Difference between revisions of "Mediterranean Sea" - New World Encyclopedia
(Wanted) |
Keisuke Noda (talk | contribs) (import from wiki) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{claimed}} | ||
| + | {{redirect|Mediterranean}} | ||
| + | [[Image:Mediterranean_Sea_political_map-en.svg|thumb|300px|Composite [[satellite]] image of the Mediterranean Sea.]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Mediterranian Sea.jpg|thumb|300px|A point between [[Minorca]] and [[Barcelona]]]] | ||
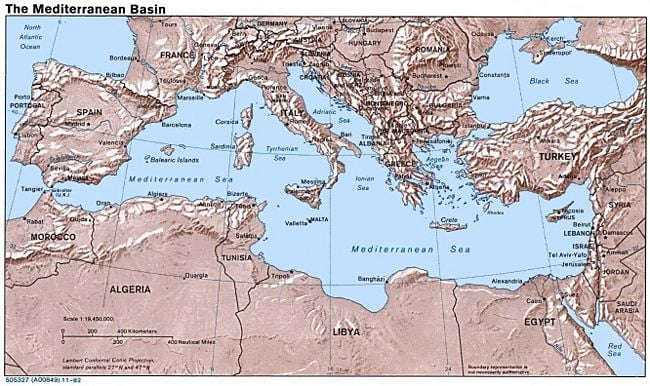
| + | The '''Mediterranean Sea''' (35 degrees north, 18 degrees east) is a [[sea]] of the [[Atlantic Ocean]] almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by [[Europe]], on the south by [[Africa]], and on the east by [[Asia]]. It covers an approximate area of [[1 E12 m²|2.5 million]] [[square kilometre|km²]] (965,000 [[square mile|sq mi]]), but its connection to the Atlantic (the [[Strait of Gibraltar]]) is only 14 km (9 mi) wide. In [[oceanography]], it is sometimes called ''the Eurafrican Mediterranean Sea'' or ''the European Mediterranean Sea'', to distinguish it from mediterranean seas elsewhere. | ||
| − | {{ | + | It was the most important route for merchants and travelers of ancient times, allowing for trade and cultural exchange between emergent peoples of the region — the [[Mesopotamia]]n, [[Ancient Egypt|Egyptian]], [[Semitic]], [[Persian Empire|Persian]], [[Phoenicia]]n, [[Carthage|Carthaginian]], [[Ancient Greece|Greek]] and [[Ancient Rome|Roman]] cultures. The [[history of the Mediterranean]] is crucial to understanding the origins and development of many modern societies. |
| + | |||
| + | ==Name== | ||
| + | {{wiktionary}} | ||
| + | The term ''Mediterranean'' derives from the [[Latin]] ''mediterraneus'', 'inland' (''medius'', 'middle' + ''terra'', 'land, earth'). To the ancient Romans, the Mediterranean was the center of the Earth as they knew it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Mediterranean Sea has been known by a number of alternative names throughout human history. It was, for example, commonly called ''[[Mare Nostrum]]'' (Latin, ''Our Sea''), and occasionally ''Mare Internum'' by the Romans. ([[Sallust]], ''Jug.'' 17). The [[Greeks]] name it ''Mesogeios'' (Μεσόγειος), meaning inland, interior | ||
| + | (μεσο, 'middle' + γαιος, 'land, earth')<ref>[http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/cgi-bin/ptext?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3D%2366422 entry μεσόγαιος] at [[Liddell & Scott]]</ref>. In the [[Old Testament]], on the west coast of the [[Holy Land]], and therefore behind a person facing the east, it is called the "Hinder Sea", sometimes translated as "Western Sea", ([[Deuteronomy|Deut.]] xi. 24; [[Book of Joel|Joel]], ii. 20), and also the "Sea of the Philistines" ([[Exodus|Exod.]] xxii. 81), because that people occupied a large portion of its shores near the [[Israelites]]. Mostly, however, it was the "Great Sea" ([[Book of Numbers|Num.]] xxxiv. 6, 7; [[Book of Joshua|Josh.]] i. 4, ix. 1, xv. 47; [[Book of Ezekiel|Ezek.]] xlvii. 10, 15, 20), or simply "The Sea" ([[1 Kings]], v. 9; ''comp.'' [[1 Macc.]] xiv. 34. xv. 11). In [[Hebrew language|Hebrew]], it is called ''HaYam HaTikhon'' (הַיָּם הַתִּיכוֹן), "the middle sea", a literal adaptation of the German equivalent ''Mittelmeer''. In [[Turkish language|Turkish]], it is ''Akdeniz'', "the white sea". In Arabic, it is ''Al-Baħr Al-Abyad Al-Muttawasit'' (البحر الأبيض المتوسط), "the middle white sea". | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==History== | ||
| + | {{main|History of the Mediterranean region}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | As a sea around which some of the most ancient human civilizations were arranged, it has had a major influence on the history and ways of life of these cultures. It provided a way of trade, colonization and war, and was the basis of life (via fishing and the gathering of other seafood) for numerous communities throughout the ages. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The combination of similar shared climate, geology and access to a common sea has led to numerous historical and cultural connections between the ancient and modern societies around the Mediterranean. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Geography and climate== | ||
| + | [[Image:Mediterranean Relief.jpg|650px|center|Map of the Mediterranean Sea.]] | ||
| + | The Mediterranean Sea is connected to the [[Atlantic Ocean]] by the [[Strait of Gibraltar]] on the west and to the [[Sea of Marmara]] and [[Black Sea]], by the [[Dardanelles]] and the [[Bosporus]] respectively, on the east. The Sea of Marmara is often considered a part of the Mediterranean Sea, whereas the Black Sea is generally not. The man-made [[Suez Canal]] in the south-east connects the Mediterranean Sea with the [[Red Sea]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Large [[island]]s in the Mediterranean include [[Cyprus]], [[Crete]], [[Euboea]], [[Rhodes]], [[Lesbos Island|Lesbos]], [[Chios]], [[Kefalonia]] and [[Corfu]] in the eastern Mediterranean; [[Sardinia]], [[Corsica]], [[Sicily]], and [[Malta]] in the central Mediterranean; and [[Ibiza]], [[Majorca]] and [[Minorca]] (the [[Balearic Islands]]) in the western Mediterranean. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[Mediterranean climate]] is generally one of wet winters and hot, dry summers. Crops of the region include [[olive]]s, [[grape]]s, [[orange (fruit)|orange]]s, [[tangerine]]s, and [[cork (material)|cork]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Oceanography== | ||
| + | Being nearly landlocked affects the Mediterranean Sea's properties; for instance, [[tide]]s are very limited as a result of the narrow connection with the Atlantic [[ocean]]. The Mediterranean is characterized and immediately recognized by its imposing deep blue color, especially around the Greek islands. | ||
| + | |||
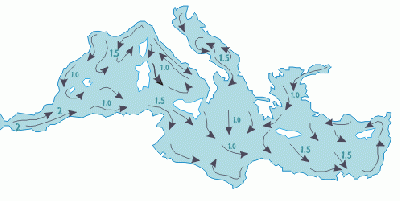
| + | [[Image:MEDCURR.GIF|thumb|400px|right|Predominant currents for June]] | ||
| + | [[Evaporation]] greatly exceeds [[Precipitation (meteorology)|precipitation]] and river runoff in the Mediterranean, a fact that is central to the water circulation within the basin.<ref>Pinet, Paul R. (1996) Invitation to Oceanography, St Paul, MN: West Publishing Co., ISBN (3rd ed.), p.202</ref> Evaporation is especially high in its eastern half, causing the water level to decrease and [[salinity]] to increase eastward.<ref>Pinet, p. 206</ref> This [[pressure gradient]] pushes relatively cool, low-salinity water from the Atlantic across the basin; it warms and becomes saltier as it travels east, then sinks in the region of the [[Levant]] and circulates westward, to spill over the Strait of Gibraltar.<ref>Pinet, pp. 206–7</ref> Thus, seawater flow is eastward in the Strait's surface waters, and westward below; once in the open ocean, this chemically-distinct "Mediterranean Intermediate Water" can persist thousands of kilometers away from its source.<ref>Pinet, p. 207</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Bordering countries== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Strait of gibraltar.jpg|thumb|right|230px|A satellite image taken from the side of the [[Strait of Gibraltar]]. At right, [[Africa]]; at left, [[Europe]]]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Twenty-one modern states have a coastline on the Mediterranean Sea. They are: | ||
| + | *'''[[Europe]]''' (from west to east): [[Spain]], [[France]], [[Monaco]], [[Italy]], the island state of [[Malta]], [[Slovenia]], [[Croatia]], [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]], [[Montenegro]], [[Albania]], [[Greece]] | ||
| + | *'''[[Asia]]''' (from north to south): [[Turkey]], [[Syria]], the island [[Republic of Cyprus]], [[Lebanon]] and [[Israel]] | ||
| + | *'''[[Africa]]''' (from east to west): [[Egypt]], [[Libya]], [[Tunisia]], [[Algeria]] and [[Morocco]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Wingate 124.jpg|thumb|300px|Mediterranian coast in Israel]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Several other territories also border the Mediterranean Sea (from west to east): | ||
| + | * The [[Crown colony]] of [[Gibraltar]] | ||
| + | * The [[Spain|Spanish]] exclaves of [[Ceuta]] and [[Melilla]] and nearby islands | ||
| + | * The autonomous monastic state of [[Mount Athos]] | ||
| + | * The [[UK sovereign base|sovereign base area]] of [[Akrotiri and Dhekelia]] | ||
| + | * The [[Gaza Strip]] (governed by the [[Palestinian National Authority]]) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Republic of Macedonia|FYROMacedonia]], [[Portugal]], [[San Marino]], [[Serbia]], and the [[Vatican City]], although they do not border the sea, are often considered Mediterranean countries in a wider sense due to their Mediterranean climate, fauna and flora, and their cultural affinity with other Mediterranean countries. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Subdivisions== | ||
| + | [[Image:Strasse von Gibraltar2004.jpg|thumb|right|A view across the [[straits of Gibraltar]]]] | ||
| + | The Mediterranean Sea is sub-divided into a number of smaller seas, each with their own designation (from west to east): | ||
| + | * the [[Alboran Sea]], between [[Spain]] and [[Morocco]], | ||
| + | * the [[Balearic Sea]], between mainland [[Spain]] and its [[Balearic Islands]], | ||
| + | * the [[Ligurian Sea]] between [[Corsica]] and [[Liguria]] (Italy), | ||
| + | * the [[Tyrrhenian Sea]] enclosed by [[Sardinia]], [[Italian peninsula]] and [[Sicily]], | ||
| + | * the [[Adriatic Sea]] between the Italian peninsula and the coasts of [[Slovenia]], [[Croatia]], [[Bosnia and Herzegovina|Bosnia]], [[Montenegro]] and [[Albania]] | ||
| + | * the [[Ionian Sea]] between [[Italy]], [[Greece]], and [[Albania]], | ||
| + | * the [[Aegean Sea]] between Greece and Turkey, with | ||
| + | ** the [[Thracian Sea]] in its north, | ||
| + | ** the [[Myrtoan Sea]] between the [[Cyclades]] and the [[Peloponnesos]], | ||
| + | ** the [[Sea of Crete]] north of Crete | ||
| + | ** the [[Libyan Sea]] south of [[Crete]], between the island and [[Libya]] | ||
| + | * the [[Sea of Marmara]] between the [[Aegean Sea|Aegean]] and [[Black Sea]]s. | ||
| + | * the [[Cilicia|Cilician Sea]] between [[Turkey]] and [[Cyprus]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Many of these smaller seas feature in local myth and folklore and derive their names from these associations. In addition to the seas, a number of [[Headlands and bays|gulfs]] and [[strait]]s are also recognised: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *the [[Saint George Bay]] in Beirut, Lebanon | ||
| + | *the [[Gulf of Corinth]], an enclosed sea between the Ionian Sea and the [[Corinth Canal]] | ||
| + | *the [[Saronic Gulf]], the gulf of [[Athens]], between the Corinth Canal and the [[Mirtoan Sea]] | ||
| + | *the [[Thermaic Gulf]], the gulf of [[Thessaloniki]], located in the northern Greek region of [[Macedonia (Greece)|Macedonia]] | ||
| + | *the [[Kvarner Gulf]], [[Croatia]] | ||
| + | *the [[Gulf of Lion]], south of [[France]] | ||
| + | *the [[Gulf of Valencia]], east of [[Spain]]. | ||
| + | *the [[Strait of Messina]], between [[Sicily]] and the toe of [[Italy]] | ||
| + | *the [[Gulf of Taranto]], southern Italy, | ||
| + | *the [[Strait of Otranto]], between [[Italy]] and [[Albania]] | ||
| + | *the [[Gulf of Haifa]], between [[Haifa]] and [[Akko]], [[Israel]] | ||
| + | *the [[Gulf of Sidra]], between [[Tunisia]] and [[Cyrenaica]] (eastern Libya) | ||
| + | *the [[Strait of Sicily]], between [[Sicily]] and [[Tunisia]] | ||
| + | *the [[Corsica Channel]], between [[Corsica]] and [[Italy]] | ||
| + | *the [[Strait of Bonifacio]], between [[Sardinia]] and [[Corsica]] | ||
| + | *the [[Gulf of İskenderun]], between [[İskenderun]] and [[Adana]] ([[Turkey]]) | ||
| + | *the [[Gulf of Antalya]], between west and east shores of Antalya ([[Turkey]]) | ||
| + | *the [[Gulf of Kotor]], on the coast of [[Montenegro]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Geology== | ||
| + | The geology of the Mediterranean is complex, involving the break-up and then collision of the African and Eurasian plates, and the [[Messinian Salinity Crisis]] in the late [[Miocene]] when the Mediterranean dried up. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Mediterranean Sea has an average depth of 1,500 [[metre|m]] and the deepest recorded point is 5,267 meters (about 3.27 miles) in the [[Calypso Deep]] in the [[Ionian Sea]]. The coastline extends for 46,000 [[kilometre|km]]. A shallow submarine ridge (the Strait of Sicily) between the island of [[Sicily]] and the coast of [[Tunisia]] divides the sea in two main subregions (which in turn are divided into subdivisions), the Western Mediterranean and the Eastern Mediterranean. The Western Mediterranean covers an area of about 0.85 million [[square kilometre|km²]] and the Eastern Mediterranean about 1.65 million [[square kilometre|km²]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Geodynamic''' | ||
| + | The [[geodynamic]] evolution of the Mediterranean Sea was provided by the convergence of European and African plates. This process was driven by the differential spreading along the Atlantic ridge, which led to the closure of the Tethys Ocean and eventually to the Alpine orogenesis. However, the Mediterranean also hosts wide extensional basins and migrating tectonic arcs, in response to its land-locked configuration. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Eastern Mediterranean: in middle Miocene times, the collision between the Arabian microplate and Eurasia led to the separation between the Tethys and the Indian ocean. This process determined profound changes in the oceanic circulation patterns, which shifted global climates towards colder contitions.The Hellenic Arc, which has a land-locked configuration, underwent a widespread extension for the last 20 Myr due to a slab roll-back process. In addition, the Hellenic Arc experienced a rapid rotation phase during the Pleistocene, with a counterclockwise component in its eastern portion and a clockwise trend in the western segment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Central Mediterranean: the opening of small oceanic basins of the central Mediterranean follows a trench migration and back-arc opening process that occurred during the last 30 Myr. This phase was characterized by the counter-clockwise rotation of the Corsica-Sardinia block, which lasted until the Langhian (ca.16 Ma), and was in turn followed by a slab detachment along the | ||
| + | northern African margin.Subsequently, a shift of this active extentional deformation led to the opening of the Tyrrenian basin. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Western Mediterranean: Since Mesozoic to [[Tertiary]] times, during convergence between Africa and Iberia, it developed the Betic-Rif mountain belts. Tectonic model for its evolution include: rapid motion of [[Alboran]] [[microplate]], [[subduction]] zone and radial extentional collapse caused by convective removal of lithosferic mantle. The development of these intramontane Betic and Rif basins led to the onset of two marine gateways which were progressively closed during the late Miocene by an interplay of tettonic and glacio-eustatic processes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Paleoclimatic''' | ||
| + | Because of its peculiar latitudinal position and its land-locked configuration, the Mediterranean is especially sensitive to astronomically induced climatic variations, which are well documented in its sedimentary record. Since the Mediterranen is involved in the deposition of eolian dust from the [[Sahara]] during dry periods, whereas riverine detrital input prevails during wet ones, the Mediterranean marine [[sapropel]]-bearing sequences provide high-resolution climatic information. These data have been employed in reconstructing astronomically calibrated time scales for the last 9 Ma of the Earth history. Furthermore, the exceptional accuracy of these paleoclimatic records improved our knowledge on the Earth’s orbital variations in the past. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Paleoenvironmental analysis''' | ||
| + | Its semi-enclosed configuration makes the oceanic gateways critical in controlling circulation and environmental evolution in the Mediterranean Sea. Water circulation patterns are driven by a number of interactive factors, such as climate and bathymetry, which can lead to precipitation of [[evaporites]]. During late Miocene times, a so-called “Messinian Salinity Crisis” (MSC hereafter) occurred, which was triggered by the closure of the Atlantic gateway. Evaporites accumulated in the [[Red Sea Basin]] (late [[Miocene]]), in the Carpatian foredeep (middle Miocene) and in the whole Mediterranean area ([[Messinian]]). | ||
| + | An accurate age estimate of the MSC (that is, 5,96 Ma) has recently been astronomically achieved; furthermore, this event seems to have occurred synchronously. Beginning of the MSC is supposed to have been of tectonic origin, however an astronomical control (eccentricity) might have been involved also. In the Mediterranean basin, diatomites are regularly found underneath the evaporitic deposits, thus suggesting (albeit not clearly so far) a connection between their geneses. | ||
| + | The present-day Atlantic gateway, i.e. the [[Strait of Gibraltar]], finds its origin in the early Pliocene. However, two other connections between the Atlantic ocean and the Mediterranean Sea which were present in the past that are the [[Betic Corridor]] (southern [[Spain]]) and the [[Rifian Corridor]] (northern [[Morocco]]). The former closed during [[Tortonian]] times, thus providing a “Tortonian Salinity Crisis”, well before the MSC; the latter closed at about 6 Ma, allowing thenceforth exchanges in the mammal fauna between [[Africa]] and [[Europe]]. | ||
| + | Nowadays, evaporation is more relevant than the water yield supplied by riverine water and precipitation, so that salinity in the Mediterranean is higher than in the Atlantic. These conditions result in the outflow of warm saline Mediterranean deep water across Gibraltar, which is in turn counterbalanced by an inflow of a less saline surface current of cold oceanic water. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the last few centuries, mankind has done much to alter Mediterranean geology. Structures have been built all along the coastlines, exacerbating and rerouting erosional patterns. Many pollution-producing boats travel the sea that unbalance the natural chemical ratios of the region. Beaches have been mismanaged, and the overuse of the sea's natural and marine resources continues to be a problem. This misuse speeds along and/or confounds natural processes. The actual geography has also been altered by the building of dams and canals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Mediterranean was once thought to be the remnant of the [[Tethys Ocean]]. It is now known to be a structurally younger ocean basin known as [[Neotethys]]. Neotethys formed during the Late [[Triassic]] and Early [[Jurassic]] [[rift]]ing of the African and Eurasian [[plate tectonics|plates]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Ecology== | ||
| + | As a result of the drying of the sea during the [[Messinian Salinity Crisis]], the marine biota of the Mediterranean are derived primarily from the [[Atlantic Ocean]]. The North Atlantic is considerably colder and more nutrient-rich than the Mediterranean, and the marine life of the Mediterranean has had to adapt to its differing conditions in the five million years since the basin was reflooded. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The opening of the [[Suez Canal]] in 1869 created the first salt-water passage between the Mediterranean and [[Red Sea|Red]] seas. The Red Sea is higher than the Eastern Mediterranean, so the canal serves as a [[tidal strait]] that pours Red Sea water into the Mediterranean. The [[Bitter Lakes]], which are hypersaline natural lakes that form part of the canal, blocked the migration of Red Sea species into the Mediterranean for many decades, but as the salinity of the lakes gradually equalized with that of the Red Sea, the barrier to migration was removed, and plants and animals from the Red Sea have begun to colonize the eastern Mediterranean. The Red Sea is generally saltier and more nutrient-poor than the Atlantic, so the Red Sea species have advantages over Atlantic species in the salty and nutrient-poor Eastern Mediterranean. Accordingly, Red Sea species invade the Mediterranean biota, and not vice versa; this phenomenon is known as the [[Lessepsian migration]] (after Ferdinand de Lesseps, the French engineer) or [[Erythrean invasion]]. The construction of the [[Aswan High Dam]] across the [[Nile River]] in the 1960s reduced the inflow of freshwater and nutrient-rich silt from the Nile into the eastern Mediterranean, making conditions there even more like the Red Sea, and worsening the impact of the [[invasive species]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Invasive species originated from the Red Sea and [[introduced species|introduced]] into the Mediterranean by the construction of the canal have become a major component of the Mediterranean ecosystem, and have serious impacts on the Mediterranean ecology, endangering many local and [[endemism|endemic]] Mediterranean species. Up to this day, about 300 species native to the Red Sea have already been identified in the Mediterranean Sea, and there are probably others yet unidentified. In recent years, the Egyptian government's announcement of its intentions to deepen and widen the canal, have raised concerns from [[marine biologist]]s, fearing that such an act will only worsen the invasion of Red Sea species into the Mediterranean, facilitating the crossing of the canal for yet additional species<ref>Galil, B.S. and Zenetos, A. (2002). A sea change: exotics in the eastern Mediterranean Sea, in: Leppäkoski, E. et al. (2002). ''Invasive aquatic species of Europe: distribution, impacts and management''. pp. 325-336. | ||
| + | </ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pollution in this region has been extremely high in the past couple years. In just one year, 1,000,000 tons of sewage has been dumped directly into the Mediterranean Sea.{{Fact|date=February 2007}} Also, many marine species, such as the [[Mediterranean Monk Seal]], have been almost wiped out because of the pollution there. The Monk Seal has been placed as one of the top ten [[endangered species]] in the world.{{Fact|date=February 2007}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | * [[Mediterranean Basin]] | ||
| + | * [[Mediterranean climate]] | ||
| + | * [[Mediterranean diet]] | ||
| + | * [[Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and shrub]] | ||
| + | * [[Mediterranean Games]] | ||
| + | * [[Mediterranean race]] | ||
| + | * [[Mediterranean sea (oceanography)|Mediterranean sea]] ([[oceanography]] term) | ||
| + | * [[Mediterranean Union]] | ||
| + | * [[Familial Mediterranean fever]] | ||
| + | * [[History of the Mediterranean region]] | ||
| + | * [[Holy League (Mediterranean)]] | ||
| + | * [[Inland Sea]], which is sometimes named after the Japanese Mediterranean Sea | ||
| + | * [[List of islands in the Mediterranean]] | ||
| + | * [[Suez Canal]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | {{reflist}} | ||
| + | {{commons|Mediterranean Sea}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | *[http://www.greenpeace.org/lebanon/en Greenpeace campaign "Defending Our Mediterranean":Threats, Solutions and Photo Petition] | ||
| + | *[http://www.planbleu.org/indexUK.html Planblue - Environment and Development in the Mediterranean Region] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea}} | ||
| + | {{Regions of the world}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{coor title d|35|N|18|E|type:waterbody_scale:30000000}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Marine ecoregions]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Mediterranean| ]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Seas]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[af:Middellandse See]] | ||
| + | [[am:ሜድትራኒያን ባሕር]] | ||
| + | [[ang:Wendelsǣ]] | ||
| + | [[ar:البحر الأبيض المتوسط]] | ||
| + | [[an:Mar Mediterranio]] | ||
| + | [[frp:Mar Mèditèrranê]] | ||
| + | [[ast:Mar Mediterraneu]] | ||
| + | [[az:Aralıq dənizi]] | ||
| + | [[zh-min-nan:Tē-tiong-hái]] | ||
| + | [[be-x-old:Міжземнае мора]] | ||
| + | [[bs:Sredozemno more]] | ||
| + | [[br:Mor Kreizdouar]] | ||
| + | [[bg:Средиземно море]] | ||
| + | [[ca:Mar Mediterrània]] | ||
| + | [[cv:Вăтаçĕр тинĕсĕ]] | ||
| + | [[cs:Středozemní moře]] | ||
| + | [[co:Mari Mediterraniu]] | ||
| + | [[cy:Y Môr Canoldir]] | ||
| + | [[da:Middelhavet]] | ||
| + | [[de:Mittelmeer]] | ||
| + | [[et:Vahemeri]] | ||
| + | [[el:Μεσόγειος Θάλασσα]] | ||
| + | [[es:Mar Mediterráneo]] | ||
| + | [[eo:Mediteraneo]] | ||
| + | [[eu:Mediterraneo itsasoa]] | ||
| + | [[fa:مدیترانه]] | ||
| + | [[fr:Mer Méditerranée]] | ||
| + | [[ga:An Mheánmhuir]] | ||
| + | [[gl:Mar Mediterráneo]] | ||
| + | [[ko:지중해]] | ||
| + | [[hi:भूमध्य सागर]] | ||
| + | [[hr:Sredozemno more]] | ||
| + | [[io:Mediteraneo]] | ||
| + | [[id:Laut Tengah]] | ||
| + | [[is:Miðjarðarhaf]] | ||
| + | [[it:Mar Mediterraneo]] | ||
| + | [[he:הים התיכון]] | ||
| + | [[ka:ხმელთაშუა ზღვა]] | ||
| + | [[sw:Bahari ya Mediteranea]] | ||
| + | [[ku:Derya Navîn]] | ||
| + | [[la:Mare Mediterraneum]] | ||
| + | [[lv:Vidusjūra]] | ||
| + | [[lb:Mëttelmier]] | ||
| + | [[lt:Viduržemio jūra]] | ||
| + | [[ln:Mediterané]] | ||
| + | [[hu:Földközi-tenger]] | ||
| + | [[mk:Средоземно Море]] | ||
| + | [[mt:Baħar Mediterran]] | ||
| + | [[mn:Газар Дундын тэнгис]] | ||
| + | [[nl:Middellandse Zee]] | ||
| + | [[nds-nl:Middellaanse Zee]] | ||
| + | [[ja:地中海]] | ||
| + | [[no:Middelhavet]] | ||
| + | [[nn:Middelhavet]] | ||
| + | [[nrm:Mé du Mitan]] | ||
| + | [[oc:Mar Mediterranèa]] | ||
| + | [[om:Gallana Mediterraniani]] | ||
| + | [[nds:Middelmeer]] | ||
| + | [[pl:Morze Śródziemne]] | ||
| + | [[pt:Mar Mediterrâneo]] | ||
| + | [[ro:Marea Mediterană]] | ||
| + | [[qu:Allpapura hatun qucha]] | ||
| + | [[ru:Средиземное море]] | ||
| + | [[scn:Mari Meditirràniu]] | ||
| + | [[simple:Mediterranean Sea]] | ||
| + | [[sk:Stredozemné more]] | ||
| + | [[sl:Sredozemsko morje]] | ||
| + | [[sr:Средоземно море]] | ||
| + | [[sh:Sredozemno more]] | ||
| + | [[fi:Välimeri]] | ||
| + | [[sv:Medelhavet]] | ||
| + | [[ta:மத்தியதரைக் கடல்]] | ||
| + | [[th:ทะเลเมดิเตอร์เรเนียน]] | ||
| + | [[vi:Địa Trung Hải]] | ||
| + | [[tr:Akdeniz]] | ||
| + | [[uk:Середземне море]] | ||
| + | [[ur:بحیرہ روم]] | ||
| + | [[vec:Mar Mediteraneo]] | ||
| + | [[wa:Mîtrinne Mer]] | ||
| + | [[zh:地中海]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{credit|142482023}} | ||
Revision as of 22:55, 4 July 2007
- "Mediterranean" redirects here.
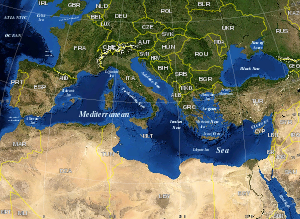
The Mediterranean Sea (35 degrees north, 18 degrees east) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Europe, on the south by Africa, and on the east by Asia. It covers an approximate area of 2.5 million km² (965,000 sq mi), but its connection to the Atlantic (the Strait of Gibraltar) is only 14 km (9 mi) wide. In oceanography, it is sometimes called the Eurafrican Mediterranean Sea or the European Mediterranean Sea, to distinguish it from mediterranean seas elsewhere.
It was the most important route for merchants and travelers of ancient times, allowing for trade and cultural exchange between emergent peoples of the region — the Mesopotamian, Egyptian, Semitic, Persian, Phoenician, Carthaginian, Greek and Roman cultures. The history of the Mediterranean is crucial to understanding the origins and development of many modern societies.
Name
The term Mediterranean derives from the Latin mediterraneus, 'inland' (medius, 'middle' + terra, 'land, earth'). To the ancient Romans, the Mediterranean was the center of the Earth as they knew it.
The Mediterranean Sea has been known by a number of alternative names throughout human history. It was, for example, commonly called Mare Nostrum (Latin, Our Sea), and occasionally Mare Internum by the Romans. (Sallust, Jug. 17). The Greeks name it Mesogeios (Μεσόγειος), meaning inland, interior (μεσο, 'middle' + γαιος, 'land, earth')[1]. In the Old Testament, on the west coast of the Holy Land, and therefore behind a person facing the east, it is called the "Hinder Sea", sometimes translated as "Western Sea", (Deut. xi. 24; Joel, ii. 20), and also the "Sea of the Philistines" (Exod. xxii. 81), because that people occupied a large portion of its shores near the Israelites. Mostly, however, it was the "Great Sea" (Num. xxxiv. 6, 7; Josh. i. 4, ix. 1, xv. 47; Ezek. xlvii. 10, 15, 20), or simply "The Sea" (1 Kings, v. 9; comp. 1 Macc. xiv. 34. xv. 11). In Hebrew, it is called HaYam HaTikhon (הַיָּם הַתִּיכוֹן), "the middle sea", a literal adaptation of the German equivalent Mittelmeer. In Turkish, it is Akdeniz, "the white sea". In Arabic, it is Al-Baħr Al-Abyad Al-Muttawasit (البحر الأبيض المتوسط), "the middle white sea".
History
As a sea around which some of the most ancient human civilizations were arranged, it has had a major influence on the history and ways of life of these cultures. It provided a way of trade, colonization and war, and was the basis of life (via fishing and the gathering of other seafood) for numerous communities throughout the ages.
The combination of similar shared climate, geology and access to a common sea has led to numerous historical and cultural connections between the ancient and modern societies around the Mediterranean.
Geography and climate
The Mediterranean Sea is connected to the Atlantic Ocean by the Strait of Gibraltar on the west and to the Sea of Marmara and Black Sea, by the Dardanelles and the Bosporus respectively, on the east. The Sea of Marmara is often considered a part of the Mediterranean Sea, whereas the Black Sea is generally not. The man-made Suez Canal in the south-east connects the Mediterranean Sea with the Red Sea.
Large islands in the Mediterranean include Cyprus, Crete, Euboea, Rhodes, Lesbos, Chios, Kefalonia and Corfu in the eastern Mediterranean; Sardinia, Corsica, Sicily, and Malta in the central Mediterranean; and Ibiza, Majorca and Minorca (the Balearic Islands) in the western Mediterranean.
The Mediterranean climate is generally one of wet winters and hot, dry summers. Crops of the region include olives, grapes, oranges, tangerines, and cork.
Oceanography
Being nearly landlocked affects the Mediterranean Sea's properties; for instance, tides are very limited as a result of the narrow connection with the Atlantic ocean. The Mediterranean is characterized and immediately recognized by its imposing deep blue color, especially around the Greek islands.
Evaporation greatly exceeds precipitation and river runoff in the Mediterranean, a fact that is central to the water circulation within the basin.[2] Evaporation is especially high in its eastern half, causing the water level to decrease and salinity to increase eastward.[3] This pressure gradient pushes relatively cool, low-salinity water from the Atlantic across the basin; it warms and becomes saltier as it travels east, then sinks in the region of the Levant and circulates westward, to spill over the Strait of Gibraltar.[4] Thus, seawater flow is eastward in the Strait's surface waters, and westward below; once in the open ocean, this chemically-distinct "Mediterranean Intermediate Water" can persist thousands of kilometers away from its source.[5]
Bordering countries

Twenty-one modern states have a coastline on the Mediterranean Sea. They are:
- Europe (from west to east): Spain, France, Monaco, Italy, the island state of Malta, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece
- Asia (from north to south): Turkey, Syria, the island Republic of Cyprus, Lebanon and Israel
- Africa (from east to west): Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria and Morocco
Several other territories also border the Mediterranean Sea (from west to east):
- The Crown colony of Gibraltar
- The Spanish exclaves of Ceuta and Melilla and nearby islands
- The autonomous monastic state of Mount Athos
- The sovereign base area of Akrotiri and Dhekelia
- The Gaza Strip (governed by the Palestinian National Authority)
FYROMacedonia, Portugal, San Marino, Serbia, and the Vatican City, although they do not border the sea, are often considered Mediterranean countries in a wider sense due to their Mediterranean climate, fauna and flora, and their cultural affinity with other Mediterranean countries.
Subdivisions
The Mediterranean Sea is sub-divided into a number of smaller seas, each with their own designation (from west to east):
- the Alboran Sea, between Spain and Morocco,
- the Balearic Sea, between mainland Spain and its Balearic Islands,
- the Ligurian Sea between Corsica and Liguria (Italy),
- the Tyrrhenian Sea enclosed by Sardinia, Italian peninsula and Sicily,
- the Adriatic Sea between the Italian peninsula and the coasts of Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia, Montenegro and Albania
- the Ionian Sea between Italy, Greece, and Albania,
- the Aegean Sea between Greece and Turkey, with
- the Thracian Sea in its north,
- the Myrtoan Sea between the Cyclades and the Peloponnesos,
- the Sea of Crete north of Crete
- the Libyan Sea south of Crete, between the island and Libya
- the Sea of Marmara between the Aegean and Black Seas.
- the Cilician Sea between Turkey and Cyprus
Many of these smaller seas feature in local myth and folklore and derive their names from these associations. In addition to the seas, a number of gulfs and straits are also recognised:
- the Saint George Bay in Beirut, Lebanon
- the Gulf of Corinth, an enclosed sea between the Ionian Sea and the Corinth Canal
- the Saronic Gulf, the gulf of Athens, between the Corinth Canal and the Mirtoan Sea
- the Thermaic Gulf, the gulf of Thessaloniki, located in the northern Greek region of Macedonia
- the Kvarner Gulf, Croatia
- the Gulf of Lion, south of France
- the Gulf of Valencia, east of Spain.
- the Strait of Messina, between Sicily and the toe of Italy
- the Gulf of Taranto, southern Italy,
- the Strait of Otranto, between Italy and Albania
- the Gulf of Haifa, between Haifa and Akko, Israel
- the Gulf of Sidra, between Tunisia and Cyrenaica (eastern Libya)
- the Strait of Sicily, between Sicily and Tunisia
- the Corsica Channel, between Corsica and Italy
- the Strait of Bonifacio, between Sardinia and Corsica
- the Gulf of İskenderun, between İskenderun and Adana (Turkey)
- the Gulf of Antalya, between west and east shores of Antalya (Turkey)
- the Gulf of Kotor, on the coast of Montenegro
Geology
The geology of the Mediterranean is complex, involving the break-up and then collision of the African and Eurasian plates, and the Messinian Salinity Crisis in the late Miocene when the Mediterranean dried up.
The Mediterranean Sea has an average depth of 1,500 m and the deepest recorded point is 5,267 meters (about 3.27 miles) in the Calypso Deep in the Ionian Sea. The coastline extends for 46,000 km. A shallow submarine ridge (the Strait of Sicily) between the island of Sicily and the coast of Tunisia divides the sea in two main subregions (which in turn are divided into subdivisions), the Western Mediterranean and the Eastern Mediterranean. The Western Mediterranean covers an area of about 0.85 million km² and the Eastern Mediterranean about 1.65 million km².
Geodynamic The geodynamic evolution of the Mediterranean Sea was provided by the convergence of European and African plates. This process was driven by the differential spreading along the Atlantic ridge, which led to the closure of the Tethys Ocean and eventually to the Alpine orogenesis. However, the Mediterranean also hosts wide extensional basins and migrating tectonic arcs, in response to its land-locked configuration.
Eastern Mediterranean: in middle Miocene times, the collision between the Arabian microplate and Eurasia led to the separation between the Tethys and the Indian ocean. This process determined profound changes in the oceanic circulation patterns, which shifted global climates towards colder contitions.The Hellenic Arc, which has a land-locked configuration, underwent a widespread extension for the last 20 Myr due to a slab roll-back process. In addition, the Hellenic Arc experienced a rapid rotation phase during the Pleistocene, with a counterclockwise component in its eastern portion and a clockwise trend in the western segment.
Central Mediterranean: the opening of small oceanic basins of the central Mediterranean follows a trench migration and back-arc opening process that occurred during the last 30 Myr. This phase was characterized by the counter-clockwise rotation of the Corsica-Sardinia block, which lasted until the Langhian (ca.16 Ma), and was in turn followed by a slab detachment along the northern African margin.Subsequently, a shift of this active extentional deformation led to the opening of the Tyrrenian basin.
Western Mediterranean: Since Mesozoic to Tertiary times, during convergence between Africa and Iberia, it developed the Betic-Rif mountain belts. Tectonic model for its evolution include: rapid motion of Alboran microplate, subduction zone and radial extentional collapse caused by convective removal of lithosferic mantle. The development of these intramontane Betic and Rif basins led to the onset of two marine gateways which were progressively closed during the late Miocene by an interplay of tettonic and glacio-eustatic processes.
Paleoclimatic Because of its peculiar latitudinal position and its land-locked configuration, the Mediterranean is especially sensitive to astronomically induced climatic variations, which are well documented in its sedimentary record. Since the Mediterranen is involved in the deposition of eolian dust from the Sahara during dry periods, whereas riverine detrital input prevails during wet ones, the Mediterranean marine sapropel-bearing sequences provide high-resolution climatic information. These data have been employed in reconstructing astronomically calibrated time scales for the last 9 Ma of the Earth history. Furthermore, the exceptional accuracy of these paleoclimatic records improved our knowledge on the Earth’s orbital variations in the past.
Paleoenvironmental analysis Its semi-enclosed configuration makes the oceanic gateways critical in controlling circulation and environmental evolution in the Mediterranean Sea. Water circulation patterns are driven by a number of interactive factors, such as climate and bathymetry, which can lead to precipitation of evaporites. During late Miocene times, a so-called “Messinian Salinity Crisis” (MSC hereafter) occurred, which was triggered by the closure of the Atlantic gateway. Evaporites accumulated in the Red Sea Basin (late Miocene), in the Carpatian foredeep (middle Miocene) and in the whole Mediterranean area (Messinian). An accurate age estimate of the MSC (that is, 5,96 Ma) has recently been astronomically achieved; furthermore, this event seems to have occurred synchronously. Beginning of the MSC is supposed to have been of tectonic origin, however an astronomical control (eccentricity) might have been involved also. In the Mediterranean basin, diatomites are regularly found underneath the evaporitic deposits, thus suggesting (albeit not clearly so far) a connection between their geneses. The present-day Atlantic gateway, i.e. the Strait of Gibraltar, finds its origin in the early Pliocene. However, two other connections between the Atlantic ocean and the Mediterranean Sea which were present in the past that are the Betic Corridor (southern Spain) and the Rifian Corridor (northern Morocco). The former closed during Tortonian times, thus providing a “Tortonian Salinity Crisis”, well before the MSC; the latter closed at about 6 Ma, allowing thenceforth exchanges in the mammal fauna between Africa and Europe. Nowadays, evaporation is more relevant than the water yield supplied by riverine water and precipitation, so that salinity in the Mediterranean is higher than in the Atlantic. These conditions result in the outflow of warm saline Mediterranean deep water across Gibraltar, which is in turn counterbalanced by an inflow of a less saline surface current of cold oceanic water.
In the last few centuries, mankind has done much to alter Mediterranean geology. Structures have been built all along the coastlines, exacerbating and rerouting erosional patterns. Many pollution-producing boats travel the sea that unbalance the natural chemical ratios of the region. Beaches have been mismanaged, and the overuse of the sea's natural and marine resources continues to be a problem. This misuse speeds along and/or confounds natural processes. The actual geography has also been altered by the building of dams and canals.
The Mediterranean was once thought to be the remnant of the Tethys Ocean. It is now known to be a structurally younger ocean basin known as Neotethys. Neotethys formed during the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic rifting of the African and Eurasian plates.
Ecology
As a result of the drying of the sea during the Messinian Salinity Crisis, the marine biota of the Mediterranean are derived primarily from the Atlantic Ocean. The North Atlantic is considerably colder and more nutrient-rich than the Mediterranean, and the marine life of the Mediterranean has had to adapt to its differing conditions in the five million years since the basin was reflooded.
The opening of the Suez Canal in 1869 created the first salt-water passage between the Mediterranean and Red seas. The Red Sea is higher than the Eastern Mediterranean, so the canal serves as a tidal strait that pours Red Sea water into the Mediterranean. The Bitter Lakes, which are hypersaline natural lakes that form part of the canal, blocked the migration of Red Sea species into the Mediterranean for many decades, but as the salinity of the lakes gradually equalized with that of the Red Sea, the barrier to migration was removed, and plants and animals from the Red Sea have begun to colonize the eastern Mediterranean. The Red Sea is generally saltier and more nutrient-poor than the Atlantic, so the Red Sea species have advantages over Atlantic species in the salty and nutrient-poor Eastern Mediterranean. Accordingly, Red Sea species invade the Mediterranean biota, and not vice versa; this phenomenon is known as the Lessepsian migration (after Ferdinand de Lesseps, the French engineer) or Erythrean invasion. The construction of the Aswan High Dam across the Nile River in the 1960s reduced the inflow of freshwater and nutrient-rich silt from the Nile into the eastern Mediterranean, making conditions there even more like the Red Sea, and worsening the impact of the invasive species.
Invasive species originated from the Red Sea and introduced into the Mediterranean by the construction of the canal have become a major component of the Mediterranean ecosystem, and have serious impacts on the Mediterranean ecology, endangering many local and endemic Mediterranean species. Up to this day, about 300 species native to the Red Sea have already been identified in the Mediterranean Sea, and there are probably others yet unidentified. In recent years, the Egyptian government's announcement of its intentions to deepen and widen the canal, have raised concerns from marine biologists, fearing that such an act will only worsen the invasion of Red Sea species into the Mediterranean, facilitating the crossing of the canal for yet additional species[6].
Pollution in this region has been extremely high in the past couple years. In just one year, 1,000,000 tons of sewage has been dumped directly into the Mediterranean Sea.[citation needed] Also, many marine species, such as the Mediterranean Monk Seal, have been almost wiped out because of the pollution there. The Monk Seal has been placed as one of the top ten endangered species in the world.[citation needed]
See also
- Mediterranean Basin
- Mediterranean climate
- Mediterranean diet
- Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and shrub
- Mediterranean Games
- Mediterranean race
- Mediterranean sea (oceanography term)
- Mediterranean Union
- Familial Mediterranean fever
- History of the Mediterranean region
- Holy League (Mediterranean)
- Inland Sea, which is sometimes named after the Japanese Mediterranean Sea
- List of islands in the Mediterranean
- Suez Canal
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ entry μεσόγαιος at Liddell & Scott
- ↑ Pinet, Paul R. (1996) Invitation to Oceanography, St Paul, MN: West Publishing Co., ISBN (3rd ed.), p.202
- ↑ Pinet, p. 206
- ↑ Pinet, pp. 206–7
- ↑ Pinet, p. 207
- ↑ Galil, B.S. and Zenetos, A. (2002). A sea change: exotics in the eastern Mediterranean Sea, in: Leppäkoski, E. et al. (2002). Invasive aquatic species of Europe: distribution, impacts and management. pp. 325-336.
External links
- Greenpeace campaign "Defending Our Mediterranean":Threats, Solutions and Photo Petition
- Planblue - Environment and Development in the Mediterranean Region
| ||||||||
| Regions of the world | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| See also Continents of the world | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
af:Middellandse See am:ሜድትራኒያን ባሕር ang:Wendelsǣ ar:البحر الأبيض المتوسط an:Mar Mediterranio frp:Mar Mèditèrranê ast:Mar Mediterraneu az:Aralıq dənizi zh-min-nan:Tē-tiong-hái be-x-old:Міжземнае мора bs:Sredozemno more br:Mor Kreizdouar bg:Средиземно море ca:Mar Mediterrània cv:Вăтаçĕр тинĕсĕ cs:Středozemní moře co:Mari Mediterraniu cy:Y Môr Canoldir da:Middelhavet de:Mittelmeer et:Vahemeri el:Μεσόγειος Θάλασσα es:Mar Mediterráneo eo:Mediteraneo eu:Mediterraneo itsasoa fa:مدیترانه fr:Mer Méditerranée ga:An Mheánmhuir gl:Mar Mediterráneo ko:지중해 hi:भूमध्य सागर hr:Sredozemno more io:Mediteraneo id:Laut Tengah is:Miðjarðarhaf it:Mar Mediterraneo he:הים התיכון ka:ხმელთაშუა ზღვა sw:Bahari ya Mediteranea ku:Derya Navîn la:Mare Mediterraneum lv:Vidusjūra lb:Mëttelmier lt:Viduržemio jūra ln:Mediterané hu:Földközi-tenger mk:Средоземно Море mt:Baħar Mediterran mn:Газар Дундын тэнгис nl:Middellandse Zee nds-nl:Middellaanse Zee ja:地中海 no:Middelhavet nn:Middelhavet nrm:Mé du Mitan oc:Mar Mediterranèa om:Gallana Mediterraniani nds:Middelmeer pl:Morze Śródziemne pt:Mar Mediterrâneo ro:Marea Mediterană qu:Allpapura hatun qucha ru:Средиземное море scn:Mari Meditirràniu simple:Mediterranean Sea sk:Stredozemné more sl:Sredozemsko morje sr:Средоземно море sh:Sredozemno more fi:Välimeri sv:Medelhavet ta:மத்தியதரைக் கடல் th:ทะเลเมดิเตอร์เรเนียน vi:Địa Trung Hải tr:Akdeniz uk:Середземне море ur:بحیرہ روم vec:Mar Mediteraneo wa:Mîtrinne Mer zh:地中海
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.