Difference between revisions of "Abortion" - New World Encyclopedia
(set up for import) |
(remove claim tag, imported as a demo) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | |
| + | {{Abortion}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--NOTE ABOUT INTRO: This is the product of extensive discussion between many Wikipedians. Please refer to Talk:Abortion/First paragraph and its archives before proposing — or making — any changes.—> | ||
| + | An '''abortion''' is the removal or expulsion of an [[embryo]] or [[fetus]] from the [[uterus]], resulting in or caused by its death. This can occur spontaneously as a [[miscarriage]], or be artificially induced by [[chemistry|chemical]], [[surgery|surgical]] or other means. Commonly, "abortion" refers to an induced procedure at any point during [[pregnancy]]; medically, it is defined as miscarriage or induced termination before twenty weeks' [[gestation]], which is considered [[Viability|nonviable]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Throughout [[History of abortion|history]] abortion has been induced by various methods. The [[Ethical aspects of abortion|moral]] and [[Abortion law|legal]] aspects of abortion are subject to intense [[Abortion debate|debate]] in many parts of the world. | ||
| + | <!--Note to editors: This article has a long and intense history of terminology debates. Please review the talk page before making changes to lines to see if there is a previous established consensus or compromise. Thank you.—> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Definitions== | ||
| + | The following medical terms are used to define abortion: | ||
| + | * ''Spontaneous abortion ([[miscarriage]])'': An abortion due to accidental trauma or [[Death by natural causes|natural causes]], such as chromosomal number discrepancy, early disease, or environmental factors. | ||
| + | *''Induced abortion'': Abortion deliberately caused. Induced abortions are further subcategorized into therapeutic, and elective: | ||
| + | **''Therapeutic abortion:''<ref>Roche, Natalie E. (2004). [http://www.emedicine.com/med/topic3311.htm Therapeutic Abortion]. Retrieved [[2006-03-08]].</ref> | ||
| + | *** To save the life of the pregnant woman. | ||
| + | *** To preserve the woman's physical or mental health. | ||
| + | *** To terminate pregnancy that would result in a child born with a [[congenital disorder]] which would be [[fatal]] or associated with significant [[morbidity]]. | ||
| + | *** To [[selective reduction|selectively reduce]] the number of [[fetus]]es to lessen health risks associated with [[multiple birth|multiple pregnancy]]. | ||
| + | **''Elective abortion'': Abortion performed for any other reason. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In common parlance, the term "abortion" is synonymous with induced abortion. However, in medical texts, the word 'abortion' can also refer to ''spontaneous abortion'' (miscarriage). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Incidence== | ||
| + | The incidence of, and reasons for induced abortion vary regionally. It has been estimated that yearly, approximately 46 million abortions are performed. Of these, 26 million are said to occur in [[abortion law|places where abortion is legal]]; the other 20 million happen where it is illegal . Some countries, such as [[Belgium]] (11.2 per 100 known pregnancies) and the [[Netherlands]] (10.6 per 100), have a low rate of induced abortion, while others like [[Russia]] (62.6 per 100) and [[Vietnam]] (43.7 per 100) have a comparatively high rate. The world ratio is 26 induced abortions per 100 known pregnancies.<ref>Henshaw, Stanley K., Singh, Susheela, & Haas, Taylor. (1999). [http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/25s3099.html The Incidence of Abortion Worldwide]. ''International Family Planning Perspectives, 25 (Supplement)'', 30–8. Retrieved [[2006-01-18]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===By gestational age and method=== | ||
| + | [[Image:UKAbortionbyGestationalAgeChart2004.png|thumb|right|220px|The percentage of abortions by [[gestational age|gestational development]] in [[England and Wales]] during 2004.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Abortion rates also vary depending upon stage of [[pregnancy]] and method practiced. In 2002, from data collected in those areas of the [[United States]] which sufficiently reported [[gestational age]], it was found that 86.7% of abortions were conducted at or prior to 12 weeks, 9.9% from 13 to 20 weeks, and 1.4% at or after 21 weeks. 91.3% percent of these were classified as having been done by "[[curettage]]" ([[Suction-aspiration abortion|suction-aspiration]], [[Dilation and curettage|D&C]], [[Dilation and evacuation|D&E]]), 5.2% by "[[medical abortion|medical]]" means ([[mifepristone]]), 0.8% by "[[instillation abortion|intrauterine instillation]]" ([[saline (medicine)|saline]] or [[prostaglandin]]), and 1.5% by "other" ([[hysterotomy abortion|hysterotomy]] and [[hysterectomy]]).<ref name="cdc2002">Strauss, Lilo T., Herndon, Joy, Chang, Jeani, Parker, Wilda Y., Bowens, Sonya V., Berg, Cynthia J. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. ([[2005-11-15]]). [http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/ss5407a1.htm Abortion Surveillance - United States, 2002]. ''Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report''. Retrieved [[2006-02-20]].</ref> The [[Guttmacher Institute]] estimated there were 2,200 [[intact dilation and extraction]] procedures in the U.S. during 2000; this accounts for 0.17% of the total number of abortions performed that year.<ref>Finer, Lawrence B. & Henshaw, Stanley K. (2003). [http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3500603.html Abortion Incidence and Services in the United States in 2000]. ''Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 35 (1).'' Retrieved [[2006-05-10]].</ref> Similarly, in [[England]] and [[Wales]] in 2004, 87.6% of terminations occurred at or under 12 weeks, 10.7% between 13 to 19 weeks, and 1.5% at or over 20 weeks. 76% of those reported were by vacuum aspiration, 4% by D&E, 19% by a chemical agent, and 1% by [[feticide]].<ref>Government Statistical Service for the Department of Health. ([[2005-07-27]]). [http://www.dh.gov.uk/PublicationsAndStatistics/Publications/PublicationsStatistics/PublicationsStatisticsArticle/fs/en?CONTENT_ID=4116461&chk=6T9UTA Abortion statistics, England and Wales: 2004]. Retrieved [[2006-05-10]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===By personal and social factors=== | ||
| + | [[Image:AGIAbortionReasonsBarChart.png|thumb|left|320px|A [[bar chart]] depicting selected data from the 1998 [[Alan Guttmacher Institute|AGI]] [[meta-study]] on the reasons women stated for having an abortion.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | A 1998 aggregated study, from 27 countries, on the reasons women seek to terminate their pregnancies concluded that common factors cited to have influenced the abortion decision were; desire to delay or end [[childbirth|childbearing]], concern over the interruption of [[employment|work]] or [[education]], issues of financial or relationship stability, and perceived immaturity.<ref name="bankole98">Bankole, Akinrinola, Singh, Susheela, & Haas, Taylor. (1998). [http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/2411798.html Reasons Why Women Have Induced Abortions: Evidence from 27 Countries]. ''International Family Planning Perspectives, 24 (3)'', 117-127 & 152. Retrieved [[2006-01-18]].</ref> A 2004 study in which [[United States|American]] women at [[abortion clinic|clinics]] answered a [[questionnaire]] yielded similar results.<ref name="finer2005">Finer, Lawrence B., Frohwirth, Lori F., Dauphinee, Lindsay A., Singh, Shusheela, & Moore, Ann M. (2005). [http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3711005.pdf Reasons U.S. women have abortions: quantative and qualitative perspectives]. ''Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 37 (3),'' 110-8. Retrieved [[2006-01-18]].</ref> In [[Finland]] and the [[United States]], concern for the health risks posed by pregnancy in individual cases was not a factor commonly given; however, in [[Bangladesh]], [[India]], and [[Kenya]] health concerns were cited by women more frequently as reasons for having an abortion.<ref name="bankole98" /> 1% of women in the 2004 survey-based U.S. study became pregnant as a result of [[rape]] and 0.5% as a result of [[incest]].<ref name="finer2005"/> Another American study in 2002 concluded that 54% of women who had an abortion were using a form of [[birth control|contraception]] at the time of becoming pregnant while 46% were not. Inconsistent use was reported by 49% of those using [[condom]]s and 76% of those using [[oral contraception]]; 42% of those using condoms reported failure through slipping or breakage.<ref>Jones, Rachel K., Darroch, Jacqueline E., Henshaw, Stanley K. (2002). [http://www.guttmacher.org/pubs/journals/3429402.pdf Contraceptive Use Among U.S. Women Having Abortions in 2000-2001]. ''Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 34 (6).'' Retrieved [[June 15]], [[2006]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some abortions are undergone as the result of societal pressures. These might include the stigmatization of [[disabled]] persons, preference for children of a specific [[sex]], disapproval of [[single parent|single motherhood]], insufficient economic support for [[family|families]], lack of access to or rejection of contraceptive methods, or efforts toward [[population control]] (such as [[People's Republic of China|China]]'s [[one-child policy]]). These factors can sometimes result in compulsory abortion or [[sex-selective abortion]]. In many areas, especially in [[developing country|developing nations]] or where abortion is illegal, women sometimes resort to "[[back-alley abortion|back-alley]]" or [[self-induced abortion|self-induced]] procedures. The [[World Health Organization]] suggests that there are 19 million terminations annually which fit its criteria for an [[Abortion#Unsafe abortion|unsafe abortion]].<ref name="whounsafe">World Health Organization. (2004). [http://www.who.int/reproductive-health/publications/unsafe_abortion_estimates_04/estimates.pdf Unsafe abortion: global and regional estimates of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2000]. Retrieved [[2006-01-12]].</ref> See [[Abortion#Social issues|social issues]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Forms of abortion== | ||
| + | ===Spontaneous abortion=== | ||
| + | {{main|Miscarriage}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!--improve me!--> | ||
| + | Spontaneous abortions, generally referred to as miscarriages, occur when an [[embryo]] or [[fetus]] is lost due to natural causes before the 20th week of [[fetal development|development]]. A pregnancy that ends earlier than 37 weeks of [[gestation]], if it results in a [[Live birth|live-born]] [[infant]], is known as a "[[premature birth]]". When a fetus dies in the uterus at some point late in gestation, beginning at about 20 weeks, or during [[childbirth|delivery]], it is termed a "[[stillbirth]]". Premature births and stillbirths are generally not considered to be miscarriages although usage of these terms can sometimes overlap. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Most miscarriages occur very early in pregnancy. Between 10% and 50% of pregnancies end in miscarriage, depending upon the age and health of the pregnant woman.<ref>"[http://wuphysicians.wustl.edu/dept.asp?pageID=8&ID=35 Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility: Recurrent Pregnancy Loss (Recurrent Miscarriage)]." (n.d.) Retrieved [[2006-01-18]] from Washington University School of Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology web site.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The risk of spontaneous abortion decreases sharply after the 8th week, i.e. when the fetal stage begins.<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/health/2176898.stm Q&A: Miscarriage]. (August 6 , 2002). ''BBC News.'' Retrieved January 10, 2007.</ref> The risk for spontaneous abortion is greater in those with a history of more than three previous (known) spontaneous abortions, those who have had a previous induced abortion, those with systemic diseases, and those over age 35. Other causes can be infection (of either the woman or the fetus), immune response, or serious systemic disease. A spontaneous abortion can also be caused by accidental [[Physical trauma|trauma]]; intentional trauma to cause miscarriage is considered induced abortion. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Induced abortion=== | ||
| + | A pregnancy can be intentionally aborted in many ways. The manner selected depends chiefly upon the [[gestational age]] of the [[fetus]], in addition to the legality, regional availability, and/or doctor-patient preference for specific procedures. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Surgical abortion==== | ||
| + | [[Image:Abortionmethods.png|thumb|380px|right|[[Gestational age]] may determine which abortion methods are practiced.]] | ||
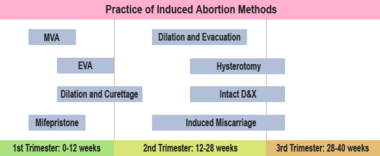
| + | In the first twelve weeks, [[suction-aspiration abortion|suction-aspiration]] or vacuum abortion is the most common method.<ref>Healthwise. [http://www.webmd.com/hw/womens_conditions/tw1078.asp#tw1112 Manual and vacuum aspiration for abortion]. (2004). ''WebMD.'' Retrieved [[2006-08-19]].</ref> ''[[Manual vacuum aspiration]]'', or MVA abortion, consists of removing the [[fetus]] or [[embryo]] by suction using a manual [[syringe]], while the ''[[Electric vacuum aspiration]]'' or EVA abortion method uses an electric [[pump]]. These techniques are comparable, differing in the mechanism used to apply suction, how early in pregnancy they can be used, and whether cervical dilation is necessary. MVA, also known as "mini-suction" and [[menstrual extraction]], can be used in very early pregnancy, and does not require cervical dilation. Surgical techniques are sometimes referred to as ''STOP'': 'Suction (or surgical) Termination Of Pregnancy'. From the fifteenth week until approximately the twenty-sixth week, a [[dilation and evacuation]] (D & E) is used. D & E consists of opening the [[cervix]] of the [[uterus]] and emptying it using surgical instruments and suction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''[[Dilation and curettage]]'' (D & C) is a standard gynecological procedure performed for a variety of reasons, including examination of the uterine lining for possible malignancy, investigation of abnormal bleeding, and abortion. ''[[Curettage]]'' refers to cleaning the walls of the [[uterus]] with a [[curette]]. The [[World Health Organization]] recommends this procedure, also called Sharp Curettage, only when MVA is unavailable.<ref>World Health Organization. (2003). [http://www.who.int/reproductive-health/impac/Procedures/Dilatetion_P61_P63.html Managing complications in pregnancy and childbirth: a guide for midwives and doctors]. Retrieved [[2006-08-19]].</ref> Sharp curettage only accounted for 2.4% of abortion procedures in the US in 2002.<ref name="cdc2002" /> The term "D and C", or sometimes ''suction curette'', is used as a euphemism for the first trimester abortion procedure, irrespective of the method used to perform it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other techniques must be used to induce abortion in the third [[trimester]]. Premature delivery can be induced with [[prostaglandin]]; this can be coupled with injecting the [[amniotic sac|amniotic fluid]] with caustic solutions containing [[saline (medicine)|saline]] or [[urea]]. Very late abortions can be induced by [[intact dilation and extraction]] (intact D & X) (also called [[Intrauterine cranial decompression]]), which requires surgical decompression of the fetus's head before evacuation, and is sometimes termed "[[partial-birth abortion]]." A [[hysterotomy abortion]], similar to a [[caesarian section]] but resulting in a terminated fetus, can also be used at late stages of pregnancy. It can be performed vaginally, with an incision just above the [[cervix]], in the late mid-trimester.{{fact}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | From the 20th to 23rd week of gestation, an [[medical injection|injection]] to stop the fetal heart can be used as the first phase of the surgical abortion procedure.<ref>Vause S, Sands J, Johnston TA, Russell S, Rimmer S. (2002). PMID 12521492 Could some fetocides be avoided by more prompt referral after diagnosis of fetal abnormality? J Obstet Gynaecol. 2002 May;22(3):243-5. Retrieved [[2006-03-17]].</ref><ref>Dommergues M, Cahen F, Garel M, Mahieu-Caputo D, Dumez Y. (2003). PMID 12576743 Feticide during second- and third-trimester termination of pregnancy: opinions of health care professionals. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2003 Mar-Apr;18(2):91-7. Retrieved [[2006-03-17]].</ref><ref>Bhide A, Sairam S, Hollis B, Thilaganathan B. (2002). PMID 12230443 Comparison of feticide carried out by cordocentesis versus cardiac puncture. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2002 Sep;20(3):230-2. Retrieved [[2006-03-17]].</ref><ref>Senat MV, Fischer C, Bernard JP, Ville Y. (2003). PMID 12628271 The use of lidocaine for fetocide in late termination of pregnancy. BJOG. 2003 Mar;110(3):296-300. Retrieved [[2006-03-17]].</ref><ref>Senat MV, Fischer C, Ville Y. (2002). PMID 12001185 Funipuncture for fetocide in late termination of pregnancy. Prenat Diagn. 2002 May;22(5):354-6. Retrieved [[2006-03-17]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Medical abortion==== | ||
| + | {{main|Medical abortion}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Effective in the first trimester of pregnancy, medical (sometimes called ''chemical abortion''), or non-surgical abortions comprise 10% of all abortions in the [[United States]] and Europe. Combined regimens include [[methotrexate]] or [[mifepristone]], followed by a [[prostaglandin]]—either [[misoprostol]] or [[gemeprost]]. Misoprostol is used in the U.S.; gemeprost is used in the UK and Sweden. When used within 49 days gestation, approximately 92% of women undergoing medical abortion with a combined regimen experience completed it without surgical intervention.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Spitz, I.M. et al|title=Early pregnancy termination with mifepristone and misoprostol in the United States|journal=New England Journal of Medicine|year=1998|volume=338|issue=18|id=PMID 9562577}}</ref> Misoprostol can be used alone, but has a lower efficacy rate than combined regimens. In cases of failure of medical abortion, vacuum or manual aspiration is used to complete the abortion surgically. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Other means of abortion==== | ||
| + | [[Image:Angkordemon.jpg|thumb|left|240px|A visual representation of an abortion caused by pounding a woman with a mallet at [[Angkor Wat]].]] | ||
| + | Historically, a number of [[herb]]s reputed to possess [[abortifacient]] properties have been used in [[folk medicine]]: [[tansy]], [[pennyroyal]], [[black cohosh]], and the now-extinct [[silphium]] (see [[Abortion#History of abortion|history of abortion]]).<ref name="riddle2">Riddle, John M. (1997). ''Eve's Herbs: A History of Contraception and Abortion in the West.'' Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.</ref> The use of herbs in such a manner can cause serious — even lethal — side effects, such as [[multiple organ dysfunction syndrome|multiple organ failure]], and is not recommended by [[physician]]s.<ref>Ciganda, C., & Laborde, A. (2003). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=12807304&query_hl=9 Herbal infusions used for induced abortion]. ''J Toxicol Clin Toxicol, 41(3),'' 235-9. Retrieved [[2006-01-25]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Abortion is sometimes attempted by causing trauma to the [[abdomen]]. The degree of force, if severe, can cause serious internal injuries without necessarily succeeding in inducing [[miscarriage]].<ref>Education for Choice. ([[2005-05-06]]). [http://www.efc.org.uk/Foryoungpeople/Factsaboutabortion/Unsafeabortion Unsafe abortion]. Retrieved [[2006-01-11]].</ref> Both accidental and deliberate abortions of this kind can be subject to criminal liability in many countries. In [[Myanmar|Burma]], [[Indonesia]], [[Malaysia]], the [[Philippines]], and [[Thailand]], there is an ancient tradition of attempting abortion through forceful abdominal [[massage]].<ref name="potts">Potts, Malcolm, & Campbell, Martha. (2002). [http://big.berkeley.edu/ifplp.history.pdf History of contraception]. ''Gynecology and Obstetrics'', vol. 6, chp. 8. Retrieved [[2005-01-25]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Reported methods of unsafe, [[self-induced abortion]] include misuse of [[misoprostol]], and insertion of non-surgical implements such as [[knitting needle]]s and [[clothes hanger]]s into the [[uterus]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Health effects== | ||
| + | <!--MAJOR REORG NEEDED. Entire section is argumentative, and biased: See Talk. —> | ||
| + | Early-term surgical abortion is a simple procedure. When performed before the 16th week by competent [[Physician|doctor]]s — or, in some states, [[nurse practitioner]]s, [[nurse midwife|nurse midwives]], and [[physician assistant]]s — it is safer than [[childbirth]].<ref>Cates W., Jr, & Tietze C. (1978). Standardized mortality rates associated with legal abortion: United States, 1972-1975 [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=639966&dopt=Abstract Electronic version]. ''Family Planning Perspectives, 10 (2)'', 109-12. Retrieved [[2006-01-28]].</ref> <ref name="grimes">Grimes, D.A. (1994). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=8178896&dopt=Abstract The morbidity and mortality of pregnancy: still risky business]. ''American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 170 (5 Pt 2)'', 1489-94. Retrieved [[December 21]], [[2006]].</ref> <!-- As I pointed out earlier, listing the negatives of this generally safe procedure first would be biased. —> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Abortion methods, like most surgical procedures, carry a small risk of potentially serious complications. These risks include: a perforated [[uterus]],<ref>Legarth, J., Peen, U.B., & Michelsen, J.W. (1991). | ||
| + | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=pubmed&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=AbstractPlus&list_uids=1936497&query_hl=2&itool=pubmed_docsum Mifepristone or vacuum aspiration in termination of early pregnancy]. ''European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Biology, 41 (2),'' 91-6. Retrieved [[December 21]], [[2006]].</ref><ref>Mittal, S., & Misra, S.L. (1985). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?itool=abstractplus&db=pubmed&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=abstractplus&list_uids=2860032 Uterine perforation following medical termination of pregnancy by vacuum aspiration]. ''International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics, 23 (1),'' 45-50. Retrieved [[December 21]], [[2006]].</ref> perforated [[bowel]]<ref>WHO Health Organization. Medical Methods for termination of pregnancy. WHO Technical Report Series 871, 1997</ref> or [[urinary bladder|bladder]],{{fact}} [[septic shock]],<ref>Dzhavakhadze, M.V., & Daraselia, M.I. (2005). | ||
| + | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=pubmed&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=AbstractPlus&list_uids=16308436&query_hl=98&itool=pubmed_docsum Mortality case analyses of obstetric-gynecologic sepsis]. ''Georgian Medical News, 127,'' 26-9. Retrieved [[December 21]], [[2006]].</ref> [[infertility|sterility]],<ref>Tzonou, A., Hsieh, C.C., Trichopoulos, D., Aravandinos, D., Kalandidi, A., Margaris, D., Goldman, M., ''et al''. (1993) [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=pubmed&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=AbstractPlus&list_uids=8436890&query_hl=37&itool=pubmed_docsum Induced abortions, miscarriages, and tobacco smoking as risk factors for secondary infertility]. ''Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 47 (1)'', 36-9. Retrieved [[December 21]], [[2006]].</ref> and death.<ref>Lanska, M.J., Lanska, D., & Rimm, A.A. (1983). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=pubmed&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=AbstractPlus&list_uids=6854898&query_hl=26&itool=pubmed_docsum Mortality from abortion and childbirth]. ''Journal of the American Medical Association, 250(3),'' 361-2. Retrieved [[December 21]], [[2006]].</ref> The risk of complications can increase depending on how far [[pregnancy]] has progressed,<ref name="pauli">Pauli, E., Haller, U., Zimmermann, R. (2005). | ||
| + | [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=pubmed&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=AbstractPlus&list_uids=15818053&query_hl=102&itool=pubmed_docsum Morbidity of dilatation and evacuation in the second trimester: an analysis]. ''Gynakol Geburtshilfliche Rundsch, 45 (2)'', 107-15. Retrieved [[December 26]], [[2006]].</ref><ref name="bartley">Bartley, J., Tong, S., Everington, D.,& Baird, D.T. (2000). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=pubmed&cmd=Retrieve&dopt=AbstractPlus&list_uids=11239616&query_hl=86&itool=pubmed_DocSum Parity is a major determinant of success rate in medical abortion: a retrospective analysis of 3161 consecutive cases...]. ''Contraception, 62(6)'', 297-303. Retrieved [[December 26]], [[2006]].</ref> but remains less than [[Complications of pregnancy|complications]] that may occur from carrying pregnancy to term.<ref name="grimes" /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Assessing the risks of induced abortion depends on a number of factors. First, there are relative health risks of induced abortion and pregnancy, which are both affected by wide variation in the quality of health services in different [[Society|societies]] and among different [[socio-economic]] groups, a lack of uniform [[definition]]s of terms, and difficulties in patient follow-up and after-care. The degree of risk is also dependent upon the skill and experience of the practitioner; maternal age, health, and [[Parity (medicine)|parity]];<ref name="bartley" /> [[gestational age]];<ref name="bartley" /><ref name="pauli" /> pre-existing conditions; methods and instruments used; [[medication]]s used; the skill and experience of those assisting the practitioner; and the quality of recovery and follow-up care. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the [[United Kingdom]], the number of deaths directly due to legal abortion between the years of 1991 and 1993 was 5, compared to 3 deaths following spontaneous miscarriage and 8 deaths caused by [[ectopic pregnancy]] during the same time frame.<ref>Department of Health. (1998). ''[http://www.archive.official-documents.co.uk/document/doh/wmd/wmd-hm.htm Why Mothers Die: Report on Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths in the United Kingdom 1994–1996].'' London: The Stationery Office. Retrieved [[2006-01-11]].</ref> In the [[United States]], during the year 1999, there were 4 deaths due to legal abortion, 10 due to [[miscarriage]], and 525 due to pregnancy-related reasons.<ref>Elam-Evans, Laurie. D., Strauss, Lilo T., Herndon, Joy, Parker, Wilda Y., Bowens, Sonya V., Zane, Suzanne, ''et al.'' Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. ([[2003-11-23]]). ''[http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/ss5212a1.htm Abortion Surveillance - United States, 2000].'' Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Retrieved [[2006-01-11]].</ref><ref>Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. ([[2003-02-20]]). [http://www.cdc.gov/od/oc/media/pressrel/fs030220.htm Fact Sheet: Pregnancy-Related Mortality Surveillance - United States, 1991-1999]. Retrieved [[2006-04-02]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some practitioners advocate using minimal [[anaesthesia]] so the patient can alert them to possible complications. Others recommend [[general anaesthesia]], to prevent patient movement, which might cause a perforation. General anaesthesia carries its own risks, including death, which is why public health officials recommend against its routine use. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Dilation]] of the [[cervix]] carries the risk of cervical tears or perforations, including small tears that might not be apparent and might cause [[cervical incompetence]] in future pregnancies. Most practitioners recommend using the smallest possible dilators, and using [[osmotic]] rather than [[Machine|mechanical]] dilators after the first [[trimester]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Instruments that are placed within the uterus can, on rare occasions, cause [[perforation]]<ref name="pauli" /> or [[laceration]] of the uterus, and damage structures surrounding the uterus. Laceration or perforation of the uterus or cervix can, again on rare occasions, lead to more serious complications. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Incomplete emptying of the uterus can cause [[hemorrhage]] and infection. Use of [[ultrasound]] verification of the location and duration of the pregnancy prior to abortion, with immediate follow-up of patients reporting continuing pregnancy symptoms after the procedure, will virtually eliminate this risk. The sooner a complication is noted and properly treated, the lower the risk of permanent injury or death. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In rare cases, abortion will be unsuccessful and pregnancy will continue. An unsuccessful abortion can result in delivery of a live [[neonate]], or infant. This, termed a failed abortion, is very rare and can only occur late in pregnancy. Some doctors have voiced concerns about the ethical and legal ramifications of letting the neonate die. As a result, recent investigations have been launched in the [[United Kingdom]] by the Confidential Enquiry into Maternal and Child Health (CEMACH) and the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, in order to determine how widespread the problem is and what an ethical response in the treatment of the infant might be.<ref>Rogers, Lois. ([[2005-11-27]]). "[http://www.timesonline.co.uk/article/0,,2087-1892696,00.html Fifty babies a year are alive after abortion]." ''The Sunday Times.'' Retrieved [[2006-01-11]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[#unsafe abortion|Unsafe abortion]] methods (e.g. use of certain drugs, herbs, or insertion of non-surgical objects into the [[uterus]]) are potentially dangerous, carrying a significantly elevated risk for permanent injury or death, as compared to abortions done by [[physician]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Suggested effects=== | ||
| + | There is controversy over a number of proposed risks and effects of abortion. Evidence, whether in support of or against such claims, might be influenced by the political and religious beliefs of the parties behind it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Breast cancer==== | ||
| + | {{main|Abortion-breast cancer hypothesis|Breast cancer}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The abortion-breast cancer (ABC) hypothesis posits a [[causality|causal relationship]] between induced abortion and increased risk of developing [[breast cancer]]. In early [[pregnancy]] the level of [[estrogen]]s increases, leading to [[breast]] [[cellular differentiation|growth]] in preparation for [[lactation]]. The ABC hypothesis proposes that if this process is interrupted with abortion – before full differentiation in the third [[trimester]] – then more relatively vulnerable undifferentiated cells could be left than there were prior to the pregnancy, resulting in greater potential risk of breast cancer. The hypothesis, however, has not been scientifically verified, and abortion is not considered a breast cancer risk by any major cancer organization. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A [[Epidemiology|epidemiological]] study by Dr. Mads Melbye et al. in 1997, with data from two national [[registry|registries]] in [[Denmark]], reported the correlation to be negligible to non-existent after [[statistical hypothesis testing|statistical adjustment]].<ref>Melbye M. et al. (1997) ''Induced abortion and the risk of breast cancer.'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=8988884 (abstract)] New England Journal of Medicine, 336, 81-5. Retrieved [[2006-01-11]] from PubMed.</ref> The [[National Cancer Institute]] conducted an official workshop with numerous experts on the issue in [[February 2003]], which concluded with its highest strength rating for the selected evidence it considered that "induced abortion is not associated with an increase in breast cancer risk."<ref>National Cancer Institute. ([[2003-03-04]]). [http://www.cancer.gov/cancerinfo/ere-workshop-report Summary Report: Early Reproductive Events and Breast Cancer Workshop]. Retrieved [[2006-01-11]].</ref> In 2004, Beral et al. published a collaborative reanalysis of 53 epidemiological studies and concluded that abortion does "not increase a woman's risk of developing breast cancer."<ref>Beral V. et al. (2004) ''Breast cancer and abortion: collaborative reanalysis of data from 53 epidemiological studies, including 83,000 women with breast cancer from 16 countries.'' [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=15051280 (abstract)] ''The Lancet, 363,'' 1007-16. Retrieved [[2006-04-12]] from PubMed.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Of over 100 experts at the National Cancer Institute workshop, [[Joel Brind|Dr. Joel Brind]], the primary advocate of an abortion-breast cancer link and an invitee to the workshop, filed the only dissenting opinion criticizing the NCI's and Melbye's conclusions.<ref>Brind, Joel. ([[2003-03-10]]). [http://www.bcpinstitute.org/nci_minority_rpt.htm Early Reproductive Events and Breast Cancer: A Minority Report]. Retrieved [[2006-03-24]].</ref> Brind argues that the majority of interview-based studies have indicated a link and some are [[statistically significant]],<ref>[http://www.etters.net/cancerTP.htm#3 Etters.net] – American abortion-breast cancer studies</ref> but there remains debate as to the reliability of these retrospective studies because of possible [[response bias]]. Most medical professionals agree with the recent prospective studies that conclude no abortion-breast cancer association,<ref>American Cancer Society. ([[2006-10-03]]) [http://www.cancer.org/docroot/CRI/content/CRI_2_4_2X_What_are_the_risk_factors_for_breast_cancer_5.asp Cancer.org] – ''What Are the Risk Factors for Breast Cancer?'' Retrieved [[2006-03-30]].</ref> and the ABC issue is seen by some as merely a part of the current [[pro-life]] "women-centered" strategy against abortion.<ref>Arthur, Joyce. (2002) [http://www.prochoiceactionnetwork-canada.org/articles/abclink.shtml ProChoiceActionNetwork-Canada.org] – ''Abortion and Breast Cancer — A Forged Link''</ref> Nevertheless, the subject continues to be one of mostly political but some scientific contention.<ref>Jasen, P. (2005) [http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=1251638 Breast Cancer and the Politics of Abortion in the United States]. ''Medical History 2005 October 1; 49(4): 423–444.''</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Fetal pain==== | ||
| + | {{main|Fetal pain}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The existence or absence of fetal sensation during abortion is a matter of medical, ethical and public policy interest. Evidence conflicts, with some authorities holding that the fetus is capable of feeling [[Pain and nociception|pain]] from the first [[trimester]],<ref>{{cite press release | title = Open Letter to President Reagan | publisher = Schmidt, Dr. Richard T. F., et. al. | date = 1984-02-13|url = http://www.mpomerle.com/NoAbort/Reagan_Fetal_Pain.shtml| accessdate = 2006-11-18 }}</ref> and others maintaining that the [[neuroanatomy|neuro-anatomical]] requirements for such experience do not exist until the second or third trimester.<ref> BBC News Article (2005). "[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/4180592.stm Foetuses 'no pain up to 29 weeks']." Retrieved [[2006-07-18]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pain receptors begin to appear in the seventh week of gestation. The [[thalamus]], the part of the brain which receives signals from the [[nervous system]] and then relays them to the [[cerebral cortex]], starts to form in the fifth week. However, other anatomical structures involved in the [[Pain and nociception|nociceptic]] process are not present until much later in [[gestation]]. Links between the thalamus and cerebral cortex form around the 23rd week.<ref>Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology. (1997). ''[http://www.parliament.uk/post/pn094.pdf Fetal Awareness].'' Retrieved [[2006-01-11]].</ref> There has been suggestion that a fetus cannot feel pain at all, as it requires mental development that only occurs outside the womb.<ref>BBC News Article (2006). "[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/4905892.stm Foetuses 'cannot experience pain']." Retrieved [[2006-07-18]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Researchers have observed changes in heart rates and [[hormones|hormonal levels]] of newborn [[infants]] after [[circumcision]], [[blood tests]], and surgery — effects which were alleviated with the administration of [[anesthesia]].<ref>Anand, K., Phil, D., & Hickey, P.R. (1987). Pain and its effects on the human neonate and fetus. ''New England Journal of Medicine, 316 (21),'' 1321-9. Retrieved [[2006-01-11]] from [http://www.cirp.org/library/pain/anand/ The Circumcision Reference Library].</ref> Others suggest that the human experience of pain, being more than just [[physiology|physiological]], cannot be measured in such [[reflexive]] responses.<ref>Lee, Susan J., Ralston, Henry J. Peter, Drey, Eleanor A., Partridge, John Colin, & Rosen, Mark A. (2005). [http://jama.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/short/294/8/947 Fetal Pain: A Systematic Multidisciplinary Review of the Evidence]. ''Journal of the American Medical Association, 294 (8)'', 947-954. Retrieved [[November 10]], [[2006]]. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Mental health==== | ||
| + | {{Main|Post-abortion syndrome|Mental health}} | ||
| + | [[Post-abortion syndrome]] (PAS) is a term used to describe a set of [[mental health]] characteristics which some researchers claim to have observed in women following an abortion.<ref name="gomez"> Gomez, Lavin C., & Zapata, Garcia R. (2005). | ||
| + | - [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=15999304&dopt=Abstract "Diagnostic categorization of post-abortion syndrome"]. ''Actas Esp Psiquiatr, 33 (4),'' 267-72. Retrieved Setepmber 8, 2006.</ref> The [[Psychopathology|psychopathological]] symptoms attributed to PAS are similar to those of [[post-traumatic stress disorder]], but have also included, "repeated and persistent dreams and [[nightmare]]s related with the abortion, intense feelings of [[guilt]] and the 'need to repair'".<ref name="gomez" /> Whether this would warrant [[nosology|classification]] as an independent [[syndrome]] is disputed by other researchers.<ref>Stotland, N.L. (1992). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=pubmed&dopt=Abstract&list_uids=1404747 The myth of the abortion trauma syndrome]. ''Journal of the American Medical Association, 268 (15),'' 2078-9. Retrieved [[December 7]], [[2006]].</ref> PAS is listed in neither the [[DSM-IV-TR]] nor the [[ICD|ICD-10]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some studies have shown abortion to have neutral or positive effects on the mental well-being of some patients. A 1989 study of [[teenager]]s who sought [[pregnancy test]]s found that, counting from the beginning of pregnancy until two years later, the level of [[Stress (medicine)|stress]] and [[anxiety]] of those who had an abortion did not differ from that of those who had not been pregnant or who had carried their pregnancy to term.<ref>Zabin, L.S., Hirsch, M.B., Emerson, M.R. (1989). [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&list_uids=2620716&dopt=Abstract When urban adolescents choose abortion: effects on education, psychological status and subsequent pregnancy]. ''Family Planning Perspectives, 21 (6),'' 248-55. Retrieved [[September 8]], [[2006]].</ref> Another study in 1992 suggested a link between elective abortion and later reports of positive [[self-esteem]]; it also noted that adverse emotional reactions to the procedure are most strongly influenced by pre-existing [[psychology|psychological]] conditions and other negative factors.<ref name="russo">Russo, N. F., & Zierk, K.L. (1992). [http://content.apa.org/journals/pro/23/4/269 Abortion, childbearing, and women]. ''Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 23(4),'' 269-280. Retrieved [[September 8]], [[2006]].</ref> Abortion, as compared to completion, of an undesired [[Gravidity|first pregnancy]] was not found to directly pose the risk of significant depression in a 2005 study.<ref>Schmiege, S. & Russo, N.F. (2005). Depression and unwanted first pregnancy: longitudinal cohort study [http://bmj.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/full/331/7528/1303 Electronic version] . ''British Medical Journal, 331 (7528),'' 1303. Retrieved [[2006-01-11]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other studies have shown a correlation between abortion and negative psychological impact. A 1996 study found that suicide is more common after miscarriage and especially after induced abortion, than in the general population.<ref>Gissler, M., Hemminki, E., & Lonnqvist, J. (1996). Suicides after pregnancy in Finland, 1987-94: register linkage study [http://bmj.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/full/313/7070/1431 Electronic version]. ''British Medical Journal, 313,'' 1431-4. Retrieved [[2006-01-11]].</ref> | ||
| + | Additional research in 2002 reported that the risk of clinical depression was higher for women who chose to have an abortion compared to those who opted to carry to term — even if the pregnancy was unwanted.<ref>Reardon, D.C. & Cougle, J.R. (2002): Depression and unintended pregnancy in the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth: a cohort study. BMJ (British Medical Journal) 19.1.2002 324:151-2. [http://bmj.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/full/324/7330/151?ijkey=6e69d766b00a6b5f6d244e90d4a8b9f9bcd165c5&keytype2=tf_ipsecsha Electronic version.]</ref> Another study in 2006, which used data gathered over a 25-year period, found an increased occurrence of [[clinical depression]], [[anxiety]], [[suicide|suicidal]] behavior, and [[substance abuse]] among women who had previously had an abortion.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Fergusson D.M., Horwood L.J., & Ridder E.M.|title=Abortion in young women and subsequent mental health|journal=Journal of Child Psychology & Psychiatry|year=2006|volume=47|issue=1|page=16-24|id=PMID 16405636}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Miscarriage]], or spontaneous abortion, is known to present an increased risk of depression.<ref>''[http://www.chmeds.ac.nz/research/chds/view1.pdf Depression Risk Increased After Miscarriage].'' ([[2002-04-01]]). Retrieved [[2006-01-11]].</ref> [[Childbirth]] can also sometimes result in [[maternity blues]] or [[postpartum depression]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==History of abortion== | ||
| + | [[Image:FrenchPeriodicalPills-January61845,BostonDailyTimes.jpg|thumb|right|140px|"French Periodical Pills." An example of a clandestine advertisement published in an 1845 edition of the ''Boston Daily Times''.]] | ||
| + | {{main|History of abortion}} | ||
| + | Induced abortion, according to some [[anthropologists]], can be traced to ancient times.<ref name="devereux">Devereux, G. (1967). [http://db.jhuccp.org/ics-wpd/exec/icswppro.dll?AC=GET_RECORD&XC=/ics-wpd/exec/icswppro.dll&BU=http%3A%2F%2Fdb.jhuccp.org%2Fics-wpd%2Fpopweb%2F&TN=popline&SN=AUTO32204&SE=1493&RN=24&MR=50&TR=0&TX=0&ES=0&CS=1&XP=&RF=ShortRecordDisplay&EF=&DF=LongRecordDisplay&RL=1&EL=0&DL=1&NP=0&ID=&MF=&MQ=&TI=0&DT=&ST=0&IR=77430&NR=0&NB=0&SV=0&BG=&FG=&QS=&OEX=ISO-8859-1&OEH=ISO-8859-1 A typological study of abortion in 350 primitive, ancient, and pre-industrial societies]. Retrieved [[April 22]], [[2006]]. In ''Abortion in America: medical, psychiatric, legal, anthropological, and religious considerations.'' Boston: Beacon Press. Retrieved [[April 22]], [[2006]].</ref> There is evidence to suggest that, historically, pregnancies were terminated through a number of methods, including the administration of [[abortifacient]] herbs, the use of sharpened implements, the application of abdominal pressure, and other techniques. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[Hippocratic Oath]], the chief statement of [[medical ethics]] in [[Ancient Greece]], forbade all doctors from helping to procure an abortion by [[pessary]]. Nonetheless, [[Soranus (Greek Physician)|Soranus]], a second-century Greek [[physician]], suggested in his work ''[[Gynaecology]]'' that women wishing to abort their pregnancies should engage in violent exercise, energetic jumping, carrying heavy objects, and riding animals. He also prescribed a number of recipes for herbal baths, pessaries, and [[bloodletting]], but advised against the use of sharp instruments to induce miscarriage due to the risk of organ [[perforation]].<ref>Lefkowitz, Mary R. & Fant, Maureen R. (1992). ''[http://www.stoa.org/diotima/anthology/wlgr/ Women's life in Greece & Rome: a source book in translation].'' Baltimore, MD: John Hopkins University Press. Retrieved [[2006-01-11]].</ref> It is also believed that, in addition to using it as a [[contraceptive]], the ancient Greeks relied upon [[silphium]] as an [[abortifacient]]. Such folk remedies, however, varied in effectiveness and were not without risk. [[Tansy]] and [[pennyroyal]], for example, are two [[poison|poisonous]] [[herbs]] with serious [[Adverse effect (medicine)|side effects]] that have at times been used to terminate pregnancy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Abortion in the 19th century continued, despite bans in both the [[United Kingdom]] and the [[United States]], as the disguised, but nonetheless open, advertisement of services in the [[Victorian era]] suggests.<ref>''[http://users.telerama.com/~jdehullu/abortion/abhist.htm Histories of Abortion].'' (n.d.) Retrieved [[2006-01-11]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Social issues== | ||
| + | |||
| + | A number of complex issues exist in the debate over abortion. These, like the suggested effects upon health listed above, are a focus of research and a fixture of discussion among members on all sides of the controversy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Effect upon crime rate=== | ||
| + | {{Main|Legalized abortion and crime effect}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | A controversial theory attempts to draw a [[correlation]] between the United States' unprecedented nationwide decline of the overall [[crime rate]] during the 1990s and the decriminalization of abortion 20 years prior. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The suggestion was brought to widespread attention by a 1999 [[academic paper]], ''[[The Impact of Legalized Abortion on Crime]]'', authored by the [[economist]]s [[Steven Levitt|Steven D. Levitt]] and John Donohue. They attributed the drop in crime to a reduction in individuals said to have a higher statistical probability of committing crimes: unwanted children, especially those born to mothers who are [[African-American]], [[poverty|impoverished]], [[teenage pregnancy|adolescent]], [[education|uneducated]], and [[single parent|single]]. The change coincided with what would have been the adolescence, or peak years of potential criminality, of those who had not been born as a result of ''[[Roe v. Wade]]'' and similar cases. Donohue and Levitt's study also noted that states which legalized abortion before the rest of the nation experienced the lowering crime rate pattern earlier, and those with higher abortion rates had more pronounced reductions.<ref>Donohue, John J. and Levitt, Steven D. (2001). [http://ssrn.com/abstract=174508 The impact of legalized abortion on crime].''Quarterly Journal of Economics'' Retrieved [[2006-02-11]]. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fellow economists Christopher Foote and Christopher Goetz criticized the [[methodology]] in the Donohue-Levitt study, noting a lack of accommodation for statewide yearly variations such as [[cocaine]] use, and recalculating based on incidence of crime [[per capita]]; they found no [[statistically significant]] results.<ref>Foote, Christopher L. and Goetz, Christopher F. (2005). [http://www.bos.frb.org/economic/wp/wp2005/wp0515.pdf Testing economic hypotheses with state-level data: a comment on Donohue and Levitt (2001)]. ''Working Papers, 05-15''. Retrieved [[2006-02-11]].</ref> Levitt and Donohue responded to this by presenting an adjusted [[data set]] which took into account these concerns and reported that the data maintained the statistical significance of their initial paper.<ref>Donohue, John J. and Levitt, Steven D. (2006). Measurement error, legalized abortion, and the decline in crime: a response to Foote and Goetz (2005). Retrieved [[2006-02-17]], from University of Chicago, Initiative on Chicago Price Theory web site: [http://pricetheory.uchicago.edu/levitt/Papers/ResponseToFooteGoetz2006.pdf ResponseToFooteGoetz2006.pdf].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Such research has been criticized by some as being [[utilitarian]], [[discrimination|discriminatory]] as to [[race]] and [[social class|socioeconomic class]], and as promoting [[eugenic]]s as a solution to [[crime]].<ref>"Crime-Abortion Study Continues to Draw Pro-life Backlash." ([[1999-08-11]]). ''The Pro-Life Infonet.'' Retrieved [[2006-02-17]] from [http://ohioroundtable.org/library/articles/life/crimeabortion.html Ohio Roundtable Online Library].</ref><ref>"[http://www.americancatholic.org/Messenger/Jan2000/Editorial.asp Abortion and the Lower Crime Rate]." (2000, January). ''St. Anthony Messenger.'' Retrieved [[2006-02-17]].</ref> Levitt states in his book, ''[[Freakonomics]]'', that they are neither promoting nor negating any course of action — merely reporting data as economists. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Sex-selective abortion=== | ||
| + | {{Main|Sex-selective abortion and infanticide}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The advent of both [[ultrasound]] and [[amniocentesis]] has allowed parents to determine [[sex]] before [[childbirth|birth]]. This has led to the occurrence of [[sex-selective abortion and infanticide|sex-selective abortion]] or the targeted termination of a [[fetus]] based upon its sex. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is suggested that sex-selective abortion might be partially responsible for the noticeable disparities between the [[birth rate]]s of male and female children in some places. The preference for male children is reported in many areas of Asia, and abortion used to limit female births has been reported in [[Mainland China]], [[Republic of China|Taiwan]], [[South Korea]], and [[India]].<ref>Banister, Judith. ([[1999-03-16]]). [http://www.census.gov/ipc/www/ebspr96a.html Son Preference in Asia - Report of a Symposium]. Retrieved [[2006-01-12]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In [[India]], the [[economic]] role of men, the costs associated with [[dowry|dowries]], and a [[Hindu]] tradition which dictates that [[funeral|funeral rites]] must be performed by a male relative have led to a [[culture|cultural]] preference for [[son]]s.<ref>Mutharayappa, Rangamuthia, Kim Choe, Minja, Arnold, Fred, & Roy, T.K. (1997). [http://www2.eastwestcenter.org/pop/misc/subj-3.pdf Son Preferences and Its Effect on Fertility in India]. ''National Family Health Survey Subject Reports, Number 3.'' Retrieved [[2006-01-12]].</ref> The widespread availability of diagnostic testing, during the 1970s and '80s, led to advertisements for services which read, "Invest 500 [[rupee]]s [for a sex test] now, save 50,000 rupees [for a dowry] later."<ref>Patel, Rita. (1996). The practice of sex selective abortion in India: may you be the mother of a hundred sons. Retrieved [[2006-01-11]], from University of North Carolina, University Center for International Studies web site: [http://www.ucis.unc.edu/resources/pubs/carolina/abortion.pdf abortion.pdf].</ref> In 1991, the male-to-female [[sex ratio]] in India was skewed from its biological norm of 105 to 100, to an average of 108 to 100.<ref>Sudha, S., & Irudaya Rajan, S. (1999). [http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/organizations/healthnet/gender/docs/sudha.html Female Demographic Disadvantage in India 1981-1991: Sex Selective Abortion, Female Infanticide and Excess Female Child Mortality]. Retrieved [[2006-01-12]] </ref> Researchers have asserted that between 1985 and 2005 as many as 10 million female fetuses may have been selectively aborted.<ref>Reaney, Patricia. ([[2006-01-09]]). "[http://www.alertnet.org/thenews/newsdesk/L06779563.htm Selective abortion blamed for India's missing girls]." ''Reuters AlertNet.'' Retrieved [[2006-01-09]].</ref> The Indian government passed an official ban of pre-natal sex screening in 1994 and moved to pass a complete ban of sex-selective abortion in 2002.<ref>Mudur, Ganapati. (2002). "[http://bmj.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/abridged/324/7334/385/b India plans new legislation to prevent sex selection]." ''British Medical Journal: News Roundup.'' Retrieved [[2006-01-12]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the [[People's Republic of China]], there is also a historic son preference. The implementation of the [[one-child policy]] in 1979, in response to population concerns, led to an increased disparity in the sex ratio as parents attempted to circumvent the law through sex-selective abortion or the abandonment of unwanted daughters.<ref>Graham, Maureen J., Larsen, Ulla, & Xu, Xiping. (1998). [http://www.agi-usa.org/pubs/journals/2407298.html Son Preference in Anhui Province, China]. ''International Family Planning Perspectives, 24 (2).'' Retrieved [[2006-01-12]].</ref> Sex-selective abortion might be an influence on the shift from the baseline male-to-female birth rate to an elevated national rate of 117:100 reported in 2002. The trend was more pronounced in rural regions: as high as 130:100 in [[Guangdong]] and 135:100 in [[Hainan]].<ref>Plafker, Ted. ([[2002-05-25]]). [http://bmj.bmjjournals.com/cgi/content/full/324/7348/1233/a?maxtoshow=&HITS=10&hits=10&RESULTFORMAT=&fulltext Sex selection in China sees 117 boys born for every 100 girls]. ''British Medical Journal: News Roundup.'' Retrieved [[2006-01-12]].</ref> A ban upon the practice of sex-selective abortion was enacted in 2003.<ref>"[http://www.china.org.cn/english/2003/Mar/59194.htm China Bans Sex-selection Abortion]." ([[2002-03-22]]). ''Xinhua News Agency.'' Retrieved [[2006-01-12]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Unsafe abortion=== | ||
| + | [[Image:RussianAbortionPoster.jpg|thumb|240px|left|[[Soviet Union|Soviet]] [[Propaganda|poster]] circa 1925. Title translation: "Abortions performed by either trained or self-taught midwives not only maim the woman, they also often lead to death."]] | ||
| + | {{main|Unsafe abortion}} | ||
| + | Where and when access to safe abortion has been barred, due to explicit sanctions or general unavailability, women seeking to terminate their pregnancies have sometimes resorted to unsafe methods. | ||
| + | |||
| + | "[[Back-alley abortion]]" is a [[slang]] term for any abortion not practiced under generally accepted standards of [[sanitation]] and [[professional|professionalism]]. The [[World Health Organization]] defines an unsafe abortion as being, "a procedure...carried out by persons lacking the necessary skills or in an environment that does not conform to minimal medical standards, or both."<ref name="whounsafe" /> This can include a person without medical training, a professional health provider operating in sub-standard conditions, or the woman herself. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Unsafe abortion remains a [[public health]] concern today due to the higher incidence and severity of its associated complications, such as incomplete abortion, [[sepsis]], [[hemorrhage]], and damage to internal organs. WHO estimates that 19 million unsafe abortions occur around the world annually and that 68,000 of these result in the woman's death.<ref name="whounsafe" /> Complications of unsafe abortion are said to account, globally, for approximately 13% of all [[maternal death|maternal mortalities]], with regional estimates including 12% in Asia, 25% in [[Latin America]], and 13% in [[sub-Saharan Africa]].<ref>Salter, C., Johnson, H.B., and Hengen, N. (1997). [http://www.infoforhealth.org/pr/l10edsum.shtml Care for postabortion complications: saving women's lives]. ''Population Reports, 25 (1).'' Retrieved [[2006-02-22]].</ref> [[Health education]], access to [[family planning]], and improvements in [[health care]] during and after abortion have been proposed to address this phenomenon.<ref>World Health Organization. (1998). [http://www.who.int/docstore/world-health-day/en/pages1998/whd98_10.html Address Unsafe Abortion]. Retrieved [[2006-03-01]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Abortion debate== | ||
| + | [[Image:March.jpg|thumb|right|240px||Pro-choice activists before the [[Washington Monument]] at the [[March for Women's Lives]].]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Pro-life protest.jpg|thumb|right|240px||Pro-life activists at the [[March for Life]] in 2002. The rally is held annually in [[Washington, DC]].]] | ||
| + | {{main|Abortion debate}} | ||
| + | Over the course of the [[history of abortion]], induced abortion has been the source of considerable [[debate]], [[controversy]], and [[activism]]. An [[opinion|individual's position]] on the complex [[ethical]], [[moral]], [[philosophical]], [[Biology|biological]], and [[legal]] issues is often related to his or her [[value system]]. Opinions of abortion may be best described as being a combination of beliefs on its morality, and beliefs on the responsibility, ethical scope, and proper extent of [[government]]al [[authority|authorities]] in [[public policy]]. [[religion|Religious ethics]] also has an influence upon both personal opinion and the greater debate over abortion (see [[religion and abortion]]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Abortion debates, especially pertaining to [[abortion law]]s, are often spearheaded by [[advocacy|advocacy groups]] belonging to one of two camps. Most often those in favor of legal prohibition of abortion describe themselves as [[pro-life]] while those against legal restrictions on abortion describe themselves as [[pro-choice]]. Both are used to indicate the central principles in arguments for and against abortion: "Is the fetus a human being with a fundamental right to ''life''?" for pro-life advocates, and, for those who are pro-choice, "Does a woman have the right to ''choose'' whether or not to have an abortion?" | ||
| + | |||
| + | In both public and private debate, arguments presented in favor of or against abortion focus on either the moral permissibility of an induced abortion, or justification of [[laws]] permitting or restricting abortion. Arguments on morality and legality tend to collide and combine, complicating the issue at hand. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Debate also focuses on whether the [[pregnancy|pregnant]] woman should have to notify and/or have the [[consent]] of others in distinct cases: a [[minor (law)|minor]], her parents; a [[marriage|legally-married]] or [[common-law marriage|common-law]] wife, her husband; or a pregnant woman, the biological father. In a 2003 [[Gallup]] poll in the [[United States]], 72% of respondents were in favor of spousal notification, with 26% opposed; of those polled, 79% of males and 67% of females responded in favor.<ref>The Pew Research Center for the People and the Press. ([[2005-11-02]]). "[http://people-press.org/commentary/display.php3?AnalysisID=122 Public Opinion Supports Alito on Spousal Notification Even as It Favors Roe v. Wade]." ''Pew Research Center Pollwatch.'' Retrieved [[2006-03-01]].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Public opinion=== | ||
| + | {{Main|Societal attitudes towards abortion}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | A number of [[opinion poll]]s around the world have explored [[public opinion]] regarding the issue of abortion. Results have varied from poll to poll, country to country, and region to region, while varying with regard to different aspects of the issue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A May 2005 survey examined attitudes toward abortion in 10 [[Europe|European]] countries, asking polltakers whether they agreed with the statement, "If a woman doesn't want children, she should be allowed to have an abortion". The highest level of approval was 81% in the [[Czech Republic]] and the highest level of disapproval was 48% in [[Poland]]. <ref>TNS Sofres. (May 2005). [http://www.thebrusselsconnection.be/tbc/upload/attachments/European%20Values%20Overall%20EN.pdf European Values]. Retrieved January 11, 2007.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In [[North America]], a December 2001 poll surveyed [[Abortion_in_Canada#Opinion_polls|Canadian opinion on abortion]], asking [[Canada|Canadians]] in what circumstances they believe abortion should be permitted; 32% responded that they believe abortion should be legal in all circumstances, 52% that it should be legal in certain circumstances, and 14% that it should be legal in no circumstances. A similar poll in January 2006 surveyed people in the [[United States]] about [[Abortion_in_the_United_States#Public_Opinion|U.S. opinion on abortion]]; 33% said that abortion should be "permitted only in cases such as rape, incest or to save the woman's life", 27% said that abortion should be "permitted in all cases", 15% that it should be "permitted, but subject to greater restrictions than it is now", 17% said that it should "only be permitted to save the woman's life", and 5% said that it should "never" be permitted.<ref>''[http://www.pollingreport.com/abortion.htm The Polling Report].'' (2006). Retrieved [[2006-01-11]].</ref> A November 2005 poll in [[Mexico]] found that 73.4% think abortion should not be legalized while 11.2% think it should. <ref>"[http://www.angus-reid.com/polls/index.cfm/fuseaction/viewItem/itemID/10042 Mexicans Support Status Quo on Social Issues]." (December 1, 2005). ''Angus Reid Global Monitor.'' Retrieved January 10, 2006.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Of attitutes in [[South America|South]] and [[Central America]], a December 2003 survey found that 30% of [[Argentina|Argentines]] thought that [[abortion in Argentina]] should be allowed "regardless of situation", 47% that it should be allowed "under some circumstances", and 23% that it should not be allowed "regardless of situation".<ref>"[http://www.angus-reid.com/polls/index.cfm/fuseaction/viewItem/itemID/2029 Argentines Assess Abortion Changes]." (Mar. 4, 2004). ''Angus Reid Global Monitor''. Retrieved January 10, 2006.</ref> A poll regarding the [[Abortion in Brazil|abortion law in Brazil]] found that 63% of [[Brazil|Brazilians]] believe that it "should not be modified", 17% that it should be expanded "to allow abortion in other cases", 11% that abortion should be "decriminalized", and 9% were "unsure". <ref>"[http://www.angus-reid.com/polls/index.cfm/fuseaction/viewItem/itemID/12850 Brazilians Satisfied with Abortion Law]." (August 20, 2006). ''Angus Reid Global Monitor''. Retrieved January 10, 2006.</ref> A July 2005 poll in [[Colombia]] found that 65.6% said they thought that abortion should remain illegal, 26.9% that it should be made legal, and 7.5% that they were unsure. <ref>"[http://www.angus-reid.com/polls/index.cfm/fuseaction/viewItem/itemID/8333 Colombians Reject Legalizing Abortion]. (August 2, 2005). ''Angus Reid Global Monitor''. Retrieved January 10, 2006.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Abortion law== | ||
| + | {{main|Abortion law|History of abortion}} | ||
| + | [[Image:AbortionLawsMap.png|thumb|240px|right|International status of abortion law ([[:Image:AbortionLawsMap.png|Detail]])]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Signing_the_Partial-Birth_Abortion_ban.jpg|thumb|240px|right|[[President of the United States|United States President]] [[George W. Bush]] signs the ''[[Partial-Birth Abortion Ban Act]] of 2003'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Before the scientific discovery that human development began at fertilization, British common law allowed abortions to be performed before [[quickening]], the earliest perception of fetal movement by a woman during the second trimester of pregnancy. In 1861, the [[British Parliament]] passed the [[Offences Against The Person Act 1861|Offences Against the Person Act]], which put the [[common law]] offence of abortion into statute throughout the [[British Empire]]. The [[Soviet Union]], with legislation in 1920, and [[Iceland]], with legislation in 1935, were two of the first countries to generally allow abortion. The second half of the 20th century saw the liberalization of abortion laws in other countries. The [[Abortion Act 1967]] allowed abortion for limited reasons in the [[United Kingdom]]. In the 1973 case, ''[[Roe v. Wade]]'', the [[Supreme Court of the United States|United States Supreme Court]] struck down state laws banning abortion in the first trimester, ruling that such laws violated an implied [[right to privacy]] in the [[United States Constitution]]. The [[Supreme Court of Canada]], similarly, in the case of ''[[R. v. Morgentaler]]'', discarded its criminal code regarding abortion in 1988, after ruling that such restrictions violated the security of person guaranteed to women under the [[Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms]]. [[Canada]] later struck down provincial regulations of abortion in the case of ''[[R. v. Morgentaler (1993)]].'' By contrast, [[Abortion in Ireland]] was affected by the addition of an [[Eighth Amendment of the Constitution of Ireland|amendment]] to the [[Republic of Ireland|Irish]] [[Constitution of Ireland|Constitution]] in 1983 by popular [[referendum]], recognizing "the right to life of the unborn". | ||
| + | |||
| + | Current laws pertaining to abortion are diverse. Religious, moral, and cultural sensibilities continue to influence abortion laws throughout the world. The [[right to life]], the right to [[liberty]], and the right to [[security of person]] are major issues of [[human rights]] that are sometimes used as justification for the existence or the absence of laws controlling abortion. Many countries in which abortion is legal require that certain criteria be met in order for an abortion to be obtained, often, but not always, using a [[trimester]]-based system to regulate the window in which abortion is still legal to perform: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * In the United States, some states impose a 24-hour waiting period before the procedure, prescribe the distribution of information on [[fetal development]], or require that [[minors and abortion|parents be contacted]] if their [[Minor (law)|minor]] daughter requests an abortion. | ||
| + | * In the United Kingdom, as in some other countries, two doctors must first certify that an abortion is medically or socially necessary before it can be performed. | ||
| + | Other countries, in which abortion is normally illegal, will allow one to be performed in the case of [[rape]], [[incest]], or danger to the pregnant woman's life or health. A handful of nations ban abortion entirely: [[Abortion in Chile|Chile]], [[El Salvador]], [[Malta]], and [[Abortion in Nicaragua|Nicaragua]], although in 2006 the [[Politics of Chile|Chilean government]] begun the free distribution of [[emergency contraception]].<ref>Ross, Jen. ([[September 12]], [[2006]]). "[http://www.csmonitor.com/2006/0912/p01s04-woam.html In Chile, free morning-after pills to teens]." ''The Christian Science Monitor.'' Retrieved 2006-12-07.</ref><ref>Gallardoi, Eduardo. ([[September 26]], [[2006]]). "[http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/09/26/AR2006092600770.html Morning-After Pill Causes Furor in Chile]." ''The Washington Post.'' Retrieved 2006-12-07. </ref> In [[Bangladesh]], abortion is illegal, but the government has long supported a network of "menstrual regulation clinics", where [[menstrual extraction]] ([[manual vacuum aspiration]]) can be performed as menstrual hygiene.<ref>{{cite web|title=Surgical Abortion: History and Overview|publisher=National Abortion Federation|accessdate=2006-09-04|url=http://www.prochoice.org/education/resources/surg_history_overview.html}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | {|width=100% | ||
| + | |-valign=top | ||
| + | |width=50%| | ||
| + | *[[List of articles about abortion by country|Abortion by country]] | ||
| + | *[[Abortion fund]] | ||
| + | *[[Contraception]] | ||
| + | *[[Fetal rights]] | ||
| + | *[[Ethical aspects of abortion]] | ||
| + | *[[Fertilisation]] | ||
| + | *[[Gynaecology]] | ||
| + | *[[Late-term abortion]] | ||
| + | *[[Legal protection of access to abortion]] | ||
| + | *[[Libertarian perspectives on abortion]] | ||
| + | |width=50%| | ||
| + | *[[Minors and abortion]] | ||
| + | *[[Obstetrics]] | ||
| + | *[[Paternal rights and abortion]] | ||
| + | *[[Pregnancy]] | ||
| + | *[[Religion and abortion]] | ||
| + | *[[Reproduction (disambiguation)|Reproduction]] | ||
| + | *[[Selective reduction]] | ||
| + | *[[Self-induced abortion]] | ||
| + | *[[Teenage pregnancy]] | ||
| + | *[[Violence in the abortion movement]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <!-- ---------------------------------------------------------- | ||
| + | See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Footnotes for a | ||
| + | discussion of different citation methods and how to generate | ||
| + | footnotes using the<ref>, </ref> and <reference /> tags | ||
| + | ----------------------------------------------------------- —> | ||
| + | <div class="references-small" style="-moz-column-count:2; column-count:2;"> | ||
| + | <references /></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | {{sisterlinks|abortion}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[http://annualreview.law.harvard.edu/population/abortion/abortionlaws.htm Abortion Laws of the World] | ||
| + | *[http://www.un.org/esa/population/publications/abortion Abortion Policies: A Global Review] | ||
| + | *"[http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/twenty/watch/abortion.html Abortion Clinic]:" a 1983 PBS ''Frontline'' episode. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/002912.htm#Definition U.S. National Library of Medicine and National Institutes of Health MedlinePlus encyclopedia] | ||
| + | *[http://www.religioustolerance.org/abortion.htm Abortion: All sides to the issue] from the [[Ontario Consultants on Religious Tolerance]] | ||
| + | *[http://www.publicagenda.org/issues/frontdoor.cfm?issue_type=abortion Issue Guide on Abortion] from Public Agenda Online | ||
| + | <!-- HELP KEEP THIS ARTICLE SHORT AND SIMPLE: DO NOT ADD MORE LINKS TO EITHER "NON-NEUTRAL" SECTION. ADD THEM TO WHICHEVER SUB-ARTICLE WOULD BE APPROPRIATE INSTEAD. ALSO, PLEASE UNDERSTAND THAT SITES CONTAINING SHOCK MATERIAL SHALL, IN NO CASE, BE ACCEPTED. THANKS! !--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''The following information resources may be created by those with a non-neutral position in the abortion debate:''' | ||
| + | *[http://www.guttmacher.org/ The Guttmacher Institute] | ||
| + | *[http://www.johnstonsarchive.net/policy/abortion Johnston's Archive: Abortion Statistics and Other Data] | ||
| + | *[http://justfacts.com/abortion.htm Just Facts: Abortion] | ||
| + | *[http://www.abortion.com/ Abortion.com: Abortion Clinics and Medical Providers] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''The following links are to groups which advocate a specific position:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[http://www.childrenbychoice.org.au Children by Choice] (Australia, pro-choice) | ||
| + | *[http://www.rtlaust.com Right to Life Australia] (pro-life) | ||
| + | *[http://www.caral.ca Canadians for Choice] (pro-choice) | ||
| + | *[http://www.lifecanada.org LifeCanada] (pro-life) | ||
| + | *[http://www.alranz.org Abortion Law Reform Association of New Zealand] (pro-choice) | ||
| + | *[http://www.voiceforlife.org.nz Voice for Life] (New Zealand, pro-life) | ||
| + | *[http://www.abortionrights.org.uk Abortion Rights] (United Kingdom, pro-choice) | ||
| + | *[http://www.lifeuk.org LifeUK] (United Kingdom, pro-life) | ||
| + | *[http://www.all.org American Life League] (pro-life) | ||
| + | *[http://www.naral.org NARAL Pro-choice America] (pro-choice) | ||
| + | *[http://www.care-net.org CareNet] (international, pro-life) | ||
| + | *[http://www.plannedparenthood.com Planned Parenthood] (international, pro-choice) | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{BirthControl}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Abortion| ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Biological reproduction]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Core issues in ethics]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Gynecology]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Pregnancy]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Obstetrics]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[ar:إجهاض]] | ||
| + | [[bn:গর্ভপাত]] | ||
| + | [[bg:Аборт]] | ||
| + | [[ca:Avortament]] | ||
| + | [[cs:Interrupce]] | ||
| + | [[da:Provokeret abort]] | ||
| + | [[de:Schwangerschaftsabbruch]] | ||
| + | [[es:Aborto]] | ||
| + | [[eo:Aborto]] | ||
| + | [[fr:Avortement]] | ||
| + | [[hr:Pobačaj]] | ||
| + | [[id:Gugur kandungan]] | ||
| + | [[ia:Aborto]] | ||
| + | [[it:Interruzione volontaria di gravidanza]] | ||
| + | [[he:הפלה מלאכותית]] | ||
| + | [[lt:Abortas]] | ||
| + | [[hu:Terhességmegszakítás]] | ||
| + | [[mk:Абортус]] | ||
| + | [[nl:Abortus]] | ||
| + | [[ja:妊娠中絶]] | ||
| + | [[no:Abort]] | ||
| + | [[nn:Abort]] | ||
| + | [[pam:Abortion]] | ||
| + | [[pl:Aborcja]] | ||
| + | [[pt:Interrupção da gravidez]] | ||
| + | [[ro:Avort]] | ||
| + | [[ru:Аборт]] | ||
| + | [[simple:Abortion]] | ||
| + | [[sk:Potrat]] | ||
| + | [[sr:Абортус]] | ||
| + | [[sh:Abortus]] | ||
| + | [[fi:Abortti]] | ||
| + | [[sv:Abort]] | ||
| + | [[tl:Pagpapalaglag]] | ||
| + | [[th:การแท้ง]] | ||
| + | [[tr:Kürtaj]] | ||
| + | [[uk:Аборт]] | ||
| + | [[yi:אבארטאציע]] | ||
| + | [[zh:堕胎]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{credit|100935021}} | ||
Revision as of 03:41, 16 January 2007
Template:Abortion
An abortion is the removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the uterus, resulting in or caused by its death. This can occur spontaneously as a miscarriage, or be artificially induced by chemical, surgical or other means. Commonly, "abortion" refers to an induced procedure at any point during pregnancy; medically, it is defined as miscarriage or induced termination before twenty weeks' gestation, which is considered nonviable.
Throughout history abortion has been induced by various methods. The moral and legal aspects of abortion are subject to intense debate in many parts of the world.
Definitions
The following medical terms are used to define abortion:
- Spontaneous abortion (miscarriage): An abortion due to accidental trauma or natural causes, such as chromosomal number discrepancy, early disease, or environmental factors.
- Induced abortion: Abortion deliberately caused. Induced abortions are further subcategorized into therapeutic, and elective:
- Therapeutic abortion:[1]
- To save the life of the pregnant woman.
- To preserve the woman's physical or mental health.
- To terminate pregnancy that would result in a child born with a congenital disorder which would be fatal or associated with significant morbidity.
- To selectively reduce the number of fetuses to lessen health risks associated with multiple pregnancy.
- Elective abortion: Abortion performed for any other reason.
- Therapeutic abortion:[1]
In common parlance, the term "abortion" is synonymous with induced abortion. However, in medical texts, the word 'abortion' can also refer to spontaneous abortion (miscarriage).
Incidence
The incidence of, and reasons for induced abortion vary regionally. It has been estimated that yearly, approximately 46 million abortions are performed. Of these, 26 million are said to occur in places where abortion is legal; the other 20 million happen where it is illegal . Some countries, such as Belgium (11.2 per 100 known pregnancies) and the Netherlands (10.6 per 100), have a low rate of induced abortion, while others like Russia (62.6 per 100) and Vietnam (43.7 per 100) have a comparatively high rate. The world ratio is 26 induced abortions per 100 known pregnancies.[2]
By gestational age and method
Abortion rates also vary depending upon stage of pregnancy and method practiced. In 2002, from data collected in those areas of the United States which sufficiently reported gestational age, it was found that 86.7% of abortions were conducted at or prior to 12 weeks, 9.9% from 13 to 20 weeks, and 1.4% at or after 21 weeks. 91.3% percent of these were classified as having been done by "curettage" (suction-aspiration, D&C, D&E), 5.2% by "medical" means (mifepristone), 0.8% by "intrauterine instillation" (saline or prostaglandin), and 1.5% by "other" (hysterotomy and hysterectomy).[3] The Guttmacher Institute estimated there were 2,200 intact dilation and extraction procedures in the U.S. during 2000; this accounts for 0.17% of the total number of abortions performed that year.[4] Similarly, in England and Wales in 2004, 87.6% of terminations occurred at or under 12 weeks, 10.7% between 13 to 19 weeks, and 1.5% at or over 20 weeks. 76% of those reported were by vacuum aspiration, 4% by D&E, 19% by a chemical agent, and 1% by feticide.[5]
By personal and social factors
A 1998 aggregated study, from 27 countries, on the reasons women seek to terminate their pregnancies concluded that common factors cited to have influenced the abortion decision were; desire to delay or end childbearing, concern over the interruption of work or education, issues of financial or relationship stability, and perceived immaturity.[6] A 2004 study in which American women at clinics answered a questionnaire yielded similar results.[7] In Finland and the United States, concern for the health risks posed by pregnancy in individual cases was not a factor commonly given; however, in Bangladesh, India, and Kenya health concerns were cited by women more frequently as reasons for having an abortion.[6] 1% of women in the 2004 survey-based U.S. study became pregnant as a result of rape and 0.5% as a result of incest.[7] Another American study in 2002 concluded that 54% of women who had an abortion were using a form of contraception at the time of becoming pregnant while 46% were not. Inconsistent use was reported by 49% of those using condoms and 76% of those using oral contraception; 42% of those using condoms reported failure through slipping or breakage.[8]
Some abortions are undergone as the result of societal pressures. These might include the stigmatization of disabled persons, preference for children of a specific sex, disapproval of single motherhood, insufficient economic support for families, lack of access to or rejection of contraceptive methods, or efforts toward population control (such as China's one-child policy). These factors can sometimes result in compulsory abortion or sex-selective abortion. In many areas, especially in developing nations or where abortion is illegal, women sometimes resort to "back-alley" or self-induced procedures. The World Health Organization suggests that there are 19 million terminations annually which fit its criteria for an unsafe abortion.[9] See social issues
Forms of abortion
Spontaneous abortion
Spontaneous abortions, generally referred to as miscarriages, occur when an embryo or fetus is lost due to natural causes before the 20th week of development. A pregnancy that ends earlier than 37 weeks of gestation, if it results in a live-born infant, is known as a "premature birth". When a fetus dies in the uterus at some point late in gestation, beginning at about 20 weeks, or during delivery, it is termed a "stillbirth". Premature births and stillbirths are generally not considered to be miscarriages although usage of these terms can sometimes overlap.
Most miscarriages occur very early in pregnancy. Between 10% and 50% of pregnancies end in miscarriage, depending upon the age and health of the pregnant woman.[10]
The risk of spontaneous abortion decreases sharply after the 8th week, i.e. when the fetal stage begins.[11] The risk for spontaneous abortion is greater in those with a history of more than three previous (known) spontaneous abortions, those who have had a previous induced abortion, those with systemic diseases, and those over age 35. Other causes can be infection (of either the woman or the fetus), immune response, or serious systemic disease. A spontaneous abortion can also be caused by accidental trauma; intentional trauma to cause miscarriage is considered induced abortion.
Induced abortion
A pregnancy can be intentionally aborted in many ways. The manner selected depends chiefly upon the gestational age of the fetus, in addition to the legality, regional availability, and/or doctor-patient preference for specific procedures.
Surgical abortion
In the first twelve weeks, suction-aspiration or vacuum abortion is the most common method.[12] Manual vacuum aspiration, or MVA abortion, consists of removing the fetus or embryo by suction using a manual syringe, while the Electric vacuum aspiration or EVA abortion method uses an electric pump. These techniques are comparable, differing in the mechanism used to apply suction, how early in pregnancy they can be used, and whether cervical dilation is necessary. MVA, also known as "mini-suction" and menstrual extraction, can be used in very early pregnancy, and does not require cervical dilation. Surgical techniques are sometimes referred to as STOP: 'Suction (or surgical) Termination Of Pregnancy'. From the fifteenth week until approximately the twenty-sixth week, a dilation and evacuation (D & E) is used. D & E consists of opening the cervix of the uterus and emptying it using surgical instruments and suction.
Dilation and curettage (D & C) is a standard gynecological procedure performed for a variety of reasons, including examination of the uterine lining for possible malignancy, investigation of abnormal bleeding, and abortion. Curettage refers to cleaning the walls of the uterus with a curette. The World Health Organization recommends this procedure, also called Sharp Curettage, only when MVA is unavailable.[13] Sharp curettage only accounted for 2.4% of abortion procedures in the US in 2002.[3] The term "D and C", or sometimes suction curette, is used as a euphemism for the first trimester abortion procedure, irrespective of the method used to perform it.
Other techniques must be used to induce abortion in the third trimester. Premature delivery can be induced with prostaglandin; this can be coupled with injecting the amniotic fluid with caustic solutions containing saline or urea. Very late abortions can be induced by intact dilation and extraction (intact D & X) (also called Intrauterine cranial decompression), which requires surgical decompression of the fetus's head before evacuation, and is sometimes termed "partial-birth abortion." A hysterotomy abortion, similar to a caesarian section but resulting in a terminated fetus, can also be used at late stages of pregnancy. It can be performed vaginally, with an incision just above the cervix, in the late mid-trimester.[citation needed]
From the 20th to 23rd week of gestation, an injection to stop the fetal heart can be used as the first phase of the surgical abortion procedure.[14][15][16][17][18]
Medical abortion
Effective in the first trimester of pregnancy, medical (sometimes called chemical abortion), or non-surgical abortions comprise 10% of all abortions in the United States and Europe. Combined regimens include methotrexate or mifepristone, followed by a prostaglandin—either misoprostol or gemeprost. Misoprostol is used in the U.S.; gemeprost is used in the UK and Sweden. When used within 49 days gestation, approximately 92% of women undergoing medical abortion with a combined regimen experience completed it without surgical intervention.[19] Misoprostol can be used alone, but has a lower efficacy rate than combined regimens. In cases of failure of medical abortion, vacuum or manual aspiration is used to complete the abortion surgically.
Other means of abortion
Historically, a number of herbs reputed to possess abortifacient properties have been used in folk medicine: tansy, pennyroyal, black cohosh, and the now-extinct silphium (see history of abortion).[20] The use of herbs in such a manner can cause serious — even lethal — side effects, such as multiple organ failure, and is not recommended by physicians.[21]
Abortion is sometimes attempted by causing trauma to the abdomen. The degree of force, if severe, can cause serious internal injuries without necessarily succeeding in inducing miscarriage.[22] Both accidental and deliberate abortions of this kind can be subject to criminal liability in many countries. In Burma, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Thailand, there is an ancient tradition of attempting abortion through forceful abdominal massage.[23]
Reported methods of unsafe, self-induced abortion include misuse of misoprostol, and insertion of non-surgical implements such as knitting needles and clothes hangers into the uterus.
Health effects
Early-term surgical abortion is a simple procedure. When performed before the 16th week by competent doctors — or, in some states, nurse practitioners, nurse midwives, and physician assistants — it is safer than childbirth.[24] [25]
Abortion methods, like most surgical procedures, carry a small risk of potentially serious complications. These risks include: a perforated uterus,[26][27] perforated bowel[28] or bladder,[citation needed] septic shock,[29] sterility,[30] and death.[31] The risk of complications can increase depending on how far pregnancy has progressed,[32][33] but remains less than complications that may occur from carrying pregnancy to term.[25]
Assessing the risks of induced abortion depends on a number of factors. First, there are relative health risks of induced abortion and pregnancy, which are both affected by wide variation in the quality of health services in different societies and among different socio-economic groups, a lack of uniform definitions of terms, and difficulties in patient follow-up and after-care. The degree of risk is also dependent upon the skill and experience of the practitioner; maternal age, health, and parity;[33] gestational age;[33][32] pre-existing conditions; methods and instruments used; medications used; the skill and experience of those assisting the practitioner; and the quality of recovery and follow-up care.
In the United Kingdom, the number of deaths directly due to legal abortion between the years of 1991 and 1993 was 5, compared to 3 deaths following spontaneous miscarriage and 8 deaths caused by ectopic pregnancy during the same time frame.[34] In the United States, during the year 1999, there were 4 deaths due to legal abortion, 10 due to miscarriage, and 525 due to pregnancy-related reasons.[35][36]
Some practitioners advocate using minimal anaesthesia so the patient can alert them to possible complications. Others recommend general anaesthesia, to prevent patient movement, which might cause a perforation. General anaesthesia carries its own risks, including death, which is why public health officials recommend against its routine use.
Dilation of the cervix carries the risk of cervical tears or perforations, including small tears that might not be apparent and might cause cervical incompetence in future pregnancies. Most practitioners recommend using the smallest possible dilators, and using osmotic rather than mechanical dilators after the first trimester.
Instruments that are placed within the uterus can, on rare occasions, cause perforation[32] or laceration of the uterus, and damage structures surrounding the uterus. Laceration or perforation of the uterus or cervix can, again on rare occasions, lead to more serious complications.
Incomplete emptying of the uterus can cause hemorrhage and infection. Use of ultrasound verification of the location and duration of the pregnancy prior to abortion, with immediate follow-up of patients reporting continuing pregnancy symptoms after the procedure, will virtually eliminate this risk. The sooner a complication is noted and properly treated, the lower the risk of permanent injury or death.
In rare cases, abortion will be unsuccessful and pregnancy will continue. An unsuccessful abortion can result in delivery of a live neonate, or infant. This, termed a failed abortion, is very rare and can only occur late in pregnancy. Some doctors have voiced concerns about the ethical and legal ramifications of letting the neonate die. As a result, recent investigations have been launched in the United Kingdom by the Confidential Enquiry into Maternal and Child Health (CEMACH) and the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, in order to determine how widespread the problem is and what an ethical response in the treatment of the infant might be.[37]
Unsafe abortion methods (e.g. use of certain drugs, herbs, or insertion of non-surgical objects into the uterus) are potentially dangerous, carrying a significantly elevated risk for permanent injury or death, as compared to abortions done by physicians.
Suggested effects
There is controversy over a number of proposed risks and effects of abortion. Evidence, whether in support of or against such claims, might be influenced by the political and religious beliefs of the parties behind it.
Breast cancer
The abortion-breast cancer (ABC) hypothesis posits a causal relationship between induced abortion and increased risk of developing breast cancer. In early pregnancy the level of estrogens increases, leading to breast growth in preparation for lactation. The ABC hypothesis proposes that if this process is interrupted with abortion – before full differentiation in the third trimester – then more relatively vulnerable undifferentiated cells could be left than there were prior to the pregnancy, resulting in greater potential risk of breast cancer. The hypothesis, however, has not been scientifically verified, and abortion is not considered a breast cancer risk by any major cancer organization.
A epidemiological study by Dr. Mads Melbye et al. in 1997, with data from two national registries in Denmark, reported the correlation to be negligible to non-existent after statistical adjustment.[38] The National Cancer Institute conducted an official workshop with numerous experts on the issue in February 2003, which concluded with its highest strength rating for the selected evidence it considered that "induced abortion is not associated with an increase in breast cancer risk."[39] In 2004, Beral et al. published a collaborative reanalysis of 53 epidemiological studies and concluded that abortion does "not increase a woman's risk of developing breast cancer."[40]
Of over 100 experts at the National Cancer Institute workshop, Dr. Joel Brind, the primary advocate of an abortion-breast cancer link and an invitee to the workshop, filed the only dissenting opinion criticizing the NCI's and Melbye's conclusions.[41] Brind argues that the majority of interview-based studies have indicated a link and some are statistically significant,[42] but there remains debate as to the reliability of these retrospective studies because of possible response bias. Most medical professionals agree with the recent prospective studies that conclude no abortion-breast cancer association,[43] and the ABC issue is seen by some as merely a part of the current pro-life "women-centered" strategy against abortion.[44] Nevertheless, the subject continues to be one of mostly political but some scientific contention.[45]
Fetal pain
The existence or absence of fetal sensation during abortion is a matter of medical, ethical and public policy interest. Evidence conflicts, with some authorities holding that the fetus is capable of feeling pain from the first trimester,[46] and others maintaining that the neuro-anatomical requirements for such experience do not exist until the second or third trimester.[47]
Pain receptors begin to appear in the seventh week of gestation. The thalamus, the part of the brain which receives signals from the nervous system and then relays them to the cerebral cortex, starts to form in the fifth week. However, other anatomical structures involved in the nociceptic process are not present until much later in gestation. Links between the thalamus and cerebral cortex form around the 23rd week.[48] There has been suggestion that a fetus cannot feel pain at all, as it requires mental development that only occurs outside the womb.[49]
Researchers have observed changes in heart rates and hormonal levels of newborn infants after circumcision, blood tests, and surgery — effects which were alleviated with the administration of anesthesia.[50] Others suggest that the human experience of pain, being more than just physiological, cannot be measured in such reflexive responses.[51]
Mental health
Post-abortion syndrome (PAS) is a term used to describe a set of mental health characteristics which some researchers claim to have observed in women following an abortion.[52] The psychopathological symptoms attributed to PAS are similar to those of post-traumatic stress disorder, but have also included, "repeated and persistent dreams and nightmares related with the abortion, intense feelings of guilt and the 'need to repair'".[52] Whether this would warrant classification as an independent syndrome is disputed by other researchers.[53] PAS is listed in neither the DSM-IV-TR nor the ICD-10.
Some studies have shown abortion to have neutral or positive effects on the mental well-being of some patients. A 1989 study of teenagers who sought pregnancy tests found that, counting from the beginning of pregnancy until two years later, the level of stress and anxiety of those who had an abortion did not differ from that of those who had not been pregnant or who had carried their pregnancy to term.[54] Another study in 1992 suggested a link between elective abortion and later reports of positive self-esteem; it also noted that adverse emotional reactions to the procedure are most strongly influenced by pre-existing psychological conditions and other negative factors.[55] Abortion, as compared to completion, of an undesired first pregnancy was not found to directly pose the risk of significant depression in a 2005 study.[56]
Other studies have shown a correlation between abortion and negative psychological impact. A 1996 study found that suicide is more common after miscarriage and especially after induced abortion, than in the general population.[57] Additional research in 2002 reported that the risk of clinical depression was higher for women who chose to have an abortion compared to those who opted to carry to term — even if the pregnancy was unwanted.[58] Another study in 2006, which used data gathered over a 25-year period, found an increased occurrence of clinical depression, anxiety, suicidal behavior, and substance abuse among women who had previously had an abortion.[59]
Miscarriage, or spontaneous abortion, is known to present an increased risk of depression.[60] Childbirth can also sometimes result in maternity blues or postpartum depression.
History of abortion
Induced abortion, according to some anthropologists, can be traced to ancient times.[61] There is evidence to suggest that, historically, pregnancies were terminated through a number of methods, including the administration of abortifacient herbs, the use of sharpened implements, the application of abdominal pressure, and other techniques.
The Hippocratic Oath, the chief statement of medical ethics in Ancient Greece, forbade all doctors from helping to procure an abortion by pessary. Nonetheless, Soranus, a second-century Greek physician, suggested in his work Gynaecology that women wishing to abort their pregnancies should engage in violent exercise, energetic jumping, carrying heavy objects, and riding animals. He also prescribed a number of recipes for herbal baths, pessaries, and bloodletting, but advised against the use of sharp instruments to induce miscarriage due to the risk of organ perforation.[62] It is also believed that, in addition to using it as a contraceptive, the ancient Greeks relied upon silphium as an abortifacient. Such folk remedies, however, varied in effectiveness and were not without risk. Tansy and pennyroyal, for example, are two poisonous herbs with serious side effects that have at times been used to terminate pregnancy.
Abortion in the 19th century continued, despite bans in both the United Kingdom and the United States, as the disguised, but nonetheless open, advertisement of services in the Victorian era suggests.[63]
Social issues
A number of complex issues exist in the debate over abortion. These, like the suggested effects upon health listed above, are a focus of research and a fixture of discussion among members on all sides of the controversy.
Effect upon crime rate
A controversial theory attempts to draw a correlation between the United States' unprecedented nationwide decline of the overall crime rate during the 1990s and the decriminalization of abortion 20 years prior.
The suggestion was brought to widespread attention by a 1999 academic paper, The Impact of Legalized Abortion on Crime, authored by the economists Steven D. Levitt and John Donohue. They attributed the drop in crime to a reduction in individuals said to have a higher statistical probability of committing crimes: unwanted children, especially those born to mothers who are African-American, impoverished, adolescent, uneducated, and single. The change coincided with what would have been the adolescence, or peak years of potential criminality, of those who had not been born as a result of Roe v. Wade and similar cases. Donohue and Levitt's study also noted that states which legalized abortion before the rest of the nation experienced the lowering crime rate pattern earlier, and those with higher abortion rates had more pronounced reductions.[64]
Fellow economists Christopher Foote and Christopher Goetz criticized the methodology in the Donohue-Levitt study, noting a lack of accommodation for statewide yearly variations such as cocaine use, and recalculating based on incidence of crime per capita; they found no statistically significant results.[65] Levitt and Donohue responded to this by presenting an adjusted data set which took into account these concerns and reported that the data maintained the statistical significance of their initial paper.[66]
Such research has been criticized by some as being utilitarian, discriminatory as to race and socioeconomic class, and as promoting eugenics as a solution to crime.[67][68] Levitt states in his book, Freakonomics, that they are neither promoting nor negating any course of action — merely reporting data as economists.
Sex-selective abortion
The advent of both ultrasound and amniocentesis has allowed parents to determine sex before birth. This has led to the occurrence of sex-selective abortion or the targeted termination of a fetus based upon its sex.
It is suggested that sex-selective abortion might be partially responsible for the noticeable disparities between the birth rates of male and female children in some places. The preference for male children is reported in many areas of Asia, and abortion used to limit female births has been reported in Mainland China, Taiwan, South Korea, and India.[69]
In India, the economic role of men, the costs associated with dowries, and a Hindu tradition which dictates that funeral rites must be performed by a male relative have led to a cultural preference for sons.[70] The widespread availability of diagnostic testing, during the 1970s and '80s, led to advertisements for services which read, "Invest 500 rupees [for a sex test] now, save 50,000 rupees [for a dowry] later."[71] In 1991, the male-to-female sex ratio in India was skewed from its biological norm of 105 to 100, to an average of 108 to 100.[72] Researchers have asserted that between 1985 and 2005 as many as 10 million female fetuses may have been selectively aborted.[73] The Indian government passed an official ban of pre-natal sex screening in 1994 and moved to pass a complete ban of sex-selective abortion in 2002.[74]
In the People's Republic of China, there is also a historic son preference. The implementation of the one-child policy in 1979, in response to population concerns, led to an increased disparity in the sex ratio as parents attempted to circumvent the law through sex-selective abortion or the abandonment of unwanted daughters.[75] Sex-selective abortion might be an influence on the shift from the baseline male-to-female birth rate to an elevated national rate of 117:100 reported in 2002. The trend was more pronounced in rural regions: as high as 130:100 in Guangdong and 135:100 in Hainan.[76] A ban upon the practice of sex-selective abortion was enacted in 2003.[77]
Unsafe abortion
Where and when access to safe abortion has been barred, due to explicit sanctions or general unavailability, women seeking to terminate their pregnancies have sometimes resorted to unsafe methods.
"Back-alley abortion" is a slang term for any abortion not practiced under generally accepted standards of sanitation and professionalism. The World Health Organization defines an unsafe abortion as being, "a procedure...carried out by persons lacking the necessary skills or in an environment that does not conform to minimal medical standards, or both."[9] This can include a person without medical training, a professional health provider operating in sub-standard conditions, or the woman herself.
Unsafe abortion remains a public health concern today due to the higher incidence and severity of its associated complications, such as incomplete abortion, sepsis, hemorrhage, and damage to internal organs. WHO estimates that 19 million unsafe abortions occur around the world annually and that 68,000 of these result in the woman's death.[9] Complications of unsafe abortion are said to account, globally, for approximately 13% of all maternal mortalities, with regional estimates including 12% in Asia, 25% in Latin America, and 13% in sub-Saharan Africa.[78] Health education, access to family planning, and improvements in health care during and after abortion have been proposed to address this phenomenon.[79]
Abortion debate
Over the course of the history of abortion, induced abortion has been the source of considerable debate, controversy, and activism. An individual's position on the complex ethical, moral, philosophical, biological, and legal issues is often related to his or her value system. Opinions of abortion may be best described as being a combination of beliefs on its morality, and beliefs on the responsibility, ethical scope, and proper extent of governmental authorities in public policy. Religious ethics also has an influence upon both personal opinion and the greater debate over abortion (see religion and abortion).
Abortion debates, especially pertaining to abortion laws, are often spearheaded by advocacy groups belonging to one of two camps. Most often those in favor of legal prohibition of abortion describe themselves as pro-life while those against legal restrictions on abortion describe themselves as pro-choice. Both are used to indicate the central principles in arguments for and against abortion: "Is the fetus a human being with a fundamental right to life?" for pro-life advocates, and, for those who are pro-choice, "Does a woman have the right to choose whether or not to have an abortion?"
In both public and private debate, arguments presented in favor of or against abortion focus on either the moral permissibility of an induced abortion, or justification of laws permitting or restricting abortion. Arguments on morality and legality tend to collide and combine, complicating the issue at hand.
Debate also focuses on whether the pregnant woman should have to notify and/or have the consent of others in distinct cases: a minor, her parents; a legally-married or common-law wife, her husband; or a pregnant woman, the biological father. In a 2003 Gallup poll in the United States, 72% of respondents were in favor of spousal notification, with 26% opposed; of those polled, 79% of males and 67% of females responded in favor.[80]
Public opinion
A number of opinion polls around the world have explored public opinion regarding the issue of abortion. Results have varied from poll to poll, country to country, and region to region, while varying with regard to different aspects of the issue.
A May 2005 survey examined attitudes toward abortion in 10 European countries, asking polltakers whether they agreed with the statement, "If a woman doesn't want children, she should be allowed to have an abortion". The highest level of approval was 81% in the Czech Republic and the highest level of disapproval was 48% in Poland. [81]
In North America, a December 2001 poll surveyed Canadian opinion on abortion, asking Canadians in what circumstances they believe abortion should be permitted; 32% responded that they believe abortion should be legal in all circumstances, 52% that it should be legal in certain circumstances, and 14% that it should be legal in no circumstances. A similar poll in January 2006 surveyed people in the United States about U.S. opinion on abortion; 33% said that abortion should be "permitted only in cases such as rape, incest or to save the woman's life", 27% said that abortion should be "permitted in all cases", 15% that it should be "permitted, but subject to greater restrictions than it is now", 17% said that it should "only be permitted to save the woman's life", and 5% said that it should "never" be permitted.[82] A November 2005 poll in Mexico found that 73.4% think abortion should not be legalized while 11.2% think it should. [83]
Of attitutes in South and Central America, a December 2003 survey found that 30% of Argentines thought that abortion in Argentina should be allowed "regardless of situation", 47% that it should be allowed "under some circumstances", and 23% that it should not be allowed "regardless of situation".[84] A poll regarding the abortion law in Brazil found that 63% of Brazilians believe that it "should not be modified", 17% that it should be expanded "to allow abortion in other cases", 11% that abortion should be "decriminalized", and 9% were "unsure". [85] A July 2005 poll in Colombia found that 65.6% said they thought that abortion should remain illegal, 26.9% that it should be made legal, and 7.5% that they were unsure. [86]
Abortion law

Before the scientific discovery that human development began at fertilization, British common law allowed abortions to be performed before quickening, the earliest perception of fetal movement by a woman during the second trimester of pregnancy. In 1861, the British Parliament passed the Offences Against the Person Act, which put the common law offence of abortion into statute throughout the British Empire. The Soviet Union, with legislation in 1920, and Iceland, with legislation in 1935, were two of the first countries to generally allow abortion. The second half of the 20th century saw the liberalization of abortion laws in other countries. The Abortion Act 1967 allowed abortion for limited reasons in the United Kingdom. In the 1973 case, Roe v. Wade, the United States Supreme Court struck down state laws banning abortion in the first trimester, ruling that such laws violated an implied right to privacy in the United States Constitution. The Supreme Court of Canada, similarly, in the case of R. v. Morgentaler, discarded its criminal code regarding abortion in 1988, after ruling that such restrictions violated the security of person guaranteed to women under the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms. Canada later struck down provincial regulations of abortion in the case of R. v. Morgentaler (1993). By contrast, Abortion in Ireland was affected by the addition of an amendment to the Irish Constitution in 1983 by popular referendum, recognizing "the right to life of the unborn".
Current laws pertaining to abortion are diverse. Religious, moral, and cultural sensibilities continue to influence abortion laws throughout the world. The right to life, the right to liberty, and the right to security of person are major issues of human rights that are sometimes used as justification for the existence or the absence of laws controlling abortion. Many countries in which abortion is legal require that certain criteria be met in order for an abortion to be obtained, often, but not always, using a trimester-based system to regulate the window in which abortion is still legal to perform:
- In the United States, some states impose a 24-hour waiting period before the procedure, prescribe the distribution of information on fetal development, or require that parents be contacted if their minor daughter requests an abortion.
- In the United Kingdom, as in some other countries, two doctors must first certify that an abortion is medically or socially necessary before it can be performed.
Other countries, in which abortion is normally illegal, will allow one to be performed in the case of rape, incest, or danger to the pregnant woman's life or health. A handful of nations ban abortion entirely: Chile, El Salvador, Malta, and Nicaragua, although in 2006 the Chilean government begun the free distribution of emergency contraception.[87][88] In Bangladesh, abortion is illegal, but the government has long supported a network of "menstrual regulation clinics", where menstrual extraction (manual vacuum aspiration) can be performed as menstrual hygiene.[89]
See also
|
|
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ Roche, Natalie E. (2004). Therapeutic Abortion. Retrieved 2006-03-08.
- ↑ Henshaw, Stanley K., Singh, Susheela, & Haas, Taylor. (1999). The Incidence of Abortion Worldwide. International Family Planning Perspectives, 25 (Supplement), 30–8. Retrieved 2006-01-18.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Strauss, Lilo T., Herndon, Joy, Chang, Jeani, Parker, Wilda Y., Bowens, Sonya V., Berg, Cynthia J. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2005-11-15). Abortion Surveillance - United States, 2002. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Retrieved 2006-02-20.
- ↑ Finer, Lawrence B. & Henshaw, Stanley K. (2003). Abortion Incidence and Services in the United States in 2000. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 35 (1). Retrieved 2006-05-10.
- ↑ Government Statistical Service for the Department of Health. (2005-07-27). Abortion statistics, England and Wales: 2004. Retrieved 2006-05-10.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Bankole, Akinrinola, Singh, Susheela, & Haas, Taylor. (1998). Reasons Why Women Have Induced Abortions: Evidence from 27 Countries. International Family Planning Perspectives, 24 (3), 117-127 & 152. Retrieved 2006-01-18.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Finer, Lawrence B., Frohwirth, Lori F., Dauphinee, Lindsay A., Singh, Shusheela, & Moore, Ann M. (2005). Reasons U.S. women have abortions: quantative and qualitative perspectives. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 37 (3), 110-8. Retrieved 2006-01-18.
- ↑ Jones, Rachel K., Darroch, Jacqueline E., Henshaw, Stanley K. (2002). Contraceptive Use Among U.S. Women Having Abortions in 2000-2001. Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health, 34 (6). Retrieved June 15, 2006.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 World Health Organization. (2004). Unsafe abortion: global and regional estimates of unsafe abortion and associated mortality in 2000. Retrieved 2006-01-12.
- ↑ "Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility: Recurrent Pregnancy Loss (Recurrent Miscarriage)." (n.d.) Retrieved 2006-01-18 from Washington University School of Medicine, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology web site.
- ↑ Q&A: Miscarriage. (August 6 , 2002). BBC News. Retrieved January 10, 2007.
- ↑ Healthwise. Manual and vacuum aspiration for abortion. (2004). WebMD. Retrieved 2006-08-19.
- ↑ World Health Organization. (2003). Managing complications in pregnancy and childbirth: a guide for midwives and doctors. Retrieved 2006-08-19.
- ↑ Vause S, Sands J, Johnston TA, Russell S, Rimmer S. (2002). PMID 12521492 Could some fetocides be avoided by more prompt referral after diagnosis of fetal abnormality? J Obstet Gynaecol. 2002 May;22(3):243-5. Retrieved 2006-03-17.
- ↑ Dommergues M, Cahen F, Garel M, Mahieu-Caputo D, Dumez Y. (2003). PMID 12576743 Feticide during second- and third-trimester termination of pregnancy: opinions of health care professionals. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2003 Mar-Apr;18(2):91-7. Retrieved 2006-03-17.
- ↑ Bhide A, Sairam S, Hollis B, Thilaganathan B. (2002). PMID 12230443 Comparison of feticide carried out by cordocentesis versus cardiac puncture. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2002 Sep;20(3):230-2. Retrieved 2006-03-17.
- ↑ Senat MV, Fischer C, Bernard JP, Ville Y. (2003). PMID 12628271 The use of lidocaine for fetocide in late termination of pregnancy. BJOG. 2003 Mar;110(3):296-300. Retrieved 2006-03-17.
- ↑ Senat MV, Fischer C, Ville Y. (2002). PMID 12001185 Funipuncture for fetocide in late termination of pregnancy. Prenat Diagn. 2002 May;22(5):354-6. Retrieved 2006-03-17.
- ↑ Spitz, I.M. et al (1998). Early pregnancy termination with mifepristone and misoprostol in the United States. New England Journal of Medicine 338 (18). PMID 9562577.
- ↑ Riddle, John M. (1997). Eve's Herbs: A History of Contraception and Abortion in the West. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- ↑ Ciganda, C., & Laborde, A. (2003). Herbal infusions used for induced abortion. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol, 41(3), 235-9. Retrieved 2006-01-25.
- ↑ Education for Choice. (2005-05-06). Unsafe abortion. Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ↑ Potts, Malcolm, & Campbell, Martha. (2002). History of contraception. Gynecology and Obstetrics, vol. 6, chp. 8. Retrieved 2005-01-25.
- ↑ Cates W., Jr, & Tietze C. (1978). Standardized mortality rates associated with legal abortion: United States, 1972-1975 Electronic version. Family Planning Perspectives, 10 (2), 109-12. Retrieved 2006-01-28.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 Grimes, D.A. (1994). The morbidity and mortality of pregnancy: still risky business. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 170 (5 Pt 2), 1489-94. Retrieved December 21, 2006.
- ↑ Legarth, J., Peen, U.B., & Michelsen, J.W. (1991). Mifepristone or vacuum aspiration in termination of early pregnancy. European Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Biology, 41 (2), 91-6. Retrieved December 21, 2006.
- ↑ Mittal, S., & Misra, S.L. (1985). Uterine perforation following medical termination of pregnancy by vacuum aspiration. International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics, 23 (1), 45-50. Retrieved December 21, 2006.
- ↑ WHO Health Organization. Medical Methods for termination of pregnancy. WHO Technical Report Series 871, 1997
- ↑ Dzhavakhadze, M.V., & Daraselia, M.I. (2005). Mortality case analyses of obstetric-gynecologic sepsis. Georgian Medical News, 127, 26-9. Retrieved December 21, 2006.
- ↑ Tzonou, A., Hsieh, C.C., Trichopoulos, D., Aravandinos, D., Kalandidi, A., Margaris, D., Goldman, M., et al. (1993) Induced abortions, miscarriages, and tobacco smoking as risk factors for secondary infertility. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 47 (1), 36-9. Retrieved December 21, 2006.
- ↑ Lanska, M.J., Lanska, D., & Rimm, A.A. (1983). Mortality from abortion and childbirth. Journal of the American Medical Association, 250(3), 361-2. Retrieved December 21, 2006.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 Pauli, E., Haller, U., Zimmermann, R. (2005). Morbidity of dilatation and evacuation in the second trimester: an analysis. Gynakol Geburtshilfliche Rundsch, 45 (2), 107-15. Retrieved December 26, 2006.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 33.2 Bartley, J., Tong, S., Everington, D.,& Baird, D.T. (2000). Parity is a major determinant of success rate in medical abortion: a retrospective analysis of 3161 consecutive cases.... Contraception, 62(6), 297-303. Retrieved December 26, 2006.
- ↑ Department of Health. (1998). Why Mothers Die: Report on Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths in the United Kingdom 1994–1996. London: The Stationery Office. Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ↑ Elam-Evans, Laurie. D., Strauss, Lilo T., Herndon, Joy, Parker, Wilda Y., Bowens, Sonya V., Zane, Suzanne, et al. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2003-11-23). Abortion Surveillance - United States, 2000. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2003-02-20). Fact Sheet: Pregnancy-Related Mortality Surveillance - United States, 1991-1999. Retrieved 2006-04-02.
- ↑ Rogers, Lois. (2005-11-27). "Fifty babies a year are alive after abortion." The Sunday Times. Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ↑ Melbye M. et al. (1997) Induced abortion and the risk of breast cancer. (abstract) New England Journal of Medicine, 336, 81-5. Retrieved 2006-01-11 from PubMed.
- ↑ National Cancer Institute. (2003-03-04). Summary Report: Early Reproductive Events and Breast Cancer Workshop. Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ↑ Beral V. et al. (2004) Breast cancer and abortion: collaborative reanalysis of data from 53 epidemiological studies, including 83,000 women with breast cancer from 16 countries. (abstract) The Lancet, 363, 1007-16. Retrieved 2006-04-12 from PubMed.
- ↑ Brind, Joel. (2003-03-10). Early Reproductive Events and Breast Cancer: A Minority Report. Retrieved 2006-03-24.
- ↑ Etters.net – American abortion-breast cancer studies
- ↑ American Cancer Society. (2006-10-03) Cancer.org – What Are the Risk Factors for Breast Cancer? Retrieved 2006-03-30.
- ↑ Arthur, Joyce. (2002) ProChoiceActionNetwork-Canada.org – Abortion and Breast Cancer — A Forged Link
- ↑ Jasen, P. (2005) Breast Cancer and the Politics of Abortion in the United States. Medical History 2005 October 1; 49(4): 423–444.
- ↑ Schmidt, Dr. Richard T. F., et. al. (1984-02-13). Open Letter to President Reagan. Press release. Retrieved on 2006-11-18.
- ↑ BBC News Article (2005). "Foetuses 'no pain up to 29 weeks'." Retrieved 2006-07-18.
- ↑ Parliamentary Office of Science and Technology. (1997). Fetal Awareness. Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ↑ BBC News Article (2006). "Foetuses 'cannot experience pain'." Retrieved 2006-07-18.
- ↑ Anand, K., Phil, D., & Hickey, P.R. (1987). Pain and its effects on the human neonate and fetus. New England Journal of Medicine, 316 (21), 1321-9. Retrieved 2006-01-11 from The Circumcision Reference Library.
- ↑ Lee, Susan J., Ralston, Henry J. Peter, Drey, Eleanor A., Partridge, John Colin, & Rosen, Mark A. (2005). Fetal Pain: A Systematic Multidisciplinary Review of the Evidence. Journal of the American Medical Association, 294 (8), 947-954. Retrieved November 10, 2006.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 Gomez, Lavin C., & Zapata, Garcia R. (2005). - "Diagnostic categorization of post-abortion syndrome". Actas Esp Psiquiatr, 33 (4), 267-72. Retrieved Setepmber 8, 2006.
- ↑ Stotland, N.L. (1992). The myth of the abortion trauma syndrome. Journal of the American Medical Association, 268 (15), 2078-9. Retrieved December 7, 2006.
- ↑ Zabin, L.S., Hirsch, M.B., Emerson, M.R. (1989). When urban adolescents choose abortion: effects on education, psychological status and subsequent pregnancy. Family Planning Perspectives, 21 (6), 248-55. Retrieved September 8, 2006.
- ↑ Russo, N. F., & Zierk, K.L. (1992). Abortion, childbearing, and women. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 23(4), 269-280. Retrieved September 8, 2006.
- ↑ Schmiege, S. & Russo, N.F. (2005). Depression and unwanted first pregnancy: longitudinal cohort study Electronic version . British Medical Journal, 331 (7528), 1303. Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ↑ Gissler, M., Hemminki, E., & Lonnqvist, J. (1996). Suicides after pregnancy in Finland, 1987-94: register linkage study Electronic version. British Medical Journal, 313, 1431-4. Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ↑ Reardon, D.C. & Cougle, J.R. (2002): Depression and unintended pregnancy in the National Longitudinal Survey of Youth: a cohort study. BMJ (British Medical Journal) 19.1.2002 324:151-2. Electronic version.
- ↑ Fergusson D.M., Horwood L.J., & Ridder E.M. (2006). Abortion in young women and subsequent mental health. Journal of Child Psychology & Psychiatry 47 (1). PMID 16405636.
- ↑ Depression Risk Increased After Miscarriage. (2002-04-01). Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ↑ Devereux, G. (1967). A typological study of abortion in 350 primitive, ancient, and pre-industrial societies. Retrieved April 22, 2006. In Abortion in America: medical, psychiatric, legal, anthropological, and religious considerations. Boston: Beacon Press. Retrieved April 22, 2006.
- ↑ Lefkowitz, Mary R. & Fant, Maureen R. (1992). Women's life in Greece & Rome: a source book in translation. Baltimore, MD: John Hopkins University Press. Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ↑ Histories of Abortion. (n.d.) Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ↑ Donohue, John J. and Levitt, Steven D. (2001). The impact of legalized abortion on crime.Quarterly Journal of Economics Retrieved 2006-02-11.
- ↑ Foote, Christopher L. and Goetz, Christopher F. (2005). Testing economic hypotheses with state-level data: a comment on Donohue and Levitt (2001). Working Papers, 05-15. Retrieved 2006-02-11.
- ↑ Donohue, John J. and Levitt, Steven D. (2006). Measurement error, legalized abortion, and the decline in crime: a response to Foote and Goetz (2005). Retrieved 2006-02-17, from University of Chicago, Initiative on Chicago Price Theory web site: ResponseToFooteGoetz2006.pdf.
- ↑ "Crime-Abortion Study Continues to Draw Pro-life Backlash." (1999-08-11). The Pro-Life Infonet. Retrieved 2006-02-17 from Ohio Roundtable Online Library.
- ↑ "Abortion and the Lower Crime Rate." (2000, January). St. Anthony Messenger. Retrieved 2006-02-17.
- ↑ Banister, Judith. (1999-03-16). Son Preference in Asia - Report of a Symposium. Retrieved 2006-01-12.
- ↑ Mutharayappa, Rangamuthia, Kim Choe, Minja, Arnold, Fred, & Roy, T.K. (1997). Son Preferences and Its Effect on Fertility in India. National Family Health Survey Subject Reports, Number 3. Retrieved 2006-01-12.
- ↑ Patel, Rita. (1996). The practice of sex selective abortion in India: may you be the mother of a hundred sons. Retrieved 2006-01-11, from University of North Carolina, University Center for International Studies web site: abortion.pdf.
- ↑ Sudha, S., & Irudaya Rajan, S. (1999). Female Demographic Disadvantage in India 1981-1991: Sex Selective Abortion, Female Infanticide and Excess Female Child Mortality. Retrieved 2006-01-12
- ↑ Reaney, Patricia. (2006-01-09). "Selective abortion blamed for India's missing girls." Reuters AlertNet. Retrieved 2006-01-09.
- ↑ Mudur, Ganapati. (2002). "India plans new legislation to prevent sex selection." British Medical Journal: News Roundup. Retrieved 2006-01-12.
- ↑ Graham, Maureen J., Larsen, Ulla, & Xu, Xiping. (1998). Son Preference in Anhui Province, China. International Family Planning Perspectives, 24 (2). Retrieved 2006-01-12.
- ↑ Plafker, Ted. (2002-05-25). Sex selection in China sees 117 boys born for every 100 girls. British Medical Journal: News Roundup. Retrieved 2006-01-12.
- ↑ "China Bans Sex-selection Abortion." (2002-03-22). Xinhua News Agency. Retrieved 2006-01-12.
- ↑ Salter, C., Johnson, H.B., and Hengen, N. (1997). Care for postabortion complications: saving women's lives. Population Reports, 25 (1). Retrieved 2006-02-22.
- ↑ World Health Organization. (1998). Address Unsafe Abortion. Retrieved 2006-03-01.
- ↑ The Pew Research Center for the People and the Press. (2005-11-02). "Public Opinion Supports Alito on Spousal Notification Even as It Favors Roe v. Wade." Pew Research Center Pollwatch. Retrieved 2006-03-01.
- ↑ TNS Sofres. (May 2005). European Values. Retrieved January 11, 2007.
- ↑ The Polling Report. (2006). Retrieved 2006-01-11.
- ↑ "Mexicans Support Status Quo on Social Issues." (December 1, 2005). Angus Reid Global Monitor. Retrieved January 10, 2006.
- ↑ "Argentines Assess Abortion Changes." (Mar. 4, 2004). Angus Reid Global Monitor. Retrieved January 10, 2006.
- ↑ "Brazilians Satisfied with Abortion Law." (August 20, 2006). Angus Reid Global Monitor. Retrieved January 10, 2006.
- ↑ "Colombians Reject Legalizing Abortion. (August 2, 2005). Angus Reid Global Monitor. Retrieved January 10, 2006.
- ↑ Ross, Jen. (September 12, 2006). "In Chile, free morning-after pills to teens." The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved 2006-12-07.
- ↑ Gallardoi, Eduardo. (September 26, 2006). "Morning-After Pill Causes Furor in Chile." The Washington Post. Retrieved 2006-12-07.
- ↑ Surgical Abortion: History and Overview. National Abortion Federation. Retrieved 2006-09-04.
External links
- Abortion Laws of the World
- Abortion Policies: A Global Review
- "Abortion Clinic:" a 1983 PBS Frontline episode.
- U.S. National Library of Medicine and National Institutes of Health MedlinePlus encyclopedia
- Abortion: All sides to the issue from the Ontario Consultants on Religious Tolerance
- Issue Guide on Abortion from Public Agenda Online
The following information resources may be created by those with a non-neutral position in the abortion debate:
- The Guttmacher Institute
- Johnston's Archive: Abortion Statistics and Other Data
- Just Facts: Abortion
- Abortion.com: Abortion Clinics and Medical Providers
The following links are to groups which advocate a specific position:
- Children by Choice (Australia, pro-choice)
- Right to Life Australia (pro-life)
- Canadians for Choice (pro-choice)
- LifeCanada (pro-life)
- Abortion Law Reform Association of New Zealand (pro-choice)
- Voice for Life (New Zealand, pro-life)
- Abortion Rights (United Kingdom, pro-choice)
- LifeUK (United Kingdom, pro-life)
- American Life League (pro-life)
- NARAL Pro-choice America (pro-choice)
- CareNet (international, pro-life)
- Planned Parenthood (international, pro-choice)
Template:BirthControl
ar:إجهاض bn:গর্ভপাত bg:Аборт ca:Avortament cs:Interrupce da:Provokeret abort de:Schwangerschaftsabbruch es:Aborto eo:Aborto fr:Avortement hr:Pobačaj id:Gugur kandungan ia:Aborto it:Interruzione volontaria di gravidanza he:הפלה מלאכותית lt:Abortas hu:Terhességmegszakítás mk:Абортус nl:Abortus ja:妊娠中絶 no:Abort nn:Abort pam:Abortion pl:Aborcja pt:Interrupção da gravidez ro:Avort ru:Аборт simple:Abortion sk:Potrat sr:Абортус sh:Abortus fi:Abortti sv:Abort tl:Pagpapalaglag th:การแท้ง tr:Kürtaj uk:Аборт yi:אבארטאציע zh:堕胎
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.