Ohio
Template:US state
Ohio is a Midwestern state of the United States of America. Part of the Great Lakes region, Ohio has long been a cultural and geographical crossroads. At the time of European contact and in the years which followed, Native Americans in today's Ohio included the Iroquois, Miamis, and Wyandots. Beginning in the 1700s, the area was settled by people from New England, the Middle States, Appalachia, and the upper south.
Prior to 1984, the United States Census Bureau considered Ohio part of the North Central Region. That region was renamed "Midwest" and split into two divisions. Ohio is now in the East North Central States division. Ohio also has the highest density of population of any state not on the Atlantic Ocean.
Ohio was the first state admitted to the Union under the Northwest Ordinance. Its U.S. postal abbreviation is OH; its old-style abbreviation was O. Natives of Ohio are known as Ohioans.
Etymology
The name Ohio is an Iroquoian Indian word. It is from the Seneca nation who inhabited the area before westward expansion of Europeans. "Ohiyo" was the Seneca name used for both the Ohio and Allegheny Rivers, and meant beautiful river.
History
The history of human habitation in the area that eventually became Ohio can be traced back more than 10,000 years from evidence of flint tools known as Clovis points. The first evidence of farming cultures, the Woodland culture, dates back 2,000 to 3,000 years. The Hopewell culture was characterized by small agricultural villages grouped around major ceremonial sites like the Newark Earthworks, believed to be two thousand year old burial mounds. Later groups left evidence of changing village cultures, and the spread of agriculture.
Native Americans

Much of the region was claimed in the 1600s by invaders from the powerful Iroquois confederation. After depleting the fur-bearing animals, particularly beaver, in their territory, the Iroquois sought to expand their control of more lands to sustain their lucrative fur trade with the European explorers and traders. This era was known as the Beaver Wars and, along with epidemics, resulted in the emptying of the Ohio region of its indigenous people by the mid-to-late seventeenth century.
The land gradually became repopulated by the mostly Algonquian-speaking descendants of its ancient inhabitants, that is, descendants of the Adena, Hopewell, and Mississippian cultures. Many of these Ohio-country nations were multi-ethnic and sometimes multi-linguistic societies emerging from the earlier devastation brought about by disease and subsequent social instability. They subsisted on agriculture (corn, sunflowers, beans, etc.) supplemented by seasonal hunts. By the 1650s they were part of a larger global economy brought about by fur trade.
The early inhabitants of the area included the
- Erie tribe (who were gradually absorbed into the new, multi-ethnic "republics," namely the Wyandot)
- Shawnee tribe (also pushed west, although they may be descended from the Fort Ancient people of Ohio)
- Kickapoo (an offshoot of the Shawnee tribe - ("Kickapoo" is thought to be a corruption of a Shawnee word for "wanderers")
Additional tribes that moved into the area after European arrival on the continent, though most clearly after 1700, included
- Miamis (a large confederation)
- Wyandots (made up of refugees, especially from the fractured Huron confederacy)
- Delawares (pushed west from their historic homeland in New Jersey),
- Ottawas (more commonly associated with the upper Great Lakes region)
- Ohio Seneca tribe, predominantly Mingo, who like the Wyandot were a recently-formed composite of refugees from Iroquois and other societies)
Colonial and Revolutionary Eras
During the 18th century, the France set up a system of trading posts to control the fur trade in the region.
In 1754, France and Great Britain fought a war known in the United States as the French and Indian War. As a result of the Treaty of Paris, the French ceded control of Ohio and the rest of the Old Northwest to Great Britain. Pontiac's Rebellion in the 1760s challenged British military control, which ended with the American victory in the American Revolution. In the Treaty of Paris in 1783 Britain ceded all claims to Ohio to the United States.
Northwest Territory: 1787-1803
The United States created the Northwest Territory under the Northwest Ordinance of 1787. Slavery was not permitted. Settlement began with the founding of Marietta by the Ohio Company of Associates, which had been formed by a group of American Revolutionary War veterans. Following the Ohio Company, the Miami Company (also referred to as the "Symmes Purchase") claimed the southwestern section and the Connecticut Land Company surveyed and settled the Connecticut Western Reserve in present-day Northeast Ohio. The old Northwest Territory originally included areas that had previously been known as Ohio Country and Illinois Country. As Ohio prepared for statehood, Indiana Territory was created, reducing the Northwest Territory to approximately the size of present-day Ohio plus the eastern half of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan and the eastern tip of the Upper Peninsula.
Under the Northwest Ordinance, states to be formed out of the Northwest Territory would be granted statehood when the population exceeded 60,000. Although Ohio's population numbered only 45,000 in December 1801, Congress determined that the population was growing rapidly and would exceed 60,000 by the time it became a state. On February 19, 1803, President Jefferson signed an act of Congress approving Ohio's boundaries and constitution. However, Congress never passed a resolution formally admitting Ohio as the 17th state. The current custom of Congress declaring an official date of statehood did not begin until 1812, with Louisiana's admission as the 18th state. When the oversight was discovered in 1953, Ohio's Rep. George H. Bender introduced a bill in Congress to admit Ohio to the Union retroactive to March 1, 1803. At a special session at the old state capital in Chillicothe, the Ohio state legislature approved a new petition for statehood that was delivered to Washington, DC on horseback. On August 7, 1953, (the year of Ohio's 150th anniversary), President Eisenhower signed an act officially declaring Ohio's admittance into the Union.
Statehood: 1803 - present
Eight U.S. presidents hailed from Ohio at the time of their elections, giving rise to the nickname "Mother of Presidents," a distinction it shares with Virginia. Seven presidents were born in Ohio, making it second to Virginia's eight, but Virginia-born William Henry Harrison and his grandson, Benjamin Harrison, (who also lived part of his adult life in Indiana) settled in, led their political careers from, and/or were buried in North Bend, Ohio on the family compound, founded by William's father-in-law, John Cleves Symmes.
In 1835, Ohio fought a mostly bloodless boundary war with Michigan over the Toledo Strip known as the Toledo War. Congress intervened and, as a condition for admittance as a state of the Union, Michigan was forced to accept the western two-thirds of the Upper Peninsula, in addition to the eastern third that was already part of the state, in exchange for giving up its claim to the Toledo Strip.
Ohio's central position and its rapidly growing population gave it an important place during the Civil War. The Ohio River, the border between Ohio and West Virginia, was a vital artery for troop and supply movements, as were Ohio's railroads. By the end of the Civil War, three leading Union generals were from Ohio: Grant, Sherman, and Sheridan. Ohio also contributed more soldiers per-capita than any other state in the Union.
In 1912 a Constitutional Convention was held with Charles B. Galbreath as Secretary. The result reflected the concerns of the Progressive Era. It introduced the initiative and the referendum, allowed the General Assembly to put questions on the ballot for the people to ratify laws and constitutional amendments originating in the Legislature as well. Under the Jeffersonian principle that laws should be reviewed once a generation, the constitution provided for a recurring question to appear on Ohio's general election ballots every 20 years. The question asks whether a new convention is required. Although the question has appeared in 1932, 1952, 1972, and 1992, it has never been approved. Instead constitutional amendments have been proposed by petition to the legislature hundreds of times and adopted in a majority of cases.
Law and government
Ohio's capital is Columbus, located close to the center of the state. Governor Ted Strickland took office as governor in January 2007. Ohio is represented by two US Senators, and has 18 seats in the US House of Representatives.
State government is headed by a term-limited Governor, elected to a four year term. The Ohio General Assembly is made up of the House of Representatives with 99 Representatives, term-limited to four successive two-year terms, and the Senate, with 33 term-limited members.
The State Supreme Court has seven Justices, elected to a six year term. The positions are not term-limited, but are age dependent; Justices serve until 70 years of age.
Geography

Ohio's geographic location has proved to be an asset for economic growth and expansion. Because Ohio links the Northeast to the Midwest, much cargo and business traffic passes through its borders on its well-developed highway system. Ohio has the nation's 10th largest highway network, and is within a one-day drive of 50% of North America's population and 70% of North America's manufacturing capacity. To the north, Lake Erie gives Ohio 312 miles (502 km) of coastline, which allows for numerous ports.
Ohio's borders were defined by metes and bounds in the Enabling Act of 1802. Ohio is bounded by the Ohio River, but the river itself belongs mostly to Kentucky and West Virginia. The finalized border with Michigan changed, as a result of the Toledo War, to angle slightly northeast to the north shore of the mouth of the Maumee River. Ohio's southern border is thus defined by the Ohio River (with the border being at the 1793 low-water mark on the north side of the river), with much of its northern border is defined by Lake Erie. Ohio's neighbors are Pennsylvania to the east, Michigan to the northwest, Ontario, Canada, to the north, Indiana to the west, Kentucky to the south, and West Virginia to the southeast.
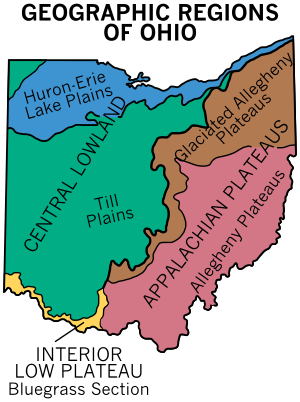
Much of Ohio features glaciated plains, with an exceptionally flat area in the northwest known as the Great Black Swamp. This glaciated region in the northwest and central state is bordered to the east and southeast first by a belt known as the glaciated Allegheny Plateau, and then by another belt known as the unglaciated Allegheny Plateau. Most of Ohio is of low relief, but the unglaciated Allegheny Plateau features rugged hills and forests.
The rugged southeastern quadrant of Ohio, stretching in an outward bow-like arc along the Ohio River from the West Virginia Panhandle to the outskirts of Cincinnati, forms a distinct socio-economic unit. Known somewhat erroneously as Ohio's "Appalachian Counties" (they are actually in the Allegheny Plateau), this area's coal mining legacy, dependence on small pockets of old manufacturing establishments, and even distinctive regional dialect set this section off from the rest of the state and, unfortunately, create a limited opportunity to participate in the generally high economic standards of Ohio. In 1965 the United States Congress passed the Appalachian Regional Development Act, an attempt to "address the persistent poverty and growing economic despair of the Appalachian Region." This act defines 29 Ohio counties as part of Appalachia. While 1/3 of Ohio's land mass is part of the federally defined Appalachian region, only 12.8% of Ohioans live there (1.476 million people.)
Significant rivers within the state include the Cuyahoga River, Great Miami River, Maumee River, Muskingum River, and Scioto River. The rivers in the northern part of the state drain into the northern Atlantic Ocean via Lake Erie and the St. Lawrence River, and the rivers in the southern part of the state drain into the Gulf of Mexico via the Ohio and then the Mississippi. The worst weather disaster in Ohio history occurred along the Great Miami River in 1913. Known as the Great Dayton Flood, the entire Miami River watershed flooded, including the downtown business district of Dayton. As a result, the Miami Conservancy District was created as the first major flood plain engineering project in Ohio and the United States.
Grand Lake St. Marys in the west central part of the state was constructed as a supply of water for canals in the canal-building era of 1820–1850. For many years this body of water, over 20 square miles (52 km²), was the largest artificial lake in the world. Ohio's canal-building projects promoted economic development; some cities, like Dayton, owe their industrial emergence to location on canals. As late as 1910, interior canals carried much of the bulk freight of the state.
Climate
The climate of Ohio is a humid continental climate (Koppen climate classification Dfa) throughout most of the state except the extreme southern counties of Ohio's Bluegrass region section that are located on the northern periphery of the humid subtropical climate and Upland South region of the United States. Summers are hot and humid throughout Ohio, while winters are generally cool to cold. Temperature ranges, north to south in the state, from 80 to 86° F (27 to 30° C) and 25 to 39° F (4 to -1° C) Precipitation is moderate year-round, around 32 to 42 inches (810 to 1070 mm). Severe weather is not uncommon in the state as it is a battleground between cold Arctic air and warm Gulf air for much of the year, although there are fewer tornadoes in Ohio than in states to the west. Severe lake effect snowstorms are also not uncommon along the southeast shore of Lake Erie, which also provides a moderating effect on the climate there.
Although predominantly not in a subtropical climate, some warmer-climate flora and fauna does reach well into Ohio. Evidencing this climatic transition from a subtropical to continental climate, several plants such as the Southern magnolia, Albizia julibrissin(mimosa), Crape Myrtle, and even the occasional Needle Palm are hardy landscape materials regularly used as street, yard, and garden plantings in the Bluegrass region of Ohio; these same plants do not thrive in much of the rest of the State.
Records
The highest recorded temperature was 113 °F (45 °C), near Gallipolis on July 21 1934. The lowest recorded temperature was -39 °F (-39 °C), at Milligan on February 10 1899.
Important cities
City and metropolitan data are from the US Census Bureau's 2006 estimates.
- Akron city 209,704, metropolitan area 700,943
- Canton city 78,924, metropolitan area 409,764
- Cincinnati city 332,252, metropolitan area 2,104,218
- Cleveland city 444,313, metropolitan area 2,114,155
- Columbus city 733,203, metropolitan area 1,725,570
- Dayton city 156,771, metropolitan area 838,940
- Toledo city 298,446, metropolitan area 653,695
- Youngstown city 81,520, metropolitan area 586,939
Note: The Cincinnati metropolitan area extends into Kentucky and Indiana, and the Youngstown metropolitan area extends into Pennsylvania.
- Toledo Ohio skyline.jpg
View of downtown Toledo.
Economy
Ohio is a major producer of machines, tires and rubber products, steel, processed foods, tools, and other manufactured goods. This is not immediately obvious because Ohio specializes in capital goods (goods used to make other goods, like machine tools, automobile parts, industrial chemicals, and plastic moldings). Nevertheless, there are well known Ohio consumer items including some Procter & Gamble products, Smuckers jams and jellies, and Day-Glo paints.
The airplane was invented in Ohio, as the outcome of brothers Wilbur and Orville Wright's experiments in Dayton. Commercial production of aircraft in the USA has left the state, but a large military experimental and design facility, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base located near Dayton, serves in the co-ordination of production of US military aircraft. Many of the Wright brothers' earliest aerodynamic experiments took place in what is now the military base, Wright Hill and Huffman Prairie. Ohio has many aerospace, defense, and NASA parts and systems suppliers scattered throughout the state as well.
As part of the Corn Belt, agriculture also plays an important role in the state's economy. There is also a small commercial fishing sector on Lake Erie, and the principal catch is yellow perch. In addition, Ohio's historical attractions, varying landscapes, and recreational opportunities are the basis for a thriving tourist industry. Over 2,500 lakes and 43,000 miles (70,000 km) of river landscapes attract boaters, fishermen, and swimmers. Three major amusement parks, Cedar Point, Geauga Lake, and Kings Island, are also important to the tourism industry. Of special historical interest are the Native American archaeological sites—including grave mounds and other sites.
The Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that Ohio's gross state product in 2004 was $419 billion[1]. Per capita personal income in 2003 was $30,129, 25th in the nation. Ohio's agricultural outputs include soybeans, dairy products, corn, tomatoes, hogs, cattle, poultry, and eggs. As of 2005, there were 76,500 farms in Ohio, covering over 14 million acres (56,656 km²). <ref: ohiohistorycentral.org> Its industrial outputs include transportation equipment, fabricated metal products, machinery, food processing, and electricity equipment. The largest companies in Ohio are in healthcare, grocery and food products, tire and rubber products, and insurance.
Ohio is recognized for its health care, due to several flagship hospitals that operate in the northeast region of the state. The Cleveland Clinic, ranked among the three leading hospitals in the U.S., has its world headquarters and main campus in Cleveland. Its rival, the University Hospitals of Cleveland health system, includes the Rainbow Babies and Children's Hospital, ranks among the top ten children's hospitals in the country.
Demographics
As of 2006, Ohio has an estimated population of 11,478,006, which is an increase of 7,321 from the prior year and an increase of 124,861 since the year 2000. This includes a natural increase since the last census of 263,004 people (that is 938,169 births minus 675,165 deaths) and a decrease from net migration of -145,718. Immigration from outside the United States contributed of a growth of 92,101 people, most coming from Asia, yet net migration within the country resulted in a decrease of 237,819 people. Ohio has witnessed an increase in the Laotian American and Thai American populations, as well as Asian Indians and Latin Americans.
The center of population of Ohio is in Morrow County, in the county seat of Mount Gilead.
| Demographics of Ohio (csv) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By race | White | Black | AIAN | Asian | NHPI |
| AIAN is American Indian or Alaskan Native - NHPI is Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander | |||||
| 2000 (total population) | 86.83% | 12.18% | 0.67% | 1.41% | 0.06% |
| 2000 (Hispanic only) | 1.70% | 0.19% | 0.05% | 0.02% | 0.01% |
| 2005 (total population) | 86.27% | 12.66% | 0.66% | 1.68% | 0.07% |
| 2005 (Hispanic only) | 2.05% | 0.20% | 0.05% | 0.03% | 0.01% |
| Growth 2000-2005 (total population) | 0.32% | 4.98% | -1.57% | 20.32% | 9.32% |
| Growth 2000-2005 (non-Hispanic only) | -0.11% | 4.97% | -1.96% | 20.48% | 11.15% |
| Growth 2000-2005 (Hispanic only) | 22.11% | 5.70% | 3.04% | 10.81% | -0.26% |
As of 2004, Ohio's population included about 390,000 foreign-born (3.4%).
The largest ancestry groups in Ohio are German (25.2%), Irish (12.7%), African American (11.5%), English (9.2%), American (8.5%), and Italian (6.0%).
German is the largest reported ancestry in most of the counties in Ohio, especially in the northwest. Ohioans who cited American and British ancestry are present throughout the state as well, particularly in the south-central part of the state. The cities of Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Dayton have large African-American communities. The cities of Cleveland and Toledo have sizable Hispanic populations, while the Cleveland and Columbus areas have the largest Asian populations. Greater Cleveland is home to a notably large Jewish community.
6.6% of Ohio's population were reported as under 5, 25.4% under 18, and 13.3% were 65 or older. Females made up approximately 51.4% of the population.
File:Ohio population map.png Ohio Population Density Map |
File:Population Growth Ohio.png Population Growth in Ohio |
Political demographics and history
"Ohio has excelled as a recruiting-ground for national political leaders. Between the Civil War and 1920, seven Ohioans were elected to the presidency, ending with Harding's election in 1920. At the same time, six Ohioans sat on the US Supreme Court and two served as Chief Justices....'Not since the Virginia dynasty dominated national government during the early years of the Republic' notes historian R. Douglas Hurt, 'had a state made such a mark on national political affairs.'
Politically, Ohio is considered a swing state. The Economist notes that, "This slice of the mid-west contains a bit of everything American—part north-eastern and part southern, part urban and part rural, part hardscrabble poverty and part booming suburb,"[1]
The mix of urban and rural areas, and the presence of both large blue-collar industries and significant white-collar commercial districts leads to a shifting balance of conservative and liberal population that (and the state's 20 electoral votes, more than most swing states) makes the state very important to the outcome of national elections. The state supported Democrat Bill Clinton in 1992 and 1996, but supported Republican George W. Bush in 2000 and 2004. Ohio was a deciding state in the 2004 presidential election between George W. Bush and John Kerry. Bush narrowly won the state's 20 electoral votes by a margin of 2 percentage points and 50.8% of the vote [2]. Ohio was also a deciding factor in the 1948 presidential election when Democrat Harry S. Truman defeated Republican Thomas Dewey (who had won the state four years earlier) and in the 1976 presidential election when Democrat Jimmy Carter defeated Republican Gerald Ford by a slim margin in Ohio and took the election.
Ohio's demographics cause many to consider the state as a microcosm of the nation as a whole. A Republican presidential candidate has never won the White House without winning Ohio, and Ohio has gone to the winner of the election in all but two contests since 1892, backing only losers Thomas E. Dewey in 1944 (Ohio's John Bricker was his running mate) and Richard M. Nixon in 1960. Consequently, the state is very important to the campaigns of both major parties.
The most solidly Democratic areas of the state are in the northeast, including Cleveland, Youngstown, Lorain/Elyria, and other industrial areas. Specifically, the core of this region includes eight counties stretching east along Lake Erie from Erie County to the Pennsylvania border and south to Mahoning County. Southwestern Ohio, especially the suburbs of Cincinnati, Warren County, Butler County, and Clermont County is particularly Republican.
Education
Ohio's system of public education is outlined in the state constitution's Article VI and Title XXXIII of the Ohio Revised Code. Ohio's system is substantially similar to other states'. Ohio has a Department of Education, a State Board of Education, and then nearly 700 districts that have their own boards of education and administrations. The Ohio Board of Regents governs and assists with Ohio's system of higher education, especially public colleges and universities.
Colleges and universities
- 13 state universities
- University of Akron, Akron, Ohio
- Bowling Green State University, Bowling Green, Ohio
- Central State University, Wilberforce, Ohio
- University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, Ohio
- Cleveland State University, Cleveland, Ohio
- Kent State University, Kent, Ohio
- Miami University, Oxford, Ohio
- Ohio University, Athens, Ohio
- Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio
- Shawnee State University, Portsmouth, Ohio
- University of Toledo, Toledo, Ohio
- Wright State University, Dayton, Ohio (Fairborn, Ohio)
- Youngstown State University, Youngstown, Ohio
- (note: the University of Dayton is not one of Ohio's state universities; it is a private, Roman Catholic university run by the Society of Mary)
- 24 state university branch and regional campuses
- 46 liberal arts colleges and universities
- 6 free-standing state-assisted medical schools
- University of Toledo College of Medicine (formerly Medical University of Ohio)
- Northeastern Ohio Universities College of Medicine
- Ohio State University College of Medicine and Public Health
- Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine
- University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
- Wright State University Boonshoft School of Medicine
- 2 private medical schools
- Ohio College of Podiatric Medicine
- Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine
- 15 community colleges
- 8 technical colleges
- over 24 independent non-profit colleges
Libraries
Ohio is home to some of the nation's highest-ranking public libraries. The 2006 study by Thomas J. Hennen Jr. ranked Ohio as number one in a state-by-state comparison. For 2006, Ohio's three largest library systems were all ranked in the top ten for American cities of 500,000 or more:
- Cuyahoga County Public Library (first)
- Columbus Metropolitan Library (third)
- The Public Library of Cincinnati and Hamilton County (eighth)
The Ohio Public Library Information Network (OPLIN) is an organization that provides Ohio residents with internet access to their 251 public libraries. OPLIN also provides Ohioans with free home access to high-quality, subscription research databases.
Ohio also offers the OhioLINK program, allowing Ohio's libraries (particularly those from colleges and universities) access to materials in other libraries. The program is largely successful in allowing researchers access to books and other media that might not otherwise be available.
Transportation
Several major east-west transportation corridors go through Ohio. One of those pioneer routes, known in the early 1900s as "Ohio Market Route 3," was chosen in 1913 to become part of the historic Lincoln Highway which was the first road across America, connecting New York City to San Francisco. In Ohio, the Lincoln Highway linked many towns and cities together across the state and had a major impact on the developing of the state. With the implementation of the federal numbered highway system in 1926, the Lincoln Highway through Ohio became U.S. Highway 30. Ohio also is home to 228 miles of the Historic National Road.
Ohio has a highly developed network of roads and interstate highways. Major east-west through routes include the Ohio Turnpike (I-80/I-90) in the north, I-76 through Akron to Pennsylvania, U.S. 30 (the Lincoln Highway) a bit further south through Canton, Mansfield, Lima, and Van Wert, I-70 through Columbus and Dayton, and the Appalachian Highway (Ohio 32) running from West Virginia to Cincinnati. Major north-south routes include I-75 in the west through Toledo, Dayton, and Cincinnati, I-71 through the middle of the state from Cleveland through Columbus and Cincinnati into Kentucky, and I-77 in the eastern part of the state from Cleveland through Akron, Canton, New Philadelphia and Marietta down into West Virginia. Interstate 75 between Cincinnati & Dayton is one of the heaviest section of traveled interstate in Ohio.
Air travel includes Cleveland Hopkins International Airport, which is a major hub for Continental Airlines, as well as Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport (located in the state of Kentucky), which is a major hub for Delta Air Lines. Other major airports are located in Dayton, Columbus, and Akron-Canton.
State symbols
- State animal: White-tailed Deer
- State bird: Cardinal
- State capital: Columbus
- State flower: Scarlet Carnation
- State wildflower: Large white trillium (Trillium grandiflorum)
- State insect: Ladybug Beetle
- State song: "Beautiful Ohio"
- State rock song: "Hang On Sloopy"
- State tree: Buckeye
- State fossil: Trilobite genus Isotelus
- State beverage: Tomato juice
- State reptile: Black racer snake
- State gemstone: Ohio Flint
- State motto: "With God all things are possible."
- Unofficial Motto 1: "The heart of it all!" Used on Ohio's license plates and welcome signs between the years 1991 and 2001.
- Unofficial Motto 2: "So much to discover." Adopted as part of state bicentennial campaign. Also used on welcome signs since 2001.
- Unofficial Motto 3: "Birthplace Of Aviation" Used on Ohio license plates and welcome signs since 2001. It also appears in Ohio's design for the 50 State Quarters program.
- The Ohio-class SSBN program and the first ship of the program, the USS Ohio (SSBN-726), were named after Ohio.
Notes
- ↑ " A grain of sand for your thoughts", The Economist, December 20 2005, retrieved December 23 2005.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Anderson, Sherwood. 1960. Winesburg, Ohio. New York: Viking Press. ISBN 0670000396 and ISBN 9780670000395
- Giblin, James, and Michael Dooling. 2006. The boy who saved Cleveland based on a true story. New York: Henry Holt. ISBN 0805073558 and ISBN 9780805073553
- Heinrichs, Ann. 1999. Ohio. America the beautiful. New York: Children's Press. ISBN 0516209957 and ISBN 9780516209951
- Hart, Joyce. 2006. Ohio. It's my state!. New York: Marshall Cavendish Benchmark. ISBN 0761419071 and ISBN 9780761419075
- Mithun, Marianne. 1999. Languages of Native North America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pg. 312
- Record Lowest Temperatures by State. NCDC. Retrieved November 21, 2007.
- Record Highest Temperatures by State. NCDC. Retrieved November 21, 2007.
- Annual Estimates of the Population for Incorporated Places in Ohio. Census.Gov. Retrieved November 21, 2007.
- Annual Estimates of the Population of Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas. Census.Gov. Retrieved November 21, 2007.
- Population and Population Centers by State. Census.Gov. Retrieved November 21, 2007.
- The American Mayor, Melvin G. Holli, Pennsylvania State University Press, 1999, Page 162. ISBN 0-271-01876-3.
External links
- United States Geological Survey. Science In Your Backyard: Ohio. Retrieved October 28, 2007.
- U.S. Census Bureau. Ohio. Retrieved October 28, 2007.
- United States Department of Agriculture. State Fact Sheets: Ohio. Retrieved October 28, 2007.
| Political divisions of the United States | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.