Difference between revisions of "Allied Powers (World War II)" - New World Encyclopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The group of countries (also known as the '''Allies of [[World War II]]''') consisted of those nations opposed to the [[Axis Powers]] during the Second World War. | The group of countries (also known as the '''Allies of [[World War II]]''') consisted of those nations opposed to the [[Axis Powers]] during the Second World War. | ||
[[Image:WWII.png|thumb|280px|World Map with the [[participants in World War II]].<br>The [[Allies of World War II|Allies]] depicted in green (those in light green entered after the [[Attack on Pearl Harbor|attack on Pearl Harbor]]), the [[Axis Powers]] in orange, and neutral countries in grey.]] | [[Image:WWII.png|thumb|280px|World Map with the [[participants in World War II]].<br>The [[Allies of World War II|Allies]] depicted in green (those in light green entered after the [[Attack on Pearl Harbor|attack on Pearl Harbor]]), the [[Axis Powers]] in orange, and neutral countries in grey.]] | ||
| − | [[Image:Tehran Conference, 1943.jpg|280px|thumb|"The Big 3": [[Joseph Stalin]], [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]] and [[Winston Churchill]] meeting at [[Tehran]] in | + | [[Image:Tehran Conference, 1943.jpg|280px|thumb|"The Big 3": [[Joseph Stalin]], [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]] and [[Winston Churchill]] meeting at [[Tehran]] in 1943.]] |
===China=== | ===China=== | ||
:''Main article: [[Second Sino-Japanese War]]'' | :''Main article: [[Second Sino-Japanese War]]'' | ||
| − | By the time World War II began, the [[Republic of China]] had been fighting the [[Empire of Japan]] since | + | By the time World War II began, the [[Republic of China]] had been fighting the [[Empire of Japan]] since 1937. |
| − | During the | + | During the 1920s, the [[Kuomintang]] government was aided by the [[Soviet Union]], which helped to reorganize the party along the Leninst model of the unification of party, state, and army. However, following the unification of China, [[Generalissimo]] [[Chiang Kai-Shek]] purged leftists from his party and refused to ally with the [[Communist Party of China]] to fight against the [[Japan]]ese, and instead opted to fight both at once. This remained the case even after the [[Mukden Incident]] and the puppet regime of [[Manchuria]] set by Japanese troops in 1931. Chiang's anti-communist campaigns continued while he fought small, incessant conflicts against Japan throughout the 1930s. This period saw China lose territories piece by piece to Japan. |
| − | Beginning in early 1930s, [[Sino-German cooperation|Germany and China became close partners]] in areas of military and industrial exchange. [[Nazi Germany]] provided the largest proportion of Chinese arms imports and technical expertise. Following the [[Marco Polo Bridge Incident]] of | + | Beginning in early 1930s, [[Sino-German cooperation|Germany and China became close partners]] in areas of military and industrial exchange. [[Nazi Germany]] provided the largest proportion of Chinese arms imports and technical expertise. Following the [[Marco Polo Bridge Incident]] of July 7, 1937, China and Japan became embroiled in a full-scale war which continued until 1945. Initially, Germany denounced [[Japanese war crimes]] in China, such as the [[Nanking Massacre]] of 1937. However Germany also recognized that Japan was more capable of fighting the Soviet Union, and soon broke off the cooperation with China in May 1938. The Soviet Union, wishing to keep China in the fight against Japan, supplied China with some military assistance until 1941, until it made peace with Japan to prepare for the [[Eastern Front (World War II)|war against Germany]]. |
| − | Even though China had been fighting the longest among all the Allied powers, it only officially joined the Allies after the [[attack on Pearl Harbor]], on | + | Even though China had been fighting the longest among all the Allied powers, it only officially joined the Allies after the [[attack on Pearl Harbor]], on 7 December 1941. Chiang Kai-shek felt Allied victory was assured with the entrance of the [[United States]] into the war and he declared war on Germany and the other Axis nations. However, Allied aid remained low as the [[Burma Road]] was closed and the Allies suffered a series of military defeats against Japan early on in the campaign. The bulk of military aid would not arrive until the spring of 1945. More than 1.5 million Japanese troops were trapped in the China Theater; troops that otherwise could have been deployed elsewhere had China collapsed and made a separate peace with Japan. |
===Key alliances are formed=== | ===Key alliances are formed=== | ||
| − | On | + | On September 1, the [[German invasion of Poland]] began World War II. Britain, France, [[Australia]] and [[New Zealand]] all declared war on Germany on September 3. [[Nepal]], [[Newfoundland]], [[Tonga]], [[South Africa]] and [[Canada]] followed suit within days. On September 17, the Soviets [[Polish Defence War of 1939#Phase 2: Soviet aggression|invaded Poland from the East]]. The following year, the USSR annexed the [[Baltic states]] ([[Estonia]], [[Latvia]] and [[Lithuania]]) together with parts of [[Romania]], and [[Winter War|attacked Finland]]. The German-Soviet agreement was brought to an end by the [[Operation Barbarossa|German invasion of the USSR]] on June 22, 1941. |
| − | The [[United States of America]] joined the Allies following the [[attack on Pearl Harbor]], on | + | The [[United States of America]] joined the Allies following the [[attack on Pearl Harbor]], on December 7, 1941. The [[Declaration by United Nations]], on January 1, 1942, officially united 26 nations as Allies. (The Declaration also formed the basis for the [[United Nations]].) The informal ''Big 3'' alliance of the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and the United States emerged in the latter half of the war, and their decisions determined Allied strategy around the world. |
==Dates on which states joined the Allies== | ==Dates on which states joined the Allies== | ||
[[Image:Ww2 allied axis.gif|thumb|280px|Western allies blue, Soviet allies red, Axis powers black over the course of the war.]] | [[Image:Ww2 allied axis.gif|thumb|280px|Western allies blue, Soviet allies red, Axis powers black over the course of the war.]] | ||
===Following the [[German invasion of Poland]]=== | ===Following the [[German invasion of Poland]]=== | ||
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Poland.svg|15px]] [[Poland]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Poland.svg|15px]] [[Poland]]: 1939 1 September |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of the United Kingdom.svg|15px]] [[United Kingdom]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of the United Kingdom.svg|15px]] [[United Kingdom]]: 1939 3 September |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of France.svg|15px]] [[French Third Republic|France]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of France.svg|15px]] [[French Third Republic|France]]: 1939 3 September |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Australia.svg|15px]] [[Australia]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Australia.svg|15px]] [[Australia]]: 1939 3 September |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of New Zealand.svg|15px]] [[New Zealand]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of New Zealand.svg|15px]] [[New Zealand]]: 1939 3 September |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Nepal.svg|15px]] [[Nepal]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Nepal.svg|15px]] [[Nepal]]: 1939 4 September |
| − | * [[Image:Newfoundland Blue Ensign.gif|15px]] [[Dominion of Newfoundland|Newfoundland]]: | + | * [[Image:Newfoundland Blue Ensign.gif|15px]] [[Dominion of Newfoundland|Newfoundland]]: 1939 4 September |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Tonga.svg|15px]] [[Tonga]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Tonga.svg|15px]] [[Tonga]]: 1939 4 September |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of South Africa 1928-1994.svg|15px]] [[South Africa]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of South Africa 1928-1994.svg|15px]] [[South Africa]]: 1939 6 September |
| − | * [[Image:Canadian Red Ensign.svg|15px]] [[Canada]]: | + | * [[Image:Canadian Red Ensign.svg|15px]] [[Canada]]: 1939 10 September |
===After the end of the [[Phony War]]=== | ===After the end of the [[Phony War]]=== | ||
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Denmark.svg|15px]] [[Denmark]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Denmark.svg|15px]] [[Denmark]]: 1940 9 April |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Norway.svg|15px]] [[Norway]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Norway.svg|15px]] [[Norway]]: 1940 9 April |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Belgium.svg|15px]] [[Belgium]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Belgium.svg|15px]] [[Belgium]]: 1940 10 May |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Luxembourg.svg|15px]] [[Luxembourg]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Luxembourg.svg|15px]] [[Luxembourg]]: 1940 10 May |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of the Netherlands.svg|15px]] [[Netherlands]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of the Netherlands.svg|15px]] [[Netherlands]]: 1940 10 May |
| − | *[[Image:Flag of Malta.svg|15px]] [[Malta]]: | + | *[[Image:Flag of Malta.svg|15px]] [[Malta]]: 1940 10 June |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Free France 1940-1944.svg|15px]] [[Free France]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Free France 1940-1944.svg|15px]] [[Free France]]: 1940 18 June |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Greece (1828-1978).svg|15px]] [[Greece]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Greece (1828-1978).svg|15px]] [[Greece]]: 1940 28 October |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.svg|15px]] [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.svg|15px]] [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia]]: 1941 6 April |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of the Soviet Union.svg|15px]] [[Soviet Union]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of the Soviet Union.svg|15px]] [[Soviet Union]]: 1941 22 June |
| − | * [[Image:Tannutuva.gif|15px]] [[Tannu Tuva]]: | + | * [[Image:Tannutuva.gif|15px]] [[Tannu Tuva]]: 1941 25 June |
===After the [[attack on Pearl Harbor]]=== | ===After the [[attack on Pearl Harbor]]=== | ||
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Panama.svg|15px]] [[Panama]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Panama.svg|15px]] [[Panama]]: 1941 7 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of the Philippines.svg|15px]] [[Philippines]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of the Philippines.svg|15px]] [[Philippines]]: 1941 7 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Costa Rica (state).svg|15px]] [[Costa Rica]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Costa Rica (state).svg|15px]] [[Costa Rica]]: 1941 8 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of the Dominican Republic.svg|15px]] [[Dominican Republic]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of the Dominican Republic.svg|15px]] [[Dominican Republic]]: 1941 8 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of El Salvador.svg|15px]] [[El Salvador]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of El Salvador.svg|15px]] [[El Salvador]]: 1941 8 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Haiti.svg|15px]] [[Haiti]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Haiti.svg|15px]] [[Haiti]]: 1941 8 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Honduras.svg|15px]] [[Honduras]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Honduras.svg|15px]] [[Honduras]]: 1941 8 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Nicaragua.svg|15px]] [[Nicaragua]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Nicaragua.svg|15px]] [[Nicaragua]]: 1941 8 December |
| − | * [[Image:US flag 48 stars.svg|15px]] [[United States|United States of America]]: | + | * [[Image:US flag 48 stars.svg|15px]] [[United States|United States of America]]: 1941 8 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of the Republic of China.svg|15px]] [[Republic of China]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of the Republic of China.svg|15px]] [[Republic of China]]: 1941 9 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Guatemala.svg|15px]] [[Guatemala]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Guatemala.svg|15px]] [[Guatemala]]: 1941 9 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Cuba.svg|15px]] [[Cuba]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Cuba.svg|15px]] [[Cuba]]: 1941 9 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of South Korea.svg|15px]] [[Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea]] (Govt. in exile): | + | * [[Image:Flag of South Korea.svg|15px]] [[Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea]] (Govt. in exile): 1941 9 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of the Czech Republic.svg|15px]] [[Czechoslovakia]] (Govt. in exile) : | + | * [[Image:Flag of the Czech Republic.svg|15px]] [[Czechoslovakia]] (Govt. in exile) : 1941 16 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Mexico 1934.png|15px]] [[Mexico]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Mexico 1934.png|15px]] [[Mexico]]: 1942 22 May |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Brazil.svg|15px]] [[Brazil]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Brazil.svg|15px]] [[Brazil]]: 1942 22 August |
| − | * [[Image:Ethiopia1897.gif|15px]] [[Ethiopia]]: | + | * [[Image:Ethiopia1897.gif|15px]] [[Ethiopia]]: 1942 14 December |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Iraq 1924.svg|15px]] [[Iraq]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Iraq 1924.svg|15px]] [[Iraq]]: 1943 17 January |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Bolivia (state).svg|15px]] [[Bolivia]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Bolivia (state).svg|15px]] [[Bolivia]]: 1943 7 April |
| − | * [[Image:Persia1906.gif|15px]] [[Iran]]: | + | * [[Image:Persia1906.gif|15px]] [[Iran]]: 1943 9 September |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Italy (1861-1946).svg|15px]] [[Italy]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Italy (1861-1946).svg|15px]] [[Italy]]: 1943 13 October (formerly a member of the Axis) |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Colombia.svg|15px]] [[Colombia]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Colombia.svg|15px]] [[Colombia]]: 1943 26 November |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Liberia.svg|15px]] [[Liberia]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Liberia.svg|15px]] [[Liberia]]: 1944 27 January |
===After [[Battle of Normandy|D-Day]]=== | ===After [[Battle of Normandy|D-Day]]=== | ||
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Romania.svg|15px]] [[Romania]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Romania.svg|15px]] [[Romania]]: 1944 25 August, (formerly a member of the Axis) |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Bulgaria.svg|15px]] [[Bulgaria]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Bulgaria.svg|15px]] [[Bulgaria]]: 1944 8 September, (formerly a member of the Axis) |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of San Marino.svg|15px]] [[San Marino]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of San Marino.svg|15px]] [[San Marino]]: 1944 21 September |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Albania.svg|15px]] [[Albania]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Albania.svg|15px]] [[Albania]]: 1944 26 October |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Hungary.svg|15px]] [[Hungary]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Hungary.svg|15px]] [[Hungary]]: 1945 20 January, (formerly a member of the Axis) |
| − | * [[Image:Bahawalpur.gif|15px]] [[Bahawalpur State|Bahawalpur]]: | + | * [[Image:Bahawalpur.gif|15px]] [[Bahawalpur State|Bahawalpur]]: 1945 2 February |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Ecuador.svg|15px]] [[Ecuador]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Ecuador.svg|15px]] [[Ecuador]]: 1945 2 February |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Paraguay.svg|15px]] [[Paraguay]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Paraguay.svg|15px]] [[Paraguay]]: 1945 7 February |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Peru.svg|15px]] [[Peru]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Peru.svg|15px]] [[Peru]]: 1945 12 February |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Uruguay.svg|15px]] [[Uruguay]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Uruguay.svg|15px]] [[Uruguay]]: 1945 15 February |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Venezuela 1930-2006.svg|15px]] [[Venezuela]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Venezuela 1930-2006.svg|15px]] [[Venezuela]]: 1945 15 February |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Turkey.svg|15px]] [[Turkey]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Turkey.svg|15px]] [[Turkey]]: 1945 23 February |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Lebanon.svg|15px]] [[Lebanon]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Lebanon.svg|15px]] [[Lebanon]]: 1945 27 February |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Saudi Arabia.svg|15px]] [[Saudi Arabia]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Saudi Arabia.svg|15px]] [[Saudi Arabia]]: 1945 March |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Argentina.svg|15px]] [[Argentina]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Argentina.svg|15px]] [[Argentina]]: 1945 27 March |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of Chile.svg|15px]] [[Chile]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of Chile.svg|15px]] [[Chile]]: 1945 11 April |
| − | * [[Image:Flag of the People's Republic of Mongolia (1949-1992).svg|15px]] [[People's Republic of Mongolia]]: | + | * [[Image:Flag of the People's Republic of Mongolia (1949-1992).svg|15px]] [[People's Republic of Mongolia]]: 1945 9 August |
==Formal alliances during the war== | ==Formal alliances during the war== | ||
| Line 98: | Line 98: | ||
| − | These countries were allied to each other by a net of common defence pacts and military alliance pacts signed before the war. The Franco-British Alliance dated back to the [[Entente Cordiale]] of | + | These countries were allied to each other by a net of common defence pacts and military alliance pacts signed before the war. The Franco-British Alliance dated back to the [[Entente Cordiale]] of 1904 and the [[Triple Entente]] of 1907, active during the [[World War I]]. The [[Franco-Polish Alliance]] was signed in 1921 and then amended in 1927 and 1939.<!-- and Polish-English?—> The original allies were those states that declared war on [[Germany|Nazi Germany]] following the German invasion of Poland in September 1939. |
The [[Polish government in exile]] after 1939 continued the [[Polish contribution to World War II]] on several fronts with hundreds of thousands of members in the [[Polish Army]] in France and UK, as well as the [[Home Army]] in occupied Poland. The Soviet Union however, did not recognize the government and in 1943 organized the [[Polish People's Army]] under [[Rokossovsky]], around which eventually it constructed the post-war [[successor state]]. | The [[Polish government in exile]] after 1939 continued the [[Polish contribution to World War II]] on several fronts with hundreds of thousands of members in the [[Polish Army]] in France and UK, as well as the [[Home Army]] in occupied Poland. The Soviet Union however, did not recognize the government and in 1943 organized the [[Polish People's Army]] under [[Rokossovsky]], around which eventually it constructed the post-war [[successor state]]. | ||
| Line 111: | Line 111: | ||
The [[Oslo Group]] was an organisation of officially neutral countries. Four members later joined the Allies, as [[governments in exile]]: the [[Kingdom of Norway]], the [[Kingdom of the Netherlands]], the [[Kingdom of Belgium]] and the [[Grand Duchy of Luxembourg]]. | The [[Oslo Group]] was an organisation of officially neutral countries. Four members later joined the Allies, as [[governments in exile]]: the [[Kingdom of Norway]], the [[Kingdom of the Netherlands]], the [[Kingdom of Belgium]] and the [[Grand Duchy of Luxembourg]]. | ||
| − | The [[Republic of Finland]] was invaded by the USSR on | + | The [[Republic of Finland]] was invaded by the USSR on November 30 1939 [http://www.ibiblio.org/pha/policy/1939/391214a.html]. Later Finland and the [[Occupation of Denmark#Danish Government 1940-43|Kingdom of Denmark]] officially joined the Axis [[Anti-Comintern Pact]]. The [[Sweden and the Winter War#Winter War|Kingdom of Sweden]] remained officially neutral. |
[[Iceland]] and [[Greenland]], respectively in union with Denmark and a Danish colony, were occupied by the Allies for most of the war. British forces took control in Iceland in 1940, and it was used to facilitate the movement of [[Lend Lease]] equipment. Forces from the United States, although they were officially neutral at the time, occupied Greenland on April 9, 1941. The US also took over in Iceland on July 7, 1941. Iceland declared full independence from Denmark in 1944, but never declared war on any of the Axis powers. | [[Iceland]] and [[Greenland]], respectively in union with Denmark and a Danish colony, were occupied by the Allies for most of the war. British forces took control in Iceland in 1940, and it was used to facilitate the movement of [[Lend Lease]] equipment. Forces from the United States, although they were officially neutral at the time, occupied Greenland on April 9, 1941. The US also took over in Iceland on July 7, 1941. Iceland declared full independence from Denmark in 1944, but never declared war on any of the Axis powers. | ||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
=== Atlantic Charter === | === Atlantic Charter === | ||
| − | The [[Atlantic Charter]] was negotiated at the ''Atlantic Conference'' by [[Prime Minister of the United Kingdom|British Prime Minister]] [[Winston Churchill]] and [[President of the United States|U.S. President]] [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]], aboard warships in a secure anchorage at [[Argentia, Newfoundland and Labrador|Argentia]], [[Newfoundland]] (located on [[Placentia Bay]]) and was issued as a joint declaration on | + | The [[Atlantic Charter]] was negotiated at the ''Atlantic Conference'' by [[Prime Minister of the United Kingdom|British Prime Minister]] [[Winston Churchill]] and [[President of the United States|U.S. President]] [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]], aboard warships in a secure anchorage at [[Argentia, Newfoundland and Labrador|Argentia]], [[Newfoundland]] (located on [[Placentia Bay]]) and was issued as a joint declaration on August 14, 1941. |
The Atlantic Charter established a vision for a post-[[World War II]] world, despite the fact the United States had yet to enter the war. | The Atlantic Charter established a vision for a post-[[World War II]] world, despite the fact the United States had yet to enter the war. | ||
| Line 137: | Line 137: | ||
=== Comintern === | === Comintern === | ||
| − | The following [[socialist]] and pro-[[Soviet]] forces also fought against the [[Axis]] | + | The following [[socialist]] and pro-[[Soviet]] forces also fought against the [[Axis Powers]] before or during the Second World War. |
* [[Union of Soviet Socialist Republics]] | * [[Union of Soviet Socialist Republics]] | ||
* [[International Brigades]] | * [[International Brigades]] | ||
Revision as of 20:27, 28 July 2006
The group of countries (also known as the Allies of World War II) consisted of those nations opposed to the Axis Powers during the Second World War.
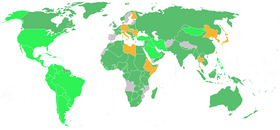
The Allies depicted in green (those in light green entered after the attack on Pearl Harbor), the Axis Powers in orange, and neutral countries in grey.
China
- Main article: Second Sino-Japanese War
By the time World War II began, the Republic of China had been fighting the Empire of Japan since 1937.
During the 1920s, the Kuomintang government was aided by the Soviet Union, which helped to reorganize the party along the Leninst model of the unification of party, state, and army. However, following the unification of China, Generalissimo Chiang Kai-Shek purged leftists from his party and refused to ally with the Communist Party of China to fight against the Japanese, and instead opted to fight both at once. This remained the case even after the Mukden Incident and the puppet regime of Manchuria set by Japanese troops in 1931. Chiang's anti-communist campaigns continued while he fought small, incessant conflicts against Japan throughout the 1930s. This period saw China lose territories piece by piece to Japan.
Beginning in early 1930s, Germany and China became close partners in areas of military and industrial exchange. Nazi Germany provided the largest proportion of Chinese arms imports and technical expertise. Following the Marco Polo Bridge Incident of July 7, 1937, China and Japan became embroiled in a full-scale war which continued until 1945. Initially, Germany denounced Japanese war crimes in China, such as the Nanking Massacre of 1937. However Germany also recognized that Japan was more capable of fighting the Soviet Union, and soon broke off the cooperation with China in May 1938. The Soviet Union, wishing to keep China in the fight against Japan, supplied China with some military assistance until 1941, until it made peace with Japan to prepare for the war against Germany.
Even though China had been fighting the longest among all the Allied powers, it only officially joined the Allies after the attack on Pearl Harbor, on 7 December 1941. Chiang Kai-shek felt Allied victory was assured with the entrance of the United States into the war and he declared war on Germany and the other Axis nations. However, Allied aid remained low as the Burma Road was closed and the Allies suffered a series of military defeats against Japan early on in the campaign. The bulk of military aid would not arrive until the spring of 1945. More than 1.5 million Japanese troops were trapped in the China Theater; troops that otherwise could have been deployed elsewhere had China collapsed and made a separate peace with Japan.
Key alliances are formed
On September 1, the German invasion of Poland began World War II. Britain, France, Australia and New Zealand all declared war on Germany on September 3. Nepal, Newfoundland, Tonga, South Africa and Canada followed suit within days. On September 17, the Soviets invaded Poland from the East. The following year, the USSR annexed the Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania) together with parts of Romania, and attacked Finland. The German-Soviet agreement was brought to an end by the German invasion of the USSR on June 22, 1941.
The United States of America joined the Allies following the attack on Pearl Harbor, on December 7, 1941. The Declaration by United Nations, on January 1, 1942, officially united 26 nations as Allies. (The Declaration also formed the basis for the United Nations.) The informal Big 3 alliance of the United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, and the United States emerged in the latter half of the war, and their decisions determined Allied strategy around the world.
Dates on which states joined the Allies
Following the German invasion of Poland
 Poland: 1939 1 September
Poland: 1939 1 September United Kingdom: 1939 3 September
United Kingdom: 1939 3 September France: 1939 3 September
France: 1939 3 September Australia: 1939 3 September
Australia: 1939 3 September New Zealand: 1939 3 September
New Zealand: 1939 3 September Nepal: 1939 4 September
Nepal: 1939 4 September- 15px Newfoundland: 1939 4 September
 Tonga: 1939 4 September
Tonga: 1939 4 September South Africa: 1939 6 September
South Africa: 1939 6 September- 15px Canada: 1939 10 September
After the end of the Phony War
 Denmark: 1940 9 April
Denmark: 1940 9 April Norway: 1940 9 April
Norway: 1940 9 April Belgium: 1940 10 May
Belgium: 1940 10 May Luxembourg: 1940 10 May
Luxembourg: 1940 10 May Netherlands: 1940 10 May
Netherlands: 1940 10 May Malta: 1940 10 June
Malta: 1940 10 June Free France: 1940 18 June
Free France: 1940 18 June Greece: 1940 28 October
Greece: 1940 28 October- 15px Kingdom of Yugoslavia: 1941 6 April
 Soviet Union: 1941 22 June
Soviet Union: 1941 22 June- 15px Tannu Tuva: 1941 25 June
After the attack on Pearl Harbor
 Panama: 1941 7 December
Panama: 1941 7 December Philippines: 1941 7 December
Philippines: 1941 7 December Costa Rica: 1941 8 December
Costa Rica: 1941 8 December Dominican Republic: 1941 8 December
Dominican Republic: 1941 8 December El Salvador: 1941 8 December
El Salvador: 1941 8 December Haiti: 1941 8 December
Haiti: 1941 8 December Honduras: 1941 8 December
Honduras: 1941 8 December Nicaragua: 1941 8 December
Nicaragua: 1941 8 December United States of America: 1941 8 December
United States of America: 1941 8 December Republic of China: 1941 9 December
Republic of China: 1941 9 December Guatemala: 1941 9 December
Guatemala: 1941 9 December Cuba: 1941 9 December
Cuba: 1941 9 December Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea (Govt. in exile): 1941 9 December
Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea (Govt. in exile): 1941 9 December Czechoslovakia (Govt. in exile) : 1941 16 December
Czechoslovakia (Govt. in exile) : 1941 16 December- 15px Mexico: 1942 22 May
 Brazil: 1942 22 August
Brazil: 1942 22 August- 15px Ethiopia: 1942 14 December
- 15px Iraq: 1943 17 January
 Bolivia: 1943 7 April
Bolivia: 1943 7 April- 15px Iran: 1943 9 September
 Italy: 1943 13 October (formerly a member of the Axis)
Italy: 1943 13 October (formerly a member of the Axis) Colombia: 1943 26 November
Colombia: 1943 26 November Liberia: 1944 27 January
Liberia: 1944 27 January
After D-Day
 Romania: 1944 25 August, (formerly a member of the Axis)
Romania: 1944 25 August, (formerly a member of the Axis) Bulgaria: 1944 8 September, (formerly a member of the Axis)
Bulgaria: 1944 8 September, (formerly a member of the Axis) San Marino: 1944 21 September
San Marino: 1944 21 September Albania: 1944 26 October
Albania: 1944 26 October Hungary: 1945 20 January, (formerly a member of the Axis)
Hungary: 1945 20 January, (formerly a member of the Axis)- 15px Bahawalpur: 1945 2 February
 Ecuador: 1945 2 February
Ecuador: 1945 2 February Paraguay: 1945 7 February
Paraguay: 1945 7 February Peru: 1945 12 February
Peru: 1945 12 February Uruguay: 1945 15 February
Uruguay: 1945 15 February- 15px Venezuela: 1945 15 February
 Turkey: 1945 23 February
Turkey: 1945 23 February Lebanon: 1945 27 February
Lebanon: 1945 27 February Saudi Arabia: 1945 March
Saudi Arabia: 1945 March Argentina: 1945 27 March
Argentina: 1945 27 March Chile: 1945 11 April
Chile: 1945 11 April People's Republic of Mongolia: 1945 9 August
People's Republic of Mongolia: 1945 9 August
Formal alliances during the war
Original allies
- French Republic
- Republic of Poland
- United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
These countries were allied to each other by a net of common defence pacts and military alliance pacts signed before the war. The Franco-British Alliance dated back to the Entente Cordiale of 1904 and the Triple Entente of 1907, active during the World War I. The Franco-Polish Alliance was signed in 1921 and then amended in 1927 and 1939. The original allies were those states that declared war on Nazi Germany following the German invasion of Poland in September 1939.
The Polish government in exile after 1939 continued the Polish contribution to World War II on several fronts with hundreds of thousands of members in the Polish Army in France and UK, as well as the Home Army in occupied Poland. The Soviet Union however, did not recognize the government and in 1943 organized the Polish People's Army under Rokossovsky, around which eventually it constructed the post-war successor state.
British, Dutch and French colonies fought alongside their metropolitan countries, and many continued their contribution also when the mother countries were occupied.
The Commonwealth
In addition to the United Kingdom, several independent members of the Commonwealth of Nations, known as the Dominions, declared war on Germany separately, either on the same day, or soon afterwards.
The Oslo Group
The Oslo Group was an organisation of officially neutral countries. Four members later joined the Allies, as governments in exile: the Kingdom of Norway, the Kingdom of the Netherlands, the Kingdom of Belgium and the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg.
The Republic of Finland was invaded by the USSR on November 30 1939 [1]. Later Finland and the Kingdom of Denmark officially joined the Axis Anti-Comintern Pact. The Kingdom of Sweden remained officially neutral.
Iceland and Greenland, respectively in union with Denmark and a Danish colony, were occupied by the Allies for most of the war. British forces took control in Iceland in 1940, and it was used to facilitate the movement of Lend Lease equipment. Forces from the United States, although they were officially neutral at the time, occupied Greenland on April 9, 1941. The US also took over in Iceland on July 7, 1941. Iceland declared full independence from Denmark in 1944, but never declared war on any of the Axis powers.
Portugal
Although Portugal remained officially neutral, the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance was invoked in World War II leading to the establishment of an Allied base in the Azores. Portugal protested the occupation of Portuguese Timor by Allied forces in 1942, but did not actively resist. The colony was subsequently occupied by Japan; Timorese and Portuguese civilians assisted Allied commandos in resisting the Japanese. (See Battle of Timor.) Macao was also occupied by Japan.
Atlantic Charter
The Atlantic Charter was negotiated at the Atlantic Conference by British Prime Minister Winston Churchill and U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, aboard warships in a secure anchorage at Argentia, Newfoundland (located on Placentia Bay) and was issued as a joint declaration on August 14, 1941.
The Atlantic Charter established a vision for a post-World War II world, despite the fact the United States had yet to enter the war.
In brief, the nine points were:
- no territorial gains sought by the United States or the United Kingdom;
- territorial adjustments must be in accord with wishes of the people;
- the right to self-determination of peoples;
- trade barriers lowered;
- global economic cooperation and advancement of social welfare;
- freedom from want and fear;
- freedom of the seas;
- disarmament of aggressor nations, postwar common disarmament
- defeat of Germany and other Axis powers
The Atlantic Charter proved to be one of the first steps towards the formation of the United Nations.
Comintern
The following socialist and pro-Soviet forces also fought against the Axis Powers before or during the Second World War.
- Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
- International Brigades
- Popular Front
- Albanian National Liberation Army
- Chinese People's Liberation Army
- Moldova [2] & Bukovina
- Communist Party of Yugoslavia
- Greek National Liberation Front
- Malayan Communist Party
- Tudeh Party of Iran
- Mongolian People's Republic
- Polish People's Army
- Viet Minh
- People's Republic of Azerbaijan [3]
- Kurdish People's Republic
Declaration by United Nations
Declaration by United Nations, January 1, 1942
(26 signatories)
- United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
- United States of America
- Republic of China
- Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
- Commonwealth of Australia
- Kingdom of Belgium
- Canada
- Republic of Costa Rica
- Republic of Cuba
- Czechoslovak Republic
- Dominican Republic
- Republic of El Salvador
- Kingdom of Greece
- Republic of Guatemala
- La Republique d' Haiti
- Republic of Honduras
- India
- Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
- Kingdom of the Netherlands
- Dominion of New Zealand
- Republic of Nicaragua
- Kingdom of Norway
- Republic of Panama
- Republic of Poland
- Union of South Africa
- Kingdom of Yugoslavia
(Note: During 1942 the declaration was adhered to by Mexico, the Commonwealth of the Philippines, and Ethiopia; in the first four months of 1943, it was adhered to by Iraq, Brazil, and Bolivia.
Tripartite Treaty of Alliance 29 January 1942
- United Kingdom
- Soviet Union
- Iran [4]
Pan American Union
[5] (21 members)
(Final Act of the Second Meeting of the Ministers of Foreign Affairs of the American Republics at Habana, Cuba, July 30, 1940)
- Bolivia
- Brazil (25 August 1942)
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Cuba
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Guatemala
- Haiti
- Honduras
- Mexico (1 June 1942)
- Nicaragua
- Panama
- United States of America
By 1945 Mexican "Aztec Eagles" or Escuadrón 201 joined the United States of America in the Pacific, specially on the bombings over Formosa (Taiwan) and Luzon (Philippines). From July 1944, a Brazilian Expeditionary Force of 25,000 personnel joined the Allies in the Italian campaign. The other countries in this group contributed support units, small combat forces, or to lesser degrees.
See also
- Participants in World War II
External links
- Changing Alliances In the International Arena
- The Atlantic Conference: Resolution of September 24, 1941
- What was known, what was done by the Allies
|
Western Europe · Eastern Europe · China · Africa · Mediterranean · Asia and the Pacific · Atlantic | |||||
|
Major participants |
Timeline |
Aspects | |||
|
Principal co-belligerents in italics. |
Prelude 1939 1940 1941 1942 |
1943 1944 1945 • more military engagements Aftermath |
• Attacks on North America Civilian impact and atrocities | ||
| Allies | Axis | ||||
|
at war from 1937 entered 1939 entered 1940 |
entered 1941 entered 1942 entered 1943 entered 1944 • others |
at war from 1937 entered 1939 entered 1940 entered 1941 entered 1942 • others | |||
| Resistance movements Austria · Baltic1 · Czechoslovakia · Denmark · Ethiopia · France · Germany · Greece · Italy · Jewish · Netherlands · Norway · Poland · Thailand · USSR · Ukraine2 · Vietnam · Yugoslavia · others | |||||
|
1 Anti-Soviet. | |||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
