Difference between revisions of "Pangolin" - New World Encyclopedia
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
''[[Sunda Pangolin|Manis javanica]]'' | ''[[Sunda Pangolin|Manis javanica]]'' | ||
}} | }} | ||
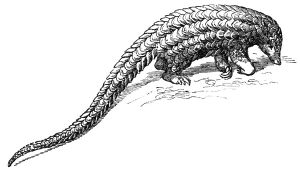
| − | '''Pangolin''', or '''scaly anteater''', is the common name for [[Africa]]s and [[Asia]] armored [[mammal]]s comprising the order '''Pholidota''', characterized by a long prehensile tail, a long and narrow snout, no teeth, a long tongue used to capture | + | '''Pangolin''', or '''scaly anteater''', is the common name for [[Africa]]s and [[Asia]] armored [[mammal]]s comprising the order '''Pholidota''', characterized by a long prehensile tail, a long and narrow snout, no teeth, a long tongue used to capture [[ant]]s and [[termite]]s, and a unique covering of large, overlapping body scales. There is only one extant [[family (biology)|family]] ('''Manidae''') and one [[genus]] ('''''Manis''''') of pangolins, comprising seven or eight [[species]]. There are also a number of extinct taxa. |
Revision as of 17:35, 23 August 2008
- "Manis" redirects here.
| Pangolins[1]
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Sunda Pangolin, Manis javanica
| ||||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
|
Manis culionensis |
Pangolin, or scaly anteater, is the common name for Africas and Asia armored mammals comprising the order Pholidota, characterized by a long prehensile tail, a long and narrow snout, no teeth, a long tongue used to capture ants and termites, and a unique covering of large, overlapping body scales. There is only one extant family (Manidae) and one genus (Manis) of pangolins, comprising seven or eight species. There are also a number of extinct taxa.
Description
The physical appearance of pangolins is marked by large, hardened, plate-like scales. The scales, which are soft on newborn pangolins but harden as the animal matures, are made of keratin, the same material of which human fingernails and tetrapod claws are made. The pangolin is often compared to a walking pine cone or globe artichoke. It can curl up into a ball when threatened, with its overlapping scales acting as armour and its face tucked under its tail. The scales are razor-sharp, providing extra defense. The front claws are so long that they are unsuited for walking, and so the animal walks with its fore paws curled over to protect them. Pangolins can also emit a noxious smelling acid from glands near the anus, similar to the spray of a skunk. Pangolins have short legs, with sharp claws which they use for burrowing into termite and ant mounds, as well as climbing.
Pangolins have large keratin scales covering their skin and are the only mammals with this adaptation.[2] They are found in tropical regions of Africa and Asia. The name "pangolin" derives from the Malay word pengguling ("something that rolls up"). Pangolins are nocturnal animals, using their well-developed sense of smell to find insects. The long-tailed pangolin is also active by day. Pangolins spend most of the daytime sleeping, curled up into a ball.[3]
Pangolins were classified with various other orders, for example Xenarthra, which includes the ordinary anteaters, sloths, and the similar-looking armadillos. But newer genetic evidence,[4] indicates that their closest living relatives are the Carnivora, with which they form a clade, the Ferae.[5] Some paleontologists have classified the pangolins in the order Cimolesta, together with several extinct groups.
The size of pangolins varies by species, ranging from 30 cm to 100 cm (12 to 39 inches). Females are generally smaller than males.
The tongues of pangolins are extremely elongated and extend into the abdominal cavity. By convergent evolution pangolins, the giant anteater, and the tube-lipped nectar bat, all have tongues which are unattached from their hyoid bone and extend past their pharynx deep into the thorax.[6] This extension lies between the sternum and the trachea. Large pangolins can extend their tongues as much as 40 cm (16 inches), with a diameter of only 0.5 cm (1/4 inch).[3]
In pangolins, the section of the brain that relates to problem solving is highly developed. Although their problem solving ability is primarily used to find food in obscure locations, when kept in captivity pangolins are remarkable escape artists.[citation needed].
Arboreal pangolins live in hollow trees, whereas the ground dwelling species dig tunnels underground, up to a depth of 3.5 meters (11 feet).[3] Pangolins are also good swimmers.[3]
Diet
Pangolins lack teeth and the ability to chew. Instead, they tear open anthills or termite mounds with their powerful front claws and probe deep into them with their very long tongues. Pangolins have an enormous salivary gland in their chests to lubricate the tongue with sticky, ant-catching saliva.
Some species, such as the Tree Pangolin, use their strong tails to hang from tree branches and strip away bark from the trunk, exposing insect nests inside.
Reproduction
Gestation is 120-150 days. African pangolin females usually give birth to a single offspring at a time, but the Asiatic species can give birth from one to three.[3] Weight at birth is 80-450 g (3-18 ounces), and the scales are initially soft. The young cling to the mother's tail as she moves about, although, in burrowing species, they remain in the burrow for the first 2-4 weeks of life. Weaning takes place at around three months of age, and pangolins becomes sexually mature at two years.[7]
Threats

Pangolin are hunted and eaten in many parts of Africa and it is one of the more popular types of bush meat. Pangolins are also in great demand in China because their meat is considered a delicacy and some Chinese believe pangolin scales reduce swelling, promote blood circulation and help breast-feeding women produce milk. This, coupled with deforestation, has led to a large decrease in the numbers of Giant Pangolins.
Pangolin populations have suffered from illegal trafficking. In May 2007, for example, Guardian Unlimited reported that 31 pangolins were found aboard an abandoned vessel off the coast of China. The boat contained some 5,000 endangered animals.
The Guardian recently provided a description of the killing and eating of pangolins: "A Guangdong chef interviewed last year in the Beijing Science and Technology Daily described how to cook a pangolin: 'We keep them alive in cages until the customer makes an order. Then we hammer them unconscious, cut their throats and drain the blood. It is a slow death. We then boil them to remove the scales. We cut the meat into small pieces and use it to make a number of dishes, including braised meat and soup. Usually the customers take the blood home with them afterwards.'" [8]
On November 10, 2007, Thai customs officers announced that they had rescued over 100 pangolins as the animals were being smuggled out of the country, en route to China, where they were to be sold for cooking. [9]
Taxonomy
- ORDER PHOLIDOTA
- Family †Epoicotheriidae
- Family †Metacheiromyidae
- Family Manidae
- Subfamily †Eurotamanduinae
- Genus †Eurotamandua
- Subfamily Maninae
- Genus †Cryptomanis
- Genus †Eomanis
- Genus †Necromanis
- Genus †Patriomanis
- Genus Manis
- Subgenus Manis
- Indian Pangolin (M. crassicaudata)
- Chinese Pangolin (M. pentadactyla)
- Subgenus Paramanis
- Sunda Pangolin (M. javanica)
- Philippine Pangolin (M. culionensis)
- Subgenus Smutsia
- Giant Pangolin (M. gigantea)
- Ground Pangolin (M. temmincki)
- Subgenus Phataginus
- Tree Pangolin (M. tricuspis)
- Subgenus Uromanis
- Long-tailed Pangolin (M. tetradactyla)
- Subgenus Manis
- Subfamily †Eurotamanduinae
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ Schlitter, D. A. 2005. In D. E. Wilson and D. M. Reeder, eds. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference, 3rd edition. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0801882214.
- ↑ (2006) The Encyclopedia of World Wildlife. Paragon Books, p63.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 (1988) in Mondadori, Arnoldo Ed.: Great Book of the Animal Kingdom. New York: Arch Cape Press, p252.
- ↑ Murphy, Willian J., et al (2001-12-14). Resolution of the Early Placental Mammal Radiation Using Bayesian Phylogenetics. Science 294 (5550): 2348–2351.
- ↑ BioMed Central | Full text | A higher-level MRP supertree of placental mammals
- ↑ Chan, Lap-Ki (1995). Extrinsic Lingual Musculature of Two Pangolins (Pholidota: Manidae). Journal of Mammalogy 76 (2): 472–480.
- ↑ Dickman, Christopher R. (1984). in Macdonald, D.: The Encyclopedia of Mammals. New York: Facts on File, 780-781. ISBN 0-87196-871-1.
- ↑ Watts, Jonathan (2007-05-26), "'Noah's Ark' of 5,000 rare animals found floating off the coast of China", The Guardian
- ↑ 2007-11-10, Thailand saves pangolins bound for China restaurants, AFP. Retrieved 2007-11-11
- Atkins, W. A. 2004. Pholidota pangolins (Manidae). Pages 107 to 120 in B. Grzimek, D. G. Kleiman, V. Geist, and M. C. McDade (eds.), Grzimek's Animal Life Encyclopedia, volume 16. Detroit: Thomson-Gale. ISBN 0787657921.
External links
- Pangolin: Wildlife summary from the African Wildlife Foundation
- A photograph of a pangolin
- Tree of Life of Pholidota
| Mammals |
|---|
| Monotremata (platypus, echidnas) |
|
Marsupialia: | Paucituberculata (shrew opossums) | Didelphimorphia (opossums) | Microbiotheria | Notoryctemorphia (marsupial moles) | Dasyuromorphia (quolls and dunnarts) | Peramelemorphia (bilbies, bandicoots) | Diprotodontia (kangaroos and relatives) |
|
Placentalia: Cingulata (armadillos) | Pilosa (anteaters, sloths) | Afrosoricida (tenrecs, golden moles) | Macroscelidea (elephant shrews) | Tubulidentata (aardvark) | Hyracoidea (hyraxes) | Proboscidea (elephants) | Sirenia (dugongs, manatees) | Soricomorpha (shrews, moles) | Erinaceomorpha (hedgehogs and relatives) Chiroptera (bats) | Pholidota (pangolins)| Carnivora | Perissodactyla (odd-toed ungulates) | Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates) | Cetacea (whales, dolphins) | Rodentia (rodents) | Lagomorpha (rabbits and relatives) | Scandentia (treeshrews) | Dermoptera (colugos) | Primates | |
Template:Pholidota
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.