of the century, with the ending of Cadiz's royally granted monopoly, trade experienced an extraordinary growth (from a relatively low base) and even witnessed the initial steps of an industrialization of the textile industry in Catalonia. Spain's effective military assistance to the rebellious British colonies in the American War of Independence won it renewed international standing.
The early nineteenth century
The reformatory efforts of Charles III and his ministers Ensenada and Floridablanca led to a profound gap between partisans of the Enlightenment (Afrancesados) and the partisans of the Old Spain. The subsequent war with France in 1793 (French Revolutionary Wars) polarized the country in an apparent reaction against the Gallicised elites. The "Afrancesados" were a minority, with a vast portion of Spain firmly attached to the "Old Order" (even though they distrusted the persons formally representing it, Charles IV, his wife Maria-Luisa de Borbon Parma and her favourite Manuel Godoy). The disastrous Spanish economic situation (and, more specifically, the ambiguous and controversial relations with the juggernaut that was Napoleonic France), led by Godoy, ended with his overthrow at the Mutiny of Aranjuez on March 17th 1808 and forced the abdication of Charles IV and his son Ferdinand, Prince of Asturias, in Bayonne later that year, in favour of Joseph Bonaparte (aka Jose I or Pepe Botella). The abdication was masterminded by Napoleon, who distrusted the uncertain ally that was House of Bourbon Spain and detested the House of Bourbon. The Afrancesados had high expectations of the nomination of Joseph Bonaparte as king, even though he was not of royal blood and a foreigner, while the rest of Spain regarded him with scorn. The new, meek, monarch was sincere in his desire to reform the country for the benefit his subjects but the fast pace of events overwhelmed him. In May 2, 1808, the people of Madrid rose in arms against the French army, commanded by Marshall Joachim Murat (the uprising was immortalized by Goya in his masterpiece The Third of May 1808). Since this was the first and sole time in Modern Spain's history that the country was in foreign hands, it can be regarded as Spain's first nationalistic rebellion. The ensuing repression was swift and merciless, but it could not avoid the fact that Napoleonic rule in Spain would be anything but peaceful. A massively destructive war known to the Spanish as the War of Independence and to the English as the Peninsular War followed, savaging the country with its cruelty. With the exception of the Battle of Bailen (July 18-22, 1808), where the Spanish army was the first to defeat a Napoleonic army in Europe, there were few ranged battles. Napoleon was forced to personally intervene, bringing the Spanish army to its knees and driving the Anglo-Portuguese forces out, but triggering a massive guerrilla war as a result. The guerrillas, aided by Wellington's Anglo-Portuguese army, were effective, their action combined with Napoleon's disastrous invasion of Russia, led to the ousting of the French from Spain in 1814, and the return of king Ferdinand VII (aka El Deseado).
Consequences of the Napoleonic rule in Spain
The French invasion had numerous consequences for Spain. The war proved disastrous for Spain's economy, reversing the improvements of the late 18th century. It also brought a political and territorial legacy, but would also leave a deeply divided country prone to great political instability for over a century. In 1812, the Liberal Courts of Cádiz redacted a Constitution, bringing to the country a new form of government, and one by which future monarchs would have to rule, more or less willingly. The power vacuum between 1808 and 1814 had enabled local juntas in the Spanish colonies in America to rule independently. Starting as early as 1809, the continent started freeing itself from Spanish rule; by 1825 with the exceptions of Cuba, Puerto Rico and the Philippines, and a number of Pacific Islands Spain had lost all its colonies in Latin America. The Trienio Liberal (1820-1823).
At the end of the 19th century, Spain lost all of its remaining old colonies in the Caribbean and Asia-Pacific regions, including Cuba, Puerto Rico, Philippines, and Guam to the United States after unwittingly and unwillingly being thrust into the Spanish-American War of 1898. In 1899 Spain sold its remaining Pacific possessions to Germany.
"The Disaster" of 1898, as the Spanish-American War was called, gave increased impetus to Spain's cultural revival (Generation of '98) in which there was much critical self examination, and relieved it from the burden of its last major colonies. However, political stability in such a dispersed and variegated land, caught between pockets of modernity and large areas of extreme rural backwardness and strongly differentiated regional identities and deep divisions over legitimacy originating from the Napoleonic period, would elude the country for some decades yet, and was ultimately imposed only by a brutal dictatorship in 1939.
The 20th century initially brought little peace; Spain played a minor part in the scramble for Africa, with the colonization of Western Sahara, Spanish Morocco and Equatorial Guinea. However the area assigned to Spain was mostly abrupt terrain populated by warlike tribesmen with an age-old history of fighting outsiders. A poorly planned and led advance into the interior due to political pressure led to military disaster in Morocco in 1921. This contributed to discrediting the monarch and worsened political instability. A period of dictatorial rule under General Miguel Primo de Rivera (1923–1931) ended with the establishment of the Second Spanish Republic. The Republic offered political autonomy to the Basque Country, Catalonia and Galicia (where the autonomy did not have any effect due to the civil war) and gave voting rights to women.
In the elections in February 1936, the left-wing coalition Popular Front won a narrow victory over the right-wing National Front coalition, but tension continued to mount with the destruction of Church property and an increasing number of politically-motivated murders, including that of prominent right-wing leader José Calvo Sotelo. In July, a number of generals attempted a military takeover which they had been planning for months. The coup failed to topple the government and the Spanish Civil War (1936-39) ensued. After nearly three years of bitter struggle, Nationalist forces led by General Francisco Franco emerged victorious with the support of Germany and Italy. The Republican side was supported by the Soviet Union and Mexico, but was crucially left isolated through the British-led policy of Non-Intervention. The Spanish Civil War has been called the first battle of the Second World War. Spanish involvement in the Second World War was in fact a continuation of its civil war, as the ideological conflicts involved had much in common (but also some important differences), despite Franco's official policy of neutrality and non-belligerency during the years of Axis success. In 1940, Francisco Franco and his brother-in-law, the foreign minister, Ramón Serrano Súñer, met Adolf Hitler in Hendaye (then in German-occupied France) to discuss Spanish participation in World War II as part of the Axis. This short trip across the border was the only time Franco left Spain during his long dictatorship. No agreement was reached and Spain remained neutral though sympathetic.
Over a hundred thousand highly motivated Spanish Civil War veterans were to give both sides the benefit of their experience throughout the Second World War in Europe, the Eastern Front and North Africa. A number of the most effective forces in the French Resistance were Spanish as was the 9th Armoured Company that spearheaded Général Leclerc's 2nd Armoured Division's liberation of Paris. On the other side, about 40,000 Spaniards fought against the Soviet Union in the Wehrmacht's División Azul (Blue Division).
The only legal party under Franco's regime was the Falange española tradicionalista y de las JONS formed in 1937 by the forceable fusion of the pseudo-fascist Falange and the monarchist Carlist movement. The party emphasized anti-Communism, Catholicism, nationalism, and imperial expansion and was one of the regime's major instruments of internal control.
After World War II, being one of few surviving authoritarian regimes in Western Europe, Spain was politically and economically isolated and was kept out of the United Nations until 1955, when it became strategically important for US president Eisenhower to establish a military presence in the Iberian peninsula. Eisenhower, signed a treaty with Franco in 1953 to build the military air base in Torrejón de Ardoz (this base had nuclear weapons) some 20km east of Madrid, the naval base of Rota, Cádiz (also with nuclear weapons in submarines), and the air bases of Morón de la Frontera, Seville, and Zaragoza. This opening to Spain was aided by Franco's opposition to Communism. In the 1960s, Spain began to enjoy economic growth (Spanish miracle) which gradually transformed it into a modern industrial economy with a thriving tourism sector. Growth continued well into the 1970s, with Franco's government going to great lengths to shield the Spanish people from the effects of the oil crisis.
Upon the death of General Franco in November 1975, his personally-designated heir Prince Juan Carlos assumed the position of king and head of state. With the approval of the Spanish Constitution of 1978 and the arrival of democracy, some regions — Basque Country, Navarra— were given complete financial autonomy, and many — Basque Country, Catalonia, Galicia and Andalusia— were given some political autonomy, which was then soon extended to all Spanish regions, resulting in what is regarded as the most decentralized territorial organization in Western Europe. In the Basque Country, moderate Basque nationalism coexists with radical nationalism supportive of the terrorist group ETA.
On January 1 1999 Spain adopted the Euro as its national currency.
Ever since the current Constitution was passed in 1978, Spain has had 5 Presidentes del Gobierno (Prime Ministers) as of September 2006: Adolfo Suárez González (1977-1981) who won the election for the Unión de Centro Democrático (UCD, now extinct), Leopoldo Calvo-Sotelo Bustelo (1981-1982) also for the UCD (under his presidency there was an attempted coup d'état on 23 February 1981), Felipe González Márquez (1982-1996) who won four consecutive elections heading the Partido Socialista Obrero Español ticket (PSOE), during his administrations Spain joined NATO and European Union) and then José María Aznar López (1996-2004) who won two consecutive elections for the Partido Popular (PP). Last in this list is current Presidente del Gobierno José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero (2004-Incumbent) again for the PSOE.
21st Century
In November 2002, the oil tanker Prestige sank near to the Galician coast, causing a huge oil spill. It has since been regarded as one of the worst environmental disasters in Spanish history.
On March 11 2004, a series of bombs exploded in commuter trains in Madrid, Spain. This act of terror killed 191 people and wounded 1,460 more, besides having a dramatic effect on the upcoming national elections. The 11 March 2004 Madrid train bombings had an adverse effect on the then-ruling conservative party Partido Popular (PP) which all the polls were giving as a sure-fire winner of the elections, thus helping the election of Zapatero's Partido Socialista Obrero Español (PSOE). There were two nights of incidents around the PP headquarters, with PSOE accusing the PP of hiding the truth by saying that the incidents were caused by ETA. These incidents are still a cause of discussion nowadays, since some factions of the PP suggest that the elections were "stolen" by means of the turmoil which followed the terrorist bombing, which was, according to this point of view, backed or fuelled by the PSOE. These incidents did interfere with the last day of campaigning when, according to the Spanish electoral system regulations, any kind of political propaganda is prohibited and PP's candidate (Mariano Rajoy) appeared in some newspapers like an interior minister.
March 14 2004 saw the PSOE party elected into government, with Zapatero becoming the new PM of Spain. Since the PSOE's election victory Zapatero's government has withdrawn Spanish troops from Iraq and legalized same-sex marriages. He also presided over the Spanish Parliament's approval of the new (and controversial) Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia. Spain has been dealing with increasing immigration since the start of the twenty-first century. With polls indicating a population increase of almost 10% in 5 years, indicating record immigration into the country. Spain currently experiences one of the highest rates of immigration in Europe, with many immigrants proceeding to other European countries, or remaining in Spain.
Government and politics
Spain is a constitutional monarchy, with a hereditary monarch and a bicameral parliament, the Cortes Generales. The executive branch consists of a Council of Ministers presided over by the President of Government (comparable to a prime minister), proposed by the monarch and elected by the National Assembly following legislative elections.
The legislative branch is made up of the Congress of Deputies (Congreso de los Diputados) with 350 members, elected by popular vote on block lists by proportional representation to serve four-year terms, and a Senate or Senado with 259 seats of which 208 are directly elected by popular vote and the other 51 appointed by the regional legislatures to also serve four-year terms.
Spain is, at present, what is called a State of Autonomies, formally unitary but, in fact, functioning as a highly decentralized Federation of Autonomous Communities, each one with slightly different levels of self-government. The little differences within this system are due to the fact that the devolution process from the centre to the periphery was a process initially thought to be asymmetrical, granting a higher degree of self government only to those autonomous governments ruled by nationalist parties (namely Catalonia and the Basque Country) who were much more vocal in the matter and seeking a more federalist kind of relationship with the rest of Spain. Conversely the rest of Autonomous Communities would have a lower self government. This pattern of asymmetrical devolution has been described as a coconstitutionalism and the devolution process adopted by the United Kingdom since 1997 shares traits with it.
However, as years passed, the Autonomous Communities which in the beginning were thought to have a lower profile have caught up in terms of self-government with the nationalist ruled Autonomous communities and the gap in terms of self-government is not that wide anymore.
In the end, Spain is regarded as probably the most decentralized State in Europe at the present moment, with all of its different territories managing locally their Health and Education systems (just to mention some aspects of the public budget) and with some other territories (the Basque Country and Navarre) even managing their own public finances without hardly any presence of the Spanish central government in this regard or, in the case of Catalonia and the Basque Country, equipped with their own, fully operative and completely autonomous, police corps which widely replaces the State police functions in these territories (see Mossos d'Esquadra and Ertzaintza).
The Government of Spain has been involved in a long-running campaign against Basque Fatherland and Liberty (ETA), a terrorist organization founded in 1959 in opposition to Franco and dedicated to promoting Basque independence through violent means. They consider themselves a guerrilla organization while they are actually listed as a terrorist organization by both the European Union and the United States in their watchlists on the matter. Although the current nationalist led Basque Autonomous government does not endorse any kind of violence, their different approaches as to how to terminate ETA and their different approaches to the separatist movement are a source of tension between the central and Basque governments.
Initially ETA targeted primarily Spanish security forces, military personnel and Spanish Government officials. As the security forces and prominent politicians improved their own security, ETA increasingly focused its attacks on the tourist seasons (scaring tourists was seen as a way of putting pressure on the government, given the sector's importance to the economy, although no tourists were injured) and local government officials in the Basque Country. The group carried out numerous bombings against Spanish Government facilities and economic targets, including a car bomb assassination attempt on then-opposition leader Aznar in 1995, in which his armored car was destroyed but he was unhurt. The Spanish Government attributes over 800 deaths to ETA during its campaign of rebellion.
On 17 May 2005, all the parties in the Congress of Deputies, except the PP, passed the Central Government's motion giving approval to the beginning of peace talks with ETA, without making political concessions and with the requirement that it give up its weapons. PSOE, CiU, ERC, PNV, IU-ICV, CC and the mixed group —BNG, CHA, EA y NB— supported it with a total of 192 votes, while the 147 PP parliamentarians objected. ETA declared a "permanent cease-fire" that came into force on March 24, 2006. In the years leading up to the permanent cease-fire, the government had had more success in controlling ETA, due in part to increased security cooperation with French authorities.
On February 20 2005, Spain became the first country to allow its people to vote on the European Union constitution that was signed in October 2004. The rules state that if any country rejects the constitution then the constitution will be declared void. Despite a very low participation (42%), the final result was very strongly in affirmation of the constitution, making Spain the first country to approve the constitution via referendum (Hungary, Lithuania and Slovenia approved it before Spain, but they did not hold referenda).
Territorial disputes
Territories claimed by Spain
Spain has called for the return of Gibraltar, a British possession on its southern coast. It was conquered during the War of the Spanish Succession in 1704 and was ceded to Britain in perpetuity in the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht. An overwhelming majority of Gibraltar's 30,000 inhabitants want to remain British, as they have repeatedly proven in referenda on the issue. The UN resolutions (2231 (XXI) and 2353 (XXII)) call on the UK and Spain to reach an agreement to resolve their differences over Gibraltar. According to Spain, these resolutions overrule the Treaty of Utrecht. However, Article 103 of the UN Charter makes clear that the right of self-determination of the people of Gibraltar is the paramount and overriding principle.
There is also dispute regarding the demarcation line. Gibraltar is officially a non-self governing territory or colony according to the UN.
Spanish territories claimed by other countries
Morocco claims the Spanish cities of Ceuta and Melilla and the Vélez, Alhucemas, Chafarinas, and Perejil islands, all on the Northern coast of Africa. Morocco points out that those territories were obtained when Morocco could not do anything to prevent it and has never signed treaties ceding them, Morocco didn't even exist in the 14th and 15th century when these places became Spanish possessions. Spain claims that these territories are integral parts of Spain and have been Spanish or linked to Spain since before the Islamic invasion of Spain in 711, return to Spain, Ceuta and Perejil Island in 1415 and the rest returned to Spanish rule only a few years after the conquest of Granada. Spain claims that Morocco's only claim on these territories is geographical. Parallelism with Egyptian ownership of the Sinai (in Asia) or Turkish ownership of Istanbul (in Europe) is often used to support the Spanish position.
Portugal does not recognize Spain's sovereignty over the territory of Olivenza. The Portuguese claim that the Treaty of Vienna (1815), to which Spain was a signatory, stipulated return of the territory to Portugal. Spain alleges that the Treaty of Vienna left the provisions of the Treaty of Badajoz intact.
Economy
Spain's mixed economy supports a GDP that on a per capita basis is 87% of that of the four leading West European economies. The centre-right government of former Prime Minister Aznar worked successfully to gain admission to the first group of countries launching the European single currency, the euro, on 1 January, 1999. The Aznar administration continued to advocate liberalization, privatization, and deregulation of the economy and introduced some tax reforms to that end. Unemployment fell steadily both under the Aznar and Zapatero administration. It affects now 7.6% of the labor force (October 2006) having fallen from a high of 20% and above in the early 1990s. It also compares favourably to the other large European countries, most notably, Germany with an unemployment of approximately 12%. Growth of 2.4% in 2003 was satisfactory given the background of a faltering European economy, and has steadied since at an annualized rate of about 3.3% in mid 2005 and 3.5% in the first quarter and 3,7% in the second quarter of 2006. There is a widespread concern, however, that the growth is too concentrated upon a few sectors (mainly residential building and those related to it). The current Prime Minister Rodríguez Zapatero has pointed out as matters to be addressed during his administration plans to reduce government intervention in business, combat tax fraud, and support innovation, research and development, but also intends to reintroduce labour market regulations that had been scrapped by the Aznar government. Adjusting to the monetary and other economic policies of an integrated Europe — and reducing unemployment — will pose challenges to Spain over the next few years. According to World Bank GDP figures[2] from 2005, Spain has the ninth largest economy in the world, after Canada, and the fifth largest in Europe, after Italy.
There is general concern that Spain's model of economic growth (based largely on mass tourism, the construction industry, and manufacturing sectors) is faltering and may prove unsustainable over the long term. The first report of the Observatory on Sustainability (Observatorio de Sostenibilidad) — published in 2005 and funded by Spain's Ministry of the Environment and Alcalá University — reveals that the country's per capita GDP grew by 25% over the last ten years, while greenhouse gas emissions have risen by 45% since 1990. Although Spain's population grew by less than 5% between 1990 and 2000, urban areas expanded by no less than 25% over the same period. Meanwhile, Spain's energy consumption has doubled over the last 20 years and is currently rising by 6% per annum. This is particularly worrying for a country whose dependence on imported oil (meeting roughly 80% of Spain's energy needs) is one of the greatest in the EU. Large-scale unsustainable development is clearly visible along Spain's Mediterranean coast in the form of housing and tourist complexes, which are placing severe strain on local land and water resources. Recent developments include the construction of reverse osmosis plants along the Spanish Costas, to probably meet over 1% of Spain's total water needs. Other perennial weak points of Spain's economy include one of the lowest rates of investment in Research and Development, and in education in the EU. This is particularly worrying, given that the country's generally poorly-trained workforce is no longer as competitive in price terms as it was several decades ago. As a result, many manufacturing jobs are going abroad — mainly to Eastern Europe and Asia.
On the brighter side, the Spanish economy is credited for having avoided the virtual zero growth rate of some of its largest partners in the EU (namely France and Germany) by the late 90's and beginning of the 21st century in a process which started with former Prime Minister Aznar's liberalization and deregulation reforms aiming to reduce the State's role in the market place. Thus, on 1,999 Spain started an economic cycle -which keeps going as of 2006- marked by an outstanding economic growth, with figures around 3% and some years well over this rate.[3]
This has narrowed steadily the economic gap between Spain and its leading partners in the EU over this period. Hence, the Spanish economy has been regarded lately as one of the most dynamic within the EU, even able to replace the leading role of much larger economies like the aforementioned, thus subsequently attracting significant amounts of foreign investment.
Demographics
Population
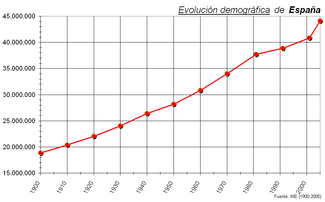
Spain's population density, at 87.8/km² (220/sq. mile), is lower than that of most Western European countries and its distribution along the country is very unequal. With the exception of the region surrounding the capital, Madrid, the most populated areas lie around the coast.
The population of Spain doubled during the twentieth century, due to the spectacular demographic boom by the 60's and early 70's. Then, after the birth rate plunged in the 80's and Spain's population became stalled, a new population increase started based initially in the return of many Spanish who emigrated to other European countries during the 70's and, more recently, it has been boosted by the large figures of foreign immigrants, mostly from Latin America (38.75% of them), Eastern Europe (16.33%), Maghreb (14.99%) and Subsaharian Africa (4.08%).[4] Also some important pockets of population coming from other countries in the European Union are found (20.77% of the foreign residents), specially along the Mediterranean costas and Balearic islands, where many choose to live their retirement or even telework. However, the pattern of growth was extremely uneven due to large-scale internal migration from the rural interior to the industrial cities during the 60's and 70's. No fewer than eleven of Spain's fifty provinces saw an absolute decline in population over the century.
Immigration in Spain
According to the Spanish government there were 3.7 million foreign residents in Spain in 2005. Around 500,000 were Moroccan, another half a million were Ecuadorian, more than 200,000 were Romanians and 270,000 were Colombian. Other important foreign communities are the British (6.09% of all the foreingn residents), the Argentinian (6.10%), the German (3.58%) and the Bolivian (2.63%). In 2005 alone, the immigrant population of Spain increased by 700,000 people. Since 2000 Spain has experienced an explosive rate of population growth, despite a birth rate that is only half of the replacement level. This sudden and ongoing flood of immigrants has caused noticeable social tensions.
Spain has the highest immigration rate of the EU. This can be explained by a number of reasons including its geographical position, the porosity of its borders, the large size of its submerged economy and the strength of the agricultural and construction sectors which demand more low cost labour than can be offered by the national workforce.
On the other hand mass immigration has put downward pressure on the wages of many workers in construction and agriculture. It is also contributing to an unsustainable property boom (which is also the result of low interest rates) that has greatly reduced the affordability of rental accommodation and homes for families of workers and many others. The result has been a massive increase in indebtedness and a rapid growth of the national current account deficit. This will inevitably aggravate social tensions. [1]
Identities
The Spanish Constitution of 1978, in its second article, recognizes historic entities ("nationalities“, a carefully chosen word in order to avoid the more politically loaded "nations") and regions, inside the unity of the Spanish nation.
But Spain's identity is for some people more an overlap of different regional identities than a sole Spanish identities, some of the regional identities may be even in conflict with the Spanish one.
Especially in the case of a large part of Catalans, Basques and Galicians, who quite frequently identify, respectively, primarily with Catalonia, the Basque Country, and Galicia first, with Spain only second. For example, according to the last CIS survey,[citation needed] 44% of Basques identify themselves first as Basques (only 8% first as Spaniards); 40% of Catalans do so with Catalonia (20% identify firstly with Spain), and 32% Galicians with Galicia (9% with Spain). Also in these regions, there is a large part of the population who identify themselves "as Catalan/Basque/Galician as Spanish".[citation needed]
Almost all communities have a majority of people identifying as much with Spain as with the Autonomous Community (except Madrid, where Spain is the primary identity, and Catalonia, Basque Country, Galicia, and the Balearics, where people tend to identify more with their Autonomous Community). It is this last feature of "shared identity" between the more local level or Autonomous Community and the Spanish level which makes the identity question in Spain complex and far from univocal.
Minority groups
Since the 16th century, the most famous minority group in the country (though not the biggest in number) have been the Gitanos, a Roma group.
Spain harbours a number of black African-blooded people — who are descendants of populations from former colonies (especially Equatorial Guinea) who chose to be in Spanish guidance and, much more important than those in numbers, immigrants from several Sub-Saharan and Caribbean countries who have been recently settling in Spain. There are also sizeable numbers of Asian-Spaniards, most of whom are from Chinese, Filipino, Middle Eastern, Pakistani and Indian origins; Spaniards of Latin American descent are also sizeable as well.
The important Jewish population of Spain was either expelled or forced to convert in 1492, with the dawn of the Spanish Inquisition. After the 19th century, some Jews have established themselves in Spain as a result of migration from former Spanish Morocco, escape from Nazi repression and immigration from Argentina. The Spanish law allows Sephardi Jews to claim Spanish citizenship.
A sizeable and increasing number of Spanish citizens also descend from these communities, as Spain applies jus soli and provides special measures for immigrants from Spanish-speaking countries to obtain Spanish citizenship.
Religion
Roman Catholicism is the most popular religion in the country. According to several sources (CIA World Fact Book 2005, Spanish official polls and others), from 94% to 81% self-identify as Catholics, whereas around 6% to 19% identify with either other religions or none at all.[5] It is important to note, however, that many Spaniards identify themselves as Catholics just because they were baptized, even though they may not be very religious.
Evidence of the secular nature of contemporary Spain can be seen in the widespread support for the legalization of same-sex marriage in Spain — over 70% of Spaniards support gay marriage according to a 2004 study by the Centre of Sociological Investigations.[6] Indeed, in June 2005 a bill was passed by 187 votes to 147 to allow gay marriage, making Spain the third country in the European Union to allow same-sex couples to marry. This vote was split along conservative-liberal lines, with PSOE and other left-leaning parties supporting the measure and PP against it. Proposed changes to the divorce laws to make the process quicker and to eliminate the need for a guilty party are also popular.
There are also many Protestant denominations, all of them with less than 50,000 members, and about 20,000 Mormons. Evangelism has been better received among Gypsies than among the general population; pastors have integrated flamenco music in their liturgy. Taken together, all self-described "Evangelicals" slightly surpass Jehovah's Witnesses (105,000) in number. Other religious faiths represented in Spain include the Bahá'í Community.
The recent waves of immigration, especially during and after the 90's, have led to an increasing number of Muslims, who have about 1 million members. Muslims had ceased to live in Spain for centuries, ever since the Reconquista, when they were given the ultimatum of either convert to Catholicism or leave the country. By the 16th century, most of them had left the Spanish kingdom. However, the colonial expansion over Northern and Western Africa during the 19th and 20th centuries supposed that large numbers of Muslim populations (those in the Spanish Morocco and the Sahara Occidental) were again under Spanish administration, with a minority of them getting full citizenship. Nowadays, Islam is the second largest religion in Spain, after Roman Catholicism, accounting for approximately 3% of the total population. Hindus and Sikhs account for less than 0.3%.
Since the expulsion of the Sephardim in 1492, Judaism was practically nonexistent until the 19th century, when Jews were again permitted to enter the country. Currently there are around 50,000 Jews in Spain, all arrivals in the past century and accounting less than 1% of the total number of inhabitants[citation needed]. There are also many Spaniards (in Spain and abroad) who claim Jewish ancestry to the Conversos, and still practise certain customs. Spain is believed to have been about 8% Jewish on the eve of the Spanish Inquisition.
Over the past thirty years, Spain has become a more secularized society as the number of believers has decreased significantly. For those who do believe, the degree of accordance and practice to their religion is diverse.
Languages
| ██ Castilian (Spanish) ██ Catalan, co-official ██ Basque, co-official ██ Galician, co-official | ██ Asturian, unofficial ██ Aragonese, unofficial ██ Aranese, co-official (dialect of Occitan) |
The Spanish Constitution, although affirming the sovereignty of the Spanish Nation, recognizes historical nationalities.
Castilian (called both español and castellano in the language itself) is an official language throughout Spain, but other regional languages are also spoken, and are the primary languages in some of their respective geographies. Without mentioning them by name, the Spanish Constitution recognizes the possibility of regional languages being co-official in their respective autonomous communities. The following languages are co-official with Spanish according to the appropriate Autonomy Statutes.
- Catalan (català) in Catalonia (Catalunya), the Balearic Islands (Illes Balears), parts of Valencia (València) (as Valencian)
- Basque (euskara) in Basque Country (Euskadi or País Vasco), and parts of Navarre (Nafarroa or Navarra). Basque is not known to be related to any other language.
- Galician (galego) in Galicia (Galicia or Galiza).
- Occitan (the Aranese dialect). Spoken in the Val d'Aran in Catalonia.
Catalan, Galician, Aranese (Occitan) and Castilian are all descended from Latin and some of them have their own dialects, some championed as separate languages by their speakers. A particular case is Valencian, the name given to a variety of Catalan, that also has the co-official language status recognized in Autonomous Community of Valencia.
There are also some other surviving Romance minority languages: Asturian / Leonese, in Asturias and parts of Leon, Zamora and Salamanca, and the Extremaduran in Caceres and Salamanca, both descendants of the historical Astur-Leonese dialect; the Aragonese or fabla in part of Aragon; the fala, spoken in three villages of Extremadura; and some Portuguese dialectal towns in Extremadura and Castile-Leon. However, unlike Catalan, Galician, and Basque, these do not have any official status.[7]
In the touristic areas of the Mediterranean costas and the islands, German and English are spoken by tourists, foreign residents and tourism workers. Recent African immigrants and large minority of their descendants speaks the official European languages of their homelands (whether standard Portuguese, English, French, or its creoles.)
--- from culture of spain Language: While nearly everyone in Spain can speak Spanish (which is almost universally known in Spain as castellano — "Castilian" — rather than español — "Spanish") other languages figure prominently in many regions: Basque (Euskara) in the Basque Country and Navarre; Catalan in Catalonia, Balearic Islands and Valencia (where it is usually referred to as Valencian), and Galician in Galicia. Spanish is official throughout the country; the rest of these have co-official status in their respective regions and all are major enough that there are numerous daily newspapers in these languages and (especially for Catalan and Basque) a significant book publishing industry. Many citizens in these regions consider their regional language as their primary language and Spanish as secondary; these languages cover broad enough regions to have multiple distinct dialects. (Spanish itself also has distinct dialects around the country, with the Andaluz dialect being closer to the Spanish of the Americas, which it heavily influenced.)
In addition, there is strong and growing support for other regional languages, some of them in danger of extinction. These include Asturian in Asturias, Aragonese in Aragon, and Aranese, a dialect of Gascon spoken only in the tiny Val d'Aran, but enough of a live language to be used in the public schools there.
With the exception of Basque, which appears to be a language isolate, all of these are Romance languages. ---
Men and women
Marriage and the family
Education
Class
Culture
The Spanish culture has roots in Celtiberian, Latin, Celtic , other European countries, the moors, Roman Catholicism, and an ongoing tension between the centralized state (dominated in recent centuries by Castile) and numerous regions and minority peoples. In addition, the history of the nation and its Mediterranean and Atlantic environment have played strong roles in shaping its culture.
Architecture
Because many of its historical buildings have remained intact today, several architectural structures in Spain, and even portions of cities, have been designated World Heritage sites. These are listed at List of World Heritage Sites in Europe: Spain.
Spain was part of the Roman Empire and many areas of Spain retain significant Roman architectural remnants. The Roman aqueduct at Segovia is still in use as of 2004; Mérida, now the Extremaduran capital but once the capital of the Roman province of Lusitania, retains over 5 miles of its Roman aqueduct, Roman bridge over the River Guadiana, an arch of Trajan, and significant remnants of a Roman forum, amphitheatre, and a temple popularly accounted to have been dedicated to Diana (goddess). Another Roman bridge crosses the Tagus River at Alcántara. Lesser Roman ruins can be found in the heart of Barcelona.
Spain is home to several fine examples of medieval architecture; outside of the areas that were under Muslim control, these are primarily in the Romanesque and Gothic styles. Spain is also home to several examples of Cathedral architecture. The Drassanes in Barcelona, originally a facility for building ships and now a maritime museum, is the largest and most complete medieval secular structure in the world.
The architecture in southern Spain reflects its Moorish history. The Alhambra is probably the most famous example, showing a mixture of Islamic architecture and European influences. Significant Moorish buildings survive as far north as Zaragoza. Throughout Spain, many former mosque and synagogue buildings survive as Christian churches or, occasionally, converted to other uses. Good examples of this are the Church of Corpus Christi in Segovia and the Church of Santa María la Blanca in Toledo, both former synagogues, and the Mezquita (Spanish for "mosque"), a 10th century mosque in Córdoba, reconsecrated in 1236 as a Christian Church. The influence of Moorish architecture did not end with the reconquista: there were many prominent mudéjar architects, Muslims living and working in Christian Spain.
When the city of Barcelona was allowed to expand beyond its historic limits in the late 19th century (a suspicious Spanish government had long kept a ring of undeveloped land around the city to make it easy for the military to deploy against any unrest), the resulting Eixample ("extension"), larger than the old city, became the site of a burst of architectural energy. Most famous among the architects represented there is Antoni Gaudí, whose works in Barcelona and elsewhere in Catalonia, mixing traditional architectural styles with the new, were a precursor to modern architecture. Perhaps the most famous example of his work is the (as of 2004) still-unfinished La Sagrada Família, the largest building in the Eixample.
Other notable Catalan architects of that period include Lluís Domènech i Montaner and Josep Puig i Cadafalch. One block on the Passeig de Gràcia contains buildings by each of the three; the clashing styles led to the nickname "manzana de la discordia", literally the "block of discord", but also a pun: "manzana" can also mean "apple", hence "apple of discord".
Alejandro de la Sota was one of the early proponents of modern architecture in Spain; the first steel framed building in Madrid is his 1961 Maravillas College Gymnasium.
Santiago Calatrava began to make his name from the 1980s and works internationally. His work is typified by a great understanding of engineering as well as nature. A notable building of his is the City of Arts & Sciences in Valencia. Enric Miralles possessed a highly esoteric style which has been compared to fellow Catalan Gaudí, and was beginning to be successful internationally, but died in 2000, at only 45 years old. His largest work, the Scottish Parliament Building was completed posthumously. The Guggenheim Museum Bilbao may be the most famous example of contemporary architecture in Spain, although the architect, Frank Gehry, is a citizen of United States and of Canadian descent.
The dry weather of Spain resulted in the importance of water fountains in Spanish urban design. In addition, ceramics figure prominently in architecture throughout Spain, especially in the tile roofs (though slate was traditional near the Atlantic coast) and the use of decorative tiles known as azulejos.
Art
Cinema
- Main article: Cinema of Spain
While mid-century Spanish directors such as Luis Buñuel worked mainly in exile, film has prospered in Spain since the reestablishment of constitutionalism. Among the leading late 20th- and early 21st-century Spanish film directors are:
- Pedro Almodóvar, Double Oscar Winner; 1999 "Foreign language film" (Todo sobre mi madre) and 2002 "Original Screenplay" (Hable con ella)
- Alejandro Amenábar, 2004 Oscar winner for "Foreign language film" (Mar Adentro).
- Pablo Berger
- Manuel Martin Cuenca
- Mateo Gil, who works with Amenábar on most of his films.
- Álex de la Iglesia
- Julio Medem, director of Lucía y el sexo
- Ventura Pons, directs mainly in Catalan
- Carlos Saura, whose five decades as a director include numerous films centered on dance (especially flamenco, as well as the official film of the 1992 Olympics in Barcelona.
Spain also has some rather notable "B movie" directors, such as:
- Santiago Segura, director of the Torrente Trilogy.
Clothing
Historically, various regions of Spain had quite distinct regional dress. Today, most people in Spain dress in a manner comparable to most other contemporary Europeans, although some regional variations persist. Dress in Extremadura and in the smaller cities of Castile remains relatively austere, even on festive occasions, while Andaluz dress on festive occasions is elaborate and ostentatious. Barcelona is one of the most stylish cities in Europe, though more restrained and with a more determinedly timeless style than Paris or Milan.
Cuisine
Spanish cuisine is made of very different kinds of dishes due to the differences in geography, culture and climate. It is heavily influenced by the variety of seafood available from the waters that surround the country. Some foods typically associated with Spain include arroz con leche, (rice with milk), which is served as a dessert, and paella, which is made with yellow rice typically garnished with a variety of meats or seafood.
As Spain has had a history with many different cultural influences, the richness and variety of its cuisine is overwhelming, but all these ingredients have made up a unique cuisine with thousands of recipes and flavours. Much influence on Spanish cuisine has come from the Jewish and Moorish traditions. The Moors were a strong influence in Spain for many centuries and their food is still eaten in Spain today. As a counterpoint, public consumption of pork (forbidden for Jews and Muslims) was a religious affirmation of being an Old Christian and pork is still enjoyed by many Spaniards.
- Chorizo, a paprika pork sausage.
- Cocido, a stew with beans and meat.
- Cuisine of Cantabria
- Fabada Asturiana, beans with chorizo and lard.
- Fideuà, a noodle paella
- Gazpacho, a cold soup or a liquid salad.
- Jamón, cured ham
- Paella, a rice dish
- Sangría, a wine cooler
- Tortilla de patatas, potato omelette.
Customs
The siesta—an hour-long mid-afternoon break from work—is generally in decline and the typical rhythm of the day in Spain is now similar to the European norm. Many shops and some museums (though relatively few other businesses) still split their hours into two distinct periods of opening with a two or three hour break in the middle; a paseo (stroll) in the early evening remains a common custom in many smaller cities and to some extent even in the larger ones.
Dinner here starts the latest in Europe, typically about 9 p.m. (in the east) or 10 p.m. (in the west); consequently night-life starts later, with many dance clubs (even in relatively small cities) opening at midnight and staying open until dawn; during summer in Madrid, there is nothing unusual about a live musical performance being scheduled for one or two o'clock in the morning. This rhythm has developed in accordance with the hours of the sun which rises and sets one or two hours later than in the rest of Europe. The routine perhaps lessens outdoor human activity in the period of the day when temperatures are hottest.
Dance
- Contradanza
- Flamenco
- Pasodoble
- Sardana
- Jota
Literature
Music
Spain's musical output includes a long history of innovation in Western and Andalusian classical music, as well as a domestic popular music industry, and diverse styles of folk music. Modern Spain has a number of performers in the fields of rock and roll, heavy metal, punk rock and hip hop, electronic music is also common between spaniards and djs such as dj marta or alex trackone are very well known in the spanish parties.
The best-known variety of Spanish folk music is probably flamenco, a diverse genre created by Andalusian Roma. Flamenco has been known since at least the 1770s, and has been through several cycles of dwindling popularity and rebirth. The style has produced many of the most famous Spanish musicians, including singer Camarón de la Isla and guitarist Carlos Montoya.
Outside of flamenco, regional Spanish folk music includes the distinct Basque trikitixa and accordion music, Galician and Asturian gaita (bagpipe) and Aragonese jota. Though some folk traditions have died out or are moribund, some retain great popularity and have been modernized and adapted to new instruments, styles and formats. These include the popular Celtic music of Galicia, the singer-songwriter tradition of nova canço and New Flamenco.
The first distinctly modern popular music of Spain began to appear in about 1959. Soon, Ye-Yé dominated the Spanish charts, followed by the import of American and British rock, French singers and other pop stars.
Spanish music today mainly consists of pop/rock/punk bands such as El Canto Del Loco , La Oreja De Van Gogh , Edurne , and Amaral. This new type of music has dominated the charts in Spain today, and many believe it will continue to do so for some time.
Theatre
Sport
- Main article: Sports in Spain
Sport in Spain is dominated by Fútbol, with La Liga, the country's professional league, drawing large attendances; Real Madrid and FC Barcelona are traditionally the most successful teams. The national team, however, underperforms consistently at the World Cup, although it did win the 1964 European Football Championship. Currently Spain is captained by Raúl González, who is very much the Golden Boy of Spanish football – he also is the top scorer for the national team and captain of his club, Real Madrid. Spain hosted the 1982 FIFA World Cup.
In Tennis, Spain won the 2005 Davis Cup championship, with teenager Rafael Nadal leading the line. Cycle racing is a major sport, hosting the 3rd biggest stage race in UCI ProTour, the Vuelta a España. Navarran Miguel Indurain is one of only five Spanish men to win the famous Tour de France. Recently, F1 Champion Fernando Alonso has spurred a rise in Formula One popularity in Spain.
Bullfighting is an icon for Spain, and despite slight recent declines in attendance it is still alive and well across the country, though is threatened by Animal Rights organizations. Another traditional Spanish sport is Pelota. Jai-alai, related to Pelota, is also a very popular sport which its first written references can be traced to XIII century in France. Spain has also achieved degrees of success in middle distance running, Golf, Basketball and Handball, amongst others.
At the 2004 Summer Olympics in Athens, Spain's athletes won 19 medals (3 gold, 11 silver and 5 bronze), finishing 20th in the medal table. In the all-time Olympic Games medal count Spain is 34th with 30 gold medals and 97 total medals.
In basketball, Spain won the gold medal at the 2006 FIBA World Championships in Japan.
International rankings
- Reporters Without Borders world-wide press freedom index 2002: Rank 40 out of 139 countries.
- The Economist Intelligence Units worldwide quality-of-life index 2005: Rank 10 out of 111 countries (above countries like the United States of America, the United Kingdom, and France)
- Nation Master's list by economic importance: Rank 9 of 25 countries, only surpassed by G-8 members (except Russia) and Australia.
- Nation Master's list by technological achievement: Rank 18 of 68 countries.
See also
| Spain Portal |
- Autonomous communities of Spain
- Civil unions in Spain
- Communications in Spain
- Culture of Spain
- Education in Spain
- Foreign relations of Spain
- Instituto Cervantes
- Languages of Spain
- List of cities in Spain
- List of municipalities in Spain
- List of Spanish birds
- List of Spanish national parks
- Military of Spain
- Music of Spain
- Places of sovereignty in North Africa
- Spanish Heraldry
- Public holidays in Spain
- Same-sex marriage in Spain
- Spanish nobility
- Spanish people
- Sports in Spain
- Tourism in Spain
- Transportation in Spain
- SEAT automobile
- Biscuter automobile
History Related Links:
- Black Legend
- Hispania
- History of Spain
- Spanish Empire
- Spanish language
- Latin America
References and notes
- John Hickman and Chris Little, "Seat/Vote Proportionality in Romanian and Spanish Parliamentary Elections", Journal of Southern Europe and the Balkans Volume 2, Number 2, November 2000.
- Harold Raley, "The Spirit of Spain", Houston: Halcyon Press 2001. (ISBN 0-9706054-9-8)
- George Orwell's Homage to Catalonia.
- Pritchett, V.S., The Spanish Temper (1954). Alfred A. Knopf, New York.
Other images
Port of Cadaqués, Catalonia
- Javea.jpg
Jávea, Xàbia
- Llanes.JPG
Llanes, Asturias
External links
- Spain World Fact Book 2007, accessed November 6, 2007.
- Spain Encyclopaedia Britannica Online, accessed November 6, 2007.
Overviews
[2] (1988)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||