Difference between revisions of "Hong Kong" - New World Encyclopedia
Keisuke Noda (talk | contribs) (import from wiki) |
MaedaMartha (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{claimed}} | {{claimed}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Infobox Country or territory | {{Infobox Country or territory | ||
|native_name = 香港特別行政區 | |native_name = 香港特別行政區 | ||
| Line 43: | Line 39: | ||
|established_date1 = [[January 25]] [[1841]] | |established_date1 = [[January 25]] [[1841]] | ||
|established_event2 = [[Treaty of Nanking]] | |established_event2 = [[Treaty of Nanking]] | ||
| − | |established_date2 = [[August 29]] [[1842]] | + | |established_date2 = [[August 29,]] [[1842]] |
|established_event3 = [[Japanese occupation of Hong Kong|Japanese occupation]] | |established_event3 = [[Japanese occupation of Hong Kong|Japanese occupation]] | ||
|established_date3 = [[December 25]] [[1941]] – [[August 15]] [[1945]] | |established_date3 = [[December 25]] [[1941]] – [[August 15]] [[1945]] | ||
| Line 65: | Line 61: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{coor title dms|22|11|00|N|114|08|00|E|}} | {{coor title dms|22|11|00|N|114|08|00|E|}} | ||
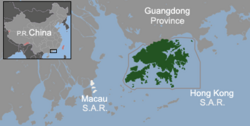
| − | The '''Hong Kong Special Administrative Region''' ( | + | The '''Hong Kong Special Administrative Region''' (香港特別行政區, 香港特别行政区, commonly known as '''Hong Kong'''<ref>The name is often written as ''Hongkong'' in older English texts. The [[Hong Kong Government]] officially adopted the current form on September 3, [[1926]] (Hongkong Government Gazette, Notification 479, 3 September 1926). While the names of most cities in the People's Republic of China are [[romanization|romanised]] into English using [[pinyin]], the official English name is ''Hong Kong'' rather than ''Xiānggǎng'' (See [[Pronunciation of Hong Kong]]).</ref> ({{zh-c|c=[[wiktionary:香|香]][[wiktionary:港|港]]}}), is one of the two [[special administrative region (People's Republic of China)|special administrative regions]] of the [[People's Republic of China]], along with [[Macau]]. Comprising more than 260 islands, the territory is located on the eastern side of the [[Pearl River Delta]], bordering [[Guangdong]] province in the north and facing the [[South China Sea]] in the east, west and south. |
| − | Hong Kong was a [[crown colony]] of the [[United Kingdom]] from 1842 until the [[transfer of the sovereignty of Hong Kong|transfer of sovereignty]] to the People's Republic of China in 1997. The [[Sino-British Joint Declaration]] and the [[Basic Law of Hong Kong]] stipulate that Hong Kong operate with a high degree of [[Autonomous entity|autonomy]] until at least 2047 | + | Hong Kong was a [[crown colony]] of the [[United Kingdom]] from 1842 until the [[transfer of the sovereignty of Hong Kong|transfer of sovereignty]] to the People's Republic of China in 1997. Hong Kong was declared a [[free port]] to serve as an [[entrepôt]] of the [[British Empire]], and grew rapidly into a center for international trade. Between [[December 25]], 1941, and the end of World War II, Hong Kong was under Japanese control. Rapid industrialization between 1960s and 1990s made Hong Kong one of the four Asian Tigers of economic growth. Driven by exports, the economy grew at an average annual rate of 8.9 percent in the 1970s. Many of the manufacturing operations moved to mainland China during the 1980s and Hong Kong became a global financial center, with industry now constituting just 9 percent of the economy. Hong Kong is one of the most densely populated countries/dependencies in the world, with an overall density of more than 6,200 people per km². The [[Sino-British Joint Declaration]] and the [[Basic Law of Hong Kong]] stipulate that Hong Kong operate with a high degree of [[Autonomous entity|autonomy]] until at least 2047. The People’s Republic of China is responsible for the territory's defense and foreign affairs, while Hong Kong maintains its own legal system, [[police force]], [[monetary system]], customs policy, [[immigration policy]], and [[delegate]]s to international organizations and events. |
==History== | ==History== | ||
{{main|History of Hong Kong}} | {{main|History of Hong Kong}} | ||
| − | Human settlement in the location now known as Hong Kong dates back to the [[Paleolithic]] era. The region was first incorporated into [[Imperial China]] | + | Human settlement in the location now known as Hong Kong dates back to the [[Paleolithic]] era. The region was first incorporated into [[Imperial China]] during the [[Qin Dynasty]], and served as a trading post and naval base during the [[Tang Dynasty]] and the [[Song Dynasty]]. The area's earliest recorded European visitor was [[Jorge Álvares]], a [[Portugal|Portuguese]] mariner who arrived in [[1513]].<ref>Porter, Jonathan. [1996] (1996). Macau, the Imaginary City: Culture and Society, 1557 to the Present. Westview Press. ISBN 0813337496</ref><ref>Edmonds. [2002] (2002) China and Europe Since 1978: A European Perspective. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521524032</ref> Contact with the [[United Kingdom]] was established after the [[British East India Company]] founded a trading post in the nearby city of [[Guangzhou|Canton]]. |
In 1839, the refusal by [[Qing Dynasty]] authorities to import [[opium]] resulted in the [[First Opium War]] between China and Britain.<ref name="Wiltshire">Wiltshire, Trea. [First published 1987] (republished & reduced 2003). Old Hong Kong. Central, Hong Kong: Text Form Asia books Ltd. Page 12. ISBN Volume 962-7283-61-4</ref> [[Hong Kong Island]] was first occupied by British forces in 1841, and then formally ceded from China under the [[Treaty of Nanking]] at the end of the war. The British established a [[Crown Colony]] with the founding of [[Victoria City]] the following year. In 1860, after China's defeat in the [[Second Opium War]], the [[Kowloon Peninsula]] south of [[Boundary Street]] and [[Stonecutter's Island]] were ceded to Britain in perpetuity under the [[Convention of Peking]]. In 1898, Britain obtained a 99-year lease of the adjacent northern lands and [[Lantau Island]], which became known as the [[New Territories]]. | In 1839, the refusal by [[Qing Dynasty]] authorities to import [[opium]] resulted in the [[First Opium War]] between China and Britain.<ref name="Wiltshire">Wiltshire, Trea. [First published 1987] (republished & reduced 2003). Old Hong Kong. Central, Hong Kong: Text Form Asia books Ltd. Page 12. ISBN Volume 962-7283-61-4</ref> [[Hong Kong Island]] was first occupied by British forces in 1841, and then formally ceded from China under the [[Treaty of Nanking]] at the end of the war. The British established a [[Crown Colony]] with the founding of [[Victoria City]] the following year. In 1860, after China's defeat in the [[Second Opium War]], the [[Kowloon Peninsula]] south of [[Boundary Street]] and [[Stonecutter's Island]] were ceded to Britain in perpetuity under the [[Convention of Peking]]. In 1898, Britain obtained a 99-year lease of the adjacent northern lands and [[Lantau Island]], which became known as the [[New Territories]]. | ||
| − | [[Image:Kellet Island and Victoria City.jpg|thumb|200px|left|Hong Kong in the late [[ | + | [[Image:Kellet Island and Victoria City.jpg|thumb|200px|left|Hong Kong in the late [[nineteenth century|nineteenth century]] was a major trading post of the [[British Empire]].]] |
[[Image:Jap occupy hk.jpg|thumb|200px|left|[[Japan]]ese troops march along [[Queen's Road]] following the British surrender in 1941.]] | [[Image:Jap occupy hk.jpg|thumb|200px|left|[[Japan]]ese troops march along [[Queen's Road]] following the British surrender in 1941.]] | ||
Hong Kong was declared a [[free port]] to serve as an [[entrepôt]] of the [[British Empire]]. The [[Kowloon-Canton Railway]] opened in 1910 with a southern terminus in [[Tsim Sha Tsui]]. An education system based on the British model was introduced. The local Chinese population had little contact with the European community of wealthy [[tai-pan]]s settled near [[Victoria Peak]].<ref name="Wiltshire" /> | Hong Kong was declared a [[free port]] to serve as an [[entrepôt]] of the [[British Empire]]. The [[Kowloon-Canton Railway]] opened in 1910 with a southern terminus in [[Tsim Sha Tsui]]. An education system based on the British model was introduced. The local Chinese population had little contact with the European community of wealthy [[tai-pan]]s settled near [[Victoria Peak]].<ref name="Wiltshire" /> | ||
| − | As part of its military campaign in [[World War II]], the [[Empire of Japan]] invaded Hong Kong on [[December 8]], [[1941]]. The [[Battle of Hong Kong]] ended with British and Canadian | + | As part of its military campaign in [[World War II]], the [[Empire of Japan]] invaded Hong Kong on [[December 8]], [[1941]]. The [[Battle of Hong Kong]] ended with British and Canadian forces surrendering control of the colony to Japan on [[December 25]], 1941. During the [[Japanese occupation of Hong Kong]], civilians suffered from widespread [[food shortage]]s caused by the imposition of rations, and [[hyper-inflation]] due to forced exchange of currency for military notes. Hong Kong's population declined from 1.6 million before the invasion to about 600,000 in 1945,<ref>New York Times. "[http://www.commondreams.org/headlines05/0418-04.htm NY Times]." ''Thousands March in Anti-Japan Protest in Hong Kong by Keith Bradsher.'' Retrieved on [[2006-04-11]].</ref> when the United Kingdom resumed control of the colony following Japan's defeat in the war. |
| − | Hong Kong's population recovered quickly after the war, as a wave of mainland migrants arrived | + | Hong Kong's population recovered quickly after the war, as a wave of mainland migrants arrived as refugees from the ongoing [[Chinese Civil War]]. With the proclamation of the [[People's Republic of China]] in 1949, more migrants fled to Hong Kong for fear of persecution by the [[Communist Party of China]].<ref name="Wiltshire" /> Many corporations in [[Shanghai]] and [[Guangzhou]] also shifted their operations to Hong Kong.<ref name="Wiltshire" /> The colony became the sole point of contact between mainland China and the Western world, as the communist government increasingly isolated the China from outside influence. Trade with the mainland was interrupted during the [[Korean War]], when the [[United Nations]] ordered a [[trade embargo]] against the communist government.<ref>Wang Yong-hua, ''[http://www.ceps.com.tw/ec/ecjnlarticleView.aspx?atliid=324751&issueiid=25237&jnliid=2518 On Embargo of Hong Kong in 1950-1954]'', Journal of Yanan University Social Science Edition, 2006.</ref> |
[[Image:Flag of Hong Kong 1959.svg|thumb|right|200px|Colonial [[flag of Hong Kong]], based on the British [[Blue Ensign]] ]] | [[Image:Flag of Hong Kong 1959.svg|thumb|right|200px|Colonial [[flag of Hong Kong]], based on the British [[Blue Ensign]] ]] | ||
[[Image:Hk1960.jpg|thumb|200px|right|View of Victoria Harbour, circa 1960]] | [[Image:Hk1960.jpg|thumb|200px|right|View of Victoria Harbour, circa 1960]] | ||
| − | The textile and manufacturing industries | + | The low cost and easy availability of labor contributed to the growth of the textile and manufacturing industries. As Hong Kong rapidly industrialized, its economy became driven by exports to international markets. Living standards rose steadily along with industrial growth. The construction of [[Shek Kip Mei Estate]] in 1953 marked the beginning of a public housing program. Hong Kong was disrupted by chaos during the riots of 1967, <ref name="Wiltshire" /> when pro-communist [[leftists]], inspired by the [[Cultural Revolution]] on the mainland, turned a labor dispute into a violent uprising against the colonial government which lasted until the end of the year. |
| − | Established in 1974, the | + | Established in 1974, the Independent Commission Against Corruption dramatically reduced corruption in the government. When the People's Republic of China initiated a set of economic reforms in 1978, Hong Kong became the main source of foreign investment for the mainland. A Special Economic Zone was established the following year in the Chinese city of [[Shenzhen]], located immediately north of the mainland's border with Hong Kong. Services gradually replaced textiles and manufacturing in the economy of Hong Kong, as the financial and banking sectors became increasingly dominant. After the [[Vietnam War]] ended in 1975, the Hong Kong government became involved in the processing of refugees from Viet Nam. |
| − | + | In the 1980s, with the lease of the New Territories due to expire within two decades, the governments of the United Kingdom and the People's Republic of China discussed the issue of Hong Kong's sovereignty, and in 1984, the two countries signed the [[Sino-British Joint Declaration]], agreeing to transfer the sovereignty of Hong Kong to the People's Republic of China in 1997.<ref name="Wiltshire" /> The declaration stipulated that Hong Kong would be governed as a special administrative region, retaining its laws and a high degree of autonomy for at least fifty years after the transfer. Lacking confidence in this arrangement, some residents chose to [[emmigration|emigrate]] from Hong Kong, particularly after the [[Tiananmen Square protests of 1989]]. | |
[[Image:Hong Kong handover.jpg|right|thumb|200px|Delegates from the United Kingdom and the People's Republic of China attend the [[handover ceremony of Hong Kong in 1997|handover ceremony of Hong Kong]] on the night of [[June 30]],[[1997]].]] | [[Image:Hong Kong handover.jpg|right|thumb|200px|Delegates from the United Kingdom and the People's Republic of China attend the [[handover ceremony of Hong Kong in 1997|handover ceremony of Hong Kong]] on the night of [[June 30]],[[1997]].]] | ||
| − | The [[Basic Law of Hong Kong]], which would serve as the constitutional document after the transfer, was ratified in 1990. Over strong objections from Beijing, [[Governor of Hong Kong|Governor]] [[Chris Patten]] introduced democratic reforms to the election process for the [[Legislative Council of Hong Kong]]. The [[transfer of the sovereignty of Hong Kong]] occurred at midnight on [[ | + | The [[Basic Law of Hong Kong]], which would serve as the constitutional document after the transfer, was ratified in 1990. Over strong objections from Beijing, [[Governor of Hong Kong|Governor]] [[Chris Patten]] introduced democratic reforms to the election process for the [[Legislative Council of Hong Kong]]. The [[transfer of the sovereignty of Hong Kong]] occurred at midnight on the night of [[June 30]], [[1997]], marked by a [[handover ceremony of Hong Kong in 1997|handover ceremony]] at the [[Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre]].<ref name="Wiltshire" /> [[Tung Chee Hwa]] assumed office as the first [[Chief Executive of Hong Kong]]. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The | + | The [[Asian financial crisis]] of 1997 that hit many East Asian markets affected Hong Kong's economy. The [[H5N1]] [[avian influenza]] also surfaced in Hong Kong that year. Implementation of the [[Airport Core Programme]] led to the opening of the new [[Hong Kong International Airport]] in 1998, after six years of construction. The project was part of the ambitious [[Port and Airport Development Strategy]] that was drafted in the early 1980s. |
| − | + | The outbreak of [[severe acute respiratory syndrome]] took hold of Hong Kong in the first half of 2003.<ref>People's Daily. "[http://english.people.com.cn/200401/16/eng20040116_132721.shtml People's Daily]." ''Links between SARS human genes.'' Retrieved on [[2007-03-06]].</ref> That year, half a million people participated in a march to voice disapproval of the Tung administration and a proposal to implement [[Hong Kong Basic Law Article 23|Article 23 of the Basic Law]], which had raised concerns over infringements on rights and freedoms. The proposal was later abandoned by the administration. In 2005, Tung submitted his resignation as chief executive. [[Donald Tsang]], the [[Chief Secretary for Administration of Hong Kong|Chief Secretary for Administration]], was selected as chief executive to complete the term. | |
| − | |||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| Line 108: | Line 101: | ||
[[Image:Hongkong victoria peak.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Hong Kong from [[Victoria Peak]]]] | [[Image:Hongkong victoria peak.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Hong Kong from [[Victoria Peak]]]] | ||
{{main|Geography of Hong Kong|Ecology of Hong Kong}} | {{main|Geography of Hong Kong|Ecology of Hong Kong}} | ||
| − | Hong Kong consists primarily of [[Hong Kong Island]], [[Lantau Island]], [[Kowloon Peninsula]] and the [[New Territories]] as well as some 260 other islands. The Kowloon Peninsula is attached to the New Territories to the north, and the New Territories spans northwards eventually connecting with [[mainland China]] across the [[Sham Chun River]] (Shenzhen River). | + | Hong Kong consists primarily of [[Hong Kong Island]], [[Lantau Island]], [[Kowloon Peninsula]] and the [[New Territories]] as well as some 260 other islands in the South China Sea. The Kowloon Peninsula is attached to the New Territories to the north, and the New Territories spans northwards, eventually connecting with [[mainland China]] across the [[Sham Chun River]] (Shenzhen River). [[Lantau Island|Lantau]] is the largest island. Hong Kong Island is the second largest island and the most populated. [[Ap Lei Chau]] is the most densely populated island in the world. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The name "Hong Kong", which literally translates to | + | The name "Hong Kong", which literally translates to "fragrant harbor," is derived from the area around present-day [[Aberdeen, Hong Kong|Aberdeen]] on Hong Kong Island, where fragrant wood products and fragrant incense were once traded.<ref>[http://ec.hku.hk/visithk/Volumes/Vol_1/VHK_Vol-1_6.pdf Visit Hong Kong: Volume 1, Spring, 2004 (p.14)], University of Hong Kong English Centre. Retrieved on [[2007-02-24]]</ref> The narrow body of water which separates Hong Kong Island from the Kowloon Peninsula is known as [[Victoria Harbor]] and is one of the deepest natural maritime [[port]]s in the world. |
| − | Despite Hong Kong's reputation of being intensely | + | Despite Hong Kong's reputation of being intensely urbanized, the territory has made much effort to promote a green environment.<ref>"[http://www.hktrader.net/200111/200104/200104s1.htm Chief Executive pledges a clean, green, world-class city]", Hong Kong Trader, November 2001. Retrieved on [[2006-05-27]].</ref> Much of the territory remains undeveloped because the terrain is mostly hilly to mountainous with steep slopes. Of the territory's 1,104 [[square kilometre]]s (426 [[square mile]]s),<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.censtatd.gov.hk/FileManager/EN/Content_810/geog.pdf|title=Geography and Climate, Hong Kong |accessdate=2007-01-10 |publisher=Census and Statistics Department, The Government of Hong Kong SAR|language=English}}</ref> less than 25% is developed. The remaining land is remarkably green with about 40% of the landmass reserved as [[Hong Kong Country Parks & Special Areas|country park]]s and [[nature reserve]]s.<ref>"[http://discoverhongkong.com/eng/touring/hiking/index.jhtml Hong Kong Hiking Tours]", The Hong Kong Tourism Board's Hiking page. Retrieved on [[2006-06-18]].</ref> Most of the territory's urban development exists on the Kowloon peninsula, along the northern shores of Hong Kong Island and in scattered settlements throughout the New Territories. |
| − | Hong Kong's long, irregular and curvaceous [[coast]]line | + | Hong Kong's long, irregular and curvaceous [[coast]]line provides many bays, rivers and [[Beaches of Hong Kong|beach]]es. Despite the territory's extensive wooded and ocean setting, Hong Kong's air ranks as among the most polluted, and environmental awareness is growing. Approximately 80% of the city's smog originates from other parts of the [[Pearl River Delta]].<ref>New York Times. "[http://www.nytimes.com/2007/03/22/world/asia/22hongkong.html?ex=1332216000&en=d298556ccd753714&ei=5088&partner=rssnyt&emc=rss NYtimes]." ''Dirty Air Becomes Divisive Issue in Hong Kong Vote.'' Retrieved on [[2006-11-05]].</ref> |
Hong Kong is 60 [[kilometre]]s (37 [[mile]]s) east of [[Macau]] on the opposite side of the Pearl River Delta. It borders the [[subprovincial city|city]] of [[Shenzhen]] in [[Guangdong Province]] to the north. The highest elevation in the territory is at [[Tai Mo Shan]], at a height of 958 [[metre]]s (3,142 [[foot (unit of length)|ft]]) above sea level. Lowlands exist in the northwestern part of the New Territories. | Hong Kong is 60 [[kilometre]]s (37 [[mile]]s) east of [[Macau]] on the opposite side of the Pearl River Delta. It borders the [[subprovincial city|city]] of [[Shenzhen]] in [[Guangdong Province]] to the north. The highest elevation in the territory is at [[Tai Mo Shan]], at a height of 958 [[metre]]s (3,142 [[foot (unit of length)|ft]]) above sea level. Lowlands exist in the northwestern part of the New Territories. | ||
==Climate== | ==Climate== | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Hkobservatorylogo.gif|thumb|right|200px|The [[Hong Kong Observatory]] is the government department responsible for providing meteorological forecasts, weather-related hazard warnings and geophysical surveys for the territory.]][[Climate of Hong Kong|Hong Kong's climate]] is [[subtropical]] and prone to [[monsoon]]s. It is cooler and dry in the [[winter]]time which lasts from around December to early March, and is hot, humid and [[rain]]y from [[Spring (season)|spring]] through [[summer]]. It is warm, [[sun]]ny, and dry in [[autumn]]. Hong Kong occasionally has [[tropical cyclone]]s in the summer and early autumn. The ecology of Hong Kong is mostly affected by the results of climatic changes. Hong Kong's climate is seasonal due to the alternating wind directions between winter and summer. Hong Kong has been geologically stable for millions of years, though landslides are common especially after heavy rainstorms. Flora and fauna in Hong Kong are affected by climatic change, sea level alternation and human impact. | |
| − | [ | + | The highest recorded temperature<ref>"[http://www.weather.gov.hk/cis/extreme/mon_extreme_e.htm Extreme Values and Dates of Occurrence of Extremes of Meteorological Elements between 1884–1939 and 1947–2006 for Hong Kong]", Hong Kong Observatory. Retrieved on [[2006-02-02]].</ref> in Hong Kong is 38°[[Celsius|C]] (100.0°[[Fahrenheit|F]]) while the lowest recorded temperature is -4°C (25.0°F). Meanwhile, the highest and lowest temperatures ever recorded by the [[Hong Kong Observatory|Observatory]] are respectively 36.1°C (97.0°F) on [[19 August]] [[1900]] and [[18 August]] [[1990]], and 0.0°C (32.0°F) on [[18 January]] [[1893]]. The average temperature<ref name="met_norms">"[http://www.weather.gov.hk/cis/normal/1971_2000/normals_e.htm Monthly Meteorological Normals for Hong Kong]", Hong Kong Observatory. Retrieved on [[2006-02-02]].</ref> in the coldest month, January, is 16.1°C (61.0°F) while the average temperature in the hottest month, July, is 28.7°C (83.7°F). |
| − | + | The territory is situated south of the [[Tropic of Cancer]] which is approximate to [[Hawaii]] in [[latitude]]. In winter, strong and cold winds generated from the north cool the city; in the summer, the wind's prevailing direction changes and brings the warm and humid air in from the southwest. This climate can support a [[tropical rainforest]]. | |
| − | The territory is situated south of the [[Tropic of Cancer]] which is approximate to [[Hawaii]] in [[latitude]]. In winter, strong and cold winds | ||
<center><!--Infobox begins—>{{Infobox Weather | <center><!--Infobox begins—>{{Infobox Weather | ||
| Line 174: | Line 164: | ||
==Politics and government== | ==Politics and government== | ||
{{main|Politics of Hong Kong}} | {{main|Politics of Hong Kong}} | ||
| − | Pursuant to the | + | Pursuant to the Hong Kong Basic Law, Hong Kong's constitutional document, the local Hong Kong government retains sovereignty over the territory except in areas of national defense and foreign relations. Only the [[Chief Executive of Hong Kong|Chief Executive]], the head of territory and head of government, is selected by the Chief Executive Election Committee composed of 800 members. All other functionaries of the government, including members the executive and legislative branch, are either appointed by the Chief Executive (directly or by proxy) or elected by voters. In theory, this arrangement guarantees that Hong Kong is governed almost independently of the PRC and can retain its unique cultural, legal and economic infrastructure. In practice, however, some have accused Beijing of excess intrusion into Hong Kong domestic affairs beyond levels permitted under Basic Law. |
[[Image:HK Chater Road LegCo view.jpg|thumb|200px|The Legislative Council of Hong Kong]] | [[Image:HK Chater Road LegCo view.jpg|thumb|200px|The Legislative Council of Hong Kong]] | ||
[[Image:GH facade.JPG|thumb|200px|The [[Government House, Hong Kong|Government House]] in Central where the [[Chief Executive of Hong Kong|Chief Executive]] resides.]] | [[Image:GH facade.JPG|thumb|200px|The [[Government House, Hong Kong|Government House]] in Central where the [[Chief Executive of Hong Kong|Chief Executive]] resides.]] | ||
| − | Laws in Hong Kong are enacted only by approval of the Chief Executive and majority consent from the 60 seat [[Legislative Council of Hong Kong]], or LegCo. | + | Laws in Hong Kong are enacted only by approval of the Chief Executive and majority consent from the 60 seat [[Legislative Council of Hong Kong]], or LegCo. Although the nature of Hong Kong's government is often said to be undemocratic, half of LegCo's seats are elected under [[universal suffrage]], with the other half selected by [[functional constituencies]] consisting of trade unions and special interests. Basic Law guarantees that all seats will eventually be elected under universal suffrage. |
| − | [[Donald Tsang]] | + | [[Donald Tsang]] has held the office of the [[Chief Executive of Hong Kong|Chief Executive]] since his election on June 16, 2005 by an electoral committee appointed by Beijing.<ref>"[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/4094248.stm Donald Tsang set to be HK leader]", BBC News, [[2005-06-15]]. Retrieved [[2006-05-14]].</ref> He was re-elected as [[Hong Kong Chief Executive election, 2007 | Chief Executive on March 25, 2007 for another five year term, which began on 1st July 2007. |
| − | The | + | The Peoples Republic of China set up a [[Provisional Legislative Council|Provisional Legislative Council (PLC)]] in 1996 just before the handover, which moved to Hong Kong to have its meetings after the handover. It repealed some laws passed by the colonial Legislative Council, and passed some new laws, such as the Public Order Ordinance,<ref>[http://www.corpun.com/hkjur4.htm Hong Kong Public Order Ordinance], World Corporal Punishment Research, February 2000. Retrieved [[14 May]] [[2006]].</ref> which requires permission from police to hold a demonstration if the number of participants exceeds thirty. Legislative Council elections were held in May, [[1998]], September]] [[2000]] and again in September of [[2004]], with the next election scheduled for 2008. According to the Hong Kong Basic Law, the present third term of the Legislative Council has 25 seats directly elected from geographical constituencies and 30 seats elected from [[functional constituency|functional constituencies]]. The 1998, 2000 and [[Hong Kong legislative election, 2004|2004]] Legislative Council elections were seen as free, open, and widely contested, despite the protests of 'pro-democratic' politicians who contended that the electoral basis for these seats is too narrow. |
| − | + | On September 24, [[2005]], twenty-five Hong Kong pro-democracy LegCo members, some of whom had been previously labeled as traitors by Beijing after the 1989 [[Tiananmen Square crackdown]] and barred from entering the mainland, crossed the border into the southern province of [[Guangdong]], following an unprecedented invitation by the Peoples Republic of China which was seen as a gesture of goodwill.<ref>"[http://www.abc.net.au/news/newsitems/200509/s1467927.htm Hong Kong democrats visit China]", [[ABC News (Australia)|ABC News Online]], [[September 25]], [[2005]]. Retrieved [[May 27]], [[2006]].</ref> | |
| − | [[Image:HK Lower Albert Road 18 bldg.JPG|thumb|200px|left|The [[Central Government Offices]] on [[Government Hill]] ]] | + | [[Image:HK Lower Albert Road 18 bldg.JPG|thumb|200px|left|The [[Central Government Offices]] on [[Government Hill]] ]] |
[[Image:Hkpolact.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Political activities in Central.]] | [[Image:Hkpolact.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Political activities in Central.]] | ||
The civil service of Hong Kong maintains its quality and neutrality following its tradition in the colonial times, operating without discernible direction from [[Beijing]]. Many government and administrative operations are located in Central on Hong Kong Island near the historical location of [[Victoria City]], the site of the original British settlements. | The civil service of Hong Kong maintains its quality and neutrality following its tradition in the colonial times, operating without discernible direction from [[Beijing]]. Many government and administrative operations are located in Central on Hong Kong Island near the historical location of [[Victoria City]], the site of the original British settlements. | ||
| − | + | While Hong Kong is not an independent country, it retains its own delegation in international organizations such as the [[Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation]] and the [[Olympic Games]], although it changed its official name in these functions from "Hong Kong" to "Hong Kong, China" after 1997. Hong Kong also participates in international events by including a delegate with the PRC's representative group. | |
| − | + | ==Legal System and Judiciary== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==Legal | ||
[[Image:Final appeal.gif|thumb|200px|right|[[Hong Kong Court of Final Appeal|The Court of Final Appeal]] in [[Central, Hong Kong|Central]]]] | [[Image:Final appeal.gif|thumb|200px|right|[[Hong Kong Court of Final Appeal|The Court of Final Appeal]] in [[Central, Hong Kong|Central]]]] | ||
[[Image:hongkongbar.jpg|thumb|200px|right|An assembly of Hong Kong [[judge]]s]] | [[Image:hongkongbar.jpg|thumb|200px|right|An assembly of Hong Kong [[judge]]s]] | ||
| Line 207: | Line 191: | ||
Structurally, Hong Kong's court system consists of the [[Hong Kong Court of Final Appeal|Court of Final Appeal]] which replaced the [[Judicial Committee of the Privy Council]], the [[High Court of Hong Kong|High Court]], which is made up of the [[Court of Appeal of Hong Kong|Court of Appeal]] and the [[Court of First Instance of Hong Kong|Court of First Instance]], and the [[District Court of Hong Kong|District Court]], which includes the [[Family Court of Hong Kong|Family Court]]. Other adjudicative bodies include the Lands Tribunal, the Magistrates' Courts, the Juvenile Court, the Coroner's Court, the Labour Tribunal, the Small Claims Tribunal, and the Obscene Articles Tribunal, which is responsible for classifying non-video pornography to be circulated in Hong Kong. Justices of the [[Hong Kong Court of Final Appeal|Court of Final Appeal]] are appointed by Hong Kong's Chief Executive. The [[Basic Law of Hong Kong]] is subject to interpretation by the [[Standing Committee of the National People's Congress]] (NPC:SC) and this power has been invoked three times: the [[Right of abode issue, Hong Kong|right of abode issue]], an interpretation regarding post-2008 election procedures, and an interpretation regarding the length of the term of the Chief Executive. | Structurally, Hong Kong's court system consists of the [[Hong Kong Court of Final Appeal|Court of Final Appeal]] which replaced the [[Judicial Committee of the Privy Council]], the [[High Court of Hong Kong|High Court]], which is made up of the [[Court of Appeal of Hong Kong|Court of Appeal]] and the [[Court of First Instance of Hong Kong|Court of First Instance]], and the [[District Court of Hong Kong|District Court]], which includes the [[Family Court of Hong Kong|Family Court]]. Other adjudicative bodies include the Lands Tribunal, the Magistrates' Courts, the Juvenile Court, the Coroner's Court, the Labour Tribunal, the Small Claims Tribunal, and the Obscene Articles Tribunal, which is responsible for classifying non-video pornography to be circulated in Hong Kong. Justices of the [[Hong Kong Court of Final Appeal|Court of Final Appeal]] are appointed by Hong Kong's Chief Executive. The [[Basic Law of Hong Kong]] is subject to interpretation by the [[Standing Committee of the National People's Congress]] (NPC:SC) and this power has been invoked three times: the [[Right of abode issue, Hong Kong|right of abode issue]], an interpretation regarding post-2008 election procedures, and an interpretation regarding the length of the term of the Chief Executive. | ||
| − | As in [[England]], [[lawyer]]s in Hong Kong | + | As in [[England]], [[lawyer]]s in Hong Kong can choose to practice as either [[barrister]]s or [[solicitor]]s. The vast majority of [[lawyer]]s are [[solicitor]]s, who are licensed and regulated by [[the Law Society of Hong Kong]]. [[Barristers]], on the other hand, are licensed and regulated by the [[Hong Kong Bar Association]]. Only [[barristers]] are allowed to appear in the [[Hong Kong Court of Final Appeal|Court of Final Appeal]] and the [[High Court of Hong Kong|High Court]]. Just as the [[common law system]] is maintained, so are British courtroom customs such as the wearing of robes and wigs by both [[judges]] and [[lawyers]]. |
According to the Article 63 of the [[Basic Law of Hong Kong]], the [[Department of Justice (Hong Kong)|Department of Justice]] controls criminal [[prosecution]]s, free from any interference. It is the largest legal institution in Hong Kong, and its responsibilities involve [[legislation]], judicial administration, prosecution, civil representation, legal and policy drafting and reform, and the legal profession. Aside from prosecuting criminal cases in Hong Kong, officials of the Department of Justice also appear in court on behalf of the government in all civil and administrative lawsuits against the government. As the protector of [[public interest]]s, it may apply for [[judicial review]]s and assign legal representation on behalf of public interest to take part in the trial of cases that involve material public interests.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.doj.gov.hk/|title=Department of Justice|publisher=Department of Justice of HKSAR|accessdate=2007-03-17}}</ref> | According to the Article 63 of the [[Basic Law of Hong Kong]], the [[Department of Justice (Hong Kong)|Department of Justice]] controls criminal [[prosecution]]s, free from any interference. It is the largest legal institution in Hong Kong, and its responsibilities involve [[legislation]], judicial administration, prosecution, civil representation, legal and policy drafting and reform, and the legal profession. Aside from prosecuting criminal cases in Hong Kong, officials of the Department of Justice also appear in court on behalf of the government in all civil and administrative lawsuits against the government. As the protector of [[public interest]]s, it may apply for [[judicial review]]s and assign legal representation on behalf of public interest to take part in the trial of cases that involve material public interests.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.doj.gov.hk/|title=Department of Justice|publisher=Department of Justice of HKSAR|accessdate=2007-03-17}}</ref> | ||
| Line 246: | Line 230: | ||
[[Image:2 International Financial Centre.jpg|200px|right|thumb|[[International Finance Centre|2 International Finance Centre]], the tallest building in Hong Kong]] | [[Image:2 International Financial Centre.jpg|200px|right|thumb|[[International Finance Centre|2 International Finance Centre]], the tallest building in Hong Kong]] | ||
{{main article|Economy of Hong Kong}} | {{main article|Economy of Hong Kong}} | ||
| − | Hong Kong maintains a | + | Hong Kong maintains a capitalistic economy built on a policy of [[free market]], low [[taxation]] and [[Economic interventionism|government non-intervention]]. It is an important centre for international finance and trade, with the greatest concentration of corporate headquarters in the [[Asia-Pacific]] region. In terms of [[gross domestic product]] per capita and [[gross metropolitan product]], Hong Kong is the wealthiest urban centre in the People's Republic of China. The [[List of countries by GDP (PPP)|GDP per capita (PPP)]] of Hong Kong even exceeded the four big economies in Western Europe (UK, France, Germany, Italy) and Japan in Asia. |
| − | Continuing the practice established under the British administration, the Government of Hong Kong | + | Continuing the practice established under the British administration, the Government of Hong Kong generally leaves the direction of the economy to market forces and the private sector. Since 1980, the government has usually played a passive role under the official policy of [[positive non-interventionism]]. Hong Kong has often been cited as a prime example of [[laissez-faire capitalism]] in practice, most notably by economist [[Milton Friedman]]. It has ranked as the world's freest economy in the [[Index of Economic Freedom]] for thirteen consecutive years, since the inception of the index in 1995.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.heritage.org/research/features/index/|title=2007 Index of Economic Freedom |publisher=Heritage Foundation}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.fraserinstitute.ca/admin/books/chapterfiles/1EFW2006ch1Rev.pdf#|title=Summary Economic Freedom Rating 2004 (Economic Freedom of the World - Annual report 2006 on page 13 or 9 of 23) |accessdate=2007-01-08 |publisher=The Fraser Institute, Canada |language=English}}</ref> It also places first in the Economic Freedom of the World Report.<ref name="FraserInst">{{cite web|url=http://www.fraserinstitute.ca/admin/books/chapterfiles/1EFW2006ch1Rev.pdf|title=Economic Freedom of the World: 2006 Annual Report|publisher=The Fraser Institute|year=2006|accessdate=2007-06-06|format=PDF}}</ref> |
| − | Hong Kong has little arable land and few natural resources within its borders, and must therefore import most of its [[food]] and raw materials. Hong Kong is the world's eleventh largest trading entity,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.info.gov.hk/info/hkbrief/eng/ahk.htm|title=About Hong Kong|publisher=Hong Kong SAR Government Information Centre|month=April|year=2006|accessdate=2007-04-12}}</ref> with the total value of [[import]]s and [[export]]s exceeding its [[gross domestic product]]. [[As of 2006]], there are | + | Hong Kong has little arable land and few natural resources within its borders, and must therefore import most of its [[food]] and raw materials. Hong Kong is the world's eleventh largest trading entity,<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.info.gov.hk/info/hkbrief/eng/ahk.htm|title=About Hong Kong|publisher=Hong Kong SAR Government Information Centre|month=April|year=2006|accessdate=2007-04-12}}</ref> with the total value of [[import]]s and [[export]]s exceeding its [[gross domestic product]]. [[As of 2006]], there are 114 countries that maintain [[consulate]]s in Hong Kong, more than any other city in the world. A large portion of Hong Kong's exports are re-exports, which are products made outside of the territory, especially in [[mainland China]], and distributed through Hong Kong. Even before the transfer of sovereignty to the People's Republic of China, Hong Kong had established extensive trade and investment ties with mainland China. The territory's autonomous status enables it to serve as a point of entry for investments and resources flowing into the mainland. It is also a connecting point for flights from the [[Republic of China]] on [[Taiwan]] destined for the mainland. |
[[Image:Hk money banknotes.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Various Hong Kong banknotes]] | [[Image:Hk money banknotes.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Various Hong Kong banknotes]] | ||
[[Image:Hk money coins.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Various Hong Kong coins]] | [[Image:Hk money coins.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Various Hong Kong coins]] | ||
| − | The currency used in Hong Kong is the [[Hong Kong dollar]]. Since 1983, it has been pegged at a [[fixed exchange rate]] to the [[United States dollar]]. The currency is allowed to trade within a range between 7.75 and 7.85 Hong Kong dollars to one United States dollar. The [[Hong Kong Stock Exchange]] is the [[List of stock exchanges|seventh largest]] in the world, with a [[market | + | The currency used in Hong Kong is the [[Hong Kong dollar]]. Since 1983, it has been pegged at a [[fixed exchange rate]] to the [[United States dollar]]. The currency is allowed to trade within a range between 7.75 and 7.85 Hong Kong dollars to one United States dollar. The [[Hong Kong Stock Exchange]] is the [[List of stock exchanges|seventh largest]] in the world, with a [[market capitalization]] of about [[United States dollar|US$]]1.69 trillion as of February 2007. In [[2006]], the total value of initial public offerings conducted in Hong Kong was second highest in the world after [[London]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.iht.com/articles/2006/12/25/business/borse.php|title=Hong Kong surpasses New York in IPOs|publisher=International Herald Tribune|date=[[2006-12-25]]|accessdate=2007-04-12}}</ref> The City of London Corporation's Global Financial Centers Index (GFCI) 2007, which evaluates the competitiveness of 46 financial centers worldwide, ranks Hong Kong as the third-best financial centre globally and the strongest centre in [[Asia]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.zyen.com/Knowledge/Research/GFCI%201%20March%202007%20Executive%20Summary.pdf|title=The Global Financial Centres Index 1 Executive Summary|publisher=City of London|month=March|year=2007|accessdate=2007-04-12|format=PDF}}</ref> |
| − | Hong Kong's economy is dominated by services, which | + | Hong Kong's economy is dominated by services, which account for over 90 percent of its gross domestic product. In the past, manufacturing had been the most important sector of the economy, as Hong Kong industrialized following the Second World War. Driven by exports, the economy grew at an average annual rate of 8.9 percent in the 1970s. Hong Kong underwent a rapid transition to a service-based economy in the 1980s, when growth averaged 7.2 percent annually. Many of the manufacturing operations moved to mainland China during this period, and industry now constitutes just 9 percent of the economy. As Hong Kong matured to become a financial center, growth slowed to an average of 2.7 percent annually in the 1990s. Together with [[Singapore]], [[South Korea]], and [[Taiwan]], Hong Kong is known as one of the [[Four Asian Tigers]] for its high growth rates and rapid industrialization between the 1960s and the 1990s.<ref>Wallace, Peter. [2002] (2002). Contemporary China: The Dynamics of Change at the Start of the New Millennium. Routledge. ISBN 0700716378</ref> |
[[Image:Hkdisneyfireworks.jpg|thumb|200px|[[Hong Kong Disneyland]] during a [[fireworks]] display]] | [[Image:Hkdisneyfireworks.jpg|thumb|200px|[[Hong Kong Disneyland]] during a [[fireworks]] display]] | ||
| − | The economy suffered a 5.3 percent decline during 1998, in the aftermath of the [[Asian financial crisis]]. A period of recovery followed, with growth rate reaching 10 percent in 2000, although [[deflation (economics)|deflation]] persisted. In 2003, the economy was greatly affected by the outbreak of [[Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome]] (SARS), which reduced economic growth to 2.3 percent that year. A revival of external and domestic demand led to a strong recovery the following year, as cost declines strengthened Hong Kong export competitiveness. The 68-month-long deflationary period ended in mid-2004, with consumer price [[inflation]] hovering at near zero levels.<ref>[http://www.info.gov.hk/gia/general/200503/16/03160166.htm 2005–06 Budget Speech by the Financial Secretary of Hong Kong], [[2005-03-16]].</ref> Beginning in 2003, the [[Individual Visit Scheme]] has allowed | + | The economy suffered a 5.3 percent decline during 1998, in the aftermath of the [[Asian financial crisis]]. A period of recovery followed, with the growth rate reaching 10 percent in 2000, although [[deflation (economics)|deflation]] persisted. In 2003, the economy was greatly affected by the outbreak of [[Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome]] (SARS), which reduced economic growth to 2.3 percent that year. A revival of external and domestic demand led to a strong recovery the following year, as cost declines strengthened Hong Kong export competitiveness. The 68-month-long deflationary period ended in mid-2004, with consumer price [[inflation]] hovering at near zero levels.<ref>[http://www.info.gov.hk/gia/general/200503/16/03160166.htm 2005–06 Budget Speech by the Financial Secretary of Hong Kong], [[2005-03-16]].</ref> Beginning in 2003, the [[Individual Visit Scheme]] has allowed travelers from some cities in mainland China to visit Hong Kong without an accompanying tour group. As a result, the [[Tourism in Hong Kong|tourism industry of Hong Kong]] has benefited from an increase in mainland visitors, further aided by the opening of [[Hong Kong Disneyland Resort]] in 2005. The economy continues to grow strongly with the return of consumer confidence and rising trade. Hong Kong has set low rates in both personal and corporate taxation. |
In 2006, Hong Kong's per-capita GDP ranked as the 6<sup>th</sup> highest in the world at US$38,127, ahead of countries such as [[Switzerland]], [[Denmark]], and [[Japan]].<ref>[[List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita|"List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita"]], Wikipedia. Retrieved on [[2007-05-02]].</ref> Its [[GDP]] ranked as the 40<sup>th</sup> highest at [[US$]]253.1 billion. | In 2006, Hong Kong's per-capita GDP ranked as the 6<sup>th</sup> highest in the world at US$38,127, ahead of countries such as [[Switzerland]], [[Denmark]], and [[Japan]].<ref>[[List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita|"List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita"]], Wikipedia. Retrieved on [[2007-05-02]].</ref> Its [[GDP]] ranked as the 40<sup>th</sup> highest at [[US$]]253.1 billion. | ||
| − | |||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
[[Image:Hksycss.jpg|thumb|right|200px|[[Sai Yeung Choi Street]] South, the most crowded street in [[Mong Kok]]]] | [[Image:Hksycss.jpg|thumb|right|200px|[[Sai Yeung Choi Street]] South, the most crowded street in [[Mong Kok]]]] | ||
{{main|Demographics of Hong Kong|Languages of Hong Kong|Bilingualism in Hong Kong}} | {{main|Demographics of Hong Kong|Languages of Hong Kong|Bilingualism in Hong Kong}} | ||
| − | Hong Kong's population increased sharply throughout the 1990s, reaching 6.99 million in 2006.<ref>"[http://www.censtatd.gov.hk/hong_kong_statistics/statistics_by_subject/index.jsp?subjectID=1&charsetID=2&displayMode=T Hong Kong Statistics - Population and Vital Events]", Census and Statistics Department. Retrieved [[2007-02-02]]</ref> About 95% of Hong Kong's population is of | + | Hong Kong's population increased sharply throughout the 1990s, reaching 6.99 million in 2006.<ref>"[http://www.censtatd.gov.hk/hong_kong_statistics/statistics_by_subject/index.jsp?subjectID=1&charsetID=2&displayMode=T Hong Kong Statistics - Population and Vital Events]", Census and Statistics Department. Retrieved [[2007-02-02]]</ref> About 95% of Hong Kong's population is of Chinese descent, the majority being Cantonese or from ethnic groups such as [[Hakka]] and [[Teochew]]. [[Standard Cantonese|Cantonese]], a Chinese language commonly spoken in southern China, is Hong Kong's official dialect. [[English language|English]] is also an official language widely spoken by more than 38% of the population. According to statistics, some 3.1% regard English as their "usual" language with 34.9% speaking it as "another" language.<ref>UCL.AC.UK. "[http://www.ucl.ac.uk/english-usage/ice/icehk.htm UCL.AC]." ''ICE Hong Kong.'' Retrieved on [[2007-06-05]].</ref> Signs displaying both Chinese and English are extremely common throughout the territory. Since the 1997 handover, new groups of [[mainland China]] immigrants have arrived, and the usage of [[Mandarin (linguistics)|Mandarin]], the official dialect of mainland China, has increased as the integration with mainland economy led to a demand in Mandarin speakers. |
| − | The remaining 5% of the population is composed of non-ethnic Chinese forming a highly visible group despite their smaller numbers. | + | The remaining 5% of the population is composed of non-ethnic Chinese forming a highly visible group despite their smaller numbers. There is a South Asian population comprised of [[India]]ns, [[Pakistan]]is and [[Nepal]]ese. Vietnamese [[refugee]]s have become permanent residents. Approximately 140,000 [[Filipinos in Hong Kong|Filipinos]] work in Hong Kong as [[Foreign domestic helpers in Hong Kong|foreign domestic helpers]]. An increasing number of domestic workers also originate from [[Indonesia]]. There are also a number of [[European]]s, [[Americans in Hong Kong|Americans]], [[Australia]]ns, [[Canadians in Hong Kong|Canadians]], [[Japanese people in Hong Kong|Japanese]], and [[Koreans in Hong Kong|Koreans]] working in Hong Kong's commercial and financial sector. |
| − | Considered as a dependency, Hong Kong is one of the | + | Considered as a dependency, Hong Kong is one of the most densely populated countries /dependencies in the world, with an overall density of more than 6,200 people per km². Hong Kong has a [[fertility rate]] of 0.95 children per woman,<ref>"[http://www.indexmundi.com/hong_kong/total_fertility_rate.html Hong Kong Total fertility rate]", Index Mundi. Retrieved [[2006-05-27]]</ref> one of the lowest in the world and far below the 2.1 children per woman required to sustain the current population. However, population in Hong Kong continues to grow due to the influx of immigrants from mainland China, approximating 45,000 per year. Life expectancy in Hong Kong is 81.6 years as of 2006, fifth highest in the world. |
Hong Kong's population has an extremely dense urban core, consisting of [[Kowloon]] and the north of [[Hong Kong Island]]. The rest is relatively sparsely populated, with millions of residents scattered irregularly throughout the [[New Territories]], south Hong Kong island and Lantau Island. An increasing number of citizens are living in [[Shenzhen]], and commuting from mainland China. | Hong Kong's population has an extremely dense urban core, consisting of [[Kowloon]] and the north of [[Hong Kong Island]]. The rest is relatively sparsely populated, with millions of residents scattered irregularly throughout the [[New Territories]], south Hong Kong island and Lantau Island. An increasing number of citizens are living in [[Shenzhen]], and commuting from mainland China. | ||
| Line 280: | Line 263: | ||
[[Image:Hkpolyu.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Hong Kong Polytechnic University]] | [[Image:Hkpolyu.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Hong Kong Polytechnic University]] | ||
| − | + | Since Hong Kong is a former British Crown colony, its [[education]] system has roughly followed the British system of education. At the higher education levels, both British and American systems exist. The [[University of Hong Kong]] (HKU), the oldest institution of tertiary education in the territory, has traditionally been based on the British model but has incorporated some elements of the American model in recent years. Second to HKU historically, the [[Chinese University of Hong Kong]] (CUHK) follows the American model with a characteristically British college system. The [[Hong Kong University of Science and Technology]] (HKUST) was established on the American model of higher education. There are nine public universities in Hong Kong, and a number of private institutions of higher educaton, such as Lingnan University in Tuen Mun, the only university in Hong Kong that provides a liberal arts education. | |
| − | + | Hong Kong's public schools are operated by the Education and Manpower Bureau of the Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region.<ref>[http://www.emb.gov.hk/FileManager/EN/Content_4405/nc%20facilities%2004(final).pdf Education for Non-Chinese Speaking Children], Education and Manpower Bureau, Government of HKSAR.</ref> | |
| + | The system features a non-compulsory three-year [[kindergarten]], followed by a compulsory six-year primary education and three-year junior [[secondary education]]; a non-compulsory two-year senior secondary education leading to the [[Hong Kong Certificate of Education Examination]]s and a two-year [[matriculation]] course leading to the [[Hong Kong Advanced Level Examination]]s. A new “3+3+4”curriculum, consisting of a three-year junior secondary, three-year senior secondary and four-year undergraduate academic system, will be implemented from 2009 (for senior secondary) and 2012 (for tertiary) onwards. There are also [[Tertiary education|tertiary institutions]] offering various Bachelor's, Master's, and Doctoral degrees, other higher diplomas, and [[associate degree]] courses. | ||
| − | + | Most comprehensive schools in Hong Kong fall under three categories: public schools, subsidized schools and private schools. Public schools are rare, and subsidized schools are the most common, run by charitable organizations, often with religious affiliations, and and partially financed by government aid and grants. The majority of such religious affiliations are [[Christianity|Christian]] and [[Catholic]], but there are also [[Buddhist]], [[Daoist]] ([[Taoist]]), [[Islam]]ic and [[Confucian]] schools. Private schools, often run by Christian organizations, base their admissions based on academic merit rather than on financial resources. Outside this system are the schools under the [[Direct Subsidy Scheme]] (DSS) and private [[international school]]s. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Most comprehensive schools in Hong Kong fall under three categories: | ||
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
| Line 293: | Line 274: | ||
[[Image:BruceLee14.jpg|thumb|left|150px|[[Bruce Lee]] battles [[Chuck Norris]] in ''[[Way of the Dragon]]''.]] | [[Image:BruceLee14.jpg|thumb|left|150px|[[Bruce Lee]] battles [[Chuck Norris]] in ''[[Way of the Dragon]]''.]] | ||
{{main|Culture of Hong Kong}} | {{main|Culture of Hong Kong}} | ||
| − | Hong Kong is frequently described as a place where East meets West, a meeting reflected in its economic | + | Hong Kong is frequently described as a place where East meets West, a meeting reflected in its economic infrastructure, architecture, education, and street culture. On one street corner, there may be traditional Chinese shops selling [[Chinese herbal medicine]], [[Buddhist]] paraphernalia or bowls of synthetic [[shark fin soup]]. But around the next, one may find theaters showing the latest [[Cinema of the United States|Hollywood]] blockbusters, an English-style pub, a [[List of Catholic Church in Hong Kong|Catholic Church]] or [[Ronald McDonald]] inviting passers-by to a [[Big Mac]]. The territory's official languages are Chinese and English; signs in both languages are omnipresent throughout Hong Kong. The government, police and most workplaces and stores conduct business bilingually. British rule may have ended a decade ago, but Western culture is deeply ingrained in Hong Kong and coexists seamlessly with traditional philosophy and practices of the Orient. |
| − | Hong Kong has an active nightlife in major entertainment districts | + | Hong Kong has an active nightlife in major entertainment districts such as [[Lan Kwai Fong]], [[Tsim Sha Tsui]], [[Wan Chai]]. These areas are frequented by visitors, expatriates and locals alike. On a clear day, [[Victoria Peak]] offers a spectacular view of the city. There is also a promenade along the [[Tsim Sha Tsui]] waterfront, which is popular among young Chinese couples. Shopping is often done at night, as evidenced by the [[Temple Street Night Market]], where one can also catch free performances of [[Beijing opera]] ([[Peking opera]]). |
| − | The city's cosmopolitan | + | The city's cosmopolitan flavor can also be seen in the wide variety of cuisines available. While different varieties of Chinese selections, especially seafood, are most popular, there are also many European, American, Japanese, Korean, and other restaurants. Ethnic dishes served in [[cha chaan teng]] (Chinese tea restaurants) and [[dai pai dong]] (open air stalls) are also popular. The people of Hong Kong take their food seriously and many top chefs make their way to the city to show off their talents to these discerning diners. |
| − | While Hong Kong is a global centre of trade, perhaps the city's most famous export is its entertainment industry, particularly in the martial arts genre. Several Hollywood performers originate from Hong Kong cinema—[[Bruce Lee]], [[Chow Yun-Fat]], [[Jackie Chan]], [[Michelle Yeoh]], and [[Jet Li]], to name a few. Behind the camera, Hong Kong filmmakers have also | + | While Hong Kong is a global centre of trade, perhaps the city's most famous export is its entertainment industry, particularly in the martial arts genre. Several Hollywood performers originate from Hong Kong cinema—[[Bruce Lee]], [[Chow Yun-Fat]], [[Jackie Chan]], [[Michelle Yeoh]], and [[Jet Li]], to name a few. Behind the camera, Hong Kong filmmakers have also found recognition in Hollywood, such as [[John Woo]], [[Wong Kar-wai]], [[Tsui Hark]] and martial arts choreographers who have designed fight scenes in the ''[[Matrix trilogy]]'', ''[[Kill Bill]]'' and ''[[Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon]]''. Back in Hong Kong, several homegrown films have also gained international recognition, such as ''[[Chungking Express]]'', ''[[Infernal Affairs]]'', ''[[Shaolin Soccer]]'', ''[[Rumble in the Bronx]]'' and ''[[In the Mood for Love]].'' Acclaimed filmmaker [[Quentin Tarantino]] has commented he was strongly influenced by [[Hong Kong action cinema]]. Hong Kong is also the world's main hub for [[Cantopop]] music.<ref name="CBM">China Briefing Media. [2004] (2004) Business Guide to the Greater Pearl River Delta. China Briefing Media Ltd. ISBN 9889867311</ref> Karaoke culture is also part of Hong Kong's nightlife. |
| − | The Hong Kong government also supports cultural institutions such as the [[Hong Kong Heritage Museum]], [[Hong Kong Museum of Art]], the [[Hong Kong Academy for Performing Arts]] and the [[Hong Kong Philharmonic Orchestra]]. Furthermore, the government's [[Leisure and Cultural Services Department]] also | + | The Hong Kong government also supports cultural institutions such as the [[Hong Kong Heritage Museum]], [[Hong Kong Museum of Art]], the [[Hong Kong Academy for Performing Arts]] and the [[Hong Kong Philharmonic Orchestra]]. Furthermore, the government's [[Leisure and Cultural Services Department]] also subsidizes and sponsors the visits of international performers to Hong Kong. |
==Religion== | ==Religion== | ||
[[Image:Buddha lantau.jpg|thumb|200px|The [[Tian Tan Buddha]] on [[Lantau]], Hong Kong, the tallest outdoor buddha statue in the world.]] | [[Image:Buddha lantau.jpg|thumb|200px|The [[Tian Tan Buddha]] on [[Lantau]], Hong Kong, the tallest outdoor buddha statue in the world.]] | ||
| − | + | Hong Kong enjoys a high degree of religious freedom, a right enshrined and protected in its constitutional document, the Basic Law. The majority of Hong Kong's population, as in [[Mainland China]], practice a folk version of [[Buddhism]]. This majority includes approximately six million people, close to 90% of a total population of less than seven million. A sizable [[Christianity|Christian]] community of around 500,000 exists, forming about 7% of the total population; it is roughly equally divided between [[Roman Catholicism|Catholic]]s and [[Protestant]]s. There are also around 200,000 followers each of authentic [[Buddhism]] and [[Taoism]]. Apart from the major religions, there are also a significant number of followers of other religions, including an estimated 23,000 [[Mormonism|Mormons]], 3,000 [[Jew]]s and a number of [[Islam|Muslim]]s, [[Hinduism|Hindu]]s, [[Sikhism|Sikh]]s and [[Bahá'í Faith|Bahá'í]]s. Apart from offering religious instructions, many major religious bodies operate schools and provide [[social welfare]] facilities. | |
| − | Hong Kong enjoys a high degree of religious freedom, a right enshrined and protected | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Hong Kong's religious beliefs are tied to the region's early role as a [[fishing]] community. The goddess Tin Hau, the protector of seafarers, has been honored with several [[Places of worship in Hong Kong|temples]] throughout Hong Kong for at least 300 years. [[Hung Shing]], another protector of seafarers, has also been honored for centuries. Hong Kong residents, especially the elder generations, visit Taoist or Buddhist temples to appease the deities and, usually, to request compassion, good health or good fortune. Gifts of [[food]], and in particular [[fruit]], are presented, and [[incense]] and [[paper]] offerings are burnt in respect. | |
| − | Hong Kong | + | With the transfer of Hong Kong to the Peoples Republic of China, there were significant concerns that restrictions would be placed on |religious freedom in Hong Kong. So far, this has proved mostly unfounded. Despite the banning of the [[Falun Gong]] movement by [[Beijing]] in 1999, adherents are still free to practice in Hong Kong. Similarly, the Catholic Church freely appoints its own bishops in Hong Kong, unlike in mainland China where the only approved 'Catholic' institution is the [[Chinese Patriotic Catholic Association]] with bishops and priests appointed by Beijing (though an unofficial and illegal Catholic church maintains contact with the Vatican). A significant issue in the normalization of ties between the PRC and the [[Vatican City|Vatican]] is Beijing's insistence that the Vatican drops its diplomatic ties with Taiwan. Hong Kong is the only place in China where missionaries from the Mormon Church can serve. |
==Architecture== | ==Architecture== | ||
[[Image:Bank of china night.jpg|thumb|right|200px|The [[Bank of China Tower]] at dusk.]] | [[Image:Bank of china night.jpg|thumb|right|200px|The [[Bank of China Tower]] at dusk.]] | ||
| − | + | Due to the [[creative destruction]] endemic to Hong Kong over the past fifty years, few historical buildings remain in Hong Kong. Instead the city has become a center for [[modern architecture]], especially in and around the Central and Western District (Central). Dense commercial skyscrapers lining the coast of [[Victoria Harbour]] between Central and Causeway Bay form one of Hong Kong's most famous tourist attractions, which is ranked as the best skyline in the world. Four of the fifteen tallest skyscrapers in the world are in Hong Kong. In [[Kowloon]], which once included the anarchistic settlement called the [[Kowloon Walled City]], strict height restrictions on structures were in force until 1998 when the nearby Kai Tak Airport was closed. With restrictions lifted, several new skyscrapers are under construction in Kowloon, including [[International Commerce Centre]] which, when completed in 2010, will become the world's fourth tallest. | |
| − | Due to the [[creative destruction]] | ||
| − | One of the notable buildings in Hong Kong is [[I. M. Pei]]'s | + | One of the notable buildings in Hong Kong is [[I. M. Pei]]'s Bank of China Tower, completed in 1990 and now Hong Kong's third tallest skyscraper. The building attracted heated controversy, as its sharp angles were said to cast negative [[feng shui]] energy into the heart of Hong Kong. Predating the Bank of China Tower, another well-known structure is the HSBC Headquarters Building, finished in 1985. It was built on the site of Hong Kong's first skyscraper, which was finished in 1935 and was the subject of a bitter heritage [[Architectural conservation|conservation]] struggle in the late 1970s. Both banks' buildings are featured on many of [[Hong Kong banknotes|Hong Kong's banknote]]s. |
| − | The tallest building in Hong Kong is the | + | The tallest building in Hong Kong is the International Finance Centre 2. One of the largest construction projects in Hong Kong was the new [[Hong Kong International Airport]] on [[Chek Lap Kok]] near [[Lantau]], a huge land reclamation project linked to the center of Hong Kong by the [[Lantau Link]], which features three new major [[bridge]]s: [[Tsing Ma Bridge|Tsing Ma]], the world's sixth largest suspension bridge; [[Kap Shui Mun Bridge|Kap Shui Mun]], the world's longest [[cable-stayed bridge]] carrying both road and railway traffic; and [[Ting Kau Bridge|Ting Kau]], the world's first major four-span cable-stayed bridge. |
| − | Particularly | + | Particularly noticeable in Hong Kong's skyline and streetscapes is the omnipresence of public housing estates, which began as a squatter resettlement program in the 1950s, and now house close to 50% of the population. These estates have evolved from seven-story walk-up apartments with public toilets and minimal amenities, allocated on a basis of 24 square feet per adult, half of that for a child; to high-quality high-rises. The public rental program has been supplemented with a government-subsidized Home Ownership Scheme. |
{{wide image|Pauliyas Hongkong.jpg|1400px|A [[Panorama|panoramic]] view of northern [[Hong Kong Island]] between [[North Point]] in the east and [[Kennedy Town]] in the west. }} | {{wide image|Pauliyas Hongkong.jpg|1400px|A [[Panorama|panoramic]] view of northern [[Hong Kong Island]] between [[North Point]] in the east and [[Kennedy Town]] in the west. }} | ||
| Line 337: | Line 314: | ||
Hong Kong is dominated by steep, hilly terrain, and some unusual methods of transport have been devised to ease movement up and down the slopes. For example, the [[Peak Tram]] has provided vertical rail transport between Central and [[Victoria Peak]] since 1888 by steeply ascending the side of a mountain. In [[Central and Western district]] there is an extensive system of [[escalator]]s and [[moving sidewalk]]s, including the longest outdoor covered escalator system in the world, the [[Central-Mid-Levels escalator|Mid-levels Escalator]]. | Hong Kong is dominated by steep, hilly terrain, and some unusual methods of transport have been devised to ease movement up and down the slopes. For example, the [[Peak Tram]] has provided vertical rail transport between Central and [[Victoria Peak]] since 1888 by steeply ascending the side of a mountain. In [[Central and Western district]] there is an extensive system of [[escalator]]s and [[moving sidewalk]]s, including the longest outdoor covered escalator system in the world, the [[Central-Mid-Levels escalator|Mid-levels Escalator]]. | ||
| − | Hong Kong has several different modes of public rail transport. The two [[metro]] systems for the city are the [[MTR]] (Mass Transit Railway) and [[KCR]] which acts as a link between Hong Kong and mainland China (KCR also operates a [[light rail]] system in northwest New Territories). These are operated by the [[MTR Corporation Limited]] and the [[Kowloon-Canton Railway Corporation]] respectively. The [[Hong Kong Tramways|tramway system]] covers the northern parts of Hong Kong Island and is the only [[tram]] system in the world run exclusively | + | Hong Kong has several different modes of public rail transport. The two [[metro]] systems for the city are the [[MTR]] (Mass Transit Railway) and [[KCR]] which acts as a link between Hong Kong and mainland China (KCR also operates a [[light rail]] system in northwest New Territories). These are operated by the [[MTR Corporation Limited]] and the [[Kowloon-Canton Railway Corporation]] respectively. The [[Hong Kong Tramways|tramway system]] covers the northern parts of Hong Kong Island and is the only [[tram]] system in the world run exclusively with [[double decker]]s. |
| − | Five separate companies ([[Kowloon Motor Bus|KMB]], [[Citybus (Hong Kong)|Citybus]], [[New World First Bus|NWFB]], [[Long Win Bus|Long Win]] & [[New Lantao Bus|NLB]]) operate franchised public [[bus]] services in Hong Kong. Double-decker buses were introduced to Hong Kong in 1949 | + | Five separate companies ([[Kowloon Motor Bus|KMB]], [[Citybus (Hong Kong)|Citybus]], [[New World First Bus|NWFB]], [[Long Win Bus|Long Win]] & [[New Lantao Bus|NLB]]) operate franchised public [[bus]] services in Hong Kong. Double-decker buses were introduced to Hong Kong in 1949 and are now used almost exclusively in Hong Kong, just as in [[Singapore]], [[Dublin]] and the [[United Kingdom]]. However, single-decker buses remain in use for routes with lower demand or roads with lower carrying capacity. Such single-decker buses are mainly used on Lantau Island and for overnight services. Most normal franchised bus routes in Hong Kong operate until 1 am. [[Public light bus]]es run the length and breadth of Hong Kong, through areas where standard bus lines cannot reach or do not reach as frequently, quickly, or directly. [[Taxicab|Taxi]]s are also widely used throughout Hong Kong. Ninety-nine percent of taxis in Hong Kong run on liquefied petroleum gas; the rest are still diesel operated. |
| − | Most ferry services are provided by licensed ferry operators serving | + | Most ferry services are provided by licensed ferry operators serving outlying islands, new towns, across [[Victoria Harbour]], [[Macau]] and cities in mainland China. The oldest service, the legendary [[Star Ferry]], operates four lines between [[Kowloon]] and Hong Kong Island and has provided cost-effective transport for over a century. It is popular with tourists desiring a panoramic view of Hong Kong's skyline and harbor, and many Hong Kong residents consider the Star Ferry as one of the city's most treasured cultural icons. Additionally, 78 "[[kai-to]]" ferries are licensed to serve remote coastal settlements. |
| − | [[Image:HKIA.JPG|thumb|200px|left|[[Hong Kong International Airport]]]]Hong Kong has one active [[international airport]], known as [[Hong Kong International Airport]] located at [[Chek Lap Kok]]. | + | [[Image:HKIA.JPG|thumb|200px|left|[[Hong Kong International Airport]]]]Hong Kong has one active [[international airport]], known as [[Hong Kong International Airport]] located at [[Chek Lap Kok]]. When it opened in 1998, this replaced the former Hong Kong International Airport, [[Kai Tak Airport]] located at Kowloon City, which was simultaneously closed. After highly-publicized delays in the cargo systems during the first few months, the airport now serves as a transport hub for [[Southeast Asia]], and as the hub for [[Cathay Pacific Airways]], [[Dragonair (airline)|Dragonair]], [[Air Hong Kong]], [[Oasis Hong Kong Airlines]], [[Hong Kong Airlines]] and [[Hong Kong Express]]. Both Hong Kong International Airport and [[Cathay Pacific Airways]] have been voted best in the world, in the airport and airline criteria respectively, by [[Skytrax]] from 2001 to 2005. [[Hong Kong International Airport]] served more than 36 million passengers in the year 2004, and increased to over 40 million passengers in 2005. |
Access to the airport includes '[[Airport Express (MTR)|Airport Express]]', 'CityFlyers' and 'Airbuses'. These services connect the airport to the rest of Hong Kong. The Airport Express zooms passengers to [[Central, Hong Kong|Central]] on Hong Kong Island in just 23 minutes. The recent opening of [[Sunny Bay (MTR)|Sunny Bay Station]] of the [[MTR]] allows easy access to the [[Hong Kong Disneyland Resort]]. | Access to the airport includes '[[Airport Express (MTR)|Airport Express]]', 'CityFlyers' and 'Airbuses'. These services connect the airport to the rest of Hong Kong. The Airport Express zooms passengers to [[Central, Hong Kong|Central]] on Hong Kong Island in just 23 minutes. The recent opening of [[Sunny Bay (MTR)|Sunny Bay Station]] of the [[MTR]] allows easy access to the [[Hong Kong Disneyland Resort]]. | ||
| − | While the [[traffic]] in [[mainland China]] | + | While the [[traffic]] in [[mainland China]] drives on the right, Hong Kong maintains its own road rules, with traffic continuing to [[drive on the left]]. The Hong Kong highway code uses the same road sign system as [[Great Britain]], whereas the Chinese system is different. There are about 517,000 registered vehicles in Hong Kong, 64% of which are privately owned passenger cars. As a metropolis for luxury in Asia, Hong Kong is world famous for having the most Rolls-Royce cars per capita in the world.<ref>[http://www.investhk.gov.hk/PageControl/ShowDynamic.aspx?act=newsdetail&newsid=273 World-famous producer of luxury cars launches first Hong Kong showroom], InvestHK, 2003-7-30. Retrieved 2007-1-20.</ref> |
| − | |||
==Military== | ==Military== | ||
[[Image:IMG 0482.jpg|thumb|200px|The headquarters of the [[People's Liberation Army]] [[People's Liberation Army Hong Kong Garrison|Hong Kong Garrison]] (former [[Prince of Wales Building]])]] | [[Image:IMG 0482.jpg|thumb|200px|The headquarters of the [[People's Liberation Army]] [[People's Liberation Army Hong Kong Garrison|Hong Kong Garrison]] (former [[Prince of Wales Building]])]] | ||
{{main|People's Liberation Army Hong Kong Garrison}} | {{main|People's Liberation Army Hong Kong Garrison}} | ||
| − | Hong Kong has never had its own military forces | + | Because it has never been a sovereign state, Hong Kong has never had its own military forces except for voluntary auxiliary forces like The Royal Hong Kong Regiment (The Volunteers). All defense matters have been dependent on the state which controls Hong Kong. Before the British handover to PRC sovereignty, defense was provided by the [[British military]], who stationed soldiers in barracks throughout Hong Kong, including the [[British Forces Overseas Hong Kong]]. These forces were supported financially by the Hong Kong Government. |
| − | The People's Republic of China [[Central People's Government]] (CPG) assumed sovereignty over Hong Kong on | + | The People's Republic of China [[Central People's Government]] (CPG) assumed sovereignty over Hong Kong on July 1, 1997, and stationed a [[garrison]] of the People's Liberation Army (PLA) there to manage its defense affairs. Although the garrison has little practical military value, the stationing of the PLA troops in Hong Kong is a significant symbol of the PRC government's assumption of sovereignty over Hong Kong. |
| − | According to Hong Kong's Basic Law, military forces stationed in Hong Kong shall not interfere with local civil affairs; the Hong Kong Government shall remain responsible for the maintenance of public order. The Hong Kong Garrison, composed of [[army|ground]], [[navy|naval]], and [[air force]]s, is under the command of the Chinese [[Central Military Commission]]. The garrison subsequently opened its barracks on [[Stonecutters Island]] and | + | According to Hong Kong's Basic Law, military forces stationed in Hong Kong shall not interfere with local civil affairs; the Hong Kong Government shall remain responsible for the maintenance of public order. The Hong Kong Garrison, composed of [[army|ground]], [[navy|naval]], and [[air force]]s, is under the command of the Chinese [[Central Military Commission]]. The garrison subsequently opened its barracks on [[Stonecutters Island]] and Stanley to the public to promote understanding and trust between the troops and residents. |
Under British rule, Chinese Hong Kong residents (and other Hong Kong residents) were able to join the [[British Forces Overseas Hong Kong]]. | Under British rule, Chinese Hong Kong residents (and other Hong Kong residents) were able to join the [[British Forces Overseas Hong Kong]]. | ||
| Line 409: | Line 385: | ||
| World's most expensive cost-of-living || [http://www.mercerhr.com/costofliving Mercer Human Resource Consulting] || 5/143 cities || | | World's most expensive cost-of-living || [http://www.mercerhr.com/costofliving Mercer Human Resource Consulting] || 5/143 cities || | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | ==Notes== | ||
| + | {{reflist|2}} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{ChineseText}} | {{ChineseText}} | ||
| − | *''A History of Hong Kong''(Third Edition). [[Frank Welsh]]. HarperCollins. [[1 October]] [[1998]]. 624 pages. ISBN 1-56836-002-9. | + | *''A History of Hong Kong'' (Third Edition). [[Frank Welsh]]. HarperCollins. [[1 October]] [[1998]]. 624 pages. ISBN 1-56836-002-9. |
*''Mathematical Modelling of Hong Kong Political and Economical Development''. Derek Lam. Guangzhou Academic Press. [[18 February]] [[1986]]. 23 pages. | *''Mathematical Modelling of Hong Kong Political and Economical Development''. Derek Lam. Guangzhou Academic Press. [[18 February]] [[1986]]. 23 pages. | ||
*''Hong Kong's History: State and Society Under Colonial Rule (Asia's Transformations)''. Tak-Wing Ngo. Routledge. [[1 August]] [[1999]]. 205 pages. ISBN 0-415-20868-8. | *''Hong Kong's History: State and Society Under Colonial Rule (Asia's Transformations)''. Tak-Wing Ngo. Routledge. [[1 August]] [[1999]]. 205 pages. ISBN 0-415-20868-8. | ||
| Line 422: | Line 400: | ||
*[http://www.lcsd.gov.hk/CE/Museum/Monument/en/monuments_list.php List of Declared Monuments in Hong Kong - 3 March 2006] from the Antiquities and Monuments Office | *[http://www.lcsd.gov.hk/CE/Museum/Monument/en/monuments_list.php List of Declared Monuments in Hong Kong - 3 March 2006] from the Antiquities and Monuments Office | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 482: | Line 458: | ||
{{link FA|zh-yue}} | {{link FA|zh-yue}} | ||
{{Link FA|ar}} | {{Link FA|ar}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{credit|142416476}} | {{credit|142416476}} | ||
Revision as of 11:50, 18 July 2007
| 香港特別行政區 Hong Kong Special Administrative Region | |||||
| |||||
| Anthem: March of the Volunteers[1] | |||||
| Capital | None[2] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Official languages | Chinese,[3] English | ||||
| Government | |||||
| - Chief Executive | Donald Tsang | ||||
| Establishment | |||||
| - British occupation | January 25 1841 | ||||
| - Treaty of Nanking | August 29, 1842 | ||||
| - Japanese occupation | December 25 1941 – August 15 1945 | ||||
| - Transfer of sovereignty | July 1 1997 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 1,104 km² (182) 426.4 sq mi | ||||
| - Water (%) | 4.6 | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - 2006 estimate | 6,864,346 | ||||
| - 2001 census | 6,708,389 | ||||
| - Density | 6,352/km² 16,469.6/sq mi | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2006 estimate | ||||
| - Total | $254.2 billion | ||||
| - Per capita | $38,127 | ||||
| HDI (2004) | |||||
| Currency | Hong Kong dollar (HKD)
| ||||
| Time zone | HKT (UTC+8) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .hk | ||||
| Calling code | +852 (01 from Macau) | ||||
The Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (香港特別行政區, 香港特别行政区, commonly known as Hong Kong[4] (Chinese: 香港), is one of the two special administrative regions of the People's Republic of China, along with Macau. Comprising more than 260 islands, the territory is located on the eastern side of the Pearl River Delta, bordering Guangdong province in the north and facing the South China Sea in the east, west and south.
Hong Kong was a crown colony of the United Kingdom from 1842 until the transfer of sovereignty to the People's Republic of China in 1997. Hong Kong was declared a free port to serve as an entrepôt of the British Empire, and grew rapidly into a center for international trade. Between December 25, 1941, and the end of World War II, Hong Kong was under Japanese control. Rapid industrialization between 1960s and 1990s made Hong Kong one of the four Asian Tigers of economic growth. Driven by exports, the economy grew at an average annual rate of 8.9 percent in the 1970s. Many of the manufacturing operations moved to mainland China during the 1980s and Hong Kong became a global financial center, with industry now constituting just 9 percent of the economy. Hong Kong is one of the most densely populated countries/dependencies in the world, with an overall density of more than 6,200 people per km². The Sino-British Joint Declaration and the Basic Law of Hong Kong stipulate that Hong Kong operate with a high degree of autonomy until at least 2047. The People’s Republic of China is responsible for the territory's defense and foreign affairs, while Hong Kong maintains its own legal system, police force, monetary system, customs policy, immigration policy, and delegates to international organizations and events.
History
Human settlement in the location now known as Hong Kong dates back to the Paleolithic era. The region was first incorporated into Imperial China during the Qin Dynasty, and served as a trading post and naval base during the Tang Dynasty and the Song Dynasty. The area's earliest recorded European visitor was Jorge Álvares, a Portuguese mariner who arrived in 1513.[5][6] Contact with the United Kingdom was established after the British East India Company founded a trading post in the nearby city of Canton.
In 1839, the refusal by Qing Dynasty authorities to import opium resulted in the First Opium War between China and Britain.[7] Hong Kong Island was first occupied by British forces in 1841, and then formally ceded from China under the Treaty of Nanking at the end of the war. The British established a Crown Colony with the founding of Victoria City the following year. In 1860, after China's defeat in the Second Opium War, the Kowloon Peninsula south of Boundary Street and Stonecutter's Island were ceded to Britain in perpetuity under the Convention of Peking. In 1898, Britain obtained a 99-year lease of the adjacent northern lands and Lantau Island, which became known as the New Territories.
Hong Kong was declared a free port to serve as an entrepôt of the British Empire. The Kowloon-Canton Railway opened in 1910 with a southern terminus in Tsim Sha Tsui. An education system based on the British model was introduced. The local Chinese population had little contact with the European community of wealthy tai-pans settled near Victoria Peak.[7]
As part of its military campaign in World War II, the Empire of Japan invaded Hong Kong on December 8, 1941. The Battle of Hong Kong ended with British and Canadian forces surrendering control of the colony to Japan on December 25, 1941. During the Japanese occupation of Hong Kong, civilians suffered from widespread food shortages caused by the imposition of rations, and hyper-inflation due to forced exchange of currency for military notes. Hong Kong's population declined from 1.6 million before the invasion to about 600,000 in 1945,[8] when the United Kingdom resumed control of the colony following Japan's defeat in the war.
Hong Kong's population recovered quickly after the war, as a wave of mainland migrants arrived as refugees from the ongoing Chinese Civil War. With the proclamation of the People's Republic of China in 1949, more migrants fled to Hong Kong for fear of persecution by the Communist Party of China.[7] Many corporations in Shanghai and Guangzhou also shifted their operations to Hong Kong.[7] The colony became the sole point of contact between mainland China and the Western world, as the communist government increasingly isolated the China from outside influence. Trade with the mainland was interrupted during the Korean War, when the United Nations ordered a trade embargo against the communist government.[9]
The low cost and easy availability of labor contributed to the growth of the textile and manufacturing industries. As Hong Kong rapidly industrialized, its economy became driven by exports to international markets. Living standards rose steadily along with industrial growth. The construction of Shek Kip Mei Estate in 1953 marked the beginning of a public housing program. Hong Kong was disrupted by chaos during the riots of 1967, [7] when pro-communist leftists, inspired by the Cultural Revolution on the mainland, turned a labor dispute into a violent uprising against the colonial government which lasted until the end of the year.
Established in 1974, the Independent Commission Against Corruption dramatically reduced corruption in the government. When the People's Republic of China initiated a set of economic reforms in 1978, Hong Kong became the main source of foreign investment for the mainland. A Special Economic Zone was established the following year in the Chinese city of Shenzhen, located immediately north of the mainland's border with Hong Kong. Services gradually replaced textiles and manufacturing in the economy of Hong Kong, as the financial and banking sectors became increasingly dominant. After the Vietnam War ended in 1975, the Hong Kong government became involved in the processing of refugees from Viet Nam.
In the 1980s, with the lease of the New Territories due to expire within two decades, the governments of the United Kingdom and the People's Republic of China discussed the issue of Hong Kong's sovereignty, and in 1984, the two countries signed the Sino-British Joint Declaration, agreeing to transfer the sovereignty of Hong Kong to the People's Republic of China in 1997.[7] The declaration stipulated that Hong Kong would be governed as a special administrative region, retaining its laws and a high degree of autonomy for at least fifty years after the transfer. Lacking confidence in this arrangement, some residents chose to emigrate from Hong Kong, particularly after the Tiananmen Square protests of 1989.
The Basic Law of Hong Kong, which would serve as the constitutional document after the transfer, was ratified in 1990. Over strong objections from Beijing, Governor Chris Patten introduced democratic reforms to the election process for the Legislative Council of Hong Kong. The transfer of the sovereignty of Hong Kong occurred at midnight on the night of June 30, 1997, marked by a handover ceremony at the Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre.[7] Tung Chee Hwa assumed office as the first Chief Executive of Hong Kong.
The Asian financial crisis of 1997 that hit many East Asian markets affected Hong Kong's economy. The H5N1 avian influenza also surfaced in Hong Kong that year. Implementation of the Airport Core Programme led to the opening of the new Hong Kong International Airport in 1998, after six years of construction. The project was part of the ambitious Port and Airport Development Strategy that was drafted in the early 1980s.
The outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome took hold of Hong Kong in the first half of 2003.[10] That year, half a million people participated in a march to voice disapproval of the Tung administration and a proposal to implement Article 23 of the Basic Law, which had raised concerns over infringements on rights and freedoms. The proposal was later abandoned by the administration. In 2005, Tung submitted his resignation as chief executive. Donald Tsang, the Chief Secretary for Administration, was selected as chief executive to complete the term.
Geography
Hong Kong consists primarily of Hong Kong Island, Lantau Island, Kowloon Peninsula and the New Territories as well as some 260 other islands in the South China Sea. The Kowloon Peninsula is attached to the New Territories to the north, and the New Territories spans northwards, eventually connecting with mainland China across the Sham Chun River (Shenzhen River). Lantau is the largest island. Hong Kong Island is the second largest island and the most populated. Ap Lei Chau is the most densely populated island in the world.
The name "Hong Kong", which literally translates to "fragrant harbor," is derived from the area around present-day Aberdeen on Hong Kong Island, where fragrant wood products and fragrant incense were once traded.[11] The narrow body of water which separates Hong Kong Island from the Kowloon Peninsula is known as Victoria Harbor and is one of the deepest natural maritime ports in the world.
Despite Hong Kong's reputation of being intensely urbanized, the territory has made much effort to promote a green environment.[12] Much of the territory remains undeveloped because the terrain is mostly hilly to mountainous with steep slopes. Of the territory's 1,104 square kilometres (426 square miles),[13] less than 25% is developed. The remaining land is remarkably green with about 40% of the landmass reserved as country parks and nature reserves.[14] Most of the territory's urban development exists on the Kowloon peninsula, along the northern shores of Hong Kong Island and in scattered settlements throughout the New Territories.
Hong Kong's long, irregular and curvaceous coastline provides many bays, rivers and beaches. Despite the territory's extensive wooded and ocean setting, Hong Kong's air ranks as among the most polluted, and environmental awareness is growing. Approximately 80% of the city's smog originates from other parts of the Pearl River Delta.[15]
Hong Kong is 60 kilometres (37 miles) east of Macau on the opposite side of the Pearl River Delta. It borders the city of Shenzhen in Guangdong Province to the north. The highest elevation in the territory is at Tai Mo Shan, at a height of 958 metres (3,142 ft) above sea level. Lowlands exist in the northwestern part of the New Territories.
Climate
Hong Kong's climate is subtropical and prone to monsoons. It is cooler and dry in the wintertime which lasts from around December to early March, and is hot, humid and rainy from spring through summer. It is warm, sunny, and dry in autumn. Hong Kong occasionally has tropical cyclones in the summer and early autumn. The ecology of Hong Kong is mostly affected by the results of climatic changes. Hong Kong's climate is seasonal due to the alternating wind directions between winter and summer. Hong Kong has been geologically stable for millions of years, though landslides are common especially after heavy rainstorms. Flora and fauna in Hong Kong are affected by climatic change, sea level alternation and human impact.
The highest recorded temperature[16] in Hong Kong is 38°C (100.0°F) while the lowest recorded temperature is -4°C (25.0°F). Meanwhile, the highest and lowest temperatures ever recorded by the Observatory are respectively 36.1°C (97.0°F) on 19 August 1900 and 18 August 1990, and 0.0°C (32.0°F) on 18 January 1893. The average temperature[17] in the coldest month, January, is 16.1°C (61.0°F) while the average temperature in the hottest month, July, is 28.7°C (83.7°F).
The territory is situated south of the Tropic of Cancer which is approximate to Hawaii in latitude. In winter, strong and cold winds generated from the north cool the city; in the summer, the wind's prevailing direction changes and brings the warm and humid air in from the southwest. This climate can support a tropical rainforest.
| Weather averages for Hong Kong | |||||||||||||
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg high °C | 18.6 | 18.6 | 21.5 | 25.1 | 28.4 | 30.4 | 31.3 | 31.1 | 30.2 | 27.7 | 24.0 | 20.3 | 25.6 |
| Avg low °C | 14.1 | 14.4 | 16.9 | 20.6 | 23.9 | 26.1 | 26.7 | 26.4 | 25.6 | 23.4 | 19.4 | 15.7 | 21.1 |
| Avg high °F | 65.5 | 65.5 | 70.7 | 77.2 | 83.1 | 86.7 | 88.3 | 88.0 | 86.4 | 81.9 | 75.2 | 68.5 | 78.1 |
| Avg low °F | 57.4 | 57.9 | 62.4 | 69.1 | 75.0 | 79.0 | 80.1 | 79.5 | 78.1 | 74.1 | 66.9 | 60.3 | 70.0 |
| Precipitation (mm) | 24.9 | 52.3 | 71.4 | 188.5 | 329.5 | 388.1 | 374.4 | 444.6 | 287.5 | 151.9 | 35.4 | 34.5 | 2382.70 |
| Precipitation (in) | 0.98 | 2.06 | 2.81 | 7.42 | 12.97 | 15.28 | 14.74 | 17.50 | 11.32 | 5.98 | 1.39 | 1.36 | 93.81 |
| Source: HKO[17] Jan 20, 2006 | |||||||||||||
Politics and government
Pursuant to the Hong Kong Basic Law, Hong Kong's constitutional document, the local Hong Kong government retains sovereignty over the territory except in areas of national defense and foreign relations. Only the Chief Executive, the head of territory and head of government, is selected by the Chief Executive Election Committee composed of 800 members. All other functionaries of the government, including members the executive and legislative branch, are either appointed by the Chief Executive (directly or by proxy) or elected by voters. In theory, this arrangement guarantees that Hong Kong is governed almost independently of the PRC and can retain its unique cultural, legal and economic infrastructure. In practice, however, some have accused Beijing of excess intrusion into Hong Kong domestic affairs beyond levels permitted under Basic Law.
Laws in Hong Kong are enacted only by approval of the Chief Executive and majority consent from the 60 seat Legislative Council of Hong Kong, or LegCo. Although the nature of Hong Kong's government is often said to be undemocratic, half of LegCo's seats are elected under universal suffrage, with the other half selected by functional constituencies consisting of trade unions and special interests. Basic Law guarantees that all seats will eventually be elected under universal suffrage.
Donald Tsang has held the office of the Chief Executive since his election on June 16, 2005 by an electoral committee appointed by Beijing.[18] He was re-elected as [[Hong Kong Chief Executive election, 2007 | Chief Executive on March 25, 2007 for another five year term, which began on 1st July 2007.
The Peoples Republic of China set up a Provisional Legislative Council (PLC) in 1996 just before the handover, which moved to Hong Kong to have its meetings after the handover. It repealed some laws passed by the colonial Legislative Council, and passed some new laws, such as the Public Order Ordinance,[19] which requires permission from police to hold a demonstration if the number of participants exceeds thirty. Legislative Council elections were held in May, 1998, September]] 2000 and again in September of 2004, with the next election scheduled for 2008. According to the Hong Kong Basic Law, the present third term of the Legislative Council has 25 seats directly elected from geographical constituencies and 30 seats elected from functional constituencies. The 1998, 2000 and 2004 Legislative Council elections were seen as free, open, and widely contested, despite the protests of 'pro-democratic' politicians who contended that the electoral basis for these seats is too narrow.
On September 24, 2005, twenty-five Hong Kong pro-democracy LegCo members, some of whom had been previously labeled as traitors by Beijing after the 1989 Tiananmen Square crackdown and barred from entering the mainland, crossed the border into the southern province of Guangdong, following an unprecedented invitation by the Peoples Republic of China which was seen as a gesture of goodwill.[20]
The civil service of Hong Kong maintains its quality and neutrality following its tradition in the colonial times, operating without discernible direction from Beijing. Many government and administrative operations are located in Central on Hong Kong Island near the historical location of Victoria City, the site of the original British settlements.
While Hong Kong is not an independent country, it retains its own delegation in international organizations such as the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation and the Olympic Games, although it changed its official name in these functions from "Hong Kong" to "Hong Kong, China" after 1997. Hong Kong also participates in international events by including a delegate with the PRC's representative group.
Legal System and Judiciary
In contrast to mainland China's civil law system, Hong Kong continues to follow the common law tradition established by British colonial rule. Article 84 of the Basic Law of Hong Kong allows Hong Kong's courts to refer to decisions (precedents) rendered by courts of other common law jurisdictions. Articles 82 and 92 allow judges from other common law jurisdictions to participate in proceedings of Hong Kong's Court of Final Appeal and sit as Hong Kong judges.
Structurally, Hong Kong's court system consists of the Court of Final Appeal which replaced the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council, the High Court, which is made up of the Court of Appeal and the Court of First Instance, and the District Court, which includes the Family Court. Other adjudicative bodies include the Lands Tribunal, the Magistrates' Courts, the Juvenile Court, the Coroner's Court, the Labour Tribunal, the Small Claims Tribunal, and the Obscene Articles Tribunal, which is responsible for classifying non-video pornography to be circulated in Hong Kong. Justices of the Court of Final Appeal are appointed by Hong Kong's Chief Executive. The Basic Law of Hong Kong is subject to interpretation by the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress (NPC:SC) and this power has been invoked three times: the right of abode issue, an interpretation regarding post-2008 election procedures, and an interpretation regarding the length of the term of the Chief Executive.
As in England, lawyers in Hong Kong can choose to practice as either barristers or solicitors. The vast majority of lawyers are solicitors, who are licensed and regulated by the Law Society of Hong Kong. Barristers, on the other hand, are licensed and regulated by the Hong Kong Bar Association. Only barristers are allowed to appear in the Court of Final Appeal and the High Court. Just as the common law system is maintained, so are British courtroom customs such as the wearing of robes and wigs by both judges and lawyers.
According to the Article 63 of the Basic Law of Hong Kong, the Department of Justice controls criminal prosecutions, free from any interference. It is the largest legal institution in Hong Kong, and its responsibilities involve legislation, judicial administration, prosecution, civil representation, legal and policy drafting and reform, and the legal profession. Aside from prosecuting criminal cases in Hong Kong, officials of the Department of Justice also appear in court on behalf of the government in all civil and administrative lawsuits against the government. As the protector of public interests, it may apply for judicial reviews and assign legal representation on behalf of public interest to take part in the trial of cases that involve material public interests.[21]
Administrative districts

Hong Kong is subdivided into 18 geographic districts for administrative purposes:
Each district is represented by a District Council that advises the Government of Hong Kong on local matters such as public facilities, community programmes, cultural activities and environmental improvements. The Home Affairs Department is the governmental body responsible for coordinating services and communicating government policies and plans to the public. It interacts with the public at the local level through corresponding district offices.
There are no formal definitions for cities and towns in Hong Kong. The historic boundaries of Victoria City, Kowloon and New Kowloon are stated in law, but these entities no longer possess any legal or administrative status.
Economy
Hong Kong maintains a capitalistic economy built on a policy of free market, low taxation and government non-intervention. It is an important centre for international finance and trade, with the greatest concentration of corporate headquarters in the Asia-Pacific region. In terms of gross domestic product per capita and gross metropolitan product, Hong Kong is the wealthiest urban centre in the People's Republic of China. The GDP per capita (PPP) of Hong Kong even exceeded the four big economies in Western Europe (UK, France, Germany, Italy) and Japan in Asia.
Continuing the practice established under the British administration, the Government of Hong Kong generally leaves the direction of the economy to market forces and the private sector. Since 1980, the government has usually played a passive role under the official policy of positive non-interventionism. Hong Kong has often been cited as a prime example of laissez-faire capitalism in practice, most notably by economist Milton Friedman. It has ranked as the world's freest economy in the Index of Economic Freedom for thirteen consecutive years, since the inception of the index in 1995.[22][23] It also places first in the Economic Freedom of the World Report.[24]
Hong Kong has little arable land and few natural resources within its borders, and must therefore import most of its food and raw materials. Hong Kong is the world's eleventh largest trading entity,[25] with the total value of imports and exports exceeding its gross domestic product. As of 2006, there are 114 countries that maintain consulates in Hong Kong, more than any other city in the world. A large portion of Hong Kong's exports are re-exports, which are products made outside of the territory, especially in mainland China, and distributed through Hong Kong. Even before the transfer of sovereignty to the People's Republic of China, Hong Kong had established extensive trade and investment ties with mainland China. The territory's autonomous status enables it to serve as a point of entry for investments and resources flowing into the mainland. It is also a connecting point for flights from the Republic of China on Taiwan destined for the mainland.
The currency used in Hong Kong is the Hong Kong dollar. Since 1983, it has been pegged at a fixed exchange rate to the United States dollar. The currency is allowed to trade within a range between 7.75 and 7.85 Hong Kong dollars to one United States dollar. The Hong Kong Stock Exchange is the seventh largest in the world, with a market capitalization of about US$1.69 trillion as of February 2007. In 2006, the total value of initial public offerings conducted in Hong Kong was second highest in the world after London.[26] The City of London Corporation's Global Financial Centers Index (GFCI) 2007, which evaluates the competitiveness of 46 financial centers worldwide, ranks Hong Kong as the third-best financial centre globally and the strongest centre in Asia.[27]
Hong Kong's economy is dominated by services, which account for over 90 percent of its gross domestic product. In the past, manufacturing had been the most important sector of the economy, as Hong Kong industrialized following the Second World War. Driven by exports, the economy grew at an average annual rate of 8.9 percent in the 1970s. Hong Kong underwent a rapid transition to a service-based economy in the 1980s, when growth averaged 7.2 percent annually. Many of the manufacturing operations moved to mainland China during this period, and industry now constitutes just 9 percent of the economy. As Hong Kong matured to become a financial center, growth slowed to an average of 2.7 percent annually in the 1990s. Together with Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan, Hong Kong is known as one of the Four Asian Tigers for its high growth rates and rapid industrialization between the 1960s and the 1990s.[28]
The economy suffered a 5.3 percent decline during 1998, in the aftermath of the Asian financial crisis. A period of recovery followed, with the growth rate reaching 10 percent in 2000, although deflation persisted. In 2003, the economy was greatly affected by the outbreak of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS), which reduced economic growth to 2.3 percent that year. A revival of external and domestic demand led to a strong recovery the following year, as cost declines strengthened Hong Kong export competitiveness. The 68-month-long deflationary period ended in mid-2004, with consumer price inflation hovering at near zero levels.[29] Beginning in 2003, the Individual Visit Scheme has allowed travelers from some cities in mainland China to visit Hong Kong without an accompanying tour group. As a result, the tourism industry of Hong Kong has benefited from an increase in mainland visitors, further aided by the opening of Hong Kong Disneyland Resort in 2005. The economy continues to grow strongly with the return of consumer confidence and rising trade. Hong Kong has set low rates in both personal and corporate taxation.
In 2006, Hong Kong's per-capita GDP ranked as the 6th highest in the world at US$38,127, ahead of countries such as Switzerland, Denmark, and Japan.[30] Its GDP ranked as the 40th highest at US$253.1 billion.
Demographics
Hong Kong's population increased sharply throughout the 1990s, reaching 6.99 million in 2006.[31] About 95% of Hong Kong's population is of Chinese descent, the majority being Cantonese or from ethnic groups such as Hakka and Teochew. Cantonese, a Chinese language commonly spoken in southern China, is Hong Kong's official dialect. English is also an official language widely spoken by more than 38% of the population. According to statistics, some 3.1% regard English as their "usual" language with 34.9% speaking it as "another" language.[32] Signs displaying both Chinese and English are extremely common throughout the territory. Since the 1997 handover, new groups of mainland China immigrants have arrived, and the usage of Mandarin, the official dialect of mainland China, has increased as the integration with mainland economy led to a demand in Mandarin speakers.
The remaining 5% of the population is composed of non-ethnic Chinese forming a highly visible group despite their smaller numbers. There is a South Asian population comprised of Indians, Pakistanis and Nepalese. Vietnamese refugees have become permanent residents. Approximately 140,000 Filipinos work in Hong Kong as foreign domestic helpers. An increasing number of domestic workers also originate from Indonesia. There are also a number of Europeans, Americans, Australians, Canadians, Japanese, and Koreans working in Hong Kong's commercial and financial sector.
Considered as a dependency, Hong Kong is one of the most densely populated countries /dependencies in the world, with an overall density of more than 6,200 people per km². Hong Kong has a fertility rate of 0.95 children per woman,[33] one of the lowest in the world and far below the 2.1 children per woman required to sustain the current population. However, population in Hong Kong continues to grow due to the influx of immigrants from mainland China, approximating 45,000 per year. Life expectancy in Hong Kong is 81.6 years as of 2006, fifth highest in the world.
Hong Kong's population has an extremely dense urban core, consisting of Kowloon and the north of Hong Kong Island. The rest is relatively sparsely populated, with millions of residents scattered irregularly throughout the New Territories, south Hong Kong island and Lantau Island. An increasing number of citizens are living in Shenzhen, and commuting from mainland China.
Education
Since Hong Kong is a former British Crown colony, its education system has roughly followed the British system of education. At the higher education levels, both British and American systems exist. The University of Hong Kong (HKU), the oldest institution of tertiary education in the territory, has traditionally been based on the British model but has incorporated some elements of the American model in recent years. Second to HKU historically, the Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) follows the American model with a characteristically British college system. The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) was established on the American model of higher education. There are nine public universities in Hong Kong, and a number of private institutions of higher educaton, such as Lingnan University in Tuen Mun, the only university in Hong Kong that provides a liberal arts education.
Hong Kong's public schools are operated by the Education and Manpower Bureau of the Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region.[34] The system features a non-compulsory three-year kindergarten, followed by a compulsory six-year primary education and three-year junior secondary education; a non-compulsory two-year senior secondary education leading to the Hong Kong Certificate of Education Examinations and a two-year matriculation course leading to the Hong Kong Advanced Level Examinations. A new “3+3+4”curriculum, consisting of a three-year junior secondary, three-year senior secondary and four-year undergraduate academic system, will be implemented from 2009 (for senior secondary) and 2012 (for tertiary) onwards. There are also tertiary institutions offering various Bachelor's, Master's, and Doctoral degrees, other higher diplomas, and associate degree courses.
Most comprehensive schools in Hong Kong fall under three categories: public schools, subsidized schools and private schools. Public schools are rare, and subsidized schools are the most common, run by charitable organizations, often with religious affiliations, and and partially financed by government aid and grants. The majority of such religious affiliations are Christian and Catholic, but there are also Buddhist, Daoist (Taoist), Islamic and Confucian schools. Private schools, often run by Christian organizations, base their admissions based on academic merit rather than on financial resources. Outside this system are the schools under the Direct Subsidy Scheme (DSS) and private international schools.
Culture
Hong Kong is frequently described as a place where East meets West, a meeting reflected in its economic infrastructure, architecture, education, and street culture. On one street corner, there may be traditional Chinese shops selling Chinese herbal medicine, Buddhist paraphernalia or bowls of synthetic shark fin soup. But around the next, one may find theaters showing the latest Hollywood blockbusters, an English-style pub, a Catholic Church or Ronald McDonald inviting passers-by to a Big Mac. The territory's official languages are Chinese and English; signs in both languages are omnipresent throughout Hong Kong. The government, police and most workplaces and stores conduct business bilingually. British rule may have ended a decade ago, but Western culture is deeply ingrained in Hong Kong and coexists seamlessly with traditional philosophy and practices of the Orient.
Hong Kong has an active nightlife in major entertainment districts such as Lan Kwai Fong, Tsim Sha Tsui, Wan Chai. These areas are frequented by visitors, expatriates and locals alike. On a clear day, Victoria Peak offers a spectacular view of the city. There is also a promenade along the Tsim Sha Tsui waterfront, which is popular among young Chinese couples. Shopping is often done at night, as evidenced by the Temple Street Night Market, where one can also catch free performances of Beijing opera (Peking opera).
The city's cosmopolitan flavor can also be seen in the wide variety of cuisines available. While different varieties of Chinese selections, especially seafood, are most popular, there are also many European, American, Japanese, Korean, and other restaurants. Ethnic dishes served in cha chaan teng (Chinese tea restaurants) and dai pai dong (open air stalls) are also popular. The people of Hong Kong take their food seriously and many top chefs make their way to the city to show off their talents to these discerning diners.
While Hong Kong is a global centre of trade, perhaps the city's most famous export is its entertainment industry, particularly in the martial arts genre. Several Hollywood performers originate from Hong Kong cinema—Bruce Lee, Chow Yun-Fat, Jackie Chan, Michelle Yeoh, and Jet Li, to name a few. Behind the camera, Hong Kong filmmakers have also found recognition in Hollywood, such as John Woo, Wong Kar-wai, Tsui Hark and martial arts choreographers who have designed fight scenes in the Matrix trilogy, Kill Bill and Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon. Back in Hong Kong, several homegrown films have also gained international recognition, such as Chungking Express, Infernal Affairs, Shaolin Soccer, Rumble in the Bronx and In the Mood for Love. Acclaimed filmmaker Quentin Tarantino has commented he was strongly influenced by Hong Kong action cinema. Hong Kong is also the world's main hub for Cantopop music.[35] Karaoke culture is also part of Hong Kong's nightlife.
The Hong Kong government also supports cultural institutions such as the Hong Kong Heritage Museum, Hong Kong Museum of Art, the Hong Kong Academy for Performing Arts and the Hong Kong Philharmonic Orchestra. Furthermore, the government's Leisure and Cultural Services Department also subsidizes and sponsors the visits of international performers to Hong Kong.
Religion
Hong Kong enjoys a high degree of religious freedom, a right enshrined and protected in its constitutional document, the Basic Law. The majority of Hong Kong's population, as in Mainland China, practice a folk version of Buddhism. This majority includes approximately six million people, close to 90% of a total population of less than seven million. A sizable Christian community of around 500,000 exists, forming about 7% of the total population; it is roughly equally divided between Catholics and Protestants. There are also around 200,000 followers each of authentic Buddhism and Taoism. Apart from the major religions, there are also a significant number of followers of other religions, including an estimated 23,000 Mormons, 3,000 Jews and a number of Muslims, Hindus, Sikhs and Bahá'ís. Apart from offering religious instructions, many major religious bodies operate schools and provide social welfare facilities.
Hong Kong's religious beliefs are tied to the region's early role as a fishing community. The goddess Tin Hau, the protector of seafarers, has been honored with several temples throughout Hong Kong for at least 300 years. Hung Shing, another protector of seafarers, has also been honored for centuries. Hong Kong residents, especially the elder generations, visit Taoist or Buddhist temples to appease the deities and, usually, to request compassion, good health or good fortune. Gifts of food, and in particular fruit, are presented, and incense and paper offerings are burnt in respect.
With the transfer of Hong Kong to the Peoples Republic of China, there were significant concerns that restrictions would be placed on |religious freedom in Hong Kong. So far, this has proved mostly unfounded. Despite the banning of the Falun Gong movement by Beijing in 1999, adherents are still free to practice in Hong Kong. Similarly, the Catholic Church freely appoints its own bishops in Hong Kong, unlike in mainland China where the only approved 'Catholic' institution is the Chinese Patriotic Catholic Association with bishops and priests appointed by Beijing (though an unofficial and illegal Catholic church maintains contact with the Vatican). A significant issue in the normalization of ties between the PRC and the Vatican is Beijing's insistence that the Vatican drops its diplomatic ties with Taiwan. Hong Kong is the only place in China where missionaries from the Mormon Church can serve.
Architecture
Due to the creative destruction endemic to Hong Kong over the past fifty years, few historical buildings remain in Hong Kong. Instead the city has become a center for modern architecture, especially in and around the Central and Western District (Central). Dense commercial skyscrapers lining the coast of Victoria Harbour between Central and Causeway Bay form one of Hong Kong's most famous tourist attractions, which is ranked as the best skyline in the world. Four of the fifteen tallest skyscrapers in the world are in Hong Kong. In Kowloon, which once included the anarchistic settlement called the Kowloon Walled City, strict height restrictions on structures were in force until 1998 when the nearby Kai Tak Airport was closed. With restrictions lifted, several new skyscrapers are under construction in Kowloon, including International Commerce Centre which, when completed in 2010, will become the world's fourth tallest.
One of the notable buildings in Hong Kong is I. M. Pei's Bank of China Tower, completed in 1990 and now Hong Kong's third tallest skyscraper. The building attracted heated controversy, as its sharp angles were said to cast negative feng shui energy into the heart of Hong Kong. Predating the Bank of China Tower, another well-known structure is the HSBC Headquarters Building, finished in 1985. It was built on the site of Hong Kong's first skyscraper, which was finished in 1935 and was the subject of a bitter heritage conservation struggle in the late 1970s. Both banks' buildings are featured on many of Hong Kong's banknotes.
The tallest building in Hong Kong is the International Finance Centre 2. One of the largest construction projects in Hong Kong was the new Hong Kong International Airport on Chek Lap Kok near Lantau, a huge land reclamation project linked to the center of Hong Kong by the Lantau Link, which features three new major bridges: Tsing Ma, the world's sixth largest suspension bridge; Kap Shui Mun, the world's longest cable-stayed bridge carrying both road and railway traffic; and Ting Kau, the world's first major four-span cable-stayed bridge.
Particularly noticeable in Hong Kong's skyline and streetscapes is the omnipresence of public housing estates, which began as a squatter resettlement program in the 1950s, and now house close to 50% of the population. These estates have evolved from seven-story walk-up apartments with public toilets and minimal amenities, allocated on a basis of 24 square feet per adult, half of that for a child; to high-quality high-rises. The public rental program has been supplemented with a government-subsidized Home Ownership Scheme.
Transport
Hong Kong has a highly developed and sophisticated transport network, encompassing both public and private transport. The Octopus card stored value smart card payment system can be used to pay for fares on almost all railways, buses and ferries in Hong Kong. The Octopus card uses RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) to allow users to scan their card without taking it out of their wallet or bag. All parking meters in Hong Kong accept payment by Octopus card only, and Octopus card payment can be made at various car parks.
Hong Kong is dominated by steep, hilly terrain, and some unusual methods of transport have been devised to ease movement up and down the slopes. For example, the Peak Tram has provided vertical rail transport between Central and Victoria Peak since 1888 by steeply ascending the side of a mountain. In Central and Western district there is an extensive system of escalators and moving sidewalks, including the longest outdoor covered escalator system in the world, the Mid-levels Escalator.
Hong Kong has several different modes of public rail transport. The two metro systems for the city are the MTR (Mass Transit Railway) and KCR which acts as a link between Hong Kong and mainland China (KCR also operates a light rail system in northwest New Territories). These are operated by the MTR Corporation Limited and the Kowloon-Canton Railway Corporation respectively. The tramway system covers the northern parts of Hong Kong Island and is the only tram system in the world run exclusively with double deckers.
Five separate companies (KMB, Citybus, NWFB, Long Win & NLB) operate franchised public bus services in Hong Kong. Double-decker buses were introduced to Hong Kong in 1949 and are now used almost exclusively in Hong Kong, just as in Singapore, Dublin and the United Kingdom. However, single-decker buses remain in use for routes with lower demand or roads with lower carrying capacity. Such single-decker buses are mainly used on Lantau Island and for overnight services. Most normal franchised bus routes in Hong Kong operate until 1 am. Public light buses run the length and breadth of Hong Kong, through areas where standard bus lines cannot reach or do not reach as frequently, quickly, or directly. Taxis are also widely used throughout Hong Kong. Ninety-nine percent of taxis in Hong Kong run on liquefied petroleum gas; the rest are still diesel operated.
Most ferry services are provided by licensed ferry operators serving outlying islands, new towns, across Victoria Harbour, Macau and cities in mainland China. The oldest service, the legendary Star Ferry, operates four lines between Kowloon and Hong Kong Island and has provided cost-effective transport for over a century. It is popular with tourists desiring a panoramic view of Hong Kong's skyline and harbor, and many Hong Kong residents consider the Star Ferry as one of the city's most treasured cultural icons. Additionally, 78 "kai-to" ferries are licensed to serve remote coastal settlements.
Hong Kong has one active international airport, known as Hong Kong International Airport located at Chek Lap Kok. When it opened in 1998, this replaced the former Hong Kong International Airport, Kai Tak Airport located at Kowloon City, which was simultaneously closed. After highly-publicized delays in the cargo systems during the first few months, the airport now serves as a transport hub for Southeast Asia, and as the hub for Cathay Pacific Airways, Dragonair, Air Hong Kong, Oasis Hong Kong Airlines, Hong Kong Airlines and Hong Kong Express. Both Hong Kong International Airport and Cathay Pacific Airways have been voted best in the world, in the airport and airline criteria respectively, by Skytrax from 2001 to 2005. Hong Kong International Airport served more than 36 million passengers in the year 2004, and increased to over 40 million passengers in 2005.
Access to the airport includes 'Airport Express', 'CityFlyers' and 'Airbuses'. These services connect the airport to the rest of Hong Kong. The Airport Express zooms passengers to Central on Hong Kong Island in just 23 minutes. The recent opening of Sunny Bay Station of the MTR allows easy access to the Hong Kong Disneyland Resort.
While the traffic in mainland China drives on the right, Hong Kong maintains its own road rules, with traffic continuing to drive on the left. The Hong Kong highway code uses the same road sign system as Great Britain, whereas the Chinese system is different. There are about 517,000 registered vehicles in Hong Kong, 64% of which are privately owned passenger cars. As a metropolis for luxury in Asia, Hong Kong is world famous for having the most Rolls-Royce cars per capita in the world.[36]
Military
Because it has never been a sovereign state, Hong Kong has never had its own military forces except for voluntary auxiliary forces like The Royal Hong Kong Regiment (The Volunteers). All defense matters have been dependent on the state which controls Hong Kong. Before the British handover to PRC sovereignty, defense was provided by the British military, who stationed soldiers in barracks throughout Hong Kong, including the British Forces Overseas Hong Kong. These forces were supported financially by the Hong Kong Government.
The People's Republic of China Central People's Government (CPG) assumed sovereignty over Hong Kong on July 1, 1997, and stationed a garrison of the People's Liberation Army (PLA) there to manage its defense affairs. Although the garrison has little practical military value, the stationing of the PLA troops in Hong Kong is a significant symbol of the PRC government's assumption of sovereignty over Hong Kong.
According to Hong Kong's Basic Law, military forces stationed in Hong Kong shall not interfere with local civil affairs; the Hong Kong Government shall remain responsible for the maintenance of public order. The Hong Kong Garrison, composed of ground, naval, and air forces, is under the command of the Chinese Central Military Commission. The garrison subsequently opened its barracks on Stonecutters Island and Stanley to the public to promote understanding and trust between the troops and residents.
Under British rule, Chinese Hong Kong residents (and other Hong Kong residents) were able to join the British Forces Overseas Hong Kong.
International rankings
| Date | Contest | Host organisation | Ranking | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001–05 | World's Best Airports | Skytrax | 1/155 countries | |
| 2005 | Ranking of Container Ports of the World | AAPA World Port Rankings | 2/50 ports by container traffic | 7/50 ports by cargo volume |
| Networked Readiness Index (NRI) | World Economic Forum | 11/115 countries | ||
| Worldwide quality-of-life index | The Economist | 18/111 countries | ||
| 2006 | 6th Annual Global e-Government Study (Brown University) | Global e-Government | 20/198 countries | |
| Annual Worldwide Press Freedom Index 2006 | Reporters Without Borders | 59/168 countries | ||
| Corruption Perceptions Index | Transparency International | 15/163 countries | ||
| World Competitiveness Yearbook 2006 | IMD International | 2/61 economies | Economies include those of countries and regions | |
| World City's Skyline/Skyscrapers | Emporis Data Committee (EDC) | 1/100 major cities | Cities ranked by the visual impact of their skylines | |
| Global Competitiveness Report - Growth Competitiveness Index Ranking | World Economic Forum | 11/125 countries | ||
| World's Best Airports | Skytrax | 2/165 countries | ||
| Business Competitiveness Index - BCI | World Economic Forum | 10/121 countries | ||
| Human Development Index - HDI | United Nations | 22/177 countries | ||
| Access Index (p.19) | FedEx: The Power of Access - 2006 Access Index | 1/75 countries | ||
| Potential Competitiveness | Japan Center for Economic Research (JCER) | 1/50 countries | ||
| 2007 | Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index | World Economic Forum | 6/124 countries | |
| Index of Economic Freedom | Heritage Foundation/The Wall Street Journal: 2006 | 1/157 countries | Ranked 1st for 13 years in a row | |
| World's most expensive city for rental accommodation | ECA International | 1/92 countries | ||
| Leading Centers of Commerce | MasterCard study | 5/63 countries | rated 63 cities according to their legal and political framework, economic stability, ease of doing business, financial flow, business center status, and knowledge creation and information flow | |
| World's most expensive cost-of-living | Mercer Human Resource Consulting | 5/143 cities |
Notes
- ↑ Since the transfer of sovereignty in 1997, Hong Kong has used the national anthem of the People's Republic of China.
- ↑ Historically, the capital of Hong Kong territory was Victoria City; government headquarters are located in the Central and Western District (22°17′N 114°08′E).
- ↑ The Hong Kong Basic Law states that the official languages are "Chinese and English." It does not explicitly specify the standard for "Chinese". While Standard Mandarin and Simplified Chinese characters are used as the spoken and written standards in mainland China, Cantonese and Traditional Chinese characters are the long-established de facto standards in Hong Kong. See Bilingualism in Hong Kong
- ↑ The name is often written as Hongkong in older English texts. The Hong Kong Government officially adopted the current form on September 3, 1926 (Hongkong Government Gazette, Notification 479, 3 September 1926). While the names of most cities in the People's Republic of China are romanised into English using pinyin, the official English name is Hong Kong rather than Xiānggǎng (See Pronunciation of Hong Kong).
- ↑ Porter, Jonathan. [1996] (1996). Macau, the Imaginary City: Culture and Society, 1557 to the Present. Westview Press. ISBN 0813337496
- ↑ Edmonds. [2002] (2002) China and Europe Since 1978: A European Perspective. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521524032
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 Wiltshire, Trea. [First published 1987] (republished & reduced 2003). Old Hong Kong. Central, Hong Kong: Text Form Asia books Ltd. Page 12. ISBN Volume 962-7283-61-4
- ↑ New York Times. "NY Times." Thousands March in Anti-Japan Protest in Hong Kong by Keith Bradsher. Retrieved on 2006-04-11.
- ↑ Wang Yong-hua, On Embargo of Hong Kong in 1950-1954, Journal of Yanan University Social Science Edition, 2006.
- ↑ People's Daily. "People's Daily." Links between SARS human genes. Retrieved on 2007-03-06.
- ↑ Visit Hong Kong: Volume 1, Spring, 2004 (p.14), University of Hong Kong English Centre. Retrieved on 2007-02-24
- ↑ "Chief Executive pledges a clean, green, world-class city", Hong Kong Trader, November 2001. Retrieved on 2006-05-27.
- ↑ Geography and Climate, Hong Kong (in English). Census and Statistics Department, The Government of Hong Kong SAR. Retrieved 2007-01-10.
- ↑ "Hong Kong Hiking Tours", The Hong Kong Tourism Board's Hiking page. Retrieved on 2006-06-18.
- ↑ New York Times. "NYtimes." Dirty Air Becomes Divisive Issue in Hong Kong Vote. Retrieved on 2006-11-05.
- ↑ "Extreme Values and Dates of Occurrence of Extremes of Meteorological Elements between 1884–1939 and 1947–2006 for Hong Kong", Hong Kong Observatory. Retrieved on 2006-02-02.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Monthly Meteorological Normals for Hong Kong", Hong Kong Observatory. Retrieved on 2006-02-02.
- ↑ "Donald Tsang set to be HK leader", BBC News, 2005-06-15. Retrieved 2006-05-14.
- ↑ Hong Kong Public Order Ordinance, World Corporal Punishment Research, February 2000. Retrieved 14 May 2006.
- ↑ "Hong Kong democrats visit China", ABC News Online, September 25, 2005. Retrieved May 27, 2006.
- ↑ Department of Justice. Department of Justice of HKSAR. Retrieved 2007-03-17.
- ↑ 2007 Index of Economic Freedom. Heritage Foundation.
- ↑ Summary Economic Freedom Rating 2004 (Economic Freedom of the World - Annual report 2006 on page 13 or 9 of 23) (in English). The Fraser Institute, Canada. Retrieved 2007-01-08.
- ↑ Economic Freedom of the World: 2006 Annual Report (PDF). The Fraser Institute (2006). Retrieved 2007-06-06.
- ↑ About Hong Kong. Hong Kong SAR Government Information Centre (April 2006). Retrieved 2007-04-12.
- ↑ Hong Kong surpasses New York in IPOs. International Herald Tribune (2006-12-25). Retrieved 2007-04-12.
- ↑ The Global Financial Centres Index 1 Executive Summary (PDF). City of London (March 2007). Retrieved 2007-04-12.
- ↑ Wallace, Peter. [2002] (2002). Contemporary China: The Dynamics of Change at the Start of the New Millennium. Routledge. ISBN 0700716378
- ↑ 2005–06 Budget Speech by the Financial Secretary of Hong Kong, 2005-03-16.
- ↑ "List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita", Wikipedia. Retrieved on 2007-05-02.
- ↑ "Hong Kong Statistics - Population and Vital Events", Census and Statistics Department. Retrieved 2007-02-02
- ↑ UCL.AC.UK. "UCL.AC." ICE Hong Kong. Retrieved on 2007-06-05.
- ↑ "Hong Kong Total fertility rate", Index Mundi. Retrieved 2006-05-27
- ↑ Education for Non-Chinese Speaking Children, Education and Manpower Bureau, Government of HKSAR.
- ↑ China Briefing Media. [2004] (2004) Business Guide to the Greater Pearl River Delta. China Briefing Media Ltd. ISBN 9889867311
- ↑ World-famous producer of luxury cars launches first Hong Kong showroom, InvestHK, 2003-7-30. Retrieved 2007-1-20.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
| This article contains Chinese text. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols instead of Chinese characters. |
- A History of Hong Kong (Third Edition). Frank Welsh. HarperCollins. 1 October 1998. 624 pages. ISBN 1-56836-002-9.
- Mathematical Modelling of Hong Kong Political and Economical Development. Derek Lam. Guangzhou Academic Press. 18 February 1986. 23 pages.
- Hong Kong's History: State and Society Under Colonial Rule (Asia's Transformations). Tak-Wing Ngo. Routledge. 1 August 1999. 205 pages. ISBN 0-415-20868-8.
- The Cinema of Hong Kong: History, Arts, Identity. Poshek Fu, David Deser. Cambridge University Press. 25 March 2002. 346 pages. ISBN 0-521-77602-3.
- A Modern History of Hong Kong. Steve Tsang. I.B. Tauris. 14 May 2004. 356 pages. ISBN 1-86064-184-9.
- An Outline History of Hong Kong. Liu Shuyong. 291 pages. ISBN 7-119-01946-5.
- Forts and Pirates - A History of Hong Kong. Hong Kong History Society. Hyperion Books. December 1990. ISBN 962-7489-01-8.
- List of Graded Historical Buildings in Hong Kong - 6 Jan 2007 from the Antiquities and Monuments Office
- List of Declared Monuments in Hong Kong - 3 March 2006 from the Antiquities and Monuments Office
See also
Template:Hong Kong Topics
External links
- GovHK - one-stop portal of the Hong Kong SAR Government
- Hong Kong Tourism Board
- Travel guide to Hong Kong from Wikitravel
- WikiSatellite view of Hong Kong at WikiMapia
- CIA - The World Factbook — Hong Kong
- Flickr - photos tagged with Hong Kong
- Census and Statistics Department in Hong Kong
| Geographic locale | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Countries and territories of East Asia
Sometimes included: Singapore · Vietnam · Russian Far East 1 Otherwise known as "Taiwan."
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Language | ||||||||||||
|
Sino-Tibetan-speaking nations and regions
Names in italics indicate non-sovereign territories.
| ||||||||||||
Albania · Angola · Antigua and Barbuda · Argentina · Armenia · Australia · Austria · Bahrain · Bangladesh · Barbados · Belize · Benin · Bolivia · Botswana · Brazil · Brunei (Brunei Darussalam) · Burkina Faso · Burundi · Cambodia · Cameroon · Canada · Central African Republic · Chad · Chile · China (PRC) · Colombia · Democratic Republic of the Congo · Republic of the Congo · Costa Rica · Cote d'Ivoire · Croatia · Cuba · Djibouti · Dominica · Dominican Republic · Ecuador · Egypt · El Salvador · European Union¹ · Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia (FYROM) · Fiji · Gabon · The Gambia · Georgia · Ghana · Grenada · Guatemala · Guinea · Guinea-Bissau · Guyana · Haiti · Honduras · Hong Kong² · Iceland · India · Indonesia · Israel · Jamaica · Japan · Jordan · Kenya · South Korea · Kuwait · Kyrgyzstan · Lesotho · Liechtenstein · Macau² · Madagascar · Malawi · Malaysia · Maldives · Mali · Mauritania · Mauritius · Mexico · Moldova · Mongolia · Morocco · Mozambique · Myanmar · Namibia · Nepal · New Zealand · Nicaragua · Niger · Nigeria · Norway · Oman · Pakistan · Panama · Papua New Guinea · Paraguay · Peru · Philippines · Qatar · Rwanda · St. Kitts and Nevis · St. Lucia · St. Vincent and the Grenadines · Saudi Arabia · Senegal · Sierra Leone · Singapore · Solomon Islands · South Africa · Sri Lanka · Suriname · Swaziland · Switzerland · Separate Customs Territory of Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen, and Matsu · Tanzania · Thailand · Togo · Trinidad and Tobago · Tunisia · Turkey · Uganda · United Arab Emirates · United States · Uruguay · Venezuela · Vietnam · Zambia · Zimbabwe
- All twenty-seven member states of the European Union are also members of the WTO in their own right: Austria • Belgium • Bulgaria • Cyprus • Czech Republic • Denmark • Estonia • Finland • France • Germany • Greece • Hungary • Ireland • Italy • Latvia • Lithuania • Luxembourg • Malta • Netherlands and Netherlands Antilles • Poland • Portugal • Romania • Slovakia • Slovenia • Spain • Sweden • United Kingdom.
- Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.