Hyena
| Hyenas | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Spotted Hyena
| ||||||||||||
|
Conservation status: Vulnerable
| ||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
|
Hyena (or Hyæna) is any terrestrial mammal in the subfamily Hyaeninae of the Hyaenidae of the order Carnivora, typically characterized by a dog-like appearance, powerful jaws, and hind limbs shorter than fore limbs. There are three extant (living) species of hyenas: Crocuta crocuta (spotted hyena or laughing hyena), Hyaena hyaena (striped hyena), and Parahyaena brunnea (brown hyena). A fourth living member of the Hyaenidae family is Proteles cristatus (the aardwolf); however, it is a member of the Protelinae subfamily. The Hyaenidae family is also known as the hyena family, and all members of this family, including the aardwolf, are sometimes designated as hyenas.
Hyenas are native to Africa, Arabia, Asia and the Indian subcontinent. Although they resemble dogs in appearance, they are more closely related to cats, and are placed in the suborder Feliformia ("cat-like") of the order Carnivora, rather than the suborder Caniformia ("dog-like").
Physiology
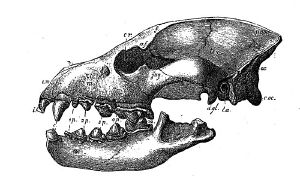
Hyenas bear some physical resemblance to canids. However, they are placed in a biological family that is most most closely related to Herpestidae (the family of mongooses and meerkats). The three living species of hyenas have among the strongest jaws in the animal kingdom and an adult of the species has only the big cats (lions) to fear. The fourth member of the hyena family, the insectivorous aardwolf, does not have as powerful jaws given its diest consists mainly of termites, other insect larvae, and carrion.
All three hyena species and the aardwolf have a distinctly bear-like gait due to their front legs being longer than their back legs. The aardwolf, striped hyena, and brown hyena have luxurious, striped pelts and manes lining the top of their necks, which erect when frightened. The spotted hyena's fur is considerably shorter and is spotted rather than striped. Unlike other species, its mane is reversed forwards.
Hyenas are highly intelligent animals. One indication of hyena intelligence is that they will move their kills closer to each other to protect them from scavengers; another indication is their strategic hunting methods (Lind 1977).
The majority of hyena species show little sexual dimorphism, usually with males being only slightly larger than the females. The spotted hyena is an exception to this as females are larger than the males and dominate them. One unusual feature of the spotted hyena is that females have an enlarged clitoris called a pseudo-penis or demi-penis. Female hyenas give birth, copulate, and urinate through their protruding genitalia, which stretches to allow the male penis to enter for copulation, and it also stretches during birth. The anatomical position of the genitalia gives females total sexual control over who is allowed to mate with them. Researchers originally thought that one of the things that causes this characteristic of the genitals is androgens that are expressed to the fetus very early on in its development. However, it was discovered that when the androgens are held back from the fetus, the development of the female genitalia was not altered.
All species, including the aardwolf, excrete an oily, yellow substance from their anal glands onto objects to mark their territories. When scent marking, the anal pouch is turned inside out, or everted. Hyenas also do this as a submissive posture to more dominant hyenas. Genitals, the anal area, and the anal glands are sniffed during greeting ceremonies in which each hyena lifts its leg and allows the other to sniff its anal sacks and genitals. All four species maintain latrines far from the main denning area where dung is deposited. Scent marking is also done by scraping the ground with the paws, which deposits scent from glands on the bottoms of the feet.
Species
Spotted hyena
The spotted hyena or laughing hyena (Crocuta crocuta) are native to Africa and are best known for a chirping, birdlike bark that resembles the sound of hysterical human laughter. Though often labeled incorrectly as a scavenger, the spotted hyena is actually a powerful hunter, the majority of its nourishment being derived from live prey. Spotted hyenas are the most common predator in sub-saharan Africa, living in savannah, dry woodland and desert habitats.
Striped hyena
The striped hyena (Hyaena hyaena) is closely related to the brown hyena. It lives in Africa, the Middle East, Pakistan, and western India. It is extinct in Europe, but can occasionally be spotted in Anatolia, Turkey. It is the smallest of the three extant hyena species. Striped hyenas are largely scavengers, but will also eat small animals, fruit, and insects. Larger subspecies are known to hunt animals as large as wild boar. They are nomadic, moving from water hole to water hole, but never straying more than 6 miles from one. Like many other animals of hot climates, their ears radiate heat.
The striped hyena is generally considered solitary, but has some social organization. It forages individually and is rarely seen in groups. It does, however, associate in small family groups at the den. The striped hyena live in the tropical savanna, grasslands, semi-desert, scrub forest, and woodland.
Brown hyena
The brown hyena (Parahyaena brunnea, formerly Hyaena brunnea) lives mainly in the Kalahari and Namib deserts of southern Africa. The intermediate-sized extant hyena, this species is 110-136 cm (43-53 in) in body length, 64-88 cm (25-35 in) tall at the shoulder, and weighs 37-55 kg (82-121 lb), though exceptional larger individuals are known. It is smaller than the spotted hyena, and unlike its spotted cousin, is largely a scavenger. It is the largest land animal to derive most of its diet from scavenging, although they will also hunt small mammals. Because of the scarcity of food in the desert, the brown hyena supplements its diet with fruit and vegetables, and along the Namib coastline they are known to snatch seal pups.
Like spotted hyena, the brown hyena lives in clans. However, brown hyena clans are much smaller (ranging between 4 and 15 members) and less organized, and do not hunt cooperatively. A particularly large food source may draw several of the clan to it, and they will work together to defend their find. They will also defend their territories as a group. Brown hyena can generally chase off leopard, caracal or cheetah, but spotted hyena will drive them from kills. Brown hyena often feed from lion kills, but lions dominate and occasionally kill brown hyena.
Unlike the spotted hyena, the females do not have enlarged clitoris, and males are slightly larger than females.
Evolution
The hyaenids have no fossil record before the mid-Miocene period, about 10 million years ago, thus making them the most recent addition to the carnivora. It is believed that the family began in Africa and spread through Europe and Asia. The peak of the Hyaenidae was during the Pleistocene, with 4 genera and 9 species of hyena (Postanowicz 2007). Extinct hyena genera included civet-like tree dwellers and speedy species designed for running down prey, along with even more powerfully developed bone crushing species similar to modern hyena. Fossil examples include the genera Protictitherium, Ictitherium, Chasmaporthetes, Adcrocuta, Pachycrocuta, and Percrocuta (of which P. gigantea was the largest Hyena which ever lived). Their success was largely due to the fact that the sabre-toothed cats, which they coexisted with, were unable to make full use of their prey due to the nature of their dentition. The hyena's powerful jaws and digestive systems allowed them to consume otherwise undigestible parts (Postanowicz 2007). As the sabre-toothed cats began to die out and be replaced by short fanged felids, which were more efficient eaters, some hyenas began to hunt for themselves and began evolving into new species, the modern spotted hyena being among them (Denis-Huot and Denis-Huot 2003).
Most lines of hyena died out towards the end of the Miocene, possibly due to competition from early canids. The running hyena Chasmaporthetes survived until the first ice ages, and the Eurasian cave hyena survived until the end of the last ice age, when they died out along with much of the Eurasian megafauna.
Habitat
With the exception of the striped hyena which has been seen in the jungles of India, all modern hyena species generally reside in arid environments like african savannahs and deserts.
Dietary habits
With the exception of the Aardwolf, all hyena species are efficient scavengers. They have extremely strong jaws in relation to their body size and have a very powerful digestive system with highly acidic fluids, making them capable of eating and digesting their entire prey, including skin, teeth, horns, bones and even hooves. Since they eat carrion, their digestive system deals very well with bacteria.
The spotted hyena is primarily a predator, unlike its cousins. Spotted hyenas are successful pack hunters of small to large sized ungulates and are the most abundant carnivore on the African continent.
The Aardwolf is a specialised feeder of termites, thus lacking the size and physical power of its cousins.
In culture
Negative associations have generally stemmed from their tendency to scavenge graves for food (being one of the few creatures naturally suited for this due to their ability to devour and digest every part of a carcass, including bone). As such, many associate hyenas with gluttony, uncleanliness, and cowardice.
Their haunting laughter-like calls inspired the idea in local cultures that they could imitate human voices and call its victims by name. Hyenas are also associated with divination and sometimes thought of as tools of demons and witches. In African folklore, witches and sorcerers are thought to ride hyenas, or even turn into them.
Christian legend reports that a hyena once brought a blind boy to Macarius the Egyptian who restored his sight to him. Isaiah says of Babylon that "hyenas will howl in their citadels" adding their voices to the sounds of desolation to be heard in this once beautiful city (Isaiah 13:22). The hyena was also a symbol of wisdom and cleverness, however, because of its constant laughter, its knowledge was seen to be that of the debased, profane, earthly, or initiatory kind. The wise hyena was a fool compared to the all-knowing God and symbolized the foolishness of man's wisdom as opposed to that of the Father (I Cor 1:25). [1]
African attitudes toward hyenas are little better than those held in the Western world. The majority of African tribes view hyenas as inedible and greedy hermaphrodites. The Bouda is a mythical tribe reputed to house members able to transform into hyenas.[2] Belief in "Werehyenas" is so entrenched within the traditional lore of the Bornu people of north-eastern Nigeria, that their language even contains a special word bultungin which translates as "I change myself into a hyena".[3]
Early naturalists thought hyenas were hermaphrodites or commonly practiced homosexuality, largely due to the female spotted hyena's unique urogenital system. According to early writings such as Ovid's Metamorphoses and the Physiologus, the hyena continually changed its sex and nature from male to female and back again. In Paedogogus, Clement of Alexandria noted that the hyena (along with the hare) was "quite obsessed with sexual intercourse." Many Europeans associated the hyena with sexual deformity, prostitution, and deviant sexual behavior.
In film
Hyenas have been used in animated movies many times, as well as having been rendered in live action films via CGI.
- A large clan of hyenas play the role of antagonistic henchman in the Disney animated film The Lion King. They are led by three notable hyenas named Shenzi, Banzai and Ed, who later reappeared as minor characters in the sequel "The Lion King 1 1/2".
- In Disney's The Chronicles of Narnia: The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe, a hyena is seen snapping at Aslan the lion's feet, when he walks to the Stone Table.
- Hyenas insinuated to be possessed or materialized by the demon Pazuzu attack and kill a young boy in Exorcist: The Beginning.
- Woof is a member of the Jokerz who has had his DNA genetically spliced with that of a hyena in Batman Beyond: Return of the Joker.
- Sami is a Tanzanian hyena swiper that appears in Dora's World Adventure.
- Yuri Orlov encounters a pack of hyenas in Lord of War.
- The Wargs in The Lord of the Rings bear a similarity to hyenas, although in the novels, they are described as intelligent wolves.
- Jane Goodall's Miss Goodall: The Hyena Story A documentary about hyenas. 16mm film, 2 reels.
In television
- A skeletal hyena monster named Skelerena plagues the Power Rangers in the Mighty Morphin' Power Rangers episode "Mirror of Regret."
- A group of evil, singing hyenas are villains in the Japanese animated series Kimba the White Lion.
- In Batman: The Animated Series and Krypto the Superdog, the Joker keeps a pair of pet hyenas named Bud and Lou (after the comedians Bud Abbott and Lou Costello).
- Hyenas figure prominently in the Buffy the Vampire Slayer Episode "The Pack", in which several characters are possessed by the spirits of a hyena pack.
- Shenzi, Banzai and Ed also appear as semi-regular characters in the Lion King television spin-off Timon & Pumbaa
- A pessimistic hyena named Hardy Har Har served as the foil to the Hanna-Barbera character Lippy the Lion.
- Hyenas have been characters in several episodes of Cow & Chicken.
- A hyena named Nebbich played a prominent role in the first season of the animated series The Legends of Treasure Island.
- Hyena was the name of a cybernetically enhanced villain on the cartoon Gargoyles
- In the animated series Biker Mice From Mars, the villanous slavers, the 'Sand Raiders' resembled humanoid hyenas.
- In Disney's Gargoyles, the brother sister duo of Jackal and Hyena were recurring villains.
In video games
- Capcom's first PlayStation 2 Mega Man X entry, Mega Man X7, featured a Maverick boss patterned after a hyena: Flame Hyenard. Like real-life hyenas, Flame Hyenard was identifiable by his loud whooping cries.
- Players encounter zombified hyenas in the Raccoon City Zoo in the "Wild Things" chapter of Resident Evil Outbreak: File 2.
- Shenzi, Banzai and Ed play minor villains alongside their hyena brethren in Kingdom Hearts 2.
- In World of Warcraft, hyenas can be seen in various locations, and trained as pets by the Hunter class.
- In the game Space Station: Silicon Valley for the Nintendo 64, you can play as a hyena in the jungle levels.
- The Pokemon Poochyena and Mightyena both resemble hyenas.
- Hyenas can be trained as pets in the massively multiplayer game Guild Wars Nightfall
In literature
- A group of were-hyena characters, led by the hermaphrodictic Narcissus play a role in Anita Blake: Vampire Hunter book Narcissus in Chains.
- In the book-series Earth's Children by Jean M. Auel, the leading character Ayla has an irrational disgust for hyenas, due to previous experiences with them.
- In Ernest Hemingway's The Snows of Kilimanjaro, a hyena watches over the dying Harry, and is constantly waking them up during the night.
- In Yann Martel's Life of Pi, the leading character, Piscine, shares a lifeboat with several zoo animals, including a hyena.
- In James Mischener's The Covenant, Mal Adriaan travels a large part of his journey with a tame Hyena named Swarts. After the death of his slave Dikkop, Adriaan begins talking to Swarts as a human being. When Swarts is killed by a Lion, Adriaan continues talking to the dead Hyena, even after returning to civilization.
- In The Island of Doctor Moreau by H. G. Wells, one of the most dangerous of the Beast People is a humanoid hybrid of hyena and swine.
In comics
- There have been two different supervillains, one male and one female, in the DC Universe to use the name "Hyena". Both are were-hyenas.
- A character named "Hyena" existed in the Amalgam Universe. He was a blend of the Joker and Sabretooth and the arch-enemy of Dark Claw.
In amusement parks
- A pair of belly-laughing hyenas are featured in the Disneyland attraction "It's a Small World".
- A small pack of hyenas are featured laughing at the plight of some natives cornered up a totem pole by a rhinoceros in the Disneyland "Jungle Cruise" attraction.
Notes
Rebecca Postanowicz, 2007. [2]
Lind, Hans. 1977. Bogen om dyrepsykologi: hvorfor handler dyr som de gør. [Kbh.]: Politiken
ISBN: 8756727178
See also
- Crocotta
- Hyena butter
External links
- Hyena: Wildlife summary from the African Wildlife Foundation
- Robin M. Weare's Hyena pages
- Excerpt about hyenas from Richard D. Estes's "The Safari Companion" (ISBN 1-890132-44-6)
- Kay E. Holekamp laboratory
- A mechanism for virilization of female spotted hyenas in utero
- The Hyaenidae Family from Lioncrusher's Domain
- The Hyaena Specialist Group
- evolution of the family
- "Hyenas" The Movie: The First Horror Movie About Hyenas
| ||||||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
- ↑ Denis-Huot, Christine & Denis-Huot, Michel (2003). The Art of being a Lion, pp.224. ISBN 158663707X.
- ↑ Hyaenidae. Retrieved 2007-05-31.