Difference between revisions of "Kaziranga National Park" - New World Encyclopedia
Dan Davies (talk | contribs) (images OK) |
|||
| (74 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{images OK}}{{ | + | {{approved}}{{submitted}}{{images OK}}{{Paid}}{{Copyedited}} |
{{Infobox Indian Jurisdiction | {{Infobox Indian Jurisdiction | ||
|type = national park | |type = national park | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|iucn_category = II | |iucn_category = II | ||
|state_name = Assam | |state_name = Assam | ||
| − | |district= | + | |district= '''[[Golaghat District|Golaghat]]''', '''[[Nagaon district|Nagaon]]''' | |
|nearest_city = [[Golaghat]] | |nearest_city = [[Golaghat]] | ||
|latd=26 |latm=40 |lats=00 |longd=93 |longm=21 |longs=00 | |latd=26 |latm=40 |lats=00 |longd=93 |longm=21 |longs=00 | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
|established_title = Established | |established_title = Established | ||
|established_date = 1974 | |established_date = 1974 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|blank_title_2 = Governing body | |blank_title_2 = Governing body | ||
|blank_value_2 = [[Government of India]], [[Government of Assam]] | |blank_value_2 = [[Government of India]], [[Government of Assam]] | ||
|inset_map_marker = yes | |inset_map_marker = yes | ||
| − | |website= | + | |website= |
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | Kaziranga | + | '''Kaziranga National Park''', a [[national park]] in the [[Golaghat district|Golaghat]] and [[Nagaon district]]s of [[Assam]], [[India]] has [[World Heritage Site]] status. Two-thirds of the world's [[Indian Rhinoceros|Great One-horned Rhinoceros]]es live in the park. Kaziranga has the highest density of [[Bengal tiger|tiger]]s among [[protected area]]s in the world, declared a [[Tiger Reserve]] in 2006. The park has large breeding populations of [[Asian Elephant|elephants]], [[Asiatic Water Buffalo|water buffalo]], and [[swamp deer]]. [[Birdlife International]] recognizes Kaziranga as an [[Important Bird Area]] for conservation of avifaunal species. The park has achieved notable success in [[wildlife conservation]] compared to other protected areas in India. Located on the edge of the [[Eastern Himalaya]] [[biodiversity hotspot]], the park combines high-species diversity and visibility. |
| + | Kaziranga hosts a vast expanse of tall [[elephant grass]], [[marshland]] and dense [[tropical moist broadleaf forests]] crisscrossed by four major rivers, including the [[Brahmaputra River|Brahmaputra]], and has numerous [[beel|small bodies]] of water. Kaziranga has been the theme of several books, documentaries and songs. The park celebrated its centenary in 2005 after its establishment in 1905 as a [[reserve forest]]. | ||
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | The Kaziranga National Park, situated in the [[Lower Himalaya]] region of [[India]], enjoys a semi-tropical [[climate]], hosting fauna of both temperate and tropical climates. The region experiences three seasons, a mild winter, hot summer and long [[monsoon]] season. The lengthy growing season promotes the abundant fauna need to support wild life. Wild life abounds; jungle mammals including [[tigers]] and [[rhinoceros]], [[birds]], [[snakes]], aquatic life. Converted from a game park early in its history, the Kaziranga National Park provides the nature lover with a firsthand experience with many creatures on the [[endangered species list]]. | ||
| + | {{IndicText}} | ||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology== | ||
| − | Though the etymology of the name Kaziranga | + | Though the etymology of the name Kaziranga remains uncertain, a number of possible explanations exist regarding its name. One legend is related to the 30th Ahom King Rudra Singh who spent a night in the house of Chieftain Ranjit Phukan while going to Guwahati. At that time, he was impressed by the weaving art of Phukan's daughter, Kamala, who made him a silk jacket as a gift. The king called her Kazi, which means an expert, and gifted land in Rongai to her husband. The people residing nearby started calling that land Kazirongai, and with time it became Kaziranga. According to another legend, Madhabdev who was the chief disciple of [[Mahapurush Srimanta Sankardeva]], the sixteenth century [[Vaisnavism|Vaisnava]] saint-scholar, once blessed a childless couple, Kazi and Rangai, and asked them to dig a big pond in the region so that their name would live on. Testimony to the history of the name appears in some records which state that while the [[Ahom Dynasty|Ahom king]] [[Pratap Singha]] (seventeenth century) passed by the region, he was particularly impressed by the taste of fish, and on inquiry about its history, he named the pond Kaziranga.<ref name=history>[http://www.kaziranganationalparkindia.in/history-about-kaziranga.html History about Kaziranga] ''Kaziranga National Park''. Retrieved April 5, 2023.</ref> |
| − | + | Some historians believe that the name Kaziranga derived from the Karbi Word ''Kajir-a-rang,'' meaning "the village of Kajir (kajiror gaon)." Among the [[Karbi]]s, Kajir commonly refers to the name for a girl child, with belief that a woman named Kajir once ruled over the area.<ref>[https://karbi.wordpress.com/ Karbis of Assam]. Retrieved April 5, 2023.</ref> Fragments of monoliths associated with Karbi rule found scattered in the area seem to bear testimony to that assertion. Kaziranga could also mean the "Land of red goats (Deer)," as the word ''Kazi'' in the Karbi language means "Goat," and ''Rangai'' means "Red."<ref name=history/> | |
==History== | ==History== | ||
| − | {{ | + | [[Image:Franz von Lenbach Portrait Lady Curzon.jpg|thumb|350px|[[Mary Curzon, Baroness Curzon of Kedleston|Mary Victoria Leiter]], the wife of the [[Governor-General of India|Viceroy of India]], [[George Curzon, 1st Marquess Curzon of Kedleston|Lord Curzon]], credited with starting the movement for conservation of rhinoceroses.]] |
| + | The history of Kaziranga as a protected area traces back to 1904, when [[Mary Curzon, Baroness Curzon of Kedleston|Mary Victoria Leiter]], the wife of the [[Governor-General of India|Viceroy of India]], [[George Curzon, 1st Marquess Curzon of Kedleston|Lord Curzon]], visited the area. After failing to spot a [[rhinoceros]], for which the area was renowned, she persuaded her husband to take urgent measures to protect the dwindling species.<ref name = "bbc">Subir Bhaumik, [http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/4274927.stm Kaziranga's centenary celebrations] ''BBC News'', February 18, 2005. Retrieved April 5, 2023.</ref> On June 1, 1905, the Kaziranga Proposed Reserve Forest was created with an area of {{convert|232|sqkm|sqmi|0|abbr=on}}. Over the next three years, the park area was extended by {{convert|152|sqkm|sqmi|0|abbr=on}}, to the banks of the [[Brahmaputra River]]. In 1908, the government designated Kaziranga a Reserve forest. In 1916, the Reserve forest converted to a game sanctuary—The Kaziranga Game Sanctuary.<ref name=history/> | ||
| − | + | P.D. Stracey, the forest conservationist, renamed the Kaziranga Game Sanctuary to the Kaziranga Wildlife Sanctuary in 1950 to rid the name of [[hunting]] connotations. In 1954, the government of [[Assam]] passed the Assam (Rhinoceros) Bill, imposing heavy penalties for rhinoceros poaching. 14 years later, in 1968, the state government passed 'The Assam National Park Act of 1968', and in 1974 Kaziranga was given the title Kaziranga National Park.<ref name=history/> In 1985, [[UNESCO]] declared Kaziranga a [[World Heritage Site]] for its unique natural environment.<ref name = "un"> [https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/337/ Kaziranga National Park] ''UNESCO''. Retrieved April 5, 2023.</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Kaziranga has witnessed several natural and man-made calamities in recent decades. [[Flood]]s caused by overflowing of river Brahmaputra have led to significant losses in animal life. Encroachment by humans along the periphery has also led to a diminished forest cover and a loss of habitat.<ref name="unescotech">V.B. Mathur, P.R. Sinha, and Manoj Mishra, [https://web.archive.org/web/20071008185555/http://www.enhancingheritage.net/docs/UNESCOEoH_Project_South_Asia_Technical_Report_04_v1.pdf Technical Report #4] ''UNESCO''. Retrieved April 5, 2023. </ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | The park celebrated its centenary with much fanfare in 2005, inviting descendants of Lord Curzon for the celebrations.<ref name = "bbc"/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The park celebrated its centenary with much fanfare in 2005, inviting descendants of Lord Curzon for the celebrations.<ref name = "bbc"/ | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
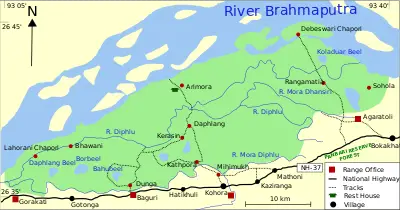
| − | + | [[Image:Kaziranga-National-Park-map-en-mod.svg|thumb|400px|Map of the Kaziranga National Park]] | |
| − | + | Kaziranga locates between latitudes 26°30' N and 26°45' N, and longitudes 93°08' E to 93°36' E within two districts in the [[India]]n state of [[Assam]]—the [[Kaliabor subdivision]] of [[Nagaon district]] and the [[Bokakhat subdivision]] of [[Golaghat district]].<ref name = "un"/> | |
| − | [[Image:Kaziranga-National-Park-map-en-mod.svg|thumb|Map of the Kaziranga National Park]] | ||
| − | Kaziranga | ||
| − | + | Approximately {{convert|40|km|mi|0|abbr=on|lk=on}} in length from east to west, Kaziranga spans {{convert|13|km|mi|0|abbr=on}} from north to south. Kaziranga covers an area of {{convert|378|sqkm|sqmi|0|abbr=on}}, with approximately {{convert|51.14|sqkm|sqmi|0|abbr=on}} lost to [[erosion]] in recent years.<ref>P. Lahan and R. Sonowal, "Kaziranga WildLife Sanctuary, Assam. A brief description and report on the census of large animals." ''Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society'' 70(2) (March 1972): 245–277. </ref> A total addition of {{convert|429|sqkm|sqmi|0|abbr=on}} along the present boundary of the park has been made and notified with separate national park status to provide extended habitat for increasing population of wildlife or as a corridor for safe movement of animals to Karbi Anglong Hills.<ref name="unescoreport"/> Elevation ranges from {{convert|40|m|ft|0|abbr=on}} to {{convert|80|m|ft|0|abbr=on}}.<ref name = "un"/> the Brahmaputra River circumscribes the park area, forming the northern and eastern boundaries, while the [[River Mora Diphlu|Mora Diphlu]] forms the southern boundary. The [[River Diphlu|Diphlu]] and [[River Mora Dhansiri|Mora Dhansiri]] flow within the park.<ref name="unescotech"/> | |
| − | |||
| − | Kaziranga has flat expanses of fertile, [[alluvial soil]] formed by [[erosion]] and silt deposition by the Brahmaputra. | + | Kaziranga has flat expanses of fertile, [[alluvial soil]] formed by [[erosion]] and silt deposition by the Brahmaputra. The landscape consists of exposed [[sandbar]]s, riverine flood-formed lakes known as ''[[beel]]s'' (which make up 5 percent of the surface area),<ref name = "un"/> and elevated regions known as ''chapories'' which provide shelter for animals during floods. Many artificial ''chapories'' have been built with the help of the [[Indian Army]] for the animals' safety.<ref>[http://web.archive.org/web/20060501222012/http://www.wildphototoursindia.com/kaziranga_national_park.htm Kaziranga National Park] ''WildPhotoToursIndia''. Retrieved April 5, 2023.</ref><ref name="unsummary"> [https://whc.unesco.org/archive/periodicreporting/APA/cycle01/section2/337-summary.pdf State of Conservation of the World Heritage Properties in the Asia-Pacific Region –Kaziranga National Park] ''UNESCO''. Retrieved April 5, 2023.</ref> The park sits in the [[Indomalaya ecozone]], and [[Brahmaputra Valley semi-evergreen forests]] of the [[tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests]] biome and a frequently flooded variant of the [[Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands]] of the [[tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands]] biome comprise the dominant [[biome]]s of the region. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Climate== | ==Climate== | ||
| − | + | The park experiences three seasons: summer, monsoon, and winter. The winter season, between November and February, experiences mild and dry weather, with a mean high of {{convert|25|°C|°F|0|lk=on}} and low of {{convert|5|°C|°F|0|lk=on}}.<ref name = "un"/> During that season, ''beels'' and ''[[nallah]]s'' (water channels) dry up.<ref name="unescotech"/> The summer season between March and May becomes hot, with temperatures reaching a high of {{convert|37|°C|°F|0|lk=on}}.<ref name = "un"/> During that season, animals usually gather near water bodies.<ref name="unescotech"/> The rainy monsoon season lasts from June to September, giving Kaziranga most of its annual rainfall of {{convert|2220|mm|in|0|abbr=on}}. During the peak months of July and August, three-fourths of the western region of the park submerge due to the rising water level of the Brahmaputra. The flooding causes most animals to migrate to elevated and forested regions outside the southern border of the park, such as the [[Mikir Hills|Mikir hills]].<ref name = "un"/> Occasional dry spells create problems as well, such as food shortages for the wildlife in the park. | |
| − | |||
| − | The park experiences three seasons: summer, monsoon, and winter. The winter season, between November and February, | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Fauna== | ==Fauna== | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Kazi rhino edit.jpg|thumb|300px|Two-thirds of the world's [[Indian Rhinoceros|Great One-horned Rhinoceros]]es live in the park.<ref>Subir Bhaumik, [http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/6564337.stm Assam rhino poaching 'spirals'] ''BBC News'', April 17, 2007. Retrieved April 5, 2023.</ref>]] | |
| − | [[ | + | Kaziranga contains significant breeding populations of 35 mammalian species,<ref name="mamlist">[https://www.kazirangatourism.com/mammals.html Kaziranga Mammals] ''Kaziranga Tourism''. Retrieved April 5, 2023. </ref> of which 15 are [[threatened]] as per the [[IUCN Red List]].<ref name = "un"/> The park has the distinction of being home to the world's largest population of the [[Indian Rhinoceros|Great Indian One-Horned Rhinoceros]],<ref name = "un"/> [[Wild Asiatic Water Buffalo]],<ref name=buffalo>'Wild buffalo census in Kaziranga', ''The Rhino Foundation for Nature in NE India, Newsletter'' No. 3, June 2001. </ref> and [[Swamp Deer|Eastern Swamp Deer]].<ref name = "trib">Parbina Rashid, [https://www.tribuneindia.com/2005/20050828/spectrum/main2.htm Here conservation is a way of life] ''The Tribune'', August 28, 2005. Retrieved April 5, 2023.</ref> Significant populations of large herbivores include elephants, [[gaur]], and [[sambar]]. Small herbivores include [[wild boar]] and [[hog deer]].<ref name = "un"/> |
| − | [[ | + | Kaziranga represents one of the few wild breeding areas outside [[Africa]] for multiple species of large cats such as [[Indian Tiger]]s and [[Indian Leopard|Leopards]]. The Indian government declared Kaziranga a [[Tiger Reserve]] in 2006 and has the highest density of tigers in the world. Other [[felid]]s include the [[Jungle Cat]], [[Fishing Cat]], and [[Leopard Cat]]s.<ref name="mamlist"/> Small mammals include the rare [[Hispid Hare]], [[Indian Gray Mongoose]], [[Small Indian Mongoose]]s, [[Large Indian Civet]], [[Small Indian Civet]]s, [[Bengal Fox]], [[Golden Jackal]], [[Sloth Bear]], [[Chinese Pangolin]], [[Indian Pangolin]]s, [[Hog Badger]], [[Chinese Ferret Badger]]s and [[Hylopetes|Particolored flying squirrel]]s.<ref name = "un"/> Nine of the 14 [[primate]] species found in India occur in the park.<ref name="bbc"/> The [[Assamese Macaque]], [[Lutung|Capped]], [[Golden Langur]], as well as the only [[ape]] found in India, the [[Hoolock Gibbon]] stand out.<ref name="mamlist"/> Kaziranga's rivers constitute home to the endangered [[Ganges Dolphin]].<ref name = "un"/> |
| − | Kaziranga | + | [[File:Coracias affinis, Kaziranga, cropped.jpg|thumb|400px|An [[Indian Roller]] at Kaziranga]] |
| − | + | Kaziranga serves as home to a variety of migratory birds, water birds, predators, scavengers, and game birds. Birds such as the [[Lesser White-fronted Goose]], [[Ferruginous Duck]], [[Baer's Pochard]] [[duck]], and [[Lesser Adjutant]], [[Greater Adjutant]], [[Black-necked Stork]], and [[Asian Openbill]] [[stork]] migrate from [[Central Asia]] to the park during winter. Riverine birds include the [[Blyth's Kingfisher]], [[White-bellied Heron]], [[Dalmatian Pelican]], [[Pelican|Spot-billed Pelican]], [[Spotted Greenshank]] and [[Black-bellied Tern]]. [[Birds of prey]] include the rare [[Eastern Imperial Eagle|Eastern Imperial]], [[Greater Spotted Eagle|Greater Spotted]], [[White-tailed Eagle|White-tailed]], [[Pallas's Fish Eagle]], [[Eagle|Grey-headed Fish Eagle]], and the [[Kestrel|Lesser Kestrel]].<ref name=forktail>M. Barua and P. Sharma, [https://web.archive.org/web/20070221210254/http://www.orientalbirdclub.org/publications/forktail/15pdfs/Barua-Kaziranga.pdf Birds of Kaziranga National Park, India] ''Forktail'' 15 (1999): 47-60. Retrieved April 6, 2023.</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Kaziranga | + | Kaziranga was once home to seven species of [[vulture]]s that nearly reached [[extinction]], possibly by feeding on animal carcasses containing the drug [[Diclofenac]]. Only the [[Indian Vulture]], [[Slender-billed Vulture]], and [[Indian White-rumped Vulture]] have survived.<ref>R. Cuthbert, R.E. Green, et al., "Rapid population declines of Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus) and red-headed vulture (Sarcogyps calvus) in India," ''Animal Conservation'' 9(3): 349–354. </ref> Game birds include the [[Swamp Francolin]], [[Bengal Florican]] and [[Pale-capped Pigeon]].<ref name="forktail"/> |
| − | [[ | + | Other families of birds inhabiting Kaziranga include the [[Great Indian Hornbill]] and [[Wreathed Hornbill]], [[Old World babbler]]s such as [[Jerdon's Babbler|Jerdon’s]] and [[Marsh Babbler]]s, [[weaver bird]]s such as the common [[Baya Weaver]], threatened [[Finn's Weaver]]s, [[Thrush (bird)|thrush]]es such as [[Hodgson's Bushchat]] and [[Old World warblers]] like the [[Bristled Grassbird]]. Other threatened species include [[Black-breasted Parrotbill]] and the [[Rufous-vented Prinia]].<ref name="forktail"/> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Two of the largest [[snake]]s in the world, the [[Reticulated Python]] and [[Rock Python]], as well as the longest venomous snake in the world, the [[King Cobra]], inhabit the park. Other snakes include the [[Cobra|Indian Cobra]], [[Daboia|Russell's Viper]], and the [[Common Krait]]. [[Monitor lizard]] species include the [[Bengal monitor]] and the [[Water Monitor]]. Other reptiles include 15 species of [[turtle]], such as the [[Endemism|endemic]] [[Kachuga sylhetensis|Assam Roofed Turtle]] and one species of tortoise, the [[Brown Hill Tortoise]].<ref>[https://www.kazirangatourism.com/reptiles.html https://www.kazirangatourism.com/reptiles.html] ''Kaziranga Tourism''. Retrieved April 6, 2023.</ref> | |
| − | + | At least 42 species of [[fish]] live in the area including the [[Tetraodon]].<ref>N. K Vasu, [https://web.archive.org/web/20070928033254/http://www.kaziranga100.com/Fishes%20Checklist.htm Fish Species Recorded in Kaziranga National Park] 'Management Plan of Kaziranga National Park''. Retrieved April 6, 2023. </ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Flora== | ==Flora== | ||
| − | [[Image:Assam 028 yfb edit.jpg|thumb|Grasslands and deciduous forests of Kaziranga]] | + | [[Image:Assam 028 yfb edit.jpg|thumb|400px|Grasslands and deciduous forests of Kaziranga]] |
| − | Four main types of vegetation types exist in the park | + | Four main types of vegetation types exist in the park: [[Flooded grasslands and savannas|alluvial inundated grassland]]s, [[Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands|alluvial savanna woodland]]s, [[Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests|tropical moist mixed deciduous forests]] and tropical semi-evergreen forests. |
| − | + | A difference in altitude exists between the eastern and western areas, with the western side at a lower altitude. Grasslands dominate the western reaches of the park. Tall elephant grass grows on higher ground, while short grasses cover the lower grounds surrounding the beels or flood-created ponds.<ref name = "un"/> Annual flooding, grazing by herbivores and [[controlled burn]]ing maintains and fertilizes the grasslands and reeds. [[Saccharum spontaneum|sugarcanes]], [[Imperata cylindrica|spear grass]], [[Arundo donax|Elephant Grass]] and the [[Phragmites|Common Reed]] comprise the common tall grasses. Numerous [[forb]]s grow along with the grasses. Trees—dominant species including [[Careya arborea|Kumbhi]], [[Indian gooseberry]], the [[Bombax ceiba|cotton]] tree (in savanna woodlands), and [[Dillenia|Elephant apple]] (in inundated grasslands) scatter amidst the grasses, providing cover and shade.<ref name = "un"/> | |
| − | Thick evergreen forests, near the Kanchanjhuri, Panbari and Tamulipathar blocks, contain trees such as ''[[Aphanamixis polystachya]], [[Talauma hodgsonii]], Dillenia indica, [[Garcinia]] tinctoria, [[Ficus]] rumphii, [[Cinnamomum]] bejolghota'' | + | Thick evergreen forests, near the Kanchanjhuri, Panbari and Tamulipathar blocks, contain trees such as ''[[Aphanamixis polystachya]], [[Talauma hodgsonii]], Dillenia indica, [[Garcinia]] tinctoria, [[Ficus]] rumphii, [[Cinnamomum]] bejolghota,'' and species of [[Syzygium]]. Tropical semi-evergreen forests thrive near Baguri, Bimali and Haldibari. ''[[Albizia]] procera, [[Duabanga]] grandiflora, [[Lagerstroemia speciosa]], [[Crateva religiosa|Crateva unilocularis]], [[Sterculia]] urens, [[Grewia]] serrulata, [[Mallotus (plant)|Mallotus]] philippensis, [[Bridelia]] retusa, [[Aphania]] rubra, [[Leea]] indica'' and ''Leea umbraculifera'' number among the common trees and shrubs.<ref>S.K. Jain and A.R.K. Sastry, [https://bsi.gov.in/uploads/documents/Public_Information/publication/books/miscellaneous/Botany%20of%20some%20Tiger%20Habitats%20in%20India.pdf Botany of some tiger habitats in India] ''Botanical Survey of India'', 1983. Retrieved April 6, 2023.</ref> |
| − | + | Many different aquatic floras grow in the lakes, ponds and along the river shores. The ubiquitous [[invasive species|invasive]] [[Water Hyacinth]] often chokes the water bodies, clears during destructive floods.<ref name = "un"/> Kaziranga staff, with help from the [[Wildlife Trust of India]], cleared another invasive species, ''[[Mimosa invisa]],'' [[toxic]] to herbivores, in 2005.<ref>Joseph Vattakkavan, N. K. Vasu, Surendra Varma, Nidhi Gureja, and Ambika Aiyadurai, [https://www.wti.org.in/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/pub_silent_stranglers.pdf Silent Stranglers, Eradication of Mimosas in Kaziranga National Park, Assam] ''Wildlife Trust of India'', 2005. Retrieved April 6, 2023.</ref> | |
==Administration== | ==Administration== | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Assam 057.jpg|thumb|400px|A board proclaiming the biological heritage of the Park]] | |
| − | [[Image:Assam 057.jpg|thumb|A board proclaiming the biological heritage of the Park]] | + | The Wildlife wing of the forest department of the Government of Assam bears responsibility for the administration and management of Kaziranga, headquartered at [[Bokakhat]].<ref name="unescotech"/> The administrative head, a conservator-level officer, serves as the park the director. A divisional forest officer serves as the administrative chief executive of the park, assisted by two officers with the rank of assistant conservator of forests. The park area divides into four ranges, overseen by range forest officers. The four ranges, the Burapahar, Baguri, Central, and Eastern, maintain headquarters at Ghorakati, Baguri, Kohora, and Agoratoli, respectively. Each range further sub-divides into beats, headed by a forester, and sub-beats, headed by a forest guard.<ref name="unescotech"/> |
| − | The Wildlife wing of the forest department of the Government of Assam | ||
| − | The park receives financial aid from the State Government as well as the [[Ministry of Environment and Forests (India)|Ministry of Environment and Forests]] of [[Government of India]] under various Plan and Non-Plan Budgets. | + | The park receives financial aid from the State Government as well as the [[Ministry of Environment and Forests (India)|Ministry of Environment and Forests]] of [[Government of India]] under various Plan and Non-Plan Budgets. The Central Government provides additional funding under the [[Project Elephant]]. In 1997–1998, the park received a grant of [[US$]] 100,000 under the Technical Co-operation for Security Reinforcement scheme from the [[World Heritage Fund]].<ref name="unsummary"/> National & international [[Non-governmental organizations]] provide additional funding. |
==Conservation management== | ==Conservation management== | ||
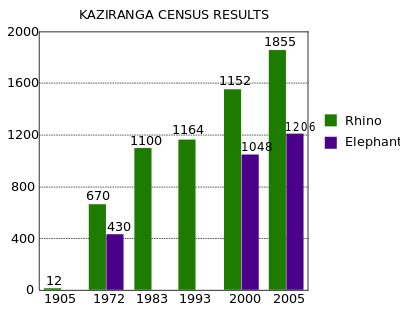
| − | + | [[Image:Kaziranga-census-results.svg|thumb|400px|Census figures for elephant and rhinoceros in Kaziranga]] | |
| − | [[Image:Kaziranga-census-results.svg|thumb|Census figures for elephant and rhinoceros in Kaziranga]] | ||
| − | Kaziranga National Park has been granted maximum protection under the Indian law for wildlife conservation. Various laws, | + | Kaziranga National Park has been granted maximum protection under the Indian law for wildlife conservation. Various laws, including the ''Assam Forest Regulation of 1891'' and the ''Biodiversity Conservation Act of 2002,'' have been enacted for protection of wildlife in the park.<ref name="unsummary"/> Poaching activities, particularly of the rhinoceroses for its horn, has been a major concern for the authorities. Between 1980 and 2005, poachers killed 567 rhinoceroses.<ref name="unescotech"/> Following a decreasing trend for the past few years, poachers killed six one-horned rhinoceroses in early 2007. Reports have suggested links between those poaching activities and funding of [[Islamic militant groups]] in [[Bangladesh]] connected to [[Al Qaida]].<ref>Poachers kill Indian Rhino, ''New York Times,'', April 17, 2007.</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[Water pollution]] due to run-offs from pesticides from tea gardens, and a petroleum refinery at [[Numaligarh]], | + | Preventive measures such as construction of anti-poaching camps and maintenance of existing ones, patrolling, intelligence gathering and control over the use of firearms around the park have reduced the number of casualties. |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Kazi fire.jpg|thumb|400px|Controlled burning of grass in Kaziranga]] | ||
| + | Perennial flooding and heavy rains have resulted in death of wild animals and damage to the conservation infrastructures.<ref name="unescoreport">[http://web.archive.org/web/20060524154236/http://whc.unesco.org/archive/periodicreporting/cycle01/section2/337.pdf Section II: Periodic Report on the State of Conservation of Kaziranga National Park, India] ''UNESCO''. Retrieved April 6, 2023.</ref> To escape the water-logged areas, many animals migrate to elevated regions outside the park boundaries, making them susceptible to hunting, hit by speeding vehicles, or subject to reprisals by villagers for damaging their crops. To mitigate the losses, the authorities have increased patrols, purchased additional speedboats for patrol, and created artificial highlands for shelter.<ref name=UN1997>[https://whc.unesco.org/en/soc/3003/ Kaziranga National Park: Factors affecting the property in 1997] ''UNESCO''. Retrieved April 5, 2023.</ref> Several corridors have been set up for the safe passage of animals across National Highway–37 which skirts around the southern boundary of the park.<ref name="highway">B.S. Bonal & S. Chowdhury, ''Evaluation of barrier effect of National Highway 37 on the wildlife of Kaziranga National Park and suggested strategies and planning for providing passage: A feasibility report to the Ministry of Environment & Forests.'' (Government of India, 2004).</ref> To prevent the spread of [[disease]]s and maintain the genetic distinctness of the wild species, the park management take systematic steps periodically such as [[immunization]] of [[livestock]] in surrounding villages, and fencing of sensitive areas of the park susceptible to encroachment by local cattle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Water pollution]] due to run-offs from pesticides from tea gardens, and a petroleum refinery at [[Numaligarh]], pose a hazard to the ecology of the region.<ref name="unescotech"/> Invasive species such as [[Mimosa]] and wild rose have posed a threat to the native plants in the region. Regular manual uprooting, weeding, and research on biological methods for controlling weeds before seed settling controls the growth and irradiation of invasive species. The park administration uses grassland management techniques, such as [[controlled burning]] annually to avoid [[forest fire]]s.<ref name="un"/> | ||
==Visitor activities== | ==Visitor activities== | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Bonoshree lodge in Kaziranga.jpg|thumb|400px|Bonoshree Tourist Lodge in Kaziranga, maintained by [[Government of Assam]] ]] | |
| − | [[Image:Bonoshree lodge in Kaziranga.jpg|thumb|Bonoshree Tourist Lodge in Kaziranga, maintained by [[Government of Assam]] ]] | ||
| − | + | Observing the wildlife, including [[birding]], constitutes the main visitor activity in and around the park. The park management allow only elephant or jeep tours; hiking has been prohibited to avoid attacks by animals. [[Observation tower]]s, situated at Sohola, Mihimukh, Kathpara, Foliamari and Harmoti, provide wildlife viewing. The [[Siwalik Hills|Lower Himalayan peaks]] frame the park's landscape of trees and grass interspersed with numerous [[beel|ponds]]. The park remains closed for visitors from mid-April to mid-October due to [[monsoon]] rains. The [[Department of Environment and Forests, Government of Assam]]maintain four tourist lodges at Kohora and three tourist lodges inside the park. Private resorts operate outside the park borders.<ref name="unescoreport"/> Increased tourism has brought an improvement in the standard of living for people living on the fringes of the park. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Transport== | ==Transport== | ||
| − | + | Authorized forest department guides accompany all travellers inside the park. Visitors book [[Mahout]]-guided [[elephant]] rides and [[Jeep]] or other four-wheel drive vehicles rides in advance. Starting from the Park Administrative Centre at [[Kohora]], those rides follow the three roadways under the jurisdiction of three ranges—Kohora, Bagori and Agaratoli. Those trails accept light vehicles from November to mid May. Visitors may bring in their own vehicles only when accompanied by guides. | |
| − | Buses owned by [[Assam State Transport Corporation]] and private agencies between [[Guwahati]], [[Tezpur]] and Upper Assam stop at the main gate of Kaziranga on NH-37 at Kohora | + | Buses owned by [[Assam State Transport Corporation]] and private agencies between [[Guwahati]], [[Tezpur]] and Upper Assam stop at the main gate of Kaziranga on NH-37 at Kohora. Major cities nearby include Guwahati ({{convert|217|km|mi|0}}) and [[Jorhat]] ({{convert|97|km|mi|0}}). [[Furkating]] {{convert|75|km|mi|0}}, under the supervision of [[Northeast Frontier Railway]], has the nearest railway station. [[Jorhat Airport]] at Rowriah ({{convert|97|km|mi|0}} away), [[Tezpur Airport]] at Salonibari (approx {{convert|100|km|mi|0}} away) and [[Lokpriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport]] in Guwahati (approximately {{convert|217|km|mi|0}} away) provide the closest airports.<ref>[https://www.kaziranga-national-park.com/ Kaziranga National Park]. Retrieved April 6, 2023</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==In popular culture== | ==In popular culture== | ||
| − | Kaziranga has been the theme, or has been mentioned in, several books, documentaries, and songs. The park first gained prominence after [[Robin Banerjee]] (a doctor turned photographer and filmmaker) produced a documentary titled ''Kaziranga'' | + | Kaziranga has been the theme, or has been mentioned in, several books, documentaries, and songs. The park first gained prominence after [[Robin Banerjee]] (a doctor turned photographer and filmmaker) produced a documentary titled ''Kaziranga,'' airing on [[Berlin]] television in 1961 and became a runaway success. [[United States|American]] [[science fiction authors|science fiction]] and fantasy author, [[Lyon Sprague de Camp]] wrote about the park in his poem, "[[Kaziranga, Assam (poem)|Kaziranga, Assam]]," first published in 1970 in ''Demons and Dinosaurs,'' a [[poetry]] collection, and reprinted as "Kaziranga" in ''Years in the Making: the Time-Travel Stories of L. Sprague de Camp'' in 2005.<ref>L. Sprague de Camp, ''Years In The Making: The Time-Travel Stories Of L. Sprague De Camp'' (Nesfa Press, 2005, ISBN 978-1886778474).</ref> |
| − | ''Kaziranga Trail'' ([[Children's Book Trust]], 1979), a [[children's literature|children's storybook]] by Arup Dutta about rhinoceros poaching in the national park, won the [[Shankar's Award]].<ref> Khorana, | + | ''Kaziranga Trail'' ([[Children's Book Trust]], 1979), a [[children's literature|children's storybook]] by Arup Dutta about [[rhinoceros]] poaching in the national park, won the [[Shankar's Award]].<ref>Meena Khorana, ''The Indian Subcontinent in Literature for Children and Young Adults'' (Greenwood Press, 1991, ISBN 0313254893).</ref> The Assamese singer [[Bhupen Hazarika]] refers to Kaziranga in one of his songs.<ref name = "trib"/> The [[BBC]] [[conservationist]] and travel writer [[Mark Shand]] authored a book and the corresponding [[BBC documentary]] ''Queen of the Elephants,'' based on the life of the first female mahout in recent times—[[Parbati Barua]] of Kaziranga.<ref>Mark Shand, ''Queen of the Elephants''. (Random House, 1996, ISBN 0099592010).</ref> The book went on to win the 1996 [[Thomas Cook Travel Book Award]] and the [[:fr:Prix littéraire de Trente millions d'amis|Prix Litteraire d'Amis]], providing publicity simultaneously to the profession of [[mahout]]s, and to Kaziranga. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| − | + | <references/> | |
| − | == | + | == References == |
| − | + | * Barthakur, Ranjit, and Bittu Sahgal. ''The Kaziranga Inheritance.'' Mumbai: Sanctuary Asia, 2005. ISBN 9788175255777 | |
| − | * | + | * Choudhury, Anwaruddin. ''The Birds of Assam.'' Guwahati: Gibbon Books and World Wide Fund for Nature, 2000. ISBN 9788190086615 |
| − | * | + | * de Camp, L. Sprague. ''Years In The Making: The Time-Travel Stories Of L. Sprague De Camp''. Nesfa Press, 2005. ISBN 978-1886778474 |
| − | * | + | * Dutta, Arup Kumar. ''Kaziranga Trail.'' Children's Book Trust, India, 1979. ISBN 0861443799 |
| − | * | + | * Dutta, Arup Kumar. ''Unicornis: The Great Indian One Horned Rhinoceros.'' New Delhi: Konark Publication, 1991. ISBN 9788122002188 |
| − | * | + | * Khorana, Meena. ''The Indian Subcontinent in Literature for Children and Young Adults: An Annotated Bibliography of English-Language Books.'' Greenwood Press, 1991. ISBN 0313254893 |
| − | * | + | * Oberai, C.P. ''Kaziranga: The Rhino Land.'' : New Delhi: B.R. Publishing, 2002. ISBN 9788176462594 |
| − | + | * Shand, Mark. ''Queen of the Elephants.'' Random House, 1996. ISBN 0099592010 | |
| − | * | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | + | All links retrieved April 2, 2023. | |
| − | * [ | + | |
| − | + | * [https://www.kaziranga-national-park.com/ Kaziranga National Park] | |
| − | * [ | + | * [https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/337/ Kaziranga National Park] ''UNESCO'' |
| − | * [ | + | * [https://forest.assam.gov.in/portlets/national-park Kaziranga National Park] ''Government Of Assam'' |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{World Heritage Sites in India}} | {{World Heritage Sites in India}} | ||
{{National Parks of India}} | {{National Parks of India}} | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Geography]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:National Parks]] | |
| + | [[Category:World Heritage Sites]] | ||
{{credits|162204277}} | {{credits|162204277}} | ||
Latest revision as of 22:14, 15 September 2023
| কাজিৰঙা ৰাষ্ট্ৰীয় উদ্যান Kaziranga National Park Assam • India | |
| IUCN Category II (National Park) | |
| Coordinates: | |
| Time zone | IST (UTC+5:30) |
| Area • Elevation |
430 km² (166 sq mi) • 80 m (262 ft) |
| Climate • Precipitation Temperature • Summer • Winter |
• 2,220 mm (87.4 in) • 37 °C (99 °F) • 5 °C (41 °F) |
| Nearest city | Golaghat |
| District(s) | Golaghat, Nagaon |
| Established | 1974 |
| Governing body | Government of India, Government of Assam |
Coordinates:
Kaziranga National Park, a national park in the Golaghat and Nagaon districts of Assam, India has World Heritage Site status. Two-thirds of the world's Great One-horned Rhinoceroses live in the park. Kaziranga has the highest density of tigers among protected areas in the world, declared a Tiger Reserve in 2006. The park has large breeding populations of elephants, water buffalo, and swamp deer. Birdlife International recognizes Kaziranga as an Important Bird Area for conservation of avifaunal species. The park has achieved notable success in wildlife conservation compared to other protected areas in India. Located on the edge of the Eastern Himalaya biodiversity hotspot, the park combines high-species diversity and visibility.
Kaziranga hosts a vast expanse of tall elephant grass, marshland and dense tropical moist broadleaf forests crisscrossed by four major rivers, including the Brahmaputra, and has numerous small bodies of water. Kaziranga has been the theme of several books, documentaries and songs. The park celebrated its centenary in 2005 after its establishment in 1905 as a reserve forest.
The Kaziranga National Park, situated in the Lower Himalaya region of India, enjoys a semi-tropical climate, hosting fauna of both temperate and tropical climates. The region experiences three seasons, a mild winter, hot summer and long monsoon season. The lengthy growing season promotes the abundant fauna need to support wild life. Wild life abounds; jungle mammals including tigers and rhinoceros, birds, snakes, aquatic life. Converted from a game park early in its history, the Kaziranga National Park provides the nature lover with a firsthand experience with many creatures on the endangered species list.
| This article contains Indic text. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks or boxes, misplaced vowels or missing conjuncts instead of Indic text. |
Etymology
Though the etymology of the name Kaziranga remains uncertain, a number of possible explanations exist regarding its name. One legend is related to the 30th Ahom King Rudra Singh who spent a night in the house of Chieftain Ranjit Phukan while going to Guwahati. At that time, he was impressed by the weaving art of Phukan's daughter, Kamala, who made him a silk jacket as a gift. The king called her Kazi, which means an expert, and gifted land in Rongai to her husband. The people residing nearby started calling that land Kazirongai, and with time it became Kaziranga. According to another legend, Madhabdev who was the chief disciple of Mahapurush Srimanta Sankardeva, the sixteenth century Vaisnava saint-scholar, once blessed a childless couple, Kazi and Rangai, and asked them to dig a big pond in the region so that their name would live on. Testimony to the history of the name appears in some records which state that while the Ahom king Pratap Singha (seventeenth century) passed by the region, he was particularly impressed by the taste of fish, and on inquiry about its history, he named the pond Kaziranga.[1]
Some historians believe that the name Kaziranga derived from the Karbi Word Kajir-a-rang, meaning "the village of Kajir (kajiror gaon)." Among the Karbis, Kajir commonly refers to the name for a girl child, with belief that a woman named Kajir once ruled over the area.[2] Fragments of monoliths associated with Karbi rule found scattered in the area seem to bear testimony to that assertion. Kaziranga could also mean the "Land of red goats (Deer)," as the word Kazi in the Karbi language means "Goat," and Rangai means "Red."[1]
History

The history of Kaziranga as a protected area traces back to 1904, when Mary Victoria Leiter, the wife of the Viceroy of India, Lord Curzon, visited the area. After failing to spot a rhinoceros, for which the area was renowned, she persuaded her husband to take urgent measures to protect the dwindling species.[3] On June 1, 1905, the Kaziranga Proposed Reserve Forest was created with an area of 232 km² (90 sq mi). Over the next three years, the park area was extended by 152 km² (59 sq mi), to the banks of the Brahmaputra River. In 1908, the government designated Kaziranga a Reserve forest. In 1916, the Reserve forest converted to a game sanctuary—The Kaziranga Game Sanctuary.[1]
P.D. Stracey, the forest conservationist, renamed the Kaziranga Game Sanctuary to the Kaziranga Wildlife Sanctuary in 1950 to rid the name of hunting connotations. In 1954, the government of Assam passed the Assam (Rhinoceros) Bill, imposing heavy penalties for rhinoceros poaching. 14 years later, in 1968, the state government passed 'The Assam National Park Act of 1968', and in 1974 Kaziranga was given the title Kaziranga National Park.[1] In 1985, UNESCO declared Kaziranga a World Heritage Site for its unique natural environment.[4]
Kaziranga has witnessed several natural and man-made calamities in recent decades. Floods caused by overflowing of river Brahmaputra have led to significant losses in animal life. Encroachment by humans along the periphery has also led to a diminished forest cover and a loss of habitat.[5]
The park celebrated its centenary with much fanfare in 2005, inviting descendants of Lord Curzon for the celebrations.[3]
Geography
Kaziranga locates between latitudes 26°30' N and 26°45' N, and longitudes 93°08' E to 93°36' E within two districts in the Indian state of Assam—the Kaliabor subdivision of Nagaon district and the Bokakhat subdivision of Golaghat district.[4]
Approximately 40 km (25 mi) in length from east to west, Kaziranga spans 13 km (8 mi) from north to south. Kaziranga covers an area of 378 km² (146 sq mi), with approximately 51.14 km² (20 sq mi) lost to erosion in recent years.[6] A total addition of 429 km² (166 sq mi) along the present boundary of the park has been made and notified with separate national park status to provide extended habitat for increasing population of wildlife or as a corridor for safe movement of animals to Karbi Anglong Hills.[7] Elevation ranges from 40 m (131 ft) to 80 m (262 ft).[4] the Brahmaputra River circumscribes the park area, forming the northern and eastern boundaries, while the Mora Diphlu forms the southern boundary. The Diphlu and Mora Dhansiri flow within the park.[5]
Kaziranga has flat expanses of fertile, alluvial soil formed by erosion and silt deposition by the Brahmaputra. The landscape consists of exposed sandbars, riverine flood-formed lakes known as beels (which make up 5 percent of the surface area),[4] and elevated regions known as chapories which provide shelter for animals during floods. Many artificial chapories have been built with the help of the Indian Army for the animals' safety.[8][9] The park sits in the Indomalaya ecozone, and Brahmaputra Valley semi-evergreen forests of the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests biome and a frequently flooded variant of the Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands of the tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome comprise the dominant biomes of the region.
Climate
The park experiences three seasons: summer, monsoon, and winter. The winter season, between November and February, experiences mild and dry weather, with a mean high of 25 °C (77 °F) and low of 5 °C (41 °F).[4] During that season, beels and nallahs (water channels) dry up.[5] The summer season between March and May becomes hot, with temperatures reaching a high of 37 °C (99 °F).[4] During that season, animals usually gather near water bodies.[5] The rainy monsoon season lasts from June to September, giving Kaziranga most of its annual rainfall of 2,220 mm (87 in). During the peak months of July and August, three-fourths of the western region of the park submerge due to the rising water level of the Brahmaputra. The flooding causes most animals to migrate to elevated and forested regions outside the southern border of the park, such as the Mikir hills.[4] Occasional dry spells create problems as well, such as food shortages for the wildlife in the park.
Fauna

Kaziranga contains significant breeding populations of 35 mammalian species,[11] of which 15 are threatened as per the IUCN Red List.[4] The park has the distinction of being home to the world's largest population of the Great Indian One-Horned Rhinoceros,[4] Wild Asiatic Water Buffalo,[12] and Eastern Swamp Deer.[13] Significant populations of large herbivores include elephants, gaur, and sambar. Small herbivores include wild boar and hog deer.[4]
Kaziranga represents one of the few wild breeding areas outside Africa for multiple species of large cats such as Indian Tigers and Leopards. The Indian government declared Kaziranga a Tiger Reserve in 2006 and has the highest density of tigers in the world. Other felids include the Jungle Cat, Fishing Cat, and Leopard Cats.[11] Small mammals include the rare Hispid Hare, Indian Gray Mongoose, Small Indian Mongooses, Large Indian Civet, Small Indian Civets, Bengal Fox, Golden Jackal, Sloth Bear, Chinese Pangolin, Indian Pangolins, Hog Badger, Chinese Ferret Badgers and Particolored flying squirrels.[4] Nine of the 14 primate species found in India occur in the park.[3] The Assamese Macaque, Capped, Golden Langur, as well as the only ape found in India, the Hoolock Gibbon stand out.[11] Kaziranga's rivers constitute home to the endangered Ganges Dolphin.[4]
Kaziranga serves as home to a variety of migratory birds, water birds, predators, scavengers, and game birds. Birds such as the Lesser White-fronted Goose, Ferruginous Duck, Baer's Pochard duck, and Lesser Adjutant, Greater Adjutant, Black-necked Stork, and Asian Openbill stork migrate from Central Asia to the park during winter. Riverine birds include the Blyth's Kingfisher, White-bellied Heron, Dalmatian Pelican, Spot-billed Pelican, Spotted Greenshank and Black-bellied Tern. Birds of prey include the rare Eastern Imperial, Greater Spotted, White-tailed, Pallas's Fish Eagle, Grey-headed Fish Eagle, and the Lesser Kestrel.[14]
Kaziranga was once home to seven species of vultures that nearly reached extinction, possibly by feeding on animal carcasses containing the drug Diclofenac. Only the Indian Vulture, Slender-billed Vulture, and Indian White-rumped Vulture have survived.[15] Game birds include the Swamp Francolin, Bengal Florican and Pale-capped Pigeon.[14]
Other families of birds inhabiting Kaziranga include the Great Indian Hornbill and Wreathed Hornbill, Old World babblers such as Jerdon’s and Marsh Babblers, weaver birds such as the common Baya Weaver, threatened Finn's Weavers, thrushes such as Hodgson's Bushchat and Old World warblers like the Bristled Grassbird. Other threatened species include Black-breasted Parrotbill and the Rufous-vented Prinia.[14]
Two of the largest snakes in the world, the Reticulated Python and Rock Python, as well as the longest venomous snake in the world, the King Cobra, inhabit the park. Other snakes include the Indian Cobra, Russell's Viper, and the Common Krait. Monitor lizard species include the Bengal monitor and the Water Monitor. Other reptiles include 15 species of turtle, such as the endemic Assam Roofed Turtle and one species of tortoise, the Brown Hill Tortoise.[16]
At least 42 species of fish live in the area including the Tetraodon.[17]
Flora
Four main types of vegetation types exist in the park: alluvial inundated grasslands, alluvial savanna woodlands, tropical moist mixed deciduous forests and tropical semi-evergreen forests.
A difference in altitude exists between the eastern and western areas, with the western side at a lower altitude. Grasslands dominate the western reaches of the park. Tall elephant grass grows on higher ground, while short grasses cover the lower grounds surrounding the beels or flood-created ponds.[4] Annual flooding, grazing by herbivores and controlled burning maintains and fertilizes the grasslands and reeds. sugarcanes, spear grass, Elephant Grass and the Common Reed comprise the common tall grasses. Numerous forbs grow along with the grasses. Trees—dominant species including Kumbhi, Indian gooseberry, the cotton tree (in savanna woodlands), and Elephant apple (in inundated grasslands) scatter amidst the grasses, providing cover and shade.[4]
Thick evergreen forests, near the Kanchanjhuri, Panbari and Tamulipathar blocks, contain trees such as Aphanamixis polystachya, Talauma hodgsonii, Dillenia indica, Garcinia tinctoria, Ficus rumphii, Cinnamomum bejolghota, and species of Syzygium. Tropical semi-evergreen forests thrive near Baguri, Bimali and Haldibari. Albizia procera, Duabanga grandiflora, Lagerstroemia speciosa, Crateva unilocularis, Sterculia urens, Grewia serrulata, Mallotus philippensis, Bridelia retusa, Aphania rubra, Leea indica and Leea umbraculifera number among the common trees and shrubs.[18]
Many different aquatic floras grow in the lakes, ponds and along the river shores. The ubiquitous invasive Water Hyacinth often chokes the water bodies, clears during destructive floods.[4] Kaziranga staff, with help from the Wildlife Trust of India, cleared another invasive species, Mimosa invisa, toxic to herbivores, in 2005.[19]
Administration
The Wildlife wing of the forest department of the Government of Assam bears responsibility for the administration and management of Kaziranga, headquartered at Bokakhat.[5] The administrative head, a conservator-level officer, serves as the park the director. A divisional forest officer serves as the administrative chief executive of the park, assisted by two officers with the rank of assistant conservator of forests. The park area divides into four ranges, overseen by range forest officers. The four ranges, the Burapahar, Baguri, Central, and Eastern, maintain headquarters at Ghorakati, Baguri, Kohora, and Agoratoli, respectively. Each range further sub-divides into beats, headed by a forester, and sub-beats, headed by a forest guard.[5]
The park receives financial aid from the State Government as well as the Ministry of Environment and Forests of Government of India under various Plan and Non-Plan Budgets. The Central Government provides additional funding under the Project Elephant. In 1997–1998, the park received a grant of US$ 100,000 under the Technical Co-operation for Security Reinforcement scheme from the World Heritage Fund.[9] National & international Non-governmental organizations provide additional funding.
Conservation management
Kaziranga National Park has been granted maximum protection under the Indian law for wildlife conservation. Various laws, including the Assam Forest Regulation of 1891 and the Biodiversity Conservation Act of 2002, have been enacted for protection of wildlife in the park.[9] Poaching activities, particularly of the rhinoceroses for its horn, has been a major concern for the authorities. Between 1980 and 2005, poachers killed 567 rhinoceroses.[5] Following a decreasing trend for the past few years, poachers killed six one-horned rhinoceroses in early 2007. Reports have suggested links between those poaching activities and funding of Islamic militant groups in Bangladesh connected to Al Qaida.[20]
Preventive measures such as construction of anti-poaching camps and maintenance of existing ones, patrolling, intelligence gathering and control over the use of firearms around the park have reduced the number of casualties.
Perennial flooding and heavy rains have resulted in death of wild animals and damage to the conservation infrastructures.[7] To escape the water-logged areas, many animals migrate to elevated regions outside the park boundaries, making them susceptible to hunting, hit by speeding vehicles, or subject to reprisals by villagers for damaging their crops. To mitigate the losses, the authorities have increased patrols, purchased additional speedboats for patrol, and created artificial highlands for shelter.[21] Several corridors have been set up for the safe passage of animals across National Highway–37 which skirts around the southern boundary of the park.[22] To prevent the spread of diseases and maintain the genetic distinctness of the wild species, the park management take systematic steps periodically such as immunization of livestock in surrounding villages, and fencing of sensitive areas of the park susceptible to encroachment by local cattle.
Water pollution due to run-offs from pesticides from tea gardens, and a petroleum refinery at Numaligarh, pose a hazard to the ecology of the region.[5] Invasive species such as Mimosa and wild rose have posed a threat to the native plants in the region. Regular manual uprooting, weeding, and research on biological methods for controlling weeds before seed settling controls the growth and irradiation of invasive species. The park administration uses grassland management techniques, such as controlled burning annually to avoid forest fires.[4]
Visitor activities
Observing the wildlife, including birding, constitutes the main visitor activity in and around the park. The park management allow only elephant or jeep tours; hiking has been prohibited to avoid attacks by animals. Observation towers, situated at Sohola, Mihimukh, Kathpara, Foliamari and Harmoti, provide wildlife viewing. The Lower Himalayan peaks frame the park's landscape of trees and grass interspersed with numerous ponds. The park remains closed for visitors from mid-April to mid-October due to monsoon rains. The Department of Environment and Forests, Government of Assammaintain four tourist lodges at Kohora and three tourist lodges inside the park. Private resorts operate outside the park borders.[7] Increased tourism has brought an improvement in the standard of living for people living on the fringes of the park.
Transport
Authorized forest department guides accompany all travellers inside the park. Visitors book Mahout-guided elephant rides and Jeep or other four-wheel drive vehicles rides in advance. Starting from the Park Administrative Centre at Kohora, those rides follow the three roadways under the jurisdiction of three ranges—Kohora, Bagori and Agaratoli. Those trails accept light vehicles from November to mid May. Visitors may bring in their own vehicles only when accompanied by guides.
Buses owned by Assam State Transport Corporation and private agencies between Guwahati, Tezpur and Upper Assam stop at the main gate of Kaziranga on NH-37 at Kohora. Major cities nearby include Guwahati (217 kilometers (135 mi)) and Jorhat (97 kilometers (60 mi)). Furkating 75 kilometers (47 mi), under the supervision of Northeast Frontier Railway, has the nearest railway station. Jorhat Airport at Rowriah (97 kilometers (60 mi) away), Tezpur Airport at Salonibari (approx 100 kilometers (62 mi) away) and Lokpriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport in Guwahati (approximately 217 kilometers (135 mi) away) provide the closest airports.[23]
In popular culture
Kaziranga has been the theme, or has been mentioned in, several books, documentaries, and songs. The park first gained prominence after Robin Banerjee (a doctor turned photographer and filmmaker) produced a documentary titled Kaziranga, airing on Berlin television in 1961 and became a runaway success. American science fiction and fantasy author, Lyon Sprague de Camp wrote about the park in his poem, "Kaziranga, Assam," first published in 1970 in Demons and Dinosaurs, a poetry collection, and reprinted as "Kaziranga" in Years in the Making: the Time-Travel Stories of L. Sprague de Camp in 2005.[24]
Kaziranga Trail (Children's Book Trust, 1979), a children's storybook by Arup Dutta about rhinoceros poaching in the national park, won the Shankar's Award.[25] The Assamese singer Bhupen Hazarika refers to Kaziranga in one of his songs.[13] The BBC conservationist and travel writer Mark Shand authored a book and the corresponding BBC documentary Queen of the Elephants, based on the life of the first female mahout in recent times—Parbati Barua of Kaziranga.[26] The book went on to win the 1996 Thomas Cook Travel Book Award and the Prix Litteraire d'Amis, providing publicity simultaneously to the profession of mahouts, and to Kaziranga.
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 History about Kaziranga Kaziranga National Park. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ↑ Karbis of Assam. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Subir Bhaumik, Kaziranga's centenary celebrations BBC News, February 18, 2005. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 4.14 4.15 Kaziranga National Park UNESCO. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 V.B. Mathur, P.R. Sinha, and Manoj Mishra, Technical Report #4 UNESCO. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ↑ P. Lahan and R. Sonowal, "Kaziranga WildLife Sanctuary, Assam. A brief description and report on the census of large animals." Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 70(2) (March 1972): 245–277.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Section II: Periodic Report on the State of Conservation of Kaziranga National Park, India UNESCO. Retrieved April 6, 2023.
- ↑ Kaziranga National Park WildPhotoToursIndia. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 State of Conservation of the World Heritage Properties in the Asia-Pacific Region –Kaziranga National Park UNESCO. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ↑ Subir Bhaumik, Assam rhino poaching 'spirals' BBC News, April 17, 2007. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Kaziranga Mammals Kaziranga Tourism. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ↑ 'Wild buffalo census in Kaziranga', The Rhino Foundation for Nature in NE India, Newsletter No. 3, June 2001.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Parbina Rashid, Here conservation is a way of life The Tribune, August 28, 2005. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 M. Barua and P. Sharma, Birds of Kaziranga National Park, India Forktail 15 (1999): 47-60. Retrieved April 6, 2023.
- ↑ R. Cuthbert, R.E. Green, et al., "Rapid population declines of Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus) and red-headed vulture (Sarcogyps calvus) in India," Animal Conservation 9(3): 349–354.
- ↑ https://www.kazirangatourism.com/reptiles.html Kaziranga Tourism. Retrieved April 6, 2023.
- ↑ N. K Vasu, Fish Species Recorded in Kaziranga National Park 'Management Plan of Kaziranga National Park. Retrieved April 6, 2023.
- ↑ S.K. Jain and A.R.K. Sastry, Botany of some tiger habitats in India Botanical Survey of India, 1983. Retrieved April 6, 2023.
- ↑ Joseph Vattakkavan, N. K. Vasu, Surendra Varma, Nidhi Gureja, and Ambika Aiyadurai, Silent Stranglers, Eradication of Mimosas in Kaziranga National Park, Assam Wildlife Trust of India, 2005. Retrieved April 6, 2023.
- ↑ Poachers kill Indian Rhino, New York Times,, April 17, 2007.
- ↑ Kaziranga National Park: Factors affecting the property in 1997 UNESCO. Retrieved April 5, 2023.
- ↑ B.S. Bonal & S. Chowdhury, Evaluation of barrier effect of National Highway 37 on the wildlife of Kaziranga National Park and suggested strategies and planning for providing passage: A feasibility report to the Ministry of Environment & Forests. (Government of India, 2004).
- ↑ Kaziranga National Park. Retrieved April 6, 2023
- ↑ L. Sprague de Camp, Years In The Making: The Time-Travel Stories Of L. Sprague De Camp (Nesfa Press, 2005, ISBN 978-1886778474).
- ↑ Meena Khorana, The Indian Subcontinent in Literature for Children and Young Adults (Greenwood Press, 1991, ISBN 0313254893).
- ↑ Mark Shand, Queen of the Elephants. (Random House, 1996, ISBN 0099592010).
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Barthakur, Ranjit, and Bittu Sahgal. The Kaziranga Inheritance. Mumbai: Sanctuary Asia, 2005. ISBN 9788175255777
- Choudhury, Anwaruddin. The Birds of Assam. Guwahati: Gibbon Books and World Wide Fund for Nature, 2000. ISBN 9788190086615
- de Camp, L. Sprague. Years In The Making: The Time-Travel Stories Of L. Sprague De Camp. Nesfa Press, 2005. ISBN 978-1886778474
- Dutta, Arup Kumar. Kaziranga Trail. Children's Book Trust, India, 1979. ISBN 0861443799
- Dutta, Arup Kumar. Unicornis: The Great Indian One Horned Rhinoceros. New Delhi: Konark Publication, 1991. ISBN 9788122002188
- Khorana, Meena. The Indian Subcontinent in Literature for Children and Young Adults: An Annotated Bibliography of English-Language Books. Greenwood Press, 1991. ISBN 0313254893
- Oberai, C.P. Kaziranga: The Rhino Land. : New Delhi: B.R. Publishing, 2002. ISBN 9788176462594
- Shand, Mark. Queen of the Elephants. Random House, 1996. ISBN 0099592010
External links
All links retrieved April 2, 2023.
- Kaziranga National Park
- Kaziranga National Park UNESCO
- Kaziranga National Park Government Of Assam
| |||||||
| Andaman & Nicobar Islands | Campbell Bay • Galathea • Mahatma Gandhi • Mt. Harriet Island • Middle Button Island • North Button Island • Rani Jhansi • Saddle Peak • South Button Island |
| Andhra Pradesh | Kasu Brahmananda Reddy • Mahavir Harina Vanasthali • Mrugavani • Sri Venkateswara) |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Mouling • Namdapha |
| Assam | Dibru-Saikhowa • Kaziranga • Manas Nameri • Orang |
| Bihar | Valmiki |
| Chhattisgarh | Indravati • Kanger Ghati |
| Goa | Mollem |
| Gujarat | Blackbuck • Gir • Gulf of Kutch • Vansda |
| Haryana | Kalesar • Sultanpur |
| Himachal Pradesh | Great Himalayan • Pin Valley |
| Jammu & Kashmir | Dachigam • Hemis • Kishtwar • Salim Ali |
| Jharkhand | Betla |
| Karnataka | Anshi • Bandipur • Bannerghatta • Kudremukh • Nagarhole |
| Kerala | Eravikulam • Mathikettan Shola • Periyar • Silent Valley |
| Madhya Pradesh | Bandhavgarh • Fossil • Kanha • Madhav • Panna • Pench Sanjay • Satpura • Van Vihar |
| Maharastra | Chandoli • Gugamal • Navegaon • Pench • Sanjay Gandhi • Tadoba |
| Manipur | Keibul Lamjao • Sirohi |
| Meghalaya | Balphakram • Nokrek |
| Mizoram | Murlen • Phawngpui |
| Nagaland | Intanki |
| Orissa | Bhitarkanika • Simlipal |
| Rajasthan | Darrah • Desert • Keoladeo • Ranthambhore • Sariska |
| Sikkim | Khangchendzonga |
| Tamil Nadu | Guindy • Gulf of Mannar • Indira Gandhi • Palani Hills • Mudumalai • Mukurthi |
| Uttar Pradesh | Nawabganj • Dudhwa |
| Uttarakhand | Corbett • Gangotri • Govind • Nanda Devi • Rajaji • Valley of Flowers |
| West Bengal | Buxa • Gorumara • Neora Valley • Singalila • Sundarbans |
| National Parks • Protected areas of India • Ministry of Environment and Forests (India) | |
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.