|
|
| (46 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | + | {{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}}{{Copyedited}} |
| | | | |
| − | '''Currently working on''' —[[User:Jennifer Tanabe|Jennifer Tanabe]] June 2021.
| + | [[File:Industrialisation.jpg|thumb|400px|Industrialization]] |
| − | | |
| − | [[File:Industrialisation.jpg|thumb|400px|Industrialisation]] | |
| | | | |
| | [[File:Kemna Lokomotiven.jpg|thumb|400px|Industrialization also means the mechanization of traditionally manual economic-sectors such as [[agriculture]].]] | | [[File:Kemna Lokomotiven.jpg|thumb|400px|Industrialization also means the mechanization of traditionally manual economic-sectors such as [[agriculture]].]] |
| | | | |
| − | | + | '''Industrialization''' (or '''industrialisation''') is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an [[agrarian society]] into an [[industrial society]]. This means converting to a socioeconomic order in which [[industry]] is dominant, which involves an extensive reorganization of the [[economy]] for the purpose of [[manufacturing]]. This process increases the food supply, creates a wider variety of jobs, stimulates technological development, and improves the external standard of living. |
| − | '''Industrialisation''' (or '''industrialization''') is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an [[agrarian society]] into an [[industrial society]]. This means converting to a socioeconomic order in which [[industry]] is dominant, which involves an extensive re-organization of an [[economy]] for the purpose of [[manufacturing]].<ref>{{cite book |last1 = O'Sullivan |first1=Arthur |author-link = Arthur O'Sullivan (economist)|first2=Steven M. |last2=Sheffrin |title = Economics: Principles in Action |publisher = Pearson Prentice Hall |year = 2003 |location = Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 |page = 472 |isbn = 0-13-063085-3 |oclc=50237774}}</ref> | + | {{toc}} |
| − | | + | However, there are also many [[unintended consequences]], both economically and socially. As industrial workers' incomes rise, markets for consumer goods and services of all kinds tend to expand and provide a further stimulus to industrial [[investment]] and [[economic growth]]. Moreover, [[family]] structures tend to shift as [[extended family|extended families]] tend not to live together in one household or location, as family members [[Human migration|migrate]] following job opportunities. Beyond these social consequences, industrialization has had negative effects on the environment, particularly through [[pollution]]. Balancing the positive and negative consequences of industrialization remains a challenge. |
| − | Historically industrialization is associated with increase of [[Pollution|polluting]] industries heavily dependent on [[fossil fuel]]s; however, with the increasing focus on [[sustainable development]] and [[green industrial policy]] practices, industrialization increasingly includes [[Leapfrogging|technological leapfrogging]], with direct investment in more advanced, cleaner technologies.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The reorganization of the economy has many [[unintended consequences]] both economically and socially. As industrial workers' incomes rise, markets for consumer goods and services of all kinds tend to expand and provide a further stimulus to industrial [[investment]] and [[economic growth]]. Moreover, family structures tend to shift as extended families tend to no longer live together in one household,location or place.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | '''Industrialization''' (also spelled '''Industrialisation''') or an '''Industrial Revolution''' is the process of converting to a socioeconomic order in which industry is dominant. This event took placew between late 1700’s to the early 1900’s.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| | | | |
| | ==History== | | ==History== |
| − | [[File:Maquina vapor Watt ETSIIM.jpg|400px|thumb|A [[Watt steam engine]], the [[steam engine]] fuelled primarily by [[coal]] that propelled the [[Industrial Revolution]] in the United Kingdom and the world.<ref>[[Watt steam engine]] image: located in the lobby of the Superior Technical School of Industrial Engineers of the UPM ([[Madrid]])</ref>]] | + | [[File:Maquina vapor Watt ETSIIM.jpg|400px|thumb|A [[Watt steam engine]], the [[steam engine]] fuelled primarily by [[coal]] that propelled the [[Industrial Revolution]] in the United Kingdom and the world.]] |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | After the last stage of the [[Proto-industrialization]], the first transformation from an agricultural to an industrial economy is known as the [[Industrial Revolution]] and took place from the mid-18th to early 19th century in certain areas in [[Europe]] and North America; starting in Great Britain, followed by Belgium, Switzerland, Germany, and France.<ref>Griffin, Emma, A short History of the British Industrial Revolution. In 1850 over 50 percent of the British lived and worked in cities. London: Palgrave (2010)</ref> Characteristics of this early industrialisation were technological progress, a shift from rural work to industrial labor, financial investments in new industrial structure, and early developments in class consciousness and theories related to this.<ref name=springer.com>{{Cite book |chapter=Sustainable Industrialization in Africa: Toward a New Development Agenda |doi=10.1007/978-1-137-56112-1_1 |publisher=Springer |date=2016 |title=Sustainable Industrialization in Africa |last1=Sampath |first1=Padmashree Gehl |pages=1–19 |isbn=978-1-349-57360-8 }}{{Verify source|date=July 2019}}</ref> Later commentators have called this the First Industrial Revolution.<ref>Pollard, Sidney: Peaceful Conquest. The Industrialisation of Europe 1760–1970, Oxford 1981.</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | The "[[Second Industrial Revolution]]" labels the later changes that came about in the mid-19th century after the refinement of the [[steam engine]], the invention of the [[internal combustion engine]], the harnessing of [[electric power|electricity]] and the construction of canals, railways and electric-power lines. The invention of the [[assembly line]] gave this phase a boost.
| + | In most pre-industrial societies, the majority of the population were focused on producing their means of survival through [[subsistence farming]]. [[Famine]]s were frequent. Some, such as [[classical Athens]], had [[trade]] and [[commerce]] as significant factors. As a result, Greeks could enjoy wealth far beyond a sustenance standard of living through the use of [[slavery]].<ref> Ben Akrigg, ''Population and Economy in Classical Athens'' (Cambridge University Press, 2019, ISBN 1107027098). </ref> |
| − | Coal mines, steelworks, and textile factories replaced homes as the place of work.
| |
| − | <ref>
| |
| − | Buchheim, Christoph: Industrielle Revolutionen. Langfristige Wirtschaftsentwicklung in Großbritannien, Europa und in Übersee, München 1994, S. 11-104.
| |
| − | </ref><ref>
| |
| − | Jones, Eric: The European Miracle: Environments, Economics and Geopolitics in the History of Europe and Asia, 3. ed. Cambridge 2003.
| |
| − | </ref><ref>
| |
| − | Henning, Friedrich-Wilhelm: Die Industrialisierung in Deutschland 1800 bis 1914, 9. Aufl., Paderborn/München/Wien/Zürich 1995, S. 15-279.</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | By the end of the 20th century, [[East Asia]] had become one of the most recently industrialised regions of the world.<ref>''Industry & Enterprise: A International Survey Of Modernisation & Development'', ISM/Google Books, revised 2nd edition, 2003. {{ISBN|978-0-906321-27-0}}. [https://books.google.com/books?id=lZS7OXZUsnMC&dq=isbn:0906321271] {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160511033359/https://books.google.com/books?id=lZS7OXZUsnMC&dq=isbn:0906321271 |date=11 May 2016 }}</ref> The BRICS states (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa) are undergoing the process of industrialisation.<ref name="springer.com"/>
| + | What some have termed "Proto-industrialization," involving regional development of rural [[handicraft]] production for external markets, took place in Europe as well as in [[Mughal India]] prior to the [[Industrial Revolution]].<ref>József Böröcz, ''The European Union and Global Social Change'' (Routledge, 2009, ISBN 0415481023).</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | There is considerable literature on the factors facilitating industrial modernisation and enterprise development.<ref>Lewis F. Abbott, ''Theories Of Industrial Modernisation & Enterprise Development: A Review'', ISM/Google Books, revised 2nd edition, 2003. {{ISBN|978-0-906321-26-3}}.[https://books.google.com/books?q=theories+of+industrial+modernisation+and+enterprise+development&btnG=Search+Books]</ref>
| + | After the last stage of this Proto-industrialization, the [[Industrial Revolution]] which transformed the agricultural to an industrial economy took place, starting in [[Great Britain]], followed by [[Belgium]], [[Switzerland]], [[Germany]], and [[France]].<ref name=Griffin>Emma Griffin, ''A short History of the British Industrial Revolution'' (Red Globe Press, 2018, ISBN 1352003244).</ref> This early industrialization was characterized by technological progress, a shift from rural work to industrial labor, financial investments in new industrial structure, and early developments in class consciousness. Later commentators have called this the First Industrial Revolution.<ref>Sidney Pollard, ''Peaceful Conquest: The Industrialization of Europe 1760–1970'' (Oxford University Press, 1981, ISBN 0198770936).</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | Most pre-industrial economies had standards of living not much above [[List of subsistence techniques|subsistence]], among that the majority of the population were focused on producing their means of survival. For example, in [[Middle Ages|medieval]] Europe, as much as 80% of the labour force was employed in subsistence [[agriculture]].{{Citation needed|date=January 2012}}
| + | Industrialization started with the mechanization of the [[textile]] industries, the development of [[iron]]-making techniques and the increased use of refined [[coal]]. Once started, it spread. Trade expansion was enabled by the introduction of [[canal]]s, improved roads and railways. The introduction of steam power (fueled primarily by coal) and powered machinery (mainly in textile manufacturing) underpinned dramatic increases in production capacity. The development of all-metal machine tools in the first two decades of the nineteenth century facilitated the manufacture of more production machines for manufacturing in other industries. The effects spread throughout Western Europe and North America during the nineteenth century, eventually affecting most of the world. |
| | | | |
| − | Some pre-industrial economies, such as [[classical Athens]], had trade and commerce as significant factors, so native Greeks could enjoy wealth far beyond a sustenance standard of living through the use of [[slavery]].<ref>Akrigg, B. (2019). Population and Economy in Classical Athens (Cambridge Classical Studies). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/9781139225250, page 95</ref> [[Famine]]s were frequent in most pre-industrial societies, although some, such as the Netherlands and England of the 17th and 18th centuries, the [[Italian city-states]] of the 15th century, the medieval Islamic [[Caliphate]], and the ancient [[Ancient Greece|Greek]] and [[Ancient Rome|Roman]] [[civilisation]]s were able to escape the famine cycle through increasing trade and [[commercialisation]] of the [[Agriculture|agricultural sector]].{{Citation needed|date=January 2012}} It is estimated that during the 17th century, {{Clarify span|after immense from the [[Mughal Bengal]] to the [[Dutch East India Company]],<ref name="Prakash">[[Om Prakash (historian)|Om Prakash]], "[http://link.galegroup.com/apps/doc/CX3447600139/WHIC?u=seat24826&xid=6b597320 Empire, Mughal]", ''History of World Trade Since 1450'', edited by John J. McCusker, vol. 1, Macmillan Reference USA, 2006, pp. 237–240, ''World History in Context''. Retrieved 3 August 2017</ref>|reason=a crucial word is missing here|date=July 2020}} Netherlands [[import]]ed nearly 70% of its grain supply; and in the 5th century B.C.E. Athens imported three-quarters of its total food supply.{{Citation needed|date=April 2011}}
| + | The "[[Second Industrial Revolution]]" labels the later changes that came about in the mid-nineteenth century after the refinement of the [[steam engine]], the invention of the [[internal combustion engine]], the harnessing of [[electric power|electricity]] and the construction of electric-power lines. The invention of the [[assembly line]] gave this phase a boost.<ref>Eric Jones, ''The European Miracle: Environments, Economics and Geopolitics in the History of Europe and Asia'' (Cambridge University Press, 2003, ISBN 052152783X).</ref> |
| − | | |
| − | A process called [[proto-industrialisation]] occurred in Europe as well as in [[Mughal India]],<ref>{{cite book|title=How India Clothed the World: The World of South Asian Textiles, 1500-1850|author=Giorgio Riello, Tirthankar Roy|publisher=[[Brill Publishers]]|year=2009|page=174|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=niuwCQAAQBAJ&pg=PA174|isbn=9789047429975}}</ref> and was the first stage prior to the [[Industrial Revolution]].<ref name="borocz">{{cite book|author=József Böröcz|title=The European Union and Global Social Change|page=21|publisher=[[Routledge]]|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=d0SPAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA21|accessdate=26 June 2017|isbn=9781135255800|date=2009-09-10|author-link=József Böröcz}}</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | In his 1728 work on the economy of England, [[A Plan of the English Commerce]], [[Daniel Defoe]] describes how England developed from being a raw [[wool]] producer to the manufacture of finished woolen [[textile]]s. Defoe writes that [[House of Tudor|Tudor]] monarchs, especially [[Henry VII of England]] and [[Elizabeth I of England|Elizabeth I]], implemented policies that today would be described as [[protectionism|protectionist]], such as imposing high [[tariff]]s on the importation of finished woolen goods, imposing high taxes on raw wool exports leaving England, bringing in artisans skilled in wool textile manufacturing from the [[Low Countries]], awarding selective [[government-granted monopoly]] rights in geographic areas of England deemed suitable for textile industrial production, and granting government-sponsored [[industrial espionage]] to develop the early English textile industry.<ref>Chang, Ha-Joon "Bad Samaritans: The Myth of Free Trade and the Secret History of Capitalism" (New York: Random House, 2008), p. 229 quoting "A Plan for the English Commerce, p. 95</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | After the victory of the [[East India Company]] in the [[Battle of Plassey]] over the rulers of the [[Bengal Subah]], industrialisation through [[innovation]] in manufacturing processes first started with the Industrial Revolution in the north-west and Midlands of England in the 18th century.<ref>[http://www.historyguide.org/intellect/lecture17a.html The Origins of the Industrial Revolution in England] by Steven Kreis. Last Revised 11 October 2006. Accessed April 2008</ref> It spread to Europe and North America in the 19th century.
| |
| | | | |
| | ==Industrial revolution in Europe== | | ==Industrial revolution in Europe== |
| | {{Main|Industrial Revolution}} | | {{Main|Industrial Revolution}} |
| − | The era known as the [[Industrial Revolution]] was a period in which fundamental changes occurred in agriculture, textile and metal manufacture, transportation, economic policies and the social structure in England ( and afterwards elsewhere in Europe). This period is appropriately labeled “revolution,” for it thoroughly destroyed the old manner of doing things; yet the term is simultaneously inappropriate, for it connotes abrupt change. | + | [[Image:Crystal Palace - interior.jpg|thumb|right|400px|[[The Crystal Palace]] [[Great Exhibition|Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of all Nations]], London, 1851.]] |
| | + | The era known as the [[Industrial Revolution]] was a period in which fundamental changes occurred in [[agriculture]], [[textile]] and [[metal]] manufacture, [[transportation]], economic policies, and the [[social structure]] beginning in Great Britain and spreading throughout Europe. This period is appropriately labeled “revolution,” for it thoroughly destroyed the old manner of doing things; yet the term is simultaneously inappropriate, for it connotes abrupt change. |
| | | | |
| | [[Image:Zeche Mittelfeld Ilmenau.jpg|thumb|400px|A factory in [[Ilmenau]] ([[Germany]]) around 1860]] | | [[Image:Zeche Mittelfeld Ilmenau.jpg|thumb|400px|A factory in [[Ilmenau]] ([[Germany]]) around 1860]] |
| | | | |
| | + | The changes that occurred during this period (1760-1850), in fact, occurred gradually. The year 1760 is generally accepted as the “eve” of the Industrial Revolution. In reality, this eve began more than two centuries before this date. The late eighteenth century and the early nineteenth century brought to fruition the ideas and discoveries of those who had long passed on, such as, [[Galileo]], [[Francis Bacon]], [[René Descartes]], and others. |
| | | | |
| − | The changes that occurred during this period (1760-1850), in fact, occurred gradually. The year 1760 is generally accepted as the “eve” of the Industrial Revolution. In reality, this eve began more than two centuries before this date. The late 18th century and the early l9th century brought to fruition the ideas and discoveries of those who had long passed on, such as, Galileo, Bacon, Descartes, and others.
| |
| − | [[Image:Crystal Palace - interior.jpg|thumb|right|400px|[[The Crystal Palace]] [[Great Exhibition|Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of all Nations]], London, 1851.]]
| |
| | [[File:Barmen (1870).jpg|thumb|400px|Early industrialization in Germany, the city of [[Barmen]] in 1870. Painting by [[August von Wille]]]] | | [[File:Barmen (1870).jpg|thumb|400px|Early industrialization in Germany, the city of [[Barmen]] in 1870. Painting by [[August von Wille]]]] |
| | [[File:Aplerbecker Hütte2.JPG|thumb|400px|Aplerbecker Hütte, an industrialised area of [[Dortmund]], Germany circa 1910.]] | | [[File:Aplerbecker Hütte2.JPG|thumb|400px|Aplerbecker Hütte, an industrialised area of [[Dortmund]], Germany circa 1910.]] |
| | | | |
| − | The United Kingdom was the first country in the world to industrialize.<ref name="Industrial Revolution">{{cite web|url=http://www.ace.mmu.ac.uk/eae/Global_Warming/Older/Industrial_Revolution.html |title=Industrial Revolution |accessdate=27 April 2008 |url-status=dead |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20080427080826/http://www.ace.mmu.ac.uk/eae/Global_warming/older/Industrial_Revolution.html |archivedate=27 April 2008 }}</ref> In the 18th and 19th centuries, the UK experienced a massive increase in agricultural productivity known as the [[British Agricultural Revolution]], which enabled an unprecedented [[population growth]], freeing a significant percentage of the workforce from farming, and helping to drive the [[Industrial Revolution]].
| + | In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, the United Kingdom experienced a massive increase in agricultural productivity known as the [[British Agricultural Revolution]], which enabled unprecedented [[population growth]], freeing a significant percentage of the workforce from farming, and helping to drive the [[Industrial Revolution]]. |
| − | | |
| − | Due to the limited amount of arable land and the overwhelming efficiency of [[mechanization|mechanized]] farming, the increased population could not be dedicated to agriculture. New agricultural techniques allowed a single [[peasant]] to feed more [[worker]]s than previously; however, these techniques also increased the demand for [[machine]]s and other [[Household hardware|hardware]], which had traditionally been provided by the [[Urban area|urban]] [[artisan]]s. Artisans, collectively called [[bourgeoisie]], employed rural [[Human migration#Ravenstein's 'laws of migration'|exodus]] workers to increase their output and meet the country's needs.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | Due to the limited amount of arable land and the overwhelming efficiency of [[mechanization|mechanized]] farming, the increased population could not be dedicated to agriculture. New agricultural techniques allowed a single [[peasant]] to feed more [[worker]]s than previously. However, these techniques also increased the demand for [[machine]]s and other [[Household hardware|hardware]], which had traditionally been provided by the [[Urban area|urban]] [[artisan]]s. Artisans employed rural workers to increase their output and meet the country's needs. |
| | | | |
| − | British industrialization involved significant changes in the way that work was performed. The process of creating a [[Good (economics and accounting)|good]] was divided into simple tasks, each one of them being gradually mechanized in order to boost [[productivity]] and thus increase [[income]]. The new machines helped to improve the productivity of each worker. However, industrialization also involved the exploitation of new forms of energy. In the pre-industrial economy, most machinery was powered by human muscle, by animals, by wood-burning or by [[hydropower|water-power]]. With industrialization these sources of fuel were replaced with coal, which could deliver significantly more energy than the alternatives. Much of the new technology that accompanied the industrial revolution was for machines which could be powered by coal. One outcome of this was an increase in the overall amount of energy consumed within the economy - a trend which has continued in all industrialized nations to the present day.<ref>{{cite web|last=Griffin|first=Emma|title=Patterns of Industrialisation|url=https://www.academia.edu/840198|accessdate=9 March 2013}}</ref> | + | British industrialization involved significant changes in the way that work was performed. The process of creating a [[Good (economics and accounting)|good]] was divided into simple tasks, each one of them being gradually mechanized in order to boost [[productivity]] and thus increase [[income]]. The new machines helped to improve the productivity of each worker. However, industrialization also involved the exploitation of new forms of energy. In the pre-industrial economy, most machinery was powered by human muscle, by animals, by wood-burning or by [[hydropower|water-power]]. With industrialization these sources of fuel were replaced with [[coal]], which could deliver significantly more energy than the alternatives. |
| | | | |
| − | The accumulation of [[capital (economics)|capital]] allowed [[investment]]s in the [[science|scientific]] [[research|conception and application of new technologies]], enabling the industrialization process to continue to evolve. The industrialization process formed a class of industrial workers who had more money to spend than their agricultural cousins. They spent this on items such as tobacco and sugar, creating new mass markets that stimulated more investment as merchants sought to exploit them.<ref>[https://www.bbc.co.uk/history/british/abolition/industrialisation_article_01.shtml Enslavement and industrialization] Robin Blackburn , BBC British History. Published: 18 December 2006 Accessed April 2008</ref> | + | The accumulation of [[capital (economics)|capital]] allowed [[investment]]s in the [[science|scientific]] conception and application of new technologies, enabling the industrialization process to continue to evolve. The industrialization process formed a class of industrial workers who had more money to spend than their agricultural cousins. They spent this on items such as [[tobacco]] and [[sugar]], creating new mass markets that stimulated more investment as merchants sought to exploit them.<ref>Robin Blackburn, [https://www.bbc.co.uk/history/british/abolition/industrialisation_article_01.shtml Enslavement and industrialization] ''BBC'', February 17, 2011. Retrieved September 24, 2021.</ref> The mechanization of production spread to other European countries and to British colonies, helping to make those areas the wealthiest, and shaping what is now known as the [[Western world]]. |
| | | | |
| − | The mechanization of production spread to the countries surrounding England geographically in Europe such as France and to British [[Settler colonialism|settler colonies]], helping to make those areas the wealthiest, and shaping what is now known as the [[Western world]].
| + | Some historians have argued that the possession of so-called 'exploitation colonies' eased the accumulation of capital to the countries that possessed them, speeding up their [[Economic development|development]].<ref>Eric Williams, ''Capitalism and Slavery'' (Franklin Classics, 2018, ISBN 0343147610).</ref> Some have stressed the importance of natural or financial resources that Britain received from its many overseas colonies or that profits from the British [[slave trade]] between Africa and the Caribbean helped fuel industrial investment.<ref>Kenneth Pomeranz, ''The Great Divergence'' (Princeton University Press, 2000, ISBN 0691005435).</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | Some economic historians argue that the possession of so-called 'exploitation colonies' eased the accumulation of capital to the countries that possessed them, speeding up their [[Economic development|development]].<ref>{{cite book|last=Williams|first=Eric|title=Capitalism and Slavery|year=1965}}</ref> The consequence was that the [[Colony|subject country]] integrated a bigger [[economic system]] in a subaltern position, emulating the countryside, which demands manufactured goods and offers raw materials, while the colonial power stressed its urban posture, providing goods and importing food. A classical example of this mechanism is said to be the [[triangular trade]], which involved England, southern United States and western Africa. Some have stressed the importance of natural or financial resources that Britain received from its many overseas colonies or that profits from the British [[slave trade]] between Africa and the Caribbean helped fuel industrial investment.<ref>{{cite book|last=Pomeranz|first=Kenneth|title=The Great Divergence|year=2000|publisher=Princeton University Press}}</ref>
| + | With these arguments still find some favor with historians of the colonies, most historians of the British Industrial Revolution do not consider that colonial possessions formed a significant role in the country's industrialization. Whilst not denying that Britain could profit from these arrangement, they believe that industrialization would have proceeded with or without the colonies.<ref name=Griffin/> |
| | | | |
| − | With these arguments still find some favor with historians of the colonies, most historians of the British Industrial Revolution do not consider that colonial possessions formed a significant role in the country's industrialization. Whilst not denying that Britain could profit from these arrangement, they believe that industrialization would have proceeded with or without the colonies.<ref>{{cite book|last=Griffin|first=Emma|title=A Short History of the British Industrial Revolution|year=2010|publisher=Palgrave}}</ref>
| + | ==Early industrialization in other countries== |
| − | | + | [[File:Zilina Slovena.jpg|thumb|right|400px|The textile factory ''Slovena'' built in 1891 in [[Žilina]] ([[Slovakia]]) - an example of a delayed industrialization in [[Central Europe]].]] |
| − | ==Early industrialisation in other countries== | |
| − | [[File:Zilina Slovena.jpg|thumb|right|400px|The textile factory ''Slovena'' built in 1891 in [[Žilina]] ([[Slovakia]]) - an example of a delayed industrialisation in [[Central Europe]].]] | |
| | The Industrial Revolution spread southwards and eastwards from its origins in Northwest Europe. | | The Industrial Revolution spread southwards and eastwards from its origins in Northwest Europe. |
| | | | |
| − | After the [[Convention of Kanagawa]] issued by Commodore [[Matthew C. Perry]] forced Japan to open the ports of Shimoda and Hakodate to American trade, the Japanese government realised that drastic reforms were necessary to stave off Western influence. The [[Bakumatsu|Tokugawa shogunate]] abolished the [[Feudalism|feudal system]]. The government instituted military reforms to modernise the Japanese army and also constructed the base for industrialisation. In the 1870s, the [[Meiji period|Meiji]] government vigorously promoted technological and industrial development that eventually changed Japan to a [[Regional power|powerful]] modern country. | + | After the [[Convention of Kanagawa]] issued by Commodore [[Matthew C. Perry]] forced [[Japan]] to open the ports of Shimoda and Hakodate to American trade, the Japanese government realized that drastic reforms were necessary to stave off Western influence. The [[Bakumatsu|Tokugawa shogunate]] abolished the [[Feudalism|feudal system]]. The government instituted military reforms to modernize the Japanese army and also constructed the base for industrialization. In the 1870s, the [[Meiji period|Meiji]] government vigorously promoted technological and industrial development that eventually changed Japan to a [[Regional power|powerful]] modern country. |
| − | | |
| − | In a similar way, Russia which suffered during the [[Allied intervention in the Russian Civil War]]. The [[Soviet Union]]'s [[Planned economy|centrally controlled economy]] decided to invest a big part of its resources to enhance its industrial production and [[infrastructure]]s to assure its survival, thus becoming a world [[superpower]].<ref>[http://www.learningcurve.gov.uk/heroesvillains/g4/ Joseph Stalin and the industrialisation of the USSR] {{webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080517122519/http://www.learningcurve.gov.uk/heroesvillains/g4 |date=2008-05-17 }} Learning Curve website, The UK National Archives. Accessed April 2008</ref> During the [[Cold war]], the other [[Warsaw Pact]] countries, organised under the [[Comecon]] framework, followed the same developing scheme, albeit with a less emphasis on [[heavy industry]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | Southern European countries such as [[Spanish economic miracle|Spain]] or [[Italian economic miracle|Italy]] industrialized moderately during the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and then experienced economic booms after the Second World War, caused by a healthy integration of the [[Economy of Europe|European economy]].<ref>[http://cronologia.leonardo.it/storia/tabello/tabe1565.htm BOOM E MIRACOLO ITALIANO ANNI '50-60 (CRONOLOGIA)]</ref><ref>[https://books.google.com/books?id=0qgvdlWlXnQC&pg=PA18&lpg=PA18&dq=milagro+espa%C3%B1ol+franco&source=web&ots=KTvntPpytP&sig=GfgfbZwAwZx7Y5425fgjeHOMdDI&hl=en&sa=X&oi=book_result&resnum=1&ct=result#PPA18,M1 Queer transitions in contemporary Spanish culture: from Franco to la movida], By Gema Pérez-Sánchez</ref>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==The Third World==
| |
| − | {{Main|Third World}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | A similar state-led developing programme was pursued in virtually all the Third World countries during the [[Cold War]], including the [[Socialism|socialist]] ones, but especially in [[Sub-Saharan Africa]] after the [[decolonization]] period.{{Citation needed|date=March 2008}} The primary scope of those projects was to achieve [[self-sufficiency]] through the local production of previously [[import]]ed goods, the mechanization of agriculture and the spread of [[education]] and [[health care]]. However, all those experiences failed bitterly{{Cn|date=April 2018}} due to a lack of realism{{Cn|date=March 2019}}: most countries did not have a pre-industrial bourgeoisie able to carry on a [[Capitalism|capitalistic]] development or even a stable and peaceful [[State (polity)|state]]. Those aborted experiences left [[Developing countries' debt|huge debts]] toward western countries and fuelled [[Political corruption|public corruption]].{{Cn|date=April 2018}}
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Petrol-producing countries===
| |
| − | Oil-rich countries saw similar failures in their economic choices.
| |
| − | An [[Energy Information Administration|EIA]] report stated that [[OPEC]] member nations were projected to earn a net amount of $1.251 trillion in 2008 from their oil exports.<ref>[http://in.reuters.com/article/businessNews/idINIndia-34433820080708 OPEC to earn $1.251 trillion from oil exports - EIA], Reutrs</ref> Because oil is both important and expensive, regions that had big [[Oil reserves|reserves of oil]] had huge [[liquidity]] incomes. However, this was rarely followed by economic development. Experience shows that local [[elite]]s were unable to re-invest the [[petrodollar]]s obtained through oil export, and currency is wasted in [[luxury good]]s.<ref>[http://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/news/opinon/2008/10/198_12838.html Understanding New Middle East], Behzad Shahandeh, The Korea Times, 31 October 2007</ref>
| |
| | | | |
| − | This is particularly evident in the [[Arab States of the Persian Gulf#Economy|Persian Gulf states]], where the [[per capita income]] is comparable to those of western nations, but where no industrialization has started. Apart from two little countries ([[Economy of Bahrain|Bahrain]] and the [[Economy of the United Arab Emirates|United Arab Emirates]]), the [[Arab States of the Persian Gulf|Persian Gulf states]] have not [[Diversity (business)|diversified their economies]], and no replacement for the [[Oil depletion|upcoming end of oil reserves]] is envisaged.<ref>[https://2009-2017.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/3584.htm Background Note: Saudi Arabia]</ref>
| + | The [[Soviet Union]] invested a large part of its resources to enhance its industrial production and [[infrastructure]]s to assure its survival, thus becoming a world [[superpower]].<ref> Joshua R. Keefe, [http://www.inquiriesjournal.com/articles/1684/stalin-and-the-drive-to-industrialize-the-soviet-union Stalin and the Drive to Industrialize the Soviet Union] ''Inquiries'' 1(10) (2009): 1. Retrieved September 24, 2021.</ref> During the [[Cold war]], the other [[Warsaw Pact]] countries, organized under the [[Comecon]] framework, followed the same developing scheme, albeit with a less emphasis on [[heavy industry]]. |
| | | | |
| | ==Industrialization in Asia== | | ==Industrialization in Asia== |
| | [[Image:Durgapur Steel Plant.jpg|thumb|350px|[[Durgapur Steel Plant]] located in [[West Bengal]], [[India]]]] | | [[Image:Durgapur Steel Plant.jpg|thumb|350px|[[Durgapur Steel Plant]] located in [[West Bengal]], [[India]]]] |
| | | | |
| − | Apart from [[Japan]], where [[industrialization of Japan|industrialization began]] in the late nineteenth century, a different pattern of industrialization followed in [[East Asia]]. One of the fastest rates of industrialization occurred in the late 20th century across four places known as the [[Four Asian Tigers|Asian tigers]] (Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea and Taiwan). Between the early 1960s and 1990s, they underwent rapid industrialization and maintained exceptionally high growth rates of more than 7 percent a year. By the early 21st century, these economies had developed into high-income economies, specializing in areas of competitive advantage. Hong Kong and Singapore have become leading international financial centers, whereas South Korea and Taiwan are leaders in manufacturing electronic components and devices. | + | Apart from [[Japan]], where [[industrialization of Japan|industrialization began]] in the late nineteenth century, a different pattern of industrialization followed in [[East Asia]]. One of the fastest rates of industrialization occurred in the late 20twentieth century across four places known as the [[Four Asian Tigers|Asian tigers]] ([[Hong Kong]], [[Singapore]], [[South Korea]], and [[Taiwan]]). Between the early 1960s and 1990s, they underwent rapid industrialization and maintained exceptionally high growth rates of more than 7 percent a year. By the early twenty-first century, these economies had developed into high-income economies, specializing in areas of competitive advantage. Hong Kong and Singapore have become leading international financial centers, whereas South Korea and Taiwan are leaders in manufacturing electronic components and devices. |
| | | | |
| − | Prior to the [[1997 Asian financial crisis]], the growth of the Four Asian Tiger economies (commonly referred to as "the Asian Miracle") has been attributed to export oriented policies and strong development policies. The existence of stable governments and well structured societies, strategic locations, heavy foreign [[investment]]s, a low cost skilled and motivated [[workforce]], a competitive [[exchange rate]], and low custom duties supported their quick growth. Unique to these economies were the sustained rapid growth and high levels of equal income distribution. A World Bank report suggests two development policies among others as sources for the Asian miracle: factor accumulation and macroeconomic management.<ref name="Page 1994">{{Cite book
| + | In the case of South Korea, the largest of the four Asian tigers, a very fast-paced industrialization took place as it quickly moved away from the manufacturing of value-added goods in the 1950s and 1960s into the more advanced steel, shipbuilding, and automotive industry in the 1970s and 1980s, focusing on the high-tech and service industry in the 1990s and 2000s. As a result, South Korea became a major [[G20 industrial nations|economic power]]. |
| − | |given=John |surname=Page
| |
| − | |chapter=The East Asian Miracle: Four Lessons for Development Policy
| |
| − | |chapter-url=http://www.nber.org/chapters/c11011
| |
| − | |pages=219–269
| |
| − | |doi=10.1086/654251
| |
| − | |title=NBER Macroeconomics Annual 1994, Volume 9
| |
| − | |journal=NBER Macroeconomics Annual
| |
| − | |volume=9
| |
| − | |editor1-given=Stanley |editor1-surname=Fischer
| |
| − | |editor2-given=Julio J. |editor2-surname=Rotemberg
| |
| − | |location=Cambridge, Massachusetts |publisher = MIT Press
| |
| − | |year=1994
| |
| − | |isbn=978-0-262-06172-8
| |
| − | |s2cid=153796598
| |
| − | |url=https://www.nber.org/books/fisc94-1
| |
| − | |url-status=live
| |
| − | |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130202071659/https://www.nber.org/books/fisc94-1
| |
| − | |archive-date=2 February 2013
| |
| | | | |
| − | }}</ref>
| + | This starting model was afterwards successfully copied in other larger Eastern and Southern Asian countries. The success of this phenomenon led to a huge wave of [[offshoring]] – Western factories or [[Tertiary sector of economic activity|Tertiary Sector]] corporations choosing to move their activities to countries where the workforce was less expensive and less collectively organized. |
| | | | |
| − | In the case of South Korea, the largest of the four Asian tigers, a very fast-paced industrialization took place as it quickly moved away from the manufacturing of value-added goods in the 1950s and 60s into the more advanced steel, shipbuilding and automotive industry in the 1970s and 80s, focusing on the high-tech and service industry in the 1990s and 2000s. As a result, South Korea became a major [[G20 industrial nations|economic power]].
| + | China and India, while basically following this development pattern, made adaptations in line with their own histories and cultures, their major size and importance in the world, and the [[Geopolitics|geo-political]] ambitions of their governments. Both China and India have also started to make significant investments in other developing countries, making them significant players in today's world economy. |
| | | | |
| − | This starting model was afterwards successfully copied in other larger Eastern and Southern Asian countries. The success of this phenomenon led to a huge wave of [[offshoring]] – i.e., Western factories or [[Tertiary sector of economic activity|Tertiary Sector]] corporations choosing to move their activities to countries where the workforce was less expensive and less collectively organized.
| + | India's government is also investing in economic sectors such as [[bioengineering]], [[nuclear technology]], [[pharmaceutics]], [[Information technology|informatics]], and technologically oriented [[higher education]], exceeding its needs, with the goal of creating several specialization poles able to conquer foreign markets. |
| − | | |
| − | China and India, while roughly following this development pattern, made adaptations in line with their own histories and cultures, their major size and importance in the world, and the [[Geopolitics|geo-political]] ambitions of their governments, etc..
| |
| − | | |
| − | Meanwhile, India's government is investing in economic sectors such as [[bioengineering]], [[nuclear technology]], [[pharmaceutics]], [[Information technology|informatics]], and technologically oriented [[higher education]], exceeding its needs, with the goal of creating several specialization poles able to conquer foreign markets.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Both China and India have also started to make significant investments in other developing countries, making them significant players in today's world economy.
| |
| | | | |
| | ==Newly industrialized countries== | | ==Newly industrialized countries== |
| − | Since the mid-late twentieth century, most countries in Latin America, Asia, and Africa, including [[Brazil]], [[Indonesia]], [[Malaysia]], [[Mexico]], [[Philippines]], [[South Africa]], and [[Turkey]] have experienced substantial industrial growth, fuelled by exporting to countries that have bigger economies: the United States, China, India and the EU. They are sometimes called [[Newly industrialized country|newly industrialized countries]] (NICs). | + | Since the mid to late twentieth century, most countries in Latin America, Asia, and Africa, including [[Brazil]], [[Indonesia]], [[Malaysia]], [[Mexico]], [[Philippines]], [[South Africa]], and [[Turkey]], have experienced substantial industrial growth, fueled by exporting to countries that have bigger economies: the United States, China, India, and the European Union. |
| | | | |
| − | These countries have economies have not yet reached a developed country's status but have, in a macroeconomic sense, outpaced their developing counterparts. Such countries are still considered developing nations and only differ from other developing nations in the rate at which an NIC's growth is much higher over a shorter allotted time period compared to other developing nations.<ref name="c10">{{cite book|title=Essentials of Comparative Politics|chapter=Chapter 10: Developing Countries|pages=304–337|author=Patrick H. O’Neil|publisher=W. W. Norton & Company|year=2018|edition=6th|isbn=978-0-393-62458-8}}</ref> Another characterization of NICs is that of countries undergoing rapid [[economic growth]] (usually [[export]]-oriented).<ref>{{cite journal|url=https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/wp/2016/wp16207.pdf|title=The Role of Newly Industrialized Economies in Global Value Chains|journal=IMF Working Paper|publisher=International Monetary Fund|author=Dominik Boddin|date=October 2016|access-date=28 September 2020}}</ref> Incipient or ongoing [[industrialization]] is an important indicator of an NIC. In many NICs, social upheaval can occur as primarily rural, or agricultural, populations migrate to the cities, where the growth of manufacturing concerns and [[Factory|factories]] can draw many thousands of laborers. NICs introduce many new immigrants looking to improve their social and/or political status through newly formed democracies and the increase in wages that most individuals who partake in such changes would obtain. | + | These countries, sometimes called [[Newly industrialized country|newly industrialized countries]] (NICs), have economies have not yet reached a developed country's status but have, in a macroeconomic sense, outpaced their developing counterparts. Such countries are still considered developing nations and only differ from other developing nations in the rate at which an NIC's growth is much higher over a shorter allotted time period compared to other developing nations.<ref>Patrick H. O’Neil, ''Essentials of Comparative Politics'' (W. W. Norton & Company, 2020, ISBN 0393532771).</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | ==Social consequences== | + | ==Consequences== |
| | | | |
| − | [[File:Bairoch.png|thumb|400px|right|The effect of industrialization shown by rising income levels in the nineteenth century. The graph shows [[gross national product]] (at [[purchasing power parity]]) [[per capita]] between 1750 and 1900 in 1990 [[US dollars]] for [[First World]] nations (Europe, United States, Canada, Japan) and [[Third World]] nations (Europe in east, Southern Asia, Africa, Latin America).<ref name="Bairoch1995">{{cite book |last=Bairoch |first=Paul |title=Economics and World History: Myths and Paradoxes |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=LaF_cCknJScC&pg=PA95 |date=1995 |publisher=University of Chicago Press |isbn=978-0-226-03463-8 |page=95}}</ref>]]
| + | ===Transportation=== |
| − | The [[Industrial Revolution|Industrial revolution]] was accompanied with a great deal of changes on the social structure, the main change being a transition from farm work to factory related activities.<ref>{{Cite web|last=revolution|first=social|title=social effects of industrial revolution|url=https://www.google.com|access-date=1 April 2021|archive-date=17 March 2012|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120317093950/https://www.google.com/|url-status=live}}</ref> This resulted to the creation of a class structure that differentiated the commoners from the well off and the working category. It distorted the family system as most people moved into cities and left the farm areas, consequently playing a major role in the transmission of diseases. The place of women in the society then shifted from being home cares to employed workers hence reducing the number of children per household. Furthermore industrialization contributed to increased cases of [[Child labour|child labor]] and thereafter education systems.<ref>{{Cite web|last=revolution|first=social|title=social effect of industrial revolution|url=https://abhiipedia.abhinamu.com}}</ref>
| + | As an integral part of determining the cost and availability of manufactured products was improvement of [[transportation]]. Finished products, raw materials, food, and people needed a reliable, quicker, and less costly system of transportation. |
| | | | |
| − | ===Urbanization===
| + | Canals and rivers had long been used as a means of internal transportation. The principles of rail transport were already in use in the late 1700s. By 1800, more than 200 miles of tramway served coal mines in Britain. It is not surprising, then, to find a number of engineers connected with coal mines, for example [[George Stephenson]], searching for a way to apply the [[steam engine]] to railways. Railroads proliferated in Britain, to more than 7,000 miles built by 1852, being the dominant form of transportation for almost a century. |
| − | {{Main|Urbanization}}
| |
| − | [[File:Guangzhou dusk panorama.jpg|thumb|400px|Guangzhou dusk panorama]]
| |
| − | As the [[Industrial Revolution]] was a shift from the agrarian society, people migrated from villages in search of jobs to places where factories were established. This shifting of rural people led to urbanization and increase in the population of towns. The concentration of labor in factories has increased urbanization and the size of settlements, to serve and house the [[factory]] workers.
| |
| | | | |
| − | ===Changes in family structure=== | + | ===Capital=== |
| − | Family structure changes with industrialisation. Sociologist [[Talcott Parsons]] noted that in pre-industrial societies there is an [[extended family]] structure spanning many generations who probably remained in the same location for generations. In industrialised societies the [[nuclear family]], consisting of only parents and their growing children, predominates. Families and children reaching adulthood are more mobile and tend to relocate to where jobs exist. Extended family bonds become more tenuous.<ref>''[http://www.blacksacademy.net/content/3236.html The effect of industrialisation on the family, Talcott Parsons, the isolated nuclear family]'' {{Webarchive|url=https://web.archive.org/web/20101120221546/http://blacksacademy.net/content/3236.html |date=20 November 2010 }} Black's Academy. Educational Database. Accessed April 2008.</ref>
| + | Prior to industrialization, land was the primary source of wealth. However, a new source of great wealth grew from the Industrial Revolution, derived from the ownership of factories and machinery. Those investors in factories and machinery, the [[Capitalism|capitalists]], gave the necessary impetus to the speedy growth of the Industrial Revolution. |
| | | | |
| − | ==Overview of Industrialization in Europe==
| + | Two kinds of capital were needed: long-term capital to expand present operations, and short-term capital to purchase raw materials, maintain inventories, and to pay wages to their employees. The long-term capital needs were met by mortgaging factory buildings and machinery. It was the need for short-term capital which presented some problems. |
| | | | |
| − | [[Image:2005gdpIndustrial.PNG|thumb|left|Industrial output in 2005]]
| + | That need was accommodated by extending credit to the manufacturers by the producers or dealers. A supplier of raw materials might wait 6 to 12 months for payment of the goods, after the manufacturer was paid for the finished product. |
| | | | |
| − | Throughout Europe the phenomena of industrialization was a regional event that took place between late 1700’s to the early 1900’s. Many factors however determined which nations were:
| + | The early 1700s brought with it the first private [[bank]]s, founded by those who were involved in a variety of endeavors (goldsmiths, merchants, manufacturers). Many industrialists favored establishing their own banks as an outlet for the capital accumulated by their business and as a means for obtaining cash for wages. Their limited resources were inadequate to meet the demands of the factory economy. A banking system was eventually set up to distribute capital to areas where it was needed, drawing it from areas where there was a surplus.<ref> Rondo Cameron, ''Banking in the Early Stages of Industrialization'' (Oxford University Press, 1967, ISBN 019500843X).</ref> |
| | | | |
| | + | ===Pollution=== |
| | + | Historically, industrialization was associated with an increase in [[pollution]] both from the toxic waste from factories, especially those producing chemicals, and from industries heavily dependent on [[fossil fuel]]s. With an increasing focus on [[sustainable development]] and [[green industrial policy]] practices, industrialization increasingly includes [[Leapfrogging|technological leapfrogging]], with direct investment in more advanced, cleaner technologies. |
| | | | |
| − | *'''''(a) Early industrializes,''''' or
| + | ===Changes in social structure=== |
| | + | [[File:Bairoch.png|thumb|400px|right|The effect of industrialization shown by rising income levels in the nineteenth century. The graph shows [[gross national product]] (at [[purchasing power parity]]) [[per capita]] between 1750 and 1900 in 1990 [[US dollars]] for [[First World]] nations (Europe, United States, Canada, Japan) and [[Third World]] nations (Europe in east, Southern Asia, Africa, Latin America).<ref>Paul Bairoch, ''Economics and World History: Myths and Paradoxes'' (University of Chicago Press, 1995, ISBN 0226034631).</ref>]] |
| | | | |
| | + | The [[Industrial Revolution]] was accompanied by changes in [[social structure]], the main change being a transition from farm work to [[factory]] related activities. This resulted in the creation of a [[Social class|class structure]] that differentiated the commoners from the well off and the working category. It distorted the [[family]] system as most people moved into cities and left the farm areas, which also played a major role in the transmission of [[disease]]s. The place of women in society then shifted from being home cares to employed workers. Furthermore, industrialization contributed to increased use of [[child labor]].<ref>Freddie Wilkinson, [https://www.nationalgeographic.org/article/industrialization-labor-and-life/12th-grade/ Industrialization, Labor, and Life] ''National Geographic'', January 27, 2020. Retrieved September 24, 2021.</ref> |
| | | | |
| − | *'''''(b) Latecomers / No-shows.'''''
| + | In the eighteenth century, the population grew at a faster rate than ever before. There are four primary reasons for this growth: a decline in the death rate, an increase in the birth rate, the virtual elimination of the dreaded plagues, and an increase in the availability of healthy food. There were several other reasons for the growth of the population: Industry provided higher wages to individuals than were being offered in the villages. This allowed young people to marry earlier in life, and to produce children earlier. Also, industry provided people with improved clothing and housing. |
| | | | |
| | + | ===Urbanization=== |
| | + | {{Main|Urbanization}} |
| | + | [[File:Guangzhou dusk panorama.jpg|thumb|400px|Guangzhou dusk panorama]] |
| | + | The concentration of labor in factories increased [[urbanization]] and the size of settlements, to serve and house the [[factory]] workers. |
| | | | |
| − | In order to show why these countries are classified this way we will have to look at Britain and compare the two groups to Britain, because Britain is associated with being the first country to industrialize. We will also have to take into account what Gerschenkron ( 1962 ) thinks about early and late industrialized countries, and the six propositions he suggested are important for problem-less industrialization.
| + | As the [[Industrial Revolution]] was a shift from the agrarian society, people migrated from villages in search of jobs to places where [[factory|factories]] were established. Settlements grew around the factories. This shifting of rural people led to urbanization and an increase in the population of towns. |
| − | | |
| − | By saying this we need to see how Britain started its industrialization and compare it to early-industrialized, latecomers or no-show nations.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Why Britain started it all ?===
| |
| − | | |
| − | We start with, already, the third and “classic version” of why Britain went “first past the post” in so far industrialization stakes go:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | “…..''While Europe's "great men" plotted grand schemes to pursue their political and intellectual ambitions during the crisis of the Old Regime, French Revolution, and Napoleonic wars, obscure British inventors designed machines whose impact would dwarf their efforts.'' ….” ( Landes 1969 ).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | One answer to this question is that Britain by far has more of everything. To be more specific Britain’s per capita income was larger compared to other countries.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In the period associated with industrialization, Britain’s economy did not have Guilds any longer, compared to France that had a law banning outside manufacturing, and it only allowed manufacturing within guilds. The eliminations of guilds could have helped in competition and an increase in productivity that could have lead to industrialization.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Property Rights and patent rights in England were also established. Also, the income distribution in England was more equal.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The fact that England is an island also played a great role in helping industrialization in England. This helped reduce transportation costs in England, which were ( sometimes substantially ) lower relative to other countries.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | England also '''''got rid itself from serfdom'''''; this made its labor market more accessible. But, above all, England has also '''''been blessed with a lot of coal'''''; a great advantage those days as the coal played a significant role when it came to industrialization. And, finally, it is known that population was growing in a faster rate ( than elsewhere in Europe ), which helped the labor market grow.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | It is not known which factor is the one that caused Britain to industrialize, it could have been any one of them, but one thing is known: she has been the first nation to industrialize.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Six conditions for early industrialization===
| |
| − | | |
| − | However, the early-industrialized countries quickly caught up. We can see that a few factors affect these countries. Cameron ( 1967, 1989 ) shows that all the early-industrialized countries had a few things in common, and they are as follows:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''Each country had a sufficient amount of coal.'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''Each country incorporated the technologies of the time.'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''High literacy rates among these countries.'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''Engaged in trade with other countries.'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''Rid them-selves of serfdom.'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''Established property rights.'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | By taking the following steps these nations were able to catch up to Britain’s standards and in some cases even surpass it. Cameron attributes political reasons to the reason as to why latecomers and no-shows did not industrialize the same time England did, as well as natural resource issues, which these countries lacked.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ====Problems for “Latecomers/No-shows”====
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The “''Latecomers and no-shows''” have had a difficult time in industrialization because of various factors:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''First of all, most of these countries lacked natural resources and most importantly coal.'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''Secondly literacy rates in these countries were low.'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''These countries also went through many political difficulties, which were a barrier to their progress as industrialized nations.'''
| |
| − | | |
| − |
| |
| − | These countries were consistent with Gerschenkron’s analysis in several ways. He claimed that,”…. ''the later a country industrializes the more capital intensive it becomes''….”( Gerschenkron 1968.)
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | This is evident with the countries that started to industrialize after England. We could see that most countries started to invest in railroad building and mining of coal and steel.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | | |
| − | He also claimed that the later a country industrializes the more capital-intensive production it becomes, and this is directly related to the previous reasoning ( ibid, 1968 ).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | As a result of intensive building of manufacturing plants a country would end up producing goods which are capital intensive as a result of building these plants. One of the natural causal chains following from that is that “…..''the later a country industrializes there is a greater role for non-market institutions.'' ….”( ibid, 1968 ). | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | This means that the government of a certain country could negotiate with banks to promote financing for certain industries. It could also mean that governments would give preferential treatment to certain industries such as cartels.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Another natural outcome is that the later a country industrializes the more discontinuous that country is. This notion is true for countries that are “no-shows or latecomers” as we wittnessed that countries that industrialize later take a much longer time to industrialize and catch up to the countries that are already in an industrialized stage.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | His most important claim, however, is: “… '''''that the later a country industrializes the more pressure is placed on consumption.''''' …..”( ibid, 1968 ).
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''EXAMPLE''': In Russia we saw, as well as in all countries that were “latecomers,” that more emphasis was directed towards railways and mining. This means that countries that needed to invest in their capital-intensive enterprises, had to suppress their consumption ( i. e. light manufacturing ) in order to boost investment in the “heavy” industries. Typically, Russia has never got rid of these “skewered policies” until the complete dissolution of her economy in 1980’s.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | As we said above, in the no-show states two common characteristics prevail: the lack of natural resources and the political situation.
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''EXAMPLE''': In Portugal the lack of natural resources caused it to be a backward nation. In Russia Serfdom and illiteracy still prevailed while industrialization was taking place, which slowed the pace of industrialization in that country. And even after Bolshevik revolution ( and all through the next 70 years, the heavy industry reign in the Russian economy till it completely destroyed any semblance of market equilibrium and the economy itself with it. )
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==The brief history of Industrialization==
| |
| − | | |
| − | In this part we shall discuss the Great Britain in greater details, as this is where Industrialization started and the then conditions had appeared to be generally valid for every industrialized countries. Then we touch upon the U.S. as the, by far, the largest producer of industrial output followed by Japan. Thus, Japan will be discussed too, while the, so called, “Third ( or “Developing”) World” will be summarily mentioned, just as “Oil rich countries” in which the industrialization has been pursued ( whenever is pursued ) and kept strictly by exogenous labour, skills, education and know-how.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | ===Great Britain===
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The following changes had occurred in individual sectors of British economy during the “Industrialization” era:
| |
| − | | |
| − |
| |
| − | *'''Agricultural Changes'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Agriculture occupied a prominent position in the English way of life of this period. Not only was its importance rooted in the subsistence of the population, but agriculture was an indispensable source of raw materials for the textile industry. Wool and cotton production for the manufacture of cloth increased in each successive year, as did the yield of food crops.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Also, in 18th century England, the enclosure of common village fields into individual landholdings, or the division of unproductive land into private property was the first significant change to occur. This concentrated the ownership of the land into the hands of a few, and made it possible to institute improved farming techniques on a wider scale.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''Textiles'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Prior to 1760 the manufacture of textiles occurred in the homes, by people who gave part of their time to it. It was a tedious process from raw material to finished product. Many of these stages of production were performed by women and children. The supply of raw material for the woolen industry was obtained domestically. In the cases of silk and cotton, the raw materials were obtained from foreign sources, such as, China, the West Indies, North American and Africa.
| |
| − | In the mid-1760s the textile industry began to experience rapid change. [[James Hargreaves]]’ jenny, a device which enabled the operator to simultaneously spin dozens of threads, was readily adopted. By 1788 nearly 20,000 of them were being employed in England. [[Arkwright]] and others developed the water frame.
| |
| − | The changes that took place in the textile industry must certainly center about the inventions and their inventors, though not necessarily be limited to them. These inventions that were perfected and employed led to tremendous change in the world of work. Gone were the days of the Domestic System, yielding to the new ways of the Factory System.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''Coal Mining'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | One finds the working conditions and practices of coal mining in the l8th and l9th centuries to be risky, at best, and suicidal at worst. This industry, even today, provokes thoughts of hazards at every turn.
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''EXAMPLE''': A fireman employed in a colliery had the duty of ridding a mine tunnel of dangerous, flammable gases. His job entailed crawling through the tunnel holding a long stick. Attached to the end of the stick was a lighted candle which exploded any gases that might be accumulated ahead of him.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Improvements in coal mining came in the form of improved tunnel ventilation, improved underground and surface transportation, the use of gunpowder to blast away at the coal seams, and improved tunnel illumination through the use of safety lamps.
| |
| − | Still, coal mining today continues to be a hazardous job, though modern machinery and safety equipment have made the industry more efficient and safe.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''Iron'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | Improvements in the iron industry came in the early l8th century. [[Abraham Darby]] successfully produced pig iron smelted with coke.
| |
| − | | |
| − | This was a significant breakthrough, for prior to this discovery pig iron was smelted with the use of charcoal that caused a serious depletion of England’s forests. Darby’s technique was gaining popularity within the industry, though problems still existed due to its use. Iron produced through this method was impure and brittle, making it unsuitable for the forgemaster to be able to fashion in into implements, so its use was limited to castings. Later, improvements would occur which produced high quality material and improved techniques in fashioning it.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''Transportation'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | As an integral part of determining the cost and availability of manufactured products was improvement of transportation that stimulated the course of the Industrial Revolution. Finished products, raw materials, food and people needed a reliable, quicker and less costly system of transportation. Canals and rivers had long been used as a means of internal transportation.
| |
| − | The principles of rail transport were already in use in the late 1700s. By 1800 more than 200 miles of tramway served coal mines. It is not surprising, then, to find a number of engineers connected with coal mines searching for a way to apply the steam engine to railways.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | A pioneer in railroads that bears mentioning is [[George Stephenson]]. The Stockton to Darlington line was the first public railroad to use locomotive traction and carry passengers, as well as freight.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Railroads dominated the transportation scene in England for nearly a century. Railroads proliferated in England, from 1,000 miles in 1836 to more than 7,000 miles built by 1852. Here again is another example of economic necessity producing innovation. The development of reliable, efficient rail service was crucial to the growth of specific industries and the overall economy.
| |
| − | | |
| − |
| |
| − | *'''Steam'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The development and subsequent application of steam power was undoubtedly the greatest technical achievement of the Industrial Revolution. A number of industries needed the ability to apply the enormous power produced by the steam engine, in order to continue their advancement in production. [[James Wat]] is credited with the invention of the steam engine.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The transfer of one technology to another is evident here, in that Watt used [[John Wilkinson]]’s device for boring cannon to accurately bore the large cylinder for his engine.
| |
| − | The development of a practical, efficient steam engine and its application to industry and transportation caused a great leap for industrialization. Its application was virtually limitless, and it was responsible for lifting industries from infancy to adolescence.
| |
| − | | |
| − |
| |
| − | *'''The Human Aspect'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | In the l8th century the population grew at a faster rate than ever before. There are four primary reasons which may be cited for this growth: a decline in the death rate, an increase in the birth rate, the virtual elimination of the dreaded plagues and an increase in the availability of food. The latter is probably the most significant of these reasons, for English people were consuming a much healthier diet.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | There were several other reasons for the growth of the population, in addition to those above. Industry provided higher wages to individuals than was being offered in the villages. This allowed young people to marry earlier in life, and to produce children earlier. Also, industry provided people with improved clothing and housing, though it took a long time for housing conditions to improve.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | With the adoption of the factory system, we find a shift in population. Settlements grew around the factories. In some cases factories started in existing towns, which was desirable because a labor pool was readily available.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | The development of the steam engine to drive machinery freed the mill owners from being locked into a site that was close to swiftly moving water. Thus, factories could be located closer to existing population centers or seaports, fulfilling the need for labor and transportation of materials.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''Capital'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Prior to industrialization in England, land was the primary source of wealth. However, a new source of great wealth grew from the Industrial Revolution, derived from the ownership of factories and machinery. Those investors in factories and machinery cannot be identified to any single class of people (landed aristocracy, industrialists, merchants). It was these capitalists who gave the necessary impetus to the speedy growth of the Industrial Revolution.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Two kinds of capital were needed: long-term capital to expand present operations, and short-term capital to purchase raw materials, maintain inventories and to pay wages to their employees. The long-term capital needs were met by mortgaging factory buildings and machinery. It was the need for short-term capital which presented some problems.
| |
| − | | |
| − | That need was accommodated by extending credit to the manufacturers by the producers or dealers. Often, a supplier of raw materials waited from 6 to 12 months for payment of his goods, after the manufacturer was paid for the finished product.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The Bank of England, established in the late 1690s, did not accommodate the needs of the manufacturers. It concentrated its interest on the financial affairs of state and those of the trading companies and merchants of London.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The early 1700s brought with it the first country ( private ) banks, founded by those who were involved in a variety of endeavors (goldsmith, merchant, manufacturer). Many industrialists favored establishing their own banks as an outlet for the capital accumulated by their business and as a means for obtaining cash for wages. Their limited resources were inadequate to meet the demands of the factory economy. A banking system was eventually set up to distribute capital to areas where it was needed, drawing it from areas where there was a surplus.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===The U.S.===
| |
| − | | |
| − | The mammoth growth of new industries and the free enterprise philosophy are both inherently American institutions. Certainly, the specific political and socio-economic conditions ( North vs. South; virtual political and social equality in the North vs. slavery in the South ) and, above all, demographic patterns ( increasing influx of immigrants from Europe)—the USA is, by definition, the nation of immigrants ( even slaves were “forced” immigrants—made the rapid and sustained industrialization inevitable.
| |
| − | | |
| − |
| |
| − | In other words, the growth of industry is key to the development of modern America. All the other early elements of the American society—settlement of the plains, immigration, and populism—all hinge somehow on the growth of industry.
| |
| − | | |
| − |
| |
| − | The American philosophy of business is free enterprise. The origins of this American philosophy, however, lie mainly in ideas brought over from Britain.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | Typically, all six basic conditions that were found to form the ideal base of industrialization in England and other early industrialized countries ( Cameron, 1967, 1989 ):
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *'''Sufficient amount of coal,'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | *'''country incorporated the technologies of the time,'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | *'''high literacy rates,'''
| |
| − |
| |
| − | *'''country is engaged in trade with other countries,'''
| |
| − |
| |
| − | *'''country got rid them-selves of serfdom,''' and
| |
| − | | |
| − | *'''established property rights,'''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | were all already present there. The frontier tradition may have been important, but key economic ideas came from [[Charles Darwin]], [[Adam Smith]], [[Herbert Spencer]], and [[William Graham Sumner]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Next came the expansion & consolidation in key industries. Through a variety of corporate devices ( the very early-on started [[patent]] laws were one of these devices ), business in the U.S. consolidated both vertically and horizontally.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Consolidation came simultaneous with expansion, as illustrated in the following industries: railroads, petroleum, steel, and communications. Some have called the leaders of this consolidation “robber barons,” while others have called them “industrial statesmen.”
| |
| − | | |
| − | Business consolidation proceeded in different ways and produced different results, for both companies and consumers, in different sectors. The railroad, petroleum, steel, and communication industries were important ones that illustrate many of the possibilities of expansion and consolidation in the late 19th Century.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The growing power of business prompted labor to organize. Some distinctions to understand include skilled v. unskilled labor and craft v. industrial union organization. Collective bargaining was central to the organization of the American Federation of Labor, under its practical leader, [[Samuel Gompers]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ===Japan===
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The story of Japan’s economic development should be told from the Edo period 1603-1867 because the pre-conditions for later industrialization and modernization were created internally during this period.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Let us list these pre-conditions at the outset and compare them with the above “six conditions” ( '''NOTE''': Typically, the only major condition, “trade with other countries” is missing; this later invoked a major political upheaval which “kick-started” the Japan’s economic might ):
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *''Political unity and stability.''
| |
| − | | |
| − | *''Agricultural development in terms of both area and productivity.''
| |
| − | | |
| − | *''The development of transportation and the emergence of nationally
| |
| − | unified markets.''
| |
| − | | |
| − | *''The rise of commerce, finance and the wealthy merchant class.''
| |
| − | | |
| − | *''The rise of pre-modern manufacturing (food processing, handicraft,
| |
| − | etc.)''
| |
| − | | |
| − | *''Industrial promotion by local governments (sometimes successful but
| |
| − | not always.)''
| |
| − | | |
| − | *''High level of education.''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | These are the features of the Edo period. '''''Note that these conditions are not met by some countries even today. We may even say that developing and transition countries equipped with all these conditions are relatively rare.'''''
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | From 1639, the local Edo government banned any foreign contact except in a very limited way and under strict official control. Under this isolationist policy, the only channel for absorbing Western knowledge, mainly medical and scientific information, was through Dutch --- Holland having a diplomatic relations “limited contact” --- books and products.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | But from the end of the 18th century, foreign ships began to approach Japan with an intention to trade. The Russians and the British were particularly eager but the government refused to talk to them.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | In 1858, the Edo local government asked for an imperial permission to sign comprehensive commercial treaties with the major powers but it was not granted by the Meiji central government. However, they signed them anyway without imperial permission.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The opening of Japanese ports led to significant social and economic changes:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *(1) Foreigners brought new ideas, technology, industry and systems, and the Japanese began to absorb them very rapidly.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | *(2) Silk and tea suddenly found huge overseas markets. The rising output and soaring prices of these commodities enriched farmers who produced them.
| |
| − | | |
| − | *(3) Enriched farmers began to buy clothes made in England instead of wearing homemade or secondhand clothes.
| |
| − | | |
| − | *(4) A new merchant class, called the Yokohama merchants, emerged to link domestic producers and markets with foreign merchants.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | Eventually, in 1868, the emperor --- after ousting the local government --- moved from Kyoto to Edo ( which was renamed Tokyo ) with the Meiji central government and set three goals to modernize Japan:
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | *(a) Industrialization (economic modernization);
| |
| − | | |
| − | *(b) introducing of a national constitution and parliament (political modernization);
| |
| − | | |
| − | *(c) external expansion (military modernization).
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | The new era establishing Japan among the superpowers in the Far East ( and later in the world ) was on.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Petrol producing countries===
| |
| − | | |
| − | Most of the [[oil]]-rich countries saw similar failures in their economic choices. The oil being both important and expensive commodity, regions with big reserves have huge liquidity income.
| |
| − | | |
| − | However, this was rarely followed by economic development. Experience shows that local [[elite]]s are unable--- or unwilling, we might add --- to re-invest the [[petrodollar]]s obtained through oil export, and currency is wasted in [[luxury good]]s.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | This is particularly evident in the [[Arab states of the Persian Gulf#Economy|Persian Gulf states]], where the [[per capita income]] is comparable to those of western nations, but where any industrialization that went on, in a very selected sectors, have been started and sustained by, virtually, all-exogenous labour force.
| |
| − | | |
| − | In other words, all technical education of the whole should-be-indigenous labour force ( blue and white collar ) and know-how to use modern technology has been supplanted by the imported labourers, teachers,engineers, professionals and government-running advisors from the West and East.
| |
| − |
| |
| − | | |
| − | Apart from two little countries ([[Economy of Bahrain|Bahrain]] and [[Economy of United Arab Emirates|United Arab Emirates]]), [[Arab world#Modern Economies|Arab states]] didn't [[Diversity (business)|diversified]] their economies as much as they could and, perhaps, should.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===The third world===
| |
| − | | |
| − | A similar state-led developing program was pursued in virtually all the third world countries during the [[Cold War]], including [[Socialism|socialist]] ones, but specially in [[Sub-Saharan Africa]] after the [[decolonization]] period. The primary scope of those projects was to achieve [[self-sufficiency]] through the local production of previously [[import]]ed goods, the mechanization of agriculture and the spread of [[education]] and [[health care]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | However, all those experiences failed bitterly due to lack of realism: most countries didn't have a pre-industrial bourgeoisie able to carry on a [[Capitalism|capitalistic]] development or even a stable and peaceful state. Those aborted experiences left [[Developing countries' debt|huge debts]] toward western countries and fueled [[Political corruption|public corruption]].
| |
| | | | |
| | + | In some cases factories started in existing towns, which was desirable because a labor pool was readily available. The development of the steam engine to drive [[machine]]ry freed the mill owners from being locked into a site that was close to swiftly moving water. Thus, factories could be located closer to existing population centers or seaports, fulfilling the need for labor and transportation of materials. |
| | | | |
| | + | ===Changes in family structure=== |
| | + | Family structure changes with industrialization. Sociologist [[Talcott Parsons]] noted that in pre-industrial societies there is an [[extended family]] structure spanning many generations who probably remained in the same location for generations. In industrialized societies the [[nuclear family]], consisting of only parents and their growing children, predominates. Families and children reaching adulthood are more mobile and tend to relocate to where jobs exist. Extended family bonds become more tenuous.<ref>Talcott Parsons and Robert E. Bales, ''Family: Socialization and Interaction Process'' (Routledge, 2007, ISBN 0415436516).</ref> |
| | | | |
| | ==Notes== | | ==Notes== |
| Line 476: |
Line 114: |
| | | | |
| | ==References== | | ==References== |
| | + | *Akrigg, Ben. ''Population and Economy in Classical Athens''. Cambridge University Press, 2019. ISBN 1107027098 |
| | + | *Bairoch, Paul. ''Economics and World History: Myths and Paradoxes''. University of Chicago Press, 1995. ISBN 0226034631 |
| | + | *Böröcz, József. ''The European Union and Global Social Change''. Routledge, 2009. ISBN 0415481023. |
| | + | *Cameron, Rondo. ''Banking in the Early Stages of Industrialization''. Oxford University Press, 1967. ISBN 019500843X) |
| | + | *Griffin, Emma. ''A Short History of the British Industrial Revolution''. Red Globe Press, 2018. ISBN 1352003244 |
| | + | *Jones, Eric. ''The European Miracle: Environments, Economics and Geopolitics in the History of Europe and Asia''. Cambridge University Press, 2003. ISBN 052152783X |
| | + | *Landes, David S. ''The Unbound Prometheus: Technological Change and Industrial Development in Western Europe from 1750 to the Present''. Cambridge University Press, 2003. ISBN 052153402X |
| | + | *O’Neil, Patrick H. ''Essentials of Comparative Politics''. W. W. Norton & Company, 2020. ISBN 0393532771 |
| | + | *Parsons, Talcott, and Robert E. Bales. ''Family: Socialization and Interaction Process''' Routledge, 2007. ISBN 0415436516 |
| | + | *Pollard, Sidney. ''Peaceful Conquest: The Industrialization of Europe 1760–1970''. Oxford University Press, 1981. ISBN 0198770936 |
| | + | *Pomeranz, Kenneth. ''The Great Divergence''. Princeton University Press, 2000. ISBN 0691005435 |
| | + | *Williams, Eric. ''Capitalism and Slavery''. Franklin Classics, 2018. ISBN 0343147610 |
| | | | |
| − | *Cameron, R. France and the Economic Development of Europe, 1800-1914, Princeton University Press Princeton, NJ, 1961
| + | [[Category:Social sciences]] |
| − | *Cameron, R.,(ed. with the collaboration of Olga Crisp, H. T. Patrick and R. Tilly), Banking in the Early Stages of Industrialization: A Study of Comparative Economic History,Oxford University Press, New York,1967
| |
| − | *Cameron, R. A Concise Economic History of the World, Oxford University Press, Oxford,1989
| |
| − | *Gerschenkron, A., Economic backwardness in historical perspective: a book of essays, Belknap Press of Harvard University Press,Cambridge, Massachusettes, 1962
| |
| − | *Gerschenkron, A., Continuity in history, and other essays, Cambridge, Massachusettes: Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, 1968
| |
| − | *Karasek, M.,”Institutional and Political Challenges and Opportunities for Integration in Central Asia” , CAG Portal Forum 2005,Exh. 3 ( & discussion ),
| |
| − | *Landes, David, The Unbound Prometheus: Technological Change and Industrial Development in Western Europe from 1750 to the Present, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1969, p. 115
| |
| − | | |
| − | [[Category:Politics and social sciences]] | |
| | [[Category:Economics]] | | [[Category:Economics]] |
| | [[Category:Sociology]] | | [[Category:Sociology]] |
| | {{Credits|Industrialisation|157431771|Industrialisation|1038554390|History_of_industrialisation|1009947670}} | | {{Credits|Industrialisation|157431771|Industrialisation|1038554390|History_of_industrialisation|1009947670}} |

Industrialization also means the mechanization of traditionally manual economic-sectors such as
agriculture.
Industrialization (or industrialisation) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This means converting to a socioeconomic order in which industry is dominant, which involves an extensive reorganization of the economy for the purpose of manufacturing. This process increases the food supply, creates a wider variety of jobs, stimulates technological development, and improves the external standard of living.
However, there are also many unintended consequences, both economically and socially. As industrial workers' incomes rise, markets for consumer goods and services of all kinds tend to expand and provide a further stimulus to industrial investment and economic growth. Moreover, family structures tend to shift as extended families tend not to live together in one household or location, as family members migrate following job opportunities. Beyond these social consequences, industrialization has had negative effects on the environment, particularly through pollution. Balancing the positive and negative consequences of industrialization remains a challenge.
History
In most pre-industrial societies, the majority of the population were focused on producing their means of survival through subsistence farming. Famines were frequent. Some, such as classical Athens, had trade and commerce as significant factors. As a result, Greeks could enjoy wealth far beyond a sustenance standard of living through the use of slavery.[1]
What some have termed "Proto-industrialization," involving regional development of rural handicraft production for external markets, took place in Europe as well as in Mughal India prior to the Industrial Revolution.[2]
After the last stage of this Proto-industrialization, the Industrial Revolution which transformed the agricultural to an industrial economy took place, starting in Great Britain, followed by Belgium, Switzerland, Germany, and France.[3] This early industrialization was characterized by technological progress, a shift from rural work to industrial labor, financial investments in new industrial structure, and early developments in class consciousness. Later commentators have called this the First Industrial Revolution.[4]
Industrialization started with the mechanization of the textile industries, the development of iron-making techniques and the increased use of refined coal. Once started, it spread. Trade expansion was enabled by the introduction of canals, improved roads and railways. The introduction of steam power (fueled primarily by coal) and powered machinery (mainly in textile manufacturing) underpinned dramatic increases in production capacity. The development of all-metal machine tools in the first two decades of the nineteenth century facilitated the manufacture of more production machines for manufacturing in other industries. The effects spread throughout Western Europe and North America during the nineteenth century, eventually affecting most of the world.
The "Second Industrial Revolution" labels the later changes that came about in the mid-nineteenth century after the refinement of the steam engine, the invention of the internal combustion engine, the harnessing of electricity and the construction of electric-power lines. The invention of the assembly line gave this phase a boost.[5]
Industrial revolution in Europe

The Crystal Palace Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of all Nations, London, 1851.
The era known as the Industrial Revolution was a period in which fundamental changes occurred in agriculture, textile and metal manufacture, transportation, economic policies, and the social structure beginning in Great Britain and spreading throughout Europe. This period is appropriately labeled “revolution,” for it thoroughly destroyed the old manner of doing things; yet the term is simultaneously inappropriate, for it connotes abrupt change.
A factory in Ilmenau (
Germany) around 1860
The changes that occurred during this period (1760-1850), in fact, occurred gradually. The year 1760 is generally accepted as the “eve” of the Industrial Revolution. In reality, this eve began more than two centuries before this date. The late eighteenth century and the early nineteenth century brought to fruition the ideas and discoveries of those who had long passed on, such as, Galileo, Francis Bacon, René Descartes, and others.

Early industrialization in Germany, the city of Barmen in 1870. Painting by August von Wille

Aplerbecker Hütte, an industrialised area of Dortmund, Germany circa 1910.
In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, the United Kingdom experienced a massive increase in agricultural productivity known as the British Agricultural Revolution, which enabled unprecedented population growth, freeing a significant percentage of the workforce from farming, and helping to drive the Industrial Revolution.
Due to the limited amount of arable land and the overwhelming efficiency of mechanized farming, the increased population could not be dedicated to agriculture. New agricultural techniques allowed a single peasant to feed more workers than previously. However, these techniques also increased the demand for machines and other hardware, which had traditionally been provided by the urban artisans. Artisans employed rural workers to increase their output and meet the country's needs.
British industrialization involved significant changes in the way that work was performed. The process of creating a good was divided into simple tasks, each one of them being gradually mechanized in order to boost productivity and thus increase income. The new machines helped to improve the productivity of each worker. However, industrialization also involved the exploitation of new forms of energy. In the pre-industrial economy, most machinery was powered by human muscle, by animals, by wood-burning or by water-power. With industrialization these sources of fuel were replaced with coal, which could deliver significantly more energy than the alternatives.
The accumulation of capital allowed investments in the scientific conception and application of new technologies, enabling the industrialization process to continue to evolve. The industrialization process formed a class of industrial workers who had more money to spend than their agricultural cousins. They spent this on items such as tobacco and sugar, creating new mass markets that stimulated more investment as merchants sought to exploit them.[6] The mechanization of production spread to other European countries and to British colonies, helping to make those areas the wealthiest, and shaping what is now known as the Western world.
Some historians have argued that the possession of so-called 'exploitation colonies' eased the accumulation of capital to the countries that possessed them, speeding up their development.[7] Some have stressed the importance of natural or financial resources that Britain received from its many overseas colonies or that profits from the British slave trade between Africa and the Caribbean helped fuel industrial investment.[8]
With these arguments still find some favor with historians of the colonies, most historians of the British Industrial Revolution do not consider that colonial possessions formed a significant role in the country's industrialization. Whilst not denying that Britain could profit from these arrangement, they believe that industrialization would have proceeded with or without the colonies.[3]
Early industrialization in other countries

The textile factory
Slovena built in 1891 in Žilina (
Slovakia) - an example of a delayed industrialization in Central Europe.
The Industrial Revolution spread southwards and eastwards from its origins in Northwest Europe.
After the Convention of Kanagawa issued by Commodore Matthew C. Perry forced Japan to open the ports of Shimoda and Hakodate to American trade, the Japanese government realized that drastic reforms were necessary to stave off Western influence. The Tokugawa shogunate abolished the feudal system. The government instituted military reforms to modernize the Japanese army and also constructed the base for industrialization. In the 1870s, the Meiji government vigorously promoted technological and industrial development that eventually changed Japan to a powerful modern country.
The Soviet Union invested a large part of its resources to enhance its industrial production and infrastructures to assure its survival, thus becoming a world superpower.[9] During the Cold war, the other Warsaw Pact countries, organized under the Comecon framework, followed the same developing scheme, albeit with a less emphasis on heavy industry.
Industrialization in Asia

Durgapur Steel Plant located in West Bengal,
IndiaApart from Japan, where industrialization began in the late nineteenth century, a different pattern of industrialization followed in East Asia. One of the fastest rates of industrialization occurred in the late 20twentieth century across four places known as the Asian tigers (Hong Kong, Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan). Between the early 1960s and 1990s, they underwent rapid industrialization and maintained exceptionally high growth rates of more than 7 percent a year. By the early twenty-first century, these economies had developed into high-income economies, specializing in areas of competitive advantage. Hong Kong and Singapore have become leading international financial centers, whereas South Korea and Taiwan are leaders in manufacturing electronic components and devices.
In the case of South Korea, the largest of the four Asian tigers, a very fast-paced industrialization took place as it quickly moved away from the manufacturing of value-added goods in the 1950s and 1960s into the more advanced steel, shipbuilding, and automotive industry in the 1970s and 1980s, focusing on the high-tech and service industry in the 1990s and 2000s. As a result, South Korea became a major economic power.
This starting model was afterwards successfully copied in other larger Eastern and Southern Asian countries. The success of this phenomenon led to a huge wave of offshoring – Western factories or Tertiary Sector corporations choosing to move their activities to countries where the workforce was less expensive and less collectively organized.
China and India, while basically following this development pattern, made adaptations in line with their own histories and cultures, their major size and importance in the world, and the geo-political ambitions of their governments. Both China and India have also started to make significant investments in other developing countries, making them significant players in today's world economy.
India's government is also investing in economic sectors such as bioengineering, nuclear technology, pharmaceutics, informatics, and technologically oriented higher education, exceeding its needs, with the goal of creating several specialization poles able to conquer foreign markets.
Newly industrialized countries
Since the mid to late twentieth century, most countries in Latin America, Asia, and Africa, including Brazil, Indonesia, Malaysia, Mexico, Philippines, South Africa, and Turkey, have experienced substantial industrial growth, fueled by exporting to countries that have bigger economies: the United States, China, India, and the European Union.
These countries, sometimes called newly industrialized countries (NICs), have economies have not yet reached a developed country's status but have, in a macroeconomic sense, outpaced their developing counterparts. Such countries are still considered developing nations and only differ from other developing nations in the rate at which an NIC's growth is much higher over a shorter allotted time period compared to other developing nations.[10]
Consequences
Transportation
As an integral part of determining the cost and availability of manufactured products was improvement of transportation. Finished products, raw materials, food, and people needed a reliable, quicker, and less costly system of transportation.
Canals and rivers had long been used as a means of internal transportation. The principles of rail transport were already in use in the late 1700s. By 1800, more than 200 miles of tramway served coal mines in Britain. It is not surprising, then, to find a number of engineers connected with coal mines, for example George Stephenson, searching for a way to apply the steam engine to railways. Railroads proliferated in Britain, to more than 7,000 miles built by 1852, being the dominant form of transportation for almost a century.
Capital
Prior to industrialization, land was the primary source of wealth. However, a new source of great wealth grew from the Industrial Revolution, derived from the ownership of factories and machinery. Those investors in factories and machinery, the capitalists, gave the necessary impetus to the speedy growth of the Industrial Revolution.
Two kinds of capital were needed: long-term capital to expand present operations, and short-term capital to purchase raw materials, maintain inventories, and to pay wages to their employees. The long-term capital needs were met by mortgaging factory buildings and machinery. It was the need for short-term capital which presented some problems.
That need was accommodated by extending credit to the manufacturers by the producers or dealers. A supplier of raw materials might wait 6 to 12 months for payment of the goods, after the manufacturer was paid for the finished product.
The early 1700s brought with it the first private banks, founded by those who were involved in a variety of endeavors (goldsmiths, merchants, manufacturers). Many industrialists favored establishing their own banks as an outlet for the capital accumulated by their business and as a means for obtaining cash for wages. Their limited resources were inadequate to meet the demands of the factory economy. A banking system was eventually set up to distribute capital to areas where it was needed, drawing it from areas where there was a surplus.[11]
Pollution
Historically, industrialization was associated with an increase in pollution both from the toxic waste from factories, especially those producing chemicals, and from industries heavily dependent on fossil fuels. With an increasing focus on sustainable development and green industrial policy practices, industrialization increasingly includes technological leapfrogging, with direct investment in more advanced, cleaner technologies.
Changes in social structure
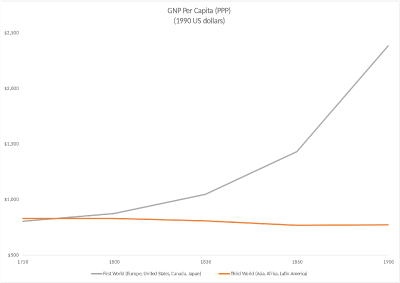
The effect of industrialization shown by rising income levels in the nineteenth century. The graph shows
gross national product (at purchasing power parity)
per capita between 1750 and 1900 in 1990 US dollars for First World nations (Europe, United States, Canada, Japan) and Third World nations (Europe in east, Southern Asia, Africa, Latin America).
[12]The Industrial Revolution was accompanied by changes in social structure, the main change being a transition from farm work to factory related activities. This resulted in the creation of a class structure that differentiated the commoners from the well off and the working category. It distorted the family system as most people moved into cities and left the farm areas, which also played a major role in the transmission of diseases. The place of women in society then shifted from being home cares to employed workers. Furthermore, industrialization contributed to increased use of child labor.[13]
In the eighteenth century, the population grew at a faster rate than ever before. There are four primary reasons for this growth: a decline in the death rate, an increase in the birth rate, the virtual elimination of the dreaded plagues, and an increase in the availability of healthy food. There were several other reasons for the growth of the population: Industry provided higher wages to individuals than were being offered in the villages. This allowed young people to marry earlier in life, and to produce children earlier. Also, industry provided people with improved clothing and housing.
Urbanization
The concentration of labor in factories increased urbanization and the size of settlements, to serve and house the factory workers.
As the Industrial Revolution was a shift from the agrarian society, people migrated from villages in search of jobs to places where factories were established. Settlements grew around the factories. This shifting of rural people led to urbanization and an increase in the population of towns.
In some cases factories started in existing towns, which was desirable because a labor pool was readily available. The development of the steam engine to drive machinery freed the mill owners from being locked into a site that was close to swiftly moving water. Thus, factories could be located closer to existing population centers or seaports, fulfilling the need for labor and transportation of materials.
Changes in family structure
Family structure changes with industrialization. Sociologist Talcott Parsons noted that in pre-industrial societies there is an extended family structure spanning many generations who probably remained in the same location for generations. In industrialized societies the nuclear family, consisting of only parents and their growing children, predominates. Families and children reaching adulthood are more mobile and tend to relocate to where jobs exist. Extended family bonds become more tenuous.[14]
Notes
- ↑ Ben Akrigg, Population and Economy in Classical Athens (Cambridge University Press, 2019, ISBN 1107027098).
- ↑ József Böröcz, The European Union and Global Social Change (Routledge, 2009, ISBN 0415481023).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Emma Griffin, A short History of the British Industrial Revolution (Red Globe Press, 2018, ISBN 1352003244).
- ↑ Sidney Pollard, Peaceful Conquest: The Industrialization of Europe 1760–1970 (Oxford University Press, 1981, ISBN 0198770936).
- ↑ Eric Jones, The European Miracle: Environments, Economics and Geopolitics in the History of Europe and Asia (Cambridge University Press, 2003, ISBN 052152783X).
- ↑ Robin Blackburn, Enslavement and industrialization BBC, February 17, 2011. Retrieved September 24, 2021.
- ↑ Eric Williams, Capitalism and Slavery (Franklin Classics, 2018, ISBN 0343147610).
- ↑ Kenneth Pomeranz, The Great Divergence (Princeton University Press, 2000, ISBN 0691005435).
- ↑ Joshua R. Keefe, Stalin and the Drive to Industrialize the Soviet Union Inquiries 1(10) (2009): 1. Retrieved September 24, 2021.
- ↑ Patrick H. O’Neil, Essentials of Comparative Politics (W. W. Norton & Company, 2020, ISBN 0393532771).
- ↑ Rondo Cameron, Banking in the Early Stages of Industrialization (Oxford University Press, 1967, ISBN 019500843X).
- ↑ Paul Bairoch, Economics and World History: Myths and Paradoxes (University of Chicago Press, 1995, ISBN 0226034631).
- ↑ Freddie Wilkinson, Industrialization, Labor, and Life National Geographic, January 27, 2020. Retrieved September 24, 2021.
- ↑ Talcott Parsons and Robert E. Bales, Family: Socialization and Interaction Process (Routledge, 2007, ISBN 0415436516).
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Akrigg, Ben. Population and Economy in Classical Athens. Cambridge University Press, 2019. ISBN 1107027098
- Bairoch, Paul. Economics and World History: Myths and Paradoxes. University of Chicago Press, 1995. ISBN 0226034631
- Böröcz, József. The European Union and Global Social Change. Routledge, 2009. ISBN 0415481023.
- Cameron, Rondo. Banking in the Early Stages of Industrialization. Oxford University Press, 1967. ISBN 019500843X)
- Griffin, Emma. A Short History of the British Industrial Revolution. Red Globe Press, 2018. ISBN 1352003244
- Jones, Eric. The European Miracle: Environments, Economics and Geopolitics in the History of Europe and Asia. Cambridge University Press, 2003. ISBN 052152783X
- Landes, David S. The Unbound Prometheus: Technological Change and Industrial Development in Western Europe from 1750 to the Present. Cambridge University Press, 2003. ISBN 052153402X
- O’Neil, Patrick H. Essentials of Comparative Politics. W. W. Norton & Company, 2020. ISBN 0393532771
- Parsons, Talcott, and Robert E. Bales. Family: Socialization and Interaction Process' Routledge, 2007. ISBN 0415436516
- Pollard, Sidney. Peaceful Conquest: The Industrialization of Europe 1760–1970. Oxford University Press, 1981. ISBN 0198770936
- Pomeranz, Kenneth. The Great Divergence. Princeton University Press, 2000. ISBN 0691005435
- Williams, Eric. Capitalism and Slavery. Franklin Classics, 2018. ISBN 0343147610
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article
in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.










