|
|
| (45 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | {{claimed}} | + | {{Approved}}{{Submitted}}{{Images OK}}{{Paid}}{{copyedited}} |
| − | | + | [[Image:US map-South Historic 1.PNG|thumb|400px|'''Historic Southern United States'''. The states in red were in the Confederacy and have historically been regarded as forming "the South." Sometimes they are collectively referred to as "Dixie." Those in stripes were considered "Border" states, and gave varying degrees of support to the Southern cause although they remained in the Union. (This image depicts the original, trans-Allegheny borders of Virginia, and so does not include West Virginia. See image below for post-1863 Virginia and West Virginia borders.)]] |
| − | [[Image:US map-South Historic 1.PNG|thumb|300px|'''Historic Southern United States'''. The states in red were in the Confederacy and have historically been regarded as forming "the South." Sometimes they are collectively referred to as "Dixie." Those in stripes were considered "Border" states, and gave varying degrees of support to the Southern cause although they remained in the Union. (This image depicts the original, trans-Allegheny borders of Virginia, and so does not include West Virginia. See image below for post-1863 Virginia and West Virginia borders.)]] | |
| − | [[Image:US map-South Modern.png|thumb|300px|'''Modern definition''' The states in dark red are almost always included in modern day definitions of the South, while those in medium red are usually included. Maryland and Missouri are occasionally considered Southern, while Delaware is seldom considered a Southern state. Oklahoma is sometimes considered Southern because the area of Oklahoma, then known as Indian Territory, was allied with the Confederacy. West Virginia is considered Southern by many, because it was once part of Virginia. <ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.unc.edu/news/archives/jun99/reed16.htm | title=UNC-CH surveys reveal where the ‘real’ South lies | author=David Williamson | accessmonthday=22 Feb | accessyear=2007}}</ref><ref>http://www.pfly.net/misc/GeographicMorphology.jpg</ref>]]
| |
| − | [[Image:Census Regions and Divisions.PNG|thumb|300px|The South as one of four regions of the United States.]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | The '''Southern United States'''—commonly referred to as the '''American South''', '''[[Dixie]]''', or simply '''the South'''—constitutes a large distinctive [[region]] in the southeastern and south-central [[United States]]. Because of the region's unique cultural and historic heritage, including early European colonial settlements, the doctrine of [[states' rights]], the institution of [[slavery]] and the legacy of the [[Confederate States of America|Confederacy]] during the [[American Civil War]], the South has developed its own customs, literature, musical styles, and varied [[Southern US cuisine|cuisines]].
| |
| | | | |
| | + | The '''Southern United States'''—commonly referred to as the '''American South''' or simply '''the South'''—constitutes a large distinctive region in the southeastern and south-central [[United States]]. Because of the region's unique cultural and historic heritage, including early European colonial settlements, the doctrine of [[states' rights]], the institution of [[slavery]], and the legacy of the [[Confederate States of America|Confederacy]] during the [[American Civil War]], the South has developed its own customs, literature, musical styles, and varied cuisines. |
| | + | {{toc}} |
| | + | After the Civil War, the South was largely devastated in terms of its population, infrastructure, and economy. Not until modern times did the situation change. During [[World War II]], new industries and military bases sprang up across the region, providing badly need capital and infrastructure. Farming shifted from [[cotton]] and [[tobacco]] to include [[soybean]]s, [[corn]], and other foods. This growth accelerated in the 1980s and 1990s. Large urban areas rose in Texas, Georgia, and Florida. Rapid expansion in industries such as [[automobile]]s, [[telecommunication]]s, [[textile]]s, [[technology]], [[banking]], and [[aviation]] gave some states an industrial strength that rivaled large states elsewhere. By the 2000 census, the South (along with the West) was leading the nation in population growth. |
| | + | [[Image:US map-South Modern.png|thumb|400px|'''Modern definition''' The states in dark red are almost always included in modern day definitions of the South, while those in medium red are usually included. Maryland and Missouri are occasionally considered Southern, while Delaware is seldom considered a Southern state. Oklahoma is sometimes considered Southern because the area of Oklahoma, then known as Indian Territory, was allied with the Confederacy. West Virginia is considered Southern by many, because it was once part of Virginia.]] |
| | + | [[Image:Census Regions and Divisions.PNG|thumb|400px|The South as one of four regions of the United States.]] |
| | ==Geography== | | ==Geography== |
| − | As defined by the [[United States Census Bureau]],<ref>http://www.census.gov/geo/www/us_regdiv.pdf US Census Bureau's official map</ref> the Southern [[region]] of the [[United States]] includes 16 states (with a total 2006 estimated population of 109,083,752) and is split into three smaller units, or divisions: | + | As defined by the U.S. Census Bureau, the southern region includes 16 states (with a total 2006 estimated population of 109,083,752) and is split into three smaller units: |
| − | *'''The [[South Atlantic States]]:''' [[Florida]], [[Georgia (U.S. state)|Georgia]], [[North Carolina]], [[South Carolina]], [[Virginia]], [[West Virginia]], [[Maryland]], and [[Delaware]] | + | *'''The South Atlantic States:''' [[Florida]], [[Georgia (state)|Georgia]], [[North Carolina]], [[South Carolina]], [[Virginia]], [[West Virginia]], [[Maryland]], and [[Delaware]] |
| − | *'''The [[East South Central States]]:''' [[Alabama]], [[Kentucky]], [[Mississippi]] and [[Tennessee]] | + | *'''The East South Central States:''' [[Alabama]], [[Kentucky]], [[Mississippi]], and [[Tennessee]] |
| − | *'''The [[West South Central States]]: ''' [[Arkansas]], [[Louisiana]], [[Oklahoma]] and [[Texas]] | + | *'''The West South Central States:''' [[Arkansas]], [[Louisiana]], [[Oklahoma]], and [[Texas]] |
| | + | [[Image:Magnolia grandiflora flower.JPG|thumb|right|400px|Flower of ''Magnolia grandiflora,'' also known as the ''Southern Magnolia''.]] |
| | + | The popular definition of the "South" is more informal and is generally associated with those states that seceded during the [[American Civil War|Civil War]] to form the [[Confederate States of America]]. Those states share commonalities of history and culture. The "border states" of the Civil War—specifically [[Missouri]], Kentucky, Maryland, and Delaware—roughly form the northern boundary of the "South." These states have a history of straddling the North-South divide, which was made clear when they did not secede during the Civil War even though they allowed slavery. Depending on the context, these states may or may not be considered part of the South. |
| | | | |
| − | Other definitions include:
| + | The South is a vast, diverse region, having numerous [[climate|climatic]] zones, including temperate, sub-tropical, tropical, and arid. Many crops grow easily in its soils and can be grown without frost for at least six months of the year. Some parts of the South, particularly the Southeast, have landscapes characterized by the presence of live [[oak]]s, [[magnolia]] trees, yellow jessamine vines, and flowering [[dogwood]]s. Another common environment is the [[bayou]]s and swampland of the Gulf Coast, especially in Louisiana. The South is a victim of [[kudzu]], an invasive fast-growing vine that covers large amounts of land and kills indigenous plant life. |
| − | *'''[[Old South|The Old South]]:''' usually the original Southern colonies''': ''' [[Delaware]], [[Georgia (U.S. state)|Georgia]], [[North Carolina]], [[South Carolina]], and [[Virginia]] <ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.gutenberg.org/dirs/etext01/pofos10.txt | title=Pioneers of the Old South, A Chronicle of English Colonial Beginnings
| |
| − | | author=Mary Johnston
| |
| − | | accessmonthday=19 May | accessyear=2007}}</ref>
| |
| − | *'''[[New South|The New South]]:''' usually including the [[South Atlantic States]]
| |
| − | *'''[[Solid South|The Solid South]]:''' region controlled by the U.S. Democratic Party from 1877 to 1964. Includes at least all the 11 former Confederate States.
| |
| − | *'''[[Appalachia|Southern Appalachia]]:''' [[Cumberland Plateau]] of [[Kentucky]] and [[Tennessee]], [[Western North Carolina]], [[Western Maryland]], [[West Virginia]], the [[Shenandoah Valley]] and [[Blue Ridge Mountains]] of [[Virginia]], and northeast [[Georgia (U.S. state)|Georgia]].
| |
| − | *'''[[Southeastern United States]]:''' usually including [[the Carolinas]], [[Virginia]], [[Tennessee]], [[Kentucky]], [[Georgia (U.S. state)|Georgia]], [[Alabama]], [[Mississippi]], and [[Florida]]
| |
| − | *'''[[Deep South|The Deep South]]:''' various definitions
| |
| − | *'''[[Gulf South|The Gulf South]]:''' various definitions, usually including Gulf coasts of [[Florida]], [[Louisiana]], [[Mississippi]], [[Texas]] and [[Alabama]]
| |
| − | *'''[[Upper South|The Upper South]]: '''[[Kentucky]], [[Virginia]], [[West Virginia]], [[Tennessee]], [[North Carolina]] [http://www.britannica.com/eb/art-3822]
| |
| − | *'''[[Dixie]]:''' various definitions, but most commonly associated with the 11 states of the Old Confederacy.
| |
| − | *'''[[South Central United States|The Mid-South]]:''' also known as the [[South Central United States]]
| |
| | | | |
| − | The popular definition of the "South" is more informal and is generally associated with those states that seceded during the [[American Civil War|Civil War]] to form the [[Confederate States of America]]. Those states share commonalities of history and culture that carry on to the present day. The "border states" of the [[American Civil War|Civil War]]- specifically [[Missouri]], [[Kentucky]], [[Maryland]], and [[Delaware]] roughly form the northern boundary of the "South". These states have a history of straddling the North-South divide, which was made clear when they did not secede during the [[American Civil War|Civil War]] even though they allowed slavery. Depending on the context, these states may or may not be considered part of the South. [[West Virginia]] is a unique case. Although [[West Virginia]] gave half its soldiers <ref>"Although early estimates noted that Union soldiers from the region outnumbered Confederates by more than three to one, more recent and detailed studies have concluded that there were nearly equal numbers of Union and Confederate soldiers." http://www.wvculture.org/HiStory/civwaran.html</ref> and nearly two-thirds of its territory<ref>Richard O. Curry "A House Divided", Univ. of Pittsburgh, 1964, pg. 49, map of Secessionist counties from vote of May 23, 1861</ref> to the Confederacy, early Union victories in the state and Union victory in the war insured that the history of the state would be written from the perspective of Wheeling rather than Richmond. This perspective is often responsible for the exclusion of [[West Virginia]] from many things Southern. Whether it is culturally part of the South again depends on context and on what distinction is drawn between [[Appalachia]]n and Southern culture and an understanding of [[West Virginia]]'s history. | + | ==History== |
| | + | [[Image:CottonNegrosSouth.jpg|thumb|300px|Picking cotton in southeastern United States, early twentieth century]] |
| | + | The predominant culture of the South has its origins with the settlement of the region by British colonists in the seventeenth century, mostly in coastal regions. In the eighteenth century, large groups of [[Scotland|Scots]] and Ulster-Scots (later called the Scots-Irish) settled in [[Appalachian Mountains|Appalachia]] and the Piedmont. These people engaged in warfare, [[trade]], and cultural exchanges with the [[Native Americans in the United States|Native American]]s already in the region (such as the [[Creek people|Creeks]] and [[Cherokee]]s). |
| | | | |
| − | Biologically, the South is a vast, diverse region, having numerous climatic zones, including [[temperate]], [[Subtropics|sub-tropical]], [[Tropical climate|tropical]], and [[arid]]. Many crops grow easily in its soils and can be grown without frost for at least six months of the year. Some parts of the South, particularly the Southeast, have landscapes characterized by the presence of [[live oak]]s, [[magnolia]] trees, [[Yellow Jessamine|yellow jessamine]] vines, and flowering [[dogwood]]s. Another common environment is the [[bayou]]s and swampland of the [[Gulf Coast of the United States|Gulf Coast]], especially in Louisiana. The South is a victim of [[kudzu]], an invasive fast-growing vine which covers large amounts of land and kills indigenous plant life.
| + | The [[Trail of Tears]] refers to the [[forced relocation]] in 1838, of the Cherokee tribe to Indian Territory (modern day [[Oklahoma]]), from what is now the state of [[Georgia]]. The forced march resulted in the deaths of an estimated 4,000 Cherokee. In the Cherokee language, the event is called ''Nunna daul Isunyi''—“the Trail Where We Cried.” The phrase originated as a description of the forcible removal of the [[Choctaw]] nation in 1831. |
| | | | |
| − | ==History==
| + | After 1700, large groups of [[Africa]]n slaves were brought in to work on the plantations that dominated export agriculture, growing [[tobacco]], [[rice]], and [[indigo plant|indigo]]. [[Cotton]] became dominant after 1800. The explosion of cotton cultivation made [[slavery]] an integral part of the South's early nineteenth century economy. |
| | | | |
| − | The predominant culture of the South has its origins with the settlement of the region by [[British colonization of the Americas|British colonists]]. In the [[17th century]], most were of [[English people|English]] origins who settled mostly on the coastal regions of the South, but in the [[18th century]], large groups of [[Scottish people|Scots]] and [[Ulster-Scots]] (later called the [[Scots-Irish]]) settled in [[Appalachia]] and the [[Piedmont (United States)|Piedmont]]. In a census taken in 2000 of Americans and their self-reported ancestries, areas where people reported '[[American ancestry|American]]' ancestry were the places where, historically, many Scottish and Scots-Irish Protestants as well as many English settlers settled in America: the interior as well as some of the coastal areas of the South, and the Appalachian region. It is believed the number of [[Scottish Americans]] could be in the region of 20 million and [[Scots-Irish Americans]] at 27 million. These people engaged in [[endemic warfare|warfare]], [[trade]], and cultural exchanges with the [[Native Americans in the United States|Native Americans]] already in the region (such as the [[Creek Indians]] and [[Cherokee]]s). After 1700, large groups of [[Africa]]n slaves were brought in to work on the large [[plantation]]s that dominated export agriculture, growing [[tobacco]], [[rice]], and [[indigo plant|indigo]]. [[Cotton]] became dominant after 1800. The explosion of cotton cultivation<ref>{{cite web| url=http://home.earthlink.net/~gfeldmeth/lec.slavery.html | title= The Peculiar Institution of American Slavery | accessmonthday=22 Aug | accessyear=2006}}</ref> made the "peculiar institution" of slavery an integral part of the South's early 19th century economy. | + | The oldest university in the South, the College of William and Mary, was founded in 1693 in Virginia; it pioneered in the teaching of [[political economy]] and educated future U.S. presidents [[Thomas Jefferson]], [[James Monroe]], and [[John Tyler]], all from [[Virginia]]. Indeed, the entire region dominated politics in that era: For example, four of the first five [[President of the United States|Presidents]]—[[George Washington]], Jefferson, [[James Madison]], and Monroe—were from Virginia. |
| | | | |
| − | The oldest university in the South, the [[College of William and Mary]], was founded in 1693 in Virginia; it pioneered in the teaching of [[political economy]] and educated future U.S. Presidents [[Thomas Jefferson|Jefferson]], [[James Monroe|Monroe]] and [[John Tyler|Tyler]], all from Virginia. Indeed, the entire region dominated politics in the [[First Party System]] era: for example, four of the first five [[President of the United States|Presidents]]— [[George Washington|Washington]], [[Thomas Jefferson|Jefferson]], [[James Madison|Madison]], and [[James Monroe|Monroe]]—were from Virginia.
| + | Two major political issues that festered in the first half of the nineteenth century strengthened the identities of North and South as distinct regions with certain strongly opposed interests and fed the arguments over states' rights that culminated in secession and the [[American Civil War]]. One of these issues concerned the protective [[tariff]]s enacted to assist the growth of the [[manufacturing]] sector, located primarily in the North. In 1832, in resistance to federal legislation increasing tariffs, South Carolina passed an ordinance of nullification, a procedure by which a state would in effect repeal a federal law. A naval flotilla was sent to Charleston harbor, and the threat of landing ground troops was used to compel the collection of tariffs. A compromise was reached by which the tariffs would be gradually reduced, but the underlying argument over states' rights continued to escalate in the following decades. |
| | | | |
| − | Two major political issues that festered in the first half of the [[19th century]] caused political alignment along sectional lines, strengthened the identities of North and South as distinct regions with certain strongly opposed interests and fed the arguments over states' rights that culminated in secession and the Civil War. One of these issues concerned the protective tariffs enacted to assist the growth of the manufacturing sector, primarily in the North. In 1832, in resistance to federal legislation increasing tariffs, South Carolina passed an ordinance of [[nullification]], a procedure in which a state would in effect repeal a Federal law. Soon a naval flotilla was sent to [[Charleston, South Carolina|Charleston]] harbor, and the threat of landing ground troops was used to compel the collection of tariffs. A compromise was reached by which the tariffs would be gradually reduced, but the underlying argument over states' rights continued to escalate in the following decades.
| + | The second issue concerned slavery, primarily the question of whether slavery would be permitted in newly admitted states. The issue was initially finessed by political compromises designed to balance the number of "free" and "slave" states. The issue resurfaced in more virulent form, however, around the time of the [[Mexican-American War|Mexican War]], which raised the stakes by adding new territories primarily on the southern side of the imaginary geographic divide. |
| − | | |
| − | The second issue concerned slavery, primarily the question of whether slavery would be permitted in newly admitted states. The issue was initially finessed by political compromises designed to balance the number of "free" and "slave" states. The issue resurfaced in more virulent form, however, around the time of the [[Mexican-American War|Mexican War]], which raised the stakes by adding new territories primarily on the Southern side of the imaginary geographic divide. | |
| | | | |
| | ===Civil War=== | | ===Civil War=== |
| | + | By 1855, the South was losing political power to the more populous North and was locked in a series of constitutional and political battles with the North regarding states' rights and the status of slavery in the territories. President [[James K. Polk]] imposed a low-tariff regime on the country, which angered [[Pennsylvania]] industrialists, and blocked proposed federal funding of national roads and port improvements. Seven states decided on secession after the election of [[Abraham Lincoln]] in 1860. They formed the [[Confederate States of America]]. In 1861, they were joined by four more states. |
| | | | |
| − | By 1855, the South was losing political power to the more populous [[Union (American Civil War)|North]] and was locked in a series of constitutional and political battles with the North regarding [[states' rights]] and the status of [[slavery]] in the territories. President [[James K. Polk]] imposed a low-tariff regime on the country ([[Walker Tariff]] of 1846), which angered [[Pennsylvania]] industrialists, and blocked proposed federal funding of national roads and port improvements. Once the North came to power in 1861, many Southerners felt it was time to secede from the union.
| + | The United States government refused to recognize the seceding states as a new country and kept in operation its second to last fort in the South, which the Confederacy captured in April 1861, at the [[Battle of Fort Sumter]], in the port of Charleston, triggering the Civil War. The Confederacy retained a low tariff regime for [[Europe]]an [[imports]] but imposed a new tax on all imports from the North. A Union blockade stopped most commerce from entering the South, so the Confederate taxes hardly mattered. The southern [[transportation]] system depended primarily on river and coastal traffic by boat; both were shut down by the Union navy. The small railroad system virtually collapsed, so that by 1864, internal travel was so difficult that the Confederate economy was crippled. |
| | | | |
| − | Seven cotton states decided on [[secession]] after the election of [[Abraham Lincoln]] in 1860. They formed the [[Confederate States of America]]. In 1861, they were joined by four more states. The United States government refused to recognize the seceding states as a new country and kept in operation its second to last fort in the South, which the Confederacy captured in April 1861 at the [[Battle of Fort Sumter]], in the port of [[Charleston, South Carolina|Charleston]], triggering the Civil War. In the four years of war which followed, the South found itself as the primary battleground, with all but two of the main battles taking place on Southern soil. The Confederacy retained a low tariff regime for [[Europe]]an imports but imposed a new tax on all imports from the North. The [[Union Army|Union]] blockade stopped most commerce from entering the South, so the Confederate taxes hardly mattered. The Southern transportation system depended primarily on river and coastal traffic by boat; both were shut down by the [[Union Navy]]. The small railroad system virtually collapsed, so that by 1864 internal travel was so difficult that the Confederate economy was crippled.
| + | The Union (so-called because they fought for the United States of America) eventually defeated the Confederate States of America. The South suffered much more than the North, primarily because the war was fought almost entirely in the South. Overall, the Confederacy suffered 95,000 killed in action and 165,000 who died of disease, for a total of 260,000,<ref>Matthew White, [http://necrometrics.com/wars19c.htm#ACW Nineteenth Century Death Tolls: American Civil War] ''Statistics of Wars, Oppressions and Atrocities of the Nineteenth Century''. Retrieved October 5, 2022. </ref> out of a total white southern population at the time of around 5.5 million. Based on 1860 census figures, 8 percent of all white males aged 13 to 43 died in the war, including 6 percent in the North and an extraordinary 18 percent in the South.<ref>Craig Lambert, [https://www.harvardmagazine.com/2001/05/the-deadliest-war-html The Deadliest War] ''Harvard Magazine''. Retrieved October 5, 2022. </ref> Northern casualties exceeded Southern casualties. |
| − | | |
| − | The Union (so-called because they fought for the United States of America) eventually defeated the [[Confederate States of America]] (the formal name of the southern American states during the Civil War). The South suffered much more than the North, primarily because the war was fought almost entirely in the South. Overall, the Confederacy suffered 95,000 killed in action and 165,000 who died of disease, for a total of 260,000,<ref>{{cite web | url=http://users.erols.com/mwhite28/wars19c.htm#ACW | title=Nineteenth Century Death Tolls: American Civil War | accessmonthday=22 Aug | accessyear=2006}}</ref> out of a total white Southern population at the time of around 5.5 million.<ref>[http://www.americancivilwar.org.uk/news_those-confederate-states_42.htm American Civil War, Those Confederate States]</ref> <!-- site no longer around apparently: i am julianne[http://www.vectorsite.net/twcw02.html] —> Based on 1860 census figures, 8% of all [[white American|white]] males aged 13 to 43 died in the war, including 6% in the North and an extraordinary 18% in the South.<ref>[http://www.harvardmagazine.com/on-line/050155.html The Deadliest War]</ref> Northern casualties exceeded Southern casualties, however. | |
| | | | |
| | ===Reconstruction=== | | ===Reconstruction=== |
| − | {{main|Reconstruction}}
| + | After the Civil War, the South was largely devastated in terms of its population, infrastructure, and economy. The republic also found itself under Reconstruction, with military troops in direct political control of the South. White southerners who had actively supported the Confederacy lost many of the basic rights of citizenship (such as voting). With passage of the [[Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution|Thirteenth Amendment]] to the [[Constitution of the United States]] (outlawing slavery), the [[Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution|Fourteenth Amendment]] (granting full U.S. citizenship to [[African-American]]s), and the [[Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution|Fifteenth Amendment]] (extending the right to vote to African-American males), blacks began to enjoy more rights than they ever had in the South. |
| − | After the Civil War, the South was largely devastated in terms of its population, [[infrastructure]] and economy. The republic also found itself under Reconstruction, with military troops in direct political control of the South. Many white Southerners who had actively supported the Confederacy lost many of the basic rights of citizenship (such as the ability to vote) while with the passage of the [[Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution|13th Amendment]] to the [[Constitution of the United States]] (which outlawed slavery), the [[Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution|14th Amendment]] (which granted full U.S. citizenship to [[African American]]s) and the [[Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution|15th amendment]] (which extended the right to vote to [[African American]] males), African Americans in the South began to enjoy more rights than they had ever had in the region. | |
| − | | |
| − | Northern [[Carpetbagger]]s came south to participate in politics and business. Some were representatives of the Freedmen's Bureau and other agencies of Reconstruction; some were humanitarians with the intent to help black people; yet some were adventurers who hoped to benefit themselves by questionable methods.[http://www.history.com/encyclopedia.do?articleId=204786]
| |
| | | | |
| − | By the 1890s, though, a political backlash against these rights had developed in the South. Organizations such as the [[Ku Klux Klan]]—a clandestine organization sworn to perpetuate [[white supremacy]]—used [[lynchings]], and other forms of violence and intimidation to keep African Americans from exercising their political rights (the well-known [[cross burning]]s did not become a Klan ritual until the emergence of the Second Ku Klux Klan in the 1920s), while the [[Jim Crow law]]s were created to legally do the same thing. It would not be until the late 1960s that these changes would be undone by the [[American Civil Rights Movement (1955-1968)|American Civil Rights Movement]]. | + | By the 1890s, though, a political backlash against these rights had developed in the South. Organizations such as the [[Ku Klux Klan]]—a clandestine organization sworn to perpetuate [[white supremacy]]—used [[lynching]]s and other forms of violence and intimidation to keep African Americans from exercising their political rights, while [[Jim Crow laws]] were created to legally do the same thing. It would not be until the late 1960s that these phenomena would be undermined by the [[American Civil Rights Movement (1955-1968)|American Civil Rights Movement]]. |
| | | | |
| − | ===20th century=== | + | ==Economy== |
| − | The first major oil well in the South was drilled at [[Spindletop]] near [[Beaumont, Texas]], on the morning of [[January 10]], [[1901]]. Other oil fields were later discovered nearby in Arkansas, Oklahoma, and under the [[Gulf of Mexico]]. The resulting “Oil Boom” permanently transformed the economy of the West South Central states and led to the first significant economic expansion after the Civil War.
| + | Nearly all southerners, black and white, suffered as a result of the Civil War. With the region devastated by its loss and the destruction of its civil infrastructure, much of the South was generally unable to recover economically until after [[World War II]]. Locked into low productivity [[agriculture]], the region's growth was slowed by limited industrial development, low levels of entrepreneurship, and the lack of capital investment. |
| | | | |
| − | The economy, which for the most part had still not recovered from the [[List of civil wars|Civil War]], was dealt a double blow by [[the Great Depression]] and the [[Dust Bowl]]. After the [[Wall Street Crash of 1929]], the economy suffered significant reversals and millions were left unemployed. Beginning in 1934 and lasting until 1939, an ecological disaster of severe wind and [[drought]] caused an exodus from Texas and Arkansas, the [[Oklahoma Panhandle]] region and the surrounding plains, in which over 500,000 [[American ancestry|Americans]] were homeless, hungry and jobless.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.pbs.org/fmc/interviews/gregory.htm | title= First Measured Century: Interview: James Gregory | accessmonthday=22 Aug|accessyear=2006}}</ref> Thousands left the region forever to seek economic opportunities along the [[West Coast of the United States|West Coast]]. | + | The first major [[petroleum|oil]] well in the South was drilled near Beaumont, [[Texas]], on the morning of January 10, 1901. Other oil fields were later discovered nearby in [[Arkansas]], [[Oklahoma]], and under the [[Gulf of Mexico]]. The resulting boom permanently transformed the economy of the western South Central states and led to the first significant economic expansion since the Civil War. |
| | | | |
| − | Nearly all southerners, black and white, suffered as a result of the Civil War. With the region devastated by its loss and the destruction of its civil infrastructure, much of the South was generally unable to recover economically until after [[World War II]]. The South was noted by President [[Franklin Delano Roosevelt]] as the "number one priority" in terms of need of assistance during the Great Depression, instituting programs such as the [[Tennessee Valley Authority]] in 1933. Locked into low productivity agriculture, the region's growth was slowed by limited industrial development, low levels of entrepreneurship, and the lack of capital investment.
| + | The economy, which for the most part had still not recovered from the [[American Civil War|Civil War]], was dealt a double blow by the [[Great Depression]] and the [[Dust Bowl]]. After the [[Wall Street Crash of 1929]], the economy suffered significant reversals and millions were left [[unemployment|unemployed]]. From 1934 until 1939, an ecological disaster of severe wind and [[drought]], known as the ''Dust Bowl,'' caused an exodus from Texas and Arkansas, the [[Oklahoma]] Panhandle region, and the surrounding plains, in which over 500,000 Americans were homeless, hungry, and jobless.<ref>[https://www.pbs.org/fmc/interviews/gregory.htm First Measured Century: Interview with James Gregory] ''PBS''. Retrieved October 5, 2022. </ref> Thousands left the region to seek economic opportunities on the West Coast. |
| | | | |
| − | World War II marked a time of change in the South as new industries and military bases sprang up across many areas of the region providing badly need capital and infrastructure. People from all parts of the US came to the South for military training and work in the regions many bases and new industries. Farming shifted from cotton and tobacco to include [[soybeans]], [[corn]], and other foods. This growth increased in the 1960 and greatly accelerated into the 80's and 90's. Large urban areas with over 4 million people rose in Texas, Georgia, and Florida. Rapid expansion in industries such as autos, telecommunications, textiles, technology, banking, and aviation gave some states in the South an industrial strength to rival large states elsewhere in the country. By the 2000 census, The South (along with the West) was leading the nation in population growth. However, with this growth came long commute times and serious air pollution problems in cites such as Dallas, Houston, Atlanta, Miami, Austin, Charlotte, and other cities. | + | [[World War II]] marked a time of change in the South, as new industries and military bases sprang up across many areas of the region, providing badly need capital and infrastructure. People from all parts of the United States came to the South for military training and to work. Farming shifted from [[cotton]] and [[tobacco]] to include [[soybean]]s, [[corn]], and other foods. This growth increased in the 1960s, and greatly accelerated in the 1980s and 1990s. Large urban areas with over four million people rose in Texas, Georgia, and Florida. Rapid expansion in industries such as [[automobile]]s, [[telecommunication]]s, [[textile]]s, [[technology]], [[banking]], and [[aviation]] gave some states in the South an industrial strength that rivaled large states elsewhere. By the 2000 census, the South (along with the West) was leading the nation in population growth. With this growth, however, came long commute times and serious air [[pollution]] problems in cities such as Dallas, Houston, Atlanta, Miami, Austin, and Charlotte. |
| | | | |
| | ===Poverty=== | | ===Poverty=== |
| | + | The South has historically been financially disadvantaged when compared to the United States as a whole. After the [[American Civil War|Civil War]], nearly the entire economic infrastructure of the region was in ruins. Since there were few industrial businesses located in the South at the time, other possible sources of income were scarce. Most former slaves had no training or experience in anything besides agriculture. |
| | | | |
| − | [[Image:southernhouseholdincome.gif|right|thumb|States in [[maroon]] have an average household income of less than $35,000.00 per year. States in [[red]] have average household incomes between $35,000.00-$40,000.00. States in [[yellow]] have household incomes between $40,000-$45,000.00. States in [[teal]] have household incomes between $50,000.00-$55,000.00 per year. Maryland is the only state with an average household income exceeding $55,000.00 per year.]] | + | After [[World War II]], the development of the [[Interstate Highway System]], household air conditioning and later, passage of federal civil rights bills, the South was successful at attracting industry and business from other parts of the country, particularly the Rust Belt region of the [[Northeastern United States|Northeast]] and the [[Great Lakes]]. [[Poverty]] rates and [[unemployment]] declined as a result. Federal programs such as the Appalachian Regional Commission also contributed to economic growth. |
| − | | |
| − | The South has historically been financially disadvantaged when compared to the United States as a whole. After the Civil War, nearly the entire economic infrastructure of the region was in ruins. As agriculture had been the foundation of the Southern economy at the time, with the passing of the 13th Amendment (which outlawed slavery), planted resources could not be farmed and harvested as efficiently, eventually sending many plantation owners region-wide into poverty. Additionally, since there were few industrial businesses located in the south at the time, there were not many other possible sources of income.
| |
| | | | |
| − | Former slaves were also a victim to this as they had no training or experience in anything besides plantation agriculture, and non-agricultural work was scarce.
| + | While much of the Southern United States has advanced considerably since World War II, poverty persists in some areas, like eastern Kentucky and southern West Virginia. The [[Mexico|Mexican]] border area in Texas takes the brunt of poverty in the South today. |
| − | | |
| − | After World War II, the development of the [[Interstate Highway System]], household air conditioning and later, passage of civil rights bills the south was successful at attracting industry and business from other parts of the country, particularly the [[Rust Belt]] region of the [[Northeastern United States|Northeast]] and the [[Great Lakes]]. Poverty rates and unemployment declined as a result. Federal programs such as the [[Appalachian Regional Commission]] also contributed to economic growth.
| |
| − | | |
| − | While much of the Southern United States has advanced considerably since World War II, poverty still persists today in some areas. Areas like the [[Black Belt (U.S. region)|Black Belt]], the [[Eastern Mountain Coal Fields|eastern Kentucky]] and [[southern West Virginia]] areas in [[Appalachia]], and the [[United States–Mexico border|Mexican border]] area along the [[Rio Grande]] in [[Texas]] make up the brunt of poverty in the South today. | |
| | | | |
| | ==Culture== | | ==Culture== |
| − | {{main|Culture of the Southern United States}}
| + | Southern culture has been and remains generally more socially [[conservatism|conservative]] than the rest of the country. Because of the central role of [[agriculture]] in the economy, society remained stratified according to land ownership. Rural communities often developed strong attachment to their [[church]]es as the primary community institution. |
| − | | |
| − | Of all the regions of the United States the South is most distinct, in both the minds of its residents and those in other parts of the country. Depending on one's attitude, and perhaps latitude, the South and the "idea" of the South is and/or has been feared, revered, hated, loved, and stereotyped, for better or worse. It is disdained by some, yet an object of intense attachment and loyalty for others. And these emotions are not necessarily aligned with the one Mason and Dixon surveyed. Some born in the South shun their history and heritage, while there are many transplanted northerners who will frankly state they would never, ever, return to the colder climes (both literally and metaphorically), from which they came.{{Fact|date=June 2007}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | All in all though, the South exists with a certain separateness from the rest of the country. Perhaps it might be summed up well by certain passages in Tim Jacobson's book "Heritage of the South." Jacobson wrote:
| |
| − | | |
| − | ''"More than any other part of America, the South stands apart...Thousands of Northerners and foreigners have migrated to it...but Southerners they will not become. For this is still a place where you must have either been born or have "people" there, to feel it is your native ground.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ''Natives will tell you this. They are proud to be Americans, but they are also proud to be Virginians, South Carolinians, Tennesseans, and Texans. But they are conscious of another loyalty too, one that transcends the usual ties of national patriotism and state pride. It is a loyalty to a place where habits are strong and memories are long. If those memories could speak, they would tell stories of a region powerfully shaped by its history and determined to pass it on to future generations.''
| |
| − | | |
| − | Or, as Florence King says in her book "Southern Ladies and Gentlemen",
| |
| − | | |
| − | ''"Put a fence around the South and you'd have one big madhouse."''
| |
| − | | |
| − | Southern culture has been and remains generally more socially [[Social conservatism|conservative]] than that of the rest of the country. Because of the central role of agriculture in the antebellum economy, society remained stratified according to land ownership. Rural communities often developed strong attachment to their [[church]]es as the primary community institution. | |
| | | | |
| − | The southern lifestyle, especially in the ''deep south'', is often joked about. Southerners are often generally viewed as more ''laid back'', and relaxed even in stressed situations. That, of course, is a [[stereotype]], and not always the case. But, traditionally, the southern lifestyle is viewed as ''slower paced'' when in more rural areas. Southerners are also stereotyped as being resistant to change, especially in societal circles, and mannerisms. Southerners are also reputed to be very polite and well-mannered and particularly welcoming to visitors; This characteristic has been labeled [[Southern hospitality]].
| + | Southerners are often viewed as more relaxed and the southern lifestyle as slower paced. Southerners are also stereotyped as being resistant to change. They are also reputed to be polite and well-mannered, particularly in welcoming visitors; this characteristic has been labeled as "southern hospitality." |
| | | | |
| | ===Religion=== | | ===Religion=== |
| − | Until the mid 19th century traditional Southerners were either [[Episcopal Church in the United States of America|Episcopalian]] or [[Presbyterian]] due to the South's close ancestral ties to [[England]], [[Scotland]] and the [[Provinces of Ireland|Irish province]] of [[Ulster]]. Around the beginning of the Civil War and from thereafter, [[Baptist]] and [[Methodist]] churches became the most prevalent forms of Christianity in the region. Perhaps more than any other region of an industrialized nation, the South has a high concentration of [[Christianity|Christian]] adherents, resulting in the reference to parts of the South as the "[[Bible Belt]]", from the presence of [[evangelicalism|evangelical]] and [[fundamentalism|fundamentalist]] [[Protestants]], [[Traditionalist Catholic|conservative Catholicism]], as well as [[Pentacostalism]] and [[Charismatics]]. | + | Until the mid nineteenth century, traditional Southerners were either [[Episcopalian]] or [[Presbyterianism|Presbyterian]] due to the South's close ancestral ties to [[England]], [[Scotland]], and the [[Ireland|Irish]] province of [[United Kingdom|Ulster]]. Around the beginning of the [[American Civil War|Civil War]] and thereafter, [[Baptist]] and [[Methodist]] churches became the most prevalent forms of Christianity in the region. Perhaps more than any other region of an industrialized nation, the South has a high concentration of [[Christianity|Christian]] adherents, resulting in the reference to parts of the South as the "Bible Belt," from the presence of [[evangelicalism|evangelical]] and [[fundamentalism|fundamentalist]] [[Protestant]]s, conservative Catholicism, as well as [[Pentacostalism]] and [[Charismatic]]s. |
| | | | |
| − | There are significant [[Roman Catholic Church|Catholic]] populations in most cities in the South, such as, [[Atlanta]], [[Savannah]], [[Mobile, Alabama|Mobile]], [[New Orleans]], [[Baltimore]] and [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]]. Rural areas of the Gulf coast, particularly those populated by [[Cajuns]] and Creoles, are also heavily Catholic. In general, the inland regions of the South such as Arkansas, Tennessee and Alabama have stronger concentrations of Baptists, Methodists, Church of Christ, and other Protestants. Eastern and northern Texas are heavily Protestant, while the southern parts of the state have [[Mexican American]] Catholic majorities. The [[South Florida]] area is home to the country's second largest concentration of Jewish people. Cities such as [[Miami]], [[Atlanta]], [[Dallas]] and [[Houston]] have significant [[Judaism|Jewish]] and [[Islam|Muslim]] communities. Immigrants from [[Southeast Asia]] and [[South Asia]] have brought [[Buddhism]] and [[Hinduism]] to the region as well. Atlanta has one of the largest Kurd populations outside of the middle east. Nashville also has some of the immigrants as well. | + | There are significant [[Roman Catholic Church|Catholic]] populations in most cities in the South, such as [[Atlanta]], Savannah, Mobile, [[New Orleans]], Baltimore, and Louisville. Rural areas of the [[Gulf of Mexico|Gulf]] coast, particularly those populated by [[Cajun]]s and Creoles, are also heavily Catholic. In general, the inland regions of the South such as Arkansas, Tennessee, and Alabama have stronger concentrations of Baptists, Methodists, Church of Christ, and other Protestants. Eastern and northern Texas are also heavily Protestant, while the southern parts of the state have Mexican American Catholic majorities. The South Florida area is home to the country's second largest concentration of [[Jewish]] people. Cities such as [[Miami]], Atlanta, [[Dallas]], and [[Houston]] have significant Jewish and [[Muslim]] communities. Immigrants from [[Southeast Asia]] and [[South Asia]] have brought [[Buddhism]] and [[Hinduism]] to the region as well. Atlanta has one of the largest [[Kurd]] populations in the world outside the [[Middle East]]. |
| | | | |
| | ===Dialects=== | | ===Dialects=== |
| − | {{main|Southern American English}}
| + | There is no single "southern accent." Rather, southern American English is a collection of [[dialect]]s of the [[English language]] spoken throughout the South. Southern American English can be divided into different sub-dialects, with speech differing between, for example, the Appalachian region and the coastal "low country" around Charleston,South Carolina, and Savannah, Georgia. Along this part of the southeastern coast, Gullah is still spoken by some [[African-American]]s, particularly the older generation. |
| − | It has been said that Southerners are most easily distinguished from other Americans by their speech, both in terms of accent and idiom. However, there is no single "Southern Accent." Rather, Southern American English is a collection of [[dialect]]s of the [[English language]] spoken throughout the South. Southern American English can be divided into different [[American English|sub-dialects]], with speech differing between, for example, the Appalachian region and the coastal "low country" around [[Charleston, South Carolina|Charleston,South Carolina] and [[Savannah, Georgia]]. Along this part of the southeastern coast [[Gullah language|Gullah]] is still spoken by some African Americans, particularly the older generation. The South Midlands dialect was influenced by the migration of Southern dialect speakers into the [[American West]]. The dialect spoken to various degrees by many African Americans, [[African American Vernacular English]], shares many similarities with Southern dialect.
| + | |
| − | Folklorists in the 1920s and later argued that Appalachian language patterns more closely mirror [[Early Modern English|Elizabethan English]] than other accents in the United States.<ref>Wilson, Charles Morrow. “Elizabethan America.” ''Atlantic Monthly,'' August 1929, 238—44. Reprinted in ''Appalachian Images in Folk and Popular Culture,'' ed. W. K. McNeil, 205—14. 1989. </ref> | + | Folklorists in the 1920s and later argued that Appalachian language patterns more closely mirror Elizabethan English than other accents in the United States.<ref>Charles Morrow Wilson, [https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/1929/08/elizabethan-america/651452/ Elizabethan America] ''Atlantic Monthly,'' August, 1929. Retrieved October 5, 2022.</ref> |
| | | | |
| | ===Cuisine=== | | ===Cuisine=== |
| | + | In addition to linguistics, the cuisine of the South is often described as one of its most distinctive traits. But just as history and culture vary across the broad region known as the South, the traditional cuisine varies as well. In modern times, there is little difference between the diet of typical Southerners and the diet in other regions of the U.S, but the South draws on multiple unique culinary influences to form its "traditional" foods. Southern cuisine also provides some of the best examples of distinctly American cuisine—that is, foods and styles that were born in the United States as opposed to adopted from elsewhere. |
| | | | |
| − | {{main|Cuisine of the Southern United States}}
| + | The food most commonly associated with the term "southern food" is often called "soul food" and is characterized by the heavy use of lards and fats. This style draws on the mix of African influences as well as Native American, Scots-Irish, and others. Southern fried chicken, black-eyed peas, cornbread, and biscuits are just a few examples of foods typically lumped into this category. |
| − | In addition to linguistics, the cuisine of the South is often described as one of its most distinctive traits. But just as history and culture varies across the broad region known as the South, the traditional cuisine varies as well. In modern times, there is little difference between the diet of typical Southerners and the diet in other regions of the U.S, but the South draws on multiple unique culinary influences to form its "traditional" foods. "Southern Cuisine" also provides some of the best examples of distinctly American cuisine - that is, foods and styles that were born in the United States as opposed to adopted from elsewhere.
| |
| | | | |
| − | The food most commonly associated with the term "Southern Food" is often called "[[soul food]]" and is characterized by the heavy use of high-calorie lards and fats. This style is often attributed to influence of the African-American slave population though it draws the mix of African influences as well as Native American, Scots-Irish, and others. Southern [[fried chicken]], vegetables cooked in lard or fat, black-eyed peas, cornbread, and biscuits are just a few examples of foods typically lumped into this broad category.
| + | Barbecue is a food typically associated with the South, though it is also common throughout the Midwest. Consisting of meat that has been slow-cooked and heavily seasoned, it is characterized by sharp regional divides in style preferences. In Texas, it is often beef based, while in North Carolina it is typically pork based. |
| | | | |
| − | [[Barbecue]] is a food typically associated with the South, however it should be noted that it is also heavily favored and common throughout the Midwest too. Consisting of meat that has been slow-cooked and heavily seasoned, it is characterized by sharp regional divides in style-preferences. In Texas it is often beef based, while in North Carolina it is typically pork based and further subdivided into Eastern and Western Carolina styles. South Carolina also has a distinct mustard-based sauce that is unique to the midlands area. Kansas City, Missouri and Memphis are also considered Barbecue hubs, drawing on styles from multiple areas. Western Kentucky is also known for its barbecue, with [[Owensboro, Kentucky|Owensboro]] hosting the [[International Bar-B-Q Festival]] the second weekend of May. | + | The unique history of Louisiana and the [[Mississippi Delta]] provides a unique culinary environment as well. Cajun and Creole evolved from the broad mix of cultural influences in this area—including [[Acadia]]n, [[Africa]]n, [[Caribbean]], [[France|French]], [[Native American]], and [[Spain|Spanish]]. |
| | | | |
| − | The unique history of Louisiana and the [[Mississippi Delta]] provides a unique [[culinary]] environment as well. [[Cajun cuisine|Cajun]] and [[Louisiana Creole cuisine|Creole]] evolved from the broad mix of cultural influences in this area - including [[Acadia]]n, [[African]], [[Caribbean]], [[France|French]], [[Indigenous peoples in the United States|Native American]], and [[Spain|Spanish]].
| + | Texas and its proximity and shared history with [[Mexico]] ultimately helped give rise to the modern [[Tex-Mex cuisine]]. |
| − | | |
| − | Texas and its proximity and shared history with Mexico ultimately helped give rise to the modern [[Tex-Mex cuisine]]. | |
| − | | |
| − | As with most of America, a wide variety of cuisines of other origins are now available throughout the South, such as [[Chinese cuisine|Chinese]], [[Italian cuisine|Italian]], [[French cuisine|French]], [[Middle Eastern cuisine|Middle Eastern]], [[Thai cuisine|Thai]], [[Japanese cuisine|Japanese]], and [[Indian cuisine|Indian]] as well as restaurants still serving primarily Southern specialties, and so-called "home cooking" establishments.
| |
| − | Atlanta in particular along with Houston, and Dallas have major Asian populations. Atlanta has more East Indians than any city in the South.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Drink===
| |
| − | | |
| − | Many of the most popular American [[soft drink]]s today originated in the South ([[Coca-Cola]], [[Pepsi-Cola]], [[Mountain Dew]], [[Royal Crown Cola]] and its related [[Nehi]] products and [[Dr Pepper]]). In addition, there are some soft drinks available only in the South to this day (such as [[Sundrop]] and [[Cheerwine]]), demonstrating its instrumental history in developing these types of drinks. A highly sweetened iced tea, typically called [[sweet tea]] is also associated with Southern cuisine. [[Lemonade]] is also a popular summer beverage. Dr. Enuf is also a regional favorite and is not widely available elsewhere. Bottled in Johnson City, TN, the beverage has been around since 1949 and is considered to be an acquired taste.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The South has long had an ambivalent attitude toward [[alcoholic beverages]]. Widespread support for [[Prohibition]] existed in the Southern states before and after the [[Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution|18th Amendment]] was in force in the USA. Many southern states are [[control states]] that monopolize and highly regulate the distribution and sale of alcoholic drinks. Many counties in the South, particularly outside of larger metropolitan areas, are [[dry counties]] that do not allow for alcohol sales in retail outlets. However, many dry counties still allow for "private clubs" (often with low daily fees) to serve alcohol on the premises. Beer is still widely popular in the South, though its consumption is often frowned upon in some religious circles.The most popular beers in the south are those produced by Anheuser Busch particularly Budweiser and Busch. Cartersville, a suburb of Atlanta, has a massive production facility for Anheuser Busch.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The upper South, specifically [[Kentucky]], is known for its production of [[bourbon whiskey]], which is also a popular base for cocktails. [[Jack Daniels]] is also produced in the South, in [[Lynchburg, Tennessee|Lynchburg, TN]]. Due to widespread restrictions on alcohol production, illegally distilled liquor or [[moonshine]] has long been associated (often rather stereotypically) with working class and poor people in much of the region. The [[mint julep]] is similarly depicted as a popular beverage among more affluent Southerners.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Tobacco===
| |
| − | The South was distinctive for its production of [[tobacco]], which earned premium prices from around the world. Most farmers grew a little for their own use or traded with neighbors who grew it. It was the main cash crop in North Carolina, Virginia, Kentucky and Maryland. Pennsylvania and Delaware also grew Tobacco but to a lesser extent. Commercial sales became important in the late 19th century as major tobacco companies rose in the South, becoming one the largest employers in cities like [[Durham, North Carolina]], [[Louisville, Kentucky]], and [[Richmond, Virginia]]. In 1938, [[R. J. Reynolds]] marketed eighty-four brands of [[chewing tobacco]], twelve brands of smoking tobacco, and the top-selling [[Camel (cigarette)|Camel]] brand of cigarettes. Reynolds sold large quantities of chewing tobacco, though that market peaked about 1910 as people shifted to cigarettes.<ref>{{cite book| author=Nannie M. Tilley | title=The R. J. Reynolds Tobacco Company | year=1985 | pages=363 | id=ISBN 0-8078-1642-6}}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | In the late 20th century, use of smokeless tobacco by adolescent American males increased by 450% for chewing tobacco and by 1500%, or fifteenfold, for snuff. From 1978 to 1984, there was a 15% compound annual growth rate in U.S. smokeless tobacco sales. Usage is highest in the South and in the rural west. In 1992, 30% of all male high school seniors in the southeastern United States were regular users of chewing tobacco or snuff—more than smoked cigarettes, according to the Center for Disease Control.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://iier.isciii.es/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/00019118.htm | title=Smokeless Tobacco Use in the United States|author= [[Centers for Disease Control]] | accessmonthday=22 Aug | accessyear=2006 | year=1987}}</ref><ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.globalink.org/tobacco/trg/Chapter17/Chap17_SmokelessPage5.html | title=The Tobacco Reference Guide: Smokeless Tobacco | author=David Moyer, MD | accessmonthday=22 Aug | accessyear=2006 | year=2000}}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | A historian of the American South in the late 1860s reported on typical usage in the region where it was grown, paying close attention to class and gender:<ref>{{cite book | title=A History of the United States since the Civil War v. 1 | author=Ellis Paxson Oberholtzer | year=1917 | pages=93 | publisher=Negro University Press | id=ISBN 0-8371-2642-8}} </ref> <blockquote>
| |
| − | The chewing of tobacco was well-nigh universal. This
| |
| − | habit had been widespread among the agricultural population of America both North and South before the war. Soldiers had found the quid a solace in the field and continued to revolve it in their mouths upon returning to their homes. Out of doors where his life was principally led the chewer spat upon his lands without offence to other men, and his homes and public buildings were supplied with spittoons. Brown and yellow parabolas were projected to right and left toward these receivers, but very often without the careful aim which
| |
| − | made for cleanly living. Even the pews of fashionable churches
| |
| − | were likely to contain these familiar conveniences. The large
| |
| − | numbers of Southern men, and these were of the better class
| |
| − | (officers in the Confederate army and planters, worth $20,000
| |
| − | or more, and barred from general amnesty) who presented themselves for the pardon of President Johnson, while they sat awaiting his pleasure in the ante-room at the White House, covered its floor with pools and rivulets of their spittle. An observant traveller in the South in 1865 said that in his belief seven-tenths of all persons above the age of twelve years, both male and female, used tobacco in some form. Women could be seen at the doors of their cabins in their bare feet, in their dirty one-piece cotton garments, their chairs tipped back, smoking pipes made of corn cobs into which were fitted reed stems or goose quills. Boys of eight or nine years of age and half-grown girls smoked. Women and girls "dipped" in their houses, on their porches, in the public parlors of hotels and in the streets. </blockquote>
| |
| | | | |
| | ===Literature=== | | ===Literature=== |
| − | {{main|Southern literature}}
| + | Perhaps the most famous southern writer is [[William Faulkner]], who won the [[Nobel Prize]] in literature in 1949. Faulkner brought new techniques, such as stream of consciousness and complex narrative, to American writing. |
| − | Perhaps the most famous southern writer is [[William Faulkner]], who won the [[Nobel Prize in Literature]] in 1949. Faulkner brought new techniques such as [[Stream of consciousness writing|stream of consciousness]] and complex narrative techniques to American writings (such as in his novel ''[[As I Lay Dying]]''). | |
| | | | |
| − | Other well-known Southern writers include [[Mark Twain]] (whose ''[[Adventures of Huckleberry Finn]]'' and ''[[The Adventures of Tom Sawyer]]'' are two of the most read books about the South), [[Zora Neale Hurston]], [[Eudora Welty]], [[Thomas Wolfe]], [[William Styron]], [[Flannery O'Connor]], [[Carson McCullers]], [[James Dickey]], [[Willie Morris]], [[Tennessee Williams]], [[Truman Capote]], [[Walker Percy]], [[Barry Hannah]], [[Robert Penn Warren]], [[Cormac McCarthy]], [[James Agee]] and [[Harry Crews]]. | + | Other well-known Southern writers include [[Mark Twain]] (whose ''[[Adventures of Huckleberry Finn]]'' and ''[[The Adventures of Tom Sawyer]]'' are two of the most read books about the South), [[Zora Neale Hurston]], [[Eudora Welty]], [[Thomas Wolfe]], [[William Styron]], [[Flannery O'Connor]], [[Carson McCullers]], James Dickey, Willie Morris, [[Tennessee Williams]], [[Truman Capote]], [[Walker Percy]], Barry Hannah, [[Robert Penn Warren]], [[Cormac McCarthy]], [[James Agee]], and Harry Crews. |
| | | | |
| − | Possibly the most famous southern novel of the 20th century is ''[[Gone with the Wind]]'' by [[Margaret Mitchell]], published in 1937. Another famous southern novel, ''[[To Kill a Mockingbird]]'' by [[Harper Lee]], won the [[Pulitzer Prize]] after it was published in 1960. | + | Possibly the most famous southern novel of the twentieth century was ''[[Gone with the Wind]]'' by [[Margaret Mitchell]], published in 1937. Another famous southern novel, ''[[To Kill a Mockingbird]]'' by [[Harper Lee]], won the [[Pulitzer Prize]] after it was published in 1960. |
| | | | |
| | ===Music=== | | ===Music=== |
| − | The South offers some of the richest music in the United States. The musical heritage of the South was developed by both whites and blacks, both influencing each other directly and indirectly. | + | The South offers some of the richest music in the United States. The musical heritage of the South was developed by both whites and blacks, influencing each other directly and indirectly. |
| − | | |
| − | The South's musical history actually starts before the Civil War, with the songs of the African slaves and the traditional folk music brought from the [[British Isles]]. [[Blues]] was developed in the rural South by Blacks at the beginning of the 20th century. In addition, [[gospel music]], [[spirituals]], [[country music]], [[rhythm and blues]], [[soul music]], [[funk]], [[rock and roll]], [[beach music]], [[bluegrass music|bluegrass]], [[jazz]] (including ragtime, popularized by Southerner [[Scott Joplin]]), and [[Appalachian folk music]] were either born in the South or developed in the region.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In general, country music is based on the folk music of white Southerners, and blues and rhythm and blues is based on black southern forms. However, whites and blacks alike have contributed to each of these genres, and there is a considerable overlap between the traditional music of blacks and whites in the South, particularly in gospel music forms. A stylish variant of country music (predominantly produced in Nashville) has been a consistent, widespread fixture of American pop since the 1950s, while insurgent forms (i.e. bluegrass) have traditionally appealed to more discerning subcultural and rural audiences. Blues dominated the Black music charts from the advent of modern recording until the mid-1950s, when it was supplanted by the less guttural and forlorn sounds of rock and R&B. Nevertheless, unadulterated blues (along with early rock and roll) is still the subject of reverential adoration throughout much of Europe and cult popularity in isolated pockets of the United States.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Zydeco, [[Cajun music|Cajun]], and [[swamp pop]], despite having never enjoyed greater regional or mainstream popularity, still thrive throughout [[French Louisiana]] and its peripheries, such as Southeastern Texas. These unique Louisianian styles of [[folk music]] are celebrated as part of the traditional heritage of the people of Louisiana. Conversely, bluegrass music has acquired a sophisticated cachet and distinct identity from mainstream country music through the fusion recordings of artists like [[Bela Fleck]], [[David Grisman]], and the [[New Grass Revival]]; traditional bluegrass and Appalachian mountain music experienced a strong resurgence after the release of 2001's ''[[O Brother, Where Art Thou?]]''.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Rock n' roll largely began in the South in the late 1940s and early 1950s. Early rock n' roll musicians from the South include [[Buddy Holly]], [[Little Richard]], [[Fats Domino]], [[Bo Diddley]], [[Elvis Presley]], [[Ray Charles]], [[James Brown]], [[Otis Redding]], [[Carl Perkins]], and [[Jerry Lee Lewis]], among many others. [[Hank Williams]] and [[Johnny Cash]], while generally regarded as "country" singers, also had a significant role in the development of rock music. In the 1960s, [[Stax Records]] emerged as a leading competitor of Motown Records, laying the groundwork for later stylistic innovations in the process.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The South has continued to produce rock music in later decades. In the 1970s, a wave of "Southern rock" and [[blues rock]] groups, led by [[The Allman Brothers Band]], [[Lynyrd Skynyrd]], [[ZZ Top]], and [[38 Special (band)|38 Special]], became popular. [[Macon, Georgia]]-based [[Capricorn Records]] helped to spearhead the Southern rock movement, and was the original home to many of the genre's most famous groups. At the other end of the spectrum, along with the aforementioned Brown and Stax, New Orleans' [[Allen Toussaint]] and [[The Meters]] helped to define the funk subgenre of rhythm and blues in the 1970s.
| |
| | | | |
| − | Many who got their start in the regional show business in the South eventually banked on mainstream national and international success as well: Elvis Presley and [[Dolly Parton]] are two such examples of artists that have transcended genres.
| + | The South's musical history actually starts before the Civil War, with the songs of the African slaves and the traditional folk music brought from the [[British Isles]]. [[Blues]] was developed in the rural South by blacks at the beginning of the twentieth century. In addition, [[gospel music]], [[Negro spiritual|spirituals]], [[country music]], [[rhythm and blues]], [[soul music]], [[funk]], [[rock and roll]], [[bluegrass music|bluegrass]], [[jazz]] (including ragtime, popularized by southerner [[Scott Joplin]]), and [[Appalachian Mountains|Appalachian]] [[Folk Music|folk music]] were either born in the South or developed in the region. |
| | | | |
| − | Many of the roots of [[alternative rock]] are often considered to come from the South as well, with bands such as [[R.E.M. (band)|R.E.M.]], [[Pylon (band)|Pylon]], and [[The B-52's]] forever associated with the musically fertile college town of [[Athens, Georgia]]. Cities such as [[Austin, Texas|Austin]], [[Knoxville, Tennessee|Knoxville]], [[Chapel Hill, North Carolina|Chapel Hill]], [[Nashville, Tennessee|Nashville]], and [[Atlanta]] also have thriving indie rock and live music scenes. Austin is home to the long-running [[South by Southwest]] music and arts festival, while several influential independent music labels (Sugar Hill, Merge, Yep Rock and the now-defunct Mammoth Records) were founded in the Chapel Hill area. Several influential [[death metal]] bands have recorded albums at [[Morrisound Recording]] in [[Temple Terrace]], [[Florida]] and the studio is considered an important touchstone in the genre's development.
| + | In general, country music is based on the folk music of white southerners, and blues and rhythm and blues are based on black southern forms. However, whites and blacks alike have contributed to each of these genres, and there is considerable overlap between the traditional music of blacks and whites in the South, particularly in gospel music forms. A stylish variant of country music (predominantly produced in Nashville) has been a consistent, widespread fixture of American pop since the 1950s, while insurgent forms (for example, bluegrass) have traditionally appealed to more discerning subcultural and rural audiences. Blues dominated the black music charts from the advent of modern recording until the mid-1950s, when it was supplanted by the less guttural and forlorn sounds of rock and R&B. |
| | | | |
| − | Recently, the spread of [[rap music]] (which is arguably the only major American music not started in the South) has led to the rise of the sub-genre [[Dirty South]]. Atlanta, Dallas, Houston, Memphis, Miami, and New Orleans have long been major centers of hip-hop culture
| + | Zydeco, Cajun, and swamp pop, despite having never enjoyed greater regional or mainstream popularity, still thrive throughout French Louisiana and its peripheries, such as southeastern Texas. |
| | | | |
| − | Also, an electronic music sub-genre known as [[Drum and Bass]] that has thrived on the East Coast has gained a recent popularity in the south, mixing with various southern Jungle, Hip-Hop and [[Breakbeat]] scenes. Notable bands and artists are [[Evol Intent]] and [[Gridlok]].
| + | Rock n' roll largely began in the South in the late 1940s and early 1950s. Early rock n' roll musicians from the South include [[Buddy Holly]], Little Richard, [[Fats Domino]], [[Bo Diddley]], [[Elvis Presley]], [[Ray Charles]], [[James Brown]], [[Otis Redding]], Carl Perkins, and Jerry Lee Lewis, among many others. [[Hank Williams]] and [[Johnny Cash]], while generally regarded as "country" singers, also had a significant role in the development of rock music. |
| | | | |
| | ===Sports=== | | ===Sports=== |
| − | ====Football==== | + | ====American football==== |
| − | While the South has had a number of professional football teams appear in the [[Super Bowl]], it is much more renowned for its love of [[College football]]. The [[Southeastern Conference|SEC]], [[Atlantic Coast Conference|ACC]], and [[Big 12 Conference|Big 12]] are the conferences in which the majority of large southern public universities play. The [[University of Alabama]] considers itself tied with [[University of Notre Dame|Notre Dame]] for the most (12) [[mythical national championship|national football championships]], and the [[University of Oklahoma]] has the highest college football winning percentage since 1936, when the AP poll was implemented. It also features very fierce, deep-seated rivalries like the [[Iron Bowl]] played annually between [[Auburn University]] and the [[University of Alabama]] near the end of every November.
| + | [[File:Dallas Cowboys in the red-zone.jpg|thumb|400px| The [[Dallas Cowboys]] are one of the region's most popular NFL teams.]] |
| − | | + | [[American football]] is heavily considered the most popular team sport in most areas of the Southern United States. |
| − | High school football is extremely competitive in the region. Texas high school football culture has been featured in movies and books such as [[Friday Night Lights]] and [[Varsity Blues]] while Virginia football was featured in the movie [[Remember the Titans]] while Alabama football was featured in the documentury [[Two-A-Days]]
| |
| | | | |
| − | ====Basketball====
| + | The region is home to numerous decorated and historic [[college football]] programs, particularly in the [[Southeastern Conference]] (known as the "SEC"), [[Atlantic Coast Conference]] (known as the "ACC"), and the [[Big 12 Conference]]. The SEC, consisting almost entirely of teams based in Southern states, is widely considered to be the strongest league in contemporary college football and includes the [[Alabama Crimson Tide]], the program with the most national championships in the sport's modern history. The sport is also highly competitive and has a spectator following at the [[high school football|high school level]], particularly in rural areas, where high school football games often serve as prominent community gatherings. |
| − | Basketball, particularly [[college basketball]], is also very popular in the South, especially in [[North Carolina]] and [[Kentucky]]; the two states are home to four of the winningest and most NCAA tournament included programs in college basketball history: the [[University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill|North Carolina Tar Heels]], [[Duke University|Duke Blue Devils]], [[University of Kentucky|Kentucky Wildcats]],and the [[Louisville Cardinals| Louisville Cardinals]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.basketball.com/menscollege/records/NCAADiv1TeamWinsTotal.shtml |title=Men's College Basketball Almanac |accessdate=2007-01-18}}</ref>. <ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.basketball.com/menscollege/records/NCAADiv1TournApps.shtml |title=Men's College Basketball Almanac NCAA Appearances. Although many may think that the University of Alabama is just a football related school they have also made many SEC championship appearances.
| |
| | | | |
| − | The south's largest state, Texas, is also home to three fo the best teams in the NBA. The San Antonio Spurs, Houston Rockets, and Dallas Mavericks. |accessdate=2007-04-19}}</ref>
| + | Though not as popular on a wider basis as the collegiate game, professional football has a growing tradition in the Southern United States. |
| | | | |
| | ====Baseball==== | | ====Baseball==== |
| − | [[Baseball]]'s popularity is often tied to [[Major League Baseball]] teams like the [[Atlanta Braves]], [[Houston Astros]], [[Texas Rangers (baseball)|Texas Rangers]], [[Tampa Bay Rays]] and [[Florida Marlins]]. Roughly half of the Major League Baseball franchises hold [[spring training]] in Florida, playing their preseason games in what is known as the "Grapefruit League". [[Minor league baseball]] is also closely followed in the South (with the South being home to more minor league teams than any other region of the United States), and [[college baseball]] is particularly popular in the southernmost tier of states. | + | [[File:Lone Star Series, Houston Astros vs Texas Rangers at Globe Life Park in Arlington, 2013.jpg|thumb|400px|[[Houston Astros|Houston]] vs [[Texas Rangers (baseball)|Texas]] face-off during the 2013 [[Lone Star Series]] in the [[American League West]] division of [[Major League Baseball]]]] |
| | + | Baseball has been played in the Southern United States dating back to the mid-nineteenth century. It was traditionally more popular than American football until the 1980s, and still accounts for the largest annual attendance amongst sports played in the South. |
| | | | |
| − | ====NASCAR==== | + | ====Auto racing==== |
| − | The South is the birthplace of [[NASCAR]] auto racing, which has an enormous and devoted following. The organization is headquartered in [[Daytona Beach, Florida]], the vast majority of teams center their operations in suburban [[Charlotte, North Carolina]], and the majority of NASCAR drivers have historically come from the South. The NASCAR [[NEXTEL Cup]] season starts each year in Daytona Beach with the [[Daytona 500]], and the series' fastest track is [[Atlanta Motor Speedway]] in [[Hampton, Georgia]]. [[Talladega, Alabama]] is home to the [[International Motorsports Hall of Fame]].
| + | [[File:Green flag at Daytona.JPG|thumb|right|400px|The start of the [[2015 Daytona 500]], the biggest race in [[NASCAR]], at [[Daytona International Speedway]] in [[Daytona Beach, Florida]]]] |
| | + | The Southern states are commonly associated with [[stock car racing]] and its most prominent competition level [[NASCAR]], which is headquartered in [[Charlotte, North Carolina|Charlotte]] and [[Daytona Beach, Florida|Daytona Beach]]. The sport was developed in the South during the early 20th century, with stock car racing's historic mecca being Daytona Beach, where cars initially raced on the wide, flat beachfront, before the construction of [[Daytona International Speedway]]. Though the sport has attained a following throughout the United States, a majority of NASCAR races continue to take place at Southern tracks. |
| | | | |
| − | ====Other sports==== | + | ====Basketball==== |
| − | The South would not seem to be a prominent winter-sports destination, but the [[Tampa Bay Lightning]], [[Dallas Stars]] and [[Carolina Hurricanes]] have all won the [[National Hockey League]]'s [[Stanley Cup]] in recent years. In addition, the mountains of West Virginia and the western parts of Virginia and North Carolina climates cold enough to host several popular [[downhill skiing]] resorts. [[Atlanta]] was the host of the [[1996 Summer Olympic Games]].
| + | Basketball is very popular throughout the Southern United States as both a recreational and spectator sport, particularly in the states of [[Kentucky]] and [[North Carolina]]. Both states are home to several prominent [[college basketball]] programs, including the [[Kentucky Wildcats men's basketball|Kentucky Wildcats]], [[Louisville Cardinals men's basketball|Louisville Cardinals]], [[Duke Blue Devils men's basketball|Duke Blue Devils]] and [[North Carolina Tar Heels men's basketball|North Carolina Tar Heels]]. |
| − | [[Lacrosse]] is also growing in the South. High School participation has increased dramatically and Colleges are beginning to add Varsity programs. High Schools from Texas, Tennessee, Georgia, and Florida can compete with teams from the traditional East Coast hotbeds.{{fact|date=July 2007}}
| |
| | | | |
| − | Many rural and some suburban Southerners view [[hunting]] and [[fishing]] as a way of life; [[deer]] and [[duck]] hunting and [[Bass (fish)|bass]] fishing are of particular social and economic importance. Squirrels and birds such as quail and dove are also hunted. The prevalence of gun ownership among many Southerners is closely tied to these traditions, and [[gun control]] measures often encounter vehement opposition in the South in part due to this cultural heritage.
| + | [[National Basketball Association|NBA]] teams based in the South include the [[San Antonio Spurs]], [[Houston Rockets]], [[Oklahoma City Thunder]], [[Dallas Mavericks]], [[Washington Wizards]], [[Charlotte Hornets]], [[Atlanta Hawks]], [[Orlando Magic]], [[Memphis Grizzlies]], [[New Orleans Pelicans]], and [[Miami Heat]]. The Spurs and Heat in particular have become prominent within the NBA, with eight championships won by the two between 1999 and 2013. |
| | | | |
| − | ===Film=== | + | ====Golf==== |
| − | The South has contributed to some of the most financially successful movies of all time, including ''[[Gone with the Wind (film)|Gone with the Wind]]'' (1939) and ''[[Smokey and the Bandit]]'' (1977). Georgia is also a huge location for film production.
| + | Golf is a popular recreational sport in most areas of the South, with the region's warm climate allowing it to host many professional tournaments and numerous destination golf resorts, particularly in the state of Florida. The region is home to [[The Masters]], one of the four [[Men's major golf championships|major championships]] in [[Professional golf tours|professional golf]]. The Masters is played at [[Augusta National Golf Club]] in [[Augusta, Georgia]], and has become one of the professional game's most important tournaments. [[Hilton Head Island]], in [[South Carolina]], is also home to a prominent American golf tournament and has several high-quality courses. |
| − | The second largest studio complex in the United States, EUE Screen Gems, is located in [[Wilmington, North Carolina]]. Over the past 20 years, many films and television programs have been made on location in eastern North Carolina.<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.imdb.com/List?endings=on&&locations=Wilmington,%20North%20Carolina,%20USA&&heading=18;with+locations+including;Wilmington,%20North%20Carolina,%20USA | title=Titles with locations including Wilmington, NC | author=IMDB | accessmonthday=22 Aug | accessyear=2006}}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | A number of film festivals - notably the [[South by Southwest]] music and arts festival in Austin and the [[Full Frame Documentary Film Festival]], based in [[Durham, North Carolina|Durham, NC]], are held within the region.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Cultural variations==
| |
| − | {{Refimprovesect|date=June 2007}}
| |
| − | There continues to be debate about what constitutes the basics elements of Southern culture.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.storysouth.com/summer2002/wheresouth.html | title=Where is the South in today's Southern literature | author=Jason Sanford | accessmonthday=22 Aug | accessyear=2006}}</ref> This debate is influenced partly because the South is such a large region. As a result, there are a number of cultural variations on display in the region.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Among the variations found in Southern culture are:
| |
| − | | |
| − | *Historical, political, and cultural divisions continue to divide the "upcountry" or "hill" culture of the [[Appalachian]] and [[Ozark]] mountain regions from that of low-lying areas such as the [[Tidewater region of Virginia|Virginia Tidewater]], [[Gulf Coast]], and [[Mississippi Delta]]. The hill country, as a rule, tends to have a much lower percentage of African-Americans than the rest of the South outside of larger cities. The hill country's population is strongly associated with a [[Scots-Irish American|Scots-Irish]] heritage. The lowland South has, aside from a generally large African American population, many whites of predominantly [[English American|English]] descent (aside from southern Louisiana). Many upland areas were also not supportive of the Confederate cause during the American Civil War (see [[Andrew Johnson]]), and contained bases of Republican Party support when the south as a whole was largely [[Democratic Party of the United States|Democratic]] (though this particular divide has been reduced with the dominance of the Republican Party in much of the south today).
| |
| − | | |
| − | * The formation of [[West Virginia]] in 1863 underlines the old divide between the highlands and the rest of the South. While West Virginia is often defined as a southern state, its peculiar geographic shape means that the northernmost tip is at about the same latitude as central [[New Jersey]]. This has caused the [[Northern Panhandle of West Virginia|northernmost part of the state]], as well as a number of northern non-panhandle cities, such as [[Morgantown, West Virginia]], which are about an hour's drive from [[Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania]], to increasingly become [[Commuter town|exurbs]] of the city, resulting in a less "Southern" culture, although elements of it are still evident. The [[Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia|easternmost tip of the state]] is close enough to [[Washington, D.C.]], that it too has started to become an exurb of that area with a unique North-South "hybrid" culture. The two easternmost counties, [[Berkeley County, West Virginia|Berkeley]] and [[Jefferson County, West Virginia|Jefferson]], are considered part of the [[Washington Metropolitan Area]] by the [[Census Bureau]]. [[Huntington, West Virginia]], near the state's boundary with [[Ohio]] and Kentucky, is often identified with the [[Rust Belt]], (although it is not officially considered part of the Rust Belt), but it also has more of a Southern climate and environment compared to the state's Northern Panhandle. West Virginia was created from 50 western counties of Virginia during the Civil War. Though two-thirds of the territory of the proposed state consisted of secessionist counties <ref>Richard Curry "A House Divided, pgs. 142-47</ref>, the Wheeling Unionists were successful in guiding their Statehood bill through Congress, which was signed by President Lincoln. Because of the confusing circumstances of its creation some do not consider West Virginia to be part of the South. However, West Virginia largely shares in the Appalachian culture that extends through a large swath of the inland South.
| |
| − | * Areas having an influx of outsiders may be less likely to hold onto a distinctly Southern identity and cultural influences. For this reason, [[urban area]]s during the Civil War were less likely to favor secession than [[agricultural]] areas. Today, partly because of continuing population migration patterns between urban areas in the North and South, even historically "Southern" cities like [[Atlanta]], [[Charlotte]], [[Raleigh, North Carolina|Raleigh]], [[Durham, North Carolina|Durham]], [[Nashville]], [[Richmond, Virginia|Richmond]], [[Dallas]], and [[Houston]] have assimilated regional identities distinct from a normal "Southern" one. However, while these metropolitan areas may have had their original southern culture somewhat diluted, they are still widely considered to be "Southern" cities.
| |
| − | | |
| − | * [[South Florida]] has been transformed by the rapid influx of migrants, [[retirees]], and [[American Jews|Jewish Americans]] from the [[Northern United States]] and immigration from [[Latin America]]. [[Miami, Florida]] has large communities of immigrants from [[Cuba]], [[Brazil]], [[Haiti]] and other parts of Latin America. While many do not see South Florida as part of the cultural South, the [[Florida Panhandle]], [[First Coast|northeastern areas]], [[North Central Florida]], [[Nature Coast]], [[Central Florida]], and the middle of South Florida (that is, the "inland" areas around the [[Lake Okeechobee]] and [[Everglades]] region) also called the [[Florida Heartland]] remain culturally tied to the South. The metropolitan areas of [[Tampa-St. Petersburg-Clearwater, Florida, Metropolitan Statistical Area|Tampa]] and [[Orlando-Kissimmee, Florida, Metropolitan Statistical Area|Orlando]] are a complex blend of fast-growing traditional "Southern" metropolitan areas, (such as Atlanta, Charlotte, Dallas, Nashville, and Raleigh-Durham) and the South Florida metropolitan area. While the areas have more southern culture than the South Florida metropolitan area, they both have less southern culture than traditional "Southern" metropolitan areas, and in addition, have considerably fast growing [[Hispanic]] populations (much like South Florida). The city of [[Palm Coast]], (one of the fastest growing cities in the [[United States]] and with most of its growth coming from [[New York]] and [[New Jersey]]), and the [[Daytona, Florida|Daytona]] [[Deltona-Daytona Beach-Ormond Beach, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area|metropolitan area]], which contain many more retirees and migrants from the northern states, fall closer as far as culture is concerned, to the South Florida metropolitan area than both the Tampa and Orlando metropolitan areas. The [[Florida Suncoast]] region is also usually excluded culturally from the southern states due to its especially high retiree and "snow-bird" population (most of who move from the [[Midwestern United States|Midwestern states]]) even for normal standards in Florida.
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Some regions of [[Texas]] are associated with the South more than the [[Southwestern United States|Southwest]] (primarily [[East Texas]], parts of [[Central Texas]], and [[North Texas]]), while other regions share more similarities with the Southwest than the South (primarily far [[West Texas]], parts of Central Texas, and [[South Texas]]). The [[Texas Panhandle]] and the [[South Plains]] parts of West Texas do not easily fit into either category. The Texas Panhandle has much in common both culturally and geographically with Midwestern states like Kansas and Nebraska, while the South Plains, though originally settled primarily by Anglo Southerners, has become a blend of both Southern and Southwestern culture due to the large and fast growing Hispanic population located there. The size and cultural distinctness of Texas prohibit easy categorization of the entire state in any recognized region of the United States; geographic, economic, and even cultural diversity between regions of the state preclude treating Texas as a region in its own right. Texas' larger cities have also attracted migrants from other regions of the United States and immigrants from Latin America and Asia. However, Texas is usually considered a Southern state rather than a Western one, as it was a member of the Confederacy, and over 86% of Texans identify themselves as living in the South.<ref>{{cite web| url=http://usadeepsouth.ms11.net/texas.html | title=Texas and the Deep South | author=Randy Hill | accessmonthday=27 Nov | accessyear=2006}}</ref> {{See|Geography of Texas}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[Image:Census-2000-Data-Top-US-Ancestries-by-County.jpg|400px|thumb|right|[[Plurality]] ancestry per US county, 2000: | |
| − | <span style="background:#c3d9e7">German</span>
| |
| − | <span style="background:#c6afcb">English</span>
| |
| − | <span style="background:#dbe7b7">Norwegian</span>
| |
| − | <span style="background:#7bc296">Finnish</span>
| |
| − | <span style="background:#008c4d; color:white">Dutch</span>
| |
| − | <span style="background:#f0aeba">Mexican</span>
| |
| − | <span style="background:#f1dfdd">Spanish</span>
| |
| − | <span style="background:#f8ce7c">Native</span>
| |
| − | <span style="background:#f6f2c2">"American"</span>
| |
| − | <span style="background:#983d71; color:white">African</span>
| |
| − | <span style="background:#9781b2; color:white">Irish</span>
| |
| − | <span style="background:#5ab3dd">French</span>
| |
| − | <span style="background:#0173b2; color:white">Italian</span>
| |
| − | ]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | * Before its statehood in 1907, [[Oklahoma]] was known as "Indian Territory." The majority of the [[Native Americans in the United States|Native American]] tribes in Indian Territory sided with the Confederacy during the Civil War. Oklahoma has the nation's largest Native American population. Oklahoma is also the home of Gilcrease Museum, which houses the world's largest, most comprehensive collection of art of the American West plus Native American art and artifacts and historical manuscripts, documents, and maps. Oklahoma is sometimes described as being part of the "Great Southwest." However, because of its geographic location, Oklahoma is privy to Southern culture. Southern culture is apparent in Oklahoma, particularly in the southeastern region of the state. On a whole, most consider Oklahoma to be a Southern state.
| |
| − | | |
| − | * [[Louisiana]], having been colonized by [[French colonisation of the Americas|France]] and [[Spanish colonization of the Americas|Spain]] rather than Great Britain, has a number of distinct cultural traditions, especially within the [[Cajun]], [[Louisiana Creole people|Creole]], [[Latin America]]n and [[Caribbean]] influenced culture of the southern portion of the state. The Gulf Coast regions of Texas, Mississippi, Alabama, and northern Florida also share a similar French/Spanish colonial history but lack the heavy concentration of French influences present in Louisiana, especially from the [[Acadian]]s and their Cajun descendants.The relatively tolerant attitudes toward alcohol use, gambling, and prostitution that have generally prevailed in the New Orleans region stand in stark contrast to the more conservative, Protestant beliefs of much of the rest of the Deep South.
| |
| − | | |
| − | *Delaware is not considered to be a southern state by many, especially [[New Castle County, Delaware|New Castle County]] (the northernmost of the state's three counties), which is essentially the outermost portion of the [[Philadelphia]] region. While Maryland retains some southern culture in rural [[Southern Maryland]] and the [[Eastern Shore of Maryland]], the areas along the [[Interstate 95|I-95]] corridor, including metropolitan [[Baltimore, Maryland|Baltimore]] and the state's [[Washington Metropolitan Area|suburbs of Washington, D.C.]], are most often considered to be culturally part of the [[Northeastern United States]]. The Washington and Baltimore metropolitan areas are sometimes combined to form the [[Baltimore-Washington Metropolitan Area]]. Like West Virginia, the state was part of the Union during the Civil War, partially because of immense pressure to remain so to avoid the District of Columbia from being completely surrounded by Confederate territory.
| |
| − | | |
| − | * [[Northern Virginia]] has been largely settled by Northerners attracted to job opportunities resulting from expansion of the federal government during and after [[World War II]]. Still more expansion resulted from the [[dot-com bubble]] around the turn of the 21st century. Economically linked to Washington, D.C., residents of the region tend to consider its culture more Northern, as do Southerners. Some in Virginia refer to the area as "Occupied Virginia."{{Fact|date=November 2007}} However, it remains politically somewhat more moderate than their neighbors across the [[Potomac River]]. Nevertheless, the region swung the 2006 Senate election to the Democrat.
| |
| − | | |
| − | * The most recent shift in "Southern" cultural influence and demographics has occurred in North Carolina. As recently as the mid-1980s, this was a very entrenched "Southern" state culturally and demographically (for example, the prominence of extremely conservative politicians such as former Senator [[Jesse Helms]]). However, many newcomers have transformed the landscape since then. Many are from the Northeast and especially from the [[New York City]] and [[Cleveland, Ohio|Cleveland]] metropolitan areas. Much of this migration has occurred in the [[Charlotte, North Carolina|Charlotte]] and [[Raleigh, North Carolina|Raleigh]]-[[Durham, North Carolina|Durham]] areas because of economic growth (banking/finance in Charlotte's case, high-tech in Raleigh-Durham's); and the [[Asheville, North Carolina|Asheville]] area by retirees who a generation ago might have moved to Florida but prefer the climatic balance produced by the combination of a relatively high elevation and a southerly latitude. The most extreme example of this is found in [[Cary, North Carolina]], a suburb in the Raleigh-Durham area that has exploded in population since 1980, almost exclusively with Northern transplants to the region. Cary has even been turned into a [[backronym]] by locals: "Concentrated Area of Relocated Yankees" or "Containment Area for Relocated Yankees". Politically, the state is still conservative (the [[United States presidential election, 2004|2004 presidential election]] was easily won by [[George W. Bush]], though early exit polling had the race much closer than initially expected), but in the Raleigh-Durham area and to a lesser extent the Charlotte area, "Southern" accents are becoming less common in metropolitan areas; and North Carolina's 3 largest metro areas (Charlotte, Raleigh-Durham and the [[Greensboro, North Carolina|Greensboro]]-[[Winston-Salem]]-[[High Point]] "Piedmont Triad" area) have experienced the fastest rise in [[Latino]] and Asian American population of any part of the Southeast during recent years. A report released by The Brookings Institute in May 2006 entitled ''Diversity Spreads Out,'' showed that North Carolina's largest metro areas have been highly attractive to some minority groups. The Charlotte metro area ranked 2nd nationally with a 49.8% growth rate in its Hispanic population between 2000 and 2004, followed in 3rd place by the Raleigh-Durham metro area at 46.7%<ref>{{cite web | url=http://www.ncatlasrevisited.org/Population/ethncpop.html | title=Ethnic Population Change | accessmonthday=7 July | accessyear=2007}}</ref>. To a much larger degree, the same effect is occurring in the [[Atlanta metropolitan area]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | *[[Kentucky]], at the confluence of the [[Upper South]] and the [[Midwest]], served as an important [[Border states (Civil War)|Border State]] during the [[American Civil War|Civil War]] and reflects the influences of both South and North <ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.4to40.com/earth/history/index.asp?article=earth_history_kentucky | title=Kentucky - USA State | author=Anand Singh | accessmonthday=27 July | accessyear=2007}}</ref>. Though the state's official government and a majority of its citizens supported the Union, a star on the Confederate flag represents a [[Russellville Convention|small rebel government]] that was present in Southern Kentucky before 1863. Cultural studies of the state present a complicated, mixed picture; A 1987 peer-reviewed study on regional geography, published by a professor of geography at the [[University of Kansas]], presented participants with a wide range of choices, including South, Midwest, East, West, and "Other"; given multiple choices, this study found only a minority - 47.8% - of Kentuckians identifying with the South, followed by 33% identifying with the Midwest; in neighboring Tennessee, a large majority of residents - over 80% - identified with the South and only 1.5% identified as Midwestern <ref>{{cite web| url=http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0004-5608%28198709%2977%3A3%3C325%3ACUOFAR%3E2.0.CO%3B2-4 | title=Changing Usage of Four American Regional Labels | author=Dr. James R. Shortridge | accessmonthday=6 Feb | accessyear=2007}}</ref>. However a recent and ongoing (late 2000's) study conducted and published by the [[University of North Carolina]] found that, 79% of Kentuckians identified the state as Southern geographically and culturally, while 68% of Kentuckians identified themselves as "Southerners" culturally. These findings were based on a simple "yes or no" choice regarding Southern identification. <ref>{{cite web| url=http://www.unc.edu/news/archives/jun99/reed16.htm | title=UNC-CH surveys reveal where the 'real' South lies | author=David Williamson | accessmonthday=22 Feb | accessyear=2007}}</ref> [http://datalin2.irss.unc.edu/VDC/View/index.jsp?op_id=vdcView%3Dadvanced%2CvdcCollection%3Dlocal%2Cou%3Dcollections%2Cou%3Ddatalin2_irss_unc_edu%2Co%3Dvdc]. As those large differences in findings between two scholarly sources reveal, exact percentages for regional affinity are difficult to establish in Kentucky, and regional identification often varies dramatically based on location in the state. For example, [[Northern Kentucky]] is considered to be the most Midwestern region of the state as it is culturally and economically attached to [[Cincinnati]]; nonetheless, studies show that a significant minority of people in Northern Kentucky still identify with the South. Conversely, [[Southern Indiana]] is highly Southern in comparison to most of the Midwest, as it is culturally and economically attached to [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]]. Some sources treat Southern Indiana as essentially the upper tip of Upland South culture while others maintain that Southern culture, while significant, is not dominant in the region.[http://www.indiana.edu/~tradarts/programs/south.html]. Louisville is also viewed as culturally and economically Midwestern in some analyses<ref>{{cite journal |last=Meyer |first=David R. |year=1989 |month=December |title=Midwestern Industrialization and the American Manufacturing Belt in the Nineteenth Century |journal=The Journal of Economic History |volume=49 |issue=4 |pages=921-937 |id= |url=http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0022-0507%28198912%2949%3A4%3C921%3AMIATAM%3E2.0.CO%3B2-J |accessdate=2007-02-05}}</ref> and as Southern in others, and it is often described as both "the Gateway to the South" and "the northernmost Southern city and southernmost Northern city." While varying degrees of [[Northern United States|Northern]] cultural influence can be found in Kentucky outside of the [[Golden Triangle (Kentucky)|Golden Triangle]] region, cities such as [[Owensboro, KY|Owensboro]], [[Bowling Green, KY|Bowling Green]], and [[Paducah, KY|Paducah]], along with most of the state's rural areas, have largely remained distinctly Southern in character.
| |
| − | *Although Missouri is often considered a Midwestern state, the [[Ozarks]] are typically lumped in with the Highland South, while [[Little Dixie (Missouri)|Little Dixie]] in north-central Missouri is an [[outlier]] of Lowland Southern culture. The large migration of blacks, as well as poor white southerners during the depression, has given the city of St. Louis a significant amount of Southern culture.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Beyond the South===
| |
| − | | |
| − | While areas west of Texas are rarely if ever included as parts of the "South," many areas of [[New Mexico]], [[Arizona]], and [[California]] were predominantly settled by Southerners, at least in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. For instance, pro-Confederate governments were established in what is now Arizona and New Mexico during the Civil War. During the [[Great Depression]] and [[Dust Bowl]] crisis, a large influx of migrants from areas such as Oklahoma, Arkansas, and the [[Texas Panhandle]] settled in California. These "Okie" and "Arkie" migrants and their descendants remain a strong influence on the culture of the [[Central Valley]] of California, especially around the cities of [[Bakersfield]] and [[Fresno]]. Similar migrations occurred after World War II of Southerners into the industrial cities up the [[Midwest]], particularly in Missouri to St. Louis, (both the state and the city are more often considered the Midwest than the South), [[Illinois]], [[Michigan]], [[Indiana]], and [[Ohio]]. Many Southerners who have emigrated to other states continue nevertheless to [[tribalism|identify proudly]] as Southerners, without actually continuing to live in the South.
| |
| − | | |
| − | African Americans from the South moved to the industrial cities of the Midwest and [[West Coast of the United States|West Coast]] in large numbers during the [[Great Migration]] beginning in [[World War I]] and extending after World War II. Many African Americans throughout the United States, as well as a considerable number of whites, have "Northern" and "Southern" branches of their families. Many elements of African American culture, such as music, literary forms, and cuisine remain rooted in the South.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Over the past half-century, a number of [[Latinos]] have migrated to the [http://www.southernspaces.org/contents/2007/sanchez/1a.htm American South] from Mexico and Latin America. Urban areas such as [http://www.southernspaces.org/contents/2006/odem/1a.htm Atlanta], [http://www.southernspaces.org/contents/2007/sanchez/1a.htm New Orleans] and [http://southernspaces.org/contents/2004/global_context/1a.htm Nashville] have seen a major increase in Latino immigrants over the past ten to fifteen years; and factory and agribusiness jobs have also brought Mexican and Latin American workers to some of the more rural regions in the U.S. South. [http://www.southernspaces.org/contents/2007/sanchez/1a.htm] [http://www.southernspaces.org/contents/2006/odem/1a.htm]
| |
| − | [http://southernspaces.org/contents/2004/global_context/1a.htm]
| |
| | | | |
| | ==Politics== | | ==Politics== |
| − | {{main| Politics of the Southern United States}}
| + | In the century after [[Reconstruction]], the white South strongly identified with the [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic Party]]. This lock on power was so strong the region was called the Solid South. Republicans controlled parts of the [[Appalachian Mountains]] and competed for power in the border states, but otherwise it was rare for a southern politician to be a Republican before the 1960s. |
| − |
| |
| − | In the century after Reconstruction, the white South strongly identified with the [[History of the United States Democratic Party|Democratic Party]]. This lock on power was so strong the region was politically called the [[Solid South]]. The Republicans controlled parts of the Appalachian mountains and competed for power in the border states, but otherwise it was rare for a Southern politician to be a Republican before the 1960s. | |
| | | | |
| − | Increasing support for civil rights legislation by the Democratic party at the national level during the 1940s caused a split between conservative Southern Democrats and other Democrats in the country. Until the passage of the Civil Rights laws of the 1960s, conservative Southern Democrats ("Dixiecrats") argued that only they could defend the region from the onslaught of northern liberals and the [[American Civil Rights Movement (1955-1968)|civil rights movement]]. In response to the [[Brown v. Board of Education|Brown decision]] of 1954, the ''[[Southern Manifesto]]'' was issued in March 1956, by 101 southern congressmen (19 senators, 82 House members). It denounced the Brown decisions as a "clear abuse of judicial power [that] climaxes a trend in the federal judiciary undertaking to legislate in derogation of the authority of Congress and to encroach upon the reserved rights of the states and the people." The manifesto lauded "those states which have declared the intention to resist enforced integration by any lawful means." It was signed by all southern senators except Majority Leader [[Lyndon B. Johnson]], and Tennessee senators [[Albert Gore, Sr.]] and [[Estes Kefauver]]. Virginia closed schools in [[Warren County, Virginia|Warren County]], [[Charlottesville, Virginia|Charlottesville]], and [[Norfolk, Virginia|Norfolk]] rather than integrate, but no other state followed suit. An element resisted integration, led by Democratic governors [[Orval Faubus]] of Arkansas, [[Ross Barnett]] of Mississippi, [[Lester Maddox]] of Georgia, and, especially [[George Wallace]] of Alabama. They appealed to a [[blue collar]] electorate. | + | Increasing support for civil rights legislation by the Democratic Party at the national level during the 1940s caused a split between conservative southern Democrats and other Democrats in the country. Until the passage of the civil rights laws of the 1960s, [[conservatism|conservative]] southern Democrats ("Dixiecrats") argued that only they could defend the region from the onslaught of northern liberals and the [[American Civil Rights Movement (1955-1968)|civil rights movement]]. In response to the ''[[Brown v. Board of Education]]'' decision of 1954, 101 southern congressmen denounced the [[United States Supreme Court|Supreme Court]] decision as a "clear abuse of judicial power." The manifesto was signed by all southern senators except Majority Leader [[Lyndon B. Johnson]] and Tennessee senators [[Albert Gore, Sr.]] and Estes Kefauver. Virginia closed some schools rather than integrate, but no other state followed suit. An element resisted integration, led by Democratic governors Orval Faubus of Arkansas, Ross Barnett of Mississippi, Lester Maddox of Georgia, and George Wallace of Alabama. |
| | | | |
| − | The Democratic Party's dramatic reversal on civil rights issues culminated when Democratic President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law the [[Civil Rights Act of 1964]]. Meanwhile, the Republicans were beginning their [[Southern strategy]], which aimed to solidify the Republican Party's electoral hold over conservative white Southerners. Southern Democrats took notice that 1964 Republican Presidential candidate [[Barry Goldwater]] had voted against the Civil Rights Act, and in the [[United States presidential election, 1964|presidential election of 1964]], Goldwater's only electoral victories outside his home state of [[Arizona]] were in the states of the [[Deep South]]. | + | The Democratic Party's dramatic reversal on civil rights issues culminated when President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law the [[Civil Rights Act of 1964]]. Meanwhile, the Republicans were beginning their southern strategy, which aimed to solidify the party's electoral hold over conservative white southerners. Southern Democrats took notice that 1964 Republican presidential candidate [[Barry Goldwater]] had voted against the Civil Rights Act, and in the presidential election of 1964, Goldwater's only electoral victories outside his home state of [[Arizona]] were in the states of the Deep South. |
| | | | |
| − | The transition to a Republican stronghold took decades. First, the states started voting Republican in presidential elections—the Democrats countered by nominating such Southerners as [[Jimmy Carter]] in 1976 and 1980, [[Bill Clinton]] in 1992 and 1996, and [[Al Gore]] in 2000. Then the states began electing Republican senators and finally governors. Georgia was the last state to do so, with [[Sonny Perdue]] taking the governorship in 2002. In addition to the middle class and business base, Republicans attracted strong majorities from the evangelical Christian vote, which had not been a distinct political demographic prior to 1980. | + | The transition to a Republican stronghold took decades. First, the states started voting Republican in presidential elections—the Democrats countered by nominating such southerners as Jimmy Carter in 1976 and 1980, Bill Clinton in 1992 and 1996, and [[Al Gore]] in 2000. Then the states began electing Republican senators and finally governors. In addition to the middle class and business base, Republicans attracted strong majorities from the [[evangelical]] [[Christian]] vote, which had not been a distinct political demographic prior to 1980. |
| | | | |
| − | There was major resistance to [[desegregation]] in the mid 1960s to early 1970s. Those issues faded away, replaced by [[culture wars]] between the conservatives and liberals over issues such as [[abortion]] and [[gay marriage]]. | + | There was major resistance to [[racial segregation|desegregation]] in the mid 1960s to early 1970s. Those issues faded away, replaced by [[culture war]]s between the conservatives and liberals over issues such as [[abortion]] and gay marriage. |
| | | | |
| | ===Presidential history=== | | ===Presidential history=== |
| − | The South has produced the first winning presidential candidates for all but one major political party in the history of the United States. The exception is the [[United States Federalist Party|Federalist Party]] which claimed its first (and only) presidential victory with [[John Adams]], of Massachusetts, in 1796. The following is a list of presidents who represent their party's first candidate to reach the country's highest office: | + | The South produced most of the U.S. presidents prior to the Civil War. After that, memories of the war made it impossible for a southerner to become president unless he either moved north (like [[Woodrow Wilson]]) or was a vice president who moved up (like [[Harry Truman]] and Lyndon B. Johnson). In 1976, [[Jimmy Carter]] became the first southerner to break the pattern since [[Zachary Taylor]] in 1848. Presidents, [[George H.W. Bush]], [[Bill Clinton]], and [[George W. Bush]], have all been from the South: George H.W. Bush was a congressman from Texas, Clinton was governor of Arkansas, and George W. Bush was governor of Texas. |
| − | | |
| − | *Democratic-Republicans: [[Thomas Jefferson]] of Virginia, in 1800.
| |
| − | *Democrats: [[Andrew Jackson]], of South Carolina/Tennessee, in 1828.
| |
| − | *Whigs: [[William Henry Harrison]], of Virginia, in 1840.
| |
| − | *Republicans: [[Abraham Lincoln]], originally from [[Hardin County, Kentucky]], in 1860.
| |
| − | (Note: The first President, George Washington, of Virginia, was unaffiliated with any political party.)
| |
| − | | |
| − | Additionally, the South produced most of the U.S. Presidents prior to the Civil War. Memories of the war made it impossible for a Southerner to become President unless he either moved North (like [[Woodrow Wilson]]) or was a vice president who moved up (like [[Harry Truman]] and [[Lyndon B. Johnson]]). In 1976, [[Jimmy Carter]] defied this trend and became the first Southerner to break the pattern since [[Zachary Taylor]] in 1848.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The last three presidents, [[George H.W. Bush]], [[Bill Clinton]], and [[George W. Bush]], have all been from the South: George H.W. Bush was a congressman from Texas, Clinton was governor of Arkansas, and George W. Bush was governor of Texas.
| |
| | | | |
| | ===Other politicians and political movements=== | | ===Other politicians and political movements=== |
| | The South has produced numerous other well-known politicians and political movements. | | The South has produced numerous other well-known politicians and political movements. |
| | | | |
| − | In 1948, a group of Democratic congressmen, led by Governor [[Strom Thurmond]] of South Carolina, split from the Democrats in reaction to an anti-segregation speech given by Senator [[Hubert Humphrey]] of [[Minnesota]], founding the States Rights Democratic or [[Dixiecrat]] Party. During that year's Presidential election, the party unsuccessfully ran Thurmond as its candidate. | + | In 1948, a group of Democratic congressmen, led by Governor [[Strom Thurmond]] of South Carolina, split from the Democrats in reaction to an anti-segregation speech given by Senator [[Hubert Humphrey]] of [[Minnesota]], founding the States Rights Democratic or Dixiecrat Party. During that year's presidential election, the party unsuccessfully ran Thurmond as its candidate. |
| | | | |
| − | In the [[United States presidential election, 1968|1968 Presidential election]], Alabama Governor [[George C. Wallace]] ran for President on the [[American Independent Party]] ticket. Wallace ran a "law and order" campaign similar to that of Republican candidate, [[Richard Nixon]]. Nixon's [[Southern Strategy]] of electoral votes downplayed race issues and focused on culturally conservative values, such as family issues, patriotism, and cultural issues that appealed to [[Southern Baptists]]. | + | In the 1968 presidential election, Alabama Governor George C. Wallace ran for president on the American Independent Party ticket. Wallace ran a "law and order" campaign similar to that of Republican candidate [[Richard Nixon]]. Nixon's Southern Strategy downplayed race issues and focused on culturally conservative values, such as family issues, patriotism, and cultural issues. |
| | | | |
| − | In 1994, another Southern politician, [[Newt Gingrich]], ushered in 12 years of GOP control of the House. Gingrich became [[Speaker of the United States House of Representatives]] in 1995, but was forced to resign after mishandling the impeachment of Southerner [[Bill Clinton]] in 1998. [[Tom DeLay]] was the most powerful Republican leader in Congress until his abrupt criminal indictment in 2005. Most recent Republican Senate leaders are from the South, including [[Howard Baker]] of Tennessee, [[Trent Lott]] of Mississippi, [[Bill Frist]] of Tennessee, and [[Mitch McConnell]] of Kentucky. | + | In 1994, another Southern politician, [[Newt Gingrich]], ushered in 12 years of GOP control of the House. Gingrich became Speaker of the [[United States Congress|House of Representatives]] in 1995, but was forced to resign after mishandling the [[impeachment]] of southerner [[Bill Clinton]] in 1998. [[Tom DeLay]] was the most powerful Republican leader in Congress until his abrupt criminal indictment in 2005. Recent Republican Senate leaders from the South included Howard Baker of Tennessee, Trent Lott of Mississippi, Bill Frist of Tennessee, and Mitch McConnell of Kentucky. |
| | | | |
| | ==Race relations== | | ==Race relations== |
| − | {{main|Racism in the United States}}
| |
| | ===History=== | | ===History=== |
| − | [[African American]]s have a long history in the South, stretching back to the early settlements in the region. Beginning in the early 17th century, black [[slaves]] were purchased from [[African slave trade|slave traders]] who brought them from Africa (or, less often, from the Caribbean) to work on plantations. Most slaves arrived in the 1700-1750 period. {{see|History of slavery in the United States}} + [[African American]]s have a long history in the South, stretching back to the early settlements in the region. Beginning in the early 17th century, slaves were purchased from slave traders who brought them to work on plantations. Most slaves arrived in the 1700-1750 period. {{see|History of slavery in the United States}} | + | [[African-American]]s have a long history in the South, stretching back to the early settlements in the region. Beginning in the early seventeenth century, black [[slavery|slaves]] were purchased from [[slave trade|slave traders]] who brought them from [[Africa]] (or, less often, from the Caribbean) to work on plantations. Most slaves arrived in the period 1700-1750. |
| | | | |
| − | - Slavery ended with the South's defeat in the American Civil War. During the Reconstruction period that followed, African Americans saw advancements in the civil rights and political power in the South. However, as Reconstruction ended, Southern [[Redeemers]] moved to prevent black people from holding power. After 1890, the Deep South disfranchised many African Americans. The leading white demagogue was Senator [[Ben Tillman]] of South Carolina, who proudly proclaimed in 1900, "We have done our level best [to prevent blacks from voting]...we have scratched our heads to find out how we could eliminate the last one of them. We stuffed ballot boxes. We shot them. We are not ashamed of it."<ref>{{cite book| author=[[Rayford Logan]] | title=The Betrayal of the Negro from Rutherford B. Hayes to Woodrow Wilson | location= New York | publisher=Da Capo Press | year=1997 | id=ISBN 0-306-80758-0 | pages=91}}</ref>
| + | Slavery ended with the South's defeat in the [[American Civil War|Civil War]]. During the Reconstruction period that followed, African Americans saw advancements in civil rights and political power in the South. As Reconstruction ended, however, southern whites took steps to prevent black people from holding power. After 1890, the Deep South disfranchised many African Americans. |
| | | | |
| − | - With no voting rights and no voice in government, blacks were subjected to what was known as the [[Jim Crow law]]s, a system of universal segregation and discrimination in all public facilities. Blacks were given separate schools (in which all students, teachers and administrators were black). Most hotels and restaurants served only whites. Movie theaters had separate seating; railroads had separate cars; buses were divided forward and rear. Neighborhoods were segregated as well. Blacks and whites did shop in the same stores. Blacks were not called to serve on juries, and they were not allowed to vote in the Democratic primary elections (which usually decided the election outcome).
| + | With no voting rights and no voice in government, blacks were subjected to what were known as [[Jim Crow laws]], a system of [[racial segregation]] and discrimination in all public facilities. Blacks were given separate schools (in which all students, teachers, and administrators were black). Most hotels and restaurants served only whites. Movie theaters had separate seating areas; railroads had separate cars; buses were divided forward and rear. Neighborhoods were segregated as well, though blacks and whites did shop in the same stores. Blacks were not called to serve on juries, and they were not allowed to vote in the primary elections (which usually decided the election outcome). |
| | | | |
| | ===Civil Rights=== | | ===Civil Rights=== |
| | + | In response to this treatment, the South witnessed two major events in the lives of twentieth century African Americans: The Great Migration and the [[American Civil Rights Movement (1955-1968)|Civil Rights Movement]]. |
| | | | |
| − | In response to this treatment, the South witnessed two major events in the lives of 20th century African Americans: the [[Great Migration (African American)|Great Migration]] and the [[American Civil Rights Movement (1955-1968)|American Civil Rights Movement]].
| + | The Great Migration began during [[World War I]] and hit its high point during [[World War II]]. Black people left the racism and lack of opportunities in the South and settled in northern cities such as [[Chicago]], where they found work in factories and other sectors of the economy. This migration produced a new sense of independence in the black community and contributed to the vibrant black urban culture seen during the [[Harlem Renaissance]]. |
| − | | |
| − | The Great Migration began during [[World War I]], hitting its high point during [[World War II]]. During this migration, Black people left the racism and lack of opportunities in the South and settled in northern cities like [[Chicago]], where they found work in factories and other sectors of the economy. (Katzman, 1996) However, Chicago quickly became the most segregated city in the north. This migration produced a new sense of independence in the Black community and contributed to the vibrant Black urban culture seen during the [[Harlem Renaissance]]. | |
| − | | |
| − | The migration also empowered the growing Civil Rights Movement. While the movement existed in all parts of the United States, its focus was against the Jim Crow laws in the South. Most of the major events in the movement occurred in the South, including the [[Montgomery Bus Boycott]], the Mississippi [[Freedom Summer]], the March on [[Selma, Alabama]], and the assassination of [[Martin Luther King, Jr]]. In addition, some of the most important writings to come out of the movement were written in the South, such as King's "[[Letter from Birmingham Jail]]". Many civil rights landmarks can be found around the South. The [[Martin Luther King, Jr. National Historic Site]] in Atlanta includes a museum that chronicles the American Civil Rights Movement as well as Martin Luther King, Jr.'s boyhood home on Auburn Avenue. Additionally, [[Ebenezer Baptist Church]] is located in the Sweet Auburn district as is the King Center, location of Martin Luther and Coretta Scott King's gravesites.
| |
| − | | |
| − | As a result of the Civil Rights Movement, Jim Crow laws across the South were dropped. Today, while many people believe race relations in the South to still be a contested issue, many others now believe the region leads the country in working to end racial strife. A second migration appears to be underway, with African Americans from the North moving to the South in record numbers.{{Fact|date=March 2007}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Symbolism==
| |
| − | The [[Rebel Flag|Battle Flag]] of the [[Confederate States of America|Confederacy]] has become a highly contentious image throughout the United States because of its use as a symbol of defiance by many in the South who opposed the Civil Rights Movement. Although it and other reminders of the [[Old South]] can be found on automobile bumper stickers, on tee shirts, and flown from homes, restrictions (notably on public buildings) have been imposed as a result groups such as the [[League of the South]] continue to promote [[secession]] from the [[United States]], citing a desire to protect and defend the heritage of the South. On the other side of this issue are groups like the [[Southern Poverty Law Center]] (SPLC), which believes that the League of the South is a hate group, and vice versa.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Other symbols of the [[Antebellum South]] include the [[Bonnie Blue Flag]] and [[Magnolia]] trees.
| |
| − | In the last two generations, the South has changed dramatically. After two centuries in which the region's main economic engine was agriculture, the South has in recent decades seen a boom in its [[service economy]], manufacturing base, high technology industries, and the financial sector. Examples of this include the surge in tourism in Florida and along the Gulf Coast; numerous new automobile production plants such as [[Mercedes-Benz]] in [[Tuscaloosa, Alabama]], [[Hyundai]] in [[Montgomery, Alabama]] and the [[BMW]] production plant in [[Spartanburg, South Carolina]]; the two largest research parks in the country, [[Research Triangle Park]] in North Carolina (the world's largest research park) and the [[Cummings Research Park]] in [[Huntsville, Alabama]] (the world's fourth largest research park); and the corporate headquarters of major banking corporations [[Bank of America]] and [[Wachovia]] in [[Charlotte]], [[Regions Financial]], [[Amsouth Bancorporation|Amsouth]], and [[Compass Bank|Compass]] in [[Birmingham]], [[SunTrust]] and the district headquarters of the [[Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta]], and [[BB&T]] in [[Winston-Salem]]; several [[Atlanta]]-based corporate headquarters and cable television networks such as [[CNN]], [[TBS (TV network)|TBS]], [[Turner Network Television|TNT]], [[Turner South]], [[Cartoon Network]], and [[The Weather Channel]]. This economic expansion has enabled parts of the South to boast some of the lowest unemployment rates in the United States.<ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | {{cite news | url = http://www.decaturdaily.com/decaturdaily/news/050819/jobless.shtml | title = State jobless rate below US average | work = The Decatur Daily | date = Aug 19, 2005 | accessdate = February 12, 2007}}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Largest Cities in the Southern U.S.==
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable sortable"
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! valign=bottom | Rank
| |
| − | ! valign=bottom | City
| |
| − | ! valign=bottom | State(s) and/or Territory
| |
| − | ! valign=bottom | July 1, 2006<br>Population Estimate
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 1
| |
| − | | [[Houston]]
| |
| − | | [[Texas|TX]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 2,144,491
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 2
| |
| − | | [[San Antonio]]
| |
| − | | [[Texas|TX]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,296,682
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 3
| |
| − | | [[Dallas]]
| |
| − | | [[Texas|TX]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,232,940
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 4
| |
| − | | [[Jacksonville]]
| |
| − | | [[Florida|FL]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 794,555
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 5
| |
| − | | [[Austin, Texas|Austin]]
| |
| − | | [[Texas|TX]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 709,893
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 6
| |
| − | | [[Memphis, Tennessee|Memphis]]
| |
| − | | [[Tennessee|TN]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 670,902
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 7
| |
| − | | [[Ft Worth]]
| |
| − | | [[Texas|TX]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 653,320
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 8
| |
| − | | [[Baltimore, Maryland|Baltimore]]
| |
| − | | [[Maryland|MD]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 631,366
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 9
| |
| − | | [[Charlotte]]
| |
| − | | [[North Carolina|NC]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 630,478
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 10
| |
| − | | [[El Paso]]
| |
| − | | [[Texas|TX]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 609,415
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Major metropolitan areas in the Southern U.S.==
| |
| − | {| class="wikitable sortable"
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | ! valign=bottom | Rank
| |
| − | ! valign=bottom | Metropolitan Area
| |
| − | ! valign=bottom | State(s) and/or Territory
| |
| − | ! valign=bottom | July 1, 2006<br>Population Estimate
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 1
| |
| − | | [[Dallas/Fort Worth Metroplex|Dallas–Fort Worth–Arlington]]
| |
| − | | [[Texas|TX]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 6,003,967
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 2
| |
| − | | [[Greater Houston|Houston–Sugar Land–Baytown]]
| |
| − | | [[Texas|TX]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 5,539,949
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 3
| |
| − | | [[Atlanta metropolitan area|Atlanta–Sandy Springs–Marietta]]
| |
| − | | [[Georgia (U.S. state)|GA]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 5,539,223
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 4
| |
| − | | [[South Florida metropolitan area|Miami–Fort Lauderdale–Pompano Beach]]
| |
| − | | [[Florida|FL]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 5,463,857
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 5
| |
| − | | [[Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV MSA|Washington–Arlington–Alexandria]]
| |
| − | | [[District of Columbia|DC]]–[[Virginia|VA]]–[[Maryland|MD]]–[[West Virginia|WV]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 5,290,400
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 6
| |
| − | | [[Tampa-St. Petersburg-Clearwater, Florida, Metropolitan Statistical Area|Tampa–St. Petersburg–Clearwater]]
| |
| − | | [[Florida|FL]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 2,697,731
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 7
| |
| − | |[[Baltimore, Maryland|Baltimore]]–[[Towson, Maryland|Towson]]
| |
| − | | [[Maryland|MD]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 2,658,405
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 8
| |
| − | | [[Charlotte metropolitan area|Charlotte–Gastonia–Concord]]
| |
| − | | [[North Carolina|NC]]–[[South Carolina|SC]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 2,191,604
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 9
| |
| − | | [[Orlando-Kissimmee, Florida, Metropolitan Statistical Area|Orlando-Kissimmee]]
| |
| − | | [[Florida|FL]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,984,855
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 10
| |
| − | | [[San Antonio]]
| |
| − | | [[Texas|TX]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,942,217
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 11
| |
| − | | [[Hampton Roads|Virginia Beach–Norfolk–Newport News]]
| |
| − | | [[Virginia|VA]]–[[North Carolina|NC]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,649,457
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 12
| |
| − | | [[The Triangle (North Carolina)|Raleigh-Durham]]
| |
| − | | [[North Carolina|NC]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,565,223
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 13
| |
| − | | [[Piedmont Triad|Greensboro-Winston-Salem-High Point]]
| |
| − | | [[North Carolina|NC]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,513,576
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 14
| |
| − | | [[Austin-Round Rock Metropolitan Statistical Area|Austin–Round Rock]]
| |
| − | | [[Texas|TX]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,513,565
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 15
| |
| − | | [[Nashville-Davidson-Murfreesboro, TN Metropolitan Statistical Area|Nashville-Davidson–Murfreesboro–Franklin]]
| |
| − | | [[Tennessee|TN]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,455,097
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 16
| |
| − | | [[Greater Jacksonville Metropolitan|Jacksonville]]
| |
| − | | [[Florida|FL]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,277,997
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 17
| |
| − | | [[Memphis, Tennessee|Memphis]]
| |
| − | | [[Tennessee|TN]]–[[Mississippi|MS]]–[[Arkansas|AR]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,274,704
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 18
| |
| − | | [[Louisville, Kentucky|Louisville]]
| |
| − | | [[Kentucky|KY]]–[[Indiana|IN]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,245,920
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 19
| |
| − | | [[The Upstate|Greenville-Spartanburg-Anderson]]
| |
| − | | [[South Carolina|SC]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,203,795
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 20
| |
| − | | [[Richmond, Virginia|Richmond]]
| |
| − | | [[Virginia|VA]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,194,008
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 21
| |
| − | | [[Birmingham-Hoover-Cullman Combined Statistical Area|Birmingham–Hoover–Cullman]]
| |
| − | | [[Alabama|AL]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,180,206
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 22
| |
| − | | [[New Orleans]]-[[Metairie, Louisiana|Metairie]]-[[Bogalusa, Louisiana|Bogalusa]]
| |
| − | | [[Louisiana|LA]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,069,428
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | align=center | 23
| |
| − | | [[Knoxville, Tennessee|Knoxville]]-[[Sevierville, Tennessee|Sevierville]]-[[La Follette, Tennessee|La Follette]]
| |
| − | | [[Tennessee|TN]]
| |
| − | | align=right | 1,010,978
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | | |
| | | | |
| | + | The migration also empowered the growing Civil Rights Movement. While the movement existed in all parts of the United States, its focus was against the [[Jim Crow laws]] in the South. Most of the major events in the movement occurred in the South, including the [[Montgomery Bus Boycott]], the Mississippi Freedom Summer, the March on Selma, Alabama, and the assassination of [[Martin Luther King|Martin Luther King, Jr]]. As a result of the Civil Rights Movement, Jim Crow laws across the South were dropped. Today, while many people believe race relations in the South to still be a contested issue, many others believe the region leads the country in working to end racial strife. A second migration appears to be underway, with African Americans from the North moving to the South in record numbers. |
| | | | |
| | ==Notes== | | ==Notes== |
| − | {{reflist}}
| + | <references/> |
| | | | |
| | ==References== | | ==References== |
| − | * Cash, Wilbur J. ''The Mind of the South'' (1941), | + | * Allen, John O., and Clayton E. Jewett. ''Slavery in the South: A State-by-State History''. Greenwood Press, 2004. ISBN 0313320195 |
| − | * {{cite book | author=Richard N. Current, et. al | title= American History: A Survey 7th ed. | location= New York | publisher= Alfred A. Knopf | year=1987 | id= ISBN 0-394-31549-9}}
| + | * Edward L. Ayers. ''The Promise of the New South: Life after Reconstruction''. Oxford University Press, 1993. ISBN 0195085485 |
| − | * Flynt, J. Wayne ''Dixie's Forgotten People: The South's Poor Whites'' (1979). deals with 20th century.
| + | * Billington, Monroe Lee. ''The Political South in the 20th Century''. Scribner, 1975. ISBN 0684139839 |
| − | * {{cite book | author=David M. Katzman | chapter=Black Migration | title= The Reader's Companion to American History | publisher= Houghton Mifflin Company}}
| + | * Black, Earl, and Merle Black. ''The Rise of Southern Republicans''. Belknap press, 2002. ISBN 0674012488 |
| − | * {{cite journal | author=James Grossman | title=Chicago and the 'Great Migration' | journal= Illinois History Teacher | volume=3 | issue= 2 | year=1996 | url=http://www.lib.niu.edu/ipo/1996/iht329633.html}}
| + | * Cash, W.J. ''The Mind of the South''. Vintage Books, 1991. ISBN 9780679736479 |
| − | * Grady McWhiney. ''In Cracker Culture: Celtic Ways in the Old South'' (1988)
| + | * Daniel, Pete. ''Lost Revolutions: The South in the 1950s''. University of North Carolina Press, 2000. ISBN 0807848484 |
| − | * Mary Odem "[http://www.southernspaces.org/contents/2007/sanchez/1a.htm Global Lives, Local Struggles: Latin American Immigrants in Atlanta'"] ''Southern Spaces'' 2006
| + | * Grissom, Michael Andrew. ''Southern by the Grace of God''. Pelican, 1989. ISBN 0882897616 |
| − | * {{cite book | author=John O. Allen and Clayton E. Jewett | title=Slavery in the South: A State-by-State History | publisher=Greenwood Press | year= 2004 | id=ISBN 0-313-32019-5}}
| + | * Kreyling, Michael. ''Inventing Southern Literature''. University Press of Mississippi, 1998. ISBN 1578060451 |
| − | *{{cite book| author=[[Rayford Logan]] | title=The Betrayal of the Negro from Rutherford B. Hayes to Woodrow Wilson | location= New York | publisher=Da Capo Press | year=1997 | id=ISBN 0-306-80758-0}}
| + | * Levine, Lawrence W. ''Black Culture and Black Consciousness: Afro-American Folk Thought from Slavery to Freedom''. Oxford University Press, 1978. ISBN 0195023749 |
| − | * {{cite book | author=William B. Hesseltine | title=A History of the South, 1607-1936 | publisher= Prentice-Hall | year=1936}}
| + | * Logan, Rayford. ''The Betrayal of the Negro from Rutherford B. Hayes to Woodrow Wilson''. New York: Da Capo Press, 1997. ISBN 0306807580 |
| − | * George Sanchez "[http://www.southernspaces.org/contents/2007/sanchez/1a.htm Latinos, the American South, and the Future of U.S. Race Relations]" ''Southern Spaces'' 2007
| + | * Parish, Peter J. ''Slavery: History and Historians''. Westview Press, 1989. ISBN 0064301826 |
| − | * {{cite book | editor=Robert W. Twyman. and David C. Roller, ed. | title=Encyclopedia of Southern History | publisher= LSU Press | year= 1979 | id= ISBN 0-8071-0575-9}}
| + | * Roller, David C., and Robert W. Twyman (eds.). ''Encyclopedia of Southern History''. LSU Press, 1979. ISBN 0807105759 |
| − | * Winders, Jamie. "[http://southernspaces.org/contents/2004/global_context/1a.htm Latino Migration and Nashville, Tennessee,]" ''Southern Spaces'' 2004.
| + | * Woodward, C. Vann. ''The Strange Career of Jim Crow''. Oxford University Press, 1955. ISBN 0195146905 |
| − | * {{cite book | editor=Charles Reagan Wilson and William Ferris, ed. | title=Encyclopedia of Southern Culture | publisher= University of North Carolina Press | year= 1989 | id=ISBN 0-8078-1823-2}}
| + | * Wright, Gavin. ''Old South, New South: Revolutions in the Southern Economy Since the Civil War''. LSU Press, 1996. ISBN 0807120987 |
| − | | |
| − | ---
| |
| − | [[External sources]]
| |
| − | *{{cite web | url=http://www.census.gov/const/regionmap.pdf | title=US Census Bureau region map | accessmonthday= 9 April | accessyear=2006}} | |
| − | *{{cite web | url=http://www.census.gov/population/www/cen2000/phc-t29.html | title=US Census Bureau metropolitan area statistics, table 3a | accessmonthday= 9 April | accessyear=2006}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==Further reading==
| |
| − | * {{cite book| author=Edward L. Ayers | title=The Promise of the New South: Life after Reconstruction | year=1993 | publisher=Oxford University Press | id=ISBN 0-19-508548-5}}
| |
| − | * {{cite book | author=Monroe Lee Billington | title=The Political South in the 20th Century | publisher=Scribner | year=1975 | id=ISBN 0-684-13983-9}} | |
| − | * {{cite book | author=Earl Black and Merle Black | title=The Rise of Southern Republicans | year=2002 | id=ISBN 0-674-01248-8 | publisher=Belknap press}} | |
| − | * {{cite book | author=W. J. Cash | title=The Mind of the South | year=1935 | id=ISBN 0-679-73647-6}} | |
| − | * {{cite book | author=Pete Daniel | title=Lost Revolutions: The South in the 1950s | publisher= University of North Carolina Press | year= 2000 | id= ISBN 0-8078-4848-4}} | |
| − | * {{cite book | author=Michael Kreyling | title=Inventing Southern Literature | publisher= University Press of Mississippi | year= 1998 | id=ISBN 1-57806-045-1}} | |
| − | *{{cite journal | journal=Poetics | title=Antebellum literary culture and the evolution of American magazines | author= Heather A. Haveman | url=http://www.columbia.edu/~hah15/H_2004_Poetics.pdf | volume=32 | year=2004 | pages=5-28}} | |
| − | * {{cite book | author=Eugene D. Genovese | title=Roll, Jordan, Roll: The World the Slaves Made | year=1976 | id =ISBN 0-394-71652-3}}
| |
| − | * {{cite book | author=Lawrence W. Levine | title=Black Culture and Black Consciousness: Afro-American Folk Thought from Slavery to Freedom | publisher= Oxford University Press | year=1978 | id=ISBN 0-19-502374-9}}
| |
| − | * {{cite book | author=Peter J. Parish | title=Slavery: History and Historians | publisher= Westview Press | year=1989 | id=ISBN 0-06-430182-6}} | |
| − | * {{cite journal | author= Howard N. Rabinowitz | title=From Exclusion to Segregation: Southern Race Relations, 1865-1890 | journal=Journal of American History | volume= 43 | date=September 1976 | pages= 325-50}} | |
| − | * {{cite book | author=Nicol C. Rae | title=Southern Democrats | year=1994 | id=ISBN 0-19-508709-7 | publisher=Oxford University Press}}
| |
| − | * {{cite book | author=Jeffrey A. Raffel | title=Historical Dictionary of School Segregation and Desegregation: The American Experience | publisher=Greenwood Press | year= 1998 | id=ISBN 0-313-29502-6}}
| |
| − | * {{cite book | author=C. Vann Woodward | title=The Strange Career of Jim Crow | year=1955 | id=ISBN 0-19-514690-5 | publisher=Oxford University Press}} | |
| − | * {{cite book | author=[[Richard Wright (author)|Richard Wright]] | title=[[Black Boy]] | publisher= Harper & Brothers | year=1945}} a novel. | |
| − | * {{cite book | author=Gavin Wright | title=Old South, New South: Revolutions in the Southern Economy Since the Civil War | yeare=1996 | id=ISBN 0-8071-2098-7 | publisher=LSU Press}}
| |
| − | * {{cite book | author=Michael Andrew Grissom | title=Southern by the Grace of God | publisher= Pelican | year=1989 | id= ISBN 0-88289-761-6}}
| |
| | | | |
| | ==External links== | | ==External links== |
| − | *[http://docsouth.unc.edu/index.html DocSouth: Documenting the American South] - numerous online text, image, and audio collections | + | All links retrieved February 4, 2023. |
| − | *[http://www.unc.edu/depts/csas/ Center for the Study of the American South] - an academic center devoted to the study of "southern history, literature, and culture as well as ongoing social, political, and economic issues" | + | *[https://docsouth.unc.edu/index.html Documenting the American South] |
| − | *[http://research.unc.edu/endeavors/spr97/south.html Dixie's dead, long live the South]
| + | *[https://www.southarts.org/ Southern Arts Federation] |
| − | *[http://www.southarts.org/ Southern Arts Federation]
| + | *[https://southernspaces.org/ Southern Spaces] an open-access peer-reviewed scholarly journal examining the spaces and places of the American South. |
| − | *[http://www.southernspaces.org/ Southern Spaces]— an open-access peer-reviewed scholarly journal examining the spaces and places of the American South. | |
| | | | |
| − | {{U.S.Regions}}
| |
| | | | |
| | [[Category:Geography]] | | [[Category:Geography]] |
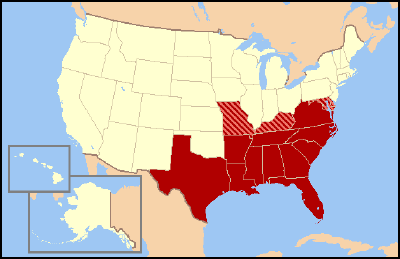
Historic Southern United States. The states in red were in the Confederacy and have historically been regarded as forming "the South." Sometimes they are collectively referred to as "Dixie." Those in stripes were considered "Border" states, and gave varying degrees of support to the Southern cause although they remained in the Union. (This image depicts the original, trans-Allegheny borders of Virginia, and so does not include West Virginia. See image below for post-1863 Virginia and West Virginia borders.)
The Southern United States—commonly referred to as the American South or simply the South—constitutes a large distinctive region in the southeastern and south-central United States. Because of the region's unique cultural and historic heritage, including early European colonial settlements, the doctrine of states' rights, the institution of slavery, and the legacy of the Confederacy during the American Civil War, the South has developed its own customs, literature, musical styles, and varied cuisines.
After the Civil War, the South was largely devastated in terms of its population, infrastructure, and economy. Not until modern times did the situation change. During World War II, new industries and military bases sprang up across the region, providing badly need capital and infrastructure. Farming shifted from cotton and tobacco to include soybeans, corn, and other foods. This growth accelerated in the 1980s and 1990s. Large urban areas rose in Texas, Georgia, and Florida. Rapid expansion in industries such as automobiles, telecommunications, textiles, technology, banking, and aviation gave some states an industrial strength that rivaled large states elsewhere. By the 2000 census, the South (along with the West) was leading the nation in population growth.

Modern definition The states in dark red are almost always included in modern day definitions of the South, while those in medium red are usually included. Maryland and Missouri are occasionally considered Southern, while Delaware is seldom considered a Southern state. Oklahoma is sometimes considered Southern because the area of Oklahoma, then known as Indian Territory, was allied with the Confederacy. West Virginia is considered Southern by many, because it was once part of Virginia.
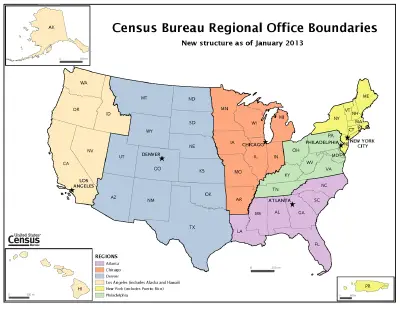
The South as one of four regions of the United States.
Geography
As defined by the U.S. Census Bureau, the southern region includes 16 states (with a total 2006 estimated population of 109,083,752) and is split into three smaller units:
- The South Atlantic States: Florida, Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, West Virginia, Maryland, and Delaware
- The East South Central States: Alabama, Kentucky, Mississippi, and Tennessee
- The West South Central States: Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas

Flower of
Magnolia grandiflora, also known as the
Southern Magnolia.
The popular definition of the "South" is more informal and is generally associated with those states that seceded during the Civil War to form the Confederate States of America. Those states share commonalities of history and culture. The "border states" of the Civil War—specifically Missouri, Kentucky, Maryland, and Delaware—roughly form the northern boundary of the "South." These states have a history of straddling the North-South divide, which was made clear when they did not secede during the Civil War even though they allowed slavery. Depending on the context, these states may or may not be considered part of the South.
The South is a vast, diverse region, having numerous climatic zones, including temperate, sub-tropical, tropical, and arid. Many crops grow easily in its soils and can be grown without frost for at least six months of the year. Some parts of the South, particularly the Southeast, have landscapes characterized by the presence of live oaks, magnolia trees, yellow jessamine vines, and flowering dogwoods. Another common environment is the bayous and swampland of the Gulf Coast, especially in Louisiana. The South is a victim of kudzu, an invasive fast-growing vine that covers large amounts of land and kills indigenous plant life.
History

Picking cotton in southeastern United States, early twentieth century
The predominant culture of the South has its origins with the settlement of the region by British colonists in the seventeenth century, mostly in coastal regions. In the eighteenth century, large groups of Scots and Ulster-Scots (later called the Scots-Irish) settled in Appalachia and the Piedmont. These people engaged in warfare, trade, and cultural exchanges with the Native Americans already in the region (such as the Creeks and Cherokees).
The Trail of Tears refers to the forced relocation in 1838, of the Cherokee tribe to Indian Territory (modern day Oklahoma), from what is now the state of Georgia. The forced march resulted in the deaths of an estimated 4,000 Cherokee. In the Cherokee language, the event is called Nunna daul Isunyi—“the Trail Where We Cried.” The phrase originated as a description of the forcible removal of the Choctaw nation in 1831.
After 1700, large groups of African slaves were brought in to work on the plantations that dominated export agriculture, growing tobacco, rice, and indigo. Cotton became dominant after 1800. The explosion of cotton cultivation made slavery an integral part of the South's early nineteenth century economy.
The oldest university in the South, the College of William and Mary, was founded in 1693 in Virginia; it pioneered in the teaching of political economy and educated future U.S. presidents Thomas Jefferson, James Monroe, and John Tyler, all from Virginia. Indeed, the entire region dominated politics in that era: For example, four of the first five Presidents—George Washington, Jefferson, James Madison, and Monroe—were from Virginia.
Two major political issues that festered in the first half of the nineteenth century strengthened the identities of North and South as distinct regions with certain strongly opposed interests and fed the arguments over states' rights that culminated in secession and the American Civil War. One of these issues concerned the protective tariffs enacted to assist the growth of the manufacturing sector, located primarily in the North. In 1832, in resistance to federal legislation increasing tariffs, South Carolina passed an ordinance of nullification, a procedure by which a state would in effect repeal a federal law. A naval flotilla was sent to Charleston harbor, and the threat of landing ground troops was used to compel the collection of tariffs. A compromise was reached by which the tariffs would be gradually reduced, but the underlying argument over states' rights continued to escalate in the following decades.
The second issue concerned slavery, primarily the question of whether slavery would be permitted in newly admitted states. The issue was initially finessed by political compromises designed to balance the number of "free" and "slave" states. The issue resurfaced in more virulent form, however, around the time of the Mexican War, which raised the stakes by adding new territories primarily on the southern side of the imaginary geographic divide.
Civil War
By 1855, the South was losing political power to the more populous North and was locked in a series of constitutional and political battles with the North regarding states' rights and the status of slavery in the territories. President James K. Polk imposed a low-tariff regime on the country, which angered Pennsylvania industrialists, and blocked proposed federal funding of national roads and port improvements. Seven states decided on secession after the election of Abraham Lincoln in 1860. They formed the Confederate States of America. In 1861, they were joined by four more states.
The United States government refused to recognize the seceding states as a new country and kept in operation its second to last fort in the South, which the Confederacy captured in April 1861, at the Battle of Fort Sumter, in the port of Charleston, triggering the Civil War. The Confederacy retained a low tariff regime for European imports but imposed a new tax on all imports from the North. A Union blockade stopped most commerce from entering the South, so the Confederate taxes hardly mattered. The southern transportation system depended primarily on river and coastal traffic by boat; both were shut down by the Union navy. The small railroad system virtually collapsed, so that by 1864, internal travel was so difficult that the Confederate economy was crippled.
The Union (so-called because they fought for the United States of America) eventually defeated the Confederate States of America. The South suffered much more than the North, primarily because the war was fought almost entirely in the South. Overall, the Confederacy suffered 95,000 killed in action and 165,000 who died of disease, for a total of 260,000,[1] out of a total white southern population at the time of around 5.5 million. Based on 1860 census figures, 8 percent of all white males aged 13 to 43 died in the war, including 6 percent in the North and an extraordinary 18 percent in the South.[2] Northern casualties exceeded Southern casualties.
Reconstruction
After the Civil War, the South was largely devastated in terms of its population, infrastructure, and economy. The republic also found itself under Reconstruction, with military troops in direct political control of the South. White southerners who had actively supported the Confederacy lost many of the basic rights of citizenship (such as voting). With passage of the Thirteenth Amendment to the Constitution of the United States (outlawing slavery), the Fourteenth Amendment (granting full U.S. citizenship to African-Americans), and the Fifteenth Amendment (extending the right to vote to African-American males), blacks began to enjoy more rights than they ever had in the South.
By the 1890s, though, a political backlash against these rights had developed in the South. Organizations such as the Ku Klux Klan—a clandestine organization sworn to perpetuate white supremacy—used lynchings and other forms of violence and intimidation to keep African Americans from exercising their political rights, while Jim Crow laws were created to legally do the same thing. It would not be until the late 1960s that these phenomena would be undermined by the American Civil Rights Movement.
Economy
Nearly all southerners, black and white, suffered as a result of the Civil War. With the region devastated by its loss and the destruction of its civil infrastructure, much of the South was generally unable to recover economically until after World War II. Locked into low productivity agriculture, the region's growth was slowed by limited industrial development, low levels of entrepreneurship, and the lack of capital investment.
The first major oil well in the South was drilled near Beaumont, Texas, on the morning of January 10, 1901. Other oil fields were later discovered nearby in Arkansas, Oklahoma, and under the Gulf of Mexico. The resulting boom permanently transformed the economy of the western South Central states and led to the first significant economic expansion since the Civil War.
The economy, which for the most part had still not recovered from the Civil War, was dealt a double blow by the Great Depression and the Dust Bowl. After the Wall Street Crash of 1929, the economy suffered significant reversals and millions were left unemployed. From 1934 until 1939, an ecological disaster of severe wind and drought, known as the Dust Bowl, caused an exodus from Texas and Arkansas, the Oklahoma Panhandle region, and the surrounding plains, in which over 500,000 Americans were homeless, hungry, and jobless.[3] Thousands left the region to seek economic opportunities on the West Coast.
World War II marked a time of change in the South, as new industries and military bases sprang up across many areas of the region, providing badly need capital and infrastructure. People from all parts of the United States came to the South for military training and to work. Farming shifted from cotton and tobacco to include soybeans, corn, and other foods. This growth increased in the 1960s, and greatly accelerated in the 1980s and 1990s. Large urban areas with over four million people rose in Texas, Georgia, and Florida. Rapid expansion in industries such as automobiles, telecommunications, textiles, technology, banking, and aviation gave some states in the South an industrial strength that rivaled large states elsewhere. By the 2000 census, the South (along with the West) was leading the nation in population growth. With this growth, however, came long commute times and serious air pollution problems in cities such as Dallas, Houston, Atlanta, Miami, Austin, and Charlotte.
Poverty
The South has historically been financially disadvantaged when compared to the United States as a whole. After the Civil War, nearly the entire economic infrastructure of the region was in ruins. Since there were few industrial businesses located in the South at the time, other possible sources of income were scarce. Most former slaves had no training or experience in anything besides agriculture.
After World War II, the development of the Interstate Highway System, household air conditioning and later, passage of federal civil rights bills, the South was successful at attracting industry and business from other parts of the country, particularly the Rust Belt region of the Northeast and the Great Lakes. Poverty rates and unemployment declined as a result. Federal programs such as the Appalachian Regional Commission also contributed to economic growth.
While much of the Southern United States has advanced considerably since World War II, poverty persists in some areas, like eastern Kentucky and southern West Virginia. The Mexican border area in Texas takes the brunt of poverty in the South today.
Culture
Southern culture has been and remains generally more socially conservative than the rest of the country. Because of the central role of agriculture in the economy, society remained stratified according to land ownership. Rural communities often developed strong attachment to their churches as the primary community institution.
Southerners are often viewed as more relaxed and the southern lifestyle as slower paced. Southerners are also stereotyped as being resistant to change. They are also reputed to be polite and well-mannered, particularly in welcoming visitors; this characteristic has been labeled as "southern hospitality."
Religion
Until the mid nineteenth century, traditional Southerners were either Episcopalian or Presbyterian due to the South's close ancestral ties to England, Scotland, and the Irish province of Ulster. Around the beginning of the Civil War and thereafter, Baptist and Methodist churches became the most prevalent forms of Christianity in the region. Perhaps more than any other region of an industrialized nation, the South has a high concentration of Christian adherents, resulting in the reference to parts of the South as the "Bible Belt," from the presence of evangelical and fundamentalist Protestants, conservative Catholicism, as well as Pentacostalism and Charismatics.
There are significant Catholic populations in most cities in the South, such as Atlanta, Savannah, Mobile, New Orleans, Baltimore, and Louisville. Rural areas of the Gulf coast, particularly those populated by Cajuns and Creoles, are also heavily Catholic. In general, the inland regions of the South such as Arkansas, Tennessee, and Alabama have stronger concentrations of Baptists, Methodists, Church of Christ, and other Protestants. Eastern and northern Texas are also heavily Protestant, while the southern parts of the state have Mexican American Catholic majorities. The South Florida area is home to the country's second largest concentration of Jewish people. Cities such as Miami, Atlanta, Dallas, and Houston have significant Jewish and Muslim communities. Immigrants from Southeast Asia and South Asia have brought Buddhism and Hinduism to the region as well. Atlanta has one of the largest Kurd populations in the world outside the Middle East.
Dialects
There is no single "southern accent." Rather, southern American English is a collection of dialects of the English language spoken throughout the South. Southern American English can be divided into different sub-dialects, with speech differing between, for example, the Appalachian region and the coastal "low country" around Charleston,South Carolina, and Savannah, Georgia. Along this part of the southeastern coast, Gullah is still spoken by some African-Americans, particularly the older generation.
Folklorists in the 1920s and later argued that Appalachian language patterns more closely mirror Elizabethan English than other accents in the United States.[4]
Cuisine
In addition to linguistics, the cuisine of the South is often described as one of its most distinctive traits. But just as history and culture vary across the broad region known as the South, the traditional cuisine varies as well. In modern times, there is little difference between the diet of typical Southerners and the diet in other regions of the U.S, but the South draws on multiple unique culinary influences to form its "traditional" foods. Southern cuisine also provides some of the best examples of distinctly American cuisine—that is, foods and styles that were born in the United States as opposed to adopted from elsewhere.
The food most commonly associated with the term "southern food" is often called "soul food" and is characterized by the heavy use of lards and fats. This style draws on the mix of African influences as well as Native American, Scots-Irish, and others. Southern fried chicken, black-eyed peas, cornbread, and biscuits are just a few examples of foods typically lumped into this category.
Barbecue is a food typically associated with the South, though it is also common throughout the Midwest. Consisting of meat that has been slow-cooked and heavily seasoned, it is characterized by sharp regional divides in style preferences. In Texas, it is often beef based, while in North Carolina it is typically pork based.
The unique history of Louisiana and the Mississippi Delta provides a unique culinary environment as well. Cajun and Creole evolved from the broad mix of cultural influences in this area—including Acadian, African, Caribbean, French, Native American, and Spanish.
Texas and its proximity and shared history with Mexico ultimately helped give rise to the modern Tex-Mex cuisine.
Literature
Perhaps the most famous southern writer is William Faulkner, who won the Nobel Prize in literature in 1949. Faulkner brought new techniques, such as stream of consciousness and complex narrative, to American writing.
Other well-known Southern writers include Mark Twain (whose Adventures of Huckleberry Finn and The Adventures of Tom Sawyer are two of the most read books about the South), Zora Neale Hurston, Eudora Welty, Thomas Wolfe, William Styron, Flannery O'Connor, Carson McCullers, James Dickey, Willie Morris, Tennessee Williams, Truman Capote, Walker Percy, Barry Hannah, Robert Penn Warren, Cormac McCarthy, James Agee, and Harry Crews.
Possibly the most famous southern novel of the twentieth century was Gone with the Wind by Margaret Mitchell, published in 1937. Another famous southern novel, To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee, won the Pulitzer Prize after it was published in 1960.
Music
The South offers some of the richest music in the United States. The musical heritage of the South was developed by both whites and blacks, influencing each other directly and indirectly.
The South's musical history actually starts before the Civil War, with the songs of the African slaves and the traditional folk music brought from the British Isles. Blues was developed in the rural South by blacks at the beginning of the twentieth century. In addition, gospel music, spirituals, country music, rhythm and blues, soul music, funk, rock and roll, bluegrass, jazz (including ragtime, popularized by southerner Scott Joplin), and Appalachian folk music were either born in the South or developed in the region.
In general, country music is based on the folk music of white southerners, and blues and rhythm and blues are based on black southern forms. However, whites and blacks alike have contributed to each of these genres, and there is considerable overlap between the traditional music of blacks and whites in the South, particularly in gospel music forms. A stylish variant of country music (predominantly produced in Nashville) has been a consistent, widespread fixture of American pop since the 1950s, while insurgent forms (for example, bluegrass) have traditionally appealed to more discerning subcultural and rural audiences. Blues dominated the black music charts from the advent of modern recording until the mid-1950s, when it was supplanted by the less guttural and forlorn sounds of rock and R&B.
Zydeco, Cajun, and swamp pop, despite having never enjoyed greater regional or mainstream popularity, still thrive throughout French Louisiana and its peripheries, such as southeastern Texas.
Rock n' roll largely began in the South in the late 1940s and early 1950s. Early rock n' roll musicians from the South include Buddy Holly, Little Richard, Fats Domino, Bo Diddley, Elvis Presley, Ray Charles, James Brown, Otis Redding, Carl Perkins, and Jerry Lee Lewis, among many others. Hank Williams and Johnny Cash, while generally regarded as "country" singers, also had a significant role in the development of rock music.
Sports

The Dallas Cowboys are one of the region's most popular NFL teams.
American football is heavily considered the most popular team sport in most areas of the Southern United States.
The region is home to numerous decorated and historic college football programs, particularly in the Southeastern Conference (known as the "SEC"), Atlantic Coast Conference (known as the "ACC"), and the Big 12 Conference. The SEC, consisting almost entirely of teams based in Southern states, is widely considered to be the strongest league in contemporary college football and includes the Alabama Crimson Tide, the program with the most national championships in the sport's modern history. The sport is also highly competitive and has a spectator following at the high school level, particularly in rural areas, where high school football games often serve as prominent community gatherings.
Though not as popular on a wider basis as the collegiate game, professional football has a growing tradition in the Southern United States.
Baseball

Houston vs Texas face-off during the 2013 Lone Star Series in the American League West division of Major League Baseball
Baseball has been played in the Southern United States dating back to the mid-nineteenth century. It was traditionally more popular than American football until the 1980s, and still accounts for the largest annual attendance amongst sports played in the South.
Auto racing

The start of the 2015 Daytona 500, the biggest race in NASCAR, at Daytona International Speedway in Daytona Beach, Florida
The Southern states are commonly associated with stock car racing and its most prominent competition level NASCAR, which is headquartered in Charlotte and Daytona Beach. The sport was developed in the South during the early 20th century, with stock car racing's historic mecca being Daytona Beach, where cars initially raced on the wide, flat beachfront, before the construction of Daytona International Speedway. Though the sport has attained a following throughout the United States, a majority of NASCAR races continue to take place at Southern tracks.
Basketball
Basketball is very popular throughout the Southern United States as both a recreational and spectator sport, particularly in the states of Kentucky and North Carolina. Both states are home to several prominent college basketball programs, including the Kentucky Wildcats, Louisville Cardinals, Duke Blue Devils and North Carolina Tar Heels.
NBA teams based in the South include the San Antonio Spurs, Houston Rockets, Oklahoma City Thunder, Dallas Mavericks, Washington Wizards, Charlotte Hornets, Atlanta Hawks, Orlando Magic, Memphis Grizzlies, New Orleans Pelicans, and Miami Heat. The Spurs and Heat in particular have become prominent within the NBA, with eight championships won by the two between 1999 and 2013.
Golf
Golf is a popular recreational sport in most areas of the South, with the region's warm climate allowing it to host many professional tournaments and numerous destination golf resorts, particularly in the state of Florida. The region is home to The Masters, one of the four major championships in professional golf. The Masters is played at Augusta National Golf Club in Augusta, Georgia, and has become one of the professional game's most important tournaments. Hilton Head Island, in South Carolina, is also home to a prominent American golf tournament and has several high-quality courses.
Politics
In the century after Reconstruction, the white South strongly identified with the Democratic Party. This lock on power was so strong the region was called the Solid South. Republicans controlled parts of the Appalachian Mountains and competed for power in the border states, but otherwise it was rare for a southern politician to be a Republican before the 1960s.
Increasing support for civil rights legislation by the Democratic Party at the national level during the 1940s caused a split between conservative southern Democrats and other Democrats in the country. Until the passage of the civil rights laws of the 1960s, conservative southern Democrats ("Dixiecrats") argued that only they could defend the region from the onslaught of northern liberals and the civil rights movement. In response to the Brown v. Board of Education decision of 1954, 101 southern congressmen denounced the Supreme Court decision as a "clear abuse of judicial power." The manifesto was signed by all southern senators except Majority Leader Lyndon B. Johnson and Tennessee senators Albert Gore, Sr. and Estes Kefauver. Virginia closed some schools rather than integrate, but no other state followed suit. An element resisted integration, led by Democratic governors Orval Faubus of Arkansas, Ross Barnett of Mississippi, Lester Maddox of Georgia, and George Wallace of Alabama.
The Democratic Party's dramatic reversal on civil rights issues culminated when President Lyndon B. Johnson signed into law the Civil Rights Act of 1964. Meanwhile, the Republicans were beginning their southern strategy, which aimed to solidify the party's electoral hold over conservative white southerners. Southern Democrats took notice that 1964 Republican presidential candidate Barry Goldwater had voted against the Civil Rights Act, and in the presidential election of 1964, Goldwater's only electoral victories outside his home state of Arizona were in the states of the Deep South.
The transition to a Republican stronghold took decades. First, the states started voting Republican in presidential elections—the Democrats countered by nominating such southerners as Jimmy Carter in 1976 and 1980, Bill Clinton in 1992 and 1996, and Al Gore in 2000. Then the states began electing Republican senators and finally governors. In addition to the middle class and business base, Republicans attracted strong majorities from the evangelical Christian vote, which had not been a distinct political demographic prior to 1980.
There was major resistance to desegregation in the mid 1960s to early 1970s. Those issues faded away, replaced by culture wars between the conservatives and liberals over issues such as abortion and gay marriage.
Presidential history
The South produced most of the U.S. presidents prior to the Civil War. After that, memories of the war made it impossible for a southerner to become president unless he either moved north (like Woodrow Wilson) or was a vice president who moved up (like Harry Truman and Lyndon B. Johnson). In 1976, Jimmy Carter became the first southerner to break the pattern since Zachary Taylor in 1848. Presidents, George H.W. Bush, Bill Clinton, and George W. Bush, have all been from the South: George H.W. Bush was a congressman from Texas, Clinton was governor of Arkansas, and George W. Bush was governor of Texas.
Other politicians and political movements
The South has produced numerous other well-known politicians and political movements.
In 1948, a group of Democratic congressmen, led by Governor Strom Thurmond of South Carolina, split from the Democrats in reaction to an anti-segregation speech given by Senator Hubert Humphrey of Minnesota, founding the States Rights Democratic or Dixiecrat Party. During that year's presidential election, the party unsuccessfully ran Thurmond as its candidate.
In the 1968 presidential election, Alabama Governor George C. Wallace ran for president on the American Independent Party ticket. Wallace ran a "law and order" campaign similar to that of Republican candidate Richard Nixon. Nixon's Southern Strategy downplayed race issues and focused on culturally conservative values, such as family issues, patriotism, and cultural issues.
In 1994, another Southern politician, Newt Gingrich, ushered in 12 years of GOP control of the House. Gingrich became Speaker of the House of Representatives in 1995, but was forced to resign after mishandling the impeachment of southerner Bill Clinton in 1998. Tom DeLay was the most powerful Republican leader in Congress until his abrupt criminal indictment in 2005. Recent Republican Senate leaders from the South included Howard Baker of Tennessee, Trent Lott of Mississippi, Bill Frist of Tennessee, and Mitch McConnell of Kentucky.
Race relations
History
African-Americans have a long history in the South, stretching back to the early settlements in the region. Beginning in the early seventeenth century, black slaves were purchased from slave traders who brought them from Africa (or, less often, from the Caribbean) to work on plantations. Most slaves arrived in the period 1700-1750.
Slavery ended with the South's defeat in the Civil War. During the Reconstruction period that followed, African Americans saw advancements in civil rights and political power in the South. As Reconstruction ended, however, southern whites took steps to prevent black people from holding power. After 1890, the Deep South disfranchised many African Americans.
With no voting rights and no voice in government, blacks were subjected to what were known as Jim Crow laws, a system of racial segregation and discrimination in all public facilities. Blacks were given separate schools (in which all students, teachers, and administrators were black). Most hotels and restaurants served only whites. Movie theaters had separate seating areas; railroads had separate cars; buses were divided forward and rear. Neighborhoods were segregated as well, though blacks and whites did shop in the same stores. Blacks were not called to serve on juries, and they were not allowed to vote in the primary elections (which usually decided the election outcome).
Civil Rights
In response to this treatment, the South witnessed two major events in the lives of twentieth century African Americans: The Great Migration and the Civil Rights Movement.
The Great Migration began during World War I and hit its high point during World War II. Black people left the racism and lack of opportunities in the South and settled in northern cities such as Chicago, where they found work in factories and other sectors of the economy. This migration produced a new sense of independence in the black community and contributed to the vibrant black urban culture seen during the Harlem Renaissance.
The migration also empowered the growing Civil Rights Movement. While the movement existed in all parts of the United States, its focus was against the Jim Crow laws in the South. Most of the major events in the movement occurred in the South, including the Montgomery Bus Boycott, the Mississippi Freedom Summer, the March on Selma, Alabama, and the assassination of Martin Luther King, Jr. As a result of the Civil Rights Movement, Jim Crow laws across the South were dropped. Today, while many people believe race relations in the South to still be a contested issue, many others believe the region leads the country in working to end racial strife. A second migration appears to be underway, with African Americans from the North moving to the South in record numbers.
Notes
- ↑ Matthew White, Nineteenth Century Death Tolls: American Civil War Statistics of Wars, Oppressions and Atrocities of the Nineteenth Century. Retrieved October 5, 2022.
- ↑ Craig Lambert, The Deadliest War Harvard Magazine. Retrieved October 5, 2022.
- ↑ First Measured Century: Interview with James Gregory PBS. Retrieved October 5, 2022.
- ↑ Charles Morrow Wilson, Elizabethan America Atlantic Monthly, August, 1929. Retrieved October 5, 2022.
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Allen, John O., and Clayton E. Jewett. Slavery in the South: A State-by-State History. Greenwood Press, 2004. ISBN 0313320195
- Edward L. Ayers. The Promise of the New South: Life after Reconstruction. Oxford University Press, 1993. ISBN 0195085485
- Billington, Monroe Lee. The Political South in the 20th Century. Scribner, 1975. ISBN 0684139839
- Black, Earl, and Merle Black. The Rise of Southern Republicans. Belknap press, 2002. ISBN 0674012488
- Cash, W.J. The Mind of the South. Vintage Books, 1991. ISBN 9780679736479
- Daniel, Pete. Lost Revolutions: The South in the 1950s. University of North Carolina Press, 2000. ISBN 0807848484
- Grissom, Michael Andrew. Southern by the Grace of God. Pelican, 1989. ISBN 0882897616
- Kreyling, Michael. Inventing Southern Literature. University Press of Mississippi, 1998. ISBN 1578060451
- Levine, Lawrence W. Black Culture and Black Consciousness: Afro-American Folk Thought from Slavery to Freedom. Oxford University Press, 1978. ISBN 0195023749
- Logan, Rayford. The Betrayal of the Negro from Rutherford B. Hayes to Woodrow Wilson. New York: Da Capo Press, 1997. ISBN 0306807580
- Parish, Peter J. Slavery: History and Historians. Westview Press, 1989. ISBN 0064301826
- Roller, David C., and Robert W. Twyman (eds.). Encyclopedia of Southern History. LSU Press, 1979. ISBN 0807105759
- Woodward, C. Vann. The Strange Career of Jim Crow. Oxford University Press, 1955. ISBN 0195146905
- Wright, Gavin. Old South, New South: Revolutions in the Southern Economy Since the Civil War. LSU Press, 1996. ISBN 0807120987
External links
All links retrieved February 4, 2023.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article
in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.







