Poland
| Rzeczpospolita Polska Republic of Poland |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: See: unofficial mottos of Poland | ||||||
| Anthem: Mazurek Dąbrowskiego (Polish) Dąbrowski's Mazurek |
||||||
| Location of Poland (orange) – on the European continent (camel white) – in the European Union (camel) [Legend] |
||||||
| Capital (and largest city) | Warsaw 52°13′N 21°02′E | |||||
| Official languages | Polish² | |||||
| Demonym | Pole | |||||
| Government | Parliamentary republic | |||||
| - | President | Lech Kaczyński | ||||
| - | Prime Minister | Donald Tusk | ||||
| Formation | ||||||
| - | Christianisation4 | 14 April 966 | ||||
| - | Redeclared | 11 November 1918 | ||||
| EU accession | 01 May 2004 | |||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 312,679 km² (6Template:9th³) 120,728 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 3.07 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2007 estimate | 38,518,241 (33rd) | ||||
| - | 2002 census | 38,530,080 | ||||
| - | Density | 122/km² (83rd) 319.9/sq mi |
||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2007 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $631.8 billion (IMF) (24) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $16,599 (IMF) (52) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2007 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $413.3 billion (IMF) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $10,858 (IMF) | ||||
| Currency | Złoty (PLN) |
|||||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .pl5 | |||||
| Calling code | +48 | |||||
| 1 See, however, Unofficial mottos of Poland. ² Although not official languages, Kashubian, Lithuanian and German are used in 19 communal offices. ³ The area of Poland according to the administrative division, as given by the Central Statistical Office,[1] amounts to 312,679 km²: land area (311 888 km²) and part of internal waters (791 km²) cut by the coast line. The area of Poland's territory, including all internal waters and the territorial sea, is 322 575 km². 4 The adoption of Christianity in Poland is seen by many Poles, regardless of their religious affiliation, as one of the most significant national historical events; the new religion was used to unify the tribes in the region. 5 Also .eu, as Poland is a member of the European Union. |
||||||
Poland (Polish: Polska), officially the Republic of Poland (Polish: Rzeczpospolita Polska), is a country in Central Europe on the boundary between Eastern and Western European continental masses, and is considered at times a part of Eastern Europe.
The first Polish state was baptized in 966, within territory similar to the present boundaries of Poland. Poland became a kingdom in 1025, and in 1569 it cemented a long association with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania by uniting to form the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Commonwealth collapsed in 1795. Poland regained its independence in 1918 after World War I but lost it again in World War II, occupied by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union, emerging several years later as a communist country within the Eastern Bloc under the control of the Soviet Union.
In 1989, communist rule was overthrown and Poland became what is informally known as the "Third Polish Republic".
Poland is the 33rd most populous country in the world. Poland is a unitary state made up of sixteen voivodeships (Polish: województwo). Poland is also a member of the European Union, NATO and OECD.
Geography
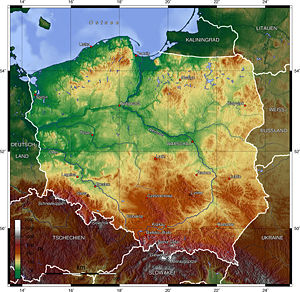

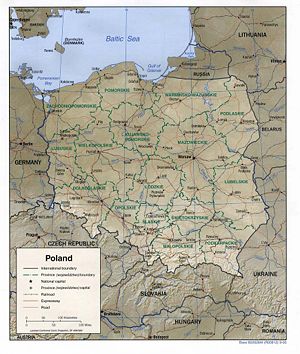
Poland is bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine and Belarus to the east; and the Baltic Sea, Lithuania and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north. The total area of Poland is 120,728 square miles (312,679 square kilometers) making it the 69th largest country in the world and seventh in Europe — or slightly smaller than New Mexico in the United States.
The geological structure of Poland has been shaped by the continental collision of Europe and Africa over the past 60 million years, on the one hand, and the Quaternary glaciations of northern Europe, on the other. Both processes shaped the Sudetes and the Carpathians. The moraine landscape of northern Poland contains soils made up mostly of sand or loam, while the ice-age river valleys of the south often contain loess. The Cracow-Częstochowa Upland, the Pieniny, and the Western Tatras consist of limestone, while the High Tatras, the Beskids, and the Karkonosze are made up mainly of granite and basalts. The Kraków-Częstochowa Upland is one of the oldest mountain ranges on earth.
Poland’s territory extends across five geographical regions. In the northwest is the Baltic seacoast, marked by several spits, coastal lakes (former bays that have been cut off from the sea), and dunes. The centre and parts of the north lie within the Northern European Lowlands. Rising gently above these lowlands is a geographical region comprising the four hilly districts of moraines and moraine-dammed lakes formed during and after the Pleistocene ice age.
The Masurian Lake District is the largest of the four and covers much of northeastern Poland. The lake districts form part of the Baltic Ridge, a series of moraine belts along the southern shore of the Baltic Sea. South of the Northern European Lowlands lie the regions of Silesia and Masovia, which are marked by broad ice-age river valleys. Farther south lies the Polish mountain region, including the Sudetes, the Cracow-Częstochowa Upland, the Świętokrzyskie Mountains, and the Carpathian Mountains, including the Beskids. The highest part of the Carpathians is the Tatra Mountains, along Poland’s southern border.
Poland has 21 mountains over 6561 feet (2000 meters) in elevation, all in the High Tatras. In the High Tatras lies Poland’s highest point, the northwestern peak of Rysy, at 8198 feet(2499 meters) in elevation. At its foot lies the mountain lake, the Morskie Oko. Among the most beautiful mountains of Poland are the Bieszczady Mountains in the far southeast of Poland, whose highest point in Poland is Tarnica, with an elevation of 4416 feet (1346 meters). Tourists also frequent the Gorce Mountains in Gorce National Park. The lowest point in Poland -— at (7 feet (two meters) below sea level -— is at Raczki Elbląskie, near Elbląg in the Vistula Delta.
The climate is oceanic in the north and west and becomes gradually warmer and continental as one moves south and east. Summers are generally warm, with average temperatures between 68°F (20°C) and 80.6°F (27°C. Winters are cold, with average temperatures around 37.4°F (3°C) in the northwest and 17.6°F (–8°C) in the northeast. Precipitation falls throughout the year, although, especially in the east; winter is drier than summer. The warmest region in Poland is Lesser Poland located in Southern Poland where temperatures in the summer average between 73.4°F (23°C) and (86°F (30°C). The coldest region is in the northeast in the Podlachian Voivodeship near the border of Belarus. Cold fronts which come from Scandinavia and Siberia bring temperatures in the winter in Podlachian ranging from 5°F (-15°C) to 24.8°F (-4°C).
The longest rivers are the Vistula, 678 miles (1047km) long; the Oder—which forms part of Poland’s western border— 531 miles (854km) long; its tributary, the Warta, 502 miles (808km) long; and the Bug —a tributary of the Vistula—480 miles (772km) long. The Vistula and the Oder flow into the Baltic Sea, as do numerous smaller rivers in Pomerania. The Łyna and the Angrapa flow by way of the Pregolya to the Baltic, and the Czarna Hańcza flows into the Baltic through the Neman.
Poland’s rivers have been used since early times for navigation. The Vikings, for example, traveled up the Vistula and the Oder in their longships. In the Middle Ages and in early modern times, when Poland-Lithuania was the breadbasket of Europe, the shipment of grain and other agricultural products down the Vistula toward Gdańsk and onward to western Europe took on great importance. For an overview of the most important rivers in Poland, see Category:Rivers of Poland.
With almost ten thousand closed bodies of water covering more than one hectare (2.47 acres) each, Poland has one of the highest numbers of lakes in the world. The largest lakes, covering more than 38.6 square miles (100 square kilometers) are Lake Śniardwy and Lake Mamry in Masuria, as well as Lake Łebsko and Lake Drawsko in Pomerania.
Among the first lakes whose shores were settled are those in the Greater Polish Lake District. The stilt house settlement of Biskupin, occupied by more than one thousand residents, was founded before the seventh century B.C.E. by people of the Lusatian culture. The ancestors of today’s Poles, the Polanie, built their first fortresses on islands in these lakes. The legendary Prince Popiel is supposed to have ruled from Kruszwica on Lake Gopło. The first historically documented ruler of Poland, Duke Mieszko I, had his palace on an island in the Warta River in Poznań.
Błędów Desert is a desert located in Southern Poland in the Lesser Poland region it also stretches over the Zagłębie Dąbrowskie region. It has a total area of 32km². It is the only desert located in Poland, and is one of five natural deserts in Europe. It was created thousands of years ago by a melting glacier. The specific geological structure has been of big importance - the average thickness of the sand layer is about 40 meters (maximum 70 meters), which made the fast and deep drainage very easy. In recent years the desert has started to shrink. The phenomenon of mirages has been known to exist there.
More than one percent of Poland’s area -— 1214 square miles (3145 square kilometers) —is protected within 23 national parks. In this respect, Poland ranks first in Europe. Forests cover 28 of Poland’s land area. More than half of the land is devoted to agriculture. While the total area under cultivation is declining, the remaining farmland is more intensively cultivated.
Many animals that have since died out in other parts of Europe survive in Poland, such as the wisent in the ancient woodland of the Białowieża Forest and in Podlachia. Other such species include the brown bear in Białowieża, in the Tatras, and in the Beskids, the gray wolf and the Eurasian lynx in various forests, the moose in northern Poland, and the beaver in Masuria, Pomerania, and Podlachia. In the forests, one also encounters game animals, such as red deer, roe deer, and boars. In eastern Poland there are a number of ancient woodlands, like Białowieża, that have never been cleared by people. There are also large forested areas in the mountains, Masuria, Pomerania, and Lower Silesia.
Poland is the most important breeding ground for European migratory birds. Out of all of the migratory birds who come to Europe for the summer, one quarter breed in Poland, particularly in the lake districts and the wetlands along the Biebrza, the Narew, and the Warta, which are part of nature reserves or national parks. In Masuria, there are villages in which storks outnumber people.
Flooding is a natural hazard. Environmental issues relate to air pollution, which remained serious in 2007 because of sulfur dioxide emissions from coal-fired power plants, and the resulting acid rain which damages forest. Water pollution from industrial and municipal sources is also a problem, as is disposal of hazardous wastes. Pollution levels were expected to decrease as industrial establishments bring their facilities up to the European Union code, but at substantial cost to business and the government.
Warsaw is the capital of Poland and is its largest city. Located on the Vistula River between the Baltic Sea coast and the Carpathian Mountains, its population in 2006 was estimated at 1,700,536, with a metropolitan area of approximately 2,600,000. The largest metropolitan areas in Poland are the Upper Silesian Coal Basin centred on Katowice (3.5 million inhabitants); Łódź (1.3 million); Kraków (1.3 million); the “Tricity” of Gdańsk-Sopot-Gdynia in the Vistula delta (1.1 million); Poznań (0.9 million); Wrocław (0.9 million); and Szczecin (0.9 million). For an overview of Polish cities, see List of cities in Poland.
History
Template:History of Poland
Prehistory
It was postulated that throughout Late Antiquity, many distinct ethnic groups populated the regions of what is now known as Poland. The exact ethnicity and linguistic affiliation of these groups was hotly debated. Many Slavic, Celtic, Baltic and Germanic tribes were among the prominent groups. The politically charged discussion on the origins of the Slavs; historically two partially opposing views are held: allochtonic or autochtonic. The purely allochtonic view is historic and has no scholar defending it, many scholars now tend toward an autochtonic view, the most radical of which is the theory of Paleolithic continuity.[2]
The most famous archeological find from the Poland's prehistory is the Biskupin fortified settlement, dating from the Lusatian culture of the early Iron Age, around 700 B.C.E.
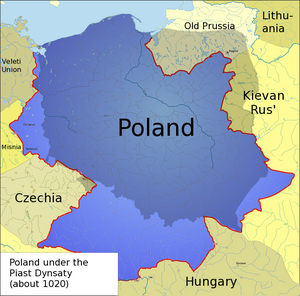
Piast dynasty
Poland began to form into a recognizable unitary and territorial entity around the middle of the tenth century under the Piast dynasty. Poland's first historically documented ruler, Mieszko I, was baptized in 966, adopting Catholic Christianity as the nation's new official religion, to which the bulk of the population converted in the course of the next centuries. In the twelfth century, Poland fragmented into several smaller states. In 1320, Władysław I became the King of a reunified Poland. His son, Kazimierz III, is remembered as one of the greatest Polish kings.
Poland was also a centre of migration of peoples and the Jewish community began to settle and flourish in Poland during this era (see History of the Jews in Poland). The Black Death which affected most parts of Europe from 1347 to 1351 did not reach Poland.[3]
Jagiellon dynasty
Under the Jagiellon dynasty, Poland forged an alliance with its neighbour, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. In 1410 a polish-Lithuanian army inflicted decisive defeat to the armies of Teutonic Knights, both countries' main adversary, in the battle of Grunwald. After Thirteen Years War the Knights state has been reduced to polish vassal. Polish culture and economy flourished under Jagiellons, and the country produced such figures as astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus and poet Jan Kochanowski. Compared to other European nations, Poland was exceptional in its tolerance for religious dissent, allowing the country to avoid religious turmoil that spread over Western Europe in that time.
Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
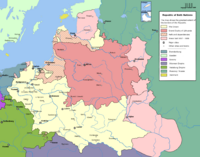
A golden age ensued during the sixteenth century after the Union of Lublin which gave birth to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. The szlachta (nobility) of Poland, far more numerous than in Western European countries, took pride in their freedoms and parliamentary system. During the Golden Age period, Poland expanded its borders to become the largest country in Europe.
In the mid-seventeenth century, a Swedish invasion ("The Deluge") and Cossack's Chmielnicki Uprising which ravaged the country marked the end of the golden age. Numerous wars against Russia coupled with government inefficiency caused by the Liberum Veto, a right which had allowed any member of the parliament to dissolve it and to veto any legislation it had passed, marked the steady deterioration of the Commonwealth from a European power into a near-anarchy controlled by its neighbours. The reforms, particularly those of the Great Sejm, which passing of the Constitution of May 3, 1791, second modern constitution of the world, were thwarted with the three partitions of Poland (1772, 1793, and 1795) which ended with Poland's being erased from the map and its territories being divided between Russia, Prussia, and Austria.
Partitions of Poland
Poles would resent their fate and would several times rebel against the partitioners, particularly in the nineteenth century. In 1807 Napoleon recreated a Polish state, the Duchy of Warsaw, but after the Napoleonic wars, Poland was again divided in 1815 by the victorious Allies at the Congress of Vienna. The eastern portion was ruled by the Russian Czar as a Congress Kingdom, and possessed a liberal constitution. However, the Czars soon reduced Polish freedoms and Russia eventually de facto annexed the country. Later in the nineteenth century, Austrian-ruled Galicia, particularly the Free City of Kraków, became a centre of Polish cultural life.
Reconstitution of Poland
During World War I, all the Allies agreed on the reconstitution of Poland that United States President Woodrow Wilson proclaimed in Point 13 of his Fourteen Points. Shortly after the surrender of Germany in November 1918, Poland regained its independence as the Second Polish Republic (II Rzeczpospolita Polska). It reaffirmed its independence after a series of military conflicts, the most notable being the Polish-Soviet War (1919–1921) when Poland inflicted a crushing defeat on the Red Army.
The 1926 May Coup of Józef Piłsudski turned the reins of the Second Polish Republic over to the Sanacja movement.
World War II
The Sanacja movement controlled Poland until the start of World War II in 1939, when Nazi Germany invaded on September 1 and the Soviet Union followed on September 17. Warsaw capitulated on September 28 1939. As agreed in the Ribbentrop-Molotov Pact, Poland was split into two zones, one occupied by Germany while the eastern provinces fell under the control of the Soviet Union.
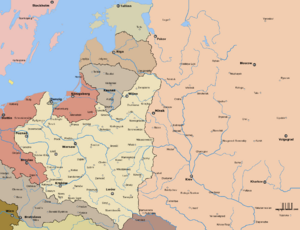
Of all the countries involved in the war, Poland lost the highest percentage of its citizens: over six million perished, half of them Polish Jews. Poland made the fourth-largest troop contribution to the Allied war effort, after the Soviets, the British and the Americans. At the war's conclusion, Poland's borders were shifted westwards, pushing the eastern border to the Curzon line. Meanwhile, the western border was moved to the Oder-Neisse line. The new Poland emerged 20% smaller by 77,500 square kilometres (29,900 sq mi). The shift forced the migration of millions of people, most of whom were Poles, Germans, Ukrainians, and Jews. The main German Nazi death camps were in Poland. Of a pre-war population of 3,300,000 Polish Jews, 3,000,000 were killed during the Holocaust.
Postwar Communist Poland
The Soviet Union instituted a new Communist government in Poland, analogous to much of the rest of the Eastern Bloc. Military alignment within the Warsaw Pact throughout the Cold War was also part of this change. The People's Republic of Poland (Polska Rzeczpospolita Ludowa) was officially proclaimed in 1952. In 1956, the régime of Władysław Gomułka became temporarily more liberal, freeing many people from prison and expanding some personal freedoms. Similar situation repeated itself in the 1970s under Edward Gierek, but most of the time persecution of communist opposition persisted.
Labour turmoil in 1980 led to the formation of the independent trade union "Solidarity" ("Solidarność"), which over time became a political force. It eroded the dominance of the Communist Party and by 1989 had triumphed in parliamentary elections. Lech Wałęsa, a Solidarity candidate, eventually won the presidency in 1990. The Solidarity movement heralded the collapse of communism across Eastern Europe.
Democratic Poland
A shock therapy programme of Leszek Balcerowicz during the early 1990s enabled the country to transform its economy into a robust market economy. Despite temporary slumps in social and economic standards, Poland was the first post-communist country to reach its pre-1989 GDP levels. Most visibly, there were numerous improvements in other human rights, such as free speech. In 1991, Poland became a member of the Visegrad Group and joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) alliance in 1999 along with the Czech Republic and Hungary. Poles then voted to join the European Union in a referendum in June 2003, with Poland becoming a full member on May 1, 2004.
Government and politics
Poland is a republic. The chief of state is a president who is elected by popular vote for a five-year term, and is eligible for a second term. The president appoints the prime minister and deputy prime ministers, as well as the cabinet according to the proposals of the prime minister, both typically from the majority coalition.
The Polish Parliament has two chambers. The lower chamber (Sejm) has 460 members, elected for a four-year term by proportional representation in multi-seat constituencies, with a five percent threshold (eight percent for coalitions, threshold waived for national minorities). The Senate (Senat) has 100 members elected for a four year term in 40 multi-seat constituencies under a rare plurality bloc voting method where several candidates with the highest support are elected from each electorate.
When sitting in joint session, members of the Sejm and Senate form the National Assembly, (Polish Zgromadzenie Narodowe). The National Assembly is formed on three occasions: Taking the oath of office by a new president, bringing an indictment against the President of the Republic to the Tribunal of State, and declaration of a president's permanent incapacity to exercise their duties due to the state of their health. Only the first kind has occurred to date.
On the approval of the Senate, the Sejm also appoints the Ombudsman or the Commissioner for Civil Rights Protection (Rzecznik Praw Obywatelskich) for a five-year term. The Ombudsman has the duty of guarding the observance and implementation of the rights and liberties of Polish citizens and residents, of the law and of principles of community life and social justice.
The judicial branch comprises the Supreme Court of Poland (Sąd Najwyższy); the Supreme Administrative Court of Poland (Naczelny Sąd Administracyjny); the Constitutional Tribunal of Poland (Trybunał Konstytucyjny); and the State Tribunal of Poland (Trybunał Stanu). Poland has a mixture of Continental (Napoleonic) civil law and holdover communist legal theory, although the latter is being gradually removed as part of a broader and ongoing reform process. The Constitutional Tribunal supervises the compliance of statutory law with the Constitution, and annuls laws which do not comply. Its rulings are final (since October 1999); court decisions can be appealed to the European Court of Human Rights in Strasbourg.
Administrative divisions
Poland's provinces ("voivodeships") are largely based on the country's historic regions, whereas those of the past two decades (till 1998) had been centered on and named for individual cities. The new units range in areas from under 10,000 km² (Opole Voivodeship) to over 35,000 km² (Masovian Voivodeship). Voivodeships are governed by voivod governments, and their legislatures are called voivodeship sejmiks.
Poland is subdivided into 16 administrative regions known as voivodeships (województwa, singular województwo). In turn, the voivodeships are divided into powiaty (singular powiat), second-level units of administration, equivalent to a county, district or prefecture in other countries (NUTS-4 or rather LAU-1) and then gminy ("communes", singular gmina).
Foreign relations
Poland has forged ahead on its economic reintegration with the West. Poland became a full member of NATO in 1999, and of the European Union in 2004. Poland became an associate member of the European Union (EU) and its defensive arm, the Western European Union (WEU) in 1994. In 1996 Poland achieved full OECD membership and submitted preliminary documentation for full EU membership. Poland joined the European Union in 2004, along with the other members of the Visegrád group.
Changes since 1989 have redrawn the map of central Europe, and Poland has had to forge relationships with seven new neighbors. Poland has actively pursued good relations with all its neighbors, signing friendship treaties replacing links severed by the collapse of the Warsaw Pact. The Poles have forged special relationships with Lithuania and particularly Ukraine in an effort to firmly anchor these states to the West.
Due to its tragic historical experience with a repeating pattern of disloyal allies and simultaneous aggression of powerful neighbours (Partitions of Poland, Second World War), Polish foreign policy pursues a close cooperation with a strong partner, apt to give a real military support in a critical situation. This creates the background of Poland's tight relations with the USA and oversensitivity complicating relations towards its main partner within the European Union, Germany. At the same time, the equally burdened attitude towards Russia results in very tense diplomatic relations, constantly worsening since Vladimir Putin's rise to power. This is an important factor for the special attention Poland pays to the political emancipation of all its Eastern neighbours: Lithuania, Belarus and Ukraine (as well as certain of those countries do to Poland itself). The authoritarian and anti-Western political course of Belarus presents a huge problem for the Polish foreign policy; the 'Orange Revolution' in Ukraine evoked a wide and authentic support within the Polish society.
Poland is a part of the multinational force in Iraq.
Economy

Poland has the second most vigorous economic growth rate among the Baltic States, with 5.8% GDP growth in 2006.[4] Since the fall of communism, Poland has steadfastly pursued a policy of liberalising the economy and today stands out as a successful example of the transition from a state-directed economy to a primarily privately owned market economy.
The privatisation of small and medium state-owned companies and a liberal law on establishing new firms have allowed the development of an aggressive private sector. As a consequence, consumer rights organizations have also appeared. Restructuring and privatisation of "sensitive sectors" such as coal, steel, railways, and energy has been continuing since 1990. Between 2007 and 2010, the government plans to float twenty public companies on the Polish stock market, including parts of the coal industry. To date (2007), the biggest privatisations have been the sale of the national telecoms firm Telekomunikacja Polska to France Telecom in 2000, and an issue of 30% of the shares in Poland's largest bank, PKO Bank Polski, on the Polish stockmarket in 2004.
Poland has a large number of private farms in its agricultural sector, with the potential to become a leading producer of food in the European Union. However, problems remain, especially under-investment. Structural reforms in health care, education, the pension system, and state administration have resulted in larger-than-expected fiscal pressures. Warsaw leads Central Europe in foreign investment.[5] GDP growth had been strong and steady from 1993 to 2000 with only a short slowdown from 2001 to 2002. The prospect of closer integration with the European Union has put the economy back on track,[citation needed] with growth of 3.7% annually in 2003, a rise from 1.4% annually in 2002. In 2004, GDP growth equaled 5.4%, in 2005 3.3% and in 2006 6.2%. For 2007, the government has set a target for GDP growth at 6.5 to 7.0%.
The long standing head of the National Bank of Poland, Leszek Balcerowicz, was replaced by Sławomir Skrzypek in January 2007. At first the markets reacted sceptically and fell,[citation needed] but since then have stabilized and then risen sharply.
Recent annual growth rates by quarters have been:
| Year | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 7.2% | 6.4% | ||
| 2006 | 5.5% | 6.3% | 6.3% | 6.6% |
| 2005 | 2.4% | 3.2% | 4.3% | 4.4% |
| 2004 | 7.0% | 6.1% | 4.8% | 4.9% |
| 2003 | 2.2% | 3.8% | 4.7% | 4.7% |
Although the Polish economy is currently undergoing economic development, there are many challenges ahead. The most notable task on the horizon is the preparation of the economy (through continuing deep structural reforms) to allow Poland to meet the strict economic criteria for entry into the European Single Currency (Euro). There is much speculation as to just when Poland might be allowed to join the Eurozone, though this will likely be sometime after 2012 or 2013.[6] For now, Poland is preparing to make the Euro its official currency (though it has not joined the ERM yet), and the Złoty may eventually be replaced by Euro in the Polish economy.
Since joining the European Union, many Poles have left their country to work in other EU countries (particularly Ireland and the UK) because of high unemployment, which is currently the second-highest in the EU with 8.8% in September 2007 (was 14.2% in May 2006).[7]
Commodities produced in Poland include: clothes, glass, china (Mikasa, Waterford), electronics, cars (including the luxurious Leopard car), buses (Autosan, Jelcz SA, Solaris, Solbus), helicopters (PZL Świdnik), transport equipment, locomotives, planes (PZL Mielec), ships, military engineering (including tanks, SPAAG systems), medicines (Polpharma, Polfa), food, chemical products and others.
Demographics
Poland's population is over 38.5 million people, concentrated mainly in urban areas.
Poland, with 38.5 million inhabitants, has the eighth-largest population in Europe and the sixth-largest in the European Union. It has a population density of 122 inhabitants per square kilometer (328 per square mile). The number of Poles living abroad is estimated at around 20 million.
Poland formerly played host to many languages, cultures, and religions. There was a particularly significant Jewish life in Poland prior to the Nazi Holocaust when Poland's Jewish population, estimated at 3 million, was reduced to about 300,000 survivors. The outcomes of World War II, particularly the westwards shift of Poland's borders to the area between the Curzon line and the Oder-Neisse line coupled with World War II evacuation and expulsion gave Poland an appearance of homogeneity.
Today 36,983,700 people, or 96.74% of the population considers itself Polish (Census 2002), 471,500 (1.23%) declared another nationality. 774,900 people (2.03%) didn't declare any nationality. Nathionalites or an ethnic groups in Poland are Silesians, Germans (most in the former Opole Voivodeship), Ukrainians, Lithuanians, Russians, Jews and Belarusians. The Polish language, a member of the West Slavic branch of the Slavic languages, functions as the official language of Poland. English and German are the most common second languages studied and spoken.
In recent years, Poland's population has decreased because of an increase in emigration and a sharp drop in the birth rate. In 2006, the census office estimated the total population of Poland at 38,536,869, a slight rise on the 2002 figure of 38,230,080. Since Poland's accession to the European Union, a significant number of Polish immigrants have moved to work in Western European countries such as the United Kingdom, Germany and Ireland. Some organisations state people have left primarily due to high unemployment (10.5%) and better opportunities for work abroad. In April 2007, the Polish population of the United Kingdom had risen to approximately 300,000 and estimates predict about 65,000 Polish people living in Ireland.
A Polish minority is still present in neighbouring countries of Ukraine, Belarus, and Lithuania, as well as in other countries (see Poles for population numbers). The largest number of ethnic Poles outside of the country can be found in the United States.
Ethnicity
In terms of ethnicity, Poland has been a homogeneous state since the end of World War II. Poles (including Silesians and Kashubians) make up an overwhelming 99.3 percent majority of the Polish population. According to the 2002 census, the remainder of the population is made up of small minorities of Germans (152,897), Belarusians (c. 49,000), and Ukrainians (c. 30,000), as well as Tatars, Lithuanians, Roma, Lemkos, Russians, Karaites, Slovaks, and Czechs. Among foreign citizens, the Vietnamese are the largest ethnic group, followed by Greeks, and Armenians.
Religion
Due to the Holocaust and the flight and removal of German and Ukrainian populations, Poland has become almost uniformly Catholic. Catholics make up about 90% of the population (94.8% according to church baptism statistics) with 46% as practising Catholics (according to opinion polls). Despite a sharp drop in religious observance in recent years, Poland remains one of the most devoutly religious countries in Europe. Religious minorities include Polish Orthodox (1.3% or about 509,500), Jehovah’s Witnesses (0.3% or about 123,034), Eastern Catholics (0.2%), Lutherans (0.2%), and smaller minorities of Mariavites, Polish Catholics, Pentecostals, Seventh-Day Adventists, Jews, Muslims (including the Tatars of Białystok) and various Protestants (about 86,880 in the largest Evangelical-Augsburg Church, plus about as many in smaller churches). Resulting from the socio-political emancipation of the county, freedom of religion has become guaranteed by the 1989 statute of the Polish constitution, allowing for the emergence of additional denominations. However, due to pressure from the Polish Episcopate, exposition of doctrine has entered public education system as well, drawing criticism from the popular media, as unconstitutional. According to 2007 survey, 72% of respondents were not against the fostering of catechism in public schools; nevertheless, the alternative courses in ethics have become available only in one percent of the entire public educational system.
Science, technology and education
Template:Seesubarticle2
Education
The education of Polish society was a goal of rulers as early as the 12th century, and Poland soon became one of the most educated European countries. The library catalogue of the Cathedral Chapter of Kraków dating back to 1110 shows that already in the early 12th century Polish intellectuals had access to the European literature. In 1364, in Kraków, the Jagiellonian University, founded by King Casimir III, became one of Europe's great early universities. In 1773 King Stanisław August Poniatowski established his Commission on National Education (Komisja Edukacji Narodowej), the world's first state ministry of education.
Current situation
Today, Poland has more than a hundred tertiary education institutions; traditional universities to be found in its major cities of Białystok, Bydgoszcz, Gdańsk, Katowice, Kraków, Lublin, Łódź, Olsztyn, Opole, Poznań, Rzeszów, Szczecin, Toruń, Warsaw, Wrocław and Zielona Góra as well as technical, medical, economic institutions elsewhere, employing around 61,000 workers. There are also around 300 research and development institutes, with about 10,000 more researchers. In total, there are around 91,000 scientists in Poland today.
According to a recent report by the European Commission, Poland ranks 21st on the list of EU states in the area of innovation. Conditions for knowledge creation are worsening, particularly because of a decline in business research and development, from 0.28% of GDP in 1998 to 0.16% in 2003. Public R&D expenditures were 0.43% of GDP in 2003. The share of university R&D funded by the business sector has also declined, indicating that firms have not turned to outsourcing research to make up for declining R&D expenditures. Because of the very low levels of R&D, the process of transition of Poland to a knowledge economy is slow.
Telecommunication and IT
Template:Seesubarticle2
The share of the telecom sector in the GDP is 4.4% (end of 2000 figure), compared to 2.5% in 1996. Nevertheless, despite high expenditures for telecom infrastructure (the coverage increased from 78 users per 1000 inhabitants in 1989 to 282 in 2000).
The value of the telecommunication market is zl 38.2bn (2006), and it grew by 12.4% in 2007 PMR [1]
the coverage mobile cellular is over 1000 users per 1000 people (2007)
- Telephones—mobile cellular: 38.7 million (Onet.pl & GUS Report, 2007)
- Telephones—main lines in use: 12.5 million (Telecom Team Report, 2005)
Culture
Polish culture has been influenced by both West and East. Today, these influences are evident in Polish architecture, folklore, and art. Poland is the birthplace of some world famous people, including Pope John Paul II (Polish: Papież Jan Paweł II), Marie Skłodowska Curie (Polish: Maria Skłodowska-Curie), Kazimierz Pułaski (Template:Lanomg-pl), Nicolaus Copernicus (Polish: Mikołaj Kopernik) and Frederic Chopin (Polish: Fryderyk Chopin).
The character of Polish art always reflected world trends. The famous Polish painter, Jan Matejko included many significant historical events in his paintings. Also, a famous person in history of Polish art was Stanisław Ignacy Witkiewicz. He was an example of a Polish Renaissance Man. Polish literature dates back to 1100s[8] and includes many famous poets and writers such as Jan Kochanowski, Adam Mickiewicz, Henryk Sienkiewicz (1905 Nobel Prize winner), Bolesław Prus, Władysław Reymont (1924 Nobel Prize winner), Juliusz Słowacki, Witold Gombrowicz, Czesław Miłosz (1980 Nobel Prize winner), Wisława Szymborska (1996 Nobel Prize winner), Stanisław Lem and, Ryszard Kapuściński. Many world renowned Polish movie directors include Academy Awards winners Roman Polański, Andrzej Wajda, Zbigniew Rybczyński, Janusz Kamiński and, Krzysztof Kieślowski. The traditional Polish music composers include world famous pianist Frederic Chopin (Polish: Fryderyk Chopin)[9] as well as Krzysztof Penderecki, Karol Szymanowski, and others.
Famous modern singers, musicians and bands from Poland include Behemoth, Myslovitz, SBB, Riverside, Edyta Górniak, Lady Pank, Anita Lipnicka and Ich Troje.
Notable foods in Polish cuisine include Polish sausage (Polish: kiełbasa), red beet soup (Polish: barszcz), Polish dumplings (Polish: pierogi), tripe soup (Polish: flaczki), cabbage rolls (Polish: gołąbki), Polish pork chops (Polish: kotlety schabowe), Polish traditional stew (Polish: bigos), various potato dishes, a fast food sandwich zapiekanka, and many more. Traditional Polish desserts include Polish doughnuts (Polish: pączki), Polish gingerbread (Polish: pierniki) and others.
Sports
International rankings
| Index | Rank | Countries reviewed |
|---|---|---|
| Human Development Index 2006 | 37th | 177 |
| Reporters Without Borders Press Freedom Index 2006 | 58th | 168 |
| Index of Economic Freedom 2007 | 87th | 157 |
| Summary Innovation Index 2005 | 27th | 33 |
| UNICEF Child Well-being league table | 14th | 21 |
| Networked Readiness Index 2006-2007 | 58th | 122 |
See also
- List of Poles
- List of World Heritage Sites in Poland
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ Central Statistical Office of Poland (2007). Mały Rocznik Statystyczny 2007. Retrieved 15 August, 2007.
- ↑ Interdisciplinary and linguistic evidence for Palaeolithic continuity of Indo-European, Uralic and Altaic populations in Eurasia, with an excursus on Slavic ethnogenesis by Mario Alinei url: http://www.continuitas.com/interdisciplinary.pdf
- ↑ Teeple, J. B. (2002). Timelines of World History. Publisher: DK Adult.
- ↑ DnB NORD Group, Baltic Rim Economies: Growth & Constraints, 2007, Chapter: The Baltics and Finland among the fastest growing countries in the EU, pg. 11 (PDF file, 2.62 MB). Retrieved on November 18, 2007.
- ↑ "Poland in the Lead", The Warsaw Voice, September 2002. Retrieved on August 11, 2007.
- ↑ Jan Cienski, "Poland Alters Stance on Euro", in the Financial Times, July 26, 2007. Retrieved August 11, 2007.
- ↑ Eurostat September 2007 - Euro area and EU27 unemployment down to 7.3%, 31 October, 2007
- ↑ (Polish) Koca, B. (2006). Polish Literature - The Middle Ages (Religious writings). Retrieved 10 December, 2006.
- ↑ (Polish) Polskie Centrum Informacji Muzycznej: Związek Kompozytorów Polskich (2002). Towarzystwo im. Fryderyka Chopina. Retrieved 8 December, 2006.
External links
- Poland World Fact Book 2007, accessed November 23, 2007.
- Poland.gov.pl - Polish national portal
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs
- Background Note: Poland
- Travel guide to Poland from Wikitravel
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.