Difference between revisions of "Ocean" - New World Encyclopedia
(Wanted) |
Keisuke Noda (talk | contribs) (import from wiki) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{claimed}} | ||
| + | [[Image:World ocean map.gif|right|thumb|250px|Animated map exhibiting the world's oceanic waters. A continuous body of water encircling the [[Earth]], the [[World Ocean|world (global) ocean]] is subdivided into a number of principal components. Five oceanic subdivisions are usually reckoned: [[Pacific Ocean|Pacific]], [[Atlantic Ocean|Atlantic]], [[Indian Ocean|Indian]], [[Arctic Ocean|Arctic]], and [[Southern Ocean|Southern]]; the last two listed are sometimes consolidated into the first three.]] | ||
| + | {{Five oceans}} | ||
| + | {{otheruses}} | ||
| + | An '''ocean''' (from {{polytonic|Ωκεανός}}, [[Oceanus|''Okeanos'' (Oceanus)]] in [[Greek language|Greek]]) is a principal part of the [[hydrosphere]]: a major body of [[Seawater|saline water]] that, in totality, covers about 70% of the [[Earth]]'s [[surface]] (or an area of some 361 million [[square kilometre|square kilometer]]s). Nearly half of the [[world]]'s [[marine (ocean)|marine (oceanic)]] waters are over 3,000 meters (9,800 ft) deep. Average oceanic [[salinity]] is around 35 [[parts per thousand]] (ppt) (3.5%), and nearly all seawater has a salinity in the range of 31 to 38 ppt. | ||
| − | {{ | + | ==Overview== |
| + | Though generally recognized as several 'separate' oceans, these waters comprise one global, interconnected body of salt water often referred to as the [[World Ocean]] or global ocean.<ref>"[http://www.answers.com/Ocean#Encyclopedia Ocean]". ''The Columbia Encyclopedia.'' 2006. New York: Columbia University Press</ref><ref name="UNAoO">"[http://www.oceansatlas.com/unatlas/about/physicalandchemicalproperties/background/seemore1.html Distribution of land and water on the planet]". ''[http://www.oceansatlas.com/ UN Atlas of the Oceans]</ref> This concept of a global ocean as a continuous body of water with relatively free interchange among its parts is of fundamental importance to [[oceanography]].<ref>Spilhaus, Athelstan F. 1942 (Jul.). "Maps of the whole world ocean." ''Geographical Review'' ([[American Geographical Society]]). Vol. 32 (3): pp. 431-5.</ref> The major oceanic subdivisions are defined in part by the [[continent]]s, various [[archipelago]]s, and other criteria: these subdivisions are (in descending order of size) the [[Pacific Ocean]], the [[Atlantic Ocean]], the [[Indian Ocean]], the [[Southern Ocean]] (which is sometimes subsumed as the southern portions of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans), and the [[Arctic Ocean]] (which is sometimes considered a [[sea]] of the Atlantic). The Pacific and Atlantic may be further subdivided by the [[equator]] into [[north]]erly and [[south]]erly portions. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, [[Headlands and bays|gulfs]], [[bay]]s and other names. There are also some smaller bodies of saltwater that are totally landlocked and ''not'' interconnected with the World Ocean, such as the [[Caspian Sea]], the [[Aral Sea]], and the [[Great Salt Lake]] – though they may be referred to as 'seas', they are actually [[salt lake]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Geologically, an ocean is an area of oceanic crust covered by water. Oceanic crust is the thin layer of solidified volcanic [[basalt]] that covers the Earth's [[mantle (geology)|mantle]] where there are no continents. From this perspective, there are three oceans today: the World Ocean, the Caspian and the [[Black Sea]]s, the latter two of which were formed by the collision of [[Cimmerian plate|Cimmeria]] with [[Laurasia]]. The [[Mediterranean Sea]] is very nearly a discrete ocean, being connected to the World Ocean through the [[Strait of Gibraltar]], and indeed several times over the last few million years [[plate tectonics|movement]] of the [[Africa|African continent]] has closed the strait off entirely. The Black Sea is connected to the Mediterranean through the [[Bosporus]], but this is in effect a natural [[canal]] cut through continental rock some 7,000 years ago, rather than a piece of oceanic sea floor like the Strait of Gibraltar. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Physical properties== | ||
| + | {{See|Sea water}} | ||
| + | The area of the World Ocean is 361 million square kilometers (139 million sq mi), its volume is over 1,340 million cubic kilometers (319 million cu mi), and its average depth is 3,711 meters (12,175 ft). Nearly half of the world's marine waters are over 3,000 meters (9,800 ft) deep.<ref name="UNAoO" /> The vast abyssal plains of the deep ocean cover about 40% of the Earth's surface. | ||
| + | This does not include seas not connected to the World Ocean, such as the [[Caspian Sea]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The total mass of the [[hydrosphere]] is about 1.4 × 10<sup>21</sup> kilograms, which is about 0.023% of the Earth's total mass. Less than 2% is [[freshwater]], the rest is [[saltwater]], mostly in the ocean. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Exploration== | ||
| + | {{main|Ocean exploration}} | ||
| + | |||
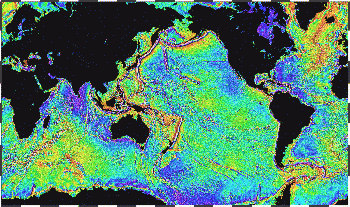
| + | [[Image:Ocean gravity map.gif|right|thumb|350px|Map of large underwater features. (1995, [[NOAA]])]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Travel on the surface of the ocean through the use of boats dates back to prehistoric times, but only in modern times has extensive underwater travel become possible. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The deepest point in the ocean is the [[Marianas Trench]] located in the Pacific Ocean near the [[Northern Mariana Islands]]. It has a maximum depth of [[1 E4 m|10,923 meters (35,838 ft)]] <ref>http://www.rain.org/ocean/ocean-studies-challenger-deep-mariana-trench.html</ref><!--- Could be 35838.0 ± 0.5 ft is 10923.27-10923.57 m --->. It was fully surveyed in [[1951]] by the British naval vessel, "Challenger II" which gave its name to the deepest part of the trench, the "[[Challenger Deep]]". In 1960, the [[Bathyscaphe Trieste|Trieste]] successfully reached the bottom of the trench, manned by a crew of two men. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Much of the bottom of the world's oceans are unexplored and unmapped. A global image of many underwater features larger than 10 kilometers (6 mi) was created in [[1995]] based on gravitational distortions of the nearby sea surface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Regions== | ||
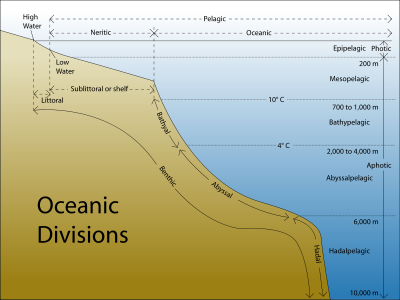
| + | [[Image:Oceanic divisions.svg|400px|thumb|The major oceanic divisions]]Oceans are divided into numerous regions depending on the physical and biological conditions of these areas. The [[pelagic zone]] includes all open ocean regions, and can be subdivided into further regions categorised by depth and light abundance. The [[photic zone]] covers the oceans from surface level to 200 metres down. This is the region where the photosynthesis most commonly occurs and therefore contains the largest biodiversity in the ocean. Since plants can only survive with photosynthesis any life found lower than this must either rely on material floating down from above (see [[marine snow]]) or find another primary source; this often comes in the form of [[hydrothermal vents]] in what is known as the [[aphotic zone]] (all depths exceeding 200m). The pelagic part of the photic zone is known as the [[epipelagic]]. The pelagic part of the aphotic zone can be further divided into regions that succeed each other vertically. The [[mesopelagic]] is the uppermost region, with its lowermost boundary at a [[thermocline]] of 10°C, which, in the tropics generally lies between 700 and 1,000m. After that is the [[bathypelagic]] lying between 10°C and 4°C, or between 700 or 1,000m and 2,000 or 4,000m. Lying along the top of the abyssal plain is the [[abyssal zone|abyssalpelagic]], whose lower boundary lies at about 6,000m. The final zone falls into the oceanic trenches, and is known as the [[hadal zone|hadalpelagic]]. This lies between 6,000m and 10,000m and is the deepest oceanic zone. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Along with pelagic aphotic zones there are also [[benthic]] aphotic zones, these correspond to the three deepest zones. The [[bathyal zone]] covers the continental slope and the rise down to about 4,000m. The [[abyssal]] zone covers the abyssal plains between 4,000 and 6,000m. Lastly, the [[hadal]] zone corresponds to the hadalpelagic zone which is found in the oceanic trenches. | ||
| + | The pelagic zone can also be split into two subregions, the [[neritic zone]] and the [[oceanic zone]]. The neritic encompasses the water mass directly above the continental shelves, while the oceanic zone includes all the completely open water. | ||
| + | In contrast, the [[littoral zone]] covers the region between low and high tide and represents the transitional area between marine and terrestrial conditions. It is also known as the [[intertidal]] zone because it is the area where tide level affects the conditions of the region. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Climate== | ||
| + | One of the most dramatic forms of [[weather]] occurs over the oceans: [[tropical cyclone]]s (also called "typhoons" and "hurricanes" depending upon where the system forms). [[Ocean current]]s greatly affect Earth's climate by transferring warm or cold air and precipitation to coastal regions, where they may be carried inland by winds. The [[Antarctic Circumpolar Current]] encircles that continent, influencing the area's climate and connecting currents in several oceans. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Ecology== | ||
| + | The oceans are home to the majority of [[plant]] and [[animal]] [[life on Earth]]. These lifeforms include: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Radiata]] | ||
| + | *[[Fish]] | ||
| + | *[[Cetacea]] such as [[whale]]s, [[dolphin]]s and [[porpoise]]s, | ||
| + | *[[Cephalopod]]s such as the [[octopus]] | ||
| + | *[[Crustacean]]s such as [[lobster]]s and [[shrimp]] | ||
| + | *[[Marine worm]]s | ||
| + | *[[Plankton]] | ||
| + | *[[Krill]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Economy== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The oceans are essential to transportation: most of the world's goods are moved by [[ship]] between the world's [[seaport]]s. Important [[ship canal]]s include the [[Saint Lawrence Seaway]], [[Panama Canal]], and [[Suez Canal]]. | ||
| + | They are also an important source of valuable foodstuffs for the [[fishing industry]]. Some of these are [[shrimp]], [[fish]], [[crabs]] and [[lobster]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Ancient oceans== | ||
| + | [[Continental drift]] has reconfigured the Earth's oceans, joining and splitting ancient oceans to form the current oceans. Ancient oceans include: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Bridge River Ocean]], the ocean between the ancient [[Insular Islands]] and [[North America]]. | ||
| + | *[[Iapetus Ocean]], the southern hemisphere ocean between [[Baltica]] and [[Avalonia]]. | ||
| + | *[[Panthalassa]], the vast world ocean that surrounded the [[Pangaea]] supercontinent. | ||
| + | *[[Rheic Ocean]] | ||
| + | *[[Slide Mountain Ocean]], the ocean between the ancient [[Intermontane Islands]] and North America. | ||
| + | *[[Tethys Ocean]], the ocean between the ancient continents of [[Gondwana]] and [[Laurasia]]. | ||
| + | *[[Khanty Ocean]], the ocean between Baltica and Siberia. | ||
| + | *[[Mirovia]], the ocean that surrounded the [[Rodinia]] supercontinent. | ||
| + | *[[Paleo-Tethys Ocean]], the ocean between Gondwana and the Hunic terranes. | ||
| + | *[[Proto-Tethys Ocean]], | ||
| + | *[[Pan-African Ocean]], the ocean that surrounded the [[Pannotia]] supercontinent. | ||
| + | *[[Superocean]], the ocean that surrounds a global supercontinent. | ||
| + | *[[Ural Ocean]], the ocean between [[Siberia]] and [[Baltica]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Extraterrestrial oceans== | ||
| + | :See also ''[[Oceans Beyond Earth]]'' | ||
| + | Earth is the only known [[planet]] with liquid water on its surface and is certainly the only one in our own [[solar system]]. However, liquid water is thought to be present under the surface of the [[Galilean moon]]s [[Europa (moon)|Europa]], and, with less certainty, [[Callisto (moon)|Callisto]] and [[Ganymede (moon)|Ganymede]]. [[Geyser]]s have been found on [[Enceladus (moon)|Enceladus]], though these may not involve bodies of liquid water. Other icy moons may have once had internal oceans that have now frozen, such as [[Triton (moon)|Triton]]. The planets [[Uranus (planet)|Uranus]] and [[Neptune (planet)|Neptune]] may also possess large oceans of liquid water under their thick atmospheres, though their internal structure is not well understood at this time. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There is currently much debate over whether [[Mars (planet)|Mars]] once had an ocean of water in its northern hemisphere, and over what happened to it if it did; recent findings by the [[Mars Exploration Rover]] mission indicate it had some long-term standing water in at least one location, but its extent is not known. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Astronomers believe that [[Atmosphere of Venus|Venus]] had liquid water and perhaps oceans in its very early history. If they existed, all trace of them seems to have vanished in later [[Geology of Venus|resurfacing]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Liquid hydrocarbons are thought to be present on the surface of [[Titan (moon)|Titan]], though it may be more accurate to describe them as "lakes" rather than an "ocean". The [[Cassini-Huygens]] space mission initially discovered only what appeared to be dry lakebeds and empty river channels, suggesting that Titan had lost what surface liquids it might have had. A more recent fly-by of Titan made by Cassini has produced radar images that strongly suggest hydrocarbon lakes near the polar regions where it is colder. Titan is also thought likely to have a subterranean water ocean under the mix of ice and hydrocarbons that forms its outer crust. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Beyond the solar system, [[Gliese 581 c]] is at the right distance from its sun for liquid water to exist on the planet's surface. Since it does not transit its sun, there is no way to know if there is any water there. [[HD 209458b]] may have water vapour in its atmosphere - this is currently being disputed. [[Gliese 436 b]] is believed to have 'hot ice'. Neither of these planets are cool enough for liquid water: but if water molecules exist there, they are likely to be found also on planets at a suitable temperature.<ref>''Hot "ice" may cover recently discovered planet'' [http://in.today.reuters.com/news/newsArticle.aspx?type=worldNews&storyID=2007-05-17T114149Z_01_NOOTR_RTRJONC_0_India-298599-1.xml&archived=False]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Mythology== | ||
| + | The original concept of "ocean" goes back to notions of [[Mesopotamian mythology|Mesopotamian]] and [[Proto-Indo-European mythology|Indo-European]] mythology, imagining the world to be encircled by a great river. ''[[Okeanos]]'', "Ωκεανός" in [[Greek mythology|Greek]], reflects the ancient Greek observation that a strong current flowed off [[Gibraltar]] and their subsequent assumption that it was a great river. (Compare also ''[[Samudra]]'' from [[Hindu mythology]] and [[Jörmungandr]] from [[Norse mythology]]). The world was imagined to be enclosed by a [[celestial ocean]] above the heavens, and an ocean of the underworld below (compare [[Rasā]], [[Varuna]]). This is evidenced for example in the account of [[Noah]]'s flood in [[Genesis]] 7:11, where | ||
| + | :''all the fountains of the great deep [were] broken up, and the windows of heaven were opened'' ([[KJV]]), | ||
| + | inundating the world with the waters of the celestial ocean (see also [[deluge (mythology)]]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Trivia== | ||
| + | {{trivia}} | ||
| + | One common misconception today is that the oceans are blue primarily because the sky is blue. In fact, water has a very slight blue colour that can only be seen in large volumes. While the sky's reflection does contribute to the blue appearance of the surface, it is not the primary cause<ref>http://amasci.com/miscon/miscon4.html#watclr</ref>. The primary cause is the absorption by the water molecules' nuclei of red photons from the incoming light, the only known example of color in nature resulting from vibrational, rather than electronic, dynamics<ref>Braun, C. L. and Smirnov, S. N. (1993) [http://www.dartmouth.edu/~etrnsfer/water.htm Why is water blue?] ''J. Chem. Edu.'' '''70''', 612.</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | * [[Oceanography]] | ||
| + | * [[International Maritime Organization]] | ||
| + | * [[Sea]] | ||
| + | * [[Mediterranean sea]] | ||
| + | * [[Marginal sea]] | ||
| + | * [[Sea level]] | ||
| + | * [[Sea level rise]] | ||
| + | * [[Sea salt]] | ||
| + | * [[Water]] | ||
| + | * [[World Ocean Day]] | ||
| + | * [[Marine biology]] | ||
| + | * [[Pelagic zone]] | ||
| + | * [[Southern Ocean]] | ||
| + | * [[Underground Ocean]]s | ||
| + | * | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | * Matthias Tomczak and J. Stuart Godfrey. 2003. ''Regional Oceanography: an Introduction''. (see [http://www.es.flinders.edu.au/~mattom/regoc/ the site]) | ||
| + | * "[http://www.oceansatlas.com/unatlas/about/howoceanswereformed2/originsofoceans/originofocean2jte.html Origins of the oceans and continents]". ''[http://www.oceansatlas.com/ UN Atlas of the Oceans].'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | {{External links}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{wiktionary}} | ||
| + | * [http://www.oceanexplorer.noaa.gov/ Ocean Explorer] - An educational and reference resource from NOAA | ||
| + | * [http://www.whoi.edu/imageOfDay.do Oceanography Image of the Day] - from the [[Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution]] | ||
| + | * [http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/4033555.stm Science taps into ocean secrets] | ||
| + | * [http://www.palomar.edu/oceanography/salty_ocean.htm Why is the ocean salty?] | ||
| + | * [http://ioc.unesco.org/ Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission] | ||
| + | * [http://oceana.org Oceana - Protecting the World's Oceans] | ||
| + | * [http://www.coreocean.org/ CORE - Consortium for Oceanographic Research and Education] | ||
| + | * [http://www.nopp.org/ NOPP - National Oceanographic Partnership Program] | ||
| + | * [http://www.nosb.org/ NOSB - National Ocean Sciences Bowl] | ||
| + | * [http://www.coml.org/ CoML - Census of Marine Life] | ||
| + | * [http://www.thew2o.net World Ocean Observatory] | ||
| + | * [http://oceans.greenpeace.org Greenpeace Defending our Oceans] | ||
| + | * [http://www.motherjones.com/news/featurex/2006/03/oceans_index.html The Last Days of the Ocean, a ''Mother Jones'' special report on the state of the ocean] | ||
| + | * [http://www.oceanvoyager.org Ocean Voyager], a five-part journey to save the seas, created by ''Mother Jones'' magazine | ||
| + | * [http://www.oceanconservancy.org/ The Ocean Conservancy] - Advocates for Wild, Healthy Oceans | ||
| + | * [http://dapper.pmel.noaa.gov/dchart NOAA DChart ] - Plot and download ocean data from your browser or Google Earth | ||
| + | * [http://www.oceansatlas.org/ UN Atlas of the Oceans] | ||
| + | * [http://www.fisheries.org/afs/ American Fisheries Society] | ||
| + | * [http://www.cousteau.org/en/ Cousteau Society] | ||
| + | * [http://www.meriresearch.org/ Marine Environmental Research Institute] | ||
| + | * [http://www.nmfs.noaa.gov/ NOAA National Fisheries] | ||
| + | * [http://www.oceanservice.noaa.gov/ NOAA National Ocean Service] | ||
| + | * [http://www.oceanalliance.org/ Ocean Alliance] | ||
| + | * [http://www.oceanfutures.org/ Ocean Futures Society] | ||
| + | * [http://www.ocean.us/ National Office for Integrated and Sustained Ocean Observations] | ||
| + | * [http://www.onefish.org/global/index.jsp One Fish] | ||
| + | * [http://www.blueocean.org/ Blue Ocean Institute] | ||
| + | * [http://www.sfu.ca/coastalstudies/changingcurrents.htm Changing Currents: Charting a Course of Action for the Future of Oceans] | ||
| + | *[http://www.lpi.usra.edu/publications/slidesets/oceans/index.shtml Shuttle Views the Earth: Oceans from Space] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Oceans| ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Oceanography|Oceans]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{credit|134366119}} | ||
Revision as of 16:19, 30 May 2007
|
| Earth's oceans |
|---|
- For other uses, see Ocean (disambiguation).
An ocean (from Ωκεανός, Okeanos (Oceanus) in Greek) is a principal part of the hydrosphere: a major body of saline water that, in totality, covers about 70% of the Earth's surface (or an area of some 361 million square kilometers). Nearly half of the world's marine (oceanic) waters are over 3,000 meters (9,800 ft) deep. Average oceanic salinity is around 35 parts per thousand (ppt) (3.5%), and nearly all seawater has a salinity in the range of 31 to 38 ppt.
Overview
Though generally recognized as several 'separate' oceans, these waters comprise one global, interconnected body of salt water often referred to as the World Ocean or global ocean.[1][2] This concept of a global ocean as a continuous body of water with relatively free interchange among its parts is of fundamental importance to oceanography.[3] The major oceanic subdivisions are defined in part by the continents, various archipelagos, and other criteria: these subdivisions are (in descending order of size) the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean (which is sometimes subsumed as the southern portions of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans), and the Arctic Ocean (which is sometimes considered a sea of the Atlantic). The Pacific and Atlantic may be further subdivided by the equator into northerly and southerly portions. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, gulfs, bays and other names. There are also some smaller bodies of saltwater that are totally landlocked and not interconnected with the World Ocean, such as the Caspian Sea, the Aral Sea, and the Great Salt Lake – though they may be referred to as 'seas', they are actually salt lakes.
Geologically, an ocean is an area of oceanic crust covered by water. Oceanic crust is the thin layer of solidified volcanic basalt that covers the Earth's mantle where there are no continents. From this perspective, there are three oceans today: the World Ocean, the Caspian and the Black Seas, the latter two of which were formed by the collision of Cimmeria with Laurasia. The Mediterranean Sea is very nearly a discrete ocean, being connected to the World Ocean through the Strait of Gibraltar, and indeed several times over the last few million years movement of the African continent has closed the strait off entirely. The Black Sea is connected to the Mediterranean through the Bosporus, but this is in effect a natural canal cut through continental rock some 7,000 years ago, rather than a piece of oceanic sea floor like the Strait of Gibraltar.
Physical properties
The area of the World Ocean is 361 million square kilometers (139 million sq mi), its volume is over 1,340 million cubic kilometers (319 million cu mi), and its average depth is 3,711 meters (12,175 ft). Nearly half of the world's marine waters are over 3,000 meters (9,800 ft) deep.[2] The vast abyssal plains of the deep ocean cover about 40% of the Earth's surface. This does not include seas not connected to the World Ocean, such as the Caspian Sea.
The total mass of the hydrosphere is about 1.4 × 1021 kilograms, which is about 0.023% of the Earth's total mass. Less than 2% is freshwater, the rest is saltwater, mostly in the ocean.
Exploration
Travel on the surface of the ocean through the use of boats dates back to prehistoric times, but only in modern times has extensive underwater travel become possible.
The deepest point in the ocean is the Marianas Trench located in the Pacific Ocean near the Northern Mariana Islands. It has a maximum depth of 10,923 meters (35,838 ft) [4]. It was fully surveyed in 1951 by the British naval vessel, "Challenger II" which gave its name to the deepest part of the trench, the "Challenger Deep". In 1960, the Trieste successfully reached the bottom of the trench, manned by a crew of two men.
Much of the bottom of the world's oceans are unexplored and unmapped. A global image of many underwater features larger than 10 kilometers (6 mi) was created in 1995 based on gravitational distortions of the nearby sea surface.
Regions
Oceans are divided into numerous regions depending on the physical and biological conditions of these areas. The pelagic zone includes all open ocean regions, and can be subdivided into further regions categorised by depth and light abundance. The photic zone covers the oceans from surface level to 200 metres down. This is the region where the photosynthesis most commonly occurs and therefore contains the largest biodiversity in the ocean. Since plants can only survive with photosynthesis any life found lower than this must either rely on material floating down from above (see marine snow) or find another primary source; this often comes in the form of hydrothermal vents in what is known as the aphotic zone (all depths exceeding 200m). The pelagic part of the photic zone is known as the epipelagic. The pelagic part of the aphotic zone can be further divided into regions that succeed each other vertically. The mesopelagic is the uppermost region, with its lowermost boundary at a thermocline of 10°C, which, in the tropics generally lies between 700 and 1,000m. After that is the bathypelagic lying between 10°C and 4°C, or between 700 or 1,000m and 2,000 or 4,000m. Lying along the top of the abyssal plain is the abyssalpelagic, whose lower boundary lies at about 6,000m. The final zone falls into the oceanic trenches, and is known as the hadalpelagic. This lies between 6,000m and 10,000m and is the deepest oceanic zone.
Along with pelagic aphotic zones there are also benthic aphotic zones, these correspond to the three deepest zones. The bathyal zone covers the continental slope and the rise down to about 4,000m. The abyssal zone covers the abyssal plains between 4,000 and 6,000m. Lastly, the hadal zone corresponds to the hadalpelagic zone which is found in the oceanic trenches. The pelagic zone can also be split into two subregions, the neritic zone and the oceanic zone. The neritic encompasses the water mass directly above the continental shelves, while the oceanic zone includes all the completely open water. In contrast, the littoral zone covers the region between low and high tide and represents the transitional area between marine and terrestrial conditions. It is also known as the intertidal zone because it is the area where tide level affects the conditions of the region.
Climate
One of the most dramatic forms of weather occurs over the oceans: tropical cyclones (also called "typhoons" and "hurricanes" depending upon where the system forms). Ocean currents greatly affect Earth's climate by transferring warm or cold air and precipitation to coastal regions, where they may be carried inland by winds. The Antarctic Circumpolar Current encircles that continent, influencing the area's climate and connecting currents in several oceans.
Ecology
The oceans are home to the majority of plant and animal life on Earth. These lifeforms include:
- Radiata
- Fish
- Cetacea such as whales, dolphins and porpoises,
- Cephalopods such as the octopus
- Crustaceans such as lobsters and shrimp
- Marine worms
- Plankton
- Krill
Economy
The oceans are essential to transportation: most of the world's goods are moved by ship between the world's seaports. Important ship canals include the Saint Lawrence Seaway, Panama Canal, and Suez Canal. They are also an important source of valuable foodstuffs for the fishing industry. Some of these are shrimp, fish, crabs and lobster.
Ancient oceans
Continental drift has reconfigured the Earth's oceans, joining and splitting ancient oceans to form the current oceans. Ancient oceans include:
- Bridge River Ocean, the ocean between the ancient Insular Islands and North America.
- Iapetus Ocean, the southern hemisphere ocean between Baltica and Avalonia.
- Panthalassa, the vast world ocean that surrounded the Pangaea supercontinent.
- Rheic Ocean
- Slide Mountain Ocean, the ocean between the ancient Intermontane Islands and North America.
- Tethys Ocean, the ocean between the ancient continents of Gondwana and Laurasia.
- Khanty Ocean, the ocean between Baltica and Siberia.
- Mirovia, the ocean that surrounded the Rodinia supercontinent.
- Paleo-Tethys Ocean, the ocean between Gondwana and the Hunic terranes.
- Proto-Tethys Ocean,
- Pan-African Ocean, the ocean that surrounded the Pannotia supercontinent.
- Superocean, the ocean that surrounds a global supercontinent.
- Ural Ocean, the ocean between Siberia and Baltica.
Extraterrestrial oceans
- See also Oceans Beyond Earth
Earth is the only known planet with liquid water on its surface and is certainly the only one in our own solar system. However, liquid water is thought to be present under the surface of the Galilean moons Europa, and, with less certainty, Callisto and Ganymede. Geysers have been found on Enceladus, though these may not involve bodies of liquid water. Other icy moons may have once had internal oceans that have now frozen, such as Triton. The planets Uranus and Neptune may also possess large oceans of liquid water under their thick atmospheres, though their internal structure is not well understood at this time.
There is currently much debate over whether Mars once had an ocean of water in its northern hemisphere, and over what happened to it if it did; recent findings by the Mars Exploration Rover mission indicate it had some long-term standing water in at least one location, but its extent is not known.
Astronomers believe that Venus had liquid water and perhaps oceans in its very early history. If they existed, all trace of them seems to have vanished in later resurfacing.
Liquid hydrocarbons are thought to be present on the surface of Titan, though it may be more accurate to describe them as "lakes" rather than an "ocean". The Cassini-Huygens space mission initially discovered only what appeared to be dry lakebeds and empty river channels, suggesting that Titan had lost what surface liquids it might have had. A more recent fly-by of Titan made by Cassini has produced radar images that strongly suggest hydrocarbon lakes near the polar regions where it is colder. Titan is also thought likely to have a subterranean water ocean under the mix of ice and hydrocarbons that forms its outer crust.
Beyond the solar system, Gliese 581 c is at the right distance from its sun for liquid water to exist on the planet's surface. Since it does not transit its sun, there is no way to know if there is any water there. HD 209458b may have water vapour in its atmosphere - this is currently being disputed. Gliese 436 b is believed to have 'hot ice'. Neither of these planets are cool enough for liquid water: but if water molecules exist there, they are likely to be found also on planets at a suitable temperature.[5]
Mythology
The original concept of "ocean" goes back to notions of Mesopotamian and Indo-European mythology, imagining the world to be encircled by a great river. Okeanos, "Ωκεανός" in Greek, reflects the ancient Greek observation that a strong current flowed off Gibraltar and their subsequent assumption that it was a great river. (Compare also Samudra from Hindu mythology and Jörmungandr from Norse mythology). The world was imagined to be enclosed by a celestial ocean above the heavens, and an ocean of the underworld below (compare Rasā, Varuna). This is evidenced for example in the account of Noah's flood in Genesis 7:11, where
- all the fountains of the great deep [were] broken up, and the windows of heaven were opened (KJV),
inundating the world with the waters of the celestial ocean (see also deluge (mythology)).
Trivia
One common misconception today is that the oceans are blue primarily because the sky is blue. In fact, water has a very slight blue colour that can only be seen in large volumes. While the sky's reflection does contribute to the blue appearance of the surface, it is not the primary cause[6]. The primary cause is the absorption by the water molecules' nuclei of red photons from the incoming light, the only known example of color in nature resulting from vibrational, rather than electronic, dynamics[7].
See also
- Oceanography
- International Maritime Organization
- Sea
- Mediterranean sea
- Marginal sea
- Sea level
- Sea level rise
- Sea salt
- Water
- World Ocean Day
- Marine biology
- Pelagic zone
- Southern Ocean
- Underground Oceans
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ "Ocean". The Columbia Encyclopedia. 2006. New York: Columbia University Press
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Distribution of land and water on the planet". UN Atlas of the Oceans
- ↑ Spilhaus, Athelstan F. 1942 (Jul.). "Maps of the whole world ocean." Geographical Review (American Geographical Society). Vol. 32 (3): pp. 431-5.
- ↑ http://www.rain.org/ocean/ocean-studies-challenger-deep-mariana-trench.html
- ↑ Hot "ice" may cover recently discovered planet [1]
- ↑ http://amasci.com/miscon/miscon4.html#watclr
- ↑ Braun, C. L. and Smirnov, S. N. (1993) Why is water blue? J. Chem. Edu. 70, 612.
- Matthias Tomczak and J. Stuart Godfrey. 2003. Regional Oceanography: an Introduction. (see the site)
- "Origins of the oceans and continents". UN Atlas of the Oceans.
External links
- Ocean Explorer - An educational and reference resource from NOAA
- Oceanography Image of the Day - from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
- Science taps into ocean secrets
- Why is the ocean salty?
- Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission
- Oceana - Protecting the World's Oceans
- CORE - Consortium for Oceanographic Research and Education
- NOPP - National Oceanographic Partnership Program
- NOSB - National Ocean Sciences Bowl
- CoML - Census of Marine Life
- World Ocean Observatory
- Greenpeace Defending our Oceans
- The Last Days of the Ocean, a Mother Jones special report on the state of the ocean
- Ocean Voyager, a five-part journey to save the seas, created by Mother Jones magazine
- The Ocean Conservancy - Advocates for Wild, Healthy Oceans
- NOAA DChart - Plot and download ocean data from your browser or Google Earth
- UN Atlas of the Oceans
- American Fisheries Society
- Cousteau Society
- Marine Environmental Research Institute
- NOAA National Fisheries
- NOAA National Ocean Service
- Ocean Alliance
- Ocean Futures Society
- National Office for Integrated and Sustained Ocean Observations
- One Fish
- Blue Ocean Institute
- Changing Currents: Charting a Course of Action for the Future of Oceans
- Shuttle Views the Earth: Oceans from Space
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.