Difference between revisions of "Sea of Galilee" - New World Encyclopedia
m (Rename to Geography) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Approved}}{{Submitted}}{{Images OK}}{{Paid}}{{copyedited}} |
{{Infobox_lake | {{Infobox_lake | ||
|lake_name = Sea of Galilee | |lake_name = Sea of Galilee | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|image_bathymetry = | |image_bathymetry = | ||
|caption_bathymetry = | |caption_bathymetry = | ||
| − | |coords = {{ | + | |coords = {{coord|32|50|N|35|35|E|type:waterbody_region:IS}} |
|type = [[Monomictic]] | |type = [[Monomictic]] | ||
|inflow = [[Jordan River]] | |inflow = [[Jordan River]] | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|length = 21 km | |length = 21 km | ||
|width = 13 km | |width = 13 km | ||
| − | |area = [ | + | |area = 170 km²<ref>[http://wldb.ilec.or.jp/Details/Lake/ASI-09 Lake Kinneret] ''World Lake Database'' Retrieved January 22, 2020.</ref> |
| − | |depth = 25.6 | + | |depth = 25.6 m |
|max-depth = 43 m | |max-depth = 43 m | ||
|volume = 4 km³ | |volume = 4 km³ | ||
| − | |residence_time = | + | |residence_time = 4.8 years |
|shore = 53 km | |shore = 53 km | ||
|elevation = -209 m | |elevation = -209 m | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|cities = | |cities = | ||
}} | }} | ||
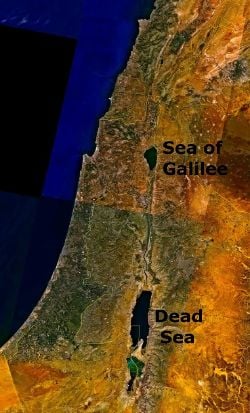
| − | The '''Sea of Galilee''' or '''Lake Kinneret''' (Hebrew '''ים כנרת'''), is [[Israel]]'s largest [[freshwater]] [[lake]]. It is approximately 53 | + | The '''Sea of Galilee''' or '''Lake Kinneret''' (Hebrew '''ים כנרת'''), is [[Israel]]'s largest [[freshwater]] [[lake]]. It is approximately 33 miles (53 km) in circumference, about 13 miles (21 km) long, and 8 miles (13 km) wide; it has a total area of 64 square miles (170 km²), and a maximum depth of approximately 43 meters. At 209 meters below sea level, it has long been thought to be the lowest freshwater lake on Earth and the second-lowest lake in the world after the [[Dead Sea]], a saltwater lake. However, the 1996 discovery of the sub-glacial [[Lake Vostok]] in [[Antarctica]] challenges both records; it is estimated to be 200 to 600 m below sea level. |
| − | The Kinneret is fed by underground springs, but its main source is the [[Jordan River]], which flows through it from north to south. The lake is situated deep in the Jordan [[Great Rift Valley]], the valley caused by the separation of the [[African Plate|African]] and [[Arabian Plate]]s. Consequently the area is subject to [[earthquake]]s and, in the past, [[volcano|volcanic]] activity. | + | The Kinneret is fed by underground springs, but its main source is the [[Jordan River]], which flows through it from north to south. The lake is situated deep in the Jordan [[Great Rift Valley]], the valley caused by the separation of the [[African Plate|African]] and [[Arabian Plate]]s. Consequently, the area is subject to [[earthquake]]s and, in the past, [[volcano|volcanic]] activity. This is evidenced by the abundant [[basalt]] and other [[igneous]] rock that defines the geology of the Sea of Galilee region. |
| − | + | The Sea of Galilee is Israel's major water reservoir. Through the ''National Water Carrier of Israel'' system, water is supplied to the country's urban centers as well as to the [[Negev Desert]] in the south. Unfortunately, the diversion of water from the [[Jordan River]] has been a source of tension with neighboring [[Syria]] and [[Jordan]], a factor which eventually contributed to the 1967 [[Six-Day War]]. In 1996, under the ''Israel-Jordan Treaty of Peace,'' Israel agreed to supply Jordan with 50 million cubic meters of water annually. | |
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | Much of the ministry of [[Jesus]] occurred in the area around the Sea of Galilee, or on the lake itself. The Synoptic gospels of [[Gospel of Mark|Mark]] (1:14-20), [[Gospel of Matthew|Matthew]] (4:18-22), and [[Gospel of Luke|Luke]] (5:1-11) describe how Jesus recruited four of his [[Twelve apostles|apostles]] from the shores of Lake Galilee. [[The Sermon on the Mount]] was given on a hill overlooking the lake, and Jesus is said to have calmed the violent lake storm here. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Etymology== |
| − | The | + | The lake often appears on maps as ''Lake Galilee'' or ''Lake Tiberias,'' while in the [[Old Testament]], it is called the "Sea of Kinneret" (Numbers 34:11; Joshua 13:27). Following the exile of the Jews to Babylon in the sixth century B.C.E., it became known as the "Lake of Gennesaret." |
| − | [[ | + | The name may originate from the [[Hebrew language|Hebrew]] word ''[[kinnor]]'' ("harp" or "lyre") in view of the shape of the lake. [[Christian]] religious texts call it ''Lake of Gennesaret'' or ''Sea of Gennesaret'' ([[Gospel of Luke|Luke]] 5:1), after a small fertile plain that lies on its western side. The [[Arabic language|Arabic]] name for the lake is ''Buhairet Tabariyya'' (بحيرة طبريا) meaning ''Lake Tiberias''. Other names for the Sea of Galilee are ''Ginnosar,'' ''Lake of Gennesar,'' ''Sea of Chinneroth,'' and ''Sea of Tiberias'' (Roman). |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==History== | |
| + | The area surrounding the Sea of Galilee has been populated from very early times. Two miles south of the lake, at El-'Ubeidiya, [[lacustrine]] formations dating from about 400,000 to 500,000 years ago have revealed prehistoric tools and two human fragments, which are among the oldest in the [[Middle East]]. Ancient [[Canaanite]] structures have been uncovered which date to between 1,000 and 2,000 B.C.E.. | ||
| − | + | ===Antiquity=== | |
| + | The Sea of Galilee lies on the ancient [[Via Maris]] which linked [[Egypt]] with the northern empires. The [[Ancient Greece|Greeks]], [[Hasmonean]]s, and [[Roman Empire|Romans]] founded flourishing towns and settlements here: [[Gadara]], [[Hippos]], [[Tiberias]], and others. | ||
| − | + | The first century historian [[Flavius Josephus]] was so impressed by the area that he wrote, "One may call this place the ambition of Nature." Josephus also reported a thriving fishing industry at the time, with 230 boats regularly working in the lake. He wrote of nine ancient cities on the lake's shores, of which only Tiberias has survived. This city, on the lake's western shore was one of four holy cities. | |
| − | + | Kefar Nahum (Capernaum), has preserved one of the most beautiful [[synagogue]]s in the region, dating from the second and third centuries B.C.E.. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:YamKineret.jpg|thumb|280px|The Sea of Galilee]] | |
| − | In [[ | + | Much of the ministry of [[Jesus]] occurred on the shores of Lake Galilee. In those days, there was a continuous ribbon development of settlements and villages around the lake and plenty of trade and ferrying by boat. The Synoptic gospels of [[Gospel of Mark|Mark]] (1:14-20), [[Gospel of Matthew|Matthew]] (4:18-22), and [[Gospel of Luke|Luke]] (5:1-11) describe how Jesus recruited four of his [[Twelve apostles|apostles]] from the shores of Lake Galilee: The fishermen [[Saint Peter|Simon]] and his brother [[Saint Andrew|Andrew]] and the brothers [[John the Apostle|John]] and [[Saint James the Great|James]]. One of Jesus' famous teaching episodes, the [[Sermon on the Mount]], was given on a hill overlooking the lake. Many of his miracles were also recorded to occur here: His walking on water, calming a storm, feeding the multitude (in [[Tabgha]]), and many others. |
| − | In | + | In 135 C.E., the second Jewish revolt against the Romans, called [[Bar Kochba|Bar Kokhba's revolt]], was put down. The Romans responded by banning all Jews from [[Jerusalem]]. The center of Jewish culture and learning shifted to the region of the Kinneret, particularly the city of [[Tiberias]]. It was in this region that the so-called "[[Jerusalem Talmud]]" was probably compiled. |
| − | + | In the time of the [[Byzantine Empire]], the lake's significance in Jesus' life made it a major destination for Christian [[pilgrim]]s. This led to the growth of a full-fledged tourist industry, complete with package tours and plenty of comfortable inns. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Medieval times=== | |
| + | [[Image:Sea-of-Galilee-1900.jpg|thumb|280px|Fisherman in the Sea of Galilee, 1890-1900.]] | ||
| − | + | The lake's importance declined when the Byzantines lost control of it. The area came under the control of the [[Umayyad Caliphate]] and subsequent [[Islam]]ic empires. Except for Tiberias, the major towns and cities were gradually abandoned. | |
| − | + | In the eleventh century, a sanctuary for the [[Druze]] was built near Kefar Hittim, near the western shore. This still stands. | |
| − | + | In 1187, [[Saladin]] defeated the armies of the [[Crusades]] at the [[Battle of Hattin]], largely because he was able to cut the Crusaders off from the valuable fresh water of the Sea of Galilee. | |
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | The warm waters of the Sea of Galilee allow a variety of flora and fauna to thrive, which have supported a significant commercial fishery for over two millennia. Local flora includes a variety of reeds along most of the shoreline as well as [[Phytoplankton]], | + | ===Modern times=== |
| + | [[File:Golan 92.jpg|thumb|200px|Israeli settlements in the Golan Heights, February 1992]] | ||
| + | In 1909, Jewish pioneers built their first cooperative farming village ([[kibbutz]]), Kvutzat Kinneret, which trained Jewish immigrants in farming and [[agriculture]]. Later, Kinneret pioneers established Kibbutz Degania. Kinneret was the cradle of the Kibbutz culture of early [[Zionism]] and was the birthplace of [[Naomi Shemer]] and the burial site of [[Rachel (poet)|Rachel]]—two of the most prominent Israeli poets. | ||
| + | |||
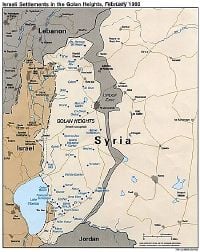
| + | In 1923, an agreement between the [[United Kingdom]] and [[France]] established the border between the [[British Mandate of Palestine]] and the [[French Mandate of Syria]]. The British handed over the southern [[Golan Heights]] to the French in return for the northern [[Jordan Valley]]. The border was re-drawn so that both sides of the [[Jordan river]] and the whole of the Sea of Galilee, including a 10-meter wide strip along the northeastern shore, were made a part of [[Palestine]]. The [[1947 UN Partition Plan]] put this territory area inside the Jewish state. | ||
| + | |||
| + | During the [[Israel's War of Independence|1948 Arab-Israeli War]], [[Israel]] occupied the lake's southwestern shore. In 1967, the State of Israel took control of the entire Sea of Galilee as well as the the western two-thirds of the Golan Heights during the [[Six-Day War]]. The Golan Heights Law in 1981 applied Israeli law to the whole territory, a move that has been described as an annexation. [[Syria]] still claims the northeastern shore of the sea, arguing it is a part of the [[Golan Heights]], which had been under Syrian control prior to the 1967 war. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Tourism==== | ||
| + | Today, tourism is again the Kinneret's most important economic activity. The entire Sea of Galilee is a popular holiday resort area. The many historical and spiritual sites around the lake, especially its main town Tiberias, are visited by local and foreign tourists every year. Other economic activities include [[fishing]] in the lake and [[agriculture]], particularly [[banana]]s, in the fertile belt of land surrounding it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A key attraction is the point at which the Kinneret's water flows into the Jordan River. Thousands of pilgrims from all over the world come to be baptized there every year. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====National Water Carrier==== | ||
| + | [[Image:Almog IL2 Movil.jpg|thumb|280px|The National Water Carrier near [[Beit Netofa]]]] | ||
| + | ''The National Water Carrier of Israel'' ({{lang-he|המוביל הארצי}}, ''HaMovil HaArtzi'') is the main [[water]] project in the country. Its main task is to transfer water from the Sea of Galilee in the north of the country to the urban center and arid south and to enable efficient use of water and regulation of the water supply throughout the country. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Most of the water works in Israel are combined with the National Water Carrier, the length of which is about 81 miles (130 kilometers). The carrier consists of a system of giant pipes, open canals, [[tunnel]]s, [[Reservoir (water)|reservoirs]] and large scale [[pumping station]]s. Building the carrier was a considerable technical challenge as it traverses a wide variety of terrains and elevations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Early plans were made prior to the establishment of the State of Israel, but detailed planning began only after Israel's independence in 1948. The construction of the project, originally known as the [[Jordan Project]], started in 1953, during the planning phase, long before the detailed final plan was completed in 1956. The project was started during the Prime Ministership of [[David Ben-Gurion]], but was completed in June 1964, under Prime Minister [[Levi Eshkol]], and cost about 420 million Israeli lira (at 1964 values). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The original goal of building the carrier was to provide [[irrigation]] water to the [[Negev]] region. Today 80 percent of the water drawn from the lake is utilized for Israel's domestic consumption. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since its construction, the resulting diversion of water from the [[Jordan River]] has been a source of tension with [[Syria]] and [[Jordan]]. In 1964, Syria attempted construction of a [[Headwater Diversion Plan]] that would have blocked the flow of water into the Sea of Galilee, sharply reducing the capacity of the carrier. This project and Israel's subsequent physical attack on those diversion efforts in 1965, were factors which played into regional tensions culminating in the 1967 [[Six-Day War]]. Israel captured the [[Golan Heights]] from Syria in the course of the war, which contain some of sources of the Sea of Galilee. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 1996, under the [[Israel-Jordan Treaty of Peace]], Israel agreed to supply Jordan with 50 million cubic meters of water annually. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Geography== | ||
| + | [[Image:Kineret-sunset.jpg|thumb|300px|Sunset over the Sea of Galilee.]] | ||
| + | ===Formation=== | ||
| + | Most of the area surrounding the Sea of Galilee is covered by [[basalt]]s that have been formed since the [[Miocene]] Epoch began about 26,000,000 years ago and that are part of the vast area of Mount Duruz, located in [[Syria]]. Beginning at that time, lacustrine [[limestone]]s and [[marl]]s (calcareous clays) have been deposited. | ||
| + | |||
| + | East of the lake lies the east African port of the [[Great Rift Valley]]. Formed in the [[Pliocene]] Epoch (5.3 to 1.6 million years ago), it was partially filled in again by lacustrine and fluvial sediments. During the humid times of the [[Quaternary]] Period (1.6 million years ago to the present) the [[Dead Sea]] extended to this point. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Environment=== | ||
| + | The [[Jordan River]] is the Sea's main source, though additional streams and wadis flow into it from the surrounding hills. | ||
| + | {{readout||right|250px|The Sea of Galilee, also known as Lake Kinneret, is [[Israel]]'s largest freshwater lake}} | ||
| + | It is surrounded by | ||
| + | *The Plain of Gennesaret, which extends in a circular arc from the north to the northwest | ||
| + | *The Plain of Bet Zayda (Buteiha) in Syria, extending to the northeast | ||
| + | *The hills of Lower Galilee on the west and southwest of the lake, which drop abruptly to the lake's edge | ||
| + | *The cliffs of the Plateau of Golan, which overlook the lake's mid-eastern section. This plateau rises again in the southeast approaching the valley of the Yarmuk River, a tributary of the Jordan | ||
| + | *The Plain of al-Ghawr is on the lake's south, though it is separated by a narrow ridge through which flows the Jordan River. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Climate=== | ||
| + | The Sea of Galilee is sheltered by the surrounding hills and plateaus, affording a mild winter. Average winter [[temperature]]s are 57° F (14° C) in January. Summers are quite warm, with an average of 88° F (31° C). Most precipitation occurs during the area's short winters, in the form of brief but powerful showers. Due to its low-lying position in the rift valley, surrounded by hills, the sea is prone to sudden violent storms. Indeed, the main feature of the lake seems to be its ever-changing character. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Flora and fauna=== | ||
| + | The warm waters of the Sea of Galilee allow a variety of flora and fauna to thrive, which have supported a significant commercial [[Fishing|fishery]] for over two millennia, providing a livelihood for various peoples through the ages. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Local flora includes a variety of reeds along most of the shoreline as well as [[Phytoplankton]]. [[Banana]]s, [[citrus fruit]], [[dates]], and [[vegetable]]s grow well in the area due to its pleasant climate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fauna consists of [[Zooplankton]], [[Benthos]], while the fish population notably includes [[Tilapia]] (locally known as St. Peter’s Fish).<ref>[https://www.bbc.com/news/blogs-news-from-elsewhere-24131312 Israel: 'St Peter's Fish' to revive the Sea of Galilee] ''BBC News'', September 18, 2013. Retrieved January 22, 2020.</ref> Other fish species in the lake include [[damselfish]], scaleless blennies, [[catfish]], mouthbreeders, and barbels; similar to those found in [[Eastern Africa]]n lakes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ::::::'''Panoramic view from Amnon, North of the Sea of Galilee''' | ||
| + | {{Wide image|Yarden_044PAN2.JPG|2200px}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Notes== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | + | * Dintaman, Anna, and David Landis. ''Walking The Jesus Trail: Nazareth to the Sea of Galilee''. Village to Village Press, 2017. ISBN 978-0984353330 | |
| + | * Metzger, Bruce Manning and Michael David Coogan. ''The Oxford Guide to People & Places of the Bible''. New York: Oxford University Press, 2001. ISBN 0195146417 | ||
| + | * Valdes, Guiliano. ''Tiberias and the Sea of Galilee''. Florence, Italy: Casa Editrice Bonechi, 1999. ISBN 8880290673 | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | + | All links retrieved January 25, 2023. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *[http://www.bibleplaces.com/seagalilee.htm Sea of Galilee] ''BiblePlaces.com''. | ||
| + | *[http://www.wilkens-art.com/galilee.htm Peace Mural of the Sea of Galilee in the Chapel of the Good Shephard—Ramallah]. | ||
| + | *[https://www.touristisrael.com/sea-of-galilee/440/ Sea of Galilee] ''Tourist Israel''. | ||
| + | *[https://www.seetheholyland.net/sea-of-galilee-article-israeloutside-jerusalem/ Sea of Galilee] ''SeeTheHolyLand.net''. | ||
| − | {{credit|155041207}} | + | {{credit|Sea_of_Galilee|155041207|National_Water_Carrier_of_Israel|172774918}} |
[[Category:Geography]] | [[Category:Geography]] | ||
[[Category:Middle East]] | [[Category:Middle East]] | ||
[[Category:Religion]] | [[Category:Religion]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:32, 25 January 2023
| Sea of Galilee | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | |
| Lake type | Monomictic |
| Primary sources | Jordan River |
| Primary outflows | Jordan River |
| Catchment area | 2,730 km² |
| Basin countries | Israel |
| Max length | 21 km |
| Max width | 13 km |
| Surface area | 170 km²[1] |
| Average depth | 25.6 m |
| Max depth | 43 m |
| Water volume | 4 km³ |
| Residence time (of lake water) | 4.8 years |
| Shore length1 | 53 km |
| Surface elevation | -209 m |
| 1 Shore length is an imprecise measure which may not be standardized for this article. | |
The Sea of Galilee or Lake Kinneret (Hebrew ים כנרת), is Israel's largest freshwater lake. It is approximately 33 miles (53 km) in circumference, about 13 miles (21 km) long, and 8 miles (13 km) wide; it has a total area of 64 square miles (170 km²), and a maximum depth of approximately 43 meters. At 209 meters below sea level, it has long been thought to be the lowest freshwater lake on Earth and the second-lowest lake in the world after the Dead Sea, a saltwater lake. However, the 1996 discovery of the sub-glacial Lake Vostok in Antarctica challenges both records; it is estimated to be 200 to 600 m below sea level.
The Kinneret is fed by underground springs, but its main source is the Jordan River, which flows through it from north to south. The lake is situated deep in the Jordan Great Rift Valley, the valley caused by the separation of the African and Arabian Plates. Consequently, the area is subject to earthquakes and, in the past, volcanic activity. This is evidenced by the abundant basalt and other igneous rock that defines the geology of the Sea of Galilee region.
The Sea of Galilee is Israel's major water reservoir. Through the National Water Carrier of Israel system, water is supplied to the country's urban centers as well as to the Negev Desert in the south. Unfortunately, the diversion of water from the Jordan River has been a source of tension with neighboring Syria and Jordan, a factor which eventually contributed to the 1967 Six-Day War. In 1996, under the Israel-Jordan Treaty of Peace, Israel agreed to supply Jordan with 50 million cubic meters of water annually.
Much of the ministry of Jesus occurred in the area around the Sea of Galilee, or on the lake itself. The Synoptic gospels of Mark (1:14-20), Matthew (4:18-22), and Luke (5:1-11) describe how Jesus recruited four of his apostles from the shores of Lake Galilee. The Sermon on the Mount was given on a hill overlooking the lake, and Jesus is said to have calmed the violent lake storm here.
Etymology
The lake often appears on maps as Lake Galilee or Lake Tiberias, while in the Old Testament, it is called the "Sea of Kinneret" (Numbers 34:11; Joshua 13:27). Following the exile of the Jews to Babylon in the sixth century B.C.E., it became known as the "Lake of Gennesaret."
The name may originate from the Hebrew word kinnor ("harp" or "lyre") in view of the shape of the lake. Christian religious texts call it Lake of Gennesaret or Sea of Gennesaret (Luke 5:1), after a small fertile plain that lies on its western side. The Arabic name for the lake is Buhairet Tabariyya (بحيرة طبريا) meaning Lake Tiberias. Other names for the Sea of Galilee are Ginnosar, Lake of Gennesar, Sea of Chinneroth, and Sea of Tiberias (Roman).
History
The area surrounding the Sea of Galilee has been populated from very early times. Two miles south of the lake, at El-'Ubeidiya, lacustrine formations dating from about 400,000 to 500,000 years ago have revealed prehistoric tools and two human fragments, which are among the oldest in the Middle East. Ancient Canaanite structures have been uncovered which date to between 1,000 and 2,000 B.C.E.
Antiquity
The Sea of Galilee lies on the ancient Via Maris which linked Egypt with the northern empires. The Greeks, Hasmoneans, and Romans founded flourishing towns and settlements here: Gadara, Hippos, Tiberias, and others.
The first century historian Flavius Josephus was so impressed by the area that he wrote, "One may call this place the ambition of Nature." Josephus also reported a thriving fishing industry at the time, with 230 boats regularly working in the lake. He wrote of nine ancient cities on the lake's shores, of which only Tiberias has survived. This city, on the lake's western shore was one of four holy cities.
Kefar Nahum (Capernaum), has preserved one of the most beautiful synagogues in the region, dating from the second and third centuries B.C.E.
Much of the ministry of Jesus occurred on the shores of Lake Galilee. In those days, there was a continuous ribbon development of settlements and villages around the lake and plenty of trade and ferrying by boat. The Synoptic gospels of Mark (1:14-20), Matthew (4:18-22), and Luke (5:1-11) describe how Jesus recruited four of his apostles from the shores of Lake Galilee: The fishermen Simon and his brother Andrew and the brothers John and James. One of Jesus' famous teaching episodes, the Sermon on the Mount, was given on a hill overlooking the lake. Many of his miracles were also recorded to occur here: His walking on water, calming a storm, feeding the multitude (in Tabgha), and many others.
In 135 C.E., the second Jewish revolt against the Romans, called Bar Kokhba's revolt, was put down. The Romans responded by banning all Jews from Jerusalem. The center of Jewish culture and learning shifted to the region of the Kinneret, particularly the city of Tiberias. It was in this region that the so-called "Jerusalem Talmud" was probably compiled.
In the time of the Byzantine Empire, the lake's significance in Jesus' life made it a major destination for Christian pilgrims. This led to the growth of a full-fledged tourist industry, complete with package tours and plenty of comfortable inns.
Medieval times
The lake's importance declined when the Byzantines lost control of it. The area came under the control of the Umayyad Caliphate and subsequent Islamic empires. Except for Tiberias, the major towns and cities were gradually abandoned.
In the eleventh century, a sanctuary for the Druze was built near Kefar Hittim, near the western shore. This still stands.
In 1187, Saladin defeated the armies of the Crusades at the Battle of Hattin, largely because he was able to cut the Crusaders off from the valuable fresh water of the Sea of Galilee.
Modern times
In 1909, Jewish pioneers built their first cooperative farming village (kibbutz), Kvutzat Kinneret, which trained Jewish immigrants in farming and agriculture. Later, Kinneret pioneers established Kibbutz Degania. Kinneret was the cradle of the Kibbutz culture of early Zionism and was the birthplace of Naomi Shemer and the burial site of Rachel—two of the most prominent Israeli poets.
In 1923, an agreement between the United Kingdom and France established the border between the British Mandate of Palestine and the French Mandate of Syria. The British handed over the southern Golan Heights to the French in return for the northern Jordan Valley. The border was re-drawn so that both sides of the Jordan river and the whole of the Sea of Galilee, including a 10-meter wide strip along the northeastern shore, were made a part of Palestine. The 1947 UN Partition Plan put this territory area inside the Jewish state.
During the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, Israel occupied the lake's southwestern shore. In 1967, the State of Israel took control of the entire Sea of Galilee as well as the the western two-thirds of the Golan Heights during the Six-Day War. The Golan Heights Law in 1981 applied Israeli law to the whole territory, a move that has been described as an annexation. Syria still claims the northeastern shore of the sea, arguing it is a part of the Golan Heights, which had been under Syrian control prior to the 1967 war.
Tourism
Today, tourism is again the Kinneret's most important economic activity. The entire Sea of Galilee is a popular holiday resort area. The many historical and spiritual sites around the lake, especially its main town Tiberias, are visited by local and foreign tourists every year. Other economic activities include fishing in the lake and agriculture, particularly bananas, in the fertile belt of land surrounding it.
A key attraction is the point at which the Kinneret's water flows into the Jordan River. Thousands of pilgrims from all over the world come to be baptized there every year.
National Water Carrier
The National Water Carrier of Israel (Hebrew: המוביל הארצי, HaMovil HaArtzi) is the main water project in the country. Its main task is to transfer water from the Sea of Galilee in the north of the country to the urban center and arid south and to enable efficient use of water and regulation of the water supply throughout the country.
Most of the water works in Israel are combined with the National Water Carrier, the length of which is about 81 miles (130 kilometers). The carrier consists of a system of giant pipes, open canals, tunnels, reservoirs and large scale pumping stations. Building the carrier was a considerable technical challenge as it traverses a wide variety of terrains and elevations.
Early plans were made prior to the establishment of the State of Israel, but detailed planning began only after Israel's independence in 1948. The construction of the project, originally known as the Jordan Project, started in 1953, during the planning phase, long before the detailed final plan was completed in 1956. The project was started during the Prime Ministership of David Ben-Gurion, but was completed in June 1964, under Prime Minister Levi Eshkol, and cost about 420 million Israeli lira (at 1964 values).
The original goal of building the carrier was to provide irrigation water to the Negev region. Today 80 percent of the water drawn from the lake is utilized for Israel's domestic consumption.
Since its construction, the resulting diversion of water from the Jordan River has been a source of tension with Syria and Jordan. In 1964, Syria attempted construction of a Headwater Diversion Plan that would have blocked the flow of water into the Sea of Galilee, sharply reducing the capacity of the carrier. This project and Israel's subsequent physical attack on those diversion efforts in 1965, were factors which played into regional tensions culminating in the 1967 Six-Day War. Israel captured the Golan Heights from Syria in the course of the war, which contain some of sources of the Sea of Galilee.
In 1996, under the Israel-Jordan Treaty of Peace, Israel agreed to supply Jordan with 50 million cubic meters of water annually.
Geography
Formation
Most of the area surrounding the Sea of Galilee is covered by basalts that have been formed since the Miocene Epoch began about 26,000,000 years ago and that are part of the vast area of Mount Duruz, located in Syria. Beginning at that time, lacustrine limestones and marls (calcareous clays) have been deposited.
East of the lake lies the east African port of the Great Rift Valley. Formed in the Pliocene Epoch (5.3 to 1.6 million years ago), it was partially filled in again by lacustrine and fluvial sediments. During the humid times of the Quaternary Period (1.6 million years ago to the present) the Dead Sea extended to this point.
Environment
The Jordan River is the Sea's main source, though additional streams and wadis flow into it from the surrounding hills.
It is surrounded by
- The Plain of Gennesaret, which extends in a circular arc from the north to the northwest
- The Plain of Bet Zayda (Buteiha) in Syria, extending to the northeast
- The hills of Lower Galilee on the west and southwest of the lake, which drop abruptly to the lake's edge
- The cliffs of the Plateau of Golan, which overlook the lake's mid-eastern section. This plateau rises again in the southeast approaching the valley of the Yarmuk River, a tributary of the Jordan
- The Plain of al-Ghawr is on the lake's south, though it is separated by a narrow ridge through which flows the Jordan River.
Climate
The Sea of Galilee is sheltered by the surrounding hills and plateaus, affording a mild winter. Average winter temperatures are 57° F (14° C) in January. Summers are quite warm, with an average of 88° F (31° C). Most precipitation occurs during the area's short winters, in the form of brief but powerful showers. Due to its low-lying position in the rift valley, surrounded by hills, the sea is prone to sudden violent storms. Indeed, the main feature of the lake seems to be its ever-changing character.
Flora and fauna
The warm waters of the Sea of Galilee allow a variety of flora and fauna to thrive, which have supported a significant commercial fishery for over two millennia, providing a livelihood for various peoples through the ages.
Local flora includes a variety of reeds along most of the shoreline as well as Phytoplankton. Bananas, citrus fruit, dates, and vegetables grow well in the area due to its pleasant climate.
Fauna consists of Zooplankton, Benthos, while the fish population notably includes Tilapia (locally known as St. Peter’s Fish).[2] Other fish species in the lake include damselfish, scaleless blennies, catfish, mouthbreeders, and barbels; similar to those found in Eastern African lakes.
- Panoramic view from Amnon, North of the Sea of Galilee
Notes
- ↑ Lake Kinneret World Lake Database Retrieved January 22, 2020.
- ↑ Israel: 'St Peter's Fish' to revive the Sea of Galilee BBC News, September 18, 2013. Retrieved January 22, 2020.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Dintaman, Anna, and David Landis. Walking The Jesus Trail: Nazareth to the Sea of Galilee. Village to Village Press, 2017. ISBN 978-0984353330
- Metzger, Bruce Manning and Michael David Coogan. The Oxford Guide to People & Places of the Bible. New York: Oxford University Press, 2001. ISBN 0195146417
- Valdes, Guiliano. Tiberias and the Sea of Galilee. Florence, Italy: Casa Editrice Bonechi, 1999. ISBN 8880290673
External links
All links retrieved January 25, 2023.
- Sea of Galilee BiblePlaces.com.
- Peace Mural of the Sea of Galilee in the Chapel of the Good Shephard—Ramallah.
- Sea of Galilee Tourist Israel.
- Sea of Galilee SeeTheHolyLand.net.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.