Difference between revisions of "Resistivity" - New World Encyclopedia
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''Electrical resistivity''' (also known as '''specific electrical resistance''') is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of [[electric current]]. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of [[electrical charge]]. The [[SI]] unit of electrical resistivity is the [[ohm]] [[ | + | {{Copyedited}}{{Images OK}}{{Approved}} |
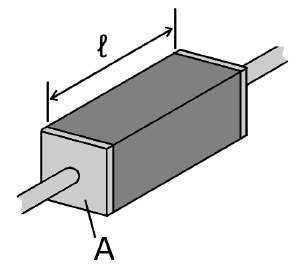
| − | + | [[Image:Resistivity geometry.png|thumb|A piece of resistive material with electrical contacts on both ends.]] | |
| + | '''Electrical resistivity''' (also known as '''specific electrical resistance''') is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of [[electric current]]. A low value of resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of [[electrical charge]]. The [[SI]] unit of electrical resistivity is the [[ohm]] [[meter]] (Ω-m). Knowledge of the resistivity of various materials is useful for the choice of materials needed for manufacturing electrical and electronic components. | ||
| + | {{toc}} | ||
== Definitions == | == Definitions == | ||
| − | |||
| − | The electrical resistivity ρ | + | The electrical resistivity ρ ''([[Rho (letter)|rho]])'' of a material is given by |
:<math>\rho=\frac{RA}{\ell}</math> | :<math>\rho=\frac{RA}{\ell}</math> | ||
where | where | ||
| − | :''ρ'' is the static resistivity (measured in ohm | + | :''ρ'' is the static resistivity (measured in ohm meters, Ω-m); |
:''R'' is the [[electrical resistance]] of a uniform specimen of the material (measured in [[ohm]]s, Ω); | :''R'' is the [[electrical resistance]] of a uniform specimen of the material (measured in [[ohm]]s, Ω); | ||
| − | :''<math>\ell</math>'' is the length of the piece of material (measured in [[ | + | :''<math>\ell</math>'' is the length of the piece of material (measured in [[meter]]s, m); |
| − | :''A'' is the cross-sectional area of the specimen (measured in square | + | :''A'' is the cross-sectional area of the specimen (measured in square meters, m²). |
Electrical resistivity can also be defined as | Electrical resistivity can also be defined as | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
where | where | ||
| − | :''E'' is the [[Magnitude (mathematics)|magnitude]] of the [[electric field]] (measured in [[volt]]s per [[ | + | :''E'' is the [[Magnitude (mathematics)|magnitude]] of the [[electric field]] (measured in [[volt]]s per [[meter]], V/m); |
| − | :''J'' is the magnitude of the [[current density]] (measured in [[ampere]]s per [[square | + | :''J'' is the magnitude of the [[current density]] (measured in [[ampere]]s per [[square meter]], A/m²). |
| − | Finally, electrical resistivity is also defined as the inverse of the [[electrical conductivity|conductivity]] ''σ'' | + | Finally, electrical resistivity is also defined as the inverse of the [[electrical conductivity|conductivity]] ''σ'' ''([[sigma (letter)|sigma]])'', of the material, or |
:<math>\rho = {1\over\sigma}.</math> | :<math>\rho = {1\over\sigma}.</math> | ||
| Line 29: | Line 30: | ||
==Table of resistivities== | ==Table of resistivities== | ||
This table shows the resistivity and [[temperature coefficient]] of various materials at 20 [[Celsius|°C]] (68 [[Fahrenheit|°F]]) | This table shows the resistivity and [[temperature coefficient]] of various materials at 20 [[Celsius|°C]] (68 [[Fahrenheit|°F]]) | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" border="1" | {| class="wikitable sortable" border="1" | ||
!Material!!Resistivity (Ω-m) at 20 °C!!Coefficient*!!Reference | !Material!!Resistivity (Ω-m) at 20 °C!!Coefficient*!!Reference | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[Silver]]||1.59×10<sup>−8</sup>||.0038||<ref name="serway"> | + | |[[Silver]]||1.59×10<sup>−8</sup>||.0038||<ref name="serway">Raymond A. Serway, ''Principles of Physics'', 2nd ed. (Fort Worth, TX; London: Saunders College Pub., 1998, ISBN 0030204577), 602.</ref><ref name="Griffiths">David Griffiths, "Chapter 7. Electrodynamics." In ''Introduction to Electrodynamics'', 3rd ed., edited by Alison Reeves (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, [1981] 1999, ISBN 013805326X), 286.</ref> |
|- | |- | ||
|[[Copper]]||1.72×10<sup>−8</sup>||.0039||<ref name="Griffiths"/> | |[[Copper]]||1.72×10<sup>−8</sup>||.0039||<ref name="Griffiths"/> | ||
| Line 57: | Line 56: | ||
|[[Lead]]||2.2×10<sup>−7</sup>||.0039||<ref name="serway"/> | |[[Lead]]||2.2×10<sup>−7</sup>||.0039||<ref name="serway"/> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[Manganin]]||4.82×10<sup>−7</sup>||.000002||<ref name="giancoli"> | + | |[[Manganin]]||4.82×10<sup>−7</sup>||.000002||<ref name="giancoli">Douglas C. Giancoli, ''Physics: Principles with Applications'', 4th ed. (London: Prentice Hall, 1995, ISBN 0131021532). See also [http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Tables/rstiv.html Table of Resistivity and Temperature Coefficient at 20 C.] Retrieved August 25, 2008.</ref> |
| − | </ref> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[Constantan]]||4.9×10<sup>−7</sup>|| 0.00001 ||<ref name="giancoli"/> | |[[Constantan]]||4.9×10<sup>−7</sup>|| 0.00001 ||<ref name="giancoli"/> | ||
| Line 90: | Line 88: | ||
==Temperature dependence== | ==Temperature dependence== | ||
| − | In general, electrical resistivity of [[metal]]s increases with [[temperature]], while the resistivity of [[semiconductor]]s decreases with increasing temperature. In both cases, | + | In general, electrical resistivity of [[metal]]s increases with [[temperature]], while the resistivity of [[semiconductor]]s decreases with increasing temperature. In both cases, electron-[[phonon]] interactions can play a key role. At high temperatures, the resistance of a metal increases linearly with temperature. As the temperature of a metal is reduced, the temperature dependence of resistivity follows a power law function of temperature. Mathematically the temperature dependence of the resistivity ρ of a metal is given by the Bloch–Grüneisen formula: |
:<math>\rho(T)=\rho(0)+A\left(\frac{T}{\Theta_R}\right)^n\int_0^{\frac{\Theta_R}{T}}\frac{x^n}{(e^x-1)(1-e^{-x})}dx</math> | :<math>\rho(T)=\rho(0)+A\left(\frac{T}{\Theta_R}\right)^n\int_0^{\frac{\Theta_R}{T}}\frac{x^n}{(e^x-1)(1-e^{-x})}dx</math> | ||
| − | where <math>\rho(0)</math> is the residual resistivity due to defect scattering, A is a constant that depends on the velocity of electrons at the fermi surface, the Debye radius and the number density of electrons in the metal. <math>\Theta_R</math> is the Debye | + | where <math>\rho(0)</math> is the residual resistivity due to defect scattering, A is a constant that depends on the velocity of electrons at the fermi surface, the Debye radius and the number density of electrons in the metal. <math>\Theta_R</math> is the Debye temperature as obtained from resistivity measurements and matches very closely with the values of Debye temperature obtained from specific heat measurements. n is an integer that depends upon the nature of interaction: |
| − | #n=5 implies that | + | #n=5 implies that the resistance is due to scattering of electrons by [[phonon]]s (as it is for simple metals) |
#n=3 implies that the resistance is due to s-d electron scattering (as is the case for transition metals) | #n=3 implies that the resistance is due to s-d electron scattering (as is the case for transition metals) | ||
#n=2 implies that the resistance is due to electron-electron interaction. | #n=2 implies that the resistance is due to electron-electron interaction. | ||
| − | As the temperature of the metal is sufficiently reduced (so as to 'freeze' all the phonons), the resistivity usually reaches a | + | As the temperature of the metal is sufficiently reduced (so as to 'freeze' all the phonons), the resistivity usually reaches a |
| − | constant value, known as the '''residual resistivity'''. This value depends not only on the type of metal, but on its purity and thermal history. The value of the residual resistivity of a metal is decided by its impurity concentration. | + | constant value, known as the '''residual resistivity'''. This value depends not only on the type of metal, but on its purity and thermal history. The value of the residual resistivity of a metal is decided by its impurity concentration. Some materials lose all electrical resistivity at sufficiently low temperatures, due to an effect known as [[superconductivity]]. |
An even better approximation of the temperature dependence of the resistivity of a semiconductor is given by the [[Steinhart–Hart equation]]: | An even better approximation of the temperature dependence of the resistivity of a semiconductor is given by the [[Steinhart–Hart equation]]: | ||
| Line 110: | Line 108: | ||
This equation is used to calibrate [[thermistor]]s. | This equation is used to calibrate [[thermistor]]s. | ||
| − | In non-crystalline semi-conductors, conduction can occur by charges [[quantum tunnelling]] from one | + | In non-crystalline semi-conductors, conduction can occur by charges [[quantum tunnelling]] from one localized site to another. This is known as [[variable range hopping]] and has the characteristic form of <math>\rho = Ae^{T^{-1/n}}</math>, where n=2,3,4 depending on the dimensionality of the system. |
==Complex resistivity== | ==Complex resistivity== | ||
| − | When analyzing the response of materials to alternating [[electric field]]s, as is done in certain types of [[tomography]], it is necessary to replace resistivity with a [[complex number|complex]] quantity called ''' | + | When analyzing the response of materials to alternating [[electric field]]s, as is done in certain types of [[tomography]], it is necessary to replace resistivity with a [[complex number|complex]] quantity called '''impedivity''' (analogous to [[electrical impedance]]). Impedivity is the sum of a real component, the resistivity, and an imaginary component, the '''reactivity''' (analogous to [[reactance]]).<ref>Otto H. Schmitt, [http://www.otto-schmitt.org/OttoPagesFinalForm/Sounds/Speeches/MutualImpedivity.htm Mutual Impedivity Spectrometry] Retrieved August 25, 2008.</ref> |
==Resistivity density products== | ==Resistivity density products== | ||
| − | In some applications where the weight of an item is very important resistivity density products are more important than absolute low resistance | + | In some applications where the weight of an item is very important, resistivity density products are more important than absolute low resistance. It is often possible to make the conductor thicker, to make up for a higher resistivity; and in that case, a low resistivity density product material (or equivalently a high conductance to density ratio) is desirable. |
| − | This | + | This knowledge is useful for long-distance overhead powerline transmission. Aluminum is used rather than copper because it is lighter for the same conductance. [[Calcium]], while theoretically better, is rarely if ever used, due to its highly reactive nature. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Material | ! Material | ||
| − | ! Resistivity ( | + | ! Resistivity (nΩ•m) |
! Density (g/cm^3) | ! Density (g/cm^3) | ||
| − | ! Resistivity - density product ( | + | ! Resistivity - density product (nΩ•m•g/cm^3) |
|- | |- | ||
| Calcium | | Calcium | ||
| Line 132: | Line 130: | ||
| 52 | | 52 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Aluminum |
| 26.50 | | 26.50 | ||
| 2.70 | | 2.70 | ||
| Line 149: | Line 147: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | * [[Electricity]] | |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Electronics]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Resistor]] |
| − | * [[ | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| Line 160: | Line 157: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| − | * Dyos, G. T., and T. Farrell. 1992. ''Electrical Resistivity Handbook.'' IEE Materials & Devices Series, 10. London, UK: Peter Peregrinus, for the Institution of Electrical Engineers. ISBN 0863412661 | + | * Dyos, G. T., and T. Farrell. 1992. ''Electrical Resistivity Handbook.'' IEE Materials & Devices Series, 10. London, UK: Peter Peregrinus, for the Institution of Electrical Engineers. ISBN 0863412661 |
| − | + | * Giancoli, Douglas. 2007. ''Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics'' (Chapters 1-37), 4th ed. Mastering Physics Series. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0136139263 | |
| − | * Giancoli, Douglas. 2007. ''Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics | + | * Plonus, Martin. 2001. ''Electronics and Communications for Scientists and Engineers.'' San Diego: Harcourt/Academic Press. ISBN 0125330847 |
| − | + | * Rossiter, Paul L. 1991. ''The Electrical Resistivity of Metals and Alloys.'' Cambridge Solid State Science Series. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521408725 | |
| − | * Rossiter, Paul L. 1991. ''The Electrical Resistivity of Metals and Alloys.'' Cambridge Solid State Science Series. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521408725 | + | * Tipler, Paul Allen, and Gene Mosca. 2004. ''Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 2: Electricity and Magnetism, Light, Modern Physics'', 5th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0716708108 |
| − | |||
| − | * Tipler, Paul Allen, and Gene Mosca. 2004. ''Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 2: Electricity and Magnetism, Light, Modern Physics | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Physical sciences]] | [[Category:Physical sciences]] | ||
Latest revision as of 04:13, 8 December 2022
Electrical resistivity (also known as specific electrical resistance) is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low value of resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electrical charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm meter (Ω-m). Knowledge of the resistivity of various materials is useful for the choice of materials needed for manufacturing electrical and electronic components.
Definitions
The electrical resistivity ρ (rho) of a material is given by
where
- ρ is the static resistivity (measured in ohm meters, Ω-m);
- R is the electrical resistance of a uniform specimen of the material (measured in ohms, Ω);
- is the length of the piece of material (measured in meters, m);
- A is the cross-sectional area of the specimen (measured in square meters, m²).
Electrical resistivity can also be defined as
where
- E is the magnitude of the electric field (measured in volts per meter, V/m);
- J is the magnitude of the current density (measured in amperes per square meter, A/m²).
Finally, electrical resistivity is also defined as the inverse of the conductivity σ (sigma), of the material, or
Table of resistivities
This table shows the resistivity and temperature coefficient of various materials at 20 °C (68 °F)
| Material | Resistivity (Ω-m) at 20 °C | Coefficient* | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silver | 1.59×10−8 | .0038 | [1][2] |
| Copper | 1.72×10−8 | .0039 | [2] |
| Gold | 2.44×10−8 | .0034 | [1] |
| Aluminium | 2.82×10−8 | .0039 | [1] |
| Calcium | 3.3x10-8 | ||
| Tungsten | 5.60×10−8 | .0045 | [1] |
| Nickel | 6.99×10−8 | ? | |
| Iron | 1.0×10−7 | .005 | [1] |
| Tin | 1.09×10−7 | .0045 | |
| Platinum | 1.1×10−7 | .00392 | [1] |
| Lead | 2.2×10−7 | .0039 | [1] |
| Manganin | 4.82×10−7 | .000002 | [3] |
| Constantan | 4.9×10−7 | 0.00001 | [3] |
| Mercury | 9.8×10−7 | .0009 | [3] |
| Nichrome[4] | 1.10×10−6 | .0004 | [1] |
| Carbon[5] | 3.5×10−5 | -.0005 | [1] |
| Germanium[5] | 4.6×10−1 | -.048 | [1][2] |
| Silicon[5] | 6.40×102 | -.075 | [1] |
| Glass | 1010 to 1014 | ? | [1][2] |
| Hard rubber | approx. 1013 | ? | [1] |
| Sulfur | 1015 | ? | [1] |
| Paraffin | 1017 | ? | |
| Quartz (fused) | 7.5×1017 | ? | [1] |
| PET | 1020 | ? | |
| Teflon | 1022 to 1024 | ? |
*The numbers in this column increase or decrease the significand portion of the resistivity. For example, at 30°C (303.15 K), the resistivity of silver is 1.65×10−8. This is calculated as Δρ = α ΔT ρo where ρo is the resistivity at 20°C and α is the temperature coefficient
Temperature dependence
In general, electrical resistivity of metals increases with temperature, while the resistivity of semiconductors decreases with increasing temperature. In both cases, electron-phonon interactions can play a key role. At high temperatures, the resistance of a metal increases linearly with temperature. As the temperature of a metal is reduced, the temperature dependence of resistivity follows a power law function of temperature. Mathematically the temperature dependence of the resistivity ρ of a metal is given by the Bloch–Grüneisen formula:
where is the residual resistivity due to defect scattering, A is a constant that depends on the velocity of electrons at the fermi surface, the Debye radius and the number density of electrons in the metal. is the Debye temperature as obtained from resistivity measurements and matches very closely with the values of Debye temperature obtained from specific heat measurements. n is an integer that depends upon the nature of interaction:
- n=5 implies that the resistance is due to scattering of electrons by phonons (as it is for simple metals)
- n=3 implies that the resistance is due to s-d electron scattering (as is the case for transition metals)
- n=2 implies that the resistance is due to electron-electron interaction.
As the temperature of the metal is sufficiently reduced (so as to 'freeze' all the phonons), the resistivity usually reaches a constant value, known as the residual resistivity. This value depends not only on the type of metal, but on its purity and thermal history. The value of the residual resistivity of a metal is decided by its impurity concentration. Some materials lose all electrical resistivity at sufficiently low temperatures, due to an effect known as superconductivity.
An even better approximation of the temperature dependence of the resistivity of a semiconductor is given by the Steinhart–Hart equation:
where A, B and C are the so-called Steinhart–Hart coefficients.
This equation is used to calibrate thermistors.
In non-crystalline semi-conductors, conduction can occur by charges quantum tunnelling from one localized site to another. This is known as variable range hopping and has the characteristic form of , where n=2,3,4 depending on the dimensionality of the system.
Complex resistivity
When analyzing the response of materials to alternating electric fields, as is done in certain types of tomography, it is necessary to replace resistivity with a complex quantity called impedivity (analogous to electrical impedance). Impedivity is the sum of a real component, the resistivity, and an imaginary component, the reactivity (analogous to reactance).[6]
Resistivity density products
In some applications where the weight of an item is very important, resistivity density products are more important than absolute low resistance. It is often possible to make the conductor thicker, to make up for a higher resistivity; and in that case, a low resistivity density product material (or equivalently a high conductance to density ratio) is desirable.
This knowledge is useful for long-distance overhead powerline transmission. Aluminum is used rather than copper because it is lighter for the same conductance. Calcium, while theoretically better, is rarely if ever used, due to its highly reactive nature.
| Material | Resistivity (nΩ•m) | Density (g/cm^3) | Resistivity - density product (nΩ•m•g/cm^3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 33.6 | 1.55 | 52 |
| Aluminum | 26.50 | 2.70 | 72 |
| Copper | 16.78 | 8.96 | 150 |
| Silver | 15.87 | 10.49 | 166 |
See also
Notes
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 Raymond A. Serway, Principles of Physics, 2nd ed. (Fort Worth, TX; London: Saunders College Pub., 1998, ISBN 0030204577), 602.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 David Griffiths, "Chapter 7. Electrodynamics." In Introduction to Electrodynamics, 3rd ed., edited by Alison Reeves (Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, [1981] 1999, ISBN 013805326X), 286.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Douglas C. Giancoli, Physics: Principles with Applications, 4th ed. (London: Prentice Hall, 1995, ISBN 0131021532). See also Table of Resistivity and Temperature Coefficient at 20 C. Retrieved August 25, 2008.
- ↑ Ni,Fe,Cr alloy commonly used in heating elements.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 The resistivity of semiconductors depends strongly on the presence of impurities in the material.
- ↑ Otto H. Schmitt, Mutual Impedivity Spectrometry Retrieved August 25, 2008.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Dyos, G. T., and T. Farrell. 1992. Electrical Resistivity Handbook. IEE Materials & Devices Series, 10. London, UK: Peter Peregrinus, for the Institution of Electrical Engineers. ISBN 0863412661
- Giancoli, Douglas. 2007. Physics for Scientists and Engineers, with Modern Physics (Chapters 1-37), 4th ed. Mastering Physics Series. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. ISBN 978-0136139263
- Plonus, Martin. 2001. Electronics and Communications for Scientists and Engineers. San Diego: Harcourt/Academic Press. ISBN 0125330847
- Rossiter, Paul L. 1991. The Electrical Resistivity of Metals and Alloys. Cambridge Solid State Science Series. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521408725
- Tipler, Paul Allen, and Gene Mosca. 2004. Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 2: Electricity and Magnetism, Light, Modern Physics, 5th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 0716708108
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.