Difference between revisions of "Neurotransmitter" - New World Encyclopedia
m ({{Contracted}}) |
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Contracted}} | {{Contracted}} | ||
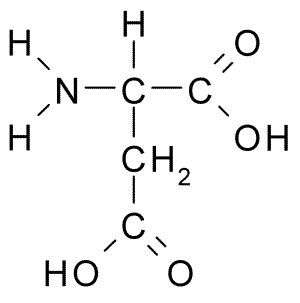
| − | [[Image:Aspartic Acid.png|thumb|Chemical structure of '''D- | + | [[Image:Aspartic Acid.png|thumb|Chemical structure of '''D-aspartic acid''', a common amino acid neurotransmitter.]] |
'''Neurotransmitters''' are [[chemistry|chemicals]] that are used to relay, amplify and modulate [[electrical]] signals between a [[neuron]] and another cell. According to the prevailing beliefs of the 1960s, a chemical can be classified as a neurotransmitter if it meets the following conditions: | '''Neurotransmitters''' are [[chemistry|chemicals]] that are used to relay, amplify and modulate [[electrical]] signals between a [[neuron]] and another cell. According to the prevailing beliefs of the 1960s, a chemical can be classified as a neurotransmitter if it meets the following conditions: | ||
* It is [[chemical synthesis|synthesized]] endogenously, that is, within the [[presynaptic]] [[neuron]]; | * It is [[chemical synthesis|synthesized]] endogenously, that is, within the [[presynaptic]] [[neuron]]; | ||
* It is available in sufficient quantity in the presynaptic neuron to exert an effect on the [[postsynaptic]] neuron; | * It is available in sufficient quantity in the presynaptic neuron to exert an effect on the [[postsynaptic]] neuron; | ||
| − | * Externally administered, it must | + | * Externally administered, it must mimic the endogenously-released substance; and |
* A [[biochemical]] mechanism for inactivation must be present. | * A [[biochemical]] mechanism for inactivation must be present. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
== Types of neurotransmitters == | == Types of neurotransmitters == | ||
| − | + | There are many different ways to classify neurotransmitters. Often, dividing them into [[amino acids]], [[peptides]], and [[monoamine]]s is sufficient for many purposes. | |
| − | + | Some more precise divisions are as follows: | |
| + | |||
| + | * Around 10 "small-molecule neurotransmitters" are known: | ||
| + | ** [[acetylcholine]] | ||
| + | ** [[monoamine]]s ([[norepinephrine]] NE, [[dopamine]] DA & [[serotonin]] 5-HT) | ||
| + | ** 3 or 4 amino acids, depending on exact definition used: (primarily [[glutamic acid]], [[gamma aminobutyric acid|GABA]], [[aspartic acid]] & [[glycine]]) | ||
| + | ** [[Purines]], (Adenosine, [[adenosine triphosphate|ATP]], [[Guanosine triphosphate|GTP]] and their derivatives) | ||
| + | ** Fatty acids are also receiving attention as the potential [[Cannabinoids#Endogenous Cannabinoids|endogenous cannabinoid]].{{Fact|date=February 2007}} | ||
| + | * Over 50 neuroactive peptides ([[vasopressin]], [[somatostatin]], [[neurotensin]], etc.) have been found, among them hormones such as LH or [[insulin]] that have specific local actions in addition to their long-range signalling properties. | ||
| + | * Single ions, such as synaptically-released [[zinc]], are also considered neurotransmitters by some.{{Fact|date=March 2007}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The major "workhorse" neurotransmitters of the brain are glutamic acid (=glutamate) and GABA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Effects== | ||
Some examples of neurotransmitter action: | Some examples of neurotransmitter action: | ||
* [[Acetylcholine]] - voluntary movement of the muscles | * [[Acetylcholine]] - voluntary movement of the muscles | ||
* [[Norepinephrine]] - wakefulness or arousal | * [[Norepinephrine]] - wakefulness or arousal | ||
| − | * [[Dopamine]] - voluntary movement and | + | * [[Dopamine]] - voluntary movement and motivation, "wanting" |
* [[Serotonin]] - memory, emotions, wakefulness, sleep and temperature regulation | * [[Serotonin]] - memory, emotions, wakefulness, sleep and temperature regulation | ||
| − | * [[GABA]] (gamma aminobutyric acid) - motor | + | * [[gamma aminobutyric acid|GABA]] (gamma aminobutyric acid) - inhibition of motor neurons |
* [[Glycine]] - spinal reflexes and motor behaviour | * [[Glycine]] - spinal reflexes and motor behaviour | ||
* [[Neuromodulator]]s - sensory transmission-especially pain | * [[Neuromodulator]]s - sensory transmission-especially pain | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is important to appreciate that it is the receptor that dictates the neurotransmitter's effect. | ||
== Mechanism of action == | == Mechanism of action == | ||
Within the [[Cell (biology)|cells]], small-molecule neurotransmitter molecules are usually packaged in [[vesicle (biology)|vesicle]]s. When an [[action potential]] travels to the [[synapse]], the rapid depolarization causes calcium ion channels to open. Calcium then stimulates the transport of vesicles to the synaptic membrane; the vesicle and [[cell membrane]] fuse, leading to the release of the packaged neurotransmitter, a mechanism called [[exocytosis]]. | Within the [[Cell (biology)|cells]], small-molecule neurotransmitter molecules are usually packaged in [[vesicle (biology)|vesicle]]s. When an [[action potential]] travels to the [[synapse]], the rapid depolarization causes calcium ion channels to open. Calcium then stimulates the transport of vesicles to the synaptic membrane; the vesicle and [[cell membrane]] fuse, leading to the release of the packaged neurotransmitter, a mechanism called [[exocytosis]]. | ||
| − | The neurotransmitters then diffuse across the [[synaptic cleft]] to bind to [[receptor (biochemistry)|receptor]]s. The receptors are broadly classified into [[ionotropic]] and [[metabotropic]] receptors. Ionotropic receptors are ligand-gated ion channels that open or close through neurotransmitter binding. Metabotropic receptors, which can have a diverse range of effects on a cell, transduct the signal by secondary messenger systems, or [[G protein|G-proteins]]. | + | The neurotransmitters then [[diffusion|diffuse]] across the [[synaptic cleft]] to bind to [[receptor (biochemistry)|receptor]]s. The receptors are broadly classified into [[ionotropic]] and [[metabotropic]] receptors. Ionotropic receptors are ligand-gated ion channels that open or close through neurotransmitter binding. Metabotropic receptors, which can have a diverse range of effects on a cell, transduct the signal by secondary messenger systems, or [[G protein|G-proteins]]. |
Neuroactive peptides are made in the neuron's [[soma (biology)|soma]] and are transported through the [[axon]] to the synapse. They are usually packaged into dense-core vesicles and are released through a similar, but metabolically distinct, form of exocytosis used for small-molecule synaptic vesicles. | Neuroactive peptides are made in the neuron's [[soma (biology)|soma]] and are transported through the [[axon]] to the synapse. They are usually packaged into dense-core vesicles and are released through a similar, but metabolically distinct, form of exocytosis used for small-molecule synaptic vesicles. | ||
== Post-synaptic effect == | == Post-synaptic effect == | ||
| − | A neurotransmitter's effect is determined by its receptor. For example, [[GABA]] can act on both rapid or slow inhibitory receptors (the [[GABA A receptor|GABA-A]] and [[GABA B receptor|GABA-B]] receptor respectively). Many other neurotransmitters, however, may have excitatory or inhibitory actions depending on which receptor they bind to. | + | A neurotransmitter's effect is determined by its receptor. For example, [[gamma aminobutyric acid|GABA]] can act on both rapid or slow inhibitory receptors (the [[GABA A receptor|GABA-A]] and [[GABA B receptor|GABA-B]] receptor respectively). Many other neurotransmitters, however, may have excitatory or inhibitory actions depending on which receptor they bind to. |
| − | Neurotransmitters may cause either excitatory or inhibitory post-synaptic potentials. That is, they may help the initiation of a nerve impulse in the receiving neuron, or they may discourage such an impulse by modifying the local membrane voltage potential. In the central nervous system, combined input from several synapses is usually required to trigger an action potential. [[Glutamate]] is the most prominent of excitatory transmitters; [[GABA]] and [[glycine]] are well-known inhibitory neurotransmitters. | + | Neurotransmitters may cause either excitatory or inhibitory post-synaptic potentials. That is, they may help the initiation of a nerve impulse in the receiving neuron, or they may discourage such an impulse by modifying the local membrane voltage potential. In the central nervous system, combined input from several synapses is usually required to trigger an action potential. [[Glutamate]] is the most prominent of excitatory transmitters; [[gamma aminobutyric acid|GABA]] and [[glycine]] are well-known inhibitory neurotransmitters. |
| − | Many neurotransmitters are removed from the synaptic cleft by a process called ''[[reuptake]]'' (or often simply | + | Many neurotransmitters are removed from the synaptic cleft by [[neurotransmitter transporter]]s in a process called ''[[reuptake]]'' (or often simply 'uptake'). Without reuptake, the molecules might continue to stimulate or inhibit the firing of the postsynaptic neuron. Another mechanism for removal of a neurotransmitter is digestion by an [[enzyme]]. For example, at cholinergic synapses (where [[acetylcholine]] is the neurotransmitter), the enzyme [[acetylcholinesterase]] breaks down the acetylcholine. Neuroactive peptides are often removed from the cleft by diffusion, and eventually broken down by proteases. |
| − | == | + | == Specifications == |
| − | While some neurotransmitters (glutamate, GABA, glycine) are used very generally throughout the central nervous system, others can have more specific effects, such as on the [[ | + | While some neurotransmitters (glutamate, GABA, glycine) are used very generally throughout the central nervous system, others can have more specific effects, such as on the [[autonomic nervous system]], by both pathways in the [[sympathetic nervous system]] and the [[parasympathetic nervous system]], and the action of others are regulated by distinct classes of nerve clusters which can be arranged in familiar pathways around the brain. For example, [[Serotonin]] is released specifically by cells in the brainstem, in an area called the [[raphe nuclei]], but travels around the brain along the [[medial forebrain bundle]] activating the [[cortex]], [[hippocampus]], [[thalamus]], [[hypothalamus]] and [[cerebellum]]. Also, it is released in the Caudal serotonin nuclei, so as to have effect on the spinal cord. In the peripherial nervous system (such as in the gut wall) serotonin regulates vascular tone. [[Dopamine]] classically modulates two systems: the brain's reward mechanism, and movement control. |
| − | Neurotransmitters that have these types of specific actions are often targeted by drugs. [[Cocaine]], for example, blocks the reuptake of [[dopamine]], leaving these neurotransmitters in the [[ | + | Neurotransmitters that have these types of specific actions are often targeted by drugs. |
| + | * [[Cocaine]], for example, blocks the reuptake of [[dopamine]], leaving these neurotransmitters in the [[synapse|synaptic gap]] longer. | ||
| + | * [[Prozac]] is a [[serotonin reuptake inhibitor]], hence potentiating its effect. | ||
| + | * [[AMPT]] prevents the conversion of tyrosine to [[L-DOPA]], the precursor to dopamine; [[reserpine]] prevents dopamine storage within [[vesicles]]; and [[deprenyl]] inhibits [[monoamine oxidase]] (MAO)-B and thus increases dopamine levels. | ||
| − | Some neurotransmitter/neuromodulators like zinc not only can modulate the sensitivity of a receptor to other neurotransmitters (allosteric modulation) but can even penetrate specific, gated channels in post-synaptic neurons, thus entering the post-synaptic cells. This "translocation" is another mechanism by which synaptic transmitters can affect postsynaptic cells. | + | Some neurotransmitter/neuromodulators like zinc not only can modulate the sensitivity of a [[receptor (biochemistry)|receptor]] to other neurotransmitters ([[allosteric]] modulation) but can even penetrate specific, gated channels in post-synaptic neurons, thus entering the post-synaptic cells. This "translocation" is another mechanism by which synaptic transmitters can affect postsynaptic cells. |
| − | Diseases may affect specific neurotransmitter pathways. For example, [[Parkinson's disease]] is at least in part related to failure of dopaminergic cells in [[deep-brain nuclei]], for example the substantia nigra. Treatments potentiating the effect of dopamine precursors have been proposed and effected, with moderate success. | + | Diseases may affect specific neurotransmitter pathways. For example, [[Parkinson's disease]] is at least in part related to failure of dopaminergic cells in [[deep-brain nuclei]], for example the [[substantia nigra]]. Treatments potentiating the effect of dopamine precursors have been proposed and effected, with moderate success. |
== Common neurotransmitters == | == Common neurotransmitters == | ||
| − | == | + | {| class="wikitable" class="sortable wikitable" |
| − | : | + | | '''Category''' || '''Name''' || '''Abbreviation''' || '''[[Metabotropic]]''' || '''[[Ionotropic]]''' |
| − | : | + | |- |
| − | : | + | | Small: Amino acids || [[Aspartate]] || || - || - |
| − | :: | + | |- |
| − | + | | Small: Amino acids || [[Glutamate]] (glutamic acid) || Glu || [[Metabotropic glutamate receptor]] || [[NMDA receptor]], [[Kainate receptor]], [[AMPA receptor]] | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | :: | + | | Small: Amino acids || [[Gamma-aminobutyric acid]] || GABA || [[GABAB receptor]] || [[GABAA receptor]], [[GABAC receptor]] |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | Small: Amino acids || [[Glycine]] || Gly || - || [[Glycine receptor]] | |
| − | : | + | |- |
| − | :: | + | | Small: Acetylcholine || [[Acetylcholine]] || Ach || [[Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor]] || [[Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor]] |
| − | :: | + | |- |
| − | :: | + | | Small: Monoamine ([[Phenylalanine|Phe]]/[[Tyrosine|Tyr]]) || [[Dopamine]] || DA || [[Dopamine receptor]] || - |
| − | :: | + | |- |
| − | :: | + | | Small: Monoamine ([[Phenylalanine|Phe]]/[[Tyrosine|Tyr]]) || [[Norepinephrine]] (noradrenaline) || NE || - || - |
| − | : | + | |- |
| − | :: | + | | Small: Monoamine ([[Phenylalanine|Phe]]/[[Tyrosine|Tyr]]) || [[Epinephrine]] (adrenaline) || Epi || - || - |
| − | :: | + | |- |
| − | : | + | | Small: Monoamine ([[Phenylalanine|Phe]]/[[Tyrosine|Tyr]]) || [[Octopamine]] || || - || - |
| − | :: | + | |- |
| + | | Small: Monoamine ([[Phenylalanine|Phe]]/[[Tyrosine|Tyr]]) || [[Tyramine]] || || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Small: Monoamine ([[Tryptophan|Trp]]) || [[Serotonin]] (5-hydroxytryptamine) || 5-HT || [[Serotonin receptor]], all but 5-HT3 || [[5-HT3]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Small: Monoamine ([[Tryptophan|Trp]]) || [[Melatonin]] || Mel || [[Melatonin receptor]] || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Small: Monoamine ([[Histamine|His]]) || [[Histamine]] || H || [[Histamine receptor]] || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Gastrins || [[Gastrin]] || || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Gastrins || [[Cholecystokinin]] || CCK || [[Cholecystokinin receptor]] || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Neurohypophyseals || [[Vasopressin]] || || [[Vasopressin receptor]] || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Neurohypophyseals || [[Oxytocin]] || || [[Oxytocin receptor]] || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Neurohypophyseals || [[Neurophysin I]] || || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Neurohypophyseals || [[Neurophysin II]] || || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Neuropeptide Y || [[Neuropeptide Y]] || NY || [[Neuropeptide Y receptor]] || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Neuropeptide Y || [[Pancreatic polypeptide]] || PP || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Neuropeptide Y || [[Peptide YY]] || PYY || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Opiods || [[Corticotropin]] (adrenocorticotropic hormone) || ACTH || [[Corticotropin receptor]] || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Opiods || [[Dynorphin]] || || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Opiods || [[Endorphin]] || || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Opiods || [[Enkephaline]] || || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Secretins || [[Secretin]] || || [[Secretin receptor]] || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Secretins || [[Motilin]] || || [[Motilin receptor]] || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Secretins || [[Glucagon]] || || [[Glucagon receptor]] || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Secretins || [[Vasoactive intestinal peptide]] || VIP || [[Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor]] || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Secretins || [[Growth hormone-releasing factor]] || GRF || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Somtostatins || [[Somatostatin]] || || [[Somatostatin receptor]] || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | SS: Tachykinins || [[Neurokinin A]] || || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | SS: Tachykinins || [[Neurokinin B]] || || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | SS: Tachykinins || [[Substance P]] || || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Other || [[Bombesin]] || || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | PP: Other || [[Gastrin releasing peptide]] || GRP || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gas || [[Nitric oxide]] || NO || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gas || [[Carbon monoxide]] || CO || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Other || [[Anandamide]] || || - || - | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Other || [[Adenosine triphosphate]] || ATP || [[P2Y12]] || [[P2X receptor]] | ||
| − | + | |} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | == See also == |
| − | + | * [[Neuropsychopharmacology]] | |
| − | + | * [[Nervous system]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | * Chamberlin, S. L., and B. Narins. 2005. ''The Gale Encyclopedia of Neurological Disorders''. Detroit: Thomson Gale. ISBN 078769150X. | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{commons|Neurotransmitter|Neurotransmitter}} |
* [http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/micro/gallery/neurotrans/neurotrans.html Molecular Expressions Photo Gallery: The Neurotransmitter Collection] | * [http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/micro/gallery/neurotrans/neurotrans.html Molecular Expressions Photo Gallery: The Neurotransmitter Collection] | ||
* [http://www.benbest.com/science/anatmind/anatmd10.html Brain Neurotransmitters] | * [http://www.benbest.com/science/anatmind/anatmd10.html Brain Neurotransmitters] | ||
* [http://www.neurotransmitter.net/neurosignaling.html Endogenous Neuroactive Extracellular Signal Transducers] | * [http://www.neurotransmitter.net/neurosignaling.html Endogenous Neuroactive Extracellular Signal Transducers] | ||
| − | {{credit| | + | {{credit|138016083}} |
[[Category:Life sciences]] | [[Category:Life sciences]] | ||
Revision as of 11:36, 14 June 2007
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that are used to relay, amplify and modulate electrical signals between a neuron and another cell. According to the prevailing beliefs of the 1960s, a chemical can be classified as a neurotransmitter if it meets the following conditions:
- It is synthesized endogenously, that is, within the presynaptic neuron;
- It is available in sufficient quantity in the presynaptic neuron to exert an effect on the postsynaptic neuron;
- Externally administered, it must mimic the endogenously-released substance; and
- A biochemical mechanism for inactivation must be present.
However, there are other materials, such as the zinc ion, that are neither synthesized nor catabolized (i.e., degraded; see Anabolism) and are considered neurotransmitters by some. Thus, the old definitions are being revised.
Types of neurotransmitters
There are many different ways to classify neurotransmitters. Often, dividing them into amino acids, peptides, and monoamines is sufficient for many purposes.
Some more precise divisions are as follows:
- Around 10 "small-molecule neurotransmitters" are known:
- acetylcholine
- monoamines (norepinephrine NE, dopamine DA & serotonin 5-HT)
- 3 or 4 amino acids, depending on exact definition used: (primarily glutamic acid, GABA, aspartic acid & glycine)
- Purines, (Adenosine, ATP, GTP and their derivatives)
- Fatty acids are also receiving attention as the potential endogenous cannabinoid.[citation needed]
- Over 50 neuroactive peptides (vasopressin, somatostatin, neurotensin, etc.) have been found, among them hormones such as LH or insulin that have specific local actions in addition to their long-range signalling properties.
- Single ions, such as synaptically-released zinc, are also considered neurotransmitters by some.[citation needed]
The major "workhorse" neurotransmitters of the brain are glutamic acid (=glutamate) and GABA.
Effects
Some examples of neurotransmitter action:
- Acetylcholine - voluntary movement of the muscles
- Norepinephrine - wakefulness or arousal
- Dopamine - voluntary movement and motivation, "wanting"
- Serotonin - memory, emotions, wakefulness, sleep and temperature regulation
- GABA (gamma aminobutyric acid) - inhibition of motor neurons
- Glycine - spinal reflexes and motor behaviour
- Neuromodulators - sensory transmission-especially pain
It is important to appreciate that it is the receptor that dictates the neurotransmitter's effect.
Mechanism of action
Within the cells, small-molecule neurotransmitter molecules are usually packaged in vesicles. When an action potential travels to the synapse, the rapid depolarization causes calcium ion channels to open. Calcium then stimulates the transport of vesicles to the synaptic membrane; the vesicle and cell membrane fuse, leading to the release of the packaged neurotransmitter, a mechanism called exocytosis.
The neurotransmitters then diffuse across the synaptic cleft to bind to receptors. The receptors are broadly classified into ionotropic and metabotropic receptors. Ionotropic receptors are ligand-gated ion channels that open or close through neurotransmitter binding. Metabotropic receptors, which can have a diverse range of effects on a cell, transduct the signal by secondary messenger systems, or G-proteins.
Neuroactive peptides are made in the neuron's soma and are transported through the axon to the synapse. They are usually packaged into dense-core vesicles and are released through a similar, but metabolically distinct, form of exocytosis used for small-molecule synaptic vesicles.
Post-synaptic effect
A neurotransmitter's effect is determined by its receptor. For example, GABA can act on both rapid or slow inhibitory receptors (the GABA-A and GABA-B receptor respectively). Many other neurotransmitters, however, may have excitatory or inhibitory actions depending on which receptor they bind to.
Neurotransmitters may cause either excitatory or inhibitory post-synaptic potentials. That is, they may help the initiation of a nerve impulse in the receiving neuron, or they may discourage such an impulse by modifying the local membrane voltage potential. In the central nervous system, combined input from several synapses is usually required to trigger an action potential. Glutamate is the most prominent of excitatory transmitters; GABA and glycine are well-known inhibitory neurotransmitters.
Many neurotransmitters are removed from the synaptic cleft by neurotransmitter transporters in a process called reuptake (or often simply 'uptake'). Without reuptake, the molecules might continue to stimulate or inhibit the firing of the postsynaptic neuron. Another mechanism for removal of a neurotransmitter is digestion by an enzyme. For example, at cholinergic synapses (where acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter), the enzyme acetylcholinesterase breaks down the acetylcholine. Neuroactive peptides are often removed from the cleft by diffusion, and eventually broken down by proteases.
Specifications
While some neurotransmitters (glutamate, GABA, glycine) are used very generally throughout the central nervous system, others can have more specific effects, such as on the autonomic nervous system, by both pathways in the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system, and the action of others are regulated by distinct classes of nerve clusters which can be arranged in familiar pathways around the brain. For example, Serotonin is released specifically by cells in the brainstem, in an area called the raphe nuclei, but travels around the brain along the medial forebrain bundle activating the cortex, hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus and cerebellum. Also, it is released in the Caudal serotonin nuclei, so as to have effect on the spinal cord. In the peripherial nervous system (such as in the gut wall) serotonin regulates vascular tone. Dopamine classically modulates two systems: the brain's reward mechanism, and movement control.
Neurotransmitters that have these types of specific actions are often targeted by drugs.
- Cocaine, for example, blocks the reuptake of dopamine, leaving these neurotransmitters in the synaptic gap longer.
- Prozac is a serotonin reuptake inhibitor, hence potentiating its effect.
- AMPT prevents the conversion of tyrosine to L-DOPA, the precursor to dopamine; reserpine prevents dopamine storage within vesicles; and deprenyl inhibits monoamine oxidase (MAO)-B and thus increases dopamine levels.
Some neurotransmitter/neuromodulators like zinc not only can modulate the sensitivity of a receptor to other neurotransmitters (allosteric modulation) but can even penetrate specific, gated channels in post-synaptic neurons, thus entering the post-synaptic cells. This "translocation" is another mechanism by which synaptic transmitters can affect postsynaptic cells.
Diseases may affect specific neurotransmitter pathways. For example, Parkinson's disease is at least in part related to failure of dopaminergic cells in deep-brain nuclei, for example the substantia nigra. Treatments potentiating the effect of dopamine precursors have been proposed and effected, with moderate success.
Common neurotransmitters
| Category | Name | Abbreviation | Metabotropic | Ionotropic |
| Small: Amino acids | Aspartate | - | - | |
| Small: Amino acids | Glutamate (glutamic acid) | Glu | Metabotropic glutamate receptor | NMDA receptor, Kainate receptor, AMPA receptor |
| Small: Amino acids | Gamma-aminobutyric acid | GABA | GABAB receptor | GABAA receptor, GABAC receptor |
| Small: Amino acids | Glycine | Gly | - | Glycine receptor |
| Small: Acetylcholine | Acetylcholine | Ach | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor | Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor |
| Small: Monoamine (Phe/Tyr) | Dopamine | DA | Dopamine receptor | - |
| Small: Monoamine (Phe/Tyr) | Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) | NE | - | - |
| Small: Monoamine (Phe/Tyr) | Epinephrine (adrenaline) | Epi | - | - |
| Small: Monoamine (Phe/Tyr) | Octopamine | - | - | |
| Small: Monoamine (Phe/Tyr) | Tyramine | - | ||
| Small: Monoamine (Trp) | Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) | 5-HT | Serotonin receptor, all but 5-HT3 | 5-HT3 |
| Small: Monoamine (Trp) | Melatonin | Mel | Melatonin receptor | - |
| Small: Monoamine (His) | Histamine | H | Histamine receptor | - |
| PP: Gastrins | Gastrin | - | - | |
| PP: Gastrins | Cholecystokinin | CCK | Cholecystokinin receptor | - |
| PP: Neurohypophyseals | Vasopressin | Vasopressin receptor | - | |
| PP: Neurohypophyseals | Oxytocin | Oxytocin receptor | - | |
| PP: Neurohypophyseals | Neurophysin I | - | - | |
| PP: Neurohypophyseals | Neurophysin II | - | - | |
| PP: Neuropeptide Y | Neuropeptide Y | NY | Neuropeptide Y receptor | - |
| PP: Neuropeptide Y | Pancreatic polypeptide | PP | - | - |
| PP: Neuropeptide Y | Peptide YY | PYY | - | - |
| PP: Opiods | Corticotropin (adrenocorticotropic hormone) | ACTH | Corticotropin receptor | - |
| PP: Opiods | Dynorphin | - | - | |
| PP: Opiods | Endorphin | - | - | |
| PP: Opiods | Enkephaline | - | - | |
| PP: Secretins | Secretin | Secretin receptor | - | |
| PP: Secretins | Motilin | Motilin receptor | - | |
| PP: Secretins | Glucagon | Glucagon receptor | - | |
| PP: Secretins | Vasoactive intestinal peptide | VIP | Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor | - |
| PP: Secretins | Growth hormone-releasing factor | GRF | - | - |
| PP: Somtostatins | Somatostatin | Somatostatin receptor | - | |
| SS: Tachykinins | Neurokinin A | - | - | |
| SS: Tachykinins | Neurokinin B | - | - | |
| SS: Tachykinins | Substance P | - | - | |
| PP: Other | Bombesin | - | - | |
| PP: Other | Gastrin releasing peptide | GRP | - | - |
| Gas | Nitric oxide | NO | - | - |
| Gas | Carbon monoxide | CO | - | - |
| Other | Anandamide | - | - | |
| Other | Adenosine triphosphate | ATP | P2Y12 | P2X receptor |
See also
- Neuropsychopharmacology
- Nervous system
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Chamberlin, S. L., and B. Narins. 2005. The Gale Encyclopedia of Neurological Disorders. Detroit: Thomson Gale. ISBN 078769150X.
External links
- Molecular Expressions Photo Gallery: The Neurotransmitter Collection
- Brain Neurotransmitters
- Endogenous Neuroactive Extracellular Signal Transducers
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.