Difference between revisions of "Alaska" - New World Encyclopedia
({{Contracted}}) |
Mary Anglin (talk | contribs) (→Flora and fauna: wildlife addition) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| Capital = [[Juneau, Alaska|Juneau]] | | Capital = [[Juneau, Alaska|Juneau]] | ||
| OfficialLang = [[English language|English]]<ref>[http://www.us-english.org/inc/official/states.asp U.S. ENGLISH,Inc]</ref> | | OfficialLang = [[English language|English]]<ref>[http://www.us-english.org/inc/official/states.asp U.S. ENGLISH,Inc]</ref> | ||
| − | | Languages = [[English language|English]] 85.7%, <br> Native North American 5.2%, <br> [[Spanish language|Spanish]] 2.9% | + | | Languages = [[English language|English]] 85.7%, <br/> Native North American 5.2%, <br/> [[Spanish language|Spanish]] 2.9% |
| LargestCity = [[Anchorage, Alaska|Anchorage]] | | LargestCity = [[Anchorage, Alaska|Anchorage]] | ||
| Governor = [[Sarah Palin]] (R) | | Governor = [[Sarah Palin]] (R) | ||
| − | | Senators = [[Ted Stevens]] (R) <br> [[Lisa Murkowski]] (R) | + | | Senators = [[Ted Stevens]] (R) <br/> [[Lisa Murkowski]] (R) |
| U.S. Representative = [[Don Young]] (R) | | U.S. Representative = [[Don Young]] (R) | ||
| PostalAbbreviation = AK | | PostalAbbreviation = AK | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
| AdmittanceOrder = 49<sup>th</sup> | | AdmittanceOrder = 49<sup>th</sup> | ||
| Alaska purchase = October 18, 1867 | | Alaska purchase = October 18, 1867 | ||
| − | | AdmittanceDate = | + | | AdmittanceDate = January 3, 1959 |
| TimeZone = [[Alaska Standard Time Zone|Alaska]]: [[Coordinated Universal Time|UTC]]-9/[[Daylight saving time|DST]]-8 | | TimeZone = [[Alaska Standard Time Zone|Alaska]]: [[Coordinated Universal Time|UTC]]-9/[[Daylight saving time|DST]]-8 | ||
| TZ1Where = east of 169° 30' | | TZ1Where = east of 169° 30' | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
| Length = 2,380 | | Length = 2,380 | ||
| LengthUS = 1,479 | | LengthUS = 1,479 | ||
| − | | HighestPoint = [[Mount McKinley]]<ref name=usgs>{{cite web| year = | + | | HighestPoint = [[Mount McKinley]]<ref name=usgs>{{cite web| year =29 April 2005 | url =http://erg.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/booklets/elvadist/elvadist.html#Highest| title =Elevations and Distances in the United States| publisher =U.S Geological Survey| accessmonthday=3 November | accessyear = 2006}}</ref> |
| HighestElev = 6,193.7 | | HighestElev = 6,193.7 | ||
| HighestElevUS = 20,320 | | HighestElevUS = 20,320 | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
| Website = www.alaska.gov | | Website = www.alaska.gov | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The area that became Alaska was purchased from [[Russia]]n interests on | + | '''Alaska''' is a state of the [[United States|United States of America]] that is located in the extreme northwest portion of [[North America]], west of [[Canada]]. It is the largest U.S. state in terms of [[List of U.S. states by area|area]] (by a substantial margin), along with being one of the wealthiest and most racially diverse.<ref> Vallano, Elissa: [http://www.phillyburbs.com/pb-dyn/news/169-02062007-1295065.html Cruising America's 'Last Frontier'], Retrieved on May 24, 2007</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | The area that became Alaska was purchased from [[Russia]]n interests on October 18 1867 for $7,200,000. The land went through several administrative changes before becoming an [[organized territory]] in 1912 and the 49th state of the U.S. on January 3, 1959. The name "Alaska" is derived from the [[Aleut language|Aleut]] ''alaxsxaq'', meaning "the mainland," or more literally "the object towards which the action of the sea is directed".<ref>Ransom, J. Ellis. 1940. ''Derivation of the Word ‘Alaska’''. American Anthropologist n.s., 42: pp. 550-551</ref> | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
Alaska's interior has an extreme subarctic climate. Summer temperatures may reach into the 80s°F (near 30 °C), while winter temperatures can fall below −60 °F (-52 °C). Interior locations often receive less than {{convert|10|in|mm|-1}} precipitation annually. | Alaska's interior has an extreme subarctic climate. Summer temperatures may reach into the 80s°F (near 30 °C), while winter temperatures can fall below −60 °F (-52 °C). Interior locations often receive less than {{convert|10|in|mm|-1}} precipitation annually. | ||
| − | The climate in the extreme north of Alaska is a [[polar climate]] (Köppen ''ET'') with long, very cold winters and short, cool summers. Even in July, the average low temperature is barely above freezing in Barrow, at 34 °F (2 °C).<ref>[http://www.wunderground.com/history/airport/PABR/2006/7/23/MonthlyHistory.html History for Barrow, Alaska. Monthly Summary for July 2006]. [[Weather Underground (weather service)|]]. Last accessed | + | The climate in the extreme north of Alaska is a [[polar climate]] (Köppen ''ET'') with long, very cold winters and short, cool summers. Even in July, the average low temperature is barely above freezing in Barrow, at 34 °F (2 °C).<ref>[http://www.wunderground.com/history/airport/PABR/2006/7/23/MonthlyHistory.html History for Barrow, Alaska. Monthly Summary for July 2006]. [[Weather Underground (weather service)|]]. Last accessed 23 October 2006.</ref> Precipitation is light in this part of Alaska, with many places averaging less than {{convert|10|in|mm|-1}} per year, mostly in the form of snow which stays on the ground almost the entire year. |
===Flora and fauna=== | ===Flora and fauna=== | ||
| − | |||
The Alaskan flora are diverse and abundant. Especially notable are its populations of large [[mammal]]s, including [[polar bear]]s, [[wolf]], [[moose]] and [[caribou]]. There are a great variety of fish, including [[Pacific salmon]]. However due to the low temperatures in much of Alaska there are relatively few species of [[reptile]]s and [[amphibians]]. | The Alaskan flora are diverse and abundant. Especially notable are its populations of large [[mammal]]s, including [[polar bear]]s, [[wolf]], [[moose]] and [[caribou]]. There are a great variety of fish, including [[Pacific salmon]]. However due to the low temperatures in much of Alaska there are relatively few species of [[reptile]]s and [[amphibians]]. | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ==Mammals== | ||
| + | For a complete list of mammals in Alaska, see [[List of Alaska mammals]]. | ||
| + | ===Brown bear=== | ||
| + | [[Image:Brown bear seaguls.jpg|thumb|250px|Brown bear at [[Katmai National Park]].]] | ||
| + | Alaska contains about 98% of the U.S. [[brown bear]] population and 70% of the total North American population.<ref name="brownbear"/> Brown bears can be found throughout the state, with the minor exceptions of the islands west of [[Unimak]] in the [[Aleutian Chain|Aleutians]], the islands south of [[Frederick Sound]] in southeast Alaska, and the islands in the [[Bering Sea]].<ref name="brownbear">Alaska Department of Fish & Game. [http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/biggame/brnbear.php "Brown Bear."] 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007.</ref> Most brown bears in Alaska are [[grizzly bear]]s (the [[subspecies]] of brown bear found throughout [[North America]]), but [[Kodiak Island]] is home to [[Kodiak bear]]s, another subspecies of brown bear that is the largest type of bear in the world.<ref name="brownbear"/> The brown bear is the top [[predator]] in Alaska. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The density of brown bear populations in Alaska varies according to the availability of food, and in some places is as high as one bear per [[square mile]].<ref name="brownbear"/> Alaska’s [[McNeil River Falls]] has one of the largest brown bear population densities in the state.<ref name="brownbear"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Brown bears can be dangerous if they are not treated with respect. Between the years 1998 and 2002, there were an average of 14.6 brown bear attacks per year in the state.<ref>from [http://www.absc.usgs.gov/research/brownbears/attacks/images/attacks_by_species.gif chart] in http://www.absc.usgs.gov/research/brownbears/attacks/bear-human_conflicts.htm</ref> Brown bears are most dangerous when they have just made a fresh kill, and when a sow has cubs.<ref name="brownbear"/><ref>Smith, Tom S. & Herrero, Steven. [http://www.absc.usgs.gov/research/brownbears/attacks/bear-human_conflicts.htm "A Century of Bear-Human Conflict in Alaska: Analyses & Implications."] 2003-9-22. Retrieved February 8, 2007.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Black bear=== | ||
| + | The [[black bear]] is much smaller than the brown bear. They are found in larger numbers on the mainland of Alaska, but are not found on the islands off of the [[Gulf of Alaska]] and the [[Seward Peninsula]].<ref name="blackbear">Alaska Department of Fish & Game. [http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/biggame/blkbear.php "Black Bear."] 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007.</ref> Black bears have been seen in Alaska in a few different shades of colors such as black, brown, cinnamon, and even a rare blue shade.<ref name="blackbear"/> They are widely scattered over Alaska, and pose more of a problem to humans because they come in close contact with them on a regular basis. They are considered a nuisance because they frequently stroll through local towns, camps, backyards, and streets because of their curiosity and easy food sources such as garbage.<ref name="blackbear"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Polar bear=== | ||
| + | [[Image:Polarbearsfamily.jpg|thumb|250px|Polar bears on the [[Beaufort Sea]] coast.]] | ||
| + | Alaska’s [[polar bear]] populations are concentrated along its Arctic [[coastlines]]. In the winter, they are most common in the [[Kuskokwim Delta]], [[St. Matthew Island]], and at the southernmost portion of [[St. Lawrence Island]]. During the summer months, they migrate to the coastlines of the [[Arctic Ocean]] and the Chukchi Sea.<ref name="polarbear">Alaska Department of Fish & Game. [http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/marine/polarbea.php "Polar Bear."] 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 8, 2007</ref> | ||
| + | There are two main polar bear populations in Alaska. The Chukchi population is found off in the western part of Alaska near the [[Wrangell Islands]], and the [[Beaufort Sea]] population is located near Alaska’s [[North Slope]].<ref name="polarbear"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Until the late 1940s, polar bears were hunted almost exclusively for subsistence by [[Inupiat]]s and dogs teams, though from the late 1940s until 1972, sport hunting by others took place.<ref name="polarbear"/> The 1959 [[Statehood Act]] set up a program for polar bear management, and further conservation efforts, including the the 1972 [[Marine Mammal Protection Act]], have limited polar bear hunts.<ref name="polarbear"/> Polar bear populations may be threatened by oil development and global warming.<ref name="polarbear"/><ref>http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/sci/tech/521451.stm</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Wolf=== | ||
| + | [[Image:Snowwolf.jpg|Wolf in the [[Kenai National Wildlife Refuge]]|thumb|250px]] | ||
| + | There are two [[subspecies]] of [[wolves]] in Alaska.<ref name="adfgwolf">Alaska Department of Fish & Game. [http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/furbear/wolf.php "Wolf."] 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007.</ref> The wolves in the southeastern part of Alaska are darker in color and smaller than those in the northern regions of the state. Coat colors of wolves range from black to white. Both gray and black wolves are common in Alaska. They are found on the mainland of Alaska, Unimak Island, and on all the major islands in the southeast except the islands of [[Baranof]], [[Chichagof]], and Admiralty.<ref name="adfgwolf"/> Alaskan game authorities suggest that there is an estimated one wolf per 25 square miles in Alaska, depending on the habitat that suits their needs.<ref name="adfgwolf"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The wolf population was once extremely fragile in Alaska. The [[mortality rate]] of these wolves was significantly affected by hunting and trapping, [[malnutrition]], disease, and conflict with humans.<ref name="adfgwolf"/> Wolves are considered of high value in Alaska for their beauty and contributions in controlling moose and caribou populations.<ref>Alaska Department of Fish & Game Division of Wildlife Conservation. [http://www.wc.adfg.state.ak.us/index.cfm?adfg=wolf.wolf_mgt "Wolf Management in Alaska with a Historic Perspective."] March 2002. Retrieved on February 10, 2007.</ref> Conservation efforts have been dedicated to ensure their future in Alaska and in the other states. The future of the wolves in Alaska is bright and secure. Wildlife authorities only fear that human expansion into their land will hinder their survival.<ref name="adfgwolf"/><ref>http://www.wc.adfg.state.ak.us/index.cfm?adfg=wolf.wolf_mgt</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Caribou=== | ||
| + | [[Image:Caribou.jpg|Caribou on the Alaska [[tundra]].|thumb|250px]] | ||
| + | Alaska is home to the ''Rangifer tarandus granti'' [[subspecies]] of [[caribou]].<ref name="caribou">Alaska Department of Fish & Game [http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/biggame/caribou.php "Caribou."] 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007.</ref> While other parts of the world use the terms "caribou" and "reindeer" synonymously, in Alaska "reindeer" refers exclusively to domesticated caribou.<ref name="caribou"/> Caribou in Alaska generally are found in [[tundra]] and mountain regions, where there are few trees. However, many herds spend the winter months in the [[boreal forest]] areas.<ref name="caribou"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Caribou are large-scale [[migration|migratory]] animals and have been known to travel up to 50 miles a day. The migratory activities of caribou are usually driven by weather conditions and food availability.<ref name="caribou"/> Changes in caribou migration can be problematic for Alaska Natives, who depend on Caribou for food.<ref name="caribou"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Caribou in Alaska are abundant; currently there are an estimated 950,000 in the state.<ref name="caribou"/> The populations of caribou are controlled by predators and hunters (who shoot about 22,000 caribou a year).<ref name="caribou"/> Though in the 1970s there were worries that oil drilling and development in Alaska would harm caribou populations, they seem to have adapted to the presence of humans, and so far there have been few adverse effects.<ref name="caribou"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Moose=== | ||
| + | [[Image:bigbullmoose.jpg|Bull moose in [[Chugach State Park]].|thumb|250px]] | ||
| + | The Alaska [[subspecies]] of [[moose]] (''Alces alces gigas'') is the largest in the world; adult males weigh 1,200 to 1,600 pounds (542-725 kg), and adult females weigh 800 to 1,300 pounds (364-591 kg)<ref name="moose">''Alaska Department of Fish & Game: Moose''. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007. http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/biggame/moose.php</ref> Alaska's substantial moose population is controlled by predators such as bears and wolves, which prey mainly on vulnerable calves, as well as by hunters.<ref name="moose"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because of the abundance of moose in Alaska, moose-human interactions are frequent. Moose have played an important role in the state's history; professional hunters once supplied moose meet to feed mining camps. [[Athapaskan Indians]] have hunted them to provide food as well as supplies for clothing and tools.<ref name="moose"/> They are now hunted frequently by big game hunters, who take 6,000 to 8,000 moose per year.<ref name="moose"/> Today, moose are often seen feeding and grazing along the state's highways. Moose can sometimes cause problems, as when they eat crops, stand in the middle of airfields, or dangerously cross the path of cars and trains.<ref name="moose"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Mountain goat=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Mountain goats]] are found in the rough and rocky mountain regions of Alaska, throughout the [[southeastern Panhandle]] and along the [[Coastal Mountains]] of the [[Cook Inlet]].<ref name="mg">''Alaska Department of Fish & Game: Mountain Goat''. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007. http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/biggame/mtn_goat.php</ref> Populations are generally confined in the areas of the [[Chugach]] and [[Wrangell Mountains]]. Mountain goats have been transplanted to the islands of Baranof and Kodiak, where they have maintained a steady population.<ref name="mg"/> The mountain goat is the only representation in North America of the goat-like [[ungulates]].<ref name="mg"/> Very little was known about mountain goats up until 1900.<ref name="mg"/> They constantly migrate to different areas from the alpine ridges in the summer, and to the tree-line in the winter. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===American bison=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[American bison]] originally came over to Alaska from [[Montana]] in 1928, where an original bison herd was released and started in the [[Delta Junction]]. Additional herds have developed along the [[Copper River]], [[Chitna River]], and Farewell from natural [[emigration]] and [[transplantation]].<ref name="bison1">''Alaska Department of Fish & Game: American Bison''. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007. http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/biggame/bison.php</ref> Small [[domesticated herd]]s have also developed near Kodiak, as well as on [[Papov Island]].<ref name="bison1"/> The American bison was once Alaska’s most common large land [[mammal]].<ref name="bison1"/> However, because of excessive hunting by Indians and [[commercial hunter]]s in the late 1800s, the American bison almost became an [[extinct]] species.<ref>''An Ultimate Ungulate Fact Sheet: American Bison''. 2004-5-22. Retrieved on February 8, 2007. http://www.ultimateungulate.com/Artiodactyla/Bison_bison.html</ref>In 1985, there were only 700 wild bison recorded in Alaska.<ref name="bison1"/> Since then, bison populations have slowly risen in Alaska. Today, bison can be seen along the highways of Alaska, and in the fields and meadows where tourists and photographers flock together to view them. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Dall sheep=== | ||
| + | [[Image:Dall sheep lambs.jpg|Dall sheep lambs on an Alaska cliff.|thumb|250px]] | ||
| + | [[Dall sheep]] live in the mountain regions of Alaska where there is rocky terrain and steep, inclined land.<ref name="sheep">''Alaska Department of Fish & Game: Dall Sheep''. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 8, 2007. [http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/biggame/dallshee.php]</ref> The mountain setting is an ideal place for them to rest and feed.<ref name="sheep"/> They are occasionally seen below their usual high elevation only when food is scarce. Alaska contains a good size population of dall sheep. In their rocky environment, they are able to avoid predators and human activities. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Orca whale=== | ||
| + | The [[orca]] whale is also known as the killer whale because it has been known to attack and eat other whales, and large prey animals such as [[pinniped|seals]] and [[sea lions]].<ref name="orca">''Alaska Department of Fish & Game: Orca''. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 8, 2007. [http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/marine/orca.php]</ref> Orcas are scattered among the [[Continental Shelf]] from southeast Alaska through the Aleutian Islands. They can also be seen in the waters of [[Prince William Sound]].<ref name="orca"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Fish== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Alaska has quite a variety of [[fish]] species. Its lakes, rivers, and oceans are home to fish such as [[trout]], [[salmon]], [[char]], [[grayling]], [[lampreys]], [[lingcod]], [[pike]], and [[whitefish]].<ref name="note"/> Every year, the [[salmon]] participate in the great spawning migration up against the river currents. They do this in large numbers and are frequently seen jumping out of the water. This is a physical effort of them trying to go against the current. Bears, particularly brown bears, take advantage of this event by swarming to the rivers, and indulging in the salmon feast. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Birds== | ||
| + | [[Image:Haliaeetus leucocephalus2.jpg|Bald Eagle on [[Kodiak Island]].|thumb|150px]] | ||
| + | Birds in Alaska include: | ||
| + | * [[American Dipper]] | ||
| + | * [[Boreal Owl]] | ||
| + | * [[Canadian Goose]] | ||
| + | * [[Bald Eagle]] | ||
| + | * [[Great Gray Owl]] | ||
| + | * [[Northern Hawk Owl]] | ||
| + | * [[Harlequin Duck]] | ||
| + | * [[Osprey]] | ||
| + | * [[Sandhill Crane]]<ref name="note"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Amphibians and reptiles== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Alaska’s extreme temperatures make it an uncharacteristic location to host many species of [[amphibians]] and [[reptiles]]. In fact, it only has two species of [[frogs]]. They are the [[spotted frog]] and [[wood frog]]. The only species of [[toad]] in Alaska is the [[western toad]].<ref>''Alaska Department of Fish & Game: Frogs & Toads''. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007. [http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/amphibia/amphib.php]</ref> The Alaskan waters are home to two species of [[turtles]]. They are the [[leatherback sea turtle]] and the [[green sea turtle]].<ref>''Alaska Department of Fish & Game: Turtle''. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007. [http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/amphibia/turtle.php]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Endangered Species== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Alaska has one of the smallest [[endangered species]] lists. According to the [[Alaska Department of Fish & Game]] there are only 5 endangered species. They are: | ||
| + | * [[Eskimo Curlew]] | ||
| + | * Humpback Whale | ||
| + | * Bowhead Whale | ||
| + | * Blue Whale | ||
| + | * [[Short-Tailed Albatross]]<ref>''Endangered & Threatened Species Curriculum''. Center For Alaskan Coastal Studies. 2006. Retrieved on February 6, 2007. [http://www.akcoastalstudies.org/Endangered.htm]</ref><ref>''Alaska Department of Fish & Game Division of Wildlife Conservation: State of Alaska Endangered Species List''. 2007. Retrieved on February 7, 2007. [http://www.wildlife.alaska.gov/index.cfm?adfg=endangered.list]</ref> | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| Line 108: | Line 194: | ||
[[Image:Miners climb Chilkoot.jpg|thumb|right|Miners and prospectors climb the [[Chilkoot Trail]] during the [[Klondike Gold Rush]].]] | [[Image:Miners climb Chilkoot.jpg|thumb|right|Miners and prospectors climb the [[Chilkoot Trail]] during the [[Klondike Gold Rush]].]] | ||
{{main|History of Alaska}} | {{main|History of Alaska}} | ||
| − | At the end of the [[Upper Paleolithic]] Period (around 12,000 | + | At the end of the [[Upper Paleolithic]] Period (around 12,000 B.C.E.), [[Asiatic]] groups crossed the [[Bering Land Bridge]] into what is now western Alaska. At the time of European contact by the [[Russian colonization of the Americas|Russian explorers]], the area was populated by [[Alaska Native]] groups. |
The first European contact with Alaska occurred in 1741, when [[Vitus Bering]] led an [[second Kamchatka expedition|expedition]] for the Russian Navy aboard the ''St. Peter''.<ref>http://memory.loc.gov/ammem/today/oct25.html</ref> After his crew returned to Russia bearing sea otter pelts judged to be the finest [[fur]] in the world, small associations of fur traders began to sail from the shores of Siberia towards the Aleutian islands. The first permanent European settlement was founded in 1784, and the [[Russian-American Company]] carried out an expanded colonization program during the early to mid-1800s. Despite these efforts, the Russians never fully colonized Alaska, and the [[colony]] was never very profitable. [[William H. Seward]], the [[United States Secretary of State|U.S. Secretary of State]], engineered the [[Alaska purchase|Alaskan purchase]] in 1867 for $7.2 million, a transaction for a short while called [[Seward's folly]]. | The first European contact with Alaska occurred in 1741, when [[Vitus Bering]] led an [[second Kamchatka expedition|expedition]] for the Russian Navy aboard the ''St. Peter''.<ref>http://memory.loc.gov/ammem/today/oct25.html</ref> After his crew returned to Russia bearing sea otter pelts judged to be the finest [[fur]] in the world, small associations of fur traders began to sail from the shores of Siberia towards the Aleutian islands. The first permanent European settlement was founded in 1784, and the [[Russian-American Company]] carried out an expanded colonization program during the early to mid-1800s. Despite these efforts, the Russians never fully colonized Alaska, and the [[colony]] was never very profitable. [[William H. Seward]], the [[United States Secretary of State|U.S. Secretary of State]], engineered the [[Alaska purchase|Alaskan purchase]] in 1867 for $7.2 million, a transaction for a short while called [[Seward's folly]]. | ||
| Line 116: | Line 202: | ||
During [[World War II]], three of the outer [[Aleutian Islands]]—Attu, Agattu and Kiska—were the only part of North America occupied by the Japanese. The [[battle of the Aleutian Islands|battle to recover the islands]] became a matter of national pride. The wartime construction of [[military bases]] and the [[Alaska Highway]] also contributed to the population growth of some Alaskan cities. | During [[World War II]], three of the outer [[Aleutian Islands]]—Attu, Agattu and Kiska—were the only part of North America occupied by the Japanese. The [[battle of the Aleutian Islands|battle to recover the islands]] became a matter of national pride. The wartime construction of [[military bases]] and the [[Alaska Highway]] also contributed to the population growth of some Alaskan cities. | ||
| − | Alaska was granted statehood on | + | Alaska was granted statehood on January 3, 1959. |
In 1964, the massive "[[Good Friday Earthquake]]" killed 131 people and leveled several villages. | In 1964, the massive "[[Good Friday Earthquake]]" killed 131 people and leveled several villages. | ||
| Line 123: | Line 209: | ||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
As of 2005, Alaska has an estimated population of 663,661, which is an increase of 5,906, or 0.9%, from the prior year and an increase of 36,730, or 5.9%, since the year 2000. In 2000, Alaska was ranked 48th out of 50 states by population.<ref>http://www.census.gov/population/cen2000/phc-t2/tab01.txt</ref> Alaska is the least densely populated state at 0.2849 people per square kilometer (1.1 per square mile), with the next nearest ranking state, Wyoming, at 1.3208 (5.1 per square mile), and the most densely populated, New Jersey, at 293.792 people per square kilometer (1,134.4 per square mile). | As of 2005, Alaska has an estimated population of 663,661, which is an increase of 5,906, or 0.9%, from the prior year and an increase of 36,730, or 5.9%, since the year 2000. In 2000, Alaska was ranked 48th out of 50 states by population.<ref>http://www.census.gov/population/cen2000/phc-t2/tab01.txt</ref> Alaska is the least densely populated state at 0.2849 people per square kilometer (1.1 per square mile), with the next nearest ranking state, Wyoming, at 1.3208 (5.1 per square mile), and the most densely populated, New Jersey, at 293.792 people per square kilometer (1,134.4 per square mile). | ||
| Line 180: | Line 257: | ||
Alaska has a well-developed [[ferry]] system, known as the [[Alaska Marine Highway]], which serves the cities of [[Alaska Panhandle|Southeast Alaska]] and the [[Alaska Peninsula]]. The system also operates a ferry service from [[Bellingham, Washington|Bellingham]], [[Washington]] up the [[Inside Passage]] to [[Skagway, Alaska|Skagway]]. The [[Inter-Island Ferry Authority]] also serves as an important marine link in the [[Prince of Wales Island, Alaska|Prince of Wales Island]] region of Southeast. Tourist sea travel is also popular on [[Alaska cruises]]. | Alaska has a well-developed [[ferry]] system, known as the [[Alaska Marine Highway]], which serves the cities of [[Alaska Panhandle|Southeast Alaska]] and the [[Alaska Peninsula]]. The system also operates a ferry service from [[Bellingham, Washington|Bellingham]], [[Washington]] up the [[Inside Passage]] to [[Skagway, Alaska|Skagway]]. The [[Inter-Island Ferry Authority]] also serves as an important marine link in the [[Prince of Wales Island, Alaska|Prince of Wales Island]] region of Southeast. Tourist sea travel is also popular on [[Alaska cruises]]. | ||
| − | Anchorage itself, and to a lesser extent Fairbanks, is served by [[Ted Stevens Anchorage International Airport#Airlines and destinations|many major airlines]]. [[Alaska Airlines]] | + | Anchorage itself, and to a lesser extent Fairbanks, is served by [[Ted Stevens Anchorage International Airport#Airlines and destinations|many major airlines]]. [[Alaska Airlines]]—which serves Anchorage, Fairbanks, and regional hubs—is the only major airline offering in-state travel with jet service (sometimes in combination cargo and passenger [[Boeing 737]]-400s). Small regional commuter airlines provide the bulk of remaining commercial flights. The smallest towns and villages must rely on scheduled or chartered [[Alaskan Bush|Bush]] flying services using general aviation aircraft such as the [[Cessna Caravan]], the most popular aircraft in use in the state. |
In areas not served by road or rail, primary summer transportation is by [[all-terrain vehicle]] and primary winter transportation is by [[snowmobile]], or "snow machine," as it is called in Alaska. | In areas not served by road or rail, primary summer transportation is by [[all-terrain vehicle]] and primary winter transportation is by [[snowmobile]], or "snow machine," as it is called in Alaska. | ||
| Line 189: | Line 266: | ||
As with the federal government of the United States, power in Alaska is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. | As with the federal government of the United States, power in Alaska is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. | ||
| − | The executive branch is headed by the [[Governor of Alaska|governor]]. The current governor is [[Sarah Palin]], a [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican]] whose term began | + | The executive branch is headed by the [[Governor of Alaska|governor]]. The current governor is [[Sarah Palin]], a [[Republican Party (United States)|Republican]] whose term began December 4, 2006. She is the first female governor of Alaska, as well as the youngest. The current [[Lieutenant Governor of Alaska]] is [[Sean Parnell]]. The offices of governor and lieutenant governor have four-year terms. |
The [[Alaska Legislature]] is a [[bicameral]] body consisting of the [[Alaska Senate|Senate]], whose 20 members serve four-year terms, and the [[Alaska House of Representatives|House of Representatives]], whose 40 members serve two-year terms. | The [[Alaska Legislature]] is a [[bicameral]] body consisting of the [[Alaska Senate|Senate]], whose 20 members serve four-year terms, and the [[Alaska House of Representatives|House of Representatives]], whose 40 members serve two-year terms. | ||
| Line 280: | Line 357: | ||
Negative aspects of health in Alaska include limited access to prenatal care (36.1% of women received inadequate prenatal care; 4th worst among states),<ref name="uhf"/> low immunization rates (24.6% of children aged 19 to 35 months fail to receive complete immunizations; 6th worst),<ref name="uhf"/> and high rates of smoking (24.9%, 6th highest).<ref name="uhf"/> | Negative aspects of health in Alaska include limited access to prenatal care (36.1% of women received inadequate prenatal care; 4th worst among states),<ref name="uhf"/> low immunization rates (24.6% of children aged 19 to 35 months fail to receive complete immunizations; 6th worst),<ref name="uhf"/> and high rates of smoking (24.9%, 6th highest).<ref name="uhf"/> | ||
| − | Alaska has long had a problem with alcohol use and abuse. Many rural communities in Alaska have outlawed its import. "Dry" | + | Alaska has long had a problem with alcohol use and abuse. Many rural communities in Alaska have outlawed its import. "Dry," "wet," and "damp" are terms describing a community's laws on liquor consumption. This problem directly relates to Alaska's high rate of [[Fetal alcohol syndrome]] (FAS) as well as contributing to the high rate of suicides. This is a controversial topic for many residents. |
[[Domestic abuse]] and other violent crimes are also at notoriously high levels in the state; this is in part linked to alcohol abuse. | [[Domestic abuse]] and other violent crimes are also at notoriously high levels in the state; this is in part linked to alcohol abuse. | ||
| Line 304: | Line 381: | ||
There are many established music festivals in Alaska, including the [[Alaska Folk Festival]], the [[Fairbanks Winter Music Fest]] the [[Anchorage Folk Festival]], the [[Athabascan Old-Time Fiddling Festival]], and the [[Sitka Summer Music Festival]]. The most prominent [[symphony]] in Alaska is the [[Anchorage Symphony Orchestra]], though the [[Juneau Symphony]] is also notable. The [[Anchorage Opera]] is currently the state's only professional opera company, though there are several volunteer and semi-professional organizations in the state as well. | There are many established music festivals in Alaska, including the [[Alaska Folk Festival]], the [[Fairbanks Winter Music Fest]] the [[Anchorage Folk Festival]], the [[Athabascan Old-Time Fiddling Festival]], and the [[Sitka Summer Music Festival]]. The most prominent [[symphony]] in Alaska is the [[Anchorage Symphony Orchestra]], though the [[Juneau Symphony]] is also notable. The [[Anchorage Opera]] is currently the state's only professional opera company, though there are several volunteer and semi-professional organizations in the state as well. | ||
| − | The official [[List of U.S. state songs|state song]] of Alaska is "[[Alaska's Flag]]" | + | The official [[List of U.S. state songs|state song]] of Alaska is "[[Alaska's Flag]]," which was adopted in 1955; it celebrates the [[flag of Alaska]]. |
==Sports and recreation== | ==Sports and recreation== | ||
| Line 357: | Line 434: | ||
| preceded = [[Arizona]] | | preceded = [[Arizona]] | ||
| office = [[List of U.S. states by date of statehood]] | | office = [[List of U.S. states by date of statehood]] | ||
| − | | years = Admitted on | + | | years = Admitted on January 3, 1959 (49th) |
| succeeded = [[Hawaii]] | | succeeded = [[Hawaii]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 01:59, 4 August 2007
Template:US state
Alaska is a state of the United States of America that is located in the extreme northwest portion of North America, west of Canada. It is the largest U.S. state in terms of area (by a substantial margin), along with being one of the wealthiest and most racially diverse.[1]
The area that became Alaska was purchased from Russian interests on October 18 1867 for $7,200,000. The land went through several administrative changes before becoming an organized territory in 1912 and the 49th state of the U.S. on January 3, 1959. The name "Alaska" is derived from the Aleut alaxsxaq, meaning "the mainland," or more literally "the object towards which the action of the sea is directed".[2]
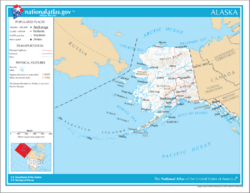
Geography
Alaska does not border any U.S. state; it abuts the Yukon and British Columbia, Canada, to the east, the Gulf of Alaska and the Pacific Ocean to the south, the Bering Sea, Bering Strait, and Chukchi Sea to the west, and the Beaufort Sea and the Arctic Ocean to the north.
Alaska has the largest land area of any U.S. state at 570,380 square miles (1,477,277 km²) and is over twice as large as Texas, the next largest state.
Because the state is so large, its geographical characteristics vary widely by region. Southcentral Alaska, the state's southern coastal region, contains Anchorage (Alaska's largest city) and most of the state's population. Southeast Alaska is home to several mid-size towns (including the state capital Juneau), tidewater glaciers, and extensive forests. Southwest Alaska is largely coastal, sparsely populated, and unconnected to the road system; it is known for wet and stormy weather, tundra landscapes. The Alaska Interior is marked by large braided rivers and Arctic tundra lands and shorelines. The Aleutian Islands that extend west from the southern tip of the Alaska Peninsula contain many active volcanoes. The North Slope is known for its oil reservoirs and extreme climate. The Alaskan Bush is a general term encompassing any remote part of the state.
With its numerous islands, Alaska has nearly 34,000 miles (54,720 km) of tidal shoreline (the most shoreline in the United States ). Alaska is home to 3.5 million lakes of 20 acres (8 ha) or larger [3]. Marshlands and wetland permafrost cover 188,320 square miles (487,747 km²) (mostly in northern, western and southwest flatlands). Frozen water, in the form of glacier ice, covers some 16,000 square miles (41,440 km²) of land and 1,200 square miles (3,110 km²) of tidal zone.
Land ownership and protected lands
The northeast corner of Alaska is covered by the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, which covers 19,049,236 acres (77,090 km²). Much of the northwest is covered by the larger National Petroleum Reserve–Alaska, which covers around 23,000,000 acres (93,100 km²).
According to an October 1998 report by the United States Bureau of Land Management, approximately 65% of Alaska is owned and managed by the U.S. federal government as national forests, national parks, and national wildlife refuges. Of these, the Bureau of Land Management manages 87 million acres (350,000 km²), or 23.8% of the state. The Arctic National Wildlife Refuge is managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service.
Of the land area, the State of Alaska owns 24.5%; another 10% is managed by thirteen regional and dozens of local Native corporations created under the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act. Various private interests own the remaining land, totaling less than 1%.
Climate
The climate of Alaska varies widely by region.
The climate in southeast Alaska is similar to that of Seattle, with a mid-latitude oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification Cfb) in the southern sections and a subarctic oceanic climate (Köppen Cfc) in the northern parts. This is both the wettest part of Alaska as well as the warmest; it is the only part of the state in which the average daytime high temperature is above freezing during the winter.
The climate in southcentral Alaska, is generally mild by Alaskan standards, due in large part to its proximity to the coast. It is a subarctic climate (Köppen Dfc) due to its short, cool summers.
The climate of Western Alaska is a subarctic oceanic climate in the southwest and a continental subarctic climate farther north. Precipitation in this area varies widely: the northern side of the Seward Peninsula receives 10 inches (250 mm) of precipitation annually, while some locations between Dillingham and Bethel receive around 100 inches (2,540 mm).[4]
Alaska's interior has an extreme subarctic climate. Summer temperatures may reach into the 80s°F (near 30 °C), while winter temperatures can fall below −60 °F (-52 °C). Interior locations often receive less than 10 inches (250 mm) precipitation annually.
The climate in the extreme north of Alaska is a polar climate (Köppen ET) with long, very cold winters and short, cool summers. Even in July, the average low temperature is barely above freezing in Barrow, at 34 °F (2 °C).[5] Precipitation is light in this part of Alaska, with many places averaging less than 10 inches (250 mm) per year, mostly in the form of snow which stays on the ground almost the entire year.
Flora and fauna
The Alaskan flora are diverse and abundant. Especially notable are its populations of large mammals, including polar bears, wolf, moose and caribou. There are a great variety of fish, including Pacific salmon. However due to the low temperatures in much of Alaska there are relatively few species of reptiles and amphibians.
Mammals
For a complete list of mammals in Alaska, see List of Alaska mammals.
Brown bear
Alaska contains about 98% of the U.S. brown bear population and 70% of the total North American population.[6] Brown bears can be found throughout the state, with the minor exceptions of the islands west of Unimak in the Aleutians, the islands south of Frederick Sound in southeast Alaska, and the islands in the Bering Sea.[6] Most brown bears in Alaska are grizzly bears (the subspecies of brown bear found throughout North America), but Kodiak Island is home to Kodiak bears, another subspecies of brown bear that is the largest type of bear in the world.[6] The brown bear is the top predator in Alaska.
The density of brown bear populations in Alaska varies according to the availability of food, and in some places is as high as one bear per square mile.[6] Alaska’s McNeil River Falls has one of the largest brown bear population densities in the state.[6]
Brown bears can be dangerous if they are not treated with respect. Between the years 1998 and 2002, there were an average of 14.6 brown bear attacks per year in the state.[7] Brown bears are most dangerous when they have just made a fresh kill, and when a sow has cubs.[6][8]
Black bear
The black bear is much smaller than the brown bear. They are found in larger numbers on the mainland of Alaska, but are not found on the islands off of the Gulf of Alaska and the Seward Peninsula.[9] Black bears have been seen in Alaska in a few different shades of colors such as black, brown, cinnamon, and even a rare blue shade.[9] They are widely scattered over Alaska, and pose more of a problem to humans because they come in close contact with them on a regular basis. They are considered a nuisance because they frequently stroll through local towns, camps, backyards, and streets because of their curiosity and easy food sources such as garbage.[9]
Polar bear
Alaska’s polar bear populations are concentrated along its Arctic coastlines. In the winter, they are most common in the Kuskokwim Delta, St. Matthew Island, and at the southernmost portion of St. Lawrence Island. During the summer months, they migrate to the coastlines of the Arctic Ocean and the Chukchi Sea.[10] There are two main polar bear populations in Alaska. The Chukchi population is found off in the western part of Alaska near the Wrangell Islands, and the Beaufort Sea population is located near Alaska’s North Slope.[10]
Until the late 1940s, polar bears were hunted almost exclusively for subsistence by Inupiats and dogs teams, though from the late 1940s until 1972, sport hunting by others took place.[10] The 1959 Statehood Act set up a program for polar bear management, and further conservation efforts, including the the 1972 Marine Mammal Protection Act, have limited polar bear hunts.[10] Polar bear populations may be threatened by oil development and global warming.[10][11]
Wolf
There are two subspecies of wolves in Alaska.[12] The wolves in the southeastern part of Alaska are darker in color and smaller than those in the northern regions of the state. Coat colors of wolves range from black to white. Both gray and black wolves are common in Alaska. They are found on the mainland of Alaska, Unimak Island, and on all the major islands in the southeast except the islands of Baranof, Chichagof, and Admiralty.[12] Alaskan game authorities suggest that there is an estimated one wolf per 25 square miles in Alaska, depending on the habitat that suits their needs.[12]
The wolf population was once extremely fragile in Alaska. The mortality rate of these wolves was significantly affected by hunting and trapping, malnutrition, disease, and conflict with humans.[12] Wolves are considered of high value in Alaska for their beauty and contributions in controlling moose and caribou populations.[13] Conservation efforts have been dedicated to ensure their future in Alaska and in the other states. The future of the wolves in Alaska is bright and secure. Wildlife authorities only fear that human expansion into their land will hinder their survival.[12][14]
Caribou

Alaska is home to the Rangifer tarandus granti subspecies of caribou.[15] While other parts of the world use the terms "caribou" and "reindeer" synonymously, in Alaska "reindeer" refers exclusively to domesticated caribou.[15] Caribou in Alaska generally are found in tundra and mountain regions, where there are few trees. However, many herds spend the winter months in the boreal forest areas.[15]
Caribou are large-scale migratory animals and have been known to travel up to 50 miles a day. The migratory activities of caribou are usually driven by weather conditions and food availability.[15] Changes in caribou migration can be problematic for Alaska Natives, who depend on Caribou for food.[15]
Caribou in Alaska are abundant; currently there are an estimated 950,000 in the state.[15] The populations of caribou are controlled by predators and hunters (who shoot about 22,000 caribou a year).[15] Though in the 1970s there were worries that oil drilling and development in Alaska would harm caribou populations, they seem to have adapted to the presence of humans, and so far there have been few adverse effects.[15]
Moose
The Alaska subspecies of moose (Alces alces gigas) is the largest in the world; adult males weigh 1,200 to 1,600 pounds (542-725 kg), and adult females weigh 800 to 1,300 pounds (364-591 kg)[16] Alaska's substantial moose population is controlled by predators such as bears and wolves, which prey mainly on vulnerable calves, as well as by hunters.[16]
Because of the abundance of moose in Alaska, moose-human interactions are frequent. Moose have played an important role in the state's history; professional hunters once supplied moose meet to feed mining camps. Athapaskan Indians have hunted them to provide food as well as supplies for clothing and tools.[16] They are now hunted frequently by big game hunters, who take 6,000 to 8,000 moose per year.[16] Today, moose are often seen feeding and grazing along the state's highways. Moose can sometimes cause problems, as when they eat crops, stand in the middle of airfields, or dangerously cross the path of cars and trains.[16]
Mountain goat
Mountain goats are found in the rough and rocky mountain regions of Alaska, throughout the southeastern Panhandle and along the Coastal Mountains of the Cook Inlet.[17] Populations are generally confined in the areas of the Chugach and Wrangell Mountains. Mountain goats have been transplanted to the islands of Baranof and Kodiak, where they have maintained a steady population.[17] The mountain goat is the only representation in North America of the goat-like ungulates.[17] Very little was known about mountain goats up until 1900.[17] They constantly migrate to different areas from the alpine ridges in the summer, and to the tree-line in the winter.
American bison
The American bison originally came over to Alaska from Montana in 1928, where an original bison herd was released and started in the Delta Junction. Additional herds have developed along the Copper River, Chitna River, and Farewell from natural emigration and transplantation.[18] Small domesticated herds have also developed near Kodiak, as well as on Papov Island.[18] The American bison was once Alaska’s most common large land mammal.[18] However, because of excessive hunting by Indians and commercial hunters in the late 1800s, the American bison almost became an extinct species.[19]In 1985, there were only 700 wild bison recorded in Alaska.[18] Since then, bison populations have slowly risen in Alaska. Today, bison can be seen along the highways of Alaska, and in the fields and meadows where tourists and photographers flock together to view them.
Dall sheep
Dall sheep live in the mountain regions of Alaska where there is rocky terrain and steep, inclined land.[20] The mountain setting is an ideal place for them to rest and feed.[20] They are occasionally seen below their usual high elevation only when food is scarce. Alaska contains a good size population of dall sheep. In their rocky environment, they are able to avoid predators and human activities.
Orca whale
The orca whale is also known as the killer whale because it has been known to attack and eat other whales, and large prey animals such as seals and sea lions.[21] Orcas are scattered among the Continental Shelf from southeast Alaska through the Aleutian Islands. They can also be seen in the waters of Prince William Sound.[21]
Fish
Alaska has quite a variety of fish species. Its lakes, rivers, and oceans are home to fish such as trout, salmon, char, grayling, lampreys, lingcod, pike, and whitefish.[22] Every year, the salmon participate in the great spawning migration up against the river currents. They do this in large numbers and are frequently seen jumping out of the water. This is a physical effort of them trying to go against the current. Bears, particularly brown bears, take advantage of this event by swarming to the rivers, and indulging in the salmon feast.
Birds

Birds in Alaska include:
- American Dipper
- Boreal Owl
- Canadian Goose
- Bald Eagle
- Great Gray Owl
- Northern Hawk Owl
- Harlequin Duck
- Osprey
- Sandhill Crane[22]
Amphibians and reptiles
Alaska’s extreme temperatures make it an uncharacteristic location to host many species of amphibians and reptiles. In fact, it only has two species of frogs. They are the spotted frog and wood frog. The only species of toad in Alaska is the western toad.[23] The Alaskan waters are home to two species of turtles. They are the leatherback sea turtle and the green sea turtle.[24]
Endangered Species
Alaska has one of the smallest endangered species lists. According to the Alaska Department of Fish & Game there are only 5 endangered species. They are:
History
Template:Alaska History
At the end of the Upper Paleolithic Period (around 12,000 B.C.E.), Asiatic groups crossed the Bering Land Bridge into what is now western Alaska. At the time of European contact by the Russian explorers, the area was populated by Alaska Native groups.
The first European contact with Alaska occurred in 1741, when Vitus Bering led an expedition for the Russian Navy aboard the St. Peter.[27] After his crew returned to Russia bearing sea otter pelts judged to be the finest fur in the world, small associations of fur traders began to sail from the shores of Siberia towards the Aleutian islands. The first permanent European settlement was founded in 1784, and the Russian-American Company carried out an expanded colonization program during the early to mid-1800s. Despite these efforts, the Russians never fully colonized Alaska, and the colony was never very profitable. William H. Seward, the U.S. Secretary of State, engineered the Alaskan purchase in 1867 for $7.2 million, a transaction for a short while called Seward's folly.
In the 1890s, gold rushes in Alaska and the nearby Yukon Territory brought thousands of miners and settlers to Alaska. Alaska was granted territorial status in 1912.
During World War II, three of the outer Aleutian Islands—Attu, Agattu and Kiska—were the only part of North America occupied by the Japanese. The battle to recover the islands became a matter of national pride. The wartime construction of military bases and the Alaska Highway also contributed to the population growth of some Alaskan cities.
Alaska was granted statehood on January 3, 1959.
In 1964, the massive "Good Friday Earthquake" killed 131 people and leveled several villages.
The 1968 discovery of oil at Prudhoe Bay and the 1977 completion of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline led to an oil boom. In 1989, the Exxon Valdez hit a reef in the Prince William Sound, spilling between 11 and 35 million US gallons (42,000 and 130,000 m³) of crude oil over 1,100 miles (1,600 km) of coastline. Today, the battle between philosophies of development and conservation is seen in the contentious debate over oil drilling in the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge.
Demographics
As of 2005, Alaska has an estimated population of 663,661, which is an increase of 5,906, or 0.9%, from the prior year and an increase of 36,730, or 5.9%, since the year 2000. In 2000, Alaska was ranked 48th out of 50 states by population.[28] Alaska is the least densely populated state at 0.2849 people per square kilometer (1.1 per square mile), with the next nearest ranking state, Wyoming, at 1.3208 (5.1 per square mile), and the most densely populated, New Jersey, at 293.792 people per square kilometer (1,134.4 per square mile).
Race and ancestry
According to the U.S. Census Bureau's 2005 American Community Survey, 66.7% of Alaska residents are non-Hispanic whites.[29] American Indians and Alaska Natives make up 14.2% of the state's population (or 18.3% if those indicating both white and American Indian/Alaska Native races are included),[29] the largest proportion of any state.[citation needed] Multiracial people are the third largest group in the state, totaling 6.9% of the population.[29] Hispanics, Asians, African Americans, and Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islanders make up 4.8%, 4.5%, 3.4%, and 0.5% of the population, respectively.[29]
The largest self-reported ancestry groups in the state are German (19.0%),[30] Alaska Native or American Indian (15.6%),[citation needed] Irish (12.7%),[30] English (11.0%),[30] American (6.0%),[30] and Norwegian (4.4%).[30]
The vast, sparsely populated regions of northern and western Alaska are primarily inhabited by Alaska Natives, who are also numerous in the southeast. Anchorage, Fairbanks, and other parts of south-central and southeast Alaska have many whites of northern and Western European ancestry. The Wrangell-Petersburg area has many residents of Scandinavian ancestry and the Aleutians contain a large Filipino population. Most of the state's black population lives in Anchorage. Fairbanks also has a sizable black population.
Languages
According to the 2000 U.S. Census, 85.7% of Alaska residents age 5 and older speak English at home. The next most common languages are Spanish (2.88%), Yupik (2.87%), Tagalog (1.54%), and Iñupiaq (1.06%).[31] A total of 5.2% of Alaskans speak one of the state's 22 indigenous languages, known locally as Native languages.
Religion
The largest study of American religious beliefs, the American Religious Identification Survey, did not include Alaska in its coverage.[32] According to an NBC exit poll taken during the 2004 presidential election, 52% of Alaskan voters were "Protestant/other Christian," 17% were Catholic, 1% were Jewish, 11% were "something else," and 19% were not religious.[33] Alaska has a relatively large Russian Orthodox population as a result of early Russian colonization and missionary work among Alaska Natives.[34] (In 2004, church officials estimated that there were up to 50,000 Russian Orthodox individuals in the state, comprising approximately 8% of the state's population.[34]) In 1990, 0.51% of the state's population was Quaker, the largest percentage of any state.[35]
Economy
The state's 2005 total gross state product was $39.9 billion. Its per-capita GSP for 2005 was $60,079, 3rd in the nation. Alaska's economy relies heavily on petroleum extraction, with more than 80 percent of the state's revenues derived from this industry. Alaska's main export product (excluding oil and natural gas) is seafood, primarily salmon, cod, pollock and crab. Agriculture represents only a fraction of the Alaska economy. Agricultural production is primarily for consumption within the state and includes nursery stock, dairy products, vegetables, and livestock. Manufacturing is limited, with most foodstuffs and general goods imported from elsewhere. Employment is primarily in government and industries such as natural resource extraction, shipping, and transportation. Military bases are a significant component of the economy in both Fairbanks and Anchorage. Its industrial outputs are crude petroleum, natural gas, coal, gold, precious metals, zinc and other mining, seafood processing, timber and wood products. There is also a growing service and tourism sector. Tourists have contributed to the economy by supporting local lodging.
Alaska's economy is heavily dependent on increasingly expensive diesel fuel for heating, transportation, electric power and light. Though wind and hydroelectric power are abundant and underutilized, proposals for state-wide energy systems (e.g. with special low-cost electric interties) were judged uneconomical (at the time of the report, 2001) due to low (<$0.50/Gal) fuel prices, long distances and low population.[36] The cost of a gallon of gas in urban Alaska today is usually $0.30-$0.60 higher than the national average; prices in rural areas are generally significantly higher but vary widely depending on transportation costs, seasonal usage peaks, nearby petroleum development infrastructure and many other factors.
Permanent Fund
The Alaska Permanent Fund is a legislatively-controlled appropriation established in 1976 to manage a surplus in state petroleum revenues from the recently constructed Trans-Alaska Pipeline System. From its initial principal of $734,000, the fund has grown to $38 billion as a result of oil royalties and capital investment programs. Starting in 1982, dividends from the fund's annual growth have been paid out each year to eligible Alaskans, with amounts ranging from $331.29 in 1984, to $1963.86 in 2000.[37]
Cost of living
The cost of goods in Alaska has long been higher than in the contiguous 48 states. This has changed for the most part in Anchorage and to a lesser extent in Fairbanks, where the cost of living has dropped somewhat in the past five years. Federal Government employees, particularly United States Postal Service (USPS) workers and active-duty military members, receive a Cost Of Living Allowance usually set at 24% of base pay because, while the cost of living has gone down, it is still one of the highest in the country.
The expanding presence of discount and chain stores in Alaska during the 1990s did much to lower prices.[38] However, rural Alaska suffers from extremely high prices for food and consumer goods, compared to the rest of the country due to the relatively limited transportation infrastructure. Many rural residents come in to these cities and purchase food and goods in bulk from warehouse clubs like Costco and Sam's Club. Some have embraced the free shipping offers of some online retailers to purchase items much more cheaply than they could in their own communities, if they are available at all.
Taxes
Alaska has the lowest individual tax burden in the US[39], and is one of only six states with no state sales tax and one of seven states that do not levy an individual income tax. To finance state government operations, Alaska depends primarily on petroleum revenues. The Department of Revenue Tax Division reports regularly on the state's revenue sources. The Department also issues an annual overview of its operations, including new state laws that directly affect the tax division.
While Alaska has no state sales tax, 89 municipalities collect a local sales tax, with a range of between 1 percent and 7 percent. Typical sales tax rates are 3 to 5 percent. Other types of local taxes levied include raw fish taxes, hotel, motel, and B&B “bed” taxes, severance taxes, liquor and tobacco taxes, gaming (pull tabs) taxes, tire taxes and fuel transfer taxes. A percentage of revenue collected from certain state taxes and license fees (such as petroleum, aviation motor fuel, telephone cooperative) is shared with municipalities in Alaska.
Property taxes are relatively low, with only 25 of 161 incorporated municipalities or boroughs in the state assessing property taxes.[citation needed] Fairbanks has one of the highest property taxes in the state as no sales or income taxes are assessed in the Fairbanks North Star Borough (FNSB). A sales tax for the FNSB has been voted on many times, but has yet to be approved, leading law makers to increase taxes dramatically on other goods such as liquor and tobacco. The average per capita property tax paid in all municipalities, excluding oil and gas properties, was US$999 (2003 data).[citation needed]
Transportation
Alaska's road system covers a relatively small area of the state, linking the central population centers and the Alaska Highway, the principal route out of the state through Canada. (Most cities and villages in the state are accessible only by sea or air.) The state capital, Juneau, is not accessible by road, which has spurred several debates over the decades about moving the capital to a city on the road system.
The Alaska Railroad runs between Seward and Fairbanks. The railroad is famous for its summertime passenger services but also plays a vital part in moving Alaska's natural resources, such as coal and gravel, to ports in Anchorage, Whittier and Seward. The railroad offers one of the last flag stop routes in the country.
Alaska has a well-developed ferry system, known as the Alaska Marine Highway, which serves the cities of Southeast Alaska and the Alaska Peninsula. The system also operates a ferry service from Bellingham, Washington up the Inside Passage to Skagway. The Inter-Island Ferry Authority also serves as an important marine link in the Prince of Wales Island region of Southeast. Tourist sea travel is also popular on Alaska cruises.
Anchorage itself, and to a lesser extent Fairbanks, is served by many major airlines. Alaska Airlines—which serves Anchorage, Fairbanks, and regional hubs—is the only major airline offering in-state travel with jet service (sometimes in combination cargo and passenger Boeing 737-400s). Small regional commuter airlines provide the bulk of remaining commercial flights. The smallest towns and villages must rely on scheduled or chartered Bush flying services using general aviation aircraft such as the Cessna Caravan, the most popular aircraft in use in the state.
In areas not served by road or rail, primary summer transportation is by all-terrain vehicle and primary winter transportation is by snowmobile, or "snow machine," as it is called in Alaska.
Law and government
State government
As with the federal government of the United States, power in Alaska is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial.
The executive branch is headed by the governor. The current governor is Sarah Palin, a Republican whose term began December 4, 2006. She is the first female governor of Alaska, as well as the youngest. The current Lieutenant Governor of Alaska is Sean Parnell. The offices of governor and lieutenant governor have four-year terms.
The Alaska Legislature is a bicameral body consisting of the Senate, whose 20 members serve four-year terms, and the House of Representatives, whose 40 members serve two-year terms.
Alaska's court system has four levels: the Alaska Supreme Court, the court of appeals, the superior courts and the district courts.[40] The superior and district courts are trial courts. Superior courts are courts of general jurisdiction, while district courts only hear certain types of cases, including misdemeanor criminal cases and civil cases valued up to $100,000.[40] The supreme court and the court of appeals are appellate courts. The court of appeals is required to hear appeals from certain lower-court decisions, including those regarding criminal prosecutions, juvenile delinquency, and habeas corpus.[40] The supreme court hears civil appeals and may in its discretion hear criminal appeals.[40]
Representation in the U.S. Congress
Alaska's members of the U.S. Congress are almost all Republican. U.S. Senator Ted Stevens was appointed to the position following the death of U.S. Senator Bob Bartlett in December of 1968, and has never lost a re-election campaign since. As the longest-serving Republican in the Senate (sometimes nicknamed "Senator-For-Life"), Stevens has been a crucial force in gaining federal money for his state.
Until his resignation from the U.S. Senate after being elected governor in 2002, Republican Frank Murkowski held the state's other senatorial position and, as governor, appointed his daughter, State Representative Lisa Murkowski as his successor (under massive public pressure, the State legislature amended the constitution to eliminate gubernatorial appointments in the future). She won a full six-year term on her own in 2004.
Alaska's sole U.S. Representative, Don Young, was re-elected to his 17th consecutive term, also in 2004. His seniority in House makes him one of the most influential Republican House members.
Current Democratic presidential candidate Mike Gravel is a former Senator from Alaska.
Politics
Alaska is often described as a Republican-leaning state with strong libertarian tendencies. In all but the 1964 presidential election, the state's electoral college votes have been won by a Republican nominee. President George W. Bush won the state's electoral votes in 2004 by a margin of 25 percentage points with 61.1% of the vote. The Alaska Legislature has recently been dominated by conservatives, generally Republicans, and recent state governors have generally been conservative, although not always Republican. The city of Juneau stands out as a stronghold of the Democratic party. As of 2004, well over half of all registered voters choose "Non-Partisan" or "Undeclared" as their affiliation [41], despite recent attempts to close primaries.
Local political communities often work on issues related to land use development, fishing, tourism, and individual rights. Alaska Natives, while organized in and around their communities, are often active within the Native corporations which have been given ownership over large tracts of land, and thus need to deliberate resource conservation and development issues.
Cities and towns
Alaska's most populous city is Anchorage, home to 260,283 people (as of 2000), 225,744 of whom live in the urbanized area. The richest location in Alaska by per capita income is Halibut Cove ($89,895). Sitka, Juneau, and Anchorage are the three largest cities in the U.S. by area.
Also notable is the rapid growth of towns in the Mat-Su Valley. Wasilla and Palmer are projected to experience over 100% population growth between 2000 and 2010.[citation needed]
Cities of 100,000 or more people
| ||||
Towns of 10,000-100,000 people
| ||||
| Towns of 1,000-10,000 people | ||||
|
|
| ||
| Smaller towns
Alaska has many smaller towns, especially in the Alaska Bush, the portion of the state that is inaccessible by road. | ||||
Health and education
Education
The Alaska Department of Education and Early Development administers many school districts in Alaska. In addition, the state operates several boarding schools, including Mt. Edgecumbe High School in Sitka, Nenana Living Center in Nenana, and Galena High School in Galena.[42]
There are more than a dozen colleges and universities in Alaska. Accredited universities in Alaska include the University of Alaska Anchorage, University of Alaska Fairbanks, University of Alaska Southeast, Sheldon Jackson College and Alaska Pacific University.[43] 43% of the population attends or attended college.[citation needed]
Alaska has also had a problem with "brain drain" as many of its young people, including most of the highest academic achievers, leave the state upon graduating high school. While for many this functions as a sort of walkabout, many do not return to the state. The University of Alaska has attempted to combat this by offering partial four-year scholarships to the top 10 percent of Alaska high school graduates, via the Alaska Scholars Program[8].
The four main libraries in the state are the Alaska State Library in Juneau, the Elmer E. Rasmuson Library in Fairbanks, the Z. J. Loussac Library in Anchorage, and the UAA/APU Consortium Library, also in Anchorage. Alaska is one of three states (the others are Delaware and Rhode Island) that does not have a Carnegie library.
Health
In 2006, the United Health Foundation ranked Alaska 30th out of 50 states for its population's overall heath.[44]
Positive aspects of health in Alaska include high per capita public health spending ($482 per person; 2nd highest among states),[44] low child poverty (12.1%; 8th lowest),[44] low rates of heart disease deaths (263.1 per 100,000; 3rd lowest),[44] and high rates of exercise (79.4% have exercised in the past month; 15th highest).[45]
Negative aspects of health in Alaska include limited access to prenatal care (36.1% of women received inadequate prenatal care; 4th worst among states),[44] low immunization rates (24.6% of children aged 19 to 35 months fail to receive complete immunizations; 6th worst),[44] and high rates of smoking (24.9%, 6th highest).[44]
Alaska has long had a problem with alcohol use and abuse. Many rural communities in Alaska have outlawed its import. "Dry," "wet," and "damp" are terms describing a community's laws on liquor consumption. This problem directly relates to Alaska's high rate of Fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) as well as contributing to the high rate of suicides. This is a controversial topic for many residents.
Domestic abuse and other violent crimes are also at notoriously high levels in the state; this is in part linked to alcohol abuse.
Culture
- See also List of artists and writers from Alaska
{{#invoke:Message box|ambox}} Some of Alaska's popular annual events are the World Ice Art Championships in Fairbanks, the Alaska Hummingbird Festival in Ketchikan, the Sitka Whale Fest, and the Stikine River Garnet Fest in Wrangell. The Stikine River features the largest springtime concentration of American Bald Eagles in the world.
The Alaska Native Heritage Center celebrates the rich heritage of Alaska's eleven cultural groups. Their purpose is to enhance self-esteem among Native people and to encourage cross-cultural exchanges among all people.
Food
Due to the northern climate and steep terrain, relatively little farming occurs in Alaska. Most farms are in either the Mat-Su Valley near Anchorage, or on the Kenai Peninsula. The short summer limits the types of crops that can be grown - primary crops are potatoes, carrots, lettuce, and cabbage. But the long days of summer can allow these vegetables to reach record size. Alaska has an abundance of seafood, with the primary fisheries in the Bering Sea, and seafood is one of the few food items that is often cheaper within the state than outside it. Hunting for subsistence, primarily caribou, moose, and sheep is still fairly common in the state, particularly in remote Bush communities. An example of a traditional native food is Akutaq, the Eskimo ice cream, consisting of reindeer fat and seal oil and some berries.
Most food in Alaska is transported into the state from outside, and is relatively expensive due to the high shipping costs.
Music
Influences on music in Alaska include the traditional music of Alaska Natives as well as folk music brought by later immigrants from Russia and Europe. Prominent musicians from Alaska include singer Jewel, traditional Aleut flautist Mary Youngblood, folk singer-songwriter Libby Roderick, the group Pamyua, and the metal band 36 Crazyfists.
There are many established music festivals in Alaska, including the Alaska Folk Festival, the Fairbanks Winter Music Fest the Anchorage Folk Festival, the Athabascan Old-Time Fiddling Festival, and the Sitka Summer Music Festival. The most prominent symphony in Alaska is the Anchorage Symphony Orchestra, though the Juneau Symphony is also notable. The Anchorage Opera is currently the state's only professional opera company, though there are several volunteer and semi-professional organizations in the state as well.
The official state song of Alaska is "Alaska's Flag," which was adopted in 1955; it celebrates the flag of Alaska.
Sports and recreation
Organized sports
Alaska's two professional sports teams are the Alaska Aces, an ECHL hockey team, and the Alaska Wild, a new Intense Football League football team.
In modern times, dog mushing is more of a sport than a practical means of transportation. Various races are held around the state, but the best known is the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race, a 1,150-mile (1850 km) trail from Anchorage to Nome. The race commemorates the famous 1925 serum run to Nome in which mushers and dogs like Balto took much-needed medicine to the diphtheria-stricken community of Nome when all other means of transportation had failed. Mushers from all over the world come to Anchorage each March to compete for cash prizes and prestige.
Notable athletes from Alaska include Carlos Boozer, Rosey Fletcher, Scott Gomez, and Trajan Langdon.
Outdoor recreation
Hiking, camping, and cross-country skiing are all very popular in Alaska. Hunting and fishing are also popular; a greater percentage of Alaskans fish than residents of any other state.[46]
State symbols
- State bird: Willow Ptarmigan, adopted by the Territorial Legislature in 1955. It is a small (15-17 inches), Arctic grouse that lives among willows and on open tundra and muskeg. Plumage is brown in summer, changing to white in winter. The Willow Ptarmigan is common in much of Alaska.
- State fish: King Salmon, adopted 1962.
- State flower: wild/native Forget-Me-Not, adopted by the Territorial Legislature in 1917.[47] It is a perennial that is found throughout Alaska, from Hyder to the Arctic Coast, and west to the Aleutians.
- State fossil: Woolly Mammoth, adopted 1986.
- State gem: Jade, adopted 1968.
- State insect: Four-spot skimmer dragonfly, adopted 1995.
- State land mammal: Moose, adopted 1998.
- State marine mammal: Bowhead Whale, adopted 1983.
- State mineral: Gold, adopted 1968.
- State song: "Alaska's Flag"
- State sport: Dog Mushing, adopted 1972.
- State tree: Sitka Spruce, adopted by the Alaska (AK) Legislature in 1962.
See also
- Alaska census statistical areas
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ Vallano, Elissa: Cruising America's 'Last Frontier', Retrieved on May 24, 2007
- ↑ Ransom, J. Ellis. 1940. Derivation of the Word ‘Alaska’. American Anthropologist n.s., 42: pp. 550-551
- ↑ http://www.knls.org/English/akfact.htm
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedAK-YK Precip - ↑ History for Barrow, Alaska. Monthly Summary for July 2006. [[Weather Underground (weather service)|]]. Last accessed 23 October 2006.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Alaska Department of Fish & Game. "Brown Bear." 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007.
- ↑ from chart in http://www.absc.usgs.gov/research/brownbears/attacks/bear-human_conflicts.htm
- ↑ Smith, Tom S. & Herrero, Steven. "A Century of Bear-Human Conflict in Alaska: Analyses & Implications." 2003-9-22. Retrieved February 8, 2007.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Alaska Department of Fish & Game. "Black Bear." 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 Alaska Department of Fish & Game. "Polar Bear." 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 8, 2007
- ↑ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/sci/tech/521451.stm
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 Alaska Department of Fish & Game. "Wolf." 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007.
- ↑ Alaska Department of Fish & Game Division of Wildlife Conservation. "Wolf Management in Alaska with a Historic Perspective." March 2002. Retrieved on February 10, 2007.
- ↑ http://www.wc.adfg.state.ak.us/index.cfm?adfg=wolf.wolf_mgt
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 15.3 15.4 15.5 15.6 15.7 Alaska Department of Fish & Game "Caribou." 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 Alaska Department of Fish & Game: Moose. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007. http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/biggame/moose.php
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 Alaska Department of Fish & Game: Mountain Goat. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007. http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/biggame/mtn_goat.php
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 Alaska Department of Fish & Game: American Bison. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007. http://www.adfg.state.ak.us/pubs/notebook/biggame/bison.php
- ↑ An Ultimate Ungulate Fact Sheet: American Bison. 2004-5-22. Retrieved on February 8, 2007. http://www.ultimateungulate.com/Artiodactyla/Bison_bison.html
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Alaska Department of Fish & Game: Dall Sheep. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 8, 2007. [1]
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Alaska Department of Fish & Game: Orca. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 8, 2007. [2]
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namednote - ↑ Alaska Department of Fish & Game: Frogs & Toads. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007. [3]
- ↑ Alaska Department of Fish & Game: Turtle. 2005-5-23. Retrieved on February 6, 2007. [4]
- ↑ Endangered & Threatened Species Curriculum. Center For Alaskan Coastal Studies. 2006. Retrieved on February 6, 2007. [5]
- ↑ Alaska Department of Fish & Game Division of Wildlife Conservation: State of Alaska Endangered Species List. 2007. Retrieved on February 7, 2007. [6]
- ↑ http://memory.loc.gov/ammem/today/oct25.html
- ↑ http://www.census.gov/population/cen2000/phc-t2/tab01.txt
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 29.3 http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/ADPTable?_bm=y&-geo_id=04000US02&-qr_name=ACS_2005_EST_G00_DP1&-context=adp&-ds_name=&-tree_id=305&-_lang=en&-redoLog=false&-format=
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 30.3 30.4 http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/ADPTable?_bm=y&-context=adp&-qr_name=ACS_2005_EST_G00_DP2&-ds_name=ACS_2005_EST_G00_&-tree_id=305&-redoLog=true&-_caller=geoselect&-geo_id=04000US02&-format=&-_lang=en
- ↑ http://www.mla.org/map_data_results&state_id=2&county_id=&mode=state_tops&zip=&place_id=&cty_id=&a=&ea=&order=&ll=all
- ↑ http://www.teachingaboutreligion.org/Demographics/map_demographics.htm
- ↑ http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/5297313/
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/americas/3531458.stm
- ↑ http://www.adherents.com/Na/Na_560.html
- ↑ Screening Report for Alaska Rural Energy Plan, April, 2001
- ↑ http://www.apfc.org/alaska/dividendprgrm.cfm
- ↑ http://www.alaska.com/about/moving/story/4485049p-4463752c.html
- ↑ CNN Money (2005). How tax friendly is your state? Retrieved from http://money.cnn.com/pf/features/lists/taxesbystate2005/index.html
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 40.2 40.3 http://www.state.ak.us/courts/ctinfo.htm
- ↑ http://www.gov.state.ak.us/ltgov/elections/regbypty.htm
- ↑ http://www.alaskaice.org/material.php?matID=138
- ↑ These are the only three universities in the state ranked by US News and World Report.[7]
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 44.2 44.3 44.4 44.5 44.6 http://www.unitedhealthfoundation.org/ahr2006/states/Alaska.html
- ↑ http://www.statemaster.com/graph/hea_phy_exe-health-physical-exercise
- ↑ Managing for Results. Minnesota DNR. Retrieved 2006-06-26.
- ↑ http://www.akcf.org/_pages/about_ACF/about_alaska/state_symbols.php
External links
- State of Alaska website
- For Sale By Owner Alaska
- Alaska Inter-Tribal Council
- USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Alaska
- US Census Bureau
- Alaska State Facts
- Alaska Community Database System
- Online Alaska history course, created by the Alaska Humanities Forum.
Template:Alaska
| Political divisions of the United States | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
| Preceded by: Arizona |
List of U.S. states by date of statehood Admitted on January 3, 1959 (49th) |
Succeeded by: Hawaii |
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.