|
|
| (132 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | {{Long}} | + | {{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}}{{Copyedited}} |
| − | {{Otheruses1|the U.S. state}} | + | {{Infobox U.S. state |
| − | {{US state|
| + | | Name = Kentucky |
| − | Name = Kentucky |
| + | | Fullname = Commonwealth of Kentucky |
| − | Fullname = Commonwealth of Kentucky|
| + | | Flag = Flag of Kentucky.svg |
| − | Flag = Flag of Kentucky.svg |
| + | | Flaglink = [[Flag of Kentucky|Flag]] |
| − | Flaglink = [[Flag of Kentucky]] |
| + | | Seal =Kentucky State Seal.svg |
| − | Seal = Kentucky State Seal.svg |
| + | | Map = Map of USA KY.svg |
| − | Map = Map of USA KY.svg |
| + | | Nickname = Bluegrass State |
| − | Nickname = Bluegrass State |
| + | | Former = Kentucky County, Virginia |
| − | Demonym = Kentuckian |
| + | | Demonym = Kentuckian |
| − | Motto = [[United we stand, divided we fall]] |
| + | | Motto = [[United we stand, divided we fall]] |
| − | Brand = Unbridled Spirit |
| + | | Brand = Unbridled Spirit |
| − | Capital = [[Frankfort, Kentucky|Frankfort]] |
| + | | Capital = [[Frankfort, Kentucky|Frankfort]] |
| − | OfficialLang = [[English language|English]]<ref name=kysym>{{cite web | title=Kentucky State Symbols | publisher=Kentucky Department for Libraries and Archives | url=http://kdla.ky.gov/resources/KYSymbols.htm | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> |
| + | | OfficialLang = English |
| − | LargestCity = [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]] |
| + | | LargestCity = [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]] |
| − | LargestMetro = [[Louisville metropolitan area|Louisville]]|
| + | | LargestMetro = [[Louisville metropolitan area]] <!-- The majority of the Cincinnati/NKY population lies in Ohio. —> |
| − | Governor = [[Steve Beshear]] (D)|
| + | | Governor = [[Steve Beshear]] (D) |
| − | Lieutenant Governor = [[Daniel Mongiardo]] (D) |
| + | | Lieutenant Governor = [[Jerry Abramson]] (D) |
| − | Senators = [[Mitch McConnell]] (R)<br/>[[Jim Bunning]] (R) |
| + | | Legislature = [[Kentucky General Assembly|General Assembly]] |
| − | PostalAbbreviation = KY |
| + | | Upperhouse = [[Kentucky Senate|Senate]] |
| − | AreaRank = 37<sup>th</sup> |
| + | | Lowerhouse = [[Kentucky House of Representatives|House of Representatives]] |
| − | TotalAreaUS =40,434 |
| + | | Senators = [[Mitch McConnell]] (R)<br />[[Rand Paul]] (R) |
| − | TotalArea = 104,749 |
| + | | Representative=4 Republicans, 2 Democrats |
| − | LandAreaUS = 39,764 |
| + | | PostalAbbreviation = KY |
| − | LandArea = 102,989 |
| + | | AreaRank = 37th |
| − | WaterAreaUS =680 |
| + | | TotalAreaUS =40,409 |
| − | WaterArea = 1,760 |
| + | | TotalArea = 104,659 |
| − | PCWater = 1.7 |
| + | | LandAreaUS = 39,729 |
| − | PopRank = 26<sup>th</sup> |
| + | | LandArea = 102,895 |
| − | 2000Pop (old) = 4,041,769 |
| + | | WaterAreaUS = 681 |
| − | 2000Pop = 4,241,474 (2007 est.) <ref>http://www.census.gov/popest/states/NST-ann-est.html 2007 Population Estimates</ref> |
| + | | WaterArea = 1,764 |
| − | DensityRank = 22<sup>nd</sup> |
| + | | PCWater = 1.7 |
| − | 2000DensityUS = 101.7 |
| + | | PopRank = 26th |
| − | 2000Density = 39.28 |
| + | | 2010Pop = 4,454,189 (2017 est.)<ref name=PopHousingEst>{{cite web|url=https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/popest.html|title=Population and Housing Unit Estimates |date=December 20, 2017 |accessdate=December 20, 2017|publisher=[[U.S. Census Bureau]]}}</ref> |
| − | AdmittanceOrder = 15<sup>th</sup> |
| + | | DensityRank = 22nd |
| − | AdmittanceDate = [[June 1]], [[1792]] |
| + | | 2010DensityUS = 110 |
| − | TimeZone = [[Eastern Standard Time Zone|Eastern]]: [[Coordinated Universal Time|UTC]]-5/[[Daylight saving time|DST]]-4 |
| + | | 2010Density = 42.5 |
| − | TZ1Where = eastern half |
| + | | AdmittanceOrder = 15th |
| − | TimeZone2 = [[Central Standard Time Zone|Central]]: UTC-6/[[Daylight saving time|DST]]-5 |
| + | | AdmittanceDate = June 1, 1792 |
| − | TZ2Where = western half |
| + | | TimeZone = [[Eastern Standard Time Zone|Eastern]]: [[Coordinated Universal Time|UTC]]-5/[[Daylight saving time|DST]]-4 |
| − | Latitude = 36° 30′ N to 39° 09′ N |
| + | | TZ1Where = eastern half |
| − | Longitude = 81° 58′ W to 89° 34′ W |
| + | | TimeZone2 = [[Central Standard Time Zone|Central]]: UTC-6/[[Daylight saving time|DST]]-5 |
| − | WidthUS = 140|
| + | | TZ2Where = western half |
| − | Width = 225 |
| + | | Latitude = 36° 30′ N to 39° 09′ N |
| − | LengthUS = 379 |
| + | | Longitude = 81° 58′ W to 89° 34′ W |
| − | Length = 610 |
| + | | WidthUS = 140 |
| − | HighestPoint = [[Black Mountain (Kentucky)|Black Mountain]]<ref name="usgs">{{cite web | title=Science In Your Backyard: Kentucky | publisher=United States Geological Survey | url=http://www.usgs.gov/state/state.asp?State=KY) | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> |
| + | | Width = 225 |
| − | HighestElevUS = 4,145|
| + | | LengthUS = 379 |
| − | HighestElev = 1,263 |
| + | | Length = 610 |
| − | MeanElevUS =755 |
| + | | HighestPoint = [[Black Mountain (Kentucky)|Black Mountain]]<ref name=USGS>{{cite web|url=http://egsc.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/booklets/elvadist/elvadist.html|title=Elevations and Distances in the United States|publisher=[[United States Geological Survey]]|date=2001|accessdate=October 21, 2011}}</ref><ref name=NAVD88>Elevation adjusted to [[North American Vertical Datum of 1988]].</ref> |
| − | MeanElev = 230 |
| + | | HighestElevUS = 4,145 |
| − | LowestPoint = [[Mississippi River]]<ref name="usgs" /> |
| + | | HighestElev = 1263 |
| − | LowestElevUS = 257 |
| + | | MeanElevUS = 750 |
| − | LowestElev = 78 |
| + | | MeanElev = 230 |
| − | ISOCode = US-KY |
| + | | LowestPoint = [[Mississippi River]] at {{nobreak|[[Kentucky Bend]]}}<ref name=USGS/><ref name=NAVD88/> |
| − | Website = Kentucky.gov
| + | | LowestElevUS = 257 |
| | + | | LowestElev = 78 |
| | + | | ISOCode = US-KY |
| | + | | Website = Kentucky.gov |
| | }} | | }} |
| − | The '''Commonwealth of Kentucky''' ({{IPAEng|kənˈtʌki}}) is a [[U.S. state|state]] located in the East Central [[United States of America]]. Kentucky is normally included in the group of [[Southern United States|Southern states]] (in particular the [[Upland South]]), but it is sometimes included, geographically and culturally, in the [[Midwestern United States|Midwest]].<ref>{{cite book |title=''The North American Midwest: A Regional Geography''|publisher=Wiley Publishers |location=[[New York, New York]] |year=1955 |isbn=0901411931}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Meyer |first=David R. |year=1989 |month=December |title=Midwestern Industrialization and the American Manufacturing Belt in the Nineteenth Century |journal=The Journal of Economic History |volume=49 |issue=4 |pages=921–937 |id= |url= |accessdate= }}</ref> Kentucky is one of four U.S. states to be officially known as a [[Commonwealth (United States)|commonwealth]]. Originally a part of [[Virginia]], in 1792 it became the 15<sup>th</sup> state to join the Union. Kentucky is the 37<sup>th</sup> largest state in terms of land area, and ranks 26<sup>th</sup> in population.
| |
| | | | |
| − | Kentucky is known as the "Bluegrass State", a nickname based on the fact that [[Poa|bluegrass]] is present in many of the lawns and pastures throughout the state. It is a land with diverse environments and abundant resources, including the world's longest cave system, the greatest length of navigable waterways and streams in the [[Lower 48]] states, and the two largest man-made lakes east of the Mississippi River. It is also home to the highest per capita number of [[White-tailed Deer|deer]] and [[Wild Turkey|turkey]] in the United States, and the nation's most productive [[coalfield]]. Kentucky is also known for [[thoroughbreds|thoroughbred horses]], [[horse racing]], [[bourbon whiskey|bourbon]] distilleries, [[bluegrass music]], [[automobile]] manufacturing, [[tobacco]], and [[college basketball]]. | + | The '''Commonwealth of Kentucky''' is a state located in the East Central [[United States of America]]. Kentucky is normally included in the group of [[Southern United States|Southern states]], but it is sometimes included, geographically and culturally, in the [[Midwestern United States|Midwest]]. Kentucky is one of four U.S. states to be officially known as a [[commonwealth]]. Originally a part of [[Virginia]], in 1792 it became the fifteenth state to join the Union. Kentucky is the 37<sup>th</sup> largest state in terms of land area, and ranks 26<sup>th</sup> in population. |
| | + | |
| | + | It is a land with diverse environments and abundant [[natural resource|resources]], including [[Mammoth Cave National Park|Mammoth Cave]], the world's longest [[cave]] system; the [[Red River Gorge]] Geological Area with more than 100 natural stone arches. The gorge is the greatest concentration of arches east of the [[Rocky Mountains]]. Kentucky also has the greatest length of [[navigation|navigable]] waterways and streams in the continental 48 states. Kentucky features the two largest man-made lakes east of the [[Mississippi River]] and the nation's most productive [[coal]]field. |
| | + | |
| | + | Both [[Abraham Lincoln]] and [[Jefferson Davis]] were born in [[log cabin]]s on the Kentucky frontier, one year and a few miles apart. They were the presidents of the [[Union (American Civil War)|Union]] and the [[Confederate States of America|Confederacy]] respectively during the [[American Civil War]]. While Kentucky remained officially neutral in that conflict, many Kentuckians enlisted on both sides. |
| | + | {{toc}} |
| | + | Kentucky is known as the "Bluegrass State," a nickname based on the fact that [[Poa|bluegrass]] is present in many of the lawns and pastures throughout the state. It is also is known for thoroughbred [[horse]]s, [[Horse Racing|horse racing]], [[bourbon whiskey|bourbon]] distilleries, [[bluegrass music]], [[automobile]] [[manufacturing]], [[gambling]], and [[tobacco]]. Though bourbon may be produced anywhere in the [[United States]] where it is legal to distill spirits, it is estimated that 95 percent of the world's bourbon is distilled and aged in Kentucky. |
| | | | |
| | ==Origin of name== | | ==Origin of name== |
| − | [[Image:Picture 1280.jpg|thumb|right|Narrow country roads bounded by stone and wood plank fences are a fixture in the Kentucky [[Bluegrass region|Bluegrass]].]] | + | [[Image:KYphysiography.jpg|thumb|left|Kentucky's regions]] |
| − | The origin of Kentucky's name (variously spelled ''Cane-tuck-ee'', ''Cantucky'', ''Kain-tuck-ee'', and ''Kentuckee'' before its modern spelling was accepted)<ref name="enken">{{cite book |title=''Encyclopedia of Kentucky'' |chapter=State Symbols |publisher=Somerset Publishers |location=[[New York, New York]] |year=1987 |isbn=0403099811}}</ref> has never been definitively identified, though some theories have been debunked. For example, Kentucky's name does not come from the combination of "cane" and "turkey"; and though it is the most popular belief, it is unlikely to mean "dark and bloody ground", because it does not occur with that meaning in any known [[Indigenous languages of the Americas|Native American language]].<ref name="kenten">{{cite book |editor=John E. Kleber (ed.) |title=The Kentucky Encyclopedia |year=1992 |publisher=University Press of Kentucky |location=[[Lexington, Kentucky]] |chapter=Place Names |isbn 0813117720 }}</ref> The most likely etymology is that it comes from an [[Iroquoian language|Iroquoian]] word for "meadow" or "prairie"<ref name="enken" /><ref>{{cite web |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554924/Kentucky.html |title=Kentucky |accessdate=2007-02-25 |work=Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2006}}</ref> (c.f. [[Mohawk language|Mohawk]] ''kenhtà:ke'', [[Seneca language|Seneca]] ''këhta’keh'').<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.krysstal.com/feedback/display_feedback.php?ftype=Borrow&fblock=4 |title=Comments by Michael McCafferty on "Readers' Feedback (page 4)" |accessdate=2007-02-23 |publisher=The KryssTal}}</ref> Other possibilities also exist: the suggestion of early Kentucky pioneer [[George Rogers Clark]] that the name means "the river of blood",<ref name="enken" /> a [[Wyandot language|Wyandot]] name meaning "land of tomorrow", a [[Shawnee language|Shawnee]] term possibly referring to the head of a river,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=Kentucky |title=Kentucky |accessdate = 2007-03-06 |publisher=[[Online Etymology Dictionary]]}}</ref> or an [[Algonquian language|Algonquian]] word for a river bottom.<ref name="kenten" /> | + | The origin of Kentucky's name (variously spelled ''Cane-tuck-ee,'' ''Cantucky,'' ''Kain-tuck-ee,'' and ''Kentuckee'' before its modern spelling was accepted) has never been definitively identified, though some theories have been debunked. For example, Kentucky's name does not come from the combination of "cane" and "turkey"; and though it is the most popular belief, it is unlikely to mean "dark and bloody ground," because it does not occur with that meaning in any known [[Native American]] language. The most likely etymology is that it comes from an [[Iroquois|Iroquoian]] word for "meadow" or "prairie" Other possibilities also exist: the suggestion of early Kentucky pioneer [[George Rogers Clark]] that the name means "the river of blood," a [[Wyandot]] name meaning "land of tomorrow," a [[Shawnee]] term possibly referring to the head of a river,<ref>''Online Etymology Dictionary''. [http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=Kentucky Kentucky] Retrieved September 25, 2008.</ref> or an [[Algonquian]] word for a [[river]] bottom. |
| | | | |
| | ==Geography== | | ==Geography== |
| − | {{seealso|List of Kentucky counties}}
| + | [[Image:Picture 1280.jpg|thumb|right|Narrow country roads bounded by stone and wood plank fences are a fixture in the Kentucky Bluegrass region.]] |
| − | [[Image:Map of Kentucky NA.png|thumb|right|Kentucky]] | + | [[Image:Kentucky Spring.jpg|thumb|A typical view of rolling hills and horse farms in the Kentucky Bluegrass.]] |
| − | [[Image:KYphysiography.jpg|thumb|right|Kentucky's regions (click on image for color coding information.)]] | + | [[Image:Picture 491.jpg|thumb|right|Lake Cumberland is the largest artificial lake, in terms of volume, east of the [[Mississippi River]].]] |
| − | | |
| − | Kentucky borders states of both the [[Midwestern United States|Midwest]] and the [[Southeastern United States|Southeast]]. [[West Virginia]] lies to the east, [[Virginia]] to the southeast, [[Tennessee]] to the south, [[Missouri]] to the west, [[Illinois]] and [[Indiana]] to the northwest, and [[Ohio]] to the north and northeast. Kentucky's northern border is formed by the [[Ohio River]] and its western border by the [[Mississippi River]]; however, the official border is based on the courses of the rivers as they existed when Kentucky became a state in 1792. In several places, the border does not follow the current course of the appropriate river. Northbound travelers on [[U.S. Route 41|US 41]] from Henderson, upon crossing the Ohio River, will find themselves still in Kentucky until they travel about a half-mile (800 m) farther north. A horse racing track, [[Ellis Park Racecourse|Ellis Park]], is located in this small piece of Kentucky. Waterworks Road is part of the only land border between Indiana and Kentucky. [http://www.mapquest.com/maps/map.adp?formtype=address&addtohistory=&address=%5b1494%2d1557%5d%20Waterworks%20Rd&city=Evansville&state=IN&zipcode=47713&country=US&location=sx5PfJLyNGOdfPC4XlmsmD4sYz8%2fcM%2f9UzxNAshApmBL3N63w0vZEKUJ7ZFErueQQVVT7jNm9im%2frMyLwvsq1tX3B0QnxqQNsp3LVvDC22VDK3WLmnQ83dOStm4oo36rfS7%2fgXA9L8%2b8CqYgeWZpmK5YKDtojM0V&ambiguity=1]
| |
| | | | |
| − | Kentucky is the only U.S. state to have a non-contiguous part exist as an [[exclave]] surrounded by other states. [[Fulton County, Kentucky|Fulton County]], in the far west corner of the state, includes a small part of land, [[Kentucky Bend]], on the Mississippi River bordered by Missouri and accessible via Tennessee, created by the [[New Madrid Earthquake]].<ref>{{cite web | title=Life on the Mississippi | publisher=[[Kentucky Educational Television]]| date=[[2002-01-28]] | url=http://www.ket.org/kentuckylife/800s/kylife804.html | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> | + | Kentucky borders states of both the [[Midwestern United States|Midwest]] and the [[Southeastern United States|Southeast]]. [[West Virginia]] lies to the east, [[Virginia]] to the southeast, [[Tennessee]] to the south, [[Missouri]] to the west, [[Illinois]] and [[Indiana]] to the northwest, and [[Ohio]] to the north and northeast. Kentucky's northern border is formed by the [[Ohio River]] and its western border by the [[Mississippi River]]; however, the official border is based on the courses of the rivers as they existed when Kentucky became a state in 1792. In several places, the border does not follow the current course of the appropriate river. Northbound travelers on US Highway 41 from Henderson, upon crossing the Ohio River, will find themselves still in Kentucky until they travel about a half-mile farther north. |
| | + | <ref>''Mapquest''. [http://www.mapquest.com/maps/map.adp?formtype=address&addtohistory=&address=%5b1494%2d1557%5d%20Waterworks%20Rd&city=Evansville&state=IN&zipcode=47713&country=US&location=sx5PfJLyNGOdfPC4XlmsmD4sYz8%2fcM%2f9UzxNAshApmBL3N63w0vZEKUJ7ZFErueQQVVT7jNm9im%2frMyLwvsq1tX3B0QnxqQNsp3LVvDC22VDK3WLmnQ83dOStm4oo36rfS7%2fgXA9L8%2b8CqYgeWZpmK5YKDtojM0V&ambiguity=1 Map of Ohio River in Evansville, IN] Retrieved September 25, 2008. </ref> |
| | | | |
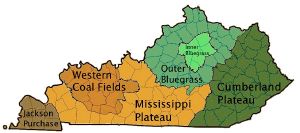
| − | Kentucky can be divided into five primary regions: the [[Cumberland Plateau]] in the east, the north-central [[Bluegrass region]], the south-central and western [[Pennyroyal Plateau]], the [[Western Coal Fields]] and the far-west [[Jackson Purchase]]. The Bluegrass region is commonly divided into two regions, the Inner Bluegrass — the encircling 90 miles (145 km) around [[Lexington, Kentucky|Lexington]] — and the Outer Bluegrass, the region that contains most of the Northern portion of the state, above the [[Knobs region|Knobs]]. Much of the outer Bluegrass is in the [[Eden Shale Hills]] area, made up of short, steep, and very narrow hills. | + | Kentucky can be divided into five primary regions: the [[Cumberland Plateau]] in the east, the north-central [[Bluegrass region]], the south-central and western [[Pennyroyal Plateau]], the [[Western Coal Fields]] and the far-west [[Jackson Purchase]]. |
| − | | |
| − | Kentucky has 120 counties, third in the U.S. behind [[Texas]]' 254 and [[Georgia (U.S. state)|Georgia]]'s 159.<ref>{{cite web | title=How Many Counties are in Your State? | publisher=Click and Learn | url=http://www.clickandlearn.com/documents2/Counties.htm | accessdate=2006-11-29 }} [[Virginia]] also has more county-level subdivisions than Kentucky; it has only 95 counties, but also has 39 [[independent city|independent cities]], for a total of 134 county-level subdivisions.</ref> The original motivation for having so many counties was to ensure that residents in the days of poor roads and horseback travel could make a round trip from their home to the county seat and back in a single day.<ref name=kye-counties>{{cite book |editor=Kleber, John E. |others=Associate editors: [[Thomas D. Clark]], Lowell H. Harrison, and James C. Klotter |title=''The Kentucky Encyclopedia'' |year=1992 |publisher=The University Press of Kentucky |location=Lexington, Kentucky |isbn=0813117720 |chapter=Counties}}</ref> Later, however, politics began to play a part, with citizens who disagreed with the present county government simply petitioning the state to create a new county. The 1891 [[Kentucky Constitution]] placed stricter limits on county creation, stipulating that a new county:
| |
| − | | |
| − | *must have a land area of at least {{convert|400|sqmi|km2|-2}};
| |
| − | *must have a population of at least 12,000 people;
| |
| − | *must not by its creation reduce the land area of an existing county to less than {{convert|400|sqmi|km2|-2}};
| |
| − | *must not by its creation reduce the population of an existing county to fewer than 12,000 people;
| |
| − | *must not create a county boundary line that passes within {{convert|10|mi|km|-1}} of an existing county seat.
| |
| − | | |
| − | These regulations have reined in the proliferation of counties in Kentucky. Since the 1891 Constitution, only [[McCreary County, Kentucky|McCreary County]] has been created.<ref name=countgov>{{cite book |title=''County Government in Kentucky: Informational Bulletin No. 115'' |publisher=Kentucky Legislative Research Commission |location=[[Frankfort, Kentucky]] |year=1996 |chapter=Fiscal Court}}</ref> Because today's largest county by area, [[Pike County, Kentucky|Pike County]], is {{convert|788|sqmi|km2|0}}, it is now impossible to create a new county from a single existing county under the current constitution. Any county created in this manner will by necessity either be smaller than {{convert|400|sqmi|km2|-2}} or reduce the land area of the old county to less than {{convert|400|sqmi|km2|-2}}. It is still theoretically possible to form a new county from portions of more than one existing county (McCreary County was created from portions of three counties), but the area and boundary restrictions would make this extremely difficult.
| |
| | | | |
| | ===Climate=== | | ===Climate=== |
| | + | Located within the southeastern interior portion of [[North America]], Kentucky has a climate that can best be described as humid subtropical. Monthly average [[temperature]]s in Kentucky range from a summer daytime high of 87°F (30.9°C) to a winter low of 23°F (-4.9°C). The average precipitation is 46 inches (116.84 cm) a year. <ref> ''NetState.com.'' [http://www.netstate.com/states/geography/ky_geography.htm The Geography of Kentucky - Climate] Retrieved September 26, 2008. </ref> Kentucky experiences all four seasons, usually with striking variations in the severity of [[summer]] and [[winter]] from year to year. |
| | | | |
| − | [[Image:Kentucky Spring.jpg|thumb|A stereotypical view of rolling hills and horse farms; photo taken in the Kentucky Bluegrass.]]
| + | ===Lakes and rivers=== |
| | | | |
| − | Located within the southeastern interior portion of North America, Kentucky has a climate that can best be described as a [[humid subtropical climate]] (Koppen ''Cfa''), or that all monthly average high temperatures are above freezing. Monthly average temperatures in Kentucky range from a summer daytime high of 87 °F (30.9 °C) to a winter low of 23 °F (-4.9 °C). The average precipitation is 46 inches (116.84 cm) a year.<ref>{{cite web | title=The Geography of Kentucky - Climate |date=[[2006-06-15]] |publisher=NetState.com | url=http://www.netstate.com/states/geography/ky_geography.htm | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> Kentucky experiences all four seasons, usually with striking variations in the severity of summer and winter from year to year.<ref>{{cite book |title=''Encyclopedia of Kentucky'' |chapter=Geographical Configuration |publisher=Somerset Publishers |location=[[New York, New York]] |year=1987 |isbn=0403099811}}</ref>
| + | Kentucky’s 90,000 miles of streams provide one of the most expansive and complex stream systems in the nation. Kentucky has both the largest [[artificial lake]] east of the Mississippi in water volume ([[Lake Cumberland]]) and surface area ([[Kentucky Lake]]). It is the only U.S. state to be bordered on three sides by rivers—the [[Mississippi River]] to the west, the [[Ohio River]] to the north, and the Big Sandy River and Tug Fork to the east. <ref name=kye-rivers> Kleber. 1992. </ref> Its major internal rivers include the [[Kentucky River]], [[Tennessee River]], [[Cumberland River]], [[Green River (Kentucky)|Green River]], and [[Licking River (Kentucky)|Licking River]]. |
| | | | |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| + | Though it has only three major natural [[lake]]s, the state is home to many artificial lakes. Kentucky also has more navigable miles of water than any other state in the union, other than [[Alaska]]. <ref> ''Corbin, Kentucky Economic Development''. [http://www.corbinkentucky.us/fishing.htm A Fisherman's Paradise] Retrieved September 26, 2008.</ref> |
| − | ! Event
| |
| − | ! Death Toll
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Mid-Mississippi Valley Tornado Outbreak of March 1890|Louisville Tornado of 1890]] || est. 76–120+
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Super Outbreak|April 3, 1974 Tornado Outbreak]] || 72
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[April 7]], [[1977]] Flooding (Cumberland River toppled Pineville floodwall) || ?
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[March 1]], [[1997]] Flooding || 18
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[2008 Super Tuesday tornado outbreak]] || 7
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | | |
| − | Major weather events that have affected Kentucky include:
| |
| − | *The [[Mid-Mississippi Valley Tornado Outbreak of March 1890]]
| |
| − | *The [[Ohio River flood of 1937]]
| |
| − | *The [[Super Outbreak]] of [[tornado]]es in 1974
| |
| − | *[http://www.enquirer.com/flood/floodphotos.html Massive flooding in 1997]
| |
| − | *The [[North American blizzard of 2003]] (mostly ice in Kentucky)
| |
| − | | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" "text-align:center;font-size:90%;"|
| |
| − | | colspan="13" style="text-align:center;font-size:120%;background:#E8EAFA;"|Monthly Normal High and Low Temperatures For Various Kentucky Cities
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color: #000000" height="17" | City
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color:#000000;" | Jan
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color:#000000;" | Feb
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color:#000000;" | Mar
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color:#000000;" | Apr
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color:#000000;" | May
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color:#000000;" | Jun
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color:#000000;" | Jul
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color:#000000;" | Aug
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color:#000000;" | Sep
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color:#000000;" | Oct
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color:#000000;" | Nov
| |
| − | ! style="background: #E5AFAA; color:#000000;" | Dec
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! style="background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" height="16;" | Lexington
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 40/24
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 45/28
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 55/36
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 65/44
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 74/54
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 82/62
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 86/66
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 85/65
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 78/58
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 67/46
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 54/37
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 44/28
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! style="background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" height="16;" | Louisville
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 41/25
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 47/28
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 57/37
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 67/46
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 75/56
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 83/65
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 87/70
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 86/68
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 79/61
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 68/48
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 56/39
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 45/30
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! style="background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" height="16;" | Paducah
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 42/24
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 48/28
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 58/37
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 68/46
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 77/55
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 85/64
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 89/68
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 87/65
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 81/57
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 71/45
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 57/36
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 46/28
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! style="background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" height="16;" | Pikeville
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 46/23
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 50/25
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 60/32
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 69/39
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 77/49
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 84/58
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 87/63
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 86/62
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 80/56
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 71/42
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 60/33
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #C5DFE1; color:#000000;" | 49/26
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! style="background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" height="16;" | Ashland
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 42/19
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 47/21
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 57/29
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 68/37
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 77/47
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 84/56
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 88/61
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 87/59
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 80/52
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 69/40
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 57/31
| |
| − | | style="text-align:center; background: #F8F3CA; color:#000000;" | 46/23
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | colspan="13" style="text-align:center;font-size:90%;background:#E8EAFA;"|''[http://www.ustravelweather.com/weather-kentucky/]''
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Lakes and rivers===
| |
| − | [[Image:Picture 491.jpg|thumb|right|[[Lake Cumberland]] is the largest artificial lake, in terms of volume, east of the [[Mississippi River]].]]
| |
| − | Kentucky’s {{convert|90000|mi|km|-4}} of streams provides one of the most expansive and complex stream systems in the nation. Kentucky has both the largest artificial lake east of the Mississippi in water volume ([[Lake Cumberland]]) and surface area ([[Kentucky Lake]]). It is the only [[U.S. state]] to be bordered on three sides by rivers — the [[Mississippi River]] to the west, the [[Ohio River]] to the north, and the [[Big Sandy River (Ohio River)|Big Sandy River]] and [[Tug Fork]] to the east.<ref name=kye-rivers>{{cite book |editor=Kleber, John E. |others=Associate editors: [[Thomas D. Clark]], Lowell H. Harrison, and James C. Klotter |title=''The Kentucky Encyclopedia'' |year=1992 |publisher=The University Press of Kentucky |location=[[Lexington, Kentucky]] |isbn=0813117720 |chapter=Rivers}}</ref> Its major internal rivers include the [[Kentucky River]], [[Tennessee River]], [[Cumberland River]], [[Green River (Kentucky)|Green River]], and [[Licking River (Kentucky)|Licking River]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | Though it has only three major natural lakes,<ref name=kye>{{cite book |editor=Kleber, John E. |others=Associate editors: [[Thomas D. Clark]], Lowell H. Harrison, and James C. Klotter |title=''The Kentucky Encyclopedia'' |year=1992 |publisher=The University Press of Kentucky |location=[[Lexington, Kentucky]] |isbn=0813117720 |chapter=Lakes}}</ref> the state is home to many [[artificial lake]]s. Kentucky also has more navigable miles of water than any other state in the union, other than [[Alaska]].<ref>{{cite web | title=Corbin, Kentucky: A Fisherman's Paradise | publisher=Corbin, Kentucky Economic Development | url=http://www.corbinkentucky.us/fishing.htm | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> | |
| | | | |
| | ===Natural environment and conservation=== | | ===Natural environment and conservation=== |
| − | Kentucky has an expansive park system which includes one national park, two National Recreation areas, two National Historic Parks, two national forests, 45 state parks, {{convert|37696|acre|km2|0}} of state forest, and 82 Wildlife Management Areas. | + | Kentucky has an expansive park system which includes one national park, two National Recreation areas, two National Historic Parks, two national forests, 45 state parks, {{convert|37696|acre|km2|0}} of state [[forest]], and 82 Wildlife Management Areas. |
| − | | |
| − | Kentucky has been part of two of the most successful wildlife reintroduction projects in [[United States]] history. In the winter of 1997, the state's eastern counties began to re-stock [[elk]], which had been extinct from the area for over 150 years. As of 2006, the state's herd was estimated at 5,700 animals, the largest herd east of the [[Mississippi River]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://fw.ky.gov/elkinfo.asp?lid=1653&NavPath=C117C147C301C547 |title=Elk Restoration Update and Hunting Information |publisher=Kentucky Department of Fish and Wildlife Resources |accessdate=2006-12-09}}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The state also stocked [[wild turkey]]s in the 1950s. Once extinct in the state, today Kentucky has more turkeys per capita than any other eastern state.{{Fact|date=May 2008}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Top tourist attractions in Kentucky===
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | ! Place
| |
| − | ! Visitors per year
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Lake Cumberland]] || 5 million<ref>
| |
| − | {{cite web |url=http://www.lrn.usace.army.mil/WolfCreek/pdf/WOL_Public_Meetings_Jan_07.pdf
| |
| − | |title=Wolf Creek Dam: Major Rehabilitation |accessdate=2007-04-30 |format= |work= }}
| |
| − | </ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Land Between the Lakes]] || 4 million<ref>[http://download.microsoft.com/documents/customerevidence/22385_Land_Between_the_Lakes_final.doc Land Between the Lakes]
| |
| − | </ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Mammoth Cave National Park]] || 2 million<ref>
| |
| − | {{cite web
| |
| − | | url = http://usparks.about.com/cs/natlparkbasics/a/plannermammoth.htm
| |
| − | | title = Mammoth Cave National Park
| |
| − | | accessdate =
| |
| − | | accessdaymonth = 4-30
| |
| − | | accessmonthday =
| |
| − | | accessyear = 2007
| |
| − | | author = Darren Smith
| |
| − | | last = Smith
| |
| − | | first = Darren
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | date =
| |
| − | | year =
| |
| − | | month =
| |
| − | | format =
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher = about. com
| |
| − | | pages =
| |
| − | | language =
| |
| − | | archiveurl =
| |
| − | | archivedate =
| |
| − | | quote =
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | </ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Big South Fork National River and Recreation Area]] || 2 million
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[Churchill Downs]]/ [[Kentucky Derby Museum]] || 1.8 million<ref>[http://www.churchilldownsincorporated.com/investors/annual_reports/Churchill%20Downs%202008%20Annual%20Report.pdf 20767_010_Sendd_Web.ps<!-- Bot generated title —>]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Red River Gorge]] / [[Natural Bridge State Park (Kentucky)|Natural Bridge]] || 1.5 million
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[Louisville Zoo]] || 800,000<ref>[http://www.louisvillezoo.org/groups/profile.htm Louisville Zoo - Group Sales<!-- Bot generated title —>]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[Cumberland Falls]] || 750,000<ref>[http://www.2geton.net/martin/moonbow/cumberlandfalls_ky.html Cumberland Falls, Kentucky<!-- Bot generated title —>]</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[Louisville Science Center]] || 550,000<ref>[http://www.louisvillescience.org/site/about/ Louisville Science Center | About Us | Mission<!-- Bot generated title —>]</ref>
| |
| − | |}
| |
| | | | |
| | ===Significant natural attractions=== | | ===Significant natural attractions=== |
| | *[[Cumberland Gap]], chief passageway through the [[Appalachian Mountains]] in early American history. | | *[[Cumberland Gap]], chief passageway through the [[Appalachian Mountains]] in early American history. |
| − | *[[Cumberland Falls]] State Park, one of the few places in the Western Hemisphere where a "[[moonbow|moon-bow]]" may be regularly seen.<ref>{{cite web | title=Cumberland Falls State Resort Park | date=[[2005-10-19]] | publisher=Kentucky Department of Parks | url=http://parks.ky.gov/resortparks/cf/ | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> | + | *[[Cumberland Falls]] State Park, one of the few places in the Western Hemisphere where a "moon-bow" may be regularly seen. |
| − | *[[Mammoth Cave National Park]], featuring the world's longest cave system.<ref>{{cite web | title=Mammoth Cave National Park | date=[[2006-10-12]] | publisher=National Park Service | url=http://www.nps.gov/maca/ | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> | + | *[[Mammoth Cave National Park]], featuring the world's longest [[cave]] system. |
| | *[[Red River Gorge]] Geological Area, part of the [[Daniel Boone National Forest]]. | | *[[Red River Gorge]] Geological Area, part of the [[Daniel Boone National Forest]]. |
| | *[[Land Between the Lakes]], a National Recreation Area managed by the [[United States Forest Service]]. | | *[[Land Between the Lakes]], a National Recreation Area managed by the [[United States Forest Service]]. |
| − | *[[Bernheim Arboretum and Research Forest]] a 14,000 acre (57 km²) arboretum, forest and nature preserve located in [[Clermont, Kentucky|Clermont]].<ref>
| |
| − | {{cite web
| |
| − | | url = http://athena.louisville.edu/a-s/biology/bernheim.html
| |
| − | | title = Bernheim Research Forest
| |
| − | | accessdate = 4-30
| |
| − | | accessdaymonth =
| |
| − | | accessmonthday =
| |
| − | | accessyear = 2007
| |
| − | | author =
| |
| − | | last =
| |
| − | | first =
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | date =
| |
| − | | year =
| |
| − | | month =
| |
| − | | format =
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher = University of Louisville
| |
| − | | pages = 1
| |
| − | | language =
| |
| − | | archiveurl =
| |
| − | | archivedate =
| |
| − | | quote =
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | </ref>
| |
| − | *[[Abraham Lincoln Birthplace National Historic Site]] in [[Hodgenville, Kentucky|Hodgenville]].
| |
| − | *[[Big South Fork National River and Recreation Area]] near [[Whitley City, Kentucky|Whitley City]].
| |
| − | *[[Trail of Tears National Historic Trail]] also passes through Kentucky.
| |
| − | *[[Black Mountain (Kentucky)|Black Mountain]], state's highest point.<ref name="usgs" /> Runs along the border of [[Harlan County, Kentucky|Harlan]] and [[Letcher County, Kentucky|Letcher]] counties.
| |
| − | *[[Bad Branch Falls State Nature Preserve]], {{convert|2639|acre|km2|0|sing=on}} state nature preserve on southern slope of Pine Mountain in [[Letcher County, Kentucky|Letcher County]]. Includes one of the largest concentrations of rare and endangered species in the state,<ref>{{cite web | title=Bad Branch State Nature Preserve | publisher=Kentucky State Nature Preserves Commission | url=http://www.naturepreserves.ky.gov/stewardship/badbranch.htm | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> as well as a {{convert|60|ft|m|0|sing=on}} waterfall and a Kentucky Wild River.
| |
| − | *[[Jefferson Memorial Forest]], located south of [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]] in the [[Knobs region]], the largest municipally run forest in the [[United States]].<ref>{{cite web | title=Jefferson Memorial Forest | url=http://www.memorialforest.com/ | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref>
| |
| − | *[[Green River Lake State Park]], located in [[Taylor County, Kentucky|Taylor County]].
| |
| − | *[[Lake Cumberland]], {{convert|1255|mi|km|0}} of shoreline located in [[South Central Kentucky]].
| |
| | | | |
| | ==History== | | ==History== |
| − | [[Image:Boone Cumberland.jpg|thumb|right|''[[Daniel Boone]] Escorting Settlers through the [[Cumberland Gap]]'' ([[George Caleb Bingham]], oil on canvas, 1851–52).]] | + | [[Image:Boone Cumberland.jpg|thumb|right|''[[Daniel Boone]] Escorting Settlers through the [[Cumberland Gap]]'' ([[George Caleb Bingham]], oil on canvas, 1851–1852).]] |
| − | [[Image:Lincoln and Davis Statue.jpg|thumb|right|Both Abraham Lincoln and [[Jefferson Davis]] were born in Kentucky.]]
| |
| − | {{expand|date=April 2008}}
| |
| − | {{mainarticle|History of Kentucky}}
| |
| − | {{seealso|Kentucky in the American Civil War|Kentucky Historical Society|Hatfield-McCoy feud}}
| |
| | | | |
| − | Although inhabited by [[Native Americans in the United States|Native Americans]] in prehistoric times, when explorers and settlers began entering Kentucky in the mid-1700s, there were no major Native American settlements in the region.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.merceronline.com/Native/native01.htm |title=The Presence |publisher=Mercer County Online |accessdate=2006-11-29 |work=History of Native Americans in Central Kentucky }}</ref> Instead, the country was used as hunting grounds by [[Shawnee]]s from the north and [[Cherokee]]s from the south. Much of what is now Kentucky was purchased from Native Americans in the treaties of [[Treaty of Fort Stanwix|Fort Stanwix]] (1768) and [[Treaty of Sycamore Shoals|Sycamore Shoals]] (1775).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://web-books.com/Classics/Nonfiction/History/Southwest2/Southwest2C7P1.htm |title=The Dark and Bloody Hunting Ground |accessdate=2006-11-29 |last=Skinner |first=Constance |work=Pioneers of the Old Southwest |publisher=WebBooks.com}}</ref> Thereafter, Kentucky grew rapidly as the first settlements west of the [[Appalachian Mountains]] were founded, with settlers (primarily from [[Virginia]], [[North Carolina]], [[Maryland]], [[Delaware]], and [[Pennsylvania]]) entering the region either over land via [[Braddock Road (Braddock expedition)|Braddock Road]] and the [[Cumberland Gap]], or by water down the [[Ohio River]] from points upstream, or up the Ohio River from the Mississippi. The first part to be settled was the northern part, along the Ohio River, with [[Lexington, Kentucky|Lexington]] and [[Washington, Kentucky|Washington]] being the first major settlements. A detailed account of this can be read in the memoirs of [[Spencer Records]]. Next, the southern part of the state was settled, via the [[Wilderness Trail]], which went along the [[Great Appalachian Valley]] and across the [[Cumberland Gap]], blazed by [[Daniel Boone]], traditionally considered one of the founders of the state.<ref>>{{cite web | title=Book Description for ''The Life of Daniel Boone: The Founder of the State of Kentucky and Colonel's Boone Autobiography''| publisher=Amazon.com | url=http://www.amazon.com/Life-Daniel-Boone-Kentucky-Autobiography/dp/1589639901 | accessdate=2006-11-29}}</ref> [[Shawnee]]s north of the Ohio River, however, were unhappy about the settlement of Kentucky, and allied themselves with the [[Great Britain|British]] in the [[American Revolutionary War]] (1775–1783).<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.polsci.wvu.edu/wv/Monongalia/monhistory.html |title=Monongalia County History |accessdate=2006-11-29 |last=Dilger |first=Dr. Robert Jay |publisher=West Virginia University }}</ref> Kentucky was a battleground during the war; the [[Battle of Blue Licks]], one of the last major battles of the Revolution, was fought in Kentucky.<ref>{{cite web | title=The Battle of Blue Licks | publisher=EarlyAmerica.com| url=http://www.earlyamerica.com/review/winter2000/bluelick.html | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> | + | Although inhabited by [[Native Americans in the United States|Native Americans]] in prehistoric times, when explorers and settlers began entering Kentucky in the mid-1700s, there were no major Native American settlements in the region.<ref>''Mercer County Online''. [http://www.merceronline.com/Native/native01.htm The Presence] History of Native Americans in Central Kentucky. Retrieved September 26, 2008.</ref> Instead, the country was used as hunting grounds by [[Shawnee]] from the north and [[Cherokee]] from the south, who lived in scattered seasonal villages. Much of what is now Kentucky was purchased from Native Americans in the treaties of [[Treaty of Fort Stanwix|Fort Stanwix]] (1768) and [[Treaty of Sycamore Shoals|Sycamore Shoals]] (1775).<ref>Constance Skinner. [http://web-books.com/Classics/Nonfiction/History/Southwest2/Southwest2C7P1.htm The Dark and Bloody Hunting Ground] Pioneers of the Old Southwest. Retrieved September 26, 2008.</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | After the American Revolution, the counties of [[Virginia]] beyond the [[Appalachian Mountains]] became known as [[Kentucky County, Virginia|Kentucky County]].<ref>{{cite web | title=About Kentucky| publisher=Ezilon Search| url=http://search.ezilon.com/about-kentucky.html | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> Eventually, the residents of Kentucky County petitioned for a separation from Virginia. Ten constitutional conventions were held in the Constitution Square Courthouse in [[Danville, Kentucky|Danville]] between 1784 and 1792. In 1790, Kentucky's delegates accepted Virginia's terms of separation, and a state constitution was drafted at the final convention in April 1792. On [[June 1]], [[1792]], Kentucky became the fifteenth state to be admitted to the union and [[Isaac Shelby]], a military veteran from Virginia, was elected the first Governor of the Commonwealth of Kentucky.<ref>{{cite web | title=Constitution Square State Historic Site | publisher=Danville-Boyle County Convention and Visitors Bureau | url=http://www.danville-ky.com/attractions2.php?category=History%20and%20Museums | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref>
| + | Thereafter, Kentucky grew rapidly as the first settlements west of the [[Appalachian Mountains]] were founded, with settlers (primarily from [[Virginia]], [[North Carolina]], [[Maryland]], [[Delaware]], and [[Pennsylvania]]) entering the region either over land via [[Braddock Road (Braddock expedition)|Braddock Road]] and the [[Cumberland Gap]], or by water down the [[Ohio River]] from points upstream, or up the Ohio River from the Mississippi. The first part to be settled was the north, along the Ohio River, with [[Lexington, Kentucky|Lexington]] and [[Washington, Kentucky|Washington]] being the first major settlements. Next, the southern part of the state was settled, via the [[Wilderness Trail]] across the Cumberland Gap, blazed by [[Daniel Boone]], traditionally considered one of the founders of the state. |
| | | | |
| − | Kentucky was a [[Border states (Civil War)|border state]] during the American Civil War.<ref>{{cite web | title=Border States in the Civil War | date=[[2002-02-15]] | publisher=CivilWarHome.com | url=http://www.civilwarhome.com/borderstates.htm | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> Although frequently described as never having seceded, a group of Kentucky soldiers stationed at [[Russellville, Kentucky|Russellville]] did pass an [[Ordinance of Secession]] under the moniker "Convention of the People of Kentucky" on [[November 20]], [[1861]],<ref>{{cite web | title=Ordinances of Secession | publisher=Historical Text Archive | url=http://historicaltextarchive.com/sections.php?op=viewarticle&artid=170 | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> establishing a [[Confederate government of Kentucky]] with its capital in [[Bowling Green, Kentucky|Bowling Green]].<ref>{{cite web | title=Civil War Sites - Bowling Green, KY | publisher=WMTH Corporation | url=http://www.trailsrus.com/monuments/reg3/bowling_green.html | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref> Though Kentucky was represented by the central star on the [[Flags of the Confederate States of America#The Battle Flag|Confederate battle flag]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://ngeorgia.com/history/flagsofga.html |title=A Concise History of the Flags of the Confederate States of America and the Sovereign State of Georgia |accessdate=2006-11-29 |last=Irby, Jr. |first=Richard E. |work=About North Georgia |publisher=Golden Ink}}</ref> the legitimacy of the [[Russellville Convention]] may well be questioned. Only a year earlier, philosopher [[Karl Marx]] wrote in a letter to [[Friedrich Engels]] that the result of a vote deciding how Kentucky would be represented at a convention of the [[Border states (Civil War)|border states]] was "100,000 for the Union ticket, only a few thousand for secession."<ref>{{cite web |url=http://marxists.org/archive/marx/works/1861/letters/61_07_05.htm |title=Marx To Engels In Manchester |accessdate=2006-11-29 |last=Marx |first=Karl |authorlink=Karl Marx |date=1861-07-05 |publisher= Marxists Internet Archive}}</ref> Kentucky officially remained "neutral" throughout the war due to Union sympathies of many of the Commonwealth's citizens. Even today, however, [[Confederate Memorial Day]] is observed by some in Kentucky on [[Confederate States of America|Confederate]] President Jefferson Davis' birthday, [[June 3]].<ref>{{cite web | title=KRS 2.110 Public Holidays | publisher=[[Kentucky General Assembly]] | url=http://www.lrc.ky.gov/KRS/002-00/110.PDF |format=PDF | accessdate=2006-11-29 }}</ref>
| + | [[Shawnee]] north of the [[Ohio River]] were unhappy about the settlement of Kentucky, however, and allied themselves with the [[Great Britain|British]] in the [[American Revolutionary War]] (1775–1783). Kentucky was a battleground during the war; the [[Battle of Blue Licks]], one of the last major battles of the Revolution, was fought in Kentucky. |
| | | | |
| − | The [[Black Patch Tobacco Wars]] occurred from 1904 to 1909. The war was started because the farmers were selling their tobacco at low prices. The "Night Riders" were a group of people who terrorized the farmers who sold their tobacco at low prices. They would go by night and use fear and intimidation to terrorize the farmers. They would burn down fields, warehouses, and barns.
| + | After the American Revolution, the counties of [[Virginia]] beyond the [[Appalachian Mountains]] became known as Kentucky County. Eventually, the residents of Kentucky County petitioned for separation. In 1790, Kentucky's delegates accepted Virginia's terms of separation, and a state constitution was drafted. On June 1, 1792, Kentucky became the fifteenth state to be admitted to the Union. <ref> ''Danville-Boyle County Convention & Visitors Bureau''. [http://www.danville-ky.com/attractions2.php?category=History%20and%20Museums Constitution Square State Historic Site] Retrieved September 26, 2008. </ref> |
| | | | |
| − | [[Image:Picture 1654.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Designed by the [[Washington Monument]]'s architect [[Robert Mills (architect)|Robert Mills]] in 1845, the [[United States Marine Hospital of Louisville|U.S. Marine Hospital]] in Louisville is considered the best remaining [[antebellum]] hospital in the [[United States]]]] | + | Kentucky was a [[Border states (Civil War)|border state]] during the [[American Civil War.]] It officially remained "neutral" throughout the war due to the Union sympathies of many of the Commonwealth's citizens. After the war, the development of burley tobacco contributed to a tremendous increase in [[tobacco]] production. |
| − | On [[January 30]], [[1900]], Governor [[William Goebel]], flanked by two bodyguards, was mortally wounded by an assailant while walking to the State Capitol in downtown Frankfort. Goebel was in the process of contesting the election of 1899, initially assumed to be won by [[William S. Taylor]]. For several months, [[J. C. W. Beckham]], Goebel's running mate, and Taylor fought over who was the real governor until the [[Supreme Court of the United States]] decided in May that Beckham was the rightful governor. Taylor fled to [[Indiana]] and was later indicted as a co-conspirator in Goebel's [[assassination]]. Goebel remains the only governor of a U.S. state to have been assassinated while in office.<ref>{{cite web | title=The Old State Capitol | publisher=[[Kentucky Historical Society]] | url=http://history.ky.gov/sub.php?pageid=23§ionid=8 |date= | accessdate=2007-11-09 }}</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | ==Law and government== | + | During [[World War II]], Kentucky began to shift from an [[agriculture|agricultural]] to an industrial economy, but it was not until 1970 that the number of urban dwellers outpaced rural dwellers. [[Tourism]] has developed into a major industry. |
| | + | |
| | + | ==Law and government== |
| | + | [[Image:KY State Capitol.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The Kentucky State Capitol in Frankfort]] |
| | + | [[Image:LincolnBirthplaceJBM82908.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The Abraham Lincoln Birthplace National Historical Site in Hodgenville. The early 19th-century cabin is enclosed within this neo-classic building.]] |
| | + | {{MetaSidebar|250px|#ffffaa|right|[[Kentucky State symbols]]| |
| | + | *'''[[State nickname|Nickname]]:''' "The Bluegrass State" |
| | + | *'''[[State mottos|Motto]]:''' "Deo gratiam habeamus" |
| | + | ::"With gratitude to God" |
| | + | *'''[[State slogan|Slogan]]:''' "Kentucky: Unbridled Spirit" |
| | + | *'''[[State song|Song]]:''' [[My Old Kentucky Home|"My Old Kentucky Home"]] |
| | + | *'''[[State dance|Dance]]:''' [[Clogging]] |
| | + | *'''[[State music|Music]]:''' [[Bluegrass music]] |
| | + | *'''[[State Musical instrument|Musical instrument]]:''' [[Appalachian Dulcimer]] |
| | + | *'''[[State mammal|Animal]]:''' [[Thoroughbred]] |
| | + | *'''[[State mammal|Wild Animal Game Species]]:''' [[Gray Squirrel]] |
| | + | *'''[[State fish|Fish]]:''' [[Spotted bass|Kentucky Spotted Bass]] |
| | + | *'''[[List of U.S. state birds|Bird]]:''' [[Northern Cardinal|Cardinal]] |
| | + | *'''[[State flower|Flower]]:''' [[Goldenrod]] |
| | + | *'''[[State grass|Grass]]:''' [[Smooth Meadow-grass|Kentucky Bluegrass]] |
| | + | *'''[[State butterfly|Butterfly]]:''' [[Viceroy Butterfly]] |
| | + | *'''[[State soil|Soil]]:''' [[Crider Soil Series]] |
| | + | *'''[[State tree|Tree]]:''' [[Tulip Poplar]] |
| | + | *'''[[State fruit|Fruit]]:''' [[Blackberry]] |
| | + | *'''[[State fossil|Fossil]]:''' [[Brachiopod]] |
| | + | *'''[[State gemstone|Gemstone]]:''' [[Pearl|Freshwater Pearl]] |
| | + | *'''[[State mineral|Mineral]]:''' [[Coal]] |
| | + | *'''[[State rock|Rock]]:''' [[Agate|Kentucky Agate]] |
| | + | }} |
| | + | Frankfort is the capital city of Kentucky and the [[county seat]] of [[Franklin County, Kentucky|Franklin County]]. The population was 27,741 at the [[United States Census, 2000|2000 census]]; by [[population]], it is the 5th smallest state capital city in the [[United States]]. |
| | + | |
| | + | After Kentucky became a state, five commissioners were appointed on June 20, 1792, to choose a location for the state capital. The [[Kentucky General Assembly]] appropriated funds to provide a house to accommodate the governor in 1796. Construction was completed in 1798. The Old Governor's Mansion is reputed to be the oldest official executive residence still in use in the [[United States]]. |
| | + | |
| | ===Government=== | | ===Government=== |
| − | [[Image:KENTUCKY COUNTIES.png|thumb|right|250px|Map of [[List of counties in Kentucky|Kentucky counties]]]]
| + | Kentucky is a commonwealth, meaning its government is run according to the common consent of its people. It is one out of only four states that call themselves commonwealths. Kentucky is also one of only five states that elects its state officials in odd numbered years (the others are [[Louisiana]], [[Mississippi]], [[New Jersey]], and [[Virginia]]). Kentucky holds elections for these offices every four years in the years preceding presidential election years. |
| − | Kentucky is a [[Commonwealth (United States)|commonwealth]], meaning its government is run according to the common consent of its people. It is one out of only four states that call themselves commonwealths. Kentucky is also one of only five states that elects its state officials in odd numbered years (The others are [[Louisiana]], [[Mississippi]], [[New Jersey]], and [[Virginia]]). Kentucky holds elections for these offices every 4 years in the years preceding Presidential election years. Thus, the last year when Kentucky elected a Governor was 2007; the next gubernatorial election will occur in 2011, with future gubernatorial elections to take place in 2015, 2019, 2023, etc. | |
| | | | |
| | ====State government==== | | ====State government==== |
| − | [[Image:KY State Capitol.jpg|thumb|right|200px|The [[Kentucky State Capitol]] building in [[Frankfort, Kentucky|Frankfort]]]]
| + | |
| − | {{seealso|List of Governors of Kentucky}}
| + | Kentucky's legislative branch consists of a bicameral body known as the Kentucky General Assembly. The Senate is considered the upper house. It has 38 members and is led by the President of the Senate. The House of Representatives has 100 members and is led by the Speaker of the House. |
| − | Kentucky's legislative branch consists of a [[bicameralism|bicameral]] body known as the [[Kentucky General Assembly]]. The [[Kentucky Senate|Senate]] is considered the [[upper house]]. It has 38 members, and is led by the [[President of the Senate]], currently [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican]] [[David L. Williams]]. The [[Kentucky House of Representatives|House of Representatives]] has 100 members, and is led by the Speaker of the House, currently [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democrat]] [[Jody Richards]]. | |
| | | | |
| − | The executive branch is headed by the [[Governor of Kentucky|governor]] and [[Lieutenant Governor of Kentucky|lieutenant governor]]. Under the current [[Kentucky Constitution]], the lieutenant governor assumes the duties of the governor only if the governor is incapacitated. (Prior to 1992, the lieutenant governor assumed power any time the governor was out of the state.) The governor and lieutenant governor usually run on a single ticket (also per a 1992 constitutional amendment), and are elected to four-year terms. Currently, the governor and lieutenant governor are Democrats [[Steve Beshear]] and [[Daniel Mongiardo]]. | + | The executive branch is headed by the governor and lieutenant governor. The governor and lieutenant governor usually run on a single ticket and are elected to four-year terms. Currently, the governor and lieutenant governor are Democrats Steve Beshear and Daniel Mongiardo. |
| | | | |
| | The judicial branch of Kentucky is made up of courts of limited jurisdiction called District Courts; courts of general jurisdiction called Circuit Courts; an intermediate appellate court, the [[Kentucky Court of Appeals]]; and a court of last resort, the [[Kentucky Supreme Court]]. Unlike federal judges, who are usually appointed, justices serving on Kentucky state courts are chosen by the state's populace in non-partisan elections. | | The judicial branch of Kentucky is made up of courts of limited jurisdiction called District Courts; courts of general jurisdiction called Circuit Courts; an intermediate appellate court, the [[Kentucky Court of Appeals]]; and a court of last resort, the [[Kentucky Supreme Court]]. Unlike federal judges, who are usually appointed, justices serving on Kentucky state courts are chosen by the state's populace in non-partisan elections. |
| | | | |
| − | The state's chief prosecutor, law enforcement officer, and law officer is the attorney general. The [[Attorney General of Kentucky|attorney general]] is elected to a four-year term and may serve two consecutive terms under the current Kentucky Constitution. The current Kentucky attorney general is Democrat [[Jack Conway]]. | + | The state's chief prosecutor, law enforcement officer, and law officer is the attorney general. The attorney general is elected to a four-year term and may serve two consecutive terms under the current Kentucky Constitution. The current Kentucky attorney general is Democrat Jack Conway. |
| − | | |
| − | ====Federal representation====
| |
| − | [[Image:KY-districts-108.JPG|thumbnail|right|A map showing Kentucky's six [[Kentucky Congressional Districts|congressional districts]]]]
| |
| − | Kentucky's two [[United States Senate|Senators]] are [[Party leaders of the United States Senate|Senate Minority Leader]] [[Mitch McConnell]] and [[Jim Bunning]], both [[Republican Party (United States)|Republicans]]. The state is divided into six [[Kentucky Congressional Districts|Congressional Districts]], represented by [[Republican Party (United States)|Republicans]] [[Ed Whitfield]] ([[Kentucky's 1st congressional district|1<sup>st</sup>]]), [[Ron Lewis]] ([[Kentucky's 2nd congressional district|2<sup>nd</sup>]]), [[Geoff Davis]] ([[Kentucky's 4th congressional district|4<sup>th</sup>]]), and [[Hal Rogers]] ([[Kentucky's 5th congressional district|5<sup>th</sup>]]), and [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democrats]] [[John Yarmuth]] ([[Kentucky's 3rd congressional district|3<sup>rd</sup>]]) and [[Ben Chandler]] ([[Kentucky's 6th congressional district|6<sup>th</sup>]]).
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Judicially, Kentucky is split into two Federal court districts: the [[United States District Court for the Eastern District of Kentucky|Kentucky Eastern District]] and the [[United States District Court for the Western District of Kentucky|Kentucky Western District]]. Appeals are heard in the [[United States Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit|Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals]] based in [[Cincinnati, Ohio]].
| |
| | | | |
| | ====Political leanings==== | | ====Political leanings==== |
| − | [[Image:LincolnBirthplaceJBM82908.jpg|thumb|right|270px|Abraham Lincoln Birthplace near [[Hodgenville, Kentucky|Hodgenville]]]]
| + | Where politics are concerned, Kentucky historically has been very hard fought and leaned slightly toward the [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic Party]], although it was never included among the "Solid South." In 2006, 57.05 percent of the state's voters were officially registered as Democrats, 36.55 percent registered [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican]], and 6.39 percent registered with some other [[political party]].<ref>''Kentucky Secretary of State''. 2006. [http://kentucky.gov/Newsroom/sos/article61.htm 2006 General Election Registration Figures Set] Retrieved September 26, 2008. </ref> |
| − | Where politics are concerned, Kentucky historically has been very hard fought and leaned slightly toward the [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic Party]], although it was never included among the "[[Solid South]]." In 2006, 57.05% of the state's voters were officially registered as Democrats, 36.55% registered [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican]], and 6.39% registered with some other [[political party]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://kentucky.gov/Newsroom/sos/article61.htm |title=2006 General Election Registration Figures Set |accessdate=2006-11-30 |date=2006-10-19 |publisher=Kentucky Secretary of State }}</ref> | |
| | | | |
| − | Kentucky has voted Republican in five of the last seven presidential elections but has supported the Democratic candidates of the [[Southern United States|South]]. The Commonwealth supported Democrats [[Jimmy Carter]] in 1976, and [[Bill Clinton]] in 1992 and 1996, but Republican [[George W. Bush]] in 2000 and 2004. Bush won the state's 8 electoral votes overwhelmingly in 2004 by a margin of 20 percentage points and 59.6% of the vote.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.cnn.com/ELECTION/2004/pages/results/states/KY/P/00/ |title=Election Results for Kentucky|publisher=CNN|accessdate=2007-04-28}}</ref> | + | Kentucky has voted Republican in five of the last seven presidential elections but has supported the Democratic candidates of the [[Southern United States|South]]. The Commonwealth supported Democrats [[Jimmy Carter]] in 1976 and [[Bill Clinton]] in 1992 and 1996 but Republican [[George W. Bush]] in 2000 and 2004. Bush won the state's 8 electoral votes overwhelmingly in 2004 by a margin of 20 percentage points and 59.6 percent of the vote.<ref> ''CNN''. [http://www.cnn.com/ELECTION/2004/pages/results/states/KY/P/00/ Election Results for Kentucky] Retrieved September 26, 2008. </ref> |
| | | | |
| | ===Law=== | | ===Law=== |
| − | Kentucky's body of laws, known as the [[Kentucky Revised Statutes]] (KRS), were enacted in 1942 to better organize and clarify the whole of Kentucky law.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.lrc.ky.gov/statrev/revoff.htm |title=Reviser of Statutes Office - History and Functions |publisher=Kentucky Legislative Research Commission |accessdate=2006-12-27}}</ref> The statutes are enforced by local [[police]], [[sheriff]]s, [[constables]], deputy sheriffs and deputy constables. Unless they have completed a [[police academy]] elsewhere, these officers are required to complete training at the Kentucky Department of Criminal Justice Training Center on the campus of [[Eastern Kentucky University]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://docjt.jus.state.ky.us/history.html |title=History of the DOCJT |publisher=Kentucky Department of Criminal Justice |accessdate=2006-12-27}}</ref> Additionally, in 1948, the [[Kentucky General Assembly]] established the [[Kentucky State Police]], making it the 38<sup>th</sup> state to create a force whose jurisdiction extends throughout the given state.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.kentuckystatepolice.org/history.htm |title=History of the Kentucky State Police |publisher=Kentucky State Police |accessdate=2006-12-27}}</ref>
| + | |
| − |
| + | Kentucky is one of 36 states in the [[United States]] that sanctions the [[Capital punishment|death penalty]] for certain crimes. Kentucky has been on the front lines of the debate over displaying the [[Ten Commandments]] on public property. In the 2005 case of ''[[McCreary County v. ACLU of Kentucky]],'' the [[Supreme Court of the United States|U.S. Supreme Court]] upheld the decision of the [[United States Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit|Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals]] that a display of the Ten Commandments in the [[Whitley City, Kentucky|Whitley City]] courthouse of [[McCreary County, Kentucky|McCreary County]] was unconstitutional.<ref>[[Cornell University]] Law School. [http://straylight.law.cornell.edu/supct/html/03-1693.ZS.html McCreary County v. ACLU of Kentucky] Retrieved September 26, 2008. </ref> Later that year, Judge [[Richard Fred Suhrheinrich]], writing for the Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals in the case of ''[[American Civil Liberties Union|ACLU]] of Kentucky v. [[Mercer County, Kentucky|Mercer County]],'' wrote that a display including the [[Mayflower Compact]], the [[United States Declaration of Independence|Declaration of Independence]], the Ten Commandments, the [[Magna Carta]], ''[[The Star-Spangled Banner]],'' and the [[In God We Trust|national motto]] could be erected in the Mercer County courthouse. <ref> ''United States Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit''. [http://www.ca6.uscourts.gov/opinions.pdf/05a0477p-06.pdf Text of decision in ACLU of Kentucky v. Mercer County, No. 03-5142] Retrieved September 26, 2008. </ref> |
| − | Kentucky is one of 36 states in the [[United States]] that sanctions the [[Capital punishment|death penalty]] for certain crimes. Those convicted of capital crimes after [[March 31]], [[1998]] are always executed by [[lethal injection]]; those convicted before this date may opt for the [[electric chair]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.deathpenaltyinfo.org/article.php?scid=8&did=245#state |title=Authorized Methods of Execution by State |publisher=Death Penalty Information Center |accessdate=2006-12-28}}</ref> Only [[List of individuals executed in Kentucky|two people]] have been executed in Kentucky since the [[Supreme Court of the United States|U.S. Supreme Court]] reinstituted the practice in 1976. The most notable execution in Kentucky, however, was that of [[Rainey Bethea]] on [[August 14]], [[1936]]. Bethea was publicly hanged in [[Owensboro, Kentucky|Owensboro]] for the [[rape]] and [[murder]] of Lischia Edwards.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.kypost.com/2001/jun/11/bethea061101.html |title='The Last Public Execution in America' |work=[[The Cincinnati Post|The Kentucky Post]] |publisher=[[E. W. Scripps Company]] |author=Paul A. Long |last=Long |first=Paul A |date=2001-06-11 |accessdate=2006-12-27 |archiveurl=http://web.archive.org/web/20060117233210/http://www.kypost.com/2001/jun/11/bethea061101.html |archivedate=2006-01-17}}</ref> Irregularities with the execution led to this becoming the last public execution in the [[United States]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.npr.org/programs/morning/features/2001/apr/010430.execution.html |title=The Last Public Execution in America |publisher=[[National Public Radio|NPR]] |last=Montagne |first=Renee |date=[[2001-05-01]] |accessdate=2006-12-27}}</ref> | + | |
| − |
| + | Prior to the adoption of the state constitution in 1891, the General Assembly had the authority to grant charters to private organizations allowing them to conduct [[lottery|lotteries]] in order to fund public works such as [[road]]s and [[school]]s. Due to a considerable amount of abuse, a prohibition on lotteries was written into the 1891 constitution (Section 226). An exception in gaming case law was the legality of pari-mutuel wagering on [[horse racing]]. In 2008, legal forms of [[gambling]] in the state included commercial, legalized gambling in horse racing, lottery sales (approved in 1988), and charitable gaming.<ref>Barry Boardman, Jack Jones, John Perry, and Murray Wood. November 2003. [http://www.lrc.ky.gov/lrcpubs/RR316.pdf Compulsive Gambling in Kentucky] ''Legislative Research Commission''. Retrieved October 23, 2008.</ref> In January 2008, electronic machine, or [[casino]]-style gambling had still not been approved by the General Assembly,<ref>Brett Guthrie. January 10, 2008. [http://www.kypolitics.org/kypolitics/2008/01/sensing-an-air.html Sensing an air of inevitability on casino gambling] ''KYPolitics.org.'' Retrieved October 23, 2008. </ref> and while prospects for approval seemed high, there were many opponents. In September 2008, a Franklin County Circuit judge ordered the transfer of the [[domain name]]s of 141 illegal Internet gambling sites to the Commonwealth of Kentucky in an effort to stop illegal and unregulated online gaming. Kentucky is the first state to bring an action against Internet gambling operators that has resulted in the seizure of domain names.<ref>''Commonwealth of Kentucky.'' September 22, 2008. [http://migration.kentucky.gov/newsroom/governor/20080922onlinegaming.htm Governor Steve Beshear's Communications Office] Retrieved October 23, 2008.</ref> |
| − | Kentucky has been on the front lines of the debate over displaying the [[Ten Commandments]] on public property. In the 2005 case of ''[[McCreary County v. ACLU of Kentucky]]'', the [[Supreme Court of the United States|U.S. Supreme Court]] upheld the decision of the [[United States Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit|Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals]] that a display of the [[Ten Commandments]] in the [[Whitley City, Kentucky|Whitley City]] courthouse of [[McCreary County, Kentucky|McCreary County]] was unconstitutional.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://straylight.law.cornell.edu/supct/html/03-1693.ZS.html |title=''McCreary County v. ACLU of Kentucky'' |publisher=[[Cornell University]] Law School |accessdate=2006-12-27}}</ref> Later that year, Judge [[Richard Fred Suhrheinrich]], writing for the [[United States Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit|Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals]] in the case of ''[[American Civil Liberties Union|ACLU]] of Kentucky v. [[Mercer County, Kentucky|Mercer County]]'', wrote that a display including the [[Mayflower Compact]], the [[United States Declaration of Independence|Declaration of Independence]], the [[Ten Commandments]], the [[Magna Carta]], ''[[The Star-Spangled Banner]]'', and the [[In God We Trust|national motto]] could be erected in the [[Mercer County, Kentucky|Mercer County]] courthouse.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ca6.uscourts.gov/opinions.pdf/05a0477p-06.pdf |format=PDF |title=Text of decision in ''ACLU of Kentucky v. Mercer County'' |accessdate=2006-12-27}}</ref> | |
| | | | |
| | ==Demographics== | | ==Demographics== |
| − | [[Image:Kentucky population map.png|thumb|left|Kentucky Population Density Map.]] | + | [[Image:Kentucky population map.png|thumb|225px|Kentucky Population Density Map.]] |
| − | {{USCensusPop
| + | [[Image:N38316642 31380476 4196.jpg|thumb|225px|Population growth is centered along and between interstates [[Interstate 65|I-65]] and [[Interstate 75|I-75]].]] |
| − | |1790 = 73677 | + | As of July 1, 2006, Kentucky had an estimated [[population]] of 4,206,074, which is an increase of 33,466, or 0.8 percent, from the prior year and an increase of 164,586, or 4.1 percent, since 2000. This includes a natural increase since the last census of 77,156 people (that is 287,222 births minus 210,066 deaths) and an increase due to net migration of 59,604 people into the state. [[Immigration to the United States|Immigration]] from outside the [[United States]] resulted in a net increase of 27,435 people, and migration within the country produced a net increase of 32,169 people. As of 2004, Kentucky's population included about 95,000 foreign-born (2.3 percent). |
| − | |1800 = 220955 | + | |
| − | |1810 = 406511 | + | Kentucky's total population has grown during every decade since records began. However during most decades of the twentieth century there was also net out-migration from Kentucky. Since 1900, rural Kentucky counties have experienced a net loss of over one million people from migration, while urban areas have experienced a slight net gain.<ref>Michael Price. 1996. [http://www.kltprc.net/books/exploring/Chpt_3.htm Migration in Kentucky: Will the Circle Be Unbroken?] ''University of Louisville''. Retrieved September 26, 2008 </ref> |
| − | |1820 = 564317 | |
| − | |1830 = 687917 | |
| − | |1840 = 779828
| |
| − | |1850 = 982405
| |
| − | |1860 = 1155684
| |
| − | |1870 = 1321011
| |
| − | |1880 = 1648690
| |
| − | |1890 = 1858635
| |
| − | |1900 = 2147174
| |
| − | |1910 = 2289905
| |
| − | |1920 = 2416630
| |
| − | |1930 = 2614589
| |
| − | |1940 = 2845627
| |
| − | |1950 = 2944806
| |
| − | |1960 = 3038156
| |
| − | |1970 = 3218706
| |
| − | |1980 = 3660777
| |
| − | |1990 = 3685296
| |
| − | |2000 = 4041769
| |
| − | | estimate= 4206074
| |
| − | | estyear= 2006
| |
| − | | estref=
| |
| − | | footnote=http://ukcc.uky.edu/census/21.txt
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | As of [[July 1]], [[2006]], Kentucky has an estimated population of 4,206,074, which is an increase of 33,466, or 0.8%, from the prior year and an increase of 164,586, or 4.1%, since the year 2000. This includes a natural increase since the last census of 77,156 people (that is 287,222 births minus 210,066 deaths) and an increase due to net migration of 59,604 people into the state. [[Immigration to the United States|Immigration]] from outside the United States resulted in a net increase of 27,435 people, and migration within the country produced a net increase of 32,169 people. As of 2004, Kentucky's population included about 95,000 foreign-born (2.3%). | |
| | | | |
| − | Kentucky's total population has grown during every decade since records began. However during most decades of the 20th century there was also net out-migration from Kentucky. Since 1900, rural Kentucky counties have experienced a net loss of over 1 million people from migration, while urban areas have experienced a slight net gain.<ref>{{cite web | + | The Greater Louisville Metro Area holds a very disproportionate share of Kentucky's population, growth, and wealth. The second largest city is Lexington. The metropolitan areas of Louisville, Lexington, and northern Kentucky had a combined population of 2,169,394 as of 2006, which is 51.5 percent of the state's total population. |
| − | | url = http://www.kltprc.net/books/exploring/Chpt_3.htm
| |
| − | | title = Migration in Kentucky: Will the Circle Be Unbroken?
| |
| − | | accessdate = 4-30
| |
| − | | accessdaymonth =
| |
| − | | accessmonthday =
| |
| − | | accessyear = 2007
| |
| − | | author = Michael Price
| |
| − | | last = Price
| |
| − | | first = Michael
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | date =
| |
| − | | year =
| |
| − | | month =
| |
| − | | format =
| |
| − | | work = Exploring the Frontier of the Future: How Kentucky Will Live, Learn and Work
| |
| − | | publisher = University of Louisville
| |
| − | | pages = pp. 5–10
| |
| − | | language =
| |
| − | | archiveurl =
| |
| − | | archivedate =
| |
| − | | quote =
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | </ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | The [[center of population]] of Kentucky is located in [[Washington County, Kentucky|Washington County]], in the city of [[Willisburg, Kentucky|Willisburg]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.census.gov/geo/www/cenpop/statecenters.txt |format=TXT |title=Population and Population Centers by State: 2000 |publisher=U.S. Census Bureau |accessdate=2006-12-27}}</ref> | + | The two other fast-growing urban areas in Kentucky are the Bowling Green area and the "Tri-Cities Region" of southeastern Kentucky, comprising the towns of Somerset, London, and Corbin. |
| | | | |
| | ===Race and ancestry=== | | ===Race and ancestry=== |
| − | The five largest ancestries in the commonwealth are: [[American ancestry|American]] (20.9%) (Mostly of [[British American|British]] ancestry), [[German American|German]] (12.7%), [[Irish American|Irish]] (10.5%), [[English American|English]] (9.7%), [[African American]] (7.8%).<ref name="census-ancestries">[http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/45/Census-2000-Data-Top-US-Ancestries-by-County.jpg Census 2000 Map - Top U.S. Ancestries by County]</ref> Only eight Kentucky counties list an ancestry other than "American" as the county's largest, those being [[Christian County, Kentucky|Christian]] and [[Fulton County, Kentucky|Fulton]], where African American is the largest reported ancestry, and the state's most urban counties of [[Jefferson County, Kentucky|Jefferson]], [[Oldham County, Kentucky|Oldham]], [[Lexington, Kentucky|Fayette]], [[Boone County, Kentucky|Boone]], [[Kenton County, Kentucky|Kenton]], and [[Campbell County, Kentucky|Campbell]], where German is the largest reported ancestry.<ref name="census-ancestries" />Southeastern Kentucky was populated by a large group of Native Americans of mixed heritage, also known as [[Melungons]], in the early 19th century. Groups like the [[Ridgetop Shawnee]] are organizing the descendants of those early Native American settlers. | + | The five largest ancestries in the commonwealth are: [[American ancestry|American]] (20.9 percent) (Mostly of [[Britain|British]] ancestry), [[Germany|German]] (12.7 percent), [[Ireland|Irish]] (10.5 percent), [[England|English]] (9.7 percent), [[African American]] (7.8 percent). Only eight Kentucky counties list an ancestry other than "American" as the county's largest, those being [[Christian County, Kentucky|Christian]] and [[Fulton County, Kentucky|Fulton]], where African-American is the largest reported ancestry, and the state's most urban counties of [[Jefferson County, Kentucky|Jefferson]], Oldham, Fayette, Boone, Kenton, and Campbell, where German is the largest reported ancestry. Southeastern Kentucky was populated by a large group of [[Native American]]s of mixed heritage, also known as [[Melungeon|Melungons]], in the early nineteenth century. |
| | | | |
| − | African Americans, who made up one-fourth of Kentucky's population prior to the [[American Civil War|Civil War]], declined in number as many moved to the industrial North in the [[Great Migration (African American)|Great Migration]]. Today 44.2% of Kentucky's African American population is in Jefferson County and 52% are in the Louisville Metro Area. Other areas with high concentrations, besides Christian and Fulton Counties, are the city of [[Paducah, Kentucky|Paducah]], the Bluegrass, and the city of [[Lexington, Kentucky|Lexington]]. Many mining communities in far Southeastern Kentucky also have populations between five and 10 percent African American. | + | African-Americans, who made up one-fourth of Kentucky's population prior to the [[American Civil War|Civil War]], declined in number as many moved to the industrial North in the [[Great Migration (African American)|Great Migration]]. Today 44.2 percent of Kentucky's African-American population is in Jefferson County and 52 percent are in the Louisville Metro Area. Other areas with high concentrations, besides Christian and Fulton Counties, are the city of [[Paducah, Kentucky|Paducah]], the Bluegrass, and the city of [[Lexington, Kentucky|Lexington]]. Many [[mining]] communities in far southeastern Kentucky also have populations that are between 5 and 10 percent African-American. |
| − | {{US Demographics}}
| |
| | | | |
| | ===Religion=== | | ===Religion=== |
| | [[Image:CollegeoftheBible-LexKY.JPG|right|thumb|Lexington Theological Seminary (then College of the Bible), 1904.]] | | [[Image:CollegeoftheBible-LexKY.JPG|right|thumb|Lexington Theological Seminary (then College of the Bible), 1904.]] |
| − | In 2000, The Association of Religion Data Archives reported<ref name=ARDA>{{cite web |url=http://www.thearda.com/mapsReports/reports/state/21_2000.asp |title=State Membership Report |publisher=The Association of Religion Data Archives |year=2000 |accessdate=2006-12-27}}</ref> that of Kentucky's 4,041,769 residents:
| + | [[Religion|Religious]] movements were important in the early history of Kentucky. Perhaps the most famous event was the interdenominational revival in August 1801 at the Cane Ridge Meeting house in Bourbon County. As part of what is now known as the "Western Revival," thousands began meeting around a [[Presbyterianism|Presbyterian]] communion service on August 6, 1801, and ended six days later on August 12, 1801 when both humans and horses ran out of food.<ref>E. Michael Rusten, 2003. ''The One Year Book of Christian History.'' (Wheaton, IL. Tyndale House. ISBN 0842355073.)</ref> Some claim that the Cane Ridge revival was propagated from an earlier [[camp meeting]] at Red River Meeting House in Logan County. |
| − | | |
| − | *33.68% were members of [[Evangelicalism|evangelical Protestant]] churches
| |
| − | **[[Southern Baptist Convention]] (979,994 members, 24.25%)
| |
| − | **[[Independent Christian Churches/Churches of Christ]] (106,638 members, 2.64%)
| |
| − | **[[Church of Christ]] (58,602 members, 1.45%)
| |
| − | *10.05% were [[Roman Catholic church|Roman Catholics]]
| |
| − | *8.77% belonged to [[Mainline (Protestant)|mainline Protestant]] churches
| |
| − | **[[United Methodist Church]] (208,720 members, 5.16%)
| |
| − | **[[Christian Church (Disciples of Christ)]] (67,611 members, 1.67%)
| |
| − | *0.05% were members of [[orthodox churches]]
| |
| − | *0.88% were affiliated with other theologies
| |
| − | *46.57% were not affiliated with any church.
| |
| | | | |
| − | Today Kentucky is home to several seminaries. [[Southern Baptist Theological Seminary]] in [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]] is the principal seminary for the [[Southern Baptist Convention]]. Louisville is also the home of the [[Louisville Presbyterian Theological Seminary]]. Lexington has two seminaries, [[Lexington Theological Seminary]], and the Baptist Seminary of Kentucky. [[Asbury Theological Seminary]] is located in nearby [[Wilmore, Kentucky|Wilmore]]. In addition to seminaries, there are several colleges affiliated with denominations. [[Transylvania University|Transylvania]] in [[Lexington, Kentucky|Lexington]] is affiliated with the [[Christian Church (Disciples of Christ)|Disciples of Christ]]. In Louisville, [[Bellarmine University|Bellarmine]] and [[Spalding University|Spalding]] are affiliated with the [[Roman Catholic Church]]. In [[Owensboro, Kentucky]], [[Kentucky Wesleyan College]] is associated with the Methodist Church and [[Brescia University]] is associated with the Roman Catholic Church. Louisville is also home to the headquarters of the [[Presbyterian Church (USA)]] and their printing press. Louisville is also home to a sizable [[Muslim]]<ref>[http://www.irfi.org/articles/articles_101_150/muslims_in_louisville.htm Muslims in Louisville]</ref> and [[Jew]]ish population.
| + | In 2000, the Association of Religion Data Archives reported <ref name=ARDA> ''Association of Religion Data Archives''. 2000. [http://www.thearda.com/mapsReports/reports/state/21_2000.asp State Membership Report] Retrieved September 26, 2008.</ref> that of Kentucky's 4,041,769 residents: |
| | | | |
| − | ====Religious movements====
| + | *33.68 percent were members of [[Evangelicalism|evangelical Protestant]] churches |
| − | Religious movements were important in the early history of Kentucky. Perhaps the most famous event was the interdenominational revival in August 1801 at the [[Cane Ridge, Kentucky|Cane Ridge]] Meeting house in [[Bourbon County, Kentucky|Bourbon County]]. As part of what is now known as the "Western Revival", thousands began meeting around a [[Presbyterianism|Presbyterian]] [[Eucharist|communion]] service on [[August 6]], [[1801]], and ended six days later on [[August 12]], [[1801]] when both humans and horses ran out of food.<ref>See E. Michael Rusten, ''The One Year Book of Christian History'', Tyndale House, 2003, pp. 438–439. ISBN 0842355073.</ref> Some claim that the [[Cane Ridge, Kentucky|Cane Ridge]] revival was propagated from an earlier [[camp meeting]] at [[Red River Meeting House]] in [[Logan County, Kentucky|Logan County]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.piney.com/CaneRidge1.html |title=Kentucky Revival - Red River to Cane Ridge |accessdate=2006-12-27}}</ref>
| + | **[[Southern Baptist Convention]] (979,994 members, 24.25 percent) |
| | + | **[[Independent Christian Churches/Churches of Christ]] (106,638 members, 2.64 percent) |
| | + | **[[Church of Christ]] (58,602 members, 1.45 percent) |
| | + | *10.05 percent were [[Roman Catholic church|Roman Catholics]] |
| | + | *8.77 percent belonged to [[Mainline (Protestant)|mainline Protestant]] churches |
| | + | **[[United Methodist Church]] (208,720 members, 5.16 percent) |
| | + | **[[Christian Church (Disciples of Christ)]] (67,611 members, 1.67 percent) |
| | + | *0.05 percent were members of [[Orthodox]] churches |
| | + | *0.88 percent were affiliated with other theologies |
| | + | *46.57 percent were not affiliated with any church. |
| | | | |
| | ==Economy== | | ==Economy== |
| − | [[Image:Kentucky quarter, reverse side, 2001.jpg|left|50px]] | + | [[Image:Kentucky quarter, reverse side, 2001.jpg|left|thumb|125px]] |
| − | [[Image:2007-Toyota-Camry-SE.jpg|thumb|right|The best selling car in the United States, the [[Toyota Camry]], is manufactured in [[Georgetown, Kentucky]].]]
| + | The total gross state product for 2006 was US$146 billion, 27<sup>th</sup> in the nation. Its per-capita personal income was US$28,513, 43<sup>rd</sup> in the nation.<ref> ''Kentucky Cabinet for Economic Development''. [http://www.thinkkentucky.com/kyedc/pdfs/kyecotrd.pdf Kentucky Economy] Retrieved September 26, 2008. </ref> |
| − | [[Image:2004-2007 Ford F-150 Lariat.jpg|thumb|right|The best selling truck in the United States, the [[Ford F-Series]], is manufactured in [[Louisville, Kentucky]].]]
| |
| − | The total gross state product for 2006 was US$146 billion, 27<sup>th</sup> in the nation. Its per-capita personal income was US$28,513, 43<sup>rd</sup> in the nation.<ref>[http://www.thinkkentucky.com/kyedc/pdfs/kyecotrd.pdf Kentucky Cabinet for Economic Development - Kentucky Economy]</ref> Kentucky's agricultural outputs are [[horse]]s, [[cattle]], [[tobacco]], [[dairy product]]s, [[hog (swine)|hogs]], [[soybean]]s, and [[maize|corn]]. Its industrial outputs are transportation equipment, chemical products, electric equipment, machinery, food processing, tobacco products, [[coal]], and [[tourism]]. The [[Eastern Mountain Coal Fields|Eastern Kentucky Coal Fields]] are recognized as being among the most productive in the nation. | |
| | | | |
| − | Kentucky ranks 4<sup>th</sup> among U.S. states in the number of automobiles and trucks assembled.<ref>{{cite web | + | Kentucky's [[agriculture|agricultural]] outputs are [[horse]]s, [[cattle]], [[tobacco]], [[dairy product]]s, [[hog (swine)|hogs]], [[soybean]]s, and [[maize|corn]]. Its industrial outputs are transportation equipment, [[chemical]] products, electric equipment, [[machinery]], [[food processing]], tobacco products, [[coal]], and [[tourism]]. The eastern Kentucky coal fields are recognized as being among the most productive in the nation. |
| − | | url = http://www.tradeandindustrydev.com/issues/article.asp?ID=66 | |
| − | | title = Kentucky: In the Middle of Auto Alley | |
| − | | accessdate =
| |
| − | | accessdaymonth = 10
| |
| − | | accessmonthday = August
| |
| − | | accessyear = 2007
| |
| − | | author = Marvin E. Strong
| |
| − | | last = Strong
| |
| − | | first = Marvin
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | date =
| |
| − | | year =
| |
| − | | month =
| |
| − | | format =
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher = Trade and Industry Development
| |
| − | | pages =
| |
| − | | language =
| |
| − | | archiveurl =
| |
| − | | archivedate =
| |
| − | | quote =
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | </ref> The [[Chevrolet Corvette]], [[Cadillac XLR]], [[Ford Explorer]], Ford Super Duty trucks, [[Toyota Camry]], [[Toyota Avalon]], and [[Toyota Solara]] are assembled in Kentucky.
| |
| | | | |
| − | Unlike many bordering states which developed a widespread industrial economy, much of rural Kentucky has maintained a farm based economy, with cattle, corn, and soybeans being the main crops. The area immediately outside Lexington is also the leading region for breeding [[Thoroughbred]] racing horses, due to the high [[calcium]] content in the soil. Despite being the 14<sup>th</sup> smallest state in terms of land area, Kentucky still ranks 5<sup>th</sup> in the total number of farms, with more farms per square mile than any other U.S. state.<ref>[http://www.nass.usda.gov/census/census02/volume1/us/st99_2_008_008.pdf U.S. Department of Agriculture 2002 Census of Agriculture]</ref> The average farm size in Kentucky is only {{convert|153|acre|km2|1}}.<ref>{{cite journal |year=2003 |month=March |title=Kentucky Farm Numbers Increase |journal=Kentucky Agri-News |volume=22 |issue=5 |accessdate=2007-05-03 |url=http://www.nass.usda.gov/ky/AgriNews/mar122.pdf |format={{dead link|date=June 2008}} – <sup>[http://scholar.google.co.uk/scholar?hl=en&lr=&q=intitle%3AKentucky+Farm+Numbers+Increase&as_publication=Kentucky+Agri-News&as_ylo=2003&as_yhi=2003&btnG=Search Scholar search]</sup> }}</ref>
| + | Kentucky ranks 4<sup>th</sup> among U.S. states in the number of automobiles and trucks assembled. The Chevrolet Corvette, Cadillac XLR, Ford Explorer, Ford Super Duty trucks, Toyota Camry, Toyota Avalon, and Toyota Solara are assembled in Kentucky. |
| | + | [[Image:Bourbon barrels.jpg|right|thumb|[[Oak]] [[casks]] used to store and age bourbon at Kentucky's Buffalo Trace Distillery.]] |
| | | | |
| − | Kentucky ranks 5th nationally in goat farming, 8th in beef cattle production,<ref> {{cite web | + | Unlike many bordering states, which developed a widespread industrial economy, much of rural Kentucky has maintained a farm-based economy, with [[cattle]], [[corn]], and [[soybean]]s being the main crops. The area immediately outside Lexington is also the leading region for breeding [[thoroughbred]] racing [[horse]]s, due to the high [[calcium]] content in the soil. Despite being the 14<sup>th</sup> smallest state in terms of land area, Kentucky still ranks 5<sup>th</sup> in the total number of farms, with more farms per square mile than any other U.S. state.<ref>''U.S. Department of Agriculture''. 2002. [http://www.nass.usda.gov/census/census02/volume1/us/st99_2_008_008.pdf Farms, Land in Farms, Value of Land and Buildings, and Land Use: 2002 and 1997] Retrieved September 26, 2008.</ref> The average farm size in Kentucky is only {{convert|153|acre|km2|1}}. Kentucky ranks 5th nationally in [[goat]] farming, 8th in beef [[cattle] production, and 14th in corn production. |
| − | | url = http://www.bamabeef.org/NewStateandCountyrankings05.htm
| |
| − | | title = 2007 Rankings of States and Counties
| |
| − | | accessdate =
| |
| − | | accessdaymonth = 1
| |
| − | | accessmonthday = May
| |
| − | | accessyear = 2007
| |
| − | | author =
| |
| − | | last =
| |
| − | | first =
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | date =
| |
| − | | year =
| |
| − | | month =
| |
| − | | format =
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher = bamabeef.org
| |
| − | | pages =
| |
| − | | language =
| |
| − | | archiveurl =
| |
| − | | archivedate =
| |
| − | | quote =
| |
| − | }} </ref> and 14th in corn production.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.econedlink.org/lessons/EM453/docs/em453_Corn_Production_Det_Answers.pdf |title=Corn Production Detective |publisher=National Council on Economic Education |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-05-03}}</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===State taxes===
| + | Since 2003, high-end [[Bourbon whiskey|bourbon]]s (aged more than six years) have seen revenue grow from $450 million to over $500 million, some 2.2 million cases, in the United States. High-end bourbon sales accounted for 8 percent of total spirits growth in 2006. In 2007, United States spirits exports, virtually all of which are American whiskey, exceeded $1 billion for the first time. This represents a 15 percent increase over 2006. American whiskey is now sold in more than 100 different countries. The leading markets are the [[United Kingdom]], [[Canada]], [[Germany]], [[Australia]], and [[Japan]]. Key emerging markets for American whiskey are [[China]], [[Vietnam]], [[Brazil]], [[Chile]], [[Romania]], and [[Bulgaria]]. More than 95 percent of the world’s Bourbon is distilled and aged in Kentucky.<ref>''Kentucky Bourbon Trail''. [http://www.kybourbontrail.com/#tour Sampler Tour] Retrieved October 22, 2008.</ref> |
| − | There are 5 [[income tax]] brackets, ranging from 2% to 6% of personal income.<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url = http://swz.salary.com/salarywizard/layouthtmls/swzl_statetaxrate_KY.html
| |
| − | | title = Kentucky Income Tax Rates
| |
| − | | accessmonthday = May 1
| |
| − | | accessyear = 2007
| |
| − | | author =
| |
| − | | last =
| |
| − | | first =
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | date =
| |
| − | | year =
| |
| − | | month =
| |
| − | | format =
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher = salary. com
| |
| − | | pages =
| |
| − | | language =
| |
| − | | archiveurl =
| |
| − | | archivedate =
| |
| − | | quote =
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | </ref> The sales tax rate in Kentucky is 6%.<ref> {{cite web
| |
| − | | url = http://revenue.ky.gov/business/salesanduse.htm
| |
| − | | title = Sales & Use Tax
| |
| − | | accessmonthday = May 1
| |
| − | | accessyear = 2007
| |
| − | | author =
| |
| − | | last =
| |
| − | | first =
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | date =
| |
| − | | year =
| |
| − | | month =
| |
| − | | format =
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher = Kentucky Department of Revenue
| |
| − | | pages =
| |
| − | | language =
| |
| − | | archiveurl =
| |
| − | | archivedate =
| |
| − | | quote =
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | </ref> Kentucky has a broadly based classified [[property tax]] system. All classes of property, unless exempted by the Constitution, are taxed by the state, although at widely varying rates.<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url = http://revenue.ky.gov/business/proptax.htm
| |
| − | | title = Property Tax
| |
| − | | accessmonthday = May 1
| |
| − | | accessyear = 2007
| |
| − | | author =
| |
| − | | last =
| |
| − | | first =
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | date =
| |
| − | | year =
| |
| − | | month =
| |
| − | | format =
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher = Kentucky Department of Revenue
| |
| − | | pages =
| |
| − | | language =
| |
| − | | archiveurl =
| |
| − | | archivedate =
| |
| − | | quote =
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | </ref> Many of these classes are exempted from taxation by local government. Of the classes that are subject to local taxation, three have special rates set by the [[Kentucky General Assembly|General Assembly]], one by the [[Kentucky Supreme Court]] and the remaining classes are subject to the full local rate, which includes the tax rate set by the local taxing bodies plus all voted levies. Real property is assessed on 100% of the fair market value and property taxes are due by [[December 31]]. Once the primary source of state and local government revenue, property taxes now account for only about 6% of the Kentucky's annual General Fund revenues.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.bankrate.com/yho/itax/edit/state/profiles/state_tax_Ky.asp |title= State Taxes - Kentucky - Overview|accessdate=2007-05-01 |last= |first= |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher=bankrate.com |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }}
| |
| − | </ref> | |
| | | | |
| − | Until [[January 1]], [[2006]], Kentucky imposed a tax on intangible personal property held by a taxpayer on [[January 1]] of each year. The Kentucky intangible tax was repealed under House Bill 272.<ref>{{cite web
| + | [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]], from 1927 to 2004, was home to [[Brown & Williamson]], the third largest company in the [[tobacco industry]] before merging with [[R. J. Reynolds]] in 2004 to form the [[Reynolds American]] Company. Brown & Williamson, one of the subjects of the tobacco industry [[corporate scandal|scandal]]s of the 1990s, was the focus of [[The Insider (film)|''The Insider'']], a 1999 film shot around the Louisville area. The end of the federal [[tobacco]] program in 2004, and the government-guaranteed prices that went with it, have forced many Kentucky growers to attempt various farming alternatives. Burley (cigarette tobacco) production was expected to total 144.9 million pounds on 69,000 acres in 2008, down from 470.4 million pounds on 240,000 acres in 1997. A growing number of cities and counties are passing restrictions on smoking, even in the heart of Kentucky's tobacco-growing region. |
| − | | url = http://www.lrc.ky.gov/record/05rs/HB272.htm
| |
| − | | title = Text of the House Bill 272
| |
| − | | accessdate =
| |
| − | | accessdaymonth = 10
| |
| − | | accessmonthday = August
| |
| − | | accessyear = 2007
| |
| − | | author =
| |
| − | | last =
| |
| − | | first =
| |
| − | | authorlink =
| |
| − | | coauthors =
| |
| − | | date =
| |
| − | | year =
| |
| − | | month =
| |
| − | | format =
| |
| − | | work =
| |
| − | | publisher = State of Kentucky
| |
| − | | pages =
| |
| − | | language =
| |
| − | | archiveurl =
| |
| − | | archivedate =
| |
| − | | quote =
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | </ref> Intangible property consisted of any property or investment which represents evidence of value or the right to value. Some types of intangible property included: bonds, notes, retail [[repurchase agreement]]s, accounts receivable, trusts, enforceable contracts sale of real estate (land contracts), money in hand, money in [[safe deposit box]]es, annuities, interests in estates, loans to stockholders, and commercial paper.
| |
| | | | |
| − | ==="Unbridled Spirit"=== | + | ==Culture== |
| − | [[Image:Kentucky.JPG|left|thumb|Kentucky state welcome sign]] | + | [[Image:Derby.jpg|250px|thumb|The Kentucky Derby. Image courtesy of [http://kentuckytourism.com/ Kentucky Dept. of Travel].]] |
| | + | Although Kentucky's culture is generally considered to be [[Southern culture|southern]], it is unique and also influenced by the [[Midwestern United States|Midwest]] and southern [[Appalachia]]. Kentucky was a [[slavery|slave]] state, and [[African-American]]s once comprised over one-quarter of its population. However, it lacked the [[cotton]] plantation system and never had the same high percentage of African-Americans as most other slave states. Kentucky adopted the [[Jim Crow laws|Jim Crow]] system of [[racial segregation]] in most public spheres after the [[American Civil War|Civil War]], but the state never disenfranchised African-American citizens to the level of the [[Deep South]] states, and it peacefully integrated its schools after the 1954 ''[[Brown v. Board of Education]]'' verdict, later adopting the first state [[civil rights]] act in the South in 1966. |
| | | | |
| − | To boost Kentucky’s image, give it a consistent reach, and help Kentucky "stand out from the crowd", former Governor [[Ernie Fletcher]] launched a comprehensive [[brand]]ing campaign with the hope of making its $12 - $14 million advertising budget more effective. The "Unbridled Spirit" brand was the result of a $500,000 contract with New West, a Kentucky-based public relations advertising and marketing firm to develop a viable brand and tag line. The administration has been aggressively marketing the brand in both the public and private sectors. The "Welcome to Kentucky" signs at border areas have Unbridled Spirit's symbol on them.
| + | Louisville is home to a number of annual cultural events. Perhaps most well-known is the [[Kentucky Derby]], held annually during the first Saturday of May. The Derby is preceded by a two-week long [[Kentucky Derby Festival]], which starts with the annual [[Thunder Over Louisville]], the largest annual [[Fireworks|fireworks display]] in the nation. The Kentucky Derby Festival also features notable events such as the Pegasus Parade, The Great Steamboat Race, Great [[Balloon flight contest|Balloon Race]], a [[marathon (sport)|marathon]], and about 70 events in total. ''Esquire'' magazine has called the Kentucky Derby "the biggest party in the south." |
| | | | |
| − | The previous campaign was neither a failure nor a success. Kentucky's "It's that friendly" slogan hoped to draw more people into the state based of the idea of southern hospitality. Though most Kentuckians liked the slogan, as it embraced southern values, it was also not an image that encouraged tourism as much as initially hoped for. Therefore it was necessary to reconfigure a slogan to embrace Kentucky as a whole while also encouraging more people to visit the Bluegrass.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://kentucky.gov/unbridledspirit/info.htm |title=Unbridled Spirit→Information |accessdate=2007-05-01 |last= |first= |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher=State of Kentucky |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }}
| + | ==Notes== |
| − | </ref> | + | <references/> |
| | | | |
| − | ==Transportation== | + | ==References== |
| − | ===Roads=== | + | ===Geography and geology=== |
| − | [[Image:Picture 697.jpg|thumb|right|At {{convert|464|mi|km}} long, [[Kentucky Route 80]] is the longest route in Kentucky, pictured here west of [[Somerset, KY|Somerset]].]] | + | * ''U.S. Energy Information Administration''. [http://tonto.eia.doe.gov/state/state_energy_profiles.cfm?sid=KY Kentucky State Energy Profiles] Retrieved September 23, 2008. |
| − | {{seealso|List of Kentucky State Highways}}
| + | *''U.S. Geological Survey''. [http://www.usgs.gov/state/state.asp?State=KY Science In Your Backyard: Kentucky] Retrieved September 23, 2008. |
| − | Kentucky is served by five major [[Interstate Highway System|interstate highways]] ([[Interstate 75|I-75]], [[Interstate 71|I-71]], [[Interstate 64|I-64]], [[Interstate 65|I-65]], [[Interstate 24|I-24]]), nine [[parkway]]s, and three bypasses and spurs. The parkways were originally [[toll road]]s, but on [[November 22]], [[2006]], Governor [[Ernie Fletcher]] ended the toll charges on the [[William H. Natcher Parkway]] and the [[Audubon Parkway]], the last two parkways in Kentucky to charge tolls for access.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.kctcs.net/todaysnews/index.cfm?tn_date=2006-09-28#6693 |title=Fletcher:Tolls to end [[November 22]] |accessdate=2007-05-01 |last=Stinnett |first=Chuck|authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher=Henderson Gleaner |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }}
| + | ===Politics=== |
| − | </ref> The related [[toll booth]]s have been demolished.<ref> {{cite web
| + | *Jewell, Malcolm E. and Everett W. Cunningham. ''Kentucky Politics.'' Univ. of Kentucky Press, 1968. |
| − | | url = http://www.courierpress.com/news/2006/nov/22/onlookers-cheer-booth-destruction-at-ceremony/
| + | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=3096856 Miller, Penny M. ''Kentucky Politics & Government: Do We Stand United?'' (1994)] ''Questia''. Retrieved September 23, 2008. |
| − | | title = Onlookers Cheer Booth Destruction at Ceremony
| + | ===History=== |
| − | | accessdate =
| + | ====Surveys and reference==== |
| − | | accessdaymonth = 10
| + | *Bodley, Temple and Samuel M. Wilson. ''History of Kentucky.'' 4 vols. 1928. |
| − | | accessmonthday = August
| + | *[[Harry M. Caudill|Caudill, Harry M.]], ''Night Comes to the Cumberlands: A Biography of a Depressed Area.'' (1963). reprint ed. Jesse Stuart Foundation, 2001. ISBN 1931672008 |
| − | | accessyear = 2007
| + | *Channing, Steven. ''Kentucky: A Bicentennial History.'' W. W. Norton and American association for State and Local History. 1977. |
| − | | author = Chuck Stinnett
| + | *Clark, Thomas Dionysius. ''A History of Kentucky.'' (many editions, 1937–1992). Jesse Stuart Foundation, ISBN 0945084307 |
| − | | last = Stinnett
| + | *Collins, Lewis. ''History of Kentucky.'' (1880). |
| − | | first = Chuck
| + | *Harrison, Lowell H. and James C. Klotter. ''A New History of Kentucky.'' University Press of Kentucky, 1997. ISBN 081312008X |
| − | | authorlink =
| + | *Klotter, James C. ''Our Kentucky: A Study of the Bluegrass State.'' 2000, high school text. |
| − | | coauthors =
| + | *Lucas, Marion Brunson and Wright, George C. ''A History of Blacks in Kentucky.'' 2 vols. (1992). Vol. 1: ''From Slavery to Segregation, 1760-1891,'' 2nd ed. Kentudky Historical Society, 2003. ISBN 0916968324. ''A History of Blacks in Kentucky: In Pursuit of Equality, 1890-1980.'' 1992. ISBN 0916968219. |
| − | | date = 2006-11-22
| + | *''University of Kentucky''. Notable Kentucky African Americans. |
| − | | year = 2006
| + | *Share, Allen J. ''Cities in the Commonwealth: Two Centuries of Urban Life in Kentucky.'' Univ Pr of Kentucky, 1982. ISBN 0813102529 |
| − | | month = November
| + | *Wallis, Frederick A. and Hambleton Tapp. ''A Sesqui-Centennial History of Kentucky'' 4 vols. (1945). |
| − | | format =
| + | *Ward, William S. ''A Literary History of Kentucky.'' 1988. ISBN 087049578X. |
| − | | work =
| + | *''Federal Writers' Project of the Work Projects Administration for the State of Kentucky.'' [http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=99066764 WPA, ''Kentucky: A Guide to the Bluegrass State'' (1939)] Retrieved September 23, 2008. |
| − | | publisher = Courier Press
| + | *Yater, George H. ''Two Hundred Years at the Fall of the Ohio: A History of Louisville and Jefferson County,'' 2nd ed. The Filson Historical Society, 1987. ISBN 0960107231 |
| − | | pages =
| |
| − | | language =
| |
| − | | archiveurl =
| |
| − | | archivedate =
| |
| − | | quote =
| |
| − | }}
| |
| − | </ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | Ending the tolls some seven months ahead of schedule was generally agreed to have been a positive economic development for transportation in Kentucky. In June 2007, a law went into effect raising the speed limit on rural portions of Kentucky Interstates from 65 to 70 [[miles per hour]].<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.courier-journal.com/apps/pbcs.dll/article?AID=2007706260437|publisher=[[Courier-Journal]]|title=Many new laws go on books today|author=Steitzer, Stephanie|date=2007-06-26}}</ref>
| + | ====Specialized scholarly studies==== |
| − | | + | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=105132587 Bakeless, John. ''Daniel Boone, Master of the Wilderness'' (1989)] ''Questia''. Retrieved September 23, 2008. |
| − | [[Greyhound Lines|Greyhound]] provides bus service to most major towns in the state.
| + | *Blakey, George T. ''Hard Times and New Deal in Kentucky, 1929–1939.'' 1986. |
| − | | + | *Coulter, E. Merton. ''The Civil War and Readjustment in Kentucky.'' (1926) |
| − | ===Rails===
| + | *Faragher, John Mack. ''Daniel Boone: The Life and Legend of an American Pioneer.'' holt, 1993. ISBN 0805030077 |
| − | [[Image:Picture 467.jpg|thumb|right|[[High Bridge of Kentucky (bridge)|High Bridge]] over the [[Kentucky River]] was the tallest rail bridge in the world when it was completed in 1877.]]
| + | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=6471305 Fenton, John H. ''Politics in the Border States: A Study of the Patterns of Political Organization, and Political Change, Common to the Border States: Maryland, West Virginia, Kentucky, and Missouri'' (1957)] ''Questia''. Retrieved September 23, 2008. |
| − | {{seealso|List of Kentucky railroads}}
| + | *Ireland, Robert M. ''The County in Kentucky History.'' (1976) |
| − | | + | *Klotter, James C. et al. ''Kentucky's Civil War 1861–1865.'' ed. Jerlene Rose. Back Home In Kentucky Inc., 2005. ISBN 0976923114 |
| − | *[[Ashland, Kentucky (Amtrak station)]]
| + | *Klotter, James C. ''Kentucky: Portrait in Paradox, 1900–1950.'' (1992) Kentucky Historical Society, 2001. |
| − | *[[South Portsmouth-South Shore (Amtrak station)]]
| + | *Pearce, John, Ed. ''Divide and Dissent: Kentucky Politics, 1930–1963.'' University Press of Kentucky, 1991. ISBN 0813108047 |
| − | *[[Fulton (Amtrak station)]] | + | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=100662336 Sonne, Niels Henry. ''Liberal Kentucky, 1780–1828'' (1939)] Questia. Retrieved September 23, 2008. |
| − | | + | *Tapp, Hambleton and James C Klotter. ''Kentucky Decades of Discord, 1865–1900.'' (1977) |
| − | [[Amtrak]], the national passenger rail system, provides service to [[Ashland, Kentucky|Ashland]], [[South Shore, Kentucky|South Portsmouth]] and [[Fulton, Kentucky]]. The [[Cardinal and Hoosier State|Cardinal]], Trains 50 and 51, is the line that offers Amtrak service to Ashland and South Portsmouth. Amtrak Trains 58 and 59, the [[City of New Orleans]] serves Fulton. The [[Northern Kentucky]] area, is served by the Cardinal at the [[Cincinnati Museum Center at Union Terminal]]. The Museum Center is just across the [[Ohio River]] in [[Cincinnati]].
| + | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=61648056 Townsend, William H. ''Lincoln and the Bluegrass: Slavery and Civil War in Kentucky'' (1955)] Questia. Retrieved September 23, 2008. |
| − | | + | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=14459929 Waldrep, Christopher ''Night Riders: Defending Community in the Black Patch, 1890–1915'' (1993)] Questia. Retrieved September 23, 2008. |
| − | As of 2004, there were approximately 2,640 miles (4,250.4 km) of railways in Kentucky, with about 65% of those being operated by [[CSX Transportation]]. [[Coal]] was by far the most common cargo, accounting for 76% of cargo loaded and 61% of cargo delivered.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.aar.org/PubCommon/Documents/AboutTheIndustry/RRState_KY.pdf |title= Railroad Service in Kentucky|accessdate=2007-05-01 |last= |first= |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher= Association of American Railroads|pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }} Also, Norfolk Southern's main north-south line runs through central and southern Kentucky, starting in Cincinnati. Formerly the CNO&TP subsidiary of Southern Railway, it is NS's most profitable line.
| |
| − | </ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[Bardstown, Kentucky|Bardstown]] features a tourist attraction known as ''My Old Kentucky Dinner Train''. Run along a {{convert|20|mi|km|-1|sing=on}} stretch of rail purchased from [[CSX Transportation|CSX]] in 1987, guests are served a four-course meal as they make a two-and-a-half hour round-trip between [[Bardstown, Kentucky|Bardstown]] and Limestone Springs.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.cincinnati.com/visitorsguide/stories/071100_dinnertrain.html |title= On the Right Track - Kentucky Dinner Train serves up railroad nostalgia|accessdate=2007-05-01 |last=Knight|first=Andy |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher=Cincinnati.com|pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }}
| |
| − | </ref> The [[Kentucky Railway Museum]] is located in nearby [[New Haven, Kentucky|New Haven]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.kyrail.org/ |title= Kentucky Railway Museum|accessdate=2007-05-01 |last= |first= |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher= |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }}
| |
| − | </ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Other areas in Kentucky are reclaiming old railways in [[rail trail]] projects. One such project is Louisville's [[Big Four Bridge (Louisville)|Big Four Bridge]]. If completed, the [[Big Four Bridge (Louisville)|Big Four Bridge]] [[rail trail]] will contain the second longest pedestrian-only bridge in the world.<ref>{{cite news|publisher=Courier-Journal|title=Bridges money may be shifted|last=Shafer|first=Sheldon|date=2007-03-05}}</ref> The longest pedestrian-only bridge is also found in Kentucky — the [[Newport Southbank Bridge]], popularly known as the "Purple People Bridge", connecting [[Newport, Kentucky|Newport]] to [[Cincinnati, Ohio]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.enquirer.com/editions/2003/04/20/loc_purplebridge20.html |title= Meet the Purple People Bridge|accessdate=2007-05-01 |last= Crowley|first= Patrick|authorlink= |coauthors= |date=[[April 23]], [[2003]] |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher= Cincinnati Enquirer|pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }}
| |
| − | </ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Air===
| |
| − | {{seealso|List of airports in Kentucky}}
| |
| − | Kentucky's primary airports include [[Louisville International Airport]] (Standiford Field), [[Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport]], and [[Blue Grass Airport]]. Louisville International Airport is home to [[United Parcel Service|UPS]]'s [[Worldport (UPS air hub)|Worldport]], its international air-sorting hub.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.flylouisville.com/about/fastfacts.asp |title= Fast Facts|accessdate=2007-09-11 |last= |first= |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher=Louisville International Airport |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }}
| |
| − | </ref> There are also a number of regional airports scattered across the state.
| |
| − | | |
| − | On [[August 27]], [[2006]], Kentucky's [[Blue Grass Airport]] in [[Lexington, Kentucky|Lexington]] was the site of a crash that killed 47 passengers and 2 crew members aboard a [[Bombardier Canadair Regional Jet]] designated [[Comair Flight 191]], or Delta Air Lines Flight 5191, sometimes mistakenly identified by the press as Comair Flight 5191.<ref>[http://www.kentucky.com/mld/kentucky/news/special_packages/crash/15378422.htm Crash Kills 49]</ref> The lone survivor was the flight's [[first officer]], James Polehinke, who doctors determined to be brain damaged and unable to recall the crash at all.<ref>{{cite web |url= http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2006/10/03/national/main2059120.shtml |title=Comair Crash Survivor Leaves Hospital |accessdate=2007-05-01 |last= |first= |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher=CBS |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Water===
| |
| − | [[Image:Picture 1650.jpg|thumb|right|A barge hauling coal in the [[Louisville and Portland Canal]], the only man made section of the [[Ohio River]]]]
| |
| − | Being bounded by the two largest rivers in [[North America]], water transportation has historically played a major role in Kentucky's economy. Most barge traffic on Kentucky waterways consists of coal that is shipped from both the Eastern and Western Coalfields, about half of which is used locally to power many power plants located directly off the [[Ohio River]], with the rest being exported to other countries, most notably [[Japan]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | Many of the largest ports in the United States are located in or adjacent to Kentucky, including:
| |
| − | *Huntington/Tri-State (includes Ashland, KY), largest inland port and 7th largest overall
| |
| − | *Cincinnati-Northern Kentucky, 5th largest inland port and 43rd overall
| |
| − | *Louisville-Southern Indiana, 7th largest inland port and 55th overall | |
| − | | |
| − | As a state, Kentucky ranks 10th overall in port tonage.<ref>[http://www.iwr.usace.army.mil/ndc/wcsc/pdf/inlandport03f.pdf Top 20 Inland U.S. Ports for 2003]</ref><ref>[http://www.iwr.usace.army.mil/ndc/wcsc/portton01.htm CY 2001 Tonnage for Selected U.S. Ports by Port Tons]</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The only natural obstacle along the entire length of the Ohio River was the [[Falls of the Ohio]], located just west of [[Downtown Louisville]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Subdivisions and settlements==
| |
| − | ===Counties===
| |
| − | {{seealso|List of counties in Kentucky|Fiscal Court}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | Kentucky is subdivided into 120 [[county (United States)|counties]], the largest being [[Pike County, Kentucky]] at 787.6 [[square miles]], and the most populous being [[Jefferson County, Kentucky]] (the county containing [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville Metro]]) with 693,604 residents as of 2000.<ref>[http://www.uky.edu/KentuckyAtlas/kentucky-counties.html Kentucky Counties], University of Kentucky</ref> | |
| − | | |
| − | County government, under the [[Kentucky Constitution]] of 1891, is vested in the [[County Judge/Executive]]), (formerly called the County Judge) who serves as the [[Executive (government)|executive]] head of the county, and a [[legislature]] called a [[Fiscal Court]]. Despite the unusual name, the Fiscal Court no longer has [[judiciary|judicial]] functions.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Consolidated city-county governments===
| |
| − | Kentucky's two most populous counties, Jefferson and Fayette, have their [[Consolidated city-county|governments consolidated with the governments of their largest cities]]. ''Louisville-Jefferson County Government'' ([[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville Metro]]) and ''Lexington-Fayette Urban County Government'' ([[Lexington, Kentucky|Lexington Metro]]) are unique in that their city councils and county Fiscal Court structures have been merged into a single entity with a single [[mayor|chief executive]], the [[Louisville Metro Mayor|Metro Mayor]] and Urban County Mayor, respectively. Although the counties still exist as subdivisions of the state, in reference the names Louisville and Lexington are used to refer to the entire area coextensive with the former cities and counties. Somewhat incongruously, when entering Lexington-Fayette the highway signs reads "Fayette County" while most signs leading into Louisville-Jefferson simply read "Welcome to Louisville Metro."
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Cities and towns===
| |
| − | <div style="float:right; padding-left:12px;">
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable"
| |
| − | ! 15 Largest Cities<ref name="census1">{{cite web |url=http://www.census.gov/popest/cities/tables/SUB-EST2006-01.csv |title=Census Population Estimates for 2006 - Annual Estimates of the Population for Incorporated Places Over 100,000 |accessdate=2007-07-01 |publisher=US Census}}</ref><ref name="census2">{{cite web |url=http://www.census.gov/popest/cities/tables/SUB-EST2006-04-21.csv |title=Census Population Estimates for 2006 - Annual Estimates of the Population for Incorporated Places in Kentucky |accessdate=2007-07-01 |publisher=US Census}}</ref>!! 2006 Population
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]] || 557,789
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Lexington, Kentucky|Lexington]] || 279,044
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Owensboro, Kentucky|Owensboro]] || 55,398
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Bowling Green, Kentucky|Bowling Green]] || 54,244
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Covington, Kentucky|Covington]] || 43,062
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Richmond, Kentucky|Richmond]] || 32,333
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Hopkinsville, Kentucky|Hopkinsville]] || 31,638
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Henderson, Kentucky|Henderson]] || 27,768
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Florence, Kentucky|Florence]] || 27,098
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Frankfort, Kentucky|Frankfort]] || 27,281
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Jeffersontown, Kentucky|Jeffersontown]] || 26,152
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Nicholasville, Kentucky|Nicholasville]] || 25,845
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Paducah, Kentucky|Paducah]] || 25,539
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Elizabethtown, Kentucky|Elizabethtown]] || 23,777
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | [[Radcliff, Kentucky|Radcliff]] || 21,933
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | </div>
| |
| − | {{seealso|List of cities in Kentucky}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | The Greater [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville Metro Area]] holds a very disproportionate share of Kentucky's population, growth and wealth, and is by definition Kentucky's [[primate city]]. The city has a 2006 estimated population of 554,496, while the [[Louisville-Elizabethtown-Scottsburg, KY-IN Combined Statistical Area|Louisville Combined Statistical Area]] (CSA) has a population of 1,356,798; including 1,003,025 in Kentucky, which is nearly 1/4 of the state's population. Since 2000 over 1/3 of the state's population growth has occurred in the Louisville CSA. In addition, the top 28 wealthiest places in Kentucky are in Jefferson County and seven of the 15 wealthiest counties in the state are located in the Louisville CSA.<ref>[http://ksdc.louisville.edu/ Kentucky State Data Center<!-- Bot generated title —>]</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The second largest city is Lexington with a 2006 census estimated population of 270,789 and its [[Lexington-Fayette-Frankfort-Richmond, KY Combined Statistical Area|CSA]] having a population of 645,006. The [[Northern Kentucky]] area (the seven Kentucky counties in the [[Cincinnati]] CSA) had an estimated population of 408,783 in 2006. The metropolitan areas of Louisville, Lexington, and Northern Kentucky have a combined population of 2,169,394 as of 2006, which is 51.5% of the state's total population.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The two other fast growing urban areas in Kentucky are the [[Bowling Green, Kentucky|Bowling Green]] area and the "Tri Cities Region" of southeastern Kentucky, comprising [[Somerset, Kentucky|Somerset]], [[London, Kentucky|London]], and [[Corbin, Kentucky|Corbin]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | The largest county in Kentucky, is Pike, which contains Pikeville, home of Hillbilly Days. It also contains the small towns of Elkhorn City, South Williamson, and Coal Run.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Although only one town in the "Tri Cities", namely Somerset, currently has more than 10,000 people, the area has been experiencing heightened population and job growth since the 1990s. Growth has been especially rapid in Laurel County, which outgrew areas such as Scott and Jessamine counties around Lexington or Shelby and Nelson Counties around Louisville. London is currently on pace to double its population in the 2000s from 5,692 in 2000 to 10,879 in 2010. London also landed a [[Wal-Mart]] distribution center in 1997, bringing thousands of jobs to the community.
| |
| | | | |
| − | In northeast Kentucky, the greater [[Ashland, Kentucky|Ashland]] area is an important transportation, manufacturing, and medical center. [[Iron]] and [[petroleum]] production, as well as the transport of coal by rail and [[barge]], have been historical pillars of the region's economy. Due to a decline in the area's industrial base, Ashland has seen a sizable reduction in its population since 1990. The population of the area has since stabilized, however, with the medical service industry taking a greater role in the local economy. The Ashland area, including the counties of [[Boyd County, Kentucky|Boyd]] and [[Greenup County, Kentucky|Greenup]], are part of the [[Huntington-Ashland, WV-KY-OH, Metropolitan Statistical Area]] (MSA). As of the 2000 census, the MSA had a population of 288,649. About 20,000 of those people reside within the city limits of Ashland.
| + | ==Image Gallery== |
| | | | |
| − | Only three US states have capitals with smaller populations than Kentucky's [[Frankfort, Kentucky|Frankfort]] (pop. 27,408), those being [[Augusta, Maine]] (pop. 18,560), [[Pierre, South Dakota]] (pop. 13,876), and [[Montpelier, Vermont]] (pop. 8,035).
| |
| | <center><gallery> | | <center><gallery> |
| − | Image:N38316642 31380476 4196.jpg|Population [http://www.census.gov/popest/counties/tables/CO-EST2005-02-21.csv growth] is centered along and between interstates [[Interstate 65|I-65]] and [[Interstate 75|I-75]].
| + | Image:LouisvilleNightSkyline2-small.jpg|[[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]] is the state's largest city, with a metro population of 1.2 million. |
| − | Image:LouisvilleNightSkyline2-small.jpg|[[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]] is the state's largest city with a metro population of 1.2 million. | + | Image:PhotodowntownLexKY.JPG|[[Lexington, Kentucky|Lexington]] is the state's second largest city, with a metro population of around 500,000. |
| − | Image:PhotodowntownLexKY.JPG|[[Lexington, Kentucky|Lexington]] is the state's second largest city with a metro population of around 500,000. | |
| | Image:Picture 127CovSky08.jpg|Although [[Covington, Kentucky]] only has a population of 42,000, the Kentucky side of the [[Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky metropolitan area]] has a population of over 450,000. | | Image:Picture 127CovSky08.jpg|Although [[Covington, Kentucky]] only has a population of 42,000, the Kentucky side of the [[Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky metropolitan area]] has a population of over 450,000. |
| | Image:Picture 124NewportKYwaterfrnt.jpg|Newport's Aquarium and waterfront | | Image:Picture 124NewportKYwaterfrnt.jpg|Newport's Aquarium and waterfront |
| − | </gallery></center>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==Education==
| |
| − | [[Image:WilliamtyounglibraryUK.JPG|thumb|right|The [[University of Kentucky]] is Kentucky's flagship university]]
| |
| − | [[Image:Speed Engineering School, Louisville, Kentucky (1067).jpg|thumb|right|The [[University of Louisville]] is Kentucky's urban research university]]
| |
| − | {{main| Education in Kentucky}}
| |
| − | {{seealso|List of colleges and universities in Kentucky|List of high schools in Kentucky|List of school districts in Kentucky}}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Kentucky maintains eight public four-year colleges and universities. The two major research institutions are the [[University of Kentucky]], which is part of the land grant system, and the [[University of Louisville]]. Both combine for over 99% of [[Financial endowment|endowment]] in the system and rank first or second in academic rankings and average ACT scores in the state system.{{Fact|date=May 2008}} The other six colleges in the state system are regional universities.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The state's sixteen public two-year colleges have been governed by the [[Kentucky Community and Technical College System]] since the passage of the Postsecondary Education Improvement Act of 1997, commonly referred to as House Bill 1.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.lrc.ky.gov/recarch/97ss/HB1/bill.doc |title=Postsecondary Education Improvement Act of 1997 |accessdate=2007-05-01 |last= |first= |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher=State of Kentucky |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }}
| |
| − | </ref> Prior to the passage of House Bill 1, most of these colleges were under the control of the [[University of Kentucky]].
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Berea College]], located at the extreme southern edge of the Bluegrass below the Cumberland Plateau, was the first coeducational college in the [[Southern United States|South]] to admit both black and white students, doing so from its very establishment in 1855.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.diversityweb.org/digest/vol10no1/mendel.cfm |title=Berea College:Learning, Labor, and Service |accessdate=2007-05-01 |last= |first= |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher=Diversity Web |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }}
| |
| − | [http://www.diversityweb.org/digest/vol10no1/mendel.cfm Berea College: Learning, Labor, and Service]</ref> This policy was successfully challenged in the [[Supreme Court of the United States|United States Supreme Court]] in the case of ''[[Berea College v. Kentucky]]'' in 1908.<ref>[http://www.brownat50.org/brownCases/PreBrownCases/BereavKty1908.html Berea College v. Kentucky]</ref> This decision effectively segregated Berea until the landmark ''[[Brown v. Board of Education]]'' in 1954.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Kentucky has been the site of much educational reform over the past two decades. In 1989, the [[Kentucky Supreme Court]] ruled that the state's education system was unconstitutional.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://eric.ed.gov/ERICWebPortal/Home.portal?_nfpb=true&_pageLabel=RecordDetails&ERICExtSearch_SearchValue_0=ED327352&ERICExtSearch_SearchType_0=eric_accno&objectId=0900000b8004b71c |title=A Guide to the Kentucky Education Reform Act of 1990 |accessdate=2007-05-01 |last= |first= |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher=Education Resources Information Center |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }}[Abstract of A Guide to the Kentucky Education Reform Act of 1990 - provided by Education Resources Information Center (ERIC)]</ref> The response of the [[Kentucky General Assembly|General Assembly]] was passage of the Kentucky Education Reform Act (KERA) the following year. Years later, Kentucky has shown progress, but most agree that further reform is needed.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.kltprc.net/foresight/Chpt_37.htm |title=Education Reform and Equitable Excellence: The Kentucky Experiment |accessdate=2007-05-01 |last=Roeder |first=Phillip |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |year= |month= |format= |work= |publisher= |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote= }}</ref>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==Culture==
| |
| − | [[Image:4th and hill.jpg|thumb|right|[[Old Louisville]] is the largest Victorian Historic neighborhood in the [[United States]].]]
| |
| − | {{seealso|Theater in Kentucky}}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Although Kentucky's culture is generally considered to be [[Southern culture|Southern]], it is unique and also influenced by the [[Midwestern United States|Midwest]] and [[Southern Appalachia]]. The state is known for [[Bourbon whiskey|bourbon]] and [[whiskey]] distiling, [[tobacco]], [[horse racing]], and [[gambling]]. Kentucky is more similar to the [[Upper South]] in terms of ancestry which is predominantly [[United States|American]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.census.gov/prod/2004pubs/c2kbr-35.pdf |title=Ancestry 2000: Census 2000 Brief |author=Brittingham, Angela & de la Cruz, G. Patricia |publisher=United States Census Bureau |format=PDF |accessdaymonth=28 June | accessyear=2007|month=June | year=2004}}</ref> Neveretheless, during the 19th century, the state Kentucky did receive a substantial number of German and Irish immigrants, who settled primarily in the Midwest. Only Maryland, Delaware, and West Virginia, all also border states, have higher German ancestry percentages than Kentucky among Census-defined Southern states.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.thearda.com/mapsReports/maps/map.asp?state=101&variable=494 |title=2000 Census: Percent Reporting Any German Ancestry |accessdate=2007-07-20}}</ref> Kentucky was a [[slave state]], and blacks once comprised over one-quarter of its population. However, it lacked the [[cotton plantation]] system and never had the same high percentage of African Americans as most other slave states. With less than 8% of its current population being black, Kentucky is rarely included in modern-day definitions of the [[Black Belt (U.S. region)|Black Belt]], despite a relatively significant rural African American population in the Central and Western areas of the state.<ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url = http://srdc.msstate.edu/poverty/ppts/cromartie.ppt
| |
| − | | title = High Poverty in the Rural U.S. and South: Progress and Persistence in the 1990s
| |
| − | | accessdaymonth = [[28 June]] | accessyear=2007
| |
| − | | author = Beale, Calvin
| |
| − | | date = [[21 July]] [[2004]]
| |
| − | | format = PowerPoint
| |
| − | }}</ref><ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url = http://srdc.msstate.edu/poverty/ppts/womack.ppt
| |
| − | | title = The American Black Belt Region: A Forgotten Place
| |
| − | | accessdaymonth = 28 June | accessyear=2007
| |
| − | | author = Womack, Veronica L.
| |
| − | | date = [[23 July]] [[2004]]
| |
| − | | format = PowerPoint
| |
| − | }}</ref><ref>{{cite web
| |
| − | | url = http://www.bowdoin.edu/~prael/branch/ex1/m4-black-belt.jpg
| |
| − | | title = Identifying the "Black Belt" of Cash-Crop Production
| |
| − | | accessdaymonth = 28 June | accessyear=2007
| |
| − | | author = Unknown
| |
| − | | date =
| |
| − | | format = JPEG Image
| |
| − | | publisher = Bowdoin College
| |
| − | }}</ref>
| |
| − | Kentucky adopted the [[Jim Crow laws|Jim Crow]] system of racial segregation in most public spheres after the Civil War, but the state never disenfranchised African American citizens to the level of the [[Deep South]] states, and it peacefully integrated its schools after the 1954 ''Brown v. Board of Education'' verdict, later adopting the first state civil rights act in the South in 1966.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761554924_12/Kentucky.html |title=Civil Rights and Women’s Rights |accessdate=2007-07-20}}</ref>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The biggest day in horse racing, the [[Kentucky Derby]], is preceded by the two-week [[Kentucky Derby Festival]]<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.kdf.org/ |title=Kentucky Derby Festival Home Page |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> in Louisville. Louisville also plays host to the [[Kentucky State Fair]],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.kystatefair.org/ |title=Kentucky State Fair |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> the [[Kentucky Shakespeare Festival]],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.kyshakes.org/ |title=Kentucky Shakespeare Festival Home Page |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> and [[Southern gospel]]'s annual highlight, the [[National Quartet Convention]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.natqc.com/ |title=National Quartet Convention Home Page |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> [[Owensboro, Kentucky|Owensboro]], Kentucky's third largest city, gives credence to its nickname of "Barbecue Capital of the World" by hosting the annual [[International Bar-B-Q Festival]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.bbqfest.com/ |title=Home Page of the International Barbecue Festival |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> [[Bowling Green, Kentucky|Bowling Green]], Kentucky's fifth largest city and home to the [[Bowling Green Assembly Plant|only assembly plant in the world]] that manufactures the [[Chevrolet Corvette]],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://bg.ky.net/Corvette/newera.htm |title=National Corvette Museum press release |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> opened the [[National Corvette Museum]] in 1994.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.corvettemuseum.com/ |title=National Corvette Museum Home Page |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Old Louisville]], the largest [[historic preservation]] district in the United States featuring [[Victorian architecture]] and the third largest overall,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ajc.com/travel/content/travel/southeast/ky_stories/0305/09lvgetaway.html |title=Stately Mansions Grace Old Louisville |publisher=''[[Atlanta Journal Constitution]]'' |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> hosts the [[St. James Court Art Show]], the largest outdoor art show in the [[United States]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.stjamescourtartshow.com/ |title=St. James Court Art Show Home Page |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> The neighborhood was also home to the [[Southern Exposition]] (1883–1887), which featured the first public display of [[Thomas Edison]]'s [[light bulb]],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://chfs.ky.gov/NR/rdonlyres/6AD56B4B-7551-4E34-AE5B-E067472C503E/0/October_2004.pdf |title=The Heart Line |publisher=Kentucky Commission on Community Volunteerism and Service |accessdate=2006-12-25|format=PDF}}</ref> and was the setting of [[Alice Hegan Rice]]'s novel, ''[[Mrs. Wiggs of the Cabbage Patch]]'' and [[Fontaine Fox]]'s comic strip, the "[[Toonerville Trolley]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.oldlouisville.com/literature/ |title=Old Louisville and Literature |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The more rural communities are not without traditions of their own, however. [[Hodgenville, Kentucky|Hodgenville]], the birthplace of [[Abraham Lincoln]], hosts the annual Lincoln Days Celebration, and will also host the kick-off for the National Abraham Lincoln Bicentennial Celebration in February 2008. [[Bardstown, Kentucky|Bardstown]] celebrates its heritage as a major bourbon-producing region with the [[Kentucky Bourbon Festival]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.kybourbonfestival.com/ |title=Kentucky Bourbon Festival Home Page |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> (Legend holds that [[Baptist]] minister [[Elijah Craig]] invented bourbon with his black slave in [[Georgetown, Kentucky|Georgetown]], but some dispute this claim.)<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.straightbourbon.com/articles/ccname.html |title=How Bourbon Whiskey ''Really'' Got Its Famous Name |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> [[Glasgow, Kentucky|Glasgow]] mimics [[Glasgow]], [[Scotland]] by hosting the [[Glasgow Highland Games]], its own version of the [[Highland Games]],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.glasgowhighlandgames.com/ |title=Glasgow, Kentucky Highland Games Home Page |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> and [[Sturgis, Kentucky|Sturgis]] hosts "Little Sturgis", a mini version of [[Sturgis, South Dakota]]'s annual [[Sturgis Motorcycle Rally]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.littlesturgisrally.net/ |title=Little Sturgis Rally Home Page |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> The residents of tiny [[Benton, Kentucky|Benton]] even pay tribute to their favorite tuber, the [[sweet potato]], by hosting [[Tater Day]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.americaslibrary.gov/cgi-bin/page.cgi/es/ky/tater_1 |title=Tater Day Festival A Local Legacy |accessdate=2006-12-25}}</ref> Residents of [[Clarkson, Kentucky|Clarkson]] in [[Grayson County, Kentucky|Grayson County]] celebrate their city's ties to the honey industry by celebrating the [[Clarkson Honeyfest]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.honeyfest.com/ |title=Clarkson Honeyfest home page |accessdate=2007-05-12}}</ref> The Clarkson Honeyfest is held the last Thursday, Friday and Saturday in September, and is the "Official State Honey Festival of Kentucky."
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===Music===
| |
| − |
| |
| − | {{main|Music of Kentucky}}
| |
| − | {{seealso|Category:Kentucky musicians}}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The breadth of music in Kentucky is indeed wide, stretching from the Purchase to the eastern mountains.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Renfro Valley, Kentucky]] is home to Renfro Valley Entertainment Center and the Kentucky Music Hall of Fame and is known as "Kentucky's Country Music Capital," a designation given it by the Kentucky State Legislature in the late 1980s. The Renfro Valley Barn Dance was where Renfro Valley's musical heritage began, in 1939, and influential country music luminaries like Red Foley, Homer & Jethro, Lily May Ledford & the Original Coon Creek Girls, Martha Carson, and many others have performed as regular members of the shows there over the years. The [[Renfro Valley Gatherin']] is today America's second oldest continually broadcast radio program of any kind. It is broadcast on local radio station [[WRVK]] and a syndicated network of nearly 200 other stations across the United States and Canada every week.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Contemporary Christian music]] star [[Steven Curtis Chapman]] is a [[Paducah, Kentucky|Paducah]] native, and [[Rock and Roll Hall of Fame]]rs [[The Everly Brothers]] are closely connected with [[Muhlenberg County, Kentucky|Muhlenberg County]], where older brother Don was born. Kentucky was also home to Mildred and [[Patty Hill]], the [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]] sisters credited with composing the tune to the ditty [[Happy Birthday to You]] in 1893; [[Loretta Lynn]] ([[Johnson County, Kentucky|Johnson County]]), and [[Billy Ray Cyrus]] ([[Flatwoods, Kentucky|Flatwoods]]). However, its depth lies in its signature sound — [[Bluegrass music]]. [[Bill Monroe]], "The Father of Bluegrass", was born in the small [[Ohio County, Kentucky|Ohio County]] town of [[Rosine, Kentucky|Rosine]], while [[Ricky Skaggs]], [[Keith Whitley]], [[David "Stringbean" Akeman]], [[Grandpa Jones|Louis Marshall "Grandpa" Jones]], Sonny and [[Bobby Osborne]], and [[Sam Bush]] (who has been compared to Monroe) all hail from Kentucky. The [[International Bluegrass Music Museum]] is located in [[Owensboro, Kentucky|Owensboro]],<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.bluegrass-museum.org/ |title=International Bluegrass Music Museum |accessdate=2006-11-30}}</ref> while the annual [[Festival of the Bluegrass]] is held in [[Lexington, Kentucky|Lexington]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.festivalofthebluegrass.com/ |title=Festival of the Bluegrass Home Page |accessdate=2006-11-30}}</ref>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Kentucky is also home to famed [[jazz]] musician and pioneer, [[Lionel Hampton]] (although this has been disputed in recent years).<ref>{{cite web |last = Voce |first = Steve |title = Obituary: Lionel Hampton |publisher=[[The Independent]] |url=http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qn4158/is_20020902/ai_n12639955/pg_5 |date = 2002-09-02 |accessdate = 2007-06-03}}</ref> [[Blues]] legend [[W.C. Handy]] and [[Rhythm and blues|R&B]] singer [[Wilson Pickett]] also spent considerable time in Kentucky. The pop bands [[Midnight Star]] and [[Nappy Roots]] were both formed in Kentucky, as were country acts [[The Kentucky Headhunters]], [[Montgomery Gentry]] and [[Halfway to Hazard]], as well as [[GMA Music Awards|Dove Award]]-winning Christian groups [[Audio Adrenaline]] (rock) and [[Bride (band)|Bride]] (metal).
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===Cuisine===
| |
| − | {{main|Cuisine of Kentucky}}
| |
| − | [[Image:Hot Brown Kurtz.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The [[Hot Brown]] was first served at Louisville's [[Brown Hotel]]]]
| |
| − | [[Kentucky cuisine|Kentucky's cuisine]], like much of the state's culture, is unique and is considered to blend elements of both the South and Midwest, given its location between the two regions.<ref>[http://southernfood.about.com/od/southernregionalfood/Southern_Recipes_and_Regional_Specialties.htm Southern Recipes - Southern Food and Recipes<!-- Bot generated title —>]</ref><ref>[http://www.iicaculinary.com/iica-ye2-sem1.htm#ac303 International Institute of Culinary Arts<!-- Bot generated title —>]</ref> One original Kentucky dish is called the [[Hot Brown]], a dish normally layered in this order: toasted bread, turkey, bacon, tomatoes and topped with mornay sauce. It was developed at the [[Brown Hotel]] in [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.brownhotel.com/dining/hot-brown.html |title=Hot Brown Recipe |publisher=[[Brown Hotel]] |accessdate=2006-12-18}}</ref> The [[Pendennis Club]] in Louisville is the Birthplace of the drink The ''[[Old Fashioned]]''.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==Sports==
| |
| − | {{Original research|date=May 2008}}
| |
| − | [[Image:144702892 da6c29607d b.jpg|thumb|right|Kentucky's [[Churchill Downs]] hosts the [[Kentucky Derby]].]]
| |
| − | {{main|Sports in Kentucky}}
| |
| − | Kentucky is the home of several sports teams such as [[Minor League Baseball]]'s Class A [[Lexington Legends]] and AAA [[Louisville Bats]]. They are also home to the [[Frontier League]]s [[Florence Freedom]] and several teams in the MCFL. The [[Lexington Horsemen]] and [[Louisville Fire]] of the [[af2]] appear to be interested in making a move up to the "major league" [[Arena Football League]]. Major league teams in nearby cities, typically have strong fan support depending on the part of the state, with [[Nashville, Tennessee|Nashville]] teams having strong fan support in South Central and most of Western Kentucky, Nashville and [[St. Louis, Missouri|St. Louis]] teams competing for loyalties in [[Jackson Purchase|the Purchase]], [[Indianapolis, Indiana|Indianapolis]], [[Cincinnati, Ohio|Cincinnati]] and [[Chicago, Illinois|Chicago]] teams predominating in the [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]] area, and [[Cincinnati, Ohio|Cincinnati]] teams having strong support in Central and Eastern Kentucky.{{Fact|date=May 2008}} The [[Northern Kentucky|northern part of the state]] lies across the [[Ohio River]] from Cincinnati, which is home to a [[National Football League]] team, the [[Cincinnati Bengals|Bengals]], and a [[Major League Baseball]] team, the [[Cincinnati Reds|Reds]]. It is not uncommon for fans to park in the city of [[Newport, Kentucky|Newport]] and use the [[Newport Southbank Bridge|Newport Southbank Pedestrian Bridge]], locally known as the "Purple People Bridge," to walk to these games in Cincinnati. Many restaurants and stores in Newport rely on business from these fans.{{Fact|date=May 2008}} Also, [[Georgetown College]] in [[Georgetown, Kentucky|Georgetown]] is the location for the Bengals' summer training camp.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.bengalscamp.com |title=About the camp |publisher=[http://www.bengalscamp.com BengalsCamp.com] |accessdate=2006-12-18}}</ref>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | As in many states, especially those without major league professional sport teams, college athletics are very important. This is especially true of the state's three [[Division I#Football Bowl Subdivision|Division I Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS)]] programs, including the [[Kentucky Wildcats]], the [[Western Kentucky University]] Hilltoppers, and the [[Louisville Cardinals]]. The Wildcats, Hilltoppers, and Cardinals are among the most tradition-rich college basketball teams in the United States, combining for nine championships and 22 NCAA Final Fours; and all three are on the lists of total all-time wins, wins per season, and average wins per season. Louisville has also stepped onto the football scene in recent years, with eight straight bowl games, including the 2007 [[Orange Bowl (game)|Orange Bowl]]. Western Kentucky, the 2002 national champion in Division I-AA football (now [[Division I#Football Championship Subdivision|Division I Football Championship Subdivision (FCS)]], is currently transitioning to Division I FBS football.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | [[Ohio Valley Wrestling]] in Louisville was the primary location for training and rehab for [[World Wrestling Entertainment|WWE]] professional wrestlers from 2000 until February 2008, when WWE ended its relationship with OVW and moved all of its contracted talent to [[Florida Championship Wrestling]].
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==State symbols==
| |
| − | {{main|List of Kentucky state insignia}}
| |
| − | {{seealso|Flag of Kentucky|Seal of Kentucky}}
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable" width=100%
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | !width=25%|[[List of U.S. state insignia|Insignia]]
| |
| − | !width=25%|Symbol
| |
| − | !width=25%|[[Binomial nomenclature]]
| |
| − | !width=25%|Year Adopted<ref>{{cite web |url=http://kdla.ky.gov/resources/KYSymbols.htm |title=Kentucky's State Symbols |publisher=Kentucky Department of Libraries and Archives |accessdate=2006-12-18}}</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state birds|Official State Bird]]
| |
| − | |[[Northern Cardinal|Cardinal]]
| |
| − | |''Cardinalis cardinalis''
| |
| − | |1926
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state butterflies|Official State Butterfly]]
| |
| − | |[[Viceroy Butterfly]]
| |
| − | |''Limenitis archippus''
| |
| − | |1990
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state dances|Official State Dance]]
| |
| − | |[[Clogging]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |2001
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state beverages|Official State Beverage]]
| |
| − | |[[Milk]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |2005
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state fish|Official State Fish]]
| |
| − | |[[Spotted bass|Kentucky Spotted Bass]]
| |
| − | |''Micropterus punctulatus''
| |
| − | |2005
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state fossils|Official State Fossil]]
| |
| − | |[[Brachiopod]]
| |
| − | |undetermined
| |
| − | |1985
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state flowers|Official State Flower]]
| |
| − | |[[Goldenrod]]
| |
| − | |''Soldiago gigantea''
| |
| − | |1926
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state fruits|Official State Fruit]]
| |
| − | |[[Blackberry]]
| |
| − | |''Rubus allegheniensis''
| |
| − | |2004
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state minerals, rocks, stones and gemstones|Official State Gemstone]]
| |
| − | |[[Pearl|Freshwater Pearl]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |1986
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state grasses|State Grass]]
| |
| − | |[[Smooth Meadow-grass|Kentucky Bluegrass]]
| |
| − | |''Poa pratensis''
| |
| − | |Traditional
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state mottos|Official State Latin Motto]]
| |
| − | |'' "Deo gratiam habeamus" ''
| |
| − | ("With gratitude to God")
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |2002
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state mammals|Official State Horse]]
| |
| − | |[[Thoroughbred]]
| |
| − | |''Equus caballus''
| |
| − | |1996
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state minerals, rocks, stones and gemstones|Official State Mineral]]
| |
| − | |[[Coal]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |1998
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |Official State Outdoor Musical
| |
| − | |"The [[Stephen Foster]] Story" (now called "Stephen Foster - The Musical")
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |2002
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[Musical instrument|Official State Instrument]]
| |
| − | |[[Appalachian Dulcimer]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |2001
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state nicknames|State Nickname]]
| |
| − | |"The Bluegrass State"
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |Traditional
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state minerals, rocks, stones and gemstones|Official State Rock]]
| |
| − | |[[Agate|Kentucky Agate]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |2000
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state slogans|Official State Slogan]]
| |
| − | |"Kentucky: Unbridled Spirit"
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |2004<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.kentucky.gov/unbridledspirit/info.htm |title=Unbridled Spirit Information |publisher=[http://www.kentucky.gov Kentucky.gov] |accessdate=2006-12-18 |date=[[2006-11-20]]}}</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[Soil|Official State Soil]]
| |
| − | |[[Crider Soil Series]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |1990
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state trees|Official State Tree]]
| |
| − | |[[Tulip Poplar]]
| |
| − | |''Liriodendron tulipifera''
| |
| − | |1994
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state mammals|Official Wild Animal Game Species]]
| |
| − | |[[Gray Squirrel]]
| |
| − | |''Sciurus carolinensis''
| |
| − | |1968
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |[[List of U.S. state songs|Official State Song]]
| |
| − | |[[My Old Kentucky Home|"My Old Kentucky Home"]]
| |
| − | (revised version)
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |1986
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |Official State Silverware Pattern
| |
| − | |''Old Kentucky Blue Grass:
| |
| − | The Georgetown Pattern''
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |1996
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |Official State Music
| |
| − | |[[Bluegrass music]]
| |
| − | |
| |
| − | |2007<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.lrc.ky.gov/RECORD/07RS/HB71/bill.doc |format=DOC |title=HB71: An act designating bluegrass music as the official state music of Kentucky |publisher=Legislative Research Commission |accessdate=2007-06-26}}</ref>
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | ===Official state places and events===
| |
| − | {{col-begin}}
| |
| − | {{col-2}}
| |
| − | *State arboretum: [[Bernheim Arboretum and Research Forest]]
| |
| − | *State botanical garden: [[University of Kentucky Arboretum|The Arboretum: State Botanical Garden of Kentucky]]
| |
| − | *State Science Center: [[Louisville Science Center]]
| |
| − | *State center for celebration of African American heritage: Kentucky Center for African American Heritage
| |
| − | *State honey festival: [[Clarkson, Kentucky|Clarkson]] Honeyfest<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.lrc.ky.gov/KRS/002-00/099.PDF |title=KRS 2.099 - State Honey Festival |publisher=[[Kentucky General Assembly]] |format=PDF |accessdate=2006-12-18}}</ref>
| |
| − | *State [[Amphitheatre|amphitheater]]: [[Iroquois Park|Iroquois]] Amphitheater ([[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]])
| |
| − | {{col-2}}
| |
| − | *State [[Tug of war|tug-o-war]] championship: The [[Fordsville, Kentucky|Fordsville]] Tug-of-War Championship
| |
| − | *[[Covered Bridge]] Capital of Kentucky: [[Fleming County, Kentucky|Fleming County]]
| |
| − | *Official [[Covered Bridge]] of Kentucky: Switzer Covered Bridge ([[Franklin County, Kentucky|Franklin County]])
| |
| − | *Official [[steam locomotive]] of Kentucky: "Old 152" (located in the [[Kentucky Railway Museum]] in [[New Haven, Kentucky|New Haven]])
| |
| − | *Official [[pipe band]]: Louisville Pipe Band
| |
| − | *State [[Bourbon whiskey|bourbon]] festival: [[Kentucky Bourbon Festival]], Incorporated, of [[Bardstown, Kentucky]]
| |
| − | {{col-end}}
| |
| − | Unless otherwise specified, all state symbol information is taken from [http://kdla.ky.gov/resources/KYSymbols.htm Kentucky State Symbols].
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==Gallery==
| |
| − | {{cleanup-gallery}}
| |
| − | <center><gallery>
| |
| | Image:LouisvilleSluggerMusem.jpg|The world famous [[Louisville Slugger]] [[baseball bat]] is made in Kentucky. | | Image:LouisvilleSluggerMusem.jpg|The world famous [[Louisville Slugger]] [[baseball bat]] is made in Kentucky. |
| − | Image:Kentucky quarter, reverse side, 2001.jpg|Kentucky's [[50 State Quarters|2001 commemorative quarter]].
| |
| | Image:Thunder over louisville 2006.jpg|[[Thunder Over Louisville]] is the largest annual fireworks show in the world. | | Image:Thunder over louisville 2006.jpg|[[Thunder Over Louisville]] is the largest annual fireworks show in the world. |
| − | Image:Picture 1289.jpg|Kentucky's horse farms are world renowned. | + | Image:Picture 1289.jpg|Kentucky's [[horse]] farms are world renowned. |
| | Image:Daniel Boone National Forest Tater Knob.jpg|The [[Daniel Boone National Forest]]. | | Image:Daniel Boone National Forest Tater Knob.jpg|The [[Daniel Boone National Forest]]. |
| | Image:Picture 282.jpg|The [[Ohio River]] forms the northern border of Kentucky. | | Image:Picture 282.jpg|The [[Ohio River]] forms the northern border of Kentucky. |
| | Image:DowntownBG.JPG|Many Kentucky cities have historic areas near downtown, such as this example in [[Bowling Green, KY|Bowling Green]]. | | Image:DowntownBG.JPG|Many Kentucky cities have historic areas near downtown, such as this example in [[Bowling Green, KY|Bowling Green]]. |
| − | Image:US 23 KY.jpg|US Highway 23 cuts through the rugged [[Cumberland Plateau]] near [[Pikeville, Kentucky|Pikeville]]. | + | Image:4th and hill.jpg|[[Old Louisville]] is the largest Victorian historic neighborhood in the [[United States]] |
| − | Image:1890TornadoMemorial.jpg|Memorial to the victims of the great [[Mid-Mississippi Valley Tornado Outbreak of March 1890|Louisville Tornado of 1890]], which was the 20th deadliest in US History.
| + | Image:5478.jpg.jpg|The largest [[river]] in [[North America]], the [[Mississippi River|Mississippi]] converges with the [[Ohio River]] along the Kentucky border near [[Wickliffe, Kentucky|Wickliffe]]. |
| − | Image:5478.jpg.jpg|The largest river in North America, the [[Mississippi River|Mississippi]] converges with the Ohio River along the Kentucky border near [[Wickliffe, Kentucky|Wickliffe]]. | |
| | </gallery></center> | | </gallery></center> |
| | | | |
| − | ==See also== | + | ==External links== |
| − | *[[List of Kentucky-related topics]]
| + | All links retrieved October 5, 2022. |
| − | {{portal|Kentucky|Flag of Kentucky.svg|left=yes}}
| |
| − | {{clear}}
| |
| − | <!-- Please place links to all topics directly related to the Commonwealth of Kentucky in the [[List of Kentucky-related topics]] —>
| |
| | | | |
| − | ==References==
| + | *[http://kentucky.gov Kentucky.gov] |
| − | {{reflist|2}}
| + | *[http://www.kentuckytourism.com Kentucky Department of Tourism] |
| | | | |
| − | ==Bibliography==
| |
| − | ===Politics===
| |
| − | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=3096856 Miller, Penny M. ''Kentucky Politics & Government: Do We Stand United?'' (1994)]
| |
| − | *Jewell, Malcolm E. and Everett W. Cunningham, ''Kentucky Politics'' (1968)
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===History===
| |
| − | ====Surveys and reference====
| |
| − | *Bodley, Temple and Samuel M. Wilson. ''History of Kentucky'' 4 vols. (1928).
| |
| − | *[[Harry M. Caudill|Caudill, Harry M.]], ''Night Comes to the Cumberlands'' (1963). ISBN 0-316-13212-8
| |
| − | *Channing, Steven. ''Kentucky: A Bicentennial History'' (1977).
| |
| − | *Clark, Thomas Dionysius. ''A History of Kentucky'' (many editions, 1937–1992).
| |
| − | *Collins, Lewis. ''History of Kentucky'' (1880).
| |
| − | *Harrison, Lowell H. and James C. Klotter. ''A New History of Kentucky'' (1997).
| |
| − | *Kleber, John E. et al ''The Kentucky Encyclopedia'' (1992), standard reference history.
| |
| − | *Klotter, James C. ''Our Kentucky: A Study of the Bluegrass State'' (2000), high school text
| |
| − | *Lucas, Marion Brunson and Wright, George C. ''A History of Blacks in Kentucky'' 2 vols. (1992).
| |
| − | *Notable Kentucky African Americans http://www.uky.edu/Subject/aakyall.html
| |
| − | *Share, Allen J. ''Cities in the Commonwealth: Two Centuries of Urban Life in Kentucky'' (1982).
| |
| − | *Wallis, Frederick A. and Hambleton Tapp. ''A Sesqui-Centennial History of Kentucky'' 4 vols. (1945).
| |
| − | *Ward, William S., ''A Literary History of Kentucky'' (1988) (ISBN 0-87049-578-X).
| |
| − | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=99066764 WPA, ''Kentucky: A Guide to the Bluegrass State '' (1939)], classic guide.
| |
| − | *{{cite book|title=Two Hundred Years at the Fall of the Ohio: A History of Louisville and Jefferson County|last=Yater|first=George H.|year=1987|publisher=[[The Filson Historical Society|Filson Club, Incorporated]]|edition=2nd edition|id = ISBN 0-9601072-3-1}}
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ====Specialized scholarly studies====
| |
| − | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=105132587 Bakeless, John. ''Daniel Boone, Master of the Wilderness'' (1989)]
| |
| − | *Blakey, George T. ''Hard Times and New Deal in Kentucky, 1929–1939'' (1986)
| |
| − | *Coulter, E. Merton. ''The Civil War and Readjustment in Kentucky'' (1926)
| |
| − | *Davis, Alice. "Heroes: Kentucky's Artists from Statehood to the New Millennium" (2004)
| |
| − | *Ellis, William E. ''The Kentucky River'' (2000).
| |
| − | *Faragher, John Mack. ''Daniel Boone'' (1993)
| |
| − | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=6471305 Fenton, John H. ''Politics in the Border States: A Study of the Patterns of Political Organization, and Political Change, Common to the Border States: Maryland, West Virginia, Kentucky, and Missouri'' (1957)]
| |
| − | *Ireland, Robert M. ''The County in Kentucky History'' (1976)
| |
| − | *{{cite book|title=Kentucky's Civil War 1861–1865| last=Klotter|first=James C.|coauthors=Lowell Harrison, James Ramage, Charles Roland, Richard Taylor, Bryan S. Bush, Tom Fugate, Dixie Hibbs, Lisa Matthews, Robert C. Moody, Marshall Myers, Stuart Sanders and Stephen McBride|editor=Jerlene Rose|year=2005|publisher=Back Home In Kentucky Inc|id = ISBN 0-9769231-1-4}}
| |
| − | *Klotter, James C. ''Kentucky: Portrait in Paradox, 1900–1950'' (1992)
| |
| − | *Pearce, John Ed. ''Divide and Dissent: Kentucky Politics, 1930–1963'' (1987)
| |
| − | *Remini, Robert V. ''Henry Clay: Statesman for the Union'' (1991).
| |
| − | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=100662336 Sonne, Niels Henry. ''Liberal Kentucky, 1780–1828'' (1939)]
| |
| − | *Tapp, Hambleton and James C Klotter. ''Kentucky Decades of Discord, 1865–1900'' (1977)
| |
| − | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=61648056 Townsend, William H. ''Lincoln and the Bluegrass: Slavery and Civil War in Kentucky'' (1955)]
| |
| − | *[http://www.questia.com/PM.qst?a=o&d=14459929 Waldrep, Christopher ''Night Riders: Defending Community in the Black Patch, 1890–1915'' (1993)] tobacco wars
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ==External links==
| |
| − | {{sisterlinks|Kentucky}}
| |
| − | *[http://kentucky.gov Kentucky.gov: My New Kentucky Home]
| |
| − | *[http://wikis.ala.org/godort/index.php/Kentucky Kentucky State Databases] - Annotated list of searchable databases produced by Kentucky state agencies and compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association.
| |
| − | *[http://www.kentuckytourism.com Kentucky Department of Tourism]
| |
| − | *[http://www.kentuckyhighlands.com/kh/index.asp The Kentucky Highlands Project]
| |
| − | *[http://www.usgs.gov/state/state.asp?State=KY USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Kentucky]
| |
| − | *[http://tonto.eia.doe.gov/state/state_energy_profiles.cfm?sid=KY Energy & Environmental Data for Kentucky]
| |
| − | *[http://www.ers.usda.gov/StateFacts/KY.htm Kentucky State Facts]
| |
| − | *[http://www.kentuckyunbridledspirit.com/ Kentucky: Unbridled Spirit]
| |
| − | *[http://www.kyvl.org/ Kentucky Virtual Library]
| |
| − | *[http://www.usgs.gov/state/state.asp?State=KY "Science In Your Backyard: Kentucky"] U.S. Department of the Interior | U.S. Geological Survey, [[July 3]], [[2006]], retrieved [[November 4]], [[2006]]
| |
| − | *[http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/states/21000.html U.S. Census Bureau Kentucky QuickFacts]
| |
| − | *[http://www.mrnussbaum.com/kentuckyflash2.htm Interactive Kentucky for Kids]
| |
| − | {{-}}
| |
| − | {{Kentucky|expanded}}
| |
| | {{United States}} | | {{United States}} |
| | {{US South}} | | {{US South}} |
| − | {{succession
| |
| − | | preceded = [[Vermont]]
| |
| − | | office = [[List of U.S. states by date of statehood]]
| |
| − | | years = Admitted on [[June 1]], [[1792]] (15th)
| |
| − | | succeeded = [[Tennessee]]
| |
| − | }}
| |
| | | | |
| | {{coor title d|37.5|N|85|W|region:US-KY_type:state}} | | {{coor title d|37.5|N|85|W|region:US-KY_type:state}} |
| | | | |
| − | [[Category: Nations and places]] | + | [[Category:Geography]] |
| − | [[Category:States of the United States]] | + | [[Category:United States]] |
| − | {{Credit|237973460}} | + | |
| | + | {{Credit|Kentucky|237973460|Frankfort,_Kentucky|240991668}} |
| Commonwealth of Kentucky
|

|

|
| Flag
|
Seal
|
| Nickname(s): Bluegrass State
|
| Motto(s): United we stand, divided we fall
|
|
|
|
| Official language(s)
|
English
|
| Capital |
Frankfort
|
| Largest city |
Louisville
|
| Largest metro area |
Louisville metropolitan area
|
| Area |
Ranked 37th
|
| - Total |
40,409 sq mi
(104,659 km²)
|
| - Width |
140 miles (225 km)
|
| - Length |
379 miles (610 km)
|
| - % water |
1.7
|
| - Latitude |
36° 30′ N to 39° 09′ N
|
| - Longitude |
81° 58′ W to 89° 34′ W
|
| Population |
Ranked 26th in the U.S.
|
| - Total |
4,454,189 (2017 est.)[1]
|
| - Density |
110/sq mi (42.5/km2)
Ranked 22nd in the U.S.
|
| Elevation |
|
| - Highest point
|
Black Mountain[2][3]
4,145 ft (1263 m)
|
| - Mean |
750 ft (230 m)
|
| - Lowest point |
Mississippi River at Kentucky Bend[2][3]
257 ft (78 m)
|
| Admission to Union
|
June 1, 1792 (15th)
|
| Governor |
Steve Beshear (D)
|
| Lieutenant Governor |
Jerry Abramson (D)
|
| U.S. Senators |
Mitch McConnell (R)
Rand Paul (R)
|
| Time zones |
|
| - eastern half |
Eastern: UTC-5/DST-4
|
| - western half |
Central: UTC-6/DST-5
|
| Abbreviations
|
KY US-KY
|
| Web site
|
Kentucky.gov
|
The Commonwealth of Kentucky is a state located in the East Central United States of America. Kentucky is normally included in the group of Southern states, but it is sometimes included, geographically and culturally, in the Midwest. Kentucky is one of four U.S. states to be officially known as a commonwealth. Originally a part of Virginia, in 1792 it became the fifteenth state to join the Union. Kentucky is the 37th largest state in terms of land area, and ranks 26th in population.
It is a land with diverse environments and abundant resources, including Mammoth Cave, the world's longest cave system; the Red River Gorge Geological Area with more than 100 natural stone arches. The gorge is the greatest concentration of arches east of the Rocky Mountains. Kentucky also has the greatest length of navigable waterways and streams in the continental 48 states. Kentucky features the two largest man-made lakes east of the Mississippi River and the nation's most productive coalfield.
Both Abraham Lincoln and Jefferson Davis were born in log cabins on the Kentucky frontier, one year and a few miles apart. They were the presidents of the Union and the Confederacy respectively during the American Civil War. While Kentucky remained officially neutral in that conflict, many Kentuckians enlisted on both sides.
Kentucky is known as the "Bluegrass State," a nickname based on the fact that bluegrass is present in many of the lawns and pastures throughout the state. It is also is known for thoroughbred horses, horse racing, bourbon distilleries, bluegrass music, automobile manufacturing, gambling, and tobacco. Though bourbon may be produced anywhere in the United States where it is legal to distill spirits, it is estimated that 95 percent of the world's bourbon is distilled and aged in Kentucky.
Origin of name
The origin of Kentucky's name (variously spelled Cane-tuck-ee, Cantucky, Kain-tuck-ee, and Kentuckee before its modern spelling was accepted) has never been definitively identified, though some theories have been debunked. For example, Kentucky's name does not come from the combination of "cane" and "turkey"; and though it is the most popular belief, it is unlikely to mean "dark and bloody ground," because it does not occur with that meaning in any known Native American language. The most likely etymology is that it comes from an Iroquoian word for "meadow" or "prairie" Other possibilities also exist: the suggestion of early Kentucky pioneer George Rogers Clark that the name means "the river of blood," a Wyandot name meaning "land of tomorrow," a Shawnee term possibly referring to the head of a river,[4] or an Algonquian word for a river bottom.
Geography
File:Picture 1280.jpg Narrow country roads bounded by stone and wood plank fences are a fixture in the Kentucky Bluegrass region.

A typical view of rolling hills and horse farms in the Kentucky Bluegrass.

Lake Cumberland is the largest artificial lake, in terms of volume, east of the
Mississippi River.
Kentucky borders states of both the Midwest and the Southeast. West Virginia lies to the east, Virginia to the southeast, Tennessee to the south, Missouri to the west, Illinois and Indiana to the northwest, and Ohio to the north and northeast. Kentucky's northern border is formed by the Ohio River and its western border by the Mississippi River; however, the official border is based on the courses of the rivers as they existed when Kentucky became a state in 1792. In several places, the border does not follow the current course of the appropriate river. Northbound travelers on US Highway 41 from Henderson, upon crossing the Ohio River, will find themselves still in Kentucky until they travel about a half-mile farther north.
[5]
Kentucky can be divided into five primary regions: the Cumberland Plateau in the east, the north-central Bluegrass region, the south-central and western Pennyroyal Plateau, the Western Coal Fields and the far-west Jackson Purchase.
Climate
Located within the southeastern interior portion of North America, Kentucky has a climate that can best be described as humid subtropical. Monthly average temperatures in Kentucky range from a summer daytime high of 87°F (30.9°C) to a winter low of 23°F (-4.9°C). The average precipitation is 46 inches (116.84 cm) a year. [6] Kentucky experiences all four seasons, usually with striking variations in the severity of summer and winter from year to year.
Lakes and rivers
Kentucky’s 90,000 miles of streams provide one of the most expansive and complex stream systems in the nation. Kentucky has both the largest artificial lake east of the Mississippi in water volume (Lake Cumberland) and surface area (Kentucky Lake). It is the only U.S. state to be bordered on three sides by rivers—the Mississippi River to the west, the Ohio River to the north, and the Big Sandy River and Tug Fork to the east. [7] Its major internal rivers include the Kentucky River, Tennessee River, Cumberland River, Green River, and Licking River.
Though it has only three major natural lakes, the state is home to many artificial lakes. Kentucky also has more navigable miles of water than any other state in the union, other than Alaska. [8]
Natural environment and conservation
Kentucky has an expansive park system which includes one national park, two National Recreation areas, two National Historic Parks, two national forests, 45 state parks, 37,696 acres (153 km²) of state forest, and 82 Wildlife Management Areas.
Significant natural attractions
- Cumberland Gap, chief passageway through the Appalachian Mountains in early American history.
- Cumberland Falls State Park, one of the few places in the Western Hemisphere where a "moon-bow" may be regularly seen.
- Mammoth Cave National Park, featuring the world's longest cave system.
- Red River Gorge Geological Area, part of the Daniel Boone National Forest.
- Land Between the Lakes, a National Recreation Area managed by the United States Forest Service.
History

Daniel Boone Escorting Settlers through the Cumberland Gap (George Caleb Bingham, oil on canvas, 1851–1852).
Although inhabited by Native Americans in prehistoric times, when explorers and settlers began entering Kentucky in the mid-1700s, there were no major Native American settlements in the region.[9] Instead, the country was used as hunting grounds by Shawnee from the north and Cherokee from the south, who lived in scattered seasonal villages. Much of what is now Kentucky was purchased from Native Americans in the treaties of Fort Stanwix (1768) and Sycamore Shoals (1775).[10]
Thereafter, Kentucky grew rapidly as the first settlements west of the Appalachian Mountains were founded, with settlers (primarily from Virginia, North Carolina, Maryland, Delaware, and Pennsylvania) entering the region either over land via Braddock Road and the Cumberland Gap, or by water down the Ohio River from points upstream, or up the Ohio River from the Mississippi. The first part to be settled was the north, along the Ohio River, with Lexington and Washington being the first major settlements. Next, the southern part of the state was settled, via the Wilderness Trail across the Cumberland Gap, blazed by Daniel Boone, traditionally considered one of the founders of the state.
Shawnee north of the Ohio River were unhappy about the settlement of Kentucky, however, and allied themselves with the British in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783). Kentucky was a battleground during the war; the Battle of Blue Licks, one of the last major battles of the Revolution, was fought in Kentucky.
After the American Revolution, the counties of Virginia beyond the Appalachian Mountains became known as Kentucky County. Eventually, the residents of Kentucky County petitioned for separation. In 1790, Kentucky's delegates accepted Virginia's terms of separation, and a state constitution was drafted. On June 1, 1792, Kentucky became the fifteenth state to be admitted to the Union. [11]
Kentucky was a border state during the American Civil War. It officially remained "neutral" throughout the war due to the Union sympathies of many of the Commonwealth's citizens. After the war, the development of burley tobacco contributed to a tremendous increase in tobacco production.
During World War II, Kentucky began to shift from an agricultural to an industrial economy, but it was not until 1970 that the number of urban dwellers outpaced rural dwellers. Tourism has developed into a major industry.
Law and government

The Kentucky State Capitol in Frankfort

The Abraham Lincoln Birthplace National Historical Site in Hodgenville. The early 19th-century cabin is enclosed within this neo-classic building.
| Kentucky State symbols
|
- Nickname: "The Bluegrass State"
- Motto: "Deo gratiam habeamus"
- "With gratitude to God"
- Slogan: "Kentucky: Unbridled Spirit"
- Song: "My Old Kentucky Home"
- Dance: Clogging
- Music: Bluegrass music
- Musical instrument: Appalachian Dulcimer
- Animal: Thoroughbred
- Wild Animal Game Species: Gray Squirrel
- Fish: Kentucky Spotted Bass
- Bird: Cardinal
- Flower: Goldenrod
- Grass: Kentucky Bluegrass
- Butterfly: Viceroy Butterfly
- Soil: Crider Soil Series
- Tree: Tulip Poplar
- Fruit: Blackberry
- Fossil: Brachiopod
- Gemstone: Freshwater Pearl
- Mineral: Coal
- Rock: Kentucky Agate
|
Frankfort is the capital city of Kentucky and the county seat of Franklin County. The population was 27,741 at the 2000 census; by population, it is the 5th smallest state capital city in the United States.
After Kentucky became a state, five commissioners were appointed on June 20, 1792, to choose a location for the state capital. The Kentucky General Assembly appropriated funds to provide a house to accommodate the governor in 1796. Construction was completed in 1798. The Old Governor's Mansion is reputed to be the oldest official executive residence still in use in the United States.
Government
Kentucky is a commonwealth, meaning its government is run according to the common consent of its people. It is one out of only four states that call themselves commonwealths. Kentucky is also one of only five states that elects its state officials in odd numbered years (the others are Louisiana, Mississippi, New Jersey, and Virginia). Kentucky holds elections for these offices every four years in the years preceding presidential election years.
State government
Kentucky's legislative branch consists of a bicameral body known as the Kentucky General Assembly. The Senate is considered the upper house. It has 38 members and is led by the President of the Senate. The House of Representatives has 100 members and is led by the Speaker of the House.
The executive branch is headed by the governor and lieutenant governor. The governor and lieutenant governor usually run on a single ticket and are elected to four-year terms. Currently, the governor and lieutenant governor are Democrats Steve Beshear and Daniel Mongiardo.
The judicial branch of Kentucky is made up of courts of limited jurisdiction called District Courts; courts of general jurisdiction called Circuit Courts; an intermediate appellate court, the Kentucky Court of Appeals; and a court of last resort, the Kentucky Supreme Court. Unlike federal judges, who are usually appointed, justices serving on Kentucky state courts are chosen by the state's populace in non-partisan elections.
The state's chief prosecutor, law enforcement officer, and law officer is the attorney general. The attorney general is elected to a four-year term and may serve two consecutive terms under the current Kentucky Constitution. The current Kentucky attorney general is Democrat Jack Conway.
Political leanings
Where politics are concerned, Kentucky historically has been very hard fought and leaned slightly toward the Democratic Party, although it was never included among the "Solid South." In 2006, 57.05 percent of the state's voters were officially registered as Democrats, 36.55 percent registered Republican, and 6.39 percent registered with some other political party.[12]
Kentucky has voted Republican in five of the last seven presidential elections but has supported the Democratic candidates of the South. The Commonwealth supported Democrats Jimmy Carter in 1976 and Bill Clinton in 1992 and 1996 but Republican George W. Bush in 2000 and 2004. Bush won the state's 8 electoral votes overwhelmingly in 2004 by a margin of 20 percentage points and 59.6 percent of the vote.[13]
Law
Kentucky is one of 36 states in the United States that sanctions the death penalty for certain crimes. Kentucky has been on the front lines of the debate over displaying the Ten Commandments on public property. In the 2005 case of McCreary County v. ACLU of Kentucky, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld the decision of the Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals that a display of the Ten Commandments in the Whitley City courthouse of McCreary County was unconstitutional.[14] Later that year, Judge Richard Fred Suhrheinrich, writing for the Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals in the case of ACLU of Kentucky v. Mercer County, wrote that a display including the Mayflower Compact, the Declaration of Independence, the Ten Commandments, the Magna Carta, The Star-Spangled Banner, and the national motto could be erected in the Mercer County courthouse. [15]
Prior to the adoption of the state constitution in 1891, the General Assembly had the authority to grant charters to private organizations allowing them to conduct lotteries in order to fund public works such as roads and schools. Due to a considerable amount of abuse, a prohibition on lotteries was written into the 1891 constitution (Section 226). An exception in gaming case law was the legality of pari-mutuel wagering on horse racing. In 2008, legal forms of gambling in the state included commercial, legalized gambling in horse racing, lottery sales (approved in 1988), and charitable gaming.[16] In January 2008, electronic machine, or casino-style gambling had still not been approved by the General Assembly,[17] and while prospects for approval seemed high, there were many opponents. In September 2008, a Franklin County Circuit judge ordered the transfer of the domain names of 141 illegal Internet gambling sites to the Commonwealth of Kentucky in an effort to stop illegal and unregulated online gaming. Kentucky is the first state to bring an action against Internet gambling operators that has resulted in the seizure of domain names.[18]
Demographics
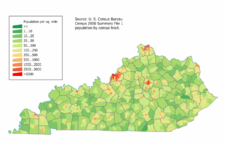
Kentucky Population Density Map.
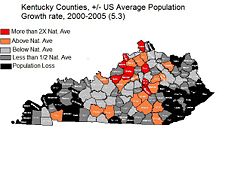
Population growth is centered along and between interstates I-65 and I-75.
As of July 1, 2006, Kentucky had an estimated population of 4,206,074, which is an increase of 33,466, or 0.8 percent, from the prior year and an increase of 164,586, or 4.1 percent, since 2000. This includes a natural increase since the last census of 77,156 people (that is 287,222 births minus 210,066 deaths) and an increase due to net migration of 59,604 people into the state. Immigration from outside the United States resulted in a net increase of 27,435 people, and migration within the country produced a net increase of 32,169 people. As of 2004, Kentucky's population included about 95,000 foreign-born (2.3 percent).
Kentucky's total population has grown during every decade since records began. However during most decades of the twentieth century there was also net out-migration from Kentucky. Since 1900, rural Kentucky counties have experienced a net loss of over one million people from migration, while urban areas have experienced a slight net gain.[19]
The Greater Louisville Metro Area holds a very disproportionate share of Kentucky's population, growth, and wealth. The second largest city is Lexington. The metropolitan areas of Louisville, Lexington, and northern Kentucky had a combined population of 2,169,394 as of 2006, which is 51.5 percent of the state's total population.
The two other fast-growing urban areas in Kentucky are the Bowling Green area and the "Tri-Cities Region" of southeastern Kentucky, comprising the towns of Somerset, London, and Corbin.
Race and ancestry
The five largest ancestries in the commonwealth are: American (20.9 percent) (Mostly of British ancestry), German (12.7 percent), Irish (10.5 percent), English (9.7 percent), African American (7.8 percent). Only eight Kentucky counties list an ancestry other than "American" as the county's largest, those being Christian and Fulton, where African-American is the largest reported ancestry, and the state's most urban counties of Jefferson, Oldham, Fayette, Boone, Kenton, and Campbell, where German is the largest reported ancestry. Southeastern Kentucky was populated by a large group of Native Americans of mixed heritage, also known as Melungons, in the early nineteenth century.
African-Americans, who made up one-fourth of Kentucky's population prior to the Civil War, declined in number as many moved to the industrial North in the Great Migration. Today 44.2 percent of Kentucky's African-American population is in Jefferson County and 52 percent are in the Louisville Metro Area. Other areas with high concentrations, besides Christian and Fulton Counties, are the city of Paducah, the Bluegrass, and the city of Lexington. Many mining communities in far southeastern Kentucky also have populations that are between 5 and 10 percent African-American.
Religion

Lexington Theological Seminary (then College of the Bible), 1904.
Religious movements were important in the early history of Kentucky. Perhaps the most famous event was the interdenominational revival in August 1801 at the Cane Ridge Meeting house in Bourbon County. As part of what is now known as the "Western Revival," thousands began meeting around a Presbyterian communion service on August 6, 1801, and ended six days later on August 12, 1801 when both humans and horses ran out of food.[20] Some claim that the Cane Ridge revival was propagated from an earlier camp meeting at Red River Meeting House in Logan County.
In 2000, the Association of Religion Data Archives reported [21] that of Kentucky's 4,041,769 residents:
- 33.68 percent were members of evangelical Protestant churches
- Southern Baptist Convention (979,994 members, 24.25 percent)
- Independent Christian Churches/Churches of Christ (106,638 members, 2.64 percent)
- Church of Christ (58,602 members, 1.45 percent)
- 10.05 percent were Roman Catholics
- 8.77 percent belonged to mainline Protestant churches
- United Methodist Church (208,720 members, 5.16 percent)
- Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) (67,611 members, 1.67 percent)
- 0.05 percent were members of Orthodox churches
- 0.88 percent were affiliated with other theologies
- 46.57 percent were not affiliated with any church.
Economy
The total gross state product for 2006 was US$146 billion, 27th in the nation. Its per-capita personal income was US$28,513, 43rd in the nation.[22]
Kentucky's agricultural outputs are horses, cattle, tobacco, dairy products, hogs, soybeans, and corn. Its industrial outputs are transportation equipment, chemical products, electric equipment, machinery, food processing, tobacco products, coal, and tourism. The eastern Kentucky coal fields are recognized as being among the most productive in the nation.
Kentucky ranks 4th among U.S. states in the number of automobiles and trucks assembled. The Chevrolet Corvette, Cadillac XLR, Ford Explorer, Ford Super Duty trucks, Toyota Camry, Toyota Avalon, and Toyota Solara are assembled in Kentucky.

Oak casks used to store and age bourbon at Kentucky's Buffalo Trace Distillery.
Unlike many bordering states, which developed a widespread industrial economy, much of rural Kentucky has maintained a farm-based economy, with cattle, corn, and soybeans being the main crops. The area immediately outside Lexington is also the leading region for breeding thoroughbred racing horses, due to the high calcium content in the soil. Despite being the 14th smallest state in terms of land area, Kentucky still ranks 5th in the total number of farms, with more farms per square mile than any other U.S. state.[23] The average farm size in Kentucky is only 153 acres (0.6 km²). Kentucky ranks 5th nationally in goat farming, 8th in beef [[cattle] production, and 14th in corn production.
Since 2003, high-end bourbons (aged more than six years) have seen revenue grow from $450 million to over $500 million, some 2.2 million cases, in the United States. High-end bourbon sales accounted for 8 percent of total spirits growth in 2006. In 2007, United States spirits exports, virtually all of which are American whiskey, exceeded $1 billion for the first time. This represents a 15 percent increase over 2006. American whiskey is now sold in more than 100 different countries. The leading markets are the United Kingdom, Canada, Germany, Australia, and Japan. Key emerging markets for American whiskey are China, Vietnam, Brazil, Chile, Romania, and Bulgaria. More than 95 percent of the world’s Bourbon is distilled and aged in Kentucky.[24]
Louisville, from 1927 to 2004, was home to Brown & Williamson, the third largest company in the tobacco industry before merging with R. J. Reynolds in 2004 to form the Reynolds American Company. Brown & Williamson, one of the subjects of the tobacco industry scandals of the 1990s, was the focus of The Insider, a 1999 film shot around the Louisville area. The end of the federal tobacco program in 2004, and the government-guaranteed prices that went with it, have forced many Kentucky growers to attempt various farming alternatives. Burley (cigarette tobacco) production was expected to total 144.9 million pounds on 69,000 acres in 2008, down from 470.4 million pounds on 240,000 acres in 1997. A growing number of cities and counties are passing restrictions on smoking, even in the heart of Kentucky's tobacco-growing region.
Culture
Although Kentucky's culture is generally considered to be southern, it is unique and also influenced by the Midwest and southern Appalachia. Kentucky was a slave state, and African-Americans once comprised over one-quarter of its population. However, it lacked the cotton plantation system and never had the same high percentage of African-Americans as most other slave states. Kentucky adopted the Jim Crow system of racial segregation in most public spheres after the Civil War, but the state never disenfranchised African-American citizens to the level of the Deep South states, and it peacefully integrated its schools after the 1954 Brown v. Board of Education verdict, later adopting the first state civil rights act in the South in 1966.
Louisville is home to a number of annual cultural events. Perhaps most well-known is the Kentucky Derby, held annually during the first Saturday of May. The Derby is preceded by a two-week long Kentucky Derby Festival, which starts with the annual Thunder Over Louisville, the largest annual fireworks display in the nation. The Kentucky Derby Festival also features notable events such as the Pegasus Parade, The Great Steamboat Race, Great Balloon Race, a marathon, and about 70 events in total. Esquire magazine has called the Kentucky Derby "the biggest party in the south."
Notes
- ↑ Population and Housing Unit Estimates. U.S. Census Bureau (December 20, 2017). Retrieved December 20, 2017.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Elevations and Distances in the United States. United States Geological Survey (2001). Retrieved October 21, 2011.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Elevation adjusted to North American Vertical Datum of 1988.
- ↑ Online Etymology Dictionary. Kentucky Retrieved September 25, 2008.
- ↑ Mapquest. Map of Ohio River in Evansville, IN Retrieved September 25, 2008.
- ↑ NetState.com. The Geography of Kentucky - Climate Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ↑ Kleber. 1992.
- ↑ Corbin, Kentucky Economic Development. A Fisherman's Paradise Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ↑ Mercer County Online. The Presence History of Native Americans in Central Kentucky. Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ↑ Constance Skinner. The Dark and Bloody Hunting Ground Pioneers of the Old Southwest. Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ↑ Danville-Boyle County Convention & Visitors Bureau. Constitution Square State Historic Site Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ↑ Kentucky Secretary of State. 2006. 2006 General Election Registration Figures Set Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ↑ CNN. Election Results for Kentucky Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ↑ Cornell University Law School. McCreary County v. ACLU of Kentucky Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ↑ United States Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit. Text of decision in ACLU of Kentucky v. Mercer County, No. 03-5142 Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ↑ Barry Boardman, Jack Jones, John Perry, and Murray Wood. November 2003. Compulsive Gambling in Kentucky Legislative Research Commission. Retrieved October 23, 2008.
- ↑ Brett Guthrie. January 10, 2008. Sensing an air of inevitability on casino gambling KYPolitics.org. Retrieved October 23, 2008.
- ↑ Commonwealth of Kentucky. September 22, 2008. Governor Steve Beshear's Communications Office Retrieved October 23, 2008.
- ↑ Michael Price. 1996. Migration in Kentucky: Will the Circle Be Unbroken? University of Louisville. Retrieved September 26, 2008
- ↑ E. Michael Rusten, 2003. The One Year Book of Christian History. (Wheaton, IL. Tyndale House. ISBN 0842355073.)
- ↑ Association of Religion Data Archives. 2000. State Membership Report Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ↑ Kentucky Cabinet for Economic Development. Kentucky Economy Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ↑ U.S. Department of Agriculture. 2002. Farms, Land in Farms, Value of Land and Buildings, and Land Use: 2002 and 1997 Retrieved September 26, 2008.
- ↑ Kentucky Bourbon Trail. Sampler Tour Retrieved October 22, 2008.
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
Geography and geology
Politics
History
Surveys and reference
- Bodley, Temple and Samuel M. Wilson. History of Kentucky. 4 vols. 1928.
- Caudill, Harry M., Night Comes to the Cumberlands: A Biography of a Depressed Area. (1963). reprint ed. Jesse Stuart Foundation, 2001. ISBN 1931672008
- Channing, Steven. Kentucky: A Bicentennial History. W. W. Norton and American association for State and Local History. 1977.
- Clark, Thomas Dionysius. A History of Kentucky. (many editions, 1937–1992). Jesse Stuart Foundation, ISBN 0945084307
- Collins, Lewis. History of Kentucky. (1880).
- Harrison, Lowell H. and James C. Klotter. A New History of Kentucky. University Press of Kentucky, 1997. ISBN 081312008X
- Klotter, James C. Our Kentucky: A Study of the Bluegrass State. 2000, high school text.
- Lucas, Marion Brunson and Wright, George C. A History of Blacks in Kentucky. 2 vols. (1992). Vol. 1: From Slavery to Segregation, 1760-1891, 2nd ed. Kentudky Historical Society, 2003. ISBN 0916968324. A History of Blacks in Kentucky: In Pursuit of Equality, 1890-1980. 1992. ISBN 0916968219.
- University of Kentucky. Notable Kentucky African Americans.
- Share, Allen J. Cities in the Commonwealth: Two Centuries of Urban Life in Kentucky. Univ Pr of Kentucky, 1982. ISBN 0813102529
- Wallis, Frederick A. and Hambleton Tapp. A Sesqui-Centennial History of Kentucky 4 vols. (1945).
- Ward, William S. A Literary History of Kentucky. 1988. ISBN 087049578X.
- Federal Writers' Project of the Work Projects Administration for the State of Kentucky. WPA, Kentucky: A Guide to the Bluegrass State (1939) Retrieved September 23, 2008.
- Yater, George H. Two Hundred Years at the Fall of the Ohio: A History of Louisville and Jefferson County, 2nd ed. The Filson Historical Society, 1987. ISBN 0960107231
Specialized scholarly studies
- Bakeless, John. Daniel Boone, Master of the Wilderness (1989) Questia. Retrieved September 23, 2008.
- Blakey, George T. Hard Times and New Deal in Kentucky, 1929–1939. 1986.
- Coulter, E. Merton. The Civil War and Readjustment in Kentucky. (1926)
- Faragher, John Mack. Daniel Boone: The Life and Legend of an American Pioneer. holt, 1993. ISBN 0805030077
- Fenton, John H. Politics in the Border States: A Study of the Patterns of Political Organization, and Political Change, Common to the Border States: Maryland, West Virginia, Kentucky, and Missouri (1957) Questia. Retrieved September 23, 2008.
- Ireland, Robert M. The County in Kentucky History. (1976)
- Klotter, James C. et al. Kentucky's Civil War 1861–1865. ed. Jerlene Rose. Back Home In Kentucky Inc., 2005. ISBN 0976923114
- Klotter, James C. Kentucky: Portrait in Paradox, 1900–1950. (1992) Kentucky Historical Society, 2001.
- Pearce, John, Ed. Divide and Dissent: Kentucky Politics, 1930–1963. University Press of Kentucky, 1991. ISBN 0813108047
- Sonne, Niels Henry. Liberal Kentucky, 1780–1828 (1939) Questia. Retrieved September 23, 2008.
- Tapp, Hambleton and James C Klotter. Kentucky Decades of Discord, 1865–1900. (1977)
- Townsend, William H. Lincoln and the Bluegrass: Slavery and Civil War in Kentucky (1955) Questia. Retrieved September 23, 2008.
- Waldrep, Christopher Night Riders: Defending Community in the Black Patch, 1890–1915 (1993) Questia. Retrieved September 23, 2008.
Image Gallery
Louisville is the state's largest city, with a metro population of 1.2 million.
PhotodowntownLexKY.JPG
Lexington is the state's second largest city, with a metro population of around 500,000.
Although Covington, Kentucky only has a population of 42,000, the Kentucky side of the Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky metropolitan area has a population of over 450,000.
Picture 124NewportKYwaterfrnt.jpg
Newport's Aquarium and waterfront
The world famous Louisville Slugger baseball bat is made in Kentucky.
Thunder Over Louisville is the largest annual fireworks show in the world.
Picture 1289.jpg
Kentucky's horse farms are world renowned.
The Daniel Boone National Forest.
Picture 282.jpg
The Ohio River forms the northern border of Kentucky.
DowntownBG.JPG
Many Kentucky cities have historic areas near downtown, such as this example in Bowling Green.
4th and hill.jpg
Old Louisville is the largest Victorian historic neighborhood in the United States
External links
All links retrieved October 5, 2022.
| US South (as defined by the United States Census Bureau) |
|---|
| |
|
Coordinates: 37.5° N 85° W
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article
in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.