Difference between revisions of "Kazakhstan" - New World Encyclopedia
({{Contracted}}) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (123 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Paid}}{{Approved}}{{Submitted}}{{Images OK}}{{Copyedited}} |
| − | {{ | + | {{Infobox country |
| − | {{Infobox | + | |native_name=Қазақстан Республикасы <br/>''Qazaqstan Respublïkası''<br/>Республика Казахстан<br/>''Respublika Kazakhstan'' |
| − | |native_name | + | |conventional_long_name=Republic of Kazakhstan |
| − | |conventional_long_name | + | |common_name=Kazakhstan |
| − | |common_name | + | |image_flag=Flag of Kazakhstan.svg |
| − | + | |image_coat=Emblem of Kazakhstan.svg | |
| − | |image_flag | + | | symbol_type = Emblem |
| − | |image_coat | + | | national_motto = |
| − | |image_map | + | | national_anthem = [[Meniń Qazaqstanym|Менің Қазақстаным]]<br/>{{transl|kk|Meniń Qazaqstanym}}<br />{{small|"My Kazakhstan"}}<br/> |
| − | | | + | |image_map=LocationKazakhstan.png |
| − | |official_languages | + | | map_caption = {{map caption |location_color= green}} |
| − | | | + | | capital = [[Astana]] |
| − | | | + | | coordinates = {{Coord|51|10|N|71|26|E|type:city}} |
| − | | | + | | largest_city = [[Almaty]] |
| − | | | + | | official_languages = [[Kazakh language|Kazakh]] {{small|(official state language)}} <br/>[[Russian language|Russian]]{{small| (used as official)<ref>[https://adilet.zan.kz/eng/docs/K950001000_ Constitution of the Republic of Kazakhstan] ''Institute of legislation and legal information of the Republic of Kazakhstan''. Retrieved January 19, 2022.</ref>}} |
| − | | | + | | ethnic_groups = Kazakh (Qazaq) 68.0%<br/>Russian 19.3%<br/>Uzbek 3.2%<br/>Ukrainian 1.5%<br/>Uighur 1.5%<br/>Tatar 1.1%<br/>German 1.0%<br/>other 4.4% |
| − | | | + | | ethnic_groups_year = 2019<ref name=CIA>CIA, [https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/kazakhstan Kazakhstan] ''World Factbook''. Retrieved January 19, 2022.</ref> |
| − | | | + | | demonym = [[Kazakhstani (disambiguation)|Kazakhstani]] (Kazakhstani includes all citizens, in contrast to Kazakh, which is the demonym for ethnic [[Kazakhs]]).<ref>Johann Schneider, Knud S. Larsen, Krum Krumov, and Grigorii Vazow, ''Advances in International Psychology: Research Approaches and Personal Dispositions, Socialization Processes and Organizational Behavior'' (Kassel University Press, 2013, ISBN 978-3862194544).</ref> |
| − | | | + | | government_type = [[Unitary state|Unitary]] [[Presidential system|presidential]] [[republic|constitutional republic]] |
| − | | | + | | leader_title1 = [[President of Kazakhstan|President]] |
| − | | | + | | leader_name1 = [[Kassym-Jomart Tokayev]] |
| − | | | + | | leader_title2 = [[Prime Minister of Kazakhstan|Prime Minister]] |
| − | | | + | | leader_name2 = [[Alihan Smaiylov]] |
| − | |percent_water | + | | legislature = [[Parliament of Kazakhstan|Parliament]] |
| − | |population_estimate | + | | upper_house = [[Senate of Kazakhstan|Senate]] |
| − | |population_estimate_year = | + | | lower_house = [[Mazhilis]] |
| − | |population_estimate_rank = | + | | sovereignty_type = [[History of Kazakhstan|Formation]] |
| − | | | + | | established_event1 = [[Kazakh Khanate]] |
| − | + | | established_date1 = 1465 | |
| − | + | | established_event2 = [[Alash Autonomy]] | |
| − | | | + | | established_date2 = 13 December 1917 |
| − | |population_density_rank | + | | established_event3 = [[Kirghiz Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic (1920–25)|Kirghiz ASSR]] |
| − | + | | established_date3 = 26 August 1920 | |
| − | |GDP_PPP | + | | established_event4 = [[Kazakh Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic|Kazak ASSR]] |
| − | |GDP_PPP_rank | + | | established_date4 = {{nowrap|19 June 1925}} |
| − | |GDP_PPP_per_capita | + | | established_event5 = [[Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic|Kazakh SSR]] |
| − | |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank | + | | established_date5 = 5 December 1936 |
| − | | | + | | established_event6 = Declared Sovereignty |
| − | | | + | | established_date6 = 25 October 1990 |
| − | | | + | | established_event7 = Reconstituted as the Republic of Kazakhstan |
| − | | | + | | established_date7 = 10 December 1991 |
| − | + | | established_event8 = Declared Independence from the [[Soviet Union|USSR]] | |
| − | | | + | | established_date8 = 16 December 1991 |
| − | | | + | | established_event9 = [[Alma-Ata Protocol|CIS Accession]] |
| − | + | | established_date9 = 21 December 1991 | |
| − | | | + | | established_event10 = [[Dissolution of the Soviet Union|Recognized]] |
| − | | | + | | established_date10 = {{nowrap|26 December 1991}} |
| − | | | + | | established_event11 = [[United Nations Security Council Resolution 732|Admitted to the]] [[United Nations]] |
| − | + | | established_date11 = 2 March 1992 | |
| − | |HDI_year | + | | established_event12 = {{nowrap|[[Constitution of Kazakhstan|Current constitution]]}} |
| − | | | + | | established_date12 = 30 August 1995 |
| − | |HDI_rank | + | | area_km2 = 2,724,900 |
| − | + | | area_rank = 9th | |
| − | |currency | + | | area_sq_mi = 1,052,085 <!--Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]]—> |
| − | |currency_code | + | | percent_water = 1.7 |
| − | | | + | | population_estimate = 19,245,793<ref name=CIA/> |
| − | | | + | | population_estimate_year = 2021 |
| − | |utc_offset | + | | population_estimate_rank = 64th |
| − | |time_zone_DST | + | | population_density_km2 = 6.49 |
| − | | | + | | population_density_sq_mi = 16.82 <!--Do not remove per [[WP:MOSNUM]]—> |
| − | |cctld | + | | population_density_rank = 227th |
| − | | | + | | GDP_PPP = {{increase}} $534.271 billion<ref name=IMF>[https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2019/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=67&pr.y=1&sy=2017&ey=2021&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=916&s=NGDPD%2CPPPGDP%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPPC&grp=0&a= World Economic Outlook Database, April 2019] ''International Monetary Fund''. Retrieved May 6, 2020.</ref> |
| − | | | + | | GDP_PPP_year = 2019 |
| + | | GDP_PPP_rank = 41st | ||
| + | | GDP_PPP_per_capita = {{increase}} $28,514<ref name=IMF /> | ||
| + | | GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 53rd | ||
| + | | GDP_nominal = {{decrease}} $164.207 billion<ref name=IMF /> | ||
| + | | GDP_nominal_year = 2019 | ||
| + | | GDP_nominal_rank = 54th | ||
| + | | GDP_nominal_per_capita = {{decrease}} $8,763<ref name=IMF /> | ||
| + | | GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 71st | ||
| + | | Gini = 27.5<ref name=WB1>[https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SI.POV.GINI?locations=KZ GINI index (World Bank estimate)] ''World Bank''. Retrieved May 6, 2020.</ref> <!--number only—> | ||
| + | | Gini_year = 2017 | ||
| + | | Gini_change = increase <!--increase/decrease/steady—> | ||
| + | | HDI = 0.800<ref name="HDI">[http://hdr.undp.org/sites/default/files/2018_human_development_statistical_update.pdf 2018 Human Development Report, 2018] ''United Nations Development Programme''. Retrieved January 19, 2022.</ref> <!--number only—> | ||
| + | | HDI_year = 2017<!-- Please use the year to which the data refers, not the publication year—> | ||
| + | | HDI_change = increase<!--increase/decrease/steady—> | ||
| + | | HDI_rank = 58th | ||
| + | | currency = [[Kazakhstani tenge|Tenge]] (₸) | ||
| + | | currency_code = KZT | ||
| + | | time_zone = [[Time in Kazakhstan|West{{\}}East]] | ||
| + | | utc_offset = [[UTC+05:00|+5]]{{\}}[[UTC+06:00|+6]] | ||
| + | | utc_offset_DST = | ||
| + | | time_zone_DST = | ||
| + | | drives_on = right | ||
| + | | calling_code = +7-6xx, +7-7xx | ||
| + | | cctld = [[.kz]], [[.қаз]] | ||
| + | | area_magnitude = 1 E12 | ||
| + | | country_code = KAZ | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Kazakhstan''' | + | '''Kazakhstan''', officially the '''Republic of Kazakhstan''', is a country that is bigger than Western Europe, and stretches over a vast expanse of northern and central [[Eurasia]] to the west of the [[Ural River]]. |
| − | + | Historians believe the vast steppes of Kazakhstan were where humans first domesticated the [[horse]]. Indeed, its name is derived from an ancient Turkic word meaning "independent, a free spirit," reflecting the Kazakh people’s nomadic horseback culture. | |
| − | + | Human activity has badly damaged the environment. The gravest threat comes from radiation, a result of the [[Soviet Union]] testing almost 500 nuclear weapons, above ground and often without notifying residents. Agricultural practices have shrunk the [[Caspian Sea]], caused extensive wind erosion, and rendered farmland sterile. Aging factories pump contaminated waste into the water supply. | |
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | Untapped oil wealth and their abundance of [[natural resource]]s offers a huge potential benefit for the nation. However, the burden of their past environmental abuses must be dealt with. | ||
| − | Kazakhstan is the [[ | + | ==Geography== |
| + | [[Image:Kazakhstan-CIA WFB Map.png|400px|thumb|left|Map of Kazakhstan]] | ||
| + | The word “Kazakh” is derived from an ancient Turkic word meaning "independent, a free spirit." It reflects the Kazakh people’s [[nomad|nomadic]] horseback culture and is related to the term "cossack." The old Persian word "stan" means "land" or "place of." | ||
| + | |||
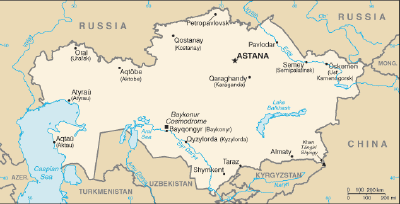
| + | Kazakhstan has borders with [[Russia]], the [[People's Republic of China]], and the [[Central Asia]]n countries [[Kyrgyzstan]], [[Uzbekistan]] and [[Turkmenistan]], and has a coastline on the [[Caspian Sea]]. With an area of 1.05 million square miles (2.7 million square kilometres), Kazakhstan is the ninth largest country in the world by area, and is the largest landlocked country in the world. It is equivalent to the size of [[Western Europe]]. | ||
| + | [[Image:Berg Belucha.jpg|400px|thumb|right|Top of the Belukha, Altay Mountains.]] | ||
| + | [[Image:AltynEmeil.jpg|thumb|400px|right|The steppes of Eastern Kazakhstan in Altyn Emeil National Park, where [[Genghis Khan]] reportedly once rode, appear to stretch out forever.]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Syrdrya River.jpg|400px|thumb|right|Syrdarya river in Kyzylorda province.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The terrain extends west to east from the [[Caspian Sea]] to the [[Altay Mountains]] and north to south from the [[Western Siberia]] plains to the [[oases]] and [[desert]]s of [[Central Asia]]. The Kazakh Steppe, with an area of around 310,600 square miles (804,500 square kilometers) occupies one-third of the country, and is the world's largest dry [[steppe]] characterized by large [[grassland]] and sandy regions. There is considerable topographical variation within Kazakhstan. The highest elevation, [[Khan Tengri Mountain]], on the [[Kyrgyzstan|Kyrgyz]] border in the [[Tian Shan]] range, is 23,000 feet (7010 meters). The lowest point, at [[Karagiye]], in the [[Caspian Depression]] in the west, is 430 feet (132 meters) below sea level. Only 12.4 percent of Kazakhstan is mountainous, mostly in the Altay and Tian Shan ranges of the east and northeast, although the [[Ural Mountains]] extend south from Russia. Many Altay and Tian Shan peaks are [[snow]] covered year-round, and their run-off is the source for Kazakhstan's rivers and streams. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Important rivers and lakes include: the [[Aral Sea]], Ili River, Irtysh River, Ishim River, Ural River, Lake Balkhash, and Lake Zaysan. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Astana]], formerly named Akmola, and [[Tselinograd]], is the third largest city and has been the capital of Kazakhstan since 1997. Other cities include [[Almaty]] (the former capital), Karaganda, Shymkent (Chimkent), Semey (Semipalatinsk), and [[Hazrat-e Turkestan|Turkestan]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Climate === | ||
| + | Because Kazakhstan is so far from the oceans, the climate is continental and dry. [[Precipitation]] in the eastern mountains averages as much as 24 inches (600 millimeters) per year, mostly as snow, but most of the republic receives only four to eight inches (100 to 200 millimeters) yearly. Kazakhstan is sunny. Average winter [[temperature]]s are 26.6°F (-3°C) in the north and 64.4°F (18°C) in the south. Summer temperatures average 66°F (19°C) in the north and 86°F (30°C) in the south. Within locations differences are extreme, and temperature can change suddenly. The winter air temperature can fall to -58°F (-50°C), and in summer the air temperature can reach as high as 122°F (50°C). | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Natural life and resources === | ||
| + | Fauna that can be found in the [[steppes]] includes the Saiga [[Antelope]], Siberian [[Roe Deer]], [[Wolf|wolves]], [[fox]]es, [[badger]]s, [[snow leopard]]s, [[eagle]]s, and [[falcon]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kazakhstan has an abundant supply of accessible mineral and fossil fuel resources. Development of [[petroleum]], [[natural gas]], and [[mineral]] extraction has attracted most of the over $40-billion in [[foreign investment]] in Kazakhstan since 1993 and accounts for some 57 percent of the nation's industrial output. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kazakhstan has the second largest [[uranium]], [[chromium]], [[lead]], and [[zinc]] reserves, the third largest [[manganese]] reserves, the fifth largest [[copper]] reserves, and ranks in the top ten for [[coal]], [[potassium]], [[iron]], and [[gold]]. [[Diamond]]s are exported. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Oil explorations have shown that the deposits on the Caspian shore are only a fraction of a larger deposit. Possibly, 3.5 billion tons of oil and 2.5 trillion cubic meters of [[natural gas]] could be found there. The total estimated oil deposits is 6.1 billion tons. There are only three refineries within the country, situated in Atirau, Pavlodar, and Shymkent, and none are capable of processing crude, which is exported to [[Russia]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Environmental concerns === | ||
| + | [[Image:AralskHarbor.jpg|thumb|400px|right|A former harbor in the city of Aral, Kazakhstan]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Natural hazards include [[earthquake]]s in the south, and [[mud slides]] around [[Almaty]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Human activity has badly damaged the environment. Most [[water]] is polluted by industrial effluents, [[pesticide]] and [[fertilizer]] residue, and, in some places, [[radioactivity]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The most visible damage has been to the [[Aral Sea]], which in the 1970s was larger than most of the [[Great Lakes]] of [[North America]]. Sharply increased irrigation caused the sea to shrink. By 1993, the Aral Sea had lost an estimated 60 percent of its volume, and was breaking into three unconnected segments. Increasing salinity and reduced habitat killed the [[fish]], destroying its fishing industry, and the receding shoreline has left the former port of Aral'sk more than 38 miles (60km) from the water's edge. The depletion of this large body of water has increased [[temperature]] variations in the region, which has harmed [[agriculture]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A much greater harm to agriculture has come from the [[salt]]- and [[pesticide]]-laden soil that the wind is known to carry to the [[Himalaya Mountains]] and the [[Pacific Ocean]]. Deposits of this saline soil on fields sterilizes them. [[Infant mortality]] in the region approaches 10 percent compared with the 1991 national rate of 2.7 percent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Meanwhile, the water level of the [[Caspian Sea]] has been rising steadily since 1978 for reasons that scientists have not been able to explain fully. At the northern end of the sea, more than 10,000 square kilometers of land in Atyrau Province have been flooded. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Wind [[erosion]] has also had an impact in the northern and central parts of the republic because of the introduction of wide-scale dryland wheat farming in the 1950s and 1960s. By the mid-1990s, an estimated 60 percent of the republic's pastureland was in various stages of [[desertification]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Industrial [[pollution]] is a greater concern in Kazakstan's manufacturing cities, where aging factories pump huge quantities of unfiltered pollutants into the air and groundwater. The former capital and largest city, [[Almaty]], is particularly threatened, in part because of the post–independence boom in private [[automobile]] ownership. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The gravest environmental threat to Kazakhstan comes from [[radiation]], especially in the Semey (Semipalatinsk) region of the northeast, where the [[Soviet Union]] tested almost 500 [[nuclear weapons]], 116 of them above ground. Often, such tests were conducted without evacuating or even alerting the local population. Although nuclear testing was halted in 1990, [[radiation poisoning]], birth defects, severe [[anemia]], and [[leukemia]] are very common in the area. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The government has established a Ministry of Ecology and Bioresources, with a separate administration for radio–ecology, but the ministry's programs are under-funded and given low priority. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| − | {{ | + | [[Image:Andronovo culture.png|thumb|350px|Map of the approximate maximal extent of the Andronovo culture. The formative Sintashta-Petrovka culture is shown in darker red. The location of the earliest spoke-wheeled chariot finds is indicated in purple. Adjacent and overlapping cultures (Afanasevo culture, Srubna culture, BMAC) are shown in green.]] |
| − | Kazakhstan has been inhabited since the [[Stone Age]], generally by | + | [[Image:Gokturkut.png|right|thumb|400px|Gokturk [[khagan]]ates at their height, c. 600 C.E. : |
| + | {{Legend|purple|Western Gokturk: Lighter area is direct rule, darker areas show sphere of influence.}} | ||
| + | {{Legend|blue|Eastern Gokturk: Lighter area is direct rule, darker areas show sphere of influence.}} | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | Kazakhstan has been inhabited since the [[Stone Age]], generally by [[nomad]]s practicing [[pastoralism]], for which the region's climate and terrain are best suited. Prehistoric [[Bronze Age]] cultures that extended onto Kazakh territory include the [[Srubna]] culture (sixteenth-ninth centuries B.C.E.), the [[Afanasevo culture]] (3500—2500 B.C.E.) and the [[Andronovo culture]] (ca. 2300–1000 B.C.E.). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Historians believe the vast steppes of Kazakhstan were where humans first [[domestication of animals|domesticated]] the [[horse]]. Following the [[Mongolian invasion]] in the early thirteenth century C.E., administrative districts were established under the [[Mongol Empire]], which eventually became the territories of the [[Kazakh Khanate]]. The major medieval cities of [[Taraz]] and Hazrat-e [[Turkestan]] were founded along the northern route of the [[Silk Road]] during this period. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Goturks=== | ||
| + | The earliest documented state in the region was the [[Turkic Kaganate]], or [[Gokturk]] state, established by the Ashina clan, in the sixth century C.E. The Qarluqs, a confederation of Turkic tribes, established a state in what is now eastern Kazakhstan in 766. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the eighth and ninth centuries, [[Arab]]s conquered portions of southern Kazakhstan and introduced [[Islam]]. The [[Oghuz Turks]] controlled western Kazakhstan from the ninth through the eleventh centuries; the [[Kimak]] and [[Kipchak]] peoples, also of Turkic origin, controlled the east at roughly the same time. The large central [[desert]] of Kazakhstan is still called [[Dashti-Kipchak]], or the [[Kipchak Steppe]]. | ||
| − | + | In the late ninth century, invaders destroyed the Qarluq state and established the large Qarakhanid state, which occupied [[Transoxiana]], the area north and east of the Oxus River (the present-day Amu Darya), extending into what is now [[China]]. Beginning in the early eleventh century, the Qarakhanids fought among themselves and with the [[Seljuk Turks]] to the south. | |
| − | In the | + | In the course of these conflicts, parts of present-day Kazakhstan shifted back and forth between the combatants. The Qarakhanids, who accepted Islam and the authority of the Arab [[Abbasid]] [[caliph]]s of [[Baghdad]], were conquered in the 1130s by the [[Karakitai]], a Turkic confederation from northern China. In the mid-twelfth century, an independent state of [[Khorazm]] along the [[Oxus River]] broke away from the weakening Karakitai, but the bulk of the Karakitai state lasted until the Mongol invasion of [[Genghis Khan]] in 1219-1221. |
| − | + | ===Mongol invasion=== | |
| + | After the Mongol capture of the Karakitai state, Kazakhstan fell under the control of a succession of rulers of the Mongolian [[Golden Horde]], the western branch of the [[Mongol Empire]]. The horde, or ''zhuz,'' is the precursor of the present-day clan. By the early fifteenth century, the ruling structure had split into several large groups known as [[khanate]]s, including the [[Nogai Horde]] and the [[Uzbek Khanate]]. | ||
| − | + | The Kazakhs emerged from a mixture of tribes living in the region in about the fifteenth century and by the middle of the sixteenth century had developed a common language, culture, and economy. In the early 1600s, the Kazakh Khanate separated into the Great, Middle and Little (or Small) Hordes (jüz)—confederations based on extended family networks. Political disunion, competition among the hordes, and a lack of an internal market weakened the Kazakh Khanate. The beginning of the eighteenth century marked the zenith of the Kazakh Khanate. | |
| − | + | ===Russian rule=== | |
| + | In the nineteenth century, the [[Russian Empire]] spread into [[Central Asia]]. The "Great Game" period of rivalry and strategic conflict between the [[British Empire]] and the Tsarist Russian Empire for supremacy in Central Asia, is regarded as running from approximately 1813 to the [[Anglo-Russian Convention]] of 1907. Following the [[October Revolution|Bolshevik Revolution]] of 1917 a second less intensive phase followed. The [[tsar]]s effectively ruled over most of the territory belonging to what is now the Republic of Kazakhstan. | ||
| − | The | + | The Russian Empire introduced a system of administration and built military garrisons and barracks in its effort to establish a presence in Central Asia. The use of the [[Russian language]] was required in all schools and government organizations, arousing resentment among the Kazakh people. By the 1860s, most Kazakhs resisted Russia's annexation because it disrupted the traditional nomadic lifestyle and livestock-based economy. A Kazakh national movement began in the late 1800s, seeking to preserve the Kazakh language and identity. From the 1890s, increasing numbers of Slavic settlers began colonizing the area, especially once the Trans-Aral Railway from Orenburg to [[Tashkent]] was completed in 1906. The competition for land and water during the final years of [[tsarist Russia]] resulted in an uprising, the Central Asian Revolt, in 1916. |
| − | + | ===Soviet rule=== | |
| − | + | A brief period of autonomy followed the collapse of the [[Russian Empire]], but the Kazakhs eventually succumbed to Soviet rule. In 1920, the area became an autonomous republic within Russia and, in 1936, a [[Soviet republic]]. | |
| − | + | Repression of the traditional elite, plus forced [[collectivization]] in late 1920s–1930s, brought mass hunger and unrest. But the [[Communism|communist]] apparatus gradually integrated Kazakhstan into the Soviet system. Thousands exiled from other parts of the [[Soviet Union]] during the 1930s arrived, as did hundreds of thousands evacuated from the [[Second World War]] battlefields. Some were deported to [[Siberia]] or Kazakhstan because of their ethnicity or beliefs, and were interned in some of the biggest Soviet labor camps. The Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic (SSR) contributed five divisions to the Soviet Union's World War II effort. In 1947, the Semipalatinsk Test Site, the USSR's main nuclear weapon test site was founded near the city of Semey. | |
| − | + | [[World War II]] brought increased mining and industrialization, although by the time Soviet leader [[Joseph Stalin]] died, Kazakhstan still had an [[Agriculture|agricultural]] economy. In 1953, Soviet leader [[Nikita Khrushchev]] initiated the ambitious "Virgin Lands" program to turn [[pasture]] into a [[grain]]-producing region for the Soviet Union. This policy, with modernizations under Soviet leader [[Leonid Brezhnev]], hastened the development of the agricultural sector, which remained the source of livelihood for a large percentage of Kazakhstan's population. | |
| + | [[Image:Nursultan Nazarbayev 1997.jpg|300px|thumb|left|Nursultan Nazarbayev]] | ||
| + | Demands for political and economic reforms within the Soviet Union came to a head in the 1980s. In December 1986, young ethnic Kazakhs in Almaty protested the replacement of the First Secretary of the Communist Party of Kazakhstan Dinmukhamed Konayev with Gennady Kolbin, an ethnic Chuvas from the Russian Federation. Dozens of demonstrators were jailed or killed. Discontent continued, resulting in Soviet president [[Mikhail Gorbachev]]'s policy of glasnost (openness). Kazakhstan declared itself a republic within the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics in October 1990. Following the August 1991 abortive coup attempt in [[Moscow]] and the subsequent dissolution of the Soviet Union, Kazakhstan declared independence on December 16, 1991. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Independence=== | ||
| + | The years following [[independence]] have been marked by significant reforms to the Soviet command-economy and political monopoly on power. [[Nursultan Nazarbayev]], who initially came to power in 1989 as the head of the Communist Party of Kazakhstan, was easily elected president in November, 1991. Kazakhstan has since made progress toward developing a market economy, and has enjoyed significant economic growth since 2000, partly due to its large oil, gas, and mineral reserves. | ||
==Politics== | ==Politics== | ||
| − | + | The politics of Kazakhstan take place in the framework of a presidential republic, whereby the President of Kazakhstan is head of state and nominates the head of government. The nature of government is authoritarian presidential rule, with little power outside the executive branch. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | The president is elected by popular vote for a seven-year term, and constitutionally had a two-term limit. The president appoints a council of ministers (cabinet). The president also is the commander in chief of the armed forces and may veto legislation that has been passed by the Parliament. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | The president appoints the prime minister and first deputy prime minister. The prime minister chairs the Cabinet of Ministers and serves as Kazakhstan's head of government. There are three deputy prime ministers and 16 ministers in the Cabinet. The president appoints a Council of Ministers. | |
| − | + | The bicameral parliament comprises a senate and a Mazhilis. The senate has 39 seats. The president appoints seven senators. Other members are elected from each of the 14 oblasts, the capital of Astana, and the city of Almaty, to serve six-year terms. Former presidents are ex-officio senators for life. The Mazhilis has 77 seats. Ten out of the 77 Mazhilis members are elected from the winning party's lists. Other members are popularly elected to serve five-year terms. Most legislation considered by the Mazhilis is proposed by the government. All aged 18 years of age and over may vote. | |
| − | |||
| − | In | + | The judiciary comprises a Supreme Court of 44 members and a Constitutional Council of seven members. Local and national courts resemble those in the Western world, but lack of checks and controls. A variety of different police units, a remnant of the Soviet era, leads to problems of jurisdiction. In urban areas, robberies and [[theft]] are common. [[Murder]], [[suicide]], and other [[violent crime]]s are increasing. The drug trade from [[Afghanistan]] has given rise to [[organized crime]]. [[Embezzlement]], [[tax fraud]], and abuse of power and privilege are tacitly accepted. |
| − | + | ===Administrative divisions=== | |
| + | Kazakhstan is divided into 14 provinces ''(oblys)'' and three municipal districts ''(qala).'' Each is headed by an ''akim'' (provincial governor) appointed by the president. Municipal akims are appointed by ''oblast akims.'' The Government of Kazakhstan transferred its capital from [[Almaty]] to [[Astana]] on December 10, 1997. | ||
| − | + | In 1995, Russia leased for 20 years an area of 2300 square miles (6000 square kilometers) enclosing the [[Baikonur Cosmodrome]] [[space launch]] center and the city of Bayqongyr (formerly Leninsk). The lease was later extended through 2050. On June 18, 2006, Kazakhstan became a space-faring nation when it launched its first commercial [[satellite]], KazSat 1, from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on a Russian-built booster [[rocket]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ===Foreign relations=== |
| − | + | Kazakhstan has stable relationships with all of its neighbors and is a member of the [[United Nations]], Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe, Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council and Organization of the Islamic Conference(OIC). It participates in the [[North Atlantic Treaty Organization]]'s (NATO) [[Partnership for Peace]] program. Kazakhstan is a member of the [[Commonwealth of Independent States]], the Economic Cooperation Organization and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization. The nations of Kazakhstan, [[Belarus]], [[Kyrgyzstan]], and [[Tajikistan]] established the Eurasian Economic Community in 2000 to harmonize [[tariff]]s and create a [[free trade]] zone. | |
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
| − | + | Since independence, Kazakhstan has sought equally good relations with [[Russia]], China, the [[United States]], and the West. Companies from the U.S., Russia, China, and [[Europe]] are present at all fields. | |
| − | + | ===Military=== | |
| + | [[Image:Kazakhstan paratrooper.jpg|thumb|left|400px|Kazakhstani soldier with AK-74.]] | ||
| + | Kazakhstan's National Security Committee was established in 1992. It includes the Service of Internal Security, Military Counterintelligence, border guard, several commando units, and Foreign Intelligence (Barlau). | ||
| − | + | Kazakhstan acquired from the Soviet Union all the units of the 40th (the former 32nd) Army and part of the 17th Army Corps, including six land force divisions, storage bases, the 14th and 35th air-landing brigades, two rocket brigades, two artillery regiments and a large amount of equipment which had been withdrawn from over the Urals after the signing of the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The Kazakh Air Defence Force's fighter aircraft element consists of the 356th Fighter Aviation Regiment, flying MiG-31s from Semipalitinsk Airport. The Republican Guard had 2500 soldiers in 1994, and is not part of the army. | |
| − | The | ||
| − | + | Kazakhstan sent 29 military engineers to Iraq as part of the [[Coalition of the Willing]] to assist the U.S. occupation in Iraq. | |
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Almatyvendor.JPG|right|thumb|300px|A meat vendor at the Green Market in [[Almaty]], Kazakhastan.]] |
| − | |||
| − | + | Kazakhstan, the largest of the former Soviet republics in territory, excluding [[Russia]], possesses enormous [[fossil]] fuel reserves and plentiful supplies of other [[mineral]]s and [[metal]]s. It also has a large [[Agriculture|agricultural]] sector featuring [[livestock]] and [[grain]]. Kazakhstan's industrial sector rests on the extraction and processing of these [[natural resource]]s and also on a growing machine-building sector specializing in construction equipment, tractors, agricultural machinery, and some defense items. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | The breakup of the [[USSR]] in December 1991 and the collapse in demand for Kazakhstan's traditional heavy industry products resulted in a short-term contraction of the economy, with the steepest annual decline occurring in 1994. In 1995-1997, the pace of the government program of economic reform and [[privatization]] quickened, resulting in a substantial shifting of assets into the private sector. | |
| − | + | Kazakhstan enjoyed double-digit growth in 2000-2001 – eight percent or more per year in 2002-2006 - due largely to its booming energy sector, but also to economic reform, good harvests, and foreign investment. The opening of the Caspian Consortium pipeline in 2001, from western Kazakhstan's Tengiz oilfield to the [[Black Sea]], substantially raised export capacity. Kazakhstan in 2006 completed the Atasu-Alashankou portion of an [[oil pipeline]] to [[China]] that is planned to extend from the country's Caspian coast eastward to the Chinese border in future construction. | |
| − | The | + | The country has embarked upon an industrial policy designed to diversify the economy away from over-dependence on the oil sector by developing light industry. The policy aims to reduce the influence of [[foreign investment]] and foreign personnel. The government has engaged in several disputes with foreign oil companies over the terms of production agreements; tensions continue. Upward pressure on the local currency continued in 2006 due to massive oil-related foreign-exchange inflows. Aided by strong growth and low [[inflation]], Kazakhstan aspires to become a regional [[financial center]] and has created a [[bank]]ing system comparable to those in Central Europe. |
| − | + | In 2000, Kazakhstan adopted a new [[tax]] code in an effort to consolidate gains. In November 2003 the new tax code was adopted, reducing [[value added tax]] from 16 percent to 15 percent, the social tax from 21 percent to 20 percent, and the personal income tax from 30 percent to 20 percent. | |
| − | [[ | ||
| − | + | ===Oil and gas=== | |
| + | [[Image:Kazah tenge.jpg|thumb|right|400px|The Tenge, Kazakhstan's currency.]] | ||
| + | Energy is the leading economic sector. Production of [[crude oil]] and [[natural gas]] condensate in Kazakhstan amounted to 51.2 million tons in 2003. Kazakhstan's 2003 oil exports were valued at more than $7-billion, representing 65 percent of overall exports and 24 percent of the GDP. Major oil and gas fields and their recoverable [[oil reserves]] are Tengiz with seven billion barrels; Karachaganak with eight billion barrels (and 1350km³ of natural gas); and Kashagan with seven to nine billion barrels. | ||
===Agriculture=== | ===Agriculture=== | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[Agriculture]] is a significant part of the Kazakh economy. Grain, potatoes, grapes, vegetables, melons, and livestock are the most important agricultural commodities. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Agricultural land occupies more than 327,000 square miles (846,000 square kilometers). Chief livestock products are [[dairy]] products, [[leather]], [[meat]], and [[wool]]. The country's major crops include [[wheat]], [[barley]], [[cotton]], and [[rice]]. Wheat exports, a major source of hard currency, rank among the leading commodities in Kazakhstan's export trade. | |
| + | |||
| + | Kazakh agriculture still has many environmental problems from mismanagement during its years in the [[Soviet Union]]. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Demographics== |
| − | Kazakhstan has | + | Kazakhstan has a diverse demography is due to the country's central location and its use by [[Russia]] as a place to send colonists, dissidents, and minority groups. From the 1930s until the 1950s, many minorities were interned in [[labor camp]]s. This makes Kazakhstan one of the few places on earth where normally-disparate Germanic, Indo-Iranian, Chinese, Chechen, and Turkic groups live together in a rural setting and not as a result of modern immigration. |
| − | + | ===Population=== | |
| + | [[Image:KazakhMountains.jpg|300px|thumb|right|Mountains located outside of Shymkent, Kazakhstan]] | ||
| + | The large migratory population of Kazakhstan, emigration, and the low population density - only about 5.5 persons per square kilometer in an area the size of Western Europe, make census figures difficult to measure. | ||
| − | + | After the fall of the [[Soviet Union]], the German population of Kazakhstan emigrated en masse as [[Germany]] was willing to repatriate them, as did much of the smaller Greek minority (to [[Greece]]), and Russians (to [[Russia]]). Other groups left because of the economic situation. This, plus a higher Kazakh birthrate, and ethnic Kazakh immigration from the [[People's Republic of China]], gave the Kazakhs a majority along with [[Mongolia]], and Russia. In the early twenty-first century, Kazakhstan became one of the leading nations in international [[adoption]]s. | |
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Ethnicity=== | |
| + | Ethnic Kazakhs make up the majority of the population (close to 70 percent), and ethnic [[Russians]] are the next largest group at close to 20 percent. An amazingly rich array of other groups include [[Ukrainians]], [[Uzbeks]], [[Germans]], [[Chechens]], [[Koreans]], and [[Uyghurs]]. There is also a small but active [[Jewish]] community. | ||
| − | Kazakhstan | + | The Russian term “Kazakhstani” was coined to describe all inhabitants of Kazakhstan, including non-Kazakhs. The word "Kazakh" is generally used to refer to people of actual Kazakh descent (including those living in China, Afghanistan, and other Central Asian countries). |
| − | + | ===Religion=== | |
| + | [[Arab]]s brought [[Islam]] in the ninth century, and 1000 years later Russian settlers introduced [[Russian Orthodoxy]]. During the 70 years of Soviet rule, religious participation was banned, and many churches and [[mosque]]s were destroyed. In 2007, the main religious groups were Muslim (mainly [[Sunni]]) 47 percent, Russian Orthodox 44 percent, [[Protestant]] 2 percent, and other 7 percent. | ||
| − | + | Although Islam was introduced in the ninth century, the [[religion]] was not fully assimilated until much later. As a result, it coexisted with earlier [[Animism|animist]] elements of [[Tengriism]], which is a traditional Kazak belief that held that separate [[spirit]]s inhabited and animated the earth, sky, water, and fire, as well as domestic animals. Honored guests in rural settings are still treated to a feast of freshly killed [[lamb]], and are sometimes asked to bless the lamb and to ask its spirit for permission to partake of its flesh. | |
| − | + | While formal religious observance is limited, many Kazakhs say a short [[prayer]] when they pass by where someone they know is buried, and say prayers after meals. [[Mosque]]s are staffed by a mullah, who conducts services as well as [[funeral]]s, [[wedding]]s, and blessings, as do priests in Russian Orthodox churches. | |
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===Language=== |
| − | + | Kazakhstan is a bilingual country. The Kazakh language, a Turkic language, is spoken by over half of the population, and has the status of the state language, while [[Russian language|Russian]] is used routinely in business. Language is a contentious issue. While Russian has been widely used as the inter-ethnic means of communications, Kazakhstan has not been able to use its distinct national language to unite ethnic communities. | |
| − | + | [[Image:Polovtsy.jpg|thumb|300px|Kipchak steppe art, as exhibited in Dnepropetrovsk.]] | |
| − | + | ===Education=== | |
| + | Education is universal and mandatory through to the secondary level. There are three main educational phases: Primary education (forms 1 to 4), basic general education (forms 5–9) and senior level education (forms 10–11 or 12) divided into continued general education and professional education. Primary education is preceded by one year of pre-school education. These three levels of education can be followed in one institution or in different ones (e.g. [[primary school]], then [[secondary school]]). | ||
| − | + | New entrants are assigned to classes of about 25 pupils in the first grade, and that class stays together until the 11th grade, with the same teacher until the fourth grade, and a different teacher through to the eleventh grade. The teachers are like second mothers or fathers, [[discipline]] is important, homework is extensive and grades difficult. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Several secondary schools, specialized schools, magnet schools, gymnasium schools, lyceums, linguistic and technical gymnasiums, have been founded. Secondary professional education is offered in special professional or technical schools, lyceums or colleges and [[vocational school]]s. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | At tertiary level, there are universities, academies, and institutes, conservatories, higher schools and higher colleges. At this level, there are three main levels: basic higher education, that provides the fundamentals of the chosen field of study and leads to a bachelor degree; specialized higher education, after which students are awarded the specialist's diploma; and scientific-pedagogical higher education, which leads to the master's degree. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Postgraduate education leads to the Kandidat Nauk (Candidate of Sciences) and the Doctor of Sciences. With the adoption of the Laws on Education and on Higher Education, a private sector has been established and several private institutions have been licensed. The adult literacy rate is 99.5 percent. | |
| − | + | In 2000, the Government of Kazakhstan joined the governments of the [[Kyrgyzstan]] and [[Tajikistan]], and [[Aga Khan IV]] to establish the world’s first internationally chartered institution of higher education, the University of Central Asia, which was intended to have three campuses of equal size and stature in each of the founding countries. | |
| − | == | + | ===Ownership=== |
| − | + | Houses built and subsidized by the former Soviet government were cheap and available to all, and most people retained their property from the Soviet years. Occupiers own most apartments, although investing in rental property is more widespread. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Class=== | |
| + | The new rich, who often flaunt their wealth, are termed "New Kazakh" or "New Russian," and contrast with the vast number of unemployed or underpaid. [[Poverty]] and accusations of unfair treatment have raised tensions between Kazakhs and non-Kazakhs. While the rich drive expensive cars, wear fashionable clothes, and throw lavish parties, the poor drive old Soviet cars or take a bus, wear cheap Chinese- or Turkish-import clothes, and save for months to pay for a wedding. | ||
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
| − | [[Image:Catchthegirl.JPG|right|thumb| | + | [[Image:Catchthegirl.JPG|right|thumb|400px|Riders in traditional dress demonstrate Kazakhstan's equestrian culture by playing a kissing game, ''Kuuz Kuu'' ("Catch the Girl"), one of a number of traditional games played on horseback.]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Because animal husbandry was central to the Kazaks' traditional lifestyle, most of their nomadic practices and customs relate in some way to livestock. Traditional curses and blessings invoked disease or fecundity among animals, and good manners required that a person ask first about the health of a man's livestock when greeting him and only afterward inquire about the human aspects of his life. | + | Before the Russian conquest, the Kazaks had a well-articulated culture based on their [[nomad]]ic pastoral economy. Because [[animal husbandry]] was central to the Kazaks' traditional lifestyle, most of their nomadic practices and customs relate in some way to [[livestock]]. Traditional curses and blessings invoked disease or fecundity among animals, and good manners required that a person ask first about the health of a man's livestock when greeting him and only afterward inquire about the human aspects of his life. [[Lamb]] has a symbolic value in the culture. |
| − | + | Kazakhs can be [[Superstition|superstitious]]. Whistling inside a house is unacceptable since it is believed that it will make the owner of the house poor. Smoking by women is not accepted. Kazakhs often don't smile at people in public except to those they know, and rarely form lines when boarding crowded buses. Women and girls often hold hands as they walk; boys hook arms or walk with their arms around each other. Kissing cheeks and embracing is perfectly acceptable between good friends. Kazakh men shake hands with an acquaintance the first time they see each other in a day. All remove their shoes when inside a house—guests remove their shoes at the door and often put on a pair of slippers. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ===Architecture=== |
| − | + | [[Image:Prokudin-Gorskii-42.jpg|thumb|400px|right|A woman at the entrance to a [[yurt]] in 1913. Picture by Sergei Mikhailovich Prokudin-Gorskii.]] | |
| − | [[Image: | + | The traditional Kazak dwelling is the [[yurt]], a tent consisting of a flexible framework of willow wood covered with varying thicknesses of felt. The open top permits smoke from the central hearth to escape. Temperature and draft can be controlled by a flap that increases or decreases the size of the opening. A properly constructed yurt can be cooled in summer and warmed in winter, and it can be disassembled or set up in less than an hour. The right side of the yurt's interior is reserved for men and the left for women. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Although yurts are used less, they remain a potent symbol. Demonstrators and hunger strikers erected yurts in front of the government building in Almaty in the spring of 1992. Yurts are frequently used as a decorative motif in restaurants and other public buildings. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Russian settlers in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries brought small A-frame houses, Russian Orthodox churches, and wooden buildings. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Buildings from the Soviet era were big and utilitarian, and often the same shape, size, and color throughout the Soviet empire. Large Soviet-designed apartment blocks were five or six stories high and had three to four apartments of one, two, or three bedrooms each per floor. Villages and collectives consisted of small two- to three-room, one-story houses, painted white and light blue (to keep away evil spirits), all built by the government. Large squares and parks were built in every town. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Oil money, and foreign investment have brought five-star high-rise hotels, casinos, Turkish fast food restaurants, American steak houses, bowling alleys and movie theaters. Private homes are bigger, with two and three stories, two-car garages and large, fenced-in yards. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ===Cuisine=== | |
| − | + | [[Image:Almaty - Kazakhstan.jpg|thumb|400px|Kazakh food preparation began to develop in the thirteenth century.]] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Daily meals are hearty, always including [[bread]] and usually [[noodle]]s or [[potato]]es and then a meat. One common dish is ''pilaf,'' a [[rice]] dish usually made with carrots, mutton, and a lot of oil. Russian ''borscht,'' usually red ([[beet]]-based) or brown (meat-based), with [[cabbage]], meat, and potatoes, and a large dollop of sour cream, is popular. Russian ''pelimnin,'' dough pockets filled with meat and onions, is often a daily meal. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | A flat, round bread called ''leipioskka'' and seasonal fruits and vegetables are served with almost every meal. Kazakhstan is known for its [[apple]]s. ''Shashlik,'' marinated meat roasted over a small flame and served on a stick, is sold at roadside cafés and corner ''shashlik'' stands. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[Tea]] is an integral part of life, and is drunk six or seven times a day. Guests are always offered tea. Muslim Kazakhs do not eat [[pork]]. Kazakhs have great respect for bread, which should never be wasted, thrown away, and should always be placed on the table right side up. Food is eaten with one's hands. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | On special occasions, ''beshbarmak,'' traditionally horse meat boiled on the bone, is served over noodles covered in a meat broth called ''souppa.'' The host gives out pieces of meat in an order of respect usually based on seniority or distance traveled. When ''beshbarmak'' is made of mutton, the head of the sheep will be boiled, intact, and served to the most honored guest. An intoxicating fermented horse's milk called ''kumis,'' believed to be therapeutic, is occasionally drunk at ceremonial occasions. [[Vodka]], which permeates the culture, is consumed in large quantities at all ceremonies. Toasts always precede a drink of vodka. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Music=== | ||
| + | Kazakh music is nomadic and rural, and is closely related to [[Uzbek]] and [[Kyrgyz]] folk forms. Traveling bards, healers and mystics called ''akyn'' are popular, and usually sing either unaccompanied or with a string instrument, especially a ''dombra,'' a mandolin-like string instrument, or ''kobyz.'' ''Akyn'' performance contests are called ''aitys''; their lyrics are often social or political, and are generally improvised, witty remarks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Traditional Kazakh music includes ensembles using instruments like the ''kobyz'' or'' dombra,'' as well as ''kyl-kobyz,'' ''sherter,'' ''sybyzgy,'' ''saszyrnay'' and ''shankobyz.'' The most common instrumental traditions are called ''kobizovaia,'' ''sibiz-govaia,'' and ''dombrovaia.'' Many songs are connected to ancient [[mythology]] and folk religious beliefs ''(kui),'' while others were composed after the rise of authored works ''(kuishi)'' by early songwriters ''(jiray)'' like Mahmud Kashgari, Kaztygana, Dospanbeta, Shalkiiza and Aktamberdi. The ''kuishi'' tradition is said to have peaked in the nineteenth century. In the twentieth century, the first star was the singer [[Mayra Shamsutdinova]], a woman. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Controlled by the [[Russian Empire]] and then the [[Soviet Union]], Kazakhstan's folk and classical traditions became connected with ethnic Russian music and Western European music. The Musical-Dramatic Training College, founded in 1932, was the first institute of higher education for music. Two years later, the Orchestra of Kazakh Folk Musical Instruments was formed | ||
| + | The Kazakhs themselves, however, did not write their own music in notation until 1931. Later, as part of the Soviet Union, Kazakh folk culture was encouraged in a sanitized manner designed to avoid political and social unrest. The result was a bland derivative of real Kazakh folk music. In 1920, A. V. Zataevich, a Russian official who created works of art music with melodies and other elements of Kazakh folk music, adapted traditional Kazakh instruments for use in Russian-style ensembles, such as by increasing the number of frets and strings. | ||
| − | + | Pop music in Kazakhstan has made a resurgence since the year 2000. Talent searches have always been an integral part of the Kazakh pop music industry, such as the project Anshi Balapan & Idol spinoff SuperStar KZ, a reality television show based on the popular British show Pop Idol. The show is a contest to determine the best young singer in Kazakhstan. | |
| − | + | ===Literature=== | |
| − | + | Kazak literary tradition is rich in oral histories. These histories were memorized and recited by the ''akyn,'' the elder responsible for remembering the [[legends]] and histories, and by ''jyrau,'' lyric [[poet]]s who traveled with the high-placed khans. Most of the legends concern the activities of a ''batir,'' or [[hero-warrior]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Among the tales that have survived are ''Koblandy-batir'' (fifteenth or sixteenth century), ''Er Sain'' (sixteenth century), and ''Er Targyn'' (sixteenth century), all of which concern the struggle against the ''Kalmyks''; ''Kozy Korpesh'' and ''Bain sulu,'' both [[epic]]s; and the love lyric ''Kyz-Zhibek.'' Usually these tales were recited in a song-like [[chant]], frequently to the accompaniment of [[drum]]s and the ''dombra.'' | |
| − | |||
| − | + | For the most part, pre-independence cultural life in Kazakstan was indistinguishable from that elsewhere in the [[Soviet Union]]. That Russified cultural establishment nevertheless produced many of the most important figures of the early stages of Kazak nationalist self-assertion, including novelist [[Anuar Alimzhanov]], who became president of the last Soviet Congress of People's Deputies, and poets [[Mukhtar Shakhanov]] and [[Olzhas Suleymenov]], who were co-presidents of the political party Popular Congress of Kazakhstan. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Suleymenov]] in 1975 became a pan-Central Asian hero by publishing a book, ''Az i Ia,'' examining the Lay of Igor's Campaign, a [[medieval]] tale vital to the Russian national culture, from the perspective of the Turkic [[Pechenegs]] whom Igor defeated. Soviet authorities subjected the book to a blistering attack. Later Suleymenov used his prestige to give authority to the Nevada-Semipalatinsk anti-nuclear movement, which helped end nuclear testing in Kazakhstan. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Sports=== | |
| − | + | Kazakhstan consistently performs well in the [[Olympic Games|Olympics]]. Dmitry Karpov and Olga Rypakova are among the most notable Kazakhstani athletics. Dmitry Karpov is a distinguished decathlete, taking bronze in both the 2004 Summer Olympics, and the 2003 and 2007 World Athletics Championships. Olga Rypakova is an athlete, specialized in triple jump (women's), taking silver in the 2011 World Championships in Athletics and Gold in the 2012 Summer Olympics. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Kazakhstan has achieved some success in international competitions in [[weightlifting]], [[ice hockey]], and [[boxing]]. Kazakh boxers are generally well known in the world. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Football (soccer)]] is popular, with the Kazakhstan Super League being the top-level competition for the sport in the country. Numerous professional cyclists competing on the European circuit come from Kazakhstan. Most notable is [[Alexander Vinokourov]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Notes == | |
| − | + | <References/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==References== | |
| − | + | * Broughton, Simon, and Mark Ellingham (ed.). ''World Music, Vol. 2: Latin & North America, Caribbean, India, Asia and Pacific.'' Rough Guides Ltd, Penguin Books, 2000. ISBN 1858286360 | |
| − | + | * Cummings, Sally N. ''Kazakhstan Power and the Elite.'' London: I.B. Tauris, 2005. ISBN 1860648541 | |
| − | + | * Demko, George J. ''The Russian Colonization of Kazakhstan, 1896-1916.'' Indiana University publications. The Hague [etc.]: Mouton, 1969. {{OCLC|63360103}} | |
| − | + | * Fergus, Michael, and Janar Jandosova. ''Kazakhstan: Coming of Age.'' London: Stacey International, 2003. ISBN 1900988615 | |
| − | + | * George, Alexandra. ''Journey into Kazakhstan: The true face of the Nazarbayev regime.'' Lanham: University Press of America, 2001. ISBN 0761819649 | |
| − | + | * Martin, Virginia. ''Law and Custom in the Steppe: The Kazakhs of the Middle Horde and Russian colonialism in the nineteenth century.'' Richmond: Curzon, 2000. ISBN 0700714057 | |
| − | + | * Nazarbaev, Nursultan. ''Epicenter of Peace.'' Hollis, NH: Puritan Press, 2001. ISBN 1884186130 | |
| − | + | * Nazpary, Joma. ''Post-soviet Chaos: Violence and dispossession in Kazakhstan.'' London: Pluto Press, 2002. ISBN 0745315038 | |
| + | * Olcott, Martha Brill. ''The Kazakhs: Studies of nationalities in the USSR.'' Stanford, CA: Hoover Institution Press, Stanford University, 1987. ISBN 0817983821 | ||
| + | * Olcott, Martha Brill. ''Kazakhstan: Unfulfilled promise.'' Washington, DC: Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, 2002. ISBN 0870031899 | ||
| + | * Rall, Ted. ''Silk Road to Ruin: Is Central Asia the new Middle East?'' New York: NBM, 2006. ISBN 1561634549 | ||
| + | * Rosten, Keith. ''Once in Kazakhstan: The snow leopard emerges.'' New York: iUniverse, 2005. ISBN 0595327826 | ||
| + | * Schneider, Johann, Knud S. Larsen, Krum Krumov, and Grigorii Vazow. ''Advances in International Psychology: Research Approaches and Personal Dispositions, Socialization Processes and Organizational Behavior''. Kassel University Press, 2013. ISBN 978-3862194544 | ||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | All links retrieved October 5, 2022. | ||
| + | * [https://www.everyculture.com/Ja-Ma/Kazakhstan.html Kazakhstan] Countries and Their Cultures | ||
| + | *[https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/kazakhstan/ Kazakhstan] CIA ''World Factbook'' | ||
| + | *[https://kazakhembus.com/ Embassy of the Republic of Kazakhstan] | ||
| + | *[http://www.nationalbank.kz/?switch=eng National Bank of Kazakhstan] | ||
| + | *[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/asia-pacific/country_profiles/1298071.stm Kazakhstan country profile] ''BBC'' | ||
| + | *[https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/kazakhstan Kazakhstan] ''The World Bank'' | ||
| − | + | {{credit|Kazakhstan|115505591|Geography_of_Kazakhstan|122725580|History_of_Kazakhstan|125263847|Culture_of_Kazakhstan|123350245|Demographics_of_Kazakhstan|120339749|Music_of_Kazakhstan|114096272}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Category:Geography]] | |
| + | [[Category:Countries]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Asia]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:17, 5 October 2022
| Republic of Kazakhstan Қазақстан Республикасы Qazaqstan Respublïkası Республика Казахстан Respublika Kazakhstan |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Anthem: Менің Қазақстаным Meniń Qazaqstanym "My Kazakhstan" |
||||||
| Location of Kazakhstan (green) |
||||||
| Capital | Astana | |||||
| Largest city | Almaty | |||||
| Official language(s) | Kazakh (official state language) Russian (used as official)[1] |
|||||
| Ethnic groups (2019[2]) | Kazakh (Qazaq) 68.0% Russian 19.3% Uzbek 3.2% Ukrainian 1.5% Uighur 1.5% Tatar 1.1% German 1.0% other 4.4% |
|||||
| Demonym | Kazakhstani (Kazakhstani includes all citizens, in contrast to Kazakh, which is the demonym for ethnic Kazakhs).[3] | |||||
| Government | Unitary presidential constitutional republic | |||||
| - | President | Kassym-Jomart Tokayev | ||||
| - | Prime Minister | Alihan Smaiylov | ||||
| Legislature | Parliament | |||||
| - | Upper House | Senate | ||||
| - | Lower House | Mazhilis | ||||
| Formation | ||||||
| - | Kazakh Khanate | 1465 | ||||
| - | Alash Autonomy | 13 December 1917 | ||||
| - | Kirghiz ASSR | 26 August 1920 | ||||
| - | Kazak ASSR | 19 June 1925 | ||||
| - | Kazakh SSR | 5 December 1936 | ||||
| - | Declared Sovereignty | 25 October 1990 | ||||
| - | Reconstituted as the Republic of Kazakhstan | 10 December 1991 | ||||
| - | Declared Independence from the USSR | 16 December 1991 | ||||
| - | CIS Accession | 21 December 1991 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 2,724,900 km2 (9th) 1,052,085 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 1.7 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2021 estimate | 19,245,793[2] (64th) | ||||
| - | Density | 6.49/km2 (227th) 16.82/sq mi |
||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | |||||
| - | Per capita | |||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | |||||
| - | Per capita | |||||
| Gini (2017) | 27.5[5] | |||||
| HDI (2017) | 0.800[6] (58th) | |||||
| Currency | Tenge (₸) (KZT) |
|||||
| Time zone | West / East (UTC+5 / +6) | |||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| Internet TLD | .kz, .қаз | |||||
| Calling code | +7-6xx, +7-7xx | |||||
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a country that is bigger than Western Europe, and stretches over a vast expanse of northern and central Eurasia to the west of the Ural River.
Historians believe the vast steppes of Kazakhstan were where humans first domesticated the horse. Indeed, its name is derived from an ancient Turkic word meaning "independent, a free spirit," reflecting the Kazakh people’s nomadic horseback culture.
Human activity has badly damaged the environment. The gravest threat comes from radiation, a result of the Soviet Union testing almost 500 nuclear weapons, above ground and often without notifying residents. Agricultural practices have shrunk the Caspian Sea, caused extensive wind erosion, and rendered farmland sterile. Aging factories pump contaminated waste into the water supply.
Untapped oil wealth and their abundance of natural resources offers a huge potential benefit for the nation. However, the burden of their past environmental abuses must be dealt with.
Geography
The word “Kazakh” is derived from an ancient Turkic word meaning "independent, a free spirit." It reflects the Kazakh people’s nomadic horseback culture and is related to the term "cossack." The old Persian word "stan" means "land" or "place of."
Kazakhstan has borders with Russia, the People's Republic of China, and the Central Asian countries Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan, and has a coastline on the Caspian Sea. With an area of 1.05 million square miles (2.7 million square kilometres), Kazakhstan is the ninth largest country in the world by area, and is the largest landlocked country in the world. It is equivalent to the size of Western Europe.

The terrain extends west to east from the Caspian Sea to the Altay Mountains and north to south from the Western Siberia plains to the oases and deserts of Central Asia. The Kazakh Steppe, with an area of around 310,600 square miles (804,500 square kilometers) occupies one-third of the country, and is the world's largest dry steppe characterized by large grassland and sandy regions. There is considerable topographical variation within Kazakhstan. The highest elevation, Khan Tengri Mountain, on the Kyrgyz border in the Tian Shan range, is 23,000 feet (7010 meters). The lowest point, at Karagiye, in the Caspian Depression in the west, is 430 feet (132 meters) below sea level. Only 12.4 percent of Kazakhstan is mountainous, mostly in the Altay and Tian Shan ranges of the east and northeast, although the Ural Mountains extend south from Russia. Many Altay and Tian Shan peaks are snow covered year-round, and their run-off is the source for Kazakhstan's rivers and streams.
Important rivers and lakes include: the Aral Sea, Ili River, Irtysh River, Ishim River, Ural River, Lake Balkhash, and Lake Zaysan.
Astana, formerly named Akmola, and Tselinograd, is the third largest city and has been the capital of Kazakhstan since 1997. Other cities include Almaty (the former capital), Karaganda, Shymkent (Chimkent), Semey (Semipalatinsk), and Turkestan.
Climate
Because Kazakhstan is so far from the oceans, the climate is continental and dry. Precipitation in the eastern mountains averages as much as 24 inches (600 millimeters) per year, mostly as snow, but most of the republic receives only four to eight inches (100 to 200 millimeters) yearly. Kazakhstan is sunny. Average winter temperatures are 26.6°F (-3°C) in the north and 64.4°F (18°C) in the south. Summer temperatures average 66°F (19°C) in the north and 86°F (30°C) in the south. Within locations differences are extreme, and temperature can change suddenly. The winter air temperature can fall to -58°F (-50°C), and in summer the air temperature can reach as high as 122°F (50°C).
Natural life and resources
Fauna that can be found in the steppes includes the Saiga Antelope, Siberian Roe Deer, wolves, foxes, badgers, snow leopards, eagles, and falcons.
Kazakhstan has an abundant supply of accessible mineral and fossil fuel resources. Development of petroleum, natural gas, and mineral extraction has attracted most of the over $40-billion in foreign investment in Kazakhstan since 1993 and accounts for some 57 percent of the nation's industrial output.
Kazakhstan has the second largest uranium, chromium, lead, and zinc reserves, the third largest manganese reserves, the fifth largest copper reserves, and ranks in the top ten for coal, potassium, iron, and gold. Diamonds are exported.
Oil explorations have shown that the deposits on the Caspian shore are only a fraction of a larger deposit. Possibly, 3.5 billion tons of oil and 2.5 trillion cubic meters of natural gas could be found there. The total estimated oil deposits is 6.1 billion tons. There are only three refineries within the country, situated in Atirau, Pavlodar, and Shymkent, and none are capable of processing crude, which is exported to Russia.
Environmental concerns
Natural hazards include earthquakes in the south, and mud slides around Almaty.
Human activity has badly damaged the environment. Most water is polluted by industrial effluents, pesticide and fertilizer residue, and, in some places, radioactivity.
The most visible damage has been to the Aral Sea, which in the 1970s was larger than most of the Great Lakes of North America. Sharply increased irrigation caused the sea to shrink. By 1993, the Aral Sea had lost an estimated 60 percent of its volume, and was breaking into three unconnected segments. Increasing salinity and reduced habitat killed the fish, destroying its fishing industry, and the receding shoreline has left the former port of Aral'sk more than 38 miles (60km) from the water's edge. The depletion of this large body of water has increased temperature variations in the region, which has harmed agriculture.
A much greater harm to agriculture has come from the salt- and pesticide-laden soil that the wind is known to carry to the Himalaya Mountains and the Pacific Ocean. Deposits of this saline soil on fields sterilizes them. Infant mortality in the region approaches 10 percent compared with the 1991 national rate of 2.7 percent.
Meanwhile, the water level of the Caspian Sea has been rising steadily since 1978 for reasons that scientists have not been able to explain fully. At the northern end of the sea, more than 10,000 square kilometers of land in Atyrau Province have been flooded.
Wind erosion has also had an impact in the northern and central parts of the republic because of the introduction of wide-scale dryland wheat farming in the 1950s and 1960s. By the mid-1990s, an estimated 60 percent of the republic's pastureland was in various stages of desertification.
Industrial pollution is a greater concern in Kazakstan's manufacturing cities, where aging factories pump huge quantities of unfiltered pollutants into the air and groundwater. The former capital and largest city, Almaty, is particularly threatened, in part because of the post–independence boom in private automobile ownership.
The gravest environmental threat to Kazakhstan comes from radiation, especially in the Semey (Semipalatinsk) region of the northeast, where the Soviet Union tested almost 500 nuclear weapons, 116 of them above ground. Often, such tests were conducted without evacuating or even alerting the local population. Although nuclear testing was halted in 1990, radiation poisoning, birth defects, severe anemia, and leukemia are very common in the area.
The government has established a Ministry of Ecology and Bioresources, with a separate administration for radio–ecology, but the ministry's programs are under-funded and given low priority.
History
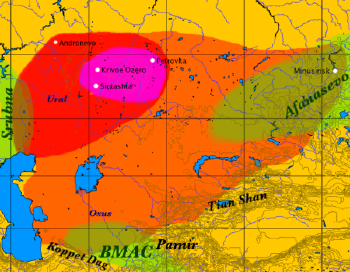
Kazakhstan has been inhabited since the Stone Age, generally by nomads practicing pastoralism, for which the region's climate and terrain are best suited. Prehistoric Bronze Age cultures that extended onto Kazakh territory include the Srubna culture (sixteenth-ninth centuries B.C.E.), the Afanasevo culture (3500—2500 B.C.E.) and the Andronovo culture (ca. 2300–1000 B.C.E.).
Historians believe the vast steppes of Kazakhstan were where humans first domesticated the horse. Following the Mongolian invasion in the early thirteenth century C.E., administrative districts were established under the Mongol Empire, which eventually became the territories of the Kazakh Khanate. The major medieval cities of Taraz and Hazrat-e Turkestan were founded along the northern route of the Silk Road during this period.
The Goturks
The earliest documented state in the region was the Turkic Kaganate, or Gokturk state, established by the Ashina clan, in the sixth century C.E. The Qarluqs, a confederation of Turkic tribes, established a state in what is now eastern Kazakhstan in 766.
In the eighth and ninth centuries, Arabs conquered portions of southern Kazakhstan and introduced Islam. The Oghuz Turks controlled western Kazakhstan from the ninth through the eleventh centuries; the Kimak and Kipchak peoples, also of Turkic origin, controlled the east at roughly the same time. The large central desert of Kazakhstan is still called Dashti-Kipchak, or the Kipchak Steppe.
In the late ninth century, invaders destroyed the Qarluq state and established the large Qarakhanid state, which occupied Transoxiana, the area north and east of the Oxus River (the present-day Amu Darya), extending into what is now China. Beginning in the early eleventh century, the Qarakhanids fought among themselves and with the Seljuk Turks to the south.
In the course of these conflicts, parts of present-day Kazakhstan shifted back and forth between the combatants. The Qarakhanids, who accepted Islam and the authority of the Arab Abbasid caliphs of Baghdad, were conquered in the 1130s by the Karakitai, a Turkic confederation from northern China. In the mid-twelfth century, an independent state of Khorazm along the Oxus River broke away from the weakening Karakitai, but the bulk of the Karakitai state lasted until the Mongol invasion of Genghis Khan in 1219-1221.
Mongol invasion
After the Mongol capture of the Karakitai state, Kazakhstan fell under the control of a succession of rulers of the Mongolian Golden Horde, the western branch of the Mongol Empire. The horde, or zhuz, is the precursor of the present-day clan. By the early fifteenth century, the ruling structure had split into several large groups known as khanates, including the Nogai Horde and the Uzbek Khanate.
The Kazakhs emerged from a mixture of tribes living in the region in about the fifteenth century and by the middle of the sixteenth century had developed a common language, culture, and economy. In the early 1600s, the Kazakh Khanate separated into the Great, Middle and Little (or Small) Hordes (jüz)—confederations based on extended family networks. Political disunion, competition among the hordes, and a lack of an internal market weakened the Kazakh Khanate. The beginning of the eighteenth century marked the zenith of the Kazakh Khanate.
Russian rule
In the nineteenth century, the Russian Empire spread into Central Asia. The "Great Game" period of rivalry and strategic conflict between the British Empire and the Tsarist Russian Empire for supremacy in Central Asia, is regarded as running from approximately 1813 to the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907. Following the Bolshevik Revolution of 1917 a second less intensive phase followed. The tsars effectively ruled over most of the territory belonging to what is now the Republic of Kazakhstan.
The Russian Empire introduced a system of administration and built military garrisons and barracks in its effort to establish a presence in Central Asia. The use of the Russian language was required in all schools and government organizations, arousing resentment among the Kazakh people. By the 1860s, most Kazakhs resisted Russia's annexation because it disrupted the traditional nomadic lifestyle and livestock-based economy. A Kazakh national movement began in the late 1800s, seeking to preserve the Kazakh language and identity. From the 1890s, increasing numbers of Slavic settlers began colonizing the area, especially once the Trans-Aral Railway from Orenburg to Tashkent was completed in 1906. The competition for land and water during the final years of tsarist Russia resulted in an uprising, the Central Asian Revolt, in 1916.
Soviet rule
A brief period of autonomy followed the collapse of the Russian Empire, but the Kazakhs eventually succumbed to Soviet rule. In 1920, the area became an autonomous republic within Russia and, in 1936, a Soviet republic.
Repression of the traditional elite, plus forced collectivization in late 1920s–1930s, brought mass hunger and unrest. But the communist apparatus gradually integrated Kazakhstan into the Soviet system. Thousands exiled from other parts of the Soviet Union during the 1930s arrived, as did hundreds of thousands evacuated from the Second World War battlefields. Some were deported to Siberia or Kazakhstan because of their ethnicity or beliefs, and were interned in some of the biggest Soviet labor camps. The Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic (SSR) contributed five divisions to the Soviet Union's World War II effort. In 1947, the Semipalatinsk Test Site, the USSR's main nuclear weapon test site was founded near the city of Semey.
World War II brought increased mining and industrialization, although by the time Soviet leader Joseph Stalin died, Kazakhstan still had an agricultural economy. In 1953, Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev initiated the ambitious "Virgin Lands" program to turn pasture into a grain-producing region for the Soviet Union. This policy, with modernizations under Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev, hastened the development of the agricultural sector, which remained the source of livelihood for a large percentage of Kazakhstan's population.
Demands for political and economic reforms within the Soviet Union came to a head in the 1980s. In December 1986, young ethnic Kazakhs in Almaty protested the replacement of the First Secretary of the Communist Party of Kazakhstan Dinmukhamed Konayev with Gennady Kolbin, an ethnic Chuvas from the Russian Federation. Dozens of demonstrators were jailed or killed. Discontent continued, resulting in Soviet president Mikhail Gorbachev's policy of glasnost (openness). Kazakhstan declared itself a republic within the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics in October 1990. Following the August 1991 abortive coup attempt in Moscow and the subsequent dissolution of the Soviet Union, Kazakhstan declared independence on December 16, 1991.
Independence
The years following independence have been marked by significant reforms to the Soviet command-economy and political monopoly on power. Nursultan Nazarbayev, who initially came to power in 1989 as the head of the Communist Party of Kazakhstan, was easily elected president in November, 1991. Kazakhstan has since made progress toward developing a market economy, and has enjoyed significant economic growth since 2000, partly due to its large oil, gas, and mineral reserves.
Politics
The politics of Kazakhstan take place in the framework of a presidential republic, whereby the President of Kazakhstan is head of state and nominates the head of government. The nature of government is authoritarian presidential rule, with little power outside the executive branch.
The president is elected by popular vote for a seven-year term, and constitutionally had a two-term limit. The president appoints a council of ministers (cabinet). The president also is the commander in chief of the armed forces and may veto legislation that has been passed by the Parliament.
The president appoints the prime minister and first deputy prime minister. The prime minister chairs the Cabinet of Ministers and serves as Kazakhstan's head of government. There are three deputy prime ministers and 16 ministers in the Cabinet. The president appoints a Council of Ministers.
The bicameral parliament comprises a senate and a Mazhilis. The senate has 39 seats. The president appoints seven senators. Other members are elected from each of the 14 oblasts, the capital of Astana, and the city of Almaty, to serve six-year terms. Former presidents are ex-officio senators for life. The Mazhilis has 77 seats. Ten out of the 77 Mazhilis members are elected from the winning party's lists. Other members are popularly elected to serve five-year terms. Most legislation considered by the Mazhilis is proposed by the government. All aged 18 years of age and over may vote.
The judiciary comprises a Supreme Court of 44 members and a Constitutional Council of seven members. Local and national courts resemble those in the Western world, but lack of checks and controls. A variety of different police units, a remnant of the Soviet era, leads to problems of jurisdiction. In urban areas, robberies and theft are common. Murder, suicide, and other violent crimes are increasing. The drug trade from Afghanistan has given rise to organized crime. Embezzlement, tax fraud, and abuse of power and privilege are tacitly accepted.
Administrative divisions
Kazakhstan is divided into 14 provinces (oblys) and three municipal districts (qala). Each is headed by an akim (provincial governor) appointed by the president. Municipal akims are appointed by oblast akims. The Government of Kazakhstan transferred its capital from Almaty to Astana on December 10, 1997.
In 1995, Russia leased for 20 years an area of 2300 square miles (6000 square kilometers) enclosing the Baikonur Cosmodrome space launch center and the city of Bayqongyr (formerly Leninsk). The lease was later extended through 2050. On June 18, 2006, Kazakhstan became a space-faring nation when it launched its first commercial satellite, KazSat 1, from the Baikonur Cosmodrome on a Russian-built booster rocket.
Foreign relations
Kazakhstan has stable relationships with all of its neighbors and is a member of the United Nations, Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe, Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council and Organization of the Islamic Conference(OIC). It participates in the North Atlantic Treaty Organization's (NATO) Partnership for Peace program. Kazakhstan is a member of the Commonwealth of Independent States, the Economic Cooperation Organization and the Shanghai Cooperation Organization. The nations of Kazakhstan, Belarus, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan established the Eurasian Economic Community in 2000 to harmonize tariffs and create a free trade zone.
Since independence, Kazakhstan has sought equally good relations with Russia, China, the United States, and the West. Companies from the U.S., Russia, China, and Europe are present at all fields.
Military
Kazakhstan's National Security Committee was established in 1992. It includes the Service of Internal Security, Military Counterintelligence, border guard, several commando units, and Foreign Intelligence (Barlau).
Kazakhstan acquired from the Soviet Union all the units of the 40th (the former 32nd) Army and part of the 17th Army Corps, including six land force divisions, storage bases, the 14th and 35th air-landing brigades, two rocket brigades, two artillery regiments and a large amount of equipment which had been withdrawn from over the Urals after the signing of the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe.
The Kazakh Air Defence Force's fighter aircraft element consists of the 356th Fighter Aviation Regiment, flying MiG-31s from Semipalitinsk Airport. The Republican Guard had 2500 soldiers in 1994, and is not part of the army.
Kazakhstan sent 29 military engineers to Iraq as part of the Coalition of the Willing to assist the U.S. occupation in Iraq.
Economy

Kazakhstan, the largest of the former Soviet republics in territory, excluding Russia, possesses enormous fossil fuel reserves and plentiful supplies of other minerals and metals. It also has a large agricultural sector featuring livestock and grain. Kazakhstan's industrial sector rests on the extraction and processing of these natural resources and also on a growing machine-building sector specializing in construction equipment, tractors, agricultural machinery, and some defense items.
The breakup of the USSR in December 1991 and the collapse in demand for Kazakhstan's traditional heavy industry products resulted in a short-term contraction of the economy, with the steepest annual decline occurring in 1994. In 1995-1997, the pace of the government program of economic reform and privatization quickened, resulting in a substantial shifting of assets into the private sector.
Kazakhstan enjoyed double-digit growth in 2000-2001 – eight percent or more per year in 2002-2006 - due largely to its booming energy sector, but also to economic reform, good harvests, and foreign investment. The opening of the Caspian Consortium pipeline in 2001, from western Kazakhstan's Tengiz oilfield to the Black Sea, substantially raised export capacity. Kazakhstan in 2006 completed the Atasu-Alashankou portion of an oil pipeline to China that is planned to extend from the country's Caspian coast eastward to the Chinese border in future construction.
The country has embarked upon an industrial policy designed to diversify the economy away from over-dependence on the oil sector by developing light industry. The policy aims to reduce the influence of foreign investment and foreign personnel. The government has engaged in several disputes with foreign oil companies over the terms of production agreements; tensions continue. Upward pressure on the local currency continued in 2006 due to massive oil-related foreign-exchange inflows. Aided by strong growth and low inflation, Kazakhstan aspires to become a regional financial center and has created a banking system comparable to those in Central Europe.
In 2000, Kazakhstan adopted a new tax code in an effort to consolidate gains. In November 2003 the new tax code was adopted, reducing value added tax from 16 percent to 15 percent, the social tax from 21 percent to 20 percent, and the personal income tax from 30 percent to 20 percent.
Oil and gas
Energy is the leading economic sector. Production of crude oil and natural gas condensate in Kazakhstan amounted to 51.2 million tons in 2003. Kazakhstan's 2003 oil exports were valued at more than $7-billion, representing 65 percent of overall exports and 24 percent of the GDP. Major oil and gas fields and their recoverable oil reserves are Tengiz with seven billion barrels; Karachaganak with eight billion barrels (and 1350km³ of natural gas); and Kashagan with seven to nine billion barrels.
Agriculture
Agriculture is a significant part of the Kazakh economy. Grain, potatoes, grapes, vegetables, melons, and livestock are the most important agricultural commodities.
Agricultural land occupies more than 327,000 square miles (846,000 square kilometers). Chief livestock products are dairy products, leather, meat, and wool. The country's major crops include wheat, barley, cotton, and rice. Wheat exports, a major source of hard currency, rank among the leading commodities in Kazakhstan's export trade.
Kazakh agriculture still has many environmental problems from mismanagement during its years in the Soviet Union.
Demographics
Kazakhstan has a diverse demography is due to the country's central location and its use by Russia as a place to send colonists, dissidents, and minority groups. From the 1930s until the 1950s, many minorities were interned in labor camps. This makes Kazakhstan one of the few places on earth where normally-disparate Germanic, Indo-Iranian, Chinese, Chechen, and Turkic groups live together in a rural setting and not as a result of modern immigration.
Population
The large migratory population of Kazakhstan, emigration, and the low population density - only about 5.5 persons per square kilometer in an area the size of Western Europe, make census figures difficult to measure.
After the fall of the Soviet Union, the German population of Kazakhstan emigrated en masse as Germany was willing to repatriate them, as did much of the smaller Greek minority (to Greece), and Russians (to Russia). Other groups left because of the economic situation. This, plus a higher Kazakh birthrate, and ethnic Kazakh immigration from the People's Republic of China, gave the Kazakhs a majority along with Mongolia, and Russia. In the early twenty-first century, Kazakhstan became one of the leading nations in international adoptions.
Ethnicity
Ethnic Kazakhs make up the majority of the population (close to 70 percent), and ethnic Russians are the next largest group at close to 20 percent. An amazingly rich array of other groups include Ukrainians, Uzbeks, Germans, Chechens, Koreans, and Uyghurs. There is also a small but active Jewish community.
The Russian term “Kazakhstani” was coined to describe all inhabitants of Kazakhstan, including non-Kazakhs. The word "Kazakh" is generally used to refer to people of actual Kazakh descent (including those living in China, Afghanistan, and other Central Asian countries).
Religion
Arabs brought Islam in the ninth century, and 1000 years later Russian settlers introduced Russian Orthodoxy. During the 70 years of Soviet rule, religious participation was banned, and many churches and mosques were destroyed. In 2007, the main religious groups were Muslim (mainly Sunni) 47 percent, Russian Orthodox 44 percent, Protestant 2 percent, and other 7 percent.
Although Islam was introduced in the ninth century, the religion was not fully assimilated until much later. As a result, it coexisted with earlier animist elements of Tengriism, which is a traditional Kazak belief that held that separate spirits inhabited and animated the earth, sky, water, and fire, as well as domestic animals. Honored guests in rural settings are still treated to a feast of freshly killed lamb, and are sometimes asked to bless the lamb and to ask its spirit for permission to partake of its flesh.
While formal religious observance is limited, many Kazakhs say a short prayer when they pass by where someone they know is buried, and say prayers after meals. Mosques are staffed by a mullah, who conducts services as well as funerals, weddings, and blessings, as do priests in Russian Orthodox churches.
Language
Kazakhstan is a bilingual country. The Kazakh language, a Turkic language, is spoken by over half of the population, and has the status of the state language, while Russian is used routinely in business. Language is a contentious issue. While Russian has been widely used as the inter-ethnic means of communications, Kazakhstan has not been able to use its distinct national language to unite ethnic communities.
Education
Education is universal and mandatory through to the secondary level. There are three main educational phases: Primary education (forms 1 to 4), basic general education (forms 5–9) and senior level education (forms 10–11 or 12) divided into continued general education and professional education. Primary education is preceded by one year of pre-school education. These three levels of education can be followed in one institution or in different ones (e.g. primary school, then secondary school).
New entrants are assigned to classes of about 25 pupils in the first grade, and that class stays together until the 11th grade, with the same teacher until the fourth grade, and a different teacher through to the eleventh grade. The teachers are like second mothers or fathers, discipline is important, homework is extensive and grades difficult.
Several secondary schools, specialized schools, magnet schools, gymnasium schools, lyceums, linguistic and technical gymnasiums, have been founded. Secondary professional education is offered in special professional or technical schools, lyceums or colleges and vocational schools.
At tertiary level, there are universities, academies, and institutes, conservatories, higher schools and higher colleges. At this level, there are three main levels: basic higher education, that provides the fundamentals of the chosen field of study and leads to a bachelor degree; specialized higher education, after which students are awarded the specialist's diploma; and scientific-pedagogical higher education, which leads to the master's degree.
Postgraduate education leads to the Kandidat Nauk (Candidate of Sciences) and the Doctor of Sciences. With the adoption of the Laws on Education and on Higher Education, a private sector has been established and several private institutions have been licensed. The adult literacy rate is 99.5 percent.
In 2000, the Government of Kazakhstan joined the governments of the Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan, and Aga Khan IV to establish the world’s first internationally chartered institution of higher education, the University of Central Asia, which was intended to have three campuses of equal size and stature in each of the founding countries.
Ownership
Houses built and subsidized by the former Soviet government were cheap and available to all, and most people retained their property from the Soviet years. Occupiers own most apartments, although investing in rental property is more widespread.
Class
The new rich, who often flaunt their wealth, are termed "New Kazakh" or "New Russian," and contrast with the vast number of unemployed or underpaid. Poverty and accusations of unfair treatment have raised tensions between Kazakhs and non-Kazakhs. While the rich drive expensive cars, wear fashionable clothes, and throw lavish parties, the poor drive old Soviet cars or take a bus, wear cheap Chinese- or Turkish-import clothes, and save for months to pay for a wedding.
Culture
Before the Russian conquest, the Kazaks had a well-articulated culture based on their nomadic pastoral economy. Because animal husbandry was central to the Kazaks' traditional lifestyle, most of their nomadic practices and customs relate in some way to livestock. Traditional curses and blessings invoked disease or fecundity among animals, and good manners required that a person ask first about the health of a man's livestock when greeting him and only afterward inquire about the human aspects of his life. Lamb has a symbolic value in the culture.
Kazakhs can be superstitious. Whistling inside a house is unacceptable since it is believed that it will make the owner of the house poor. Smoking by women is not accepted. Kazakhs often don't smile at people in public except to those they know, and rarely form lines when boarding crowded buses. Women and girls often hold hands as they walk; boys hook arms or walk with their arms around each other. Kissing cheeks and embracing is perfectly acceptable between good friends. Kazakh men shake hands with an acquaintance the first time they see each other in a day. All remove their shoes when inside a house—guests remove their shoes at the door and often put on a pair of slippers.
Architecture

The traditional Kazak dwelling is the yurt, a tent consisting of a flexible framework of willow wood covered with varying thicknesses of felt. The open top permits smoke from the central hearth to escape. Temperature and draft can be controlled by a flap that increases or decreases the size of the opening. A properly constructed yurt can be cooled in summer and warmed in winter, and it can be disassembled or set up in less than an hour. The right side of the yurt's interior is reserved for men and the left for women.
Although yurts are used less, they remain a potent symbol. Demonstrators and hunger strikers erected yurts in front of the government building in Almaty in the spring of 1992. Yurts are frequently used as a decorative motif in restaurants and other public buildings.
Russian settlers in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries brought small A-frame houses, Russian Orthodox churches, and wooden buildings.
Buildings from the Soviet era were big and utilitarian, and often the same shape, size, and color throughout the Soviet empire. Large Soviet-designed apartment blocks were five or six stories high and had three to four apartments of one, two, or three bedrooms each per floor. Villages and collectives consisted of small two- to three-room, one-story houses, painted white and light blue (to keep away evil spirits), all built by the government. Large squares and parks were built in every town.
Oil money, and foreign investment have brought five-star high-rise hotels, casinos, Turkish fast food restaurants, American steak houses, bowling alleys and movie theaters. Private homes are bigger, with two and three stories, two-car garages and large, fenced-in yards.
Cuisine
Daily meals are hearty, always including bread and usually noodles or potatoes and then a meat. One common dish is pilaf, a rice dish usually made with carrots, mutton, and a lot of oil. Russian borscht, usually red (beet-based) or brown (meat-based), with cabbage, meat, and potatoes, and a large dollop of sour cream, is popular. Russian pelimnin, dough pockets filled with meat and onions, is often a daily meal.
A flat, round bread called leipioskka and seasonal fruits and vegetables are served with almost every meal. Kazakhstan is known for its apples. Shashlik, marinated meat roasted over a small flame and served on a stick, is sold at roadside cafés and corner shashlik stands.
Tea is an integral part of life, and is drunk six or seven times a day. Guests are always offered tea. Muslim Kazakhs do not eat pork. Kazakhs have great respect for bread, which should never be wasted, thrown away, and should always be placed on the table right side up. Food is eaten with one's hands.
On special occasions, beshbarmak, traditionally horse meat boiled on the bone, is served over noodles covered in a meat broth called souppa. The host gives out pieces of meat in an order of respect usually based on seniority or distance traveled. When beshbarmak is made of mutton, the head of the sheep will be boiled, intact, and served to the most honored guest. An intoxicating fermented horse's milk called kumis, believed to be therapeutic, is occasionally drunk at ceremonial occasions. Vodka, which permeates the culture, is consumed in large quantities at all ceremonies. Toasts always precede a drink of vodka.
Music
Kazakh music is nomadic and rural, and is closely related to Uzbek and Kyrgyz folk forms. Traveling bards, healers and mystics called akyn are popular, and usually sing either unaccompanied or with a string instrument, especially a dombra, a mandolin-like string instrument, or kobyz. Akyn performance contests are called aitys; their lyrics are often social or political, and are generally improvised, witty remarks.
Traditional Kazakh music includes ensembles using instruments like the kobyz or dombra, as well as kyl-kobyz, sherter, sybyzgy, saszyrnay and shankobyz. The most common instrumental traditions are called kobizovaia, sibiz-govaia, and dombrovaia. Many songs are connected to ancient mythology and folk religious beliefs (kui), while others were composed after the rise of authored works (kuishi) by early songwriters (jiray) like Mahmud Kashgari, Kaztygana, Dospanbeta, Shalkiiza and Aktamberdi. The kuishi tradition is said to have peaked in the nineteenth century. In the twentieth century, the first star was the singer Mayra Shamsutdinova, a woman.
Controlled by the Russian Empire and then the Soviet Union, Kazakhstan's folk and classical traditions became connected with ethnic Russian music and Western European music. The Musical-Dramatic Training College, founded in 1932, was the first institute of higher education for music. Two years later, the Orchestra of Kazakh Folk Musical Instruments was formed
The Kazakhs themselves, however, did not write their own music in notation until 1931. Later, as part of the Soviet Union, Kazakh folk culture was encouraged in a sanitized manner designed to avoid political and social unrest. The result was a bland derivative of real Kazakh folk music. In 1920, A. V. Zataevich, a Russian official who created works of art music with melodies and other elements of Kazakh folk music, adapted traditional Kazakh instruments for use in Russian-style ensembles, such as by increasing the number of frets and strings.
Pop music in Kazakhstan has made a resurgence since the year 2000. Talent searches have always been an integral part of the Kazakh pop music industry, such as the project Anshi Balapan & Idol spinoff SuperStar KZ, a reality television show based on the popular British show Pop Idol. The show is a contest to determine the best young singer in Kazakhstan.
Literature
Kazak literary tradition is rich in oral histories. These histories were memorized and recited by the akyn, the elder responsible for remembering the legends and histories, and by jyrau, lyric poets who traveled with the high-placed khans. Most of the legends concern the activities of a batir, or hero-warrior.
Among the tales that have survived are Koblandy-batir (fifteenth or sixteenth century), Er Sain (sixteenth century), and Er Targyn (sixteenth century), all of which concern the struggle against the Kalmyks; Kozy Korpesh and Bain sulu, both epics; and the love lyric Kyz-Zhibek. Usually these tales were recited in a song-like chant, frequently to the accompaniment of drums and the dombra.
For the most part, pre-independence cultural life in Kazakstan was indistinguishable from that elsewhere in the Soviet Union. That Russified cultural establishment nevertheless produced many of the most important figures of the early stages of Kazak nationalist self-assertion, including novelist Anuar Alimzhanov, who became president of the last Soviet Congress of People's Deputies, and poets Mukhtar Shakhanov and Olzhas Suleymenov, who were co-presidents of the political party Popular Congress of Kazakhstan.
Suleymenov in 1975 became a pan-Central Asian hero by publishing a book, Az i Ia, examining the Lay of Igor's Campaign, a medieval tale vital to the Russian national culture, from the perspective of the Turkic Pechenegs whom Igor defeated. Soviet authorities subjected the book to a blistering attack. Later Suleymenov used his prestige to give authority to the Nevada-Semipalatinsk anti-nuclear movement, which helped end nuclear testing in Kazakhstan.
Sports
Kazakhstan consistently performs well in the Olympics. Dmitry Karpov and Olga Rypakova are among the most notable Kazakhstani athletics. Dmitry Karpov is a distinguished decathlete, taking bronze in both the 2004 Summer Olympics, and the 2003 and 2007 World Athletics Championships. Olga Rypakova is an athlete, specialized in triple jump (women's), taking silver in the 2011 World Championships in Athletics and Gold in the 2012 Summer Olympics.
Kazakhstan has achieved some success in international competitions in weightlifting, ice hockey, and boxing. Kazakh boxers are generally well known in the world.
Football (soccer) is popular, with the Kazakhstan Super League being the top-level competition for the sport in the country. Numerous professional cyclists competing on the European circuit come from Kazakhstan. Most notable is Alexander Vinokourov.
Notes
- ↑ Constitution of the Republic of Kazakhstan Institute of legislation and legal information of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Retrieved January 19, 2022.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 CIA, Kazakhstan World Factbook. Retrieved January 19, 2022.
- ↑ Johann Schneider, Knud S. Larsen, Krum Krumov, and Grigorii Vazow, Advances in International Psychology: Research Approaches and Personal Dispositions, Socialization Processes and Organizational Behavior (Kassel University Press, 2013, ISBN 978-3862194544).
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 World Economic Outlook Database, April 2019 International Monetary Fund. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ↑ GINI index (World Bank estimate) World Bank. Retrieved May 6, 2020.
- ↑ 2018 Human Development Report, 2018 United Nations Development Programme. Retrieved January 19, 2022.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Broughton, Simon, and Mark Ellingham (ed.). World Music, Vol. 2: Latin & North America, Caribbean, India, Asia and Pacific. Rough Guides Ltd, Penguin Books, 2000. ISBN 1858286360
- Cummings, Sally N. Kazakhstan Power and the Elite. London: I.B. Tauris, 2005. ISBN 1860648541
- Demko, George J. The Russian Colonization of Kazakhstan, 1896-1916. Indiana University publications. The Hague [etc.]: Mouton, 1969. OCLC 63360103
- Fergus, Michael, and Janar Jandosova. Kazakhstan: Coming of Age. London: Stacey International, 2003. ISBN 1900988615
- George, Alexandra. Journey into Kazakhstan: The true face of the Nazarbayev regime. Lanham: University Press of America, 2001. ISBN 0761819649
- Martin, Virginia. Law and Custom in the Steppe: The Kazakhs of the Middle Horde and Russian colonialism in the nineteenth century. Richmond: Curzon, 2000. ISBN 0700714057
- Nazarbaev, Nursultan. Epicenter of Peace. Hollis, NH: Puritan Press, 2001. ISBN 1884186130
- Nazpary, Joma. Post-soviet Chaos: Violence and dispossession in Kazakhstan. London: Pluto Press, 2002. ISBN 0745315038
- Olcott, Martha Brill. The Kazakhs: Studies of nationalities in the USSR. Stanford, CA: Hoover Institution Press, Stanford University, 1987. ISBN 0817983821
- Olcott, Martha Brill. Kazakhstan: Unfulfilled promise. Washington, DC: Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, 2002. ISBN 0870031899
- Rall, Ted. Silk Road to Ruin: Is Central Asia the new Middle East? New York: NBM, 2006. ISBN 1561634549
- Rosten, Keith. Once in Kazakhstan: The snow leopard emerges. New York: iUniverse, 2005. ISBN 0595327826
- Schneider, Johann, Knud S. Larsen, Krum Krumov, and Grigorii Vazow. Advances in International Psychology: Research Approaches and Personal Dispositions, Socialization Processes and Organizational Behavior. Kassel University Press, 2013. ISBN 978-3862194544
External links
All links retrieved October 5, 2022.
- Kazakhstan Countries and Their Cultures
- Kazakhstan CIA World Factbook
- Embassy of the Republic of Kazakhstan
- National Bank of Kazakhstan
- Kazakhstan country profile BBC
- Kazakhstan The World Bank
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
- Kazakhstan history
- Geography_of_Kazakhstan history
- History_of_Kazakhstan history
- Culture_of_Kazakhstan history
- Demographics_of_Kazakhstan history
- Music_of_Kazakhstan history
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.