Difference between revisions of "Seven Wonders of the World" - New World Encyclopedia
({{Contracted}}) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (93 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Ebcompleted}}{{Copyedited}}{{Images OK}}{{submitted}}{{approved}}{{Paid}}{{2Copyedited}} |
| − | + | [[Image:SevenWondersOfTheWorld.png|thumb|300px|The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World (from left to right, top to bottom): [[Great Pyramid of Giza]], [[Hanging Gardens of Babylon]], [[Temple of Artemis]], [[Statue of Zeus at Olympia]], [[Mausoleum of Maussollos]], [[Colossus of Rhodes]], and the [[Lighthouse of Alexandria]] as depicted by sixteenth-century Dutch artist [[Maarten van Heemskerck]].]] | |
| − | [[Image:SevenWondersOfTheWorld.png|thumb| | + | The '''Seven Wonders of the World''' (or the '''Seven Wonders of the Ancient World''') is a widely known list of seven remarkable constructions of [[antiquity]]. It was based on guide-books popular among [[Ancient Greece|Hellenic]] sightseers and includes only works located around the [[Mediterranean]] rim. Later lists include those for the medieval world and the modern world. |
| − | The '''Seven Wonders of the World''' (or the '''Seven Wonders of the Ancient World''') is a widely | + | |
| + | The original Seven Wonders of the World consists of: The [[Great Pyramid of Giza]] (the most ancient as well as the only surviving structure), the [[Hanging Gardens of Babylon]], the [[Temple of Artemis]] at Ephesus, the [[Statue of Zeus at Olympia]], the [[Mausoleum of Maussollos]] at Halicarnassus, the [[Colossus of Rhodes]], and the [[Lighthouse of Alexandria]]. | ||
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | The notion of "Seven Wonders" can be traced to a Hellenistic recognition of trans-cultural human achievement that found expression throughout the Hellenistic world. For thousands of years, the Seven Wonders of the World have inspired humankind as representative works symbolic of the great civilizations of antiquity. In terms of innovative design, elaborate construction, technological mastery, and symbolic meaning, the Seven Wonders have not only showcased the high points of diverse civilizations, but tied humankind together in the common pursuit of intellectual excellence and self-expression. | ||
==Seven Wonders of the Ancient World== | ==Seven Wonders of the Ancient World== | ||
| − | The historian [[Herodotus]] and the scholar [[Callimachus]] of [[Cyrene]] ( | + | The historian [[Herodotus]] and the scholar [[Callimachus]] of [[Cyrene]] (c. 305 – 240 B.C.E.) made early lists of "seven wonders," but these writings have not survived, except as references. The earliest extant version of a list of seven wonders was compiled by [[Antipater of Sidon]], who described the structures in a poem around 140 B.C.E.: |
| − | + | <blockquote>I have set eyes on the wall of lofty Babylon on which is a road for chariots, and the statue of Zeus by the Alpheus, and the hanging gardens, and the Colossus of the Sun, and the huge labor of the high pyramids, and the vast tomb of Mausolus; but when I saw the house of Artemis that mounted to the clouds, those other marvels lost their brilliancy, and I said, "Lo, apart from Olympus, the Sun never looked on aught so grand"<ref> Paul Trebilco, ''The Early Christians in Ephesus from Paul to Ignatius'' (Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing Co., 2007, ISBN 0802807690).</ref></blockquote> | |
| − | A later list, under various titles | + | A later list, under various titles such as ''De septem orbis spactaculis'' and traditionally, though incorrectly, attributed to the engineer [[Philo of Byzantium]], may date as late as the fifth century C.E., although the author writes as if the [[Colossus of Rhodes]], destroyed by an [[earthquake]] in 224 B.C.E., were still standing. |
| − | + | The basic characteristics of each of the Seven Wonders are given in the table below: | |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 23: | Line 26: | ||
|- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | ||
| [[Great Pyramid of Giza]] | | [[Great Pyramid of Giza]] | ||
| − | | 2650 | + | | 2650 – 2500 B.C.E. |
| [[Ancient Egypt|Egyptians]] | | [[Ancient Egypt|Egyptians]] | ||
| Built as the tomb of [[Fourth dynasty of Egypt|Fourth dynasty]] [[ancient Egypt|Egyptian]] pharaoh [[Khufu (pharaoh)|Khufu]]. | | Built as the tomb of [[Fourth dynasty of Egypt|Fourth dynasty]] [[ancient Egypt|Egyptian]] pharaoh [[Khufu (pharaoh)|Khufu]]. | ||
| Still standing | | Still standing | ||
| − | | - | + | | - |
|- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | ||
| [[Hanging Gardens of Babylon]] | | [[Hanging Gardens of Babylon]] | ||
| Line 33: | Line 36: | ||
| [[Babylonia]]ns | | [[Babylonia]]ns | ||
| [[Herodotus]] claimed the outer walls were 56 miles in length, 80 feet thick and 320 feet high (although some archaeological findings suggest otherwise). | | [[Herodotus]] claimed the outer walls were 56 miles in length, 80 feet thick and 320 feet high (although some archaeological findings suggest otherwise). | ||
| − | | After | + | | After first century B.C.E. |
| [[Earthquake]] | | [[Earthquake]] | ||
|- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | ||
| Line 39: | Line 42: | ||
| 550 B.C.E. | | 550 B.C.E. | ||
| [[Lydia]]ns, [[Achaemenid Empire|Persians]], [[ancient Greece|Greeks]] | | [[Lydia]]ns, [[Achaemenid Empire|Persians]], [[ancient Greece|Greeks]] | ||
| − | | Dedicated to the [[Greek mythology|Greek]] [[goddess]] [[Artemis]], | + | | Dedicated to the [[Greek mythology|Greek]] [[goddess]] [[Artemis]], the temple was begun by [[Croesus]] of Lydia and took 120 years to build. It was destroyed by arson in 356 B.C.E., rebuilt and destroyed during a raid by the [[Goths]] in 262, rebuilt again and finally demolished by a mob allegedly led by [[John Chrysostom]].<ref>John Freely, ''The Western Shores of Turkey: Discovering the Aegean and Mediterranean Coast'' (Tauris Parke Paperbacks, 2004, ISBN 978-1850436188).</ref> |
| − | | 356 B.C.E. | + | | 356 B.C.E. and 401 C.E. |
| − | | [[Arson]] | + | | [[Arson]] and later demolition |
|- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | ||
| [[Statue of Zeus at Olympia]] | | [[Statue of Zeus at Olympia]] | ||
| 435 B.C.E. | | 435 B.C.E. | ||
| [[ancient Greece|Greeks]] | | [[ancient Greece|Greeks]] | ||
| − | | Occupied the whole width of the aisle of the temple that was built to house it, and was 40 feet | + | | Occupied the whole width of the aisle of the temple that was built to house it, and was 40 feet tall. |
| − | | | + | | fifth and sixth centuries C.E. |
| [[Fire]] | | [[Fire]] | ||
|- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | ||
| Line 53: | Line 56: | ||
| 351 B.C.E. | | 351 B.C.E. | ||
| [[Seleucid Empire|Persians]], [[ancient Greece|Greeks]] | | [[Seleucid Empire|Persians]], [[ancient Greece|Greeks]] | ||
| − | | Stood approximately | + | | Stood approximately 135 feet tall with each of the four sides adorned with sculptural reliefs. Origin of the word ''mausoleum''. |
| − | | by | + | | by 1494 C.E. |
| [[Earthquake]] | | [[Earthquake]] | ||
|- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | ||
| [[Colossus of Rhodes]] | | [[Colossus of Rhodes]] | ||
| − | | 292 | + | | 292 – 280 B.C.E. |
| [[Hellenistic Greece]] | | [[Hellenistic Greece]] | ||
| A giant [[statue]] of the [[Greek mythology|Greek]] [[God (male deity)|god]] [[Helios]] roughly the same size as today's [[Statue of Liberty]] in [[New York City|New York]]. | | A giant [[statue]] of the [[Greek mythology|Greek]] [[God (male deity)|god]] [[Helios]] roughly the same size as today's [[Statue of Liberty]] in [[New York City|New York]]. | ||
| Line 65: | Line 68: | ||
|- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | ||
| [[Lighthouse of Alexandria]] | | [[Lighthouse of Alexandria]] | ||
| − | | | + | | Third century B.C.E. |
| [[Ptolemaic Egypt|Hellenistic Egypt]] | | [[Ptolemaic Egypt|Hellenistic Egypt]] | ||
| − | | Between | + | | Between 383 feet to 440 feet tall it was among the tallest man-made structures on Earth for many centuries. |
| − | | | + | | 1303 – 1480 C.E. |
| [[Earthquake]] | | [[Earthquake]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | {{readout||right|250px|Instead of the Seven "Wonders" the ancient Greeks spoke of "theamata" or "sights," "things worth seeing"}} | ||
| + | The Greek category to describe what people call "wonders" today was "''theamata''," which translates as "something worth seeing" or "must-sees." Since the list came mostly from [[ancient Greece|ancient Greek]] writings, only sites that would have been known and visited by the ancient Greeks were included. Sites from eastern [[Asia]], the Americas, [[Africa]], and northern [[Europe]] were thus omitted. Five of the seven entries are a celebration of Greek accomplishments in the arts and architecture (the exceptions being the Pyramids of Giza and the Hanging Gardens of Babylon). Antipater's earlier list replaced the [[Lighthouse of Alexandria]] with the [[Babylon]]'s famous [[Ishtar Gate]]. | ||
| − | + | It was not until the sixth century C.E. that the list above was used. Of these wonders, the only one that has survived to the present day is the [[Great Pyramid of Giza]]. One of wonders, the [[Temple of Artemis]], was destroyed intentionally, first by [[arson]] and finally by a mob allegedly led by the [[Christian]] bishop St. [[John Chrysostom]]. The [[Statue of Zeus]] was destroyed by fire. Four of the wonders were destroyed by [[earthquake]]s—the Hanging Gardens, the [[Lighthouse of Alexandria]], the [[Colossus of Rhodes]], and the [[Mausoleum of Maussollos]]. (The existence of the Hanging Gardens, however, has not been definitively proven.) There are sculptures from the Mausoleum of Maussollos and the Temple of Artemis in the [[British Museum]] in [[London]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Later lists== | |
| + | [[Image:Stonehenge Total.jpg|thumb|400px|Stonehenge]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Colosseum at night.jpg|thumb|400px|The Colosseum]] | ||
| + | Many lists of "wonders of the world" are said to have existed during the [[Middle Ages]], although it is unlikely that these lists originated at that time. These lists go by names such as "Wonders of the Middle Ages" (implying no specific limitation to seven), "Seven Wonders of the Middle Ages," "Medieval Mind," and "Architectural Wonders of the Middle Ages." Many of the structures on these lists were built much earlier than the Medieval Ages, but were well known. The lists are more properly seen as a continuing type or [[genre]] in the Seven Wonders tradition than a specific list. | ||
| − | + | The following is a typical representative of such lists: | |
| − | + | *[[Stonehenge]] | |
| − | + | *[[Colosseum]] | |
| − | + | *[[Catacombs of Kom el Shoqafa]] | |
| − | + | *[[Great Wall of China]] | |
| − | + | *[[Porcelain Tower of Nanjing]] | |
| − | + | *[[Hagia Sophia]] | |
| − | + | *[[Leaning Tower of Pisa]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Other sites that have been mentioned include: | Other sites that have been mentioned include: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *[[Cairo Citadel]] | |
| − | + | *[[Ely Cathedral]] | |
| + | *[[Taj Mahal]] | ||
| + | *[[Cluny Abbey]] | ||
| − | === | + | == Modern lists == |
| − | The [[American Society of Civil Engineers]] compiled | + | Many lists have been made of the greatest structures built during modern times or of the greatest wonders existing today. Some of the most notable lists are presented below. |
| + | === American Society of Civil Engineers === | ||
| + | The [[American Society of Civil Engineers]] compiled a list of wonders of the modern world:<ref>[https://7wonders.org/civil-engineering-wonders/ Civil Engineering Wonders] ''7wonders.org''. Retrieved April 8, 2022.</ref> | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 114: | Line 113: | ||
|December 1, 1987 | |December 1, 1987 | ||
|May 6, 1994 | |May 6, 1994 | ||
| − | |[[Strait of Dover]], between | + | |[[Strait of Dover]], between the [[United Kingdom]] and [[France]] |
|- | |- | ||
|[[CN Tower]] | |[[CN Tower]] | ||
|February 6, 1973 | |February 6, 1973 | ||
| − | |June 26, 1976<!--Tower construction completed in 75 and opened to the public in 76—> | + | |June 26, 1976, tallest land structure in the world until September 12, 2007. Surpassed by [[Burj Dubai]]<!--Tower construction completed in 75 and opened to the public in 76—> |
|[[Toronto]], [[Ontario]], [[Canada]] | |[[Toronto]], [[Ontario]], [[Canada]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 124: | Line 123: | ||
|January 22, 1930 | |January 22, 1930 | ||
|May 1, 1931 | |May 1, 1931 | ||
| − | |[[New York City|New York]], [[New York | + | |[[New York City|New York]], [[New York|NY]], [[United States|U.S.]] |
|- | |- | ||
|[[Golden Gate Bridge]] | |[[Golden Gate Bridge]] | ||
|January 5, 1933 | |January 5, 1933 | ||
|May 27, 1937 | |May 27, 1937 | ||
| − | |[[Golden Gate Strait]], north of [[San Francisco, California]], [[ | + | |[[Golden Gate Strait]], north of [[San Francisco, California|San Francisco]], [[California]], [[United States|U.S.]] |
|- | |- | ||
|[[Itaipu|Itaipu Dam]] | |[[Itaipu|Itaipu Dam]] | ||
|January 1970 | |January 1970 | ||
|May 5, 1984 | |May 5, 1984 | ||
| − | |[[Paraná River]], | + | |[[Paraná River]], between [[Brazil]] and [[Paraguay]] |
|- | |- | ||
|[[Delta Works]] | |[[Delta Works]] | ||
| − | | | + | |1950 |
|May 10, 1997 | |May 10, 1997 | ||
| − | |[[Netherlands]] | + | |[[Netherlands]] |
|- | |- | ||
|[[Panama Canal]] | |[[Panama Canal]] | ||
|January 1, 1880 | |January 1, 1880 | ||
|January 7, 1914 | |January 7, 1914 | ||
| − | |[[Isthmus of Panama | + | |[[Isthmus of Panama]] |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | === | + | === New7Wonders Foundation's seven wonders of the world === |
| − | + | {{Main|New Seven Wonders of the World}} | |
| + | [[File:GreatWall6.jpg|thumb|400px|Great Wall of China]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Taj1.jpg|thumb|400px|The Taj Mahal]] | ||
| + | [[File:Peru Machu Picchu Sunrise.jpg|thumb|300px|Machu Pichu]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Canyon midday.jpg|thumb|400px|The Grand Canyon]] | ||
| + | In 2001, an initiative was started by the Swiss corporation New7Wonders Foundation to choose the [[New Seven Wonders of the World]] from a selection of 200 existing monuments for profit.<ref> [https://www.new7wonders.com/?id=3&L=0 New Seven Wonders] ''New 7 Wonders''. Retrieved April 8, 2022</ref> Twenty-one finalists were announced on January 1, 2006.<ref>[https://www.new7wonders.com/?id=3&L=0 Finalist Page] ''New 7 Wonders''. Retrieved April 8, 2022.</ref> [[Egypt]] was not happy with the fact that the only original wonder would have to compete with the likes of the [[Statue of Liberty]], the [[Sydney Opera House]], and other landmarks; and called the project absurd. To solve this, [[Great Pyramid of Giza|Giza]] was named an honorary Candidate. The results were announced on July 7, 2007 in [[Benfica]]'s stadium in a big ceremony in Lisbon, Portugal:<ref> [https://www.abc.net.au/news/2007-07-08/opera-house-snubbed-as-new-wonders-unveiled/92898 Opera House snubbed as new Wonders unveiled] ''ABC News'', July 7, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2022.</ref> | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | ! Wonder | |
| − | + | ! Date of construction | |
| − | + | ! Location | |
| − | + | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |
| − | + | | [[Great Wall of China]] | |
| − | + | | Fifth century B.C.E. – sixteenth century CE | |
| − | + | | [[China]] | |
| − | + | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |
| − | + | | [[Petra]] | |
| − | + | | Sixth century B.C.E. | |
| − | + | | [[Jordan]] | |
| − | + | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |
| − | + | | [[Christ the Redeemer (statue)|Christ the Redeemer]] | |
| − | + | | Opened October 12, 1931 | |
| − | + | | [[Brazil]] | |
| − | + | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |
| − | + | | [[Machu Picchu]] | |
| − | + | | ''c.'' 1450 | |
| − | + | | [[Peru]] | |
| − | + | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |
| − | + | | [[Chichen Itza]] | |
| − | + | | ''c.'' 600 | |
| − | + | | [[Mexico]] | |
| − | + | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |
| − | + | | [[Roman Colosseum]] | |
| − | + | | Completed 80 C.E. | |
| − | + | | [[Italy]] | |
| − | + | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |
| − | + | | [[Taj Mahal]] | |
| − | + | | Completed ''c.'' 1648 | |
| − | + | | [[India]] | |
| − | + | |- style="vertical-align: middle;" | |
| − | + | | [[Great Pyramid]] (Honorary Candidate) | |
| − | + | | Completed ''c.'' 2560 B.C.E. | |
| + | | [[Egypt]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | {{anchor|New Seven Wonders}} | |
| − | In November 2006 the American national newspaper ''[[USA Today]]'' in | + | === ''USA Today'''s New Seven Wonders === |
| + | In November 2006, the American national newspaper, ''[[USA Today]],'' in cooperation with the American television show, ''[[Good Morning America]],'' revealed a list of New Seven Wonders as chosen by six judges. The wonders were announced one per day over a week on ''Good Morning America''. An eighth wonder was chosen on November 24 from viewer feedback.<ref> What Are The USA Today 7 Wonders Of The World? ''Listerious'', December 15, 2020. </ref> | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 202: | Line 209: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 2 | | 2 | ||
| − | | [[Old City of Jerusalem]] | + | | [[Old City (Jerusalem)|Old City of Jerusalem]] |
| − | | [[Israel]] | + | | [[Jerusalem]], [[Israel]] |
|- | |- | ||
| 3 | | 3 | ||
| Line 210: | Line 217: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 4 | | 4 | ||
| − | | [[ | + | | [[Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument]] |
| [[Hawaii]], [[United States]] | | [[Hawaii]], [[United States]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 218: | Line 225: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 6 | | 6 | ||
| − | | [[Maya civilization| | + | | [[Maya civilization|Maya]] [[Maya architecture|ruins]] |
| − | | [[Yucatán Peninsula]], [[ | + | | [[Yucatán Peninsula]], [[México]] |
|- | |- | ||
| 7 | | 7 | ||
| Line 230: | Line 237: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | == | + | === Seven Natural Wonders of the World === |
| − | + | {{see also|Natural 7 Wonders}} | |
| − | * [[Seven | + | |
| − | * [[ | + | Similar to the other lists of wonders, there is no consensus on a list of seven natural wonders of the world, as there has been debate over how large the list should be. One of the many lists was compiled by [[CNN]]:<ref> [https://web.archive.org/web/20060721011803/http://www.cnn.com/TRAVEL/DESTINATIONS/9711/natural.wonders/ The Seven Natural Wonders of the World] ''CNN'', 1997. Retrieved April 8, 2022.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | *[[Grand Canyon]] | ||
| + | *[[Great Barrier Reef]] | ||
| + | *Harbour of [[Rio de Janeiro]] | ||
| + | *[[Mount Everest]] | ||
| + | *[[Aurora (astronomy)|Aurora]] | ||
| + | *[[Parícutin]] volcano | ||
| + | *[[Victoria Falls]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Seven wonders of the underwater world ==== | ||
| + | [[Image:Part of Great Barrier Reef from Helecopter.JPG|thumb|right|400px|An aerial photograph of the [[Great Barrier Reef]]]] | ||
| + | The Seven Underwater Wonders of the World was a list drawn up by [[CEDAM International]], an American-based non-profit group for divers, dedicated to ocean preservation and research. In 1989, CEDAM brought together a panel of marine scientists, including Dr. Eugenie Clark, to pick underwater areas which they considered to be worthy of protection. The results were announced at The National Aquarium in Washington DC by actor [[Lloyd Bridges]], who played in a TV show titled ''[[Sea Hunt]]'':<ref> [https://web.archive.org/web/20170613234745/http://wonderclub.com/WorldWonders/UnderWaterWonders.html The Seven Underwater Wonders of the World] Retrieved April 8, 2022.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Palau]] | ||
| + | *[[Belize Barrier Reef]] | ||
| + | *[[Great Barrier Reef]] | ||
| + | *[[Hydrothermal vent|Deep-Sea Vents]] | ||
| + | *[[Galápagos Islands]] | ||
| + | *[[Lake Baikal]] | ||
| + | *[[Red Sea|Northern Red Sea]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Seven Wonders of the Industrial World === | ||
| + | [[File:Panama Canal Map EN.png|thumb|350px|Schematic of the [[Panama Canal]], illustrating the sequence of locks and passages]] | ||
| + | British author [[Deborah Cadbury]] wrote ''[[Seven Wonders of the Industrial World]],'' a book telling the stories of seven great feats of engineering of the [[nineteenth century|nineteenth]] and early [[twentieth century|twentieth]] centuries. In 2003 the [[BBC]] made a seven-part [[television documentary|documentary]] series on the book, with each episode dramatising the construction one of the wonders. The seven industrial wonders are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[SS Great Eastern|SS ''Great Eastern'']] | ||
| + | *[[Bell Rock Lighthouse]] | ||
| + | *[[Brooklyn Bridge]] | ||
| + | *[[London sewerage system]] | ||
| + | *[[First Transcontinental Railroad]] | ||
| + | *[[Panama Canal]] | ||
| + | *[[Hoover Dam]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Travel wonders of the world === | ||
| + | Travel writer [[Howard Hillman]] is one of many such writers who has compiled lists of the top man-made<ref>Howard Hillman, [http://www.hillmanwonders.com/top_10_man_made_wonders/top_10_man_made_wonders.htm World's top 10 man-made travel wonders] ''Hillman's Top 10 Lists for Travelers''. Retrieved April 8 2022.</ref> | ||
| + | and natural<ref>Howard Hillman, [http://www.hillmanwonders.com/top_10_natural_wonders/top_10_natural_wonders.htm World's top 10 natural travel wonders,] ''Hillman's Top 10 Lists for Travelers''. Retrieved April 8 2022.</ref> tourist travel wonders of the world. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Man-made travel wonders ==== | ||
| + | [[File:Forbidden city 07.jpg|thumb|400px|[[Forbidden City]] located in the center of [[Beijing]], [[China]]]] | ||
| + | # [[Giza pyramid complex]] | ||
| + | # [[Great Wall of China]] | ||
| + | # [[Taj Mahal]] | ||
| + | # [[Machu Picchu]] | ||
| + | # [[Bali]] | ||
| + | # [[Angkor Wat]] | ||
| + | # [[Forbidden City]] | ||
| + | # [[Bagan#Cultural sites|Bagan Temples & Pagodas]] | ||
| + | # [[Karnak Temple]] | ||
| + | # [[Teotihuacán]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Natural travel wonders ==== | ||
| + | [[Image:Victoria Falls2003.jpg|thumb|300px|[[Victoria Falls]], seen from the [[Zambia]]n side.]] | ||
| + | # [[Serengeti|Serengeti Migration]] | ||
| + | # [[Galápagos Islands]] | ||
| + | # [[Grand Canyon]] | ||
| + | # [[Iguazu Falls]] | ||
| + | # [[Amazon Rainforest]] | ||
| + | # [[Ngorongoro Crater]] | ||
| + | # [[Great Barrier Reef]] | ||
| + | # [[Victoria Falls]] | ||
| + | # [[Bora Bora]] | ||
| + | # [[Cappadocia]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Notes == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| − | + | * Cox, Reg, and Neil Morris. ''The Seven Wonders of the Modern World''. Chelsea House Publications, 2000. ISBN 0791060489. | |
| − | + | * Cox, Reg, Neil Morris, and James Field. ''The Seven Wonders of the Medieval World''. Chelsea House Publications, 2000. ISBN 0791060470. | |
| − | + | * D'Epiro, Peter, and Mary Desmond Pinkowish. ''What Are the Seven Wonders of the World? and 100 Other Great Cultural Lists''. Anchor, 1998. ISBN 0385490623. | |
| − | * Cox, Reg, and Neil Morris | + | * Freely, John. ''The Western Shores of Turkey: Discovering the Aegean and Mediterranean Coast''. Tauris Parke Paperbacks, 2004. ISBN 978-1850436188 |
| − | * Cox, Reg, Neil Morris, and James Field | + | * Morris, Neil. ''The Seven Wonders of the Natural World''. Chrysalis Books, 2002. ISBN 184138495X. |
| − | * D'Epiro, Peter, and Mary Desmond Pinkowish | + | * Trebilco, Paul. ''The Early Christians in Ephesus from Paul to Ignatius''. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing Co., 2007. ISBN 0802807690 |
| − | * Morris, Neil | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| + | All links retrieved January 26, 2023. | ||
=== Seven Ancient Wonders === | === Seven Ancient Wonders === | ||
| − | * [http:// | + | *[http://www.guardian.co.uk/international/story/0,,2030611,00.html "Eternal wonder of humanity's first great achievements" by Jonathan Glancey], ''The Guardian''. |
| − | + | * Parkin, Tim, ed. [http://web.archive.org/web/20041011114644/http://www.clas.canterbury.ac.nz/wonders.html ''Researching Ancient Wonders: A Research Guide'' (U. of Canterbury, New Zealand)] | |
| − | * Parkin, Tim, [http://web.archive.org/web/20041011114644/http://www.clas.canterbury.ac.nz/wonders.html ''Researching Ancient Wonders: A Research Guide'' | + | * [https://www.history.com/topics/ancient-history/seven-wonders-of-the-ancient-world |
| − | * [ | + | Seven Wonders of the Ancient World] ''History.com'' |
| − | |||
=== Other wonders === | === Other wonders === | ||
| − | + | * [http://www.wonderclub.com/AllWorldWonders.html Complete Listing of World Wonders] ''Wonder Club'' | |
| − | * [http://www.wonderclub.com/AllWorldWonders.html | + | * [http://www.hillmanwonders.com/ Hillman Wonders of the World] Howard Hillman's Top 100 Wonders |
| − | * [http://www. | + | * [https://theplanetd.com/wonders-of-the-world/ 7 Wonders of the World – The New, the Natural, and the Ancient] ''The Planet D'' |
| − | *[ | ||
| − | |||
| + | {{Credits|Seven_Wonders_of_the_World|130796789|Wonders_of_the_World|248409778}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Geography]] |
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 19:50, 21 April 2023

The Seven Wonders of the World (or the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World) is a widely known list of seven remarkable constructions of antiquity. It was based on guide-books popular among Hellenic sightseers and includes only works located around the Mediterranean rim. Later lists include those for the medieval world and the modern world.
The original Seven Wonders of the World consists of: The Great Pyramid of Giza (the most ancient as well as the only surviving structure), the Hanging Gardens of Babylon, the Temple of Artemis at Ephesus, the Statue of Zeus at Olympia, the Mausoleum of Maussollos at Halicarnassus, the Colossus of Rhodes, and the Lighthouse of Alexandria.
The notion of "Seven Wonders" can be traced to a Hellenistic recognition of trans-cultural human achievement that found expression throughout the Hellenistic world. For thousands of years, the Seven Wonders of the World have inspired humankind as representative works symbolic of the great civilizations of antiquity. In terms of innovative design, elaborate construction, technological mastery, and symbolic meaning, the Seven Wonders have not only showcased the high points of diverse civilizations, but tied humankind together in the common pursuit of intellectual excellence and self-expression.
Seven Wonders of the Ancient World
The historian Herodotus and the scholar Callimachus of Cyrene (c. 305 – 240 B.C.E.) made early lists of "seven wonders," but these writings have not survived, except as references. The earliest extant version of a list of seven wonders was compiled by Antipater of Sidon, who described the structures in a poem around 140 B.C.E.:
I have set eyes on the wall of lofty Babylon on which is a road for chariots, and the statue of Zeus by the Alpheus, and the hanging gardens, and the Colossus of the Sun, and the huge labor of the high pyramids, and the vast tomb of Mausolus; but when I saw the house of Artemis that mounted to the clouds, those other marvels lost their brilliancy, and I said, "Lo, apart from Olympus, the Sun never looked on aught so grand"[1]
A later list, under various titles such as De septem orbis spactaculis and traditionally, though incorrectly, attributed to the engineer Philo of Byzantium, may date as late as the fifth century C.E., although the author writes as if the Colossus of Rhodes, destroyed by an earthquake in 224 B.C.E., were still standing.
The basic characteristics of each of the Seven Wonders are given in the table below:
| Wonder | Date of construction | Builder | Notable features | Date of destruction | Cause of destruction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Great Pyramid of Giza | 2650 – 2500 B.C.E. | Egyptians | Built as the tomb of Fourth dynasty Egyptian pharaoh Khufu. | Still standing | - |
| Hanging Gardens of Babylon | 600 B.C.E. | Babylonians | Herodotus claimed the outer walls were 56 miles in length, 80 feet thick and 320 feet high (although some archaeological findings suggest otherwise). | After first century B.C.E. | Earthquake |
| Temple of Artemis at Ephesus | 550 B.C.E. | Lydians, Persians, Greeks | Dedicated to the Greek goddess Artemis, the temple was begun by Croesus of Lydia and took 120 years to build. It was destroyed by arson in 356 B.C.E., rebuilt and destroyed during a raid by the Goths in 262, rebuilt again and finally demolished by a mob allegedly led by John Chrysostom.[2] | 356 B.C.E. and 401 C.E. | Arson and later demolition |
| Statue of Zeus at Olympia | 435 B.C.E. | Greeks | Occupied the whole width of the aisle of the temple that was built to house it, and was 40 feet tall. | fifth and sixth centuries C.E. | Fire |
| Mausoleum of Maussollos at Halicarnassus | 351 B.C.E. | Persians, Greeks | Stood approximately 135 feet tall with each of the four sides adorned with sculptural reliefs. Origin of the word mausoleum. | by 1494 C.E. | Earthquake |
| Colossus of Rhodes | 292 – 280 B.C.E. | Hellenistic Greece | A giant statue of the Greek god Helios roughly the same size as today's Statue of Liberty in New York. | 224 B.C.E. | Earthquake |
| Lighthouse of Alexandria | Third century B.C.E. | Hellenistic Egypt | Between 383 feet to 440 feet tall it was among the tallest man-made structures on Earth for many centuries. | 1303 – 1480 C.E. | Earthquake |
The Greek category to describe what people call "wonders" today was "theamata," which translates as "something worth seeing" or "must-sees." Since the list came mostly from ancient Greek writings, only sites that would have been known and visited by the ancient Greeks were included. Sites from eastern Asia, the Americas, Africa, and northern Europe were thus omitted. Five of the seven entries are a celebration of Greek accomplishments in the arts and architecture (the exceptions being the Pyramids of Giza and the Hanging Gardens of Babylon). Antipater's earlier list replaced the Lighthouse of Alexandria with the Babylon's famous Ishtar Gate.
It was not until the sixth century C.E. that the list above was used. Of these wonders, the only one that has survived to the present day is the Great Pyramid of Giza. One of wonders, the Temple of Artemis, was destroyed intentionally, first by arson and finally by a mob allegedly led by the Christian bishop St. John Chrysostom. The Statue of Zeus was destroyed by fire. Four of the wonders were destroyed by earthquakes—the Hanging Gardens, the Lighthouse of Alexandria, the Colossus of Rhodes, and the Mausoleum of Maussollos. (The existence of the Hanging Gardens, however, has not been definitively proven.) There are sculptures from the Mausoleum of Maussollos and the Temple of Artemis in the British Museum in London.
Later lists
Many lists of "wonders of the world" are said to have existed during the Middle Ages, although it is unlikely that these lists originated at that time. These lists go by names such as "Wonders of the Middle Ages" (implying no specific limitation to seven), "Seven Wonders of the Middle Ages," "Medieval Mind," and "Architectural Wonders of the Middle Ages." Many of the structures on these lists were built much earlier than the Medieval Ages, but were well known. The lists are more properly seen as a continuing type or genre in the Seven Wonders tradition than a specific list.
The following is a typical representative of such lists:
- Stonehenge
- Colosseum
- Catacombs of Kom el Shoqafa
- Great Wall of China
- Porcelain Tower of Nanjing
- Hagia Sophia
- Leaning Tower of Pisa
Other sites that have been mentioned include:
- Cairo Citadel
- Ely Cathedral
- Taj Mahal
- Cluny Abbey
Modern lists
Many lists have been made of the greatest structures built during modern times or of the greatest wonders existing today. Some of the most notable lists are presented below.
American Society of Civil Engineers
The American Society of Civil Engineers compiled a list of wonders of the modern world:[3]
| Wonder | Date Started | Date Finished | Locations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channel Tunnel | December 1, 1987 | May 6, 1994 | Strait of Dover, between the United Kingdom and France |
| CN Tower | February 6, 1973 | June 26, 1976, tallest land structure in the world until September 12, 2007. Surpassed by Burj Dubai | Toronto, Ontario, Canada |
| Empire State Building | January 22, 1930 | May 1, 1931 | New York, NY, U.S. |
| Golden Gate Bridge | January 5, 1933 | May 27, 1937 | Golden Gate Strait, north of San Francisco, California, U.S. |
| Itaipu Dam | January 1970 | May 5, 1984 | Paraná River, between Brazil and Paraguay |
| Delta Works | 1950 | May 10, 1997 | Netherlands |
| Panama Canal | January 1, 1880 | January 7, 1914 | Isthmus of Panama |
New7Wonders Foundation's seven wonders of the world
In 2001, an initiative was started by the Swiss corporation New7Wonders Foundation to choose the New Seven Wonders of the World from a selection of 200 existing monuments for profit.[4] Twenty-one finalists were announced on January 1, 2006.[5] Egypt was not happy with the fact that the only original wonder would have to compete with the likes of the Statue of Liberty, the Sydney Opera House, and other landmarks; and called the project absurd. To solve this, Giza was named an honorary Candidate. The results were announced on July 7, 2007 in Benfica's stadium in a big ceremony in Lisbon, Portugal:[6]
| Wonder | Date of construction | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Great Wall of China | Fifth century B.C.E. – sixteenth century CE | China |
| Petra | Sixth century B.C.E. | Jordan |
| Christ the Redeemer | Opened October 12, 1931 | Brazil |
| Machu Picchu | c. 1450 | Peru |
| Chichen Itza | c. 600 | Mexico |
| Roman Colosseum | Completed 80 C.E. | Italy |
| Taj Mahal | Completed c. 1648 | India |
| Great Pyramid (Honorary Candidate) | Completed c. 2560 B.C.E. | Egypt |
USA Today's New Seven Wonders
In November 2006, the American national newspaper, USA Today, in cooperation with the American television show, Good Morning America, revealed a list of New Seven Wonders as chosen by six judges. The wonders were announced one per day over a week on Good Morning America. An eighth wonder was chosen on November 24 from viewer feedback.[7]
| Number | Wonder | Location |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Potala Palace | Lhasa, Tibet, China |
| 2 | Old City of Jerusalem | Jerusalem, Israel |
| 3 | Polar ice caps | Polar regions |
| 4 | Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument | Hawaii, United States |
| 5 | Internet | N/A |
| 6 | Maya ruins | Yucatán Peninsula, México |
| 7 | Great Migration of Serengeti and Masai Mara | Tanzania and Kenya |
| 8 | Grand Canyon (viewer-chosen eighth wonder) | Arizona, United States |
Seven Natural Wonders of the World
Similar to the other lists of wonders, there is no consensus on a list of seven natural wonders of the world, as there has been debate over how large the list should be. One of the many lists was compiled by CNN:[8]
- Grand Canyon
- Great Barrier Reef
- Harbour of Rio de Janeiro
- Mount Everest
- Aurora
- Parícutin volcano
- Victoria Falls
Seven wonders of the underwater world

The Seven Underwater Wonders of the World was a list drawn up by CEDAM International, an American-based non-profit group for divers, dedicated to ocean preservation and research. In 1989, CEDAM brought together a panel of marine scientists, including Dr. Eugenie Clark, to pick underwater areas which they considered to be worthy of protection. The results were announced at The National Aquarium in Washington DC by actor Lloyd Bridges, who played in a TV show titled Sea Hunt:[9]
- Palau
- Belize Barrier Reef
- Great Barrier Reef
- Deep-Sea Vents
- Galápagos Islands
- Lake Baikal
- Northern Red Sea
Seven Wonders of the Industrial World
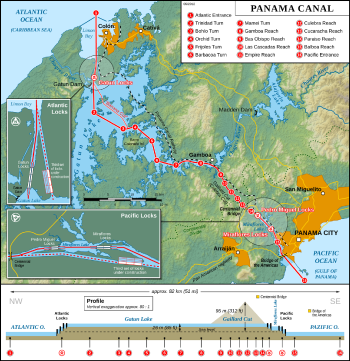
British author Deborah Cadbury wrote Seven Wonders of the Industrial World, a book telling the stories of seven great feats of engineering of the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. In 2003 the BBC made a seven-part documentary series on the book, with each episode dramatising the construction one of the wonders. The seven industrial wonders are:
- SS Great Eastern
- Bell Rock Lighthouse
- Brooklyn Bridge
- London sewerage system
- First Transcontinental Railroad
- Panama Canal
- Hoover Dam
Travel wonders of the world
Travel writer Howard Hillman is one of many such writers who has compiled lists of the top man-made[10] and natural[11] tourist travel wonders of the world.
Man-made travel wonders
- Giza pyramid complex
- Great Wall of China
- Taj Mahal
- Machu Picchu
- Bali
- Angkor Wat
- Forbidden City
- Bagan Temples & Pagodas
- Karnak Temple
- Teotihuacán
Natural travel wonders
- Serengeti Migration
- Galápagos Islands
- Grand Canyon
- Iguazu Falls
- Amazon Rainforest
- Ngorongoro Crater
- Great Barrier Reef
- Victoria Falls
- Bora Bora
- Cappadocia
Notes
- ↑ Paul Trebilco, The Early Christians in Ephesus from Paul to Ignatius (Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing Co., 2007, ISBN 0802807690).
- ↑ John Freely, The Western Shores of Turkey: Discovering the Aegean and Mediterranean Coast (Tauris Parke Paperbacks, 2004, ISBN 978-1850436188).
- ↑ Civil Engineering Wonders 7wonders.org. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ↑ New Seven Wonders New 7 Wonders. Retrieved April 8, 2022
- ↑ Finalist Page New 7 Wonders. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ↑ Opera House snubbed as new Wonders unveiled ABC News, July 7, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ↑ What Are The USA Today 7 Wonders Of The World? Listerious, December 15, 2020.
- ↑ The Seven Natural Wonders of the World CNN, 1997. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ↑ The Seven Underwater Wonders of the World Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ↑ Howard Hillman, World's top 10 man-made travel wonders Hillman's Top 10 Lists for Travelers. Retrieved April 8 2022.
- ↑ Howard Hillman, World's top 10 natural travel wonders, Hillman's Top 10 Lists for Travelers. Retrieved April 8 2022.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Cox, Reg, and Neil Morris. The Seven Wonders of the Modern World. Chelsea House Publications, 2000. ISBN 0791060489.
- Cox, Reg, Neil Morris, and James Field. The Seven Wonders of the Medieval World. Chelsea House Publications, 2000. ISBN 0791060470.
- D'Epiro, Peter, and Mary Desmond Pinkowish. What Are the Seven Wonders of the World? and 100 Other Great Cultural Lists. Anchor, 1998. ISBN 0385490623.
- Freely, John. The Western Shores of Turkey: Discovering the Aegean and Mediterranean Coast. Tauris Parke Paperbacks, 2004. ISBN 978-1850436188
- Morris, Neil. The Seven Wonders of the Natural World. Chrysalis Books, 2002. ISBN 184138495X.
- Trebilco, Paul. The Early Christians in Ephesus from Paul to Ignatius. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing Co., 2007. ISBN 0802807690
External links
All links retrieved January 26, 2023.
Seven Ancient Wonders
- "Eternal wonder of humanity's first great achievements" by Jonathan Glancey, The Guardian.
- Parkin, Tim, ed. Researching Ancient Wonders: A Research Guide (U. of Canterbury, New Zealand)
- [https://www.history.com/topics/ancient-history/seven-wonders-of-the-ancient-world
Seven Wonders of the Ancient World] History.com
Other wonders
- Complete Listing of World Wonders Wonder Club
- Hillman Wonders of the World Howard Hillman's Top 100 Wonders
- 7 Wonders of the World – The New, the Natural, and the Ancient The Planet D
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.







