Difference between revisions of "Andalusia" - New World Encyclopedia
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Approved}}{{Submitted}}{{Images OK}}{{Paid}}{{Copyedited}} |
{{Autonomous community | {{Autonomous community | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|full-name = Comunidad Autónoma de Andalucía | |full-name = Comunidad Autónoma de Andalucía | ||
|flag = Bandera de Andalucía.png | |flag = Bandera de Andalucía.png | ||
| − | |coat-of-arms = Escudo Andalucía. | + | |coat-of-arms = Escudo de Andalucía (oficial2).svg |
|motto = Andalucía por sí, para España y la humanidad<br/>(Andalusia by herself, for Spain, and for humankind) | |motto = Andalucía por sí, para España y la humanidad<br/>(Andalusia by herself, for Spain, and for humankind) | ||
|map = Localización de Andalucía.png | |map = Localización de Andalucía.png | ||
| − | |capital = [[Image:EscudoSevilla3.jpg| | + | |capital = [[Image:EscudoSevilla3.jpg|30px]] [[Seville]] |
|language = [[Spanish language|Spanish]] | |language = [[Spanish language|Spanish]] | ||
|area = 87,268 | |area = 87,268 | ||
|area-rank = 2nd | |area-rank = 2nd | ||
|area-magnitude = E10 | |area-magnitude = E10 | ||
| − | |area-percent = 17.2 | + | |area-percent = 17.2 percent |
|pop = 7,975,672 | |pop = 7,975,672 | ||
|pop-rank = 1st | |pop-rank = 1st | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
|english-name = Andalusian | |english-name = Andalusian | ||
|spanish-name = Andaluz, andaluza | |spanish-name = Andaluz, andaluza | ||
| − | |autonomy = | + | |autonomy = December 30, 1981 |
|congress = 62 | |congress = 62 | ||
|senate = 40 | |senate = 40 | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
|anthem = [[La bandera blanca y verde]] | |anthem = [[La bandera blanca y verde]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Andalusia, located in the southern portion of [[Spain]], is one of the seventeen autonomous regions of the country. It contains eight distinct provinces, all with individual cultural traditions and identity. With eight provinces ( [[Almeria]], [[Cadiz]], [[Cordoba]], [[Granada]], [[Huelva]], [[Jaen]], [[Malaga]],and [[Seville]] ) , Andalusia boasts the largest population of any of the autonomous Spanish states. In terms of land mass, Andalusia is the second largest of the autonomous regions of Spain, second only to the region of [[Castilla y Leon]]. | |
| + | |||
| + | Andalusia lies to the south of [[Extremadura]] and [[Castilla-La Mancha]], meeting the [[Mediterranean Sea]] on its southern border. Its eastern neighbor is the autonomous community of [[Murcia]], while the country of [[Portugal]] lies along its western border. Past Portugal to the west lies the [[Atlantic Ocean]]. Andalusia is also conveniently located along the [[strait of Gibraltar]], the passage between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. The prime position along the strait was also recognized by [[Great Britain]], who controls a small area of land bordering Andalusia. | ||
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | Five hundred years of [[Muslim]] rule during the [[Middle Ages]] greatly influenced Andalusia's culture. During this time it became an extremely wealthy and influential political force that actively cultivated scholarship and advances in many areas. This Moorish influence continues to be evident in the region's character through its [[architecture]], [[language]] and customs. With its tradition of bull fights and [[Gypsy]] flamenco music and dance, Andalusia provides the strongest external image of Spain. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Etymology== | ||
| + | It is believed that the name ''Al-Andalus,'' [[Arabic language|Arabic]] for "Country of the Vandals," was originally applied to the entire [[Iberian Peninsula]] by the Muslim (Moors) who occupied the area for 500 years. As Christians began to reconquer the peninsula in the eleventh century, the name was used only to describe the area still under [[Muslim]] control. Eventually a form of the name, Andalusia, came to be attached to the modern-day region of Spain. | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| + | Alpine [[mountain]]s and [[pine]] forests exist at the high elevations of Andalusia while arid, barren [[desert]]s exist at the lower points. Fertile, irrigated plains support plantations of subtropical [[fruit]]s. [[Orange]]s, [[grape]]s, [[olive]]s, [[wheat]] and sugarcane are abundant crops. The rich [[mineral]] resources, exploited since Phoenician and Roman times, include [[copper]], [[iron]], [[zinc]], and [[lead]]. Cattle, bulls (for bullfighting) and fine horses are bred there. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The terrain of Andalusia varies greatly depending on the region. Toward the coast the terrain descends into the famous beaches of Spain, notable for their fine [[sand]]s and constant sunshine. | ||
| − | + | Most of lowland Andalusia has a mild, Mediterranean climate, while the interior of the region is cooler. The weather, beach, and nearly constant sunshine, however, are not the only reasons that tourists flock to Andalusia. The [[mountain]]s are also spectacular, and they host a unique combination of [[plant]] and [[animal]] life. | |
| − | The main geographic feature of the region is the Andalusian Plain, which runs from the Sierra Morena in the north to the Sistema Penibetico in the south. The plain is fundamentally a large river valley that surrounds the Rio Guadlquivir, and it broadens | + | The main geographic feature of the region is the [[Andalusian Plain]], which runs from the Sierra Morena in the north to the [[Sistema Penibetico]] in the south. The plain is fundamentally a large river valley that surrounds the [[Rio Guadlquivir]], and it broadens wherever possible. The valley reaches its narrowest point where the [[Sierra Morena]] and the Sistema Penibetico meet in the eastern portion of the region. Minor valleys are also common in Andalusia, although none rival the breath and size of the Andalusian Plain. |
| − | == | + | ==History== |
| + | [[Image:Calatrava Puente del Alamillo Seville.jpg|thumb|275px|[[Puente del Alamillo|Alamillo Bridge]], [[Seville]] designed by [[Santiago Calatrava]].]] | ||
| + | The earliest records of settled [[civilization]] in Andalusia describe colonial occupation in Pre-Roman times. In the early twelfth century B.C.E. the [[Phoenician empire]] formed colonies along the coast to help with trade. The settlement founded by the Phoenicians was called [[Tartessos]], which later rose to become a major political force in the region. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The colonies of the Phoenicians eventually declined in power following the dissolution of the Phoenician empire. The next major political force to emerge in the region was the city of [[Carthage]], whose emphasis on trade gave the straits of [[Gibraltar]] and the Andalusia region economic importance. As a trading center, Carthage saw the economic value of controlling the strait, and began a campaign to gain control of the region. Between the first and second [[Carthaginian wars]], Carthage extended its power over Andalusia, using the coast to launch many of its invasions into [[Roman Empire|Roman territory]]. Carthage, however, was unsuccessful in its campaign against Rome. With the decline of Carthage, Andalusia remained, for a brief period, without a strong political identity. Rome stepped in to fill the power vacuum, renaming the area ''Betica.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Roman control over the area did not last long, with the area briefly falling under the control of the [[Vandal]]s. As the Vandals passed through the region on their way to [[North Africa]], they took control of Andalusia. Following their brief occupation, the [[Visigoth]]s took control, only to be replaced by [[Muslim]] rule in the early eighth century C.E. The Muslim invasion proved to be an extremely influential action in the formation of a distinct Andalusian identity. | ||
| − | Andalusia | + | During the half millennium of Muslim rule during the [[Middle Ages]], Andalusia became an extremely wealthy and influential political force that actively cultivated scholarship and advances in many areas. [[Córdoba, Spain|Córdoba]] became the largest and richest city in [[Western Europe]] and one of the largest in the world. The [[Moors]] established universities in Andalucia, and cultivated scholarship, bringing together the greatest achievements of all of the civilizations they had encountered. During that period Moorish and [[Jew]]ish scholars played a major part in reviving and contributing to Western [[astronomy]], [[medicine]], [[philosophy]] and [[mathematics]]. |
| + | [[Image:Mosque of Cordoba Spain.jpg|thumb|right|275px|The Mezquita Mosque in Córdoba.]] | ||
| + | In 1248 Seville fell to Castilian rule. After the fall of [[Seville]], the Andalusia region began to experience a large influx of [[Moor]]s who were fleeing the [[Reconquista]]. | ||
| − | + | Spain began declining in the sixteenth century, and Andalusia suffered as a consequence, although the ports of Seville and Cádiz flourished as centers of trade with the New World. In 1713 Gibraltar was ceded to Great Britain. In 1833 Andalusia was divided into the present eight provinces. | |
| − | + | Catalonia and Andalusia were strongholds of [[anarchism]] during the Spanish Republic, which was established in 1931. It fell to the Insurgents in the [[Spanish civil war of 1936–1939]]. Demonstrations against the national government of [[Francisco Franco]] were common. In 1981 Andalusia became an autonomous region and in 1982 it elected its first parliament. | |
| − | + | == Government == | |
| + | Andalusia began its own distinct political force in 1978, when the Spanish constitution established historical nationalities. Historical nationalities in Spain, like Andalusia, were granted a special, autonomous status that was based on the idea that the area contained a specific nationality. Another major idea behind historical nationalities was their supposed independence from Spain as a whole. Under this idea ''Historical Nationalities'' were areas that were considered culturally independent prior to the second Spanish War. Andalusia is one of only four such regions in Spain, with the other historical nationalities found in [[Catalonia]], [[Basque]], and [[Galicia]]. Many other communities in Spain were recognized as a result of the constitution, but other communities were not granted the political and cultural independence of historical nationalities. | ||
| − | + | ===Administrative divisions=== | |
| + | [[Image:Mapa de las provincias de Andalucía.png|thumb|right|200px|Provinces of Andalusia]] | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Province !! Capital !! Population !! Density !! Municipalities | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[Almería (province)|Almería]] | ||
| + | | [[Almería]] || 635.850 || 72,47 hab./km² || [[List of municipalities in Almería|Municipalities]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[Cádiz (province)|Cádiz]] | ||
| + | | [[Cádiz]] || 1.180.817 || 158,80 hab./km² || [[List of municipalities in Cádiz|Municipalities]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[Córdoba (province)|Córdoba]] | ||
| + | | [[Córdoba, Spain|Córdoba]] || 788.287 || 72,47 hab./km² || [[List of municipalities in Córdoba|Municipalities]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[Granada (province)|Granada]] | ||
| + | | [[Granada]] || 882.184 || 68,70 hab./km² || [[List of municipalities in Granada|Municipalities]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[Huelva (province)|Huelva]] | ||
| + | | [[Huelva]] || 483.792 || 47,67 hab./km² || [[List of municipalities in Huelva|Municipalities]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[Jaén (province)|Jaén]] | ||
| + | | [[Jaén]] || 662.751 || 49,09 hab./km² || [[List of municipalities in Jaén|Municipalities]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[Málaga (province)|Málaga]] | ||
| + | | [[Málaga]] || 1.491.287 || 204,06 hab./km² || [[List of municipalities in Málaga|Municipalities]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [[Seville (province)|Seville]] | ||
| + | | [[Seville]] || 1.813.908 || 129,23 hab./km² || [[List of municipalities in Seville|Municipalities]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | Other important Andalusian cities are: | |
| + | *El Ejido, and Roquetas de Mar, Almería | ||
| + | *La Línea de la Concepción, Algeciras, Sanlúcar de Barrameda, Rota, San Fernando, Jerez, and El Puerto, Cádiz | ||
| + | *Almuñécar, Guadix, Loja and Motril, Granada | ||
| + | *Linares, Úbeda and Baeza, Jaén | ||
| + | *Antequera, Ronda and Marbella, Málaga | ||
| + | *Dos Hermanas, Lebrija, Osuna and Utrera, Sevilla | ||
| − | + | ==Economy== | |
| + | Andalusia is particularly rich in [[natural resource]]s, but despite this fact, Andalusia continues to have one of the lowest GDP per capita in Spain and [[poverty]] is widespread. The economic difficulties of the region are commonly attributed to poor [[soil]] conditions. With rocky soil throughout the state and a subtropical climate, Andalusia is agriculturally comparable to [[North Africa]]. Major [[agriculture|agricultural]] products of the region include [[olive oil]] and [[wine]], whose production levels are gradually increasing with increased mechanization. The natural wealth of the region is found in its [[mineral]] deposits, particularly [[copper]], [[iron]], [[zinc]], and [[lead]]. These minerals have been drawn from the region since Phoenician and Roman times. | ||
| − | + | While the agricultural portions of the economy continue to struggle, the service sector is becoming a significant part of the national product of Andalusia. Manufacturing and service sectors are growing exponentially, with the growth rates in Andalusia exceeding those found elsewhere in Spain. High growth rates in the service sector are expected to continue, especially as tourism becomes more prominent in the area. | |
== Culture == | == Culture == | ||
| + | [[Image:Malecón de La Caleta, Cádiz.JPG|thumb|275px|[[Malecón]] of La Caleta, Cádiz.]] | ||
| + | The Moorish influx contributed most significantly to the distinctive Andalusian [[culture]] that is apparent today. Moorish influences were particularly strong in [[architecture]], with prominent examples found at the [[Alhambra]] and the [[Giralda towers]]. | ||
| − | + | Andalusia is considered to be one of the most colorful regions of Spain, with ornamentation playing a large role in clothing. [[Dance]] and [[music]] are also vital to the culture of Andalusia, with the most popular performance dance being the [[flamenco]]. Flamenco, while most often performed by [[Roma]] gypsies has gained popularity around the globe. Two distinct types of flamenco exist in Andalusia, those which are choreographed, and those which are not. Unchoreographed flamenco dance is referred to as cante jondo, and has a less structured musical rhythm than choreographed flamenco. | |
| − | + | [[Archaeology|Archaeological]] ruins include [[Medina Azahara]], near [[Córdoba]], and the Roman city of [[Itálica]], near [[Seville]], and at Palos, in the province of [[Huelva]], the Andalusian port from which [[Christopher Columbus|Columbus's]] expedition of discovery was launched. | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | The Spanish language spoken in [[The Americas]] today is largely descended from the [[Andalusian dialect]] of [[Spanish language|Spanish]]. The Spanish spoken at the Canary Islands resembles more the Spanish spoken in the Caribbean due to the role played by [[Seville]] as the gateway to Spain's American territories during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. |
| + | |||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | * The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition. 2003. [http://www.answers.com/topic/andalusia Andalusia] ''Answers.com., Columbia University Press''. Retrieved November 22, 2007. | ||
| + | * Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Andalusia ''Encyclopædia Britannica Online''. | ||
| + | * Lewis, Brenda Ralph. 2002. ''Great Civilizations.'' Bath, UK: Parragon Publishing. ISBN 0752561413 | ||
| + | *Costantino, Maria. 2001. ''The Illustrated Flag Handbook.'' New York: Gramercy Books. ISBN 0517218100 | ||
| + | *Noble, John. 2007. ''Lonely Planet Andalucia.'' Lonely Planet Publications. ISBN 174059973X | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | + | All links retrieved July 26, 2023. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | *[http://www.infoplease.com/ce6/world/A0803911.html, Andalusia] | |
| − | |||
| − | *[http://www.infoplease.com/ce6/world/A0803911.html, Andalusia] | ||
{{Provinces of Andalusia}} | {{Provinces of Andalusia}} | ||
| Line 83: | Line 141: | ||
[[Category:Europe]] | [[Category:Europe]] | ||
| − | {{credit|Andalusia|165349425|Historical_regions_in_Spain|148721450|Geography_of_Spain|164605922|Music_of_Andalusia|168407131 | + | {{credit|Andalusia|165349425|Historical_regions_in_Spain|148721450|Geography_of_Spain|164605922|Music_of_Andalusia|168407131}} |
Latest revision as of 19:54, 26 July 2023
| |||||
| Motto: Andalucía por sí, para España y la humanidad (Andalusia by herself, for Spain, and for humankind) | |||||
| Anthem: La bandera blanca y verde | |||||
| |||||
| Capital | |||||
| Official language(s) | Spanish | ||||
| Area – Total – % of Spain |
Ranked 2nd 87,268 km² 17.2 percent | ||||
| Population – Total (2006) – % of Spain – Density |
Ranked 1st 7,975,672 17.84 91.39/km² | ||||
| Demonym – English – Spanish |
Andalusian Andaluz, andaluza | ||||
| Statute of Autonomy | December 30, 1981 | ||||
| Parliamentary representation – Congress seats – Senate seats |
62 40 | ||||
| President | Manuel Chaves González (PSOE) | ||||
| ISO 3166-2 | AN | ||||
| Junta de Andalucía | |||||
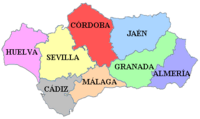
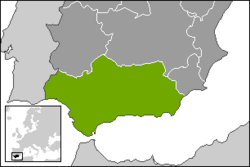
Andalusia, located in the southern portion of Spain, is one of the seventeen autonomous regions of the country. It contains eight distinct provinces, all with individual cultural traditions and identity. With eight provinces ( Almeria, Cadiz, Cordoba, Granada, Huelva, Jaen, Malaga,and Seville ) , Andalusia boasts the largest population of any of the autonomous Spanish states. In terms of land mass, Andalusia is the second largest of the autonomous regions of Spain, second only to the region of Castilla y Leon.
Andalusia lies to the south of Extremadura and Castilla-La Mancha, meeting the Mediterranean Sea on its southern border. Its eastern neighbor is the autonomous community of Murcia, while the country of Portugal lies along its western border. Past Portugal to the west lies the Atlantic Ocean. Andalusia is also conveniently located along the strait of Gibraltar, the passage between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. The prime position along the strait was also recognized by Great Britain, who controls a small area of land bordering Andalusia.
Five hundred years of Muslim rule during the Middle Ages greatly influenced Andalusia's culture. During this time it became an extremely wealthy and influential political force that actively cultivated scholarship and advances in many areas. This Moorish influence continues to be evident in the region's character through its architecture, language and customs. With its tradition of bull fights and Gypsy flamenco music and dance, Andalusia provides the strongest external image of Spain.
Etymology
It is believed that the name Al-Andalus, Arabic for "Country of the Vandals," was originally applied to the entire Iberian Peninsula by the Muslim (Moors) who occupied the area for 500 years. As Christians began to reconquer the peninsula in the eleventh century, the name was used only to describe the area still under Muslim control. Eventually a form of the name, Andalusia, came to be attached to the modern-day region of Spain.
Geography
Alpine mountains and pine forests exist at the high elevations of Andalusia while arid, barren deserts exist at the lower points. Fertile, irrigated plains support plantations of subtropical fruits. Oranges, grapes, olives, wheat and sugarcane are abundant crops. The rich mineral resources, exploited since Phoenician and Roman times, include copper, iron, zinc, and lead. Cattle, bulls (for bullfighting) and fine horses are bred there.
The terrain of Andalusia varies greatly depending on the region. Toward the coast the terrain descends into the famous beaches of Spain, notable for their fine sands and constant sunshine.
Most of lowland Andalusia has a mild, Mediterranean climate, while the interior of the region is cooler. The weather, beach, and nearly constant sunshine, however, are not the only reasons that tourists flock to Andalusia. The mountains are also spectacular, and they host a unique combination of plant and animal life.
The main geographic feature of the region is the Andalusian Plain, which runs from the Sierra Morena in the north to the Sistema Penibetico in the south. The plain is fundamentally a large river valley that surrounds the Rio Guadlquivir, and it broadens wherever possible. The valley reaches its narrowest point where the Sierra Morena and the Sistema Penibetico meet in the eastern portion of the region. Minor valleys are also common in Andalusia, although none rival the breath and size of the Andalusian Plain.
History
The earliest records of settled civilization in Andalusia describe colonial occupation in Pre-Roman times. In the early twelfth century B.C.E. the Phoenician empire formed colonies along the coast to help with trade. The settlement founded by the Phoenicians was called Tartessos, which later rose to become a major political force in the region.
The colonies of the Phoenicians eventually declined in power following the dissolution of the Phoenician empire. The next major political force to emerge in the region was the city of Carthage, whose emphasis on trade gave the straits of Gibraltar and the Andalusia region economic importance. As a trading center, Carthage saw the economic value of controlling the strait, and began a campaign to gain control of the region. Between the first and second Carthaginian wars, Carthage extended its power over Andalusia, using the coast to launch many of its invasions into Roman territory. Carthage, however, was unsuccessful in its campaign against Rome. With the decline of Carthage, Andalusia remained, for a brief period, without a strong political identity. Rome stepped in to fill the power vacuum, renaming the area Betica.
Roman control over the area did not last long, with the area briefly falling under the control of the Vandals. As the Vandals passed through the region on their way to North Africa, they took control of Andalusia. Following their brief occupation, the Visigoths took control, only to be replaced by Muslim rule in the early eighth century C.E. The Muslim invasion proved to be an extremely influential action in the formation of a distinct Andalusian identity.
During the half millennium of Muslim rule during the Middle Ages, Andalusia became an extremely wealthy and influential political force that actively cultivated scholarship and advances in many areas. Córdoba became the largest and richest city in Western Europe and one of the largest in the world. The Moors established universities in Andalucia, and cultivated scholarship, bringing together the greatest achievements of all of the civilizations they had encountered. During that period Moorish and Jewish scholars played a major part in reviving and contributing to Western astronomy, medicine, philosophy and mathematics.
In 1248 Seville fell to Castilian rule. After the fall of Seville, the Andalusia region began to experience a large influx of Moors who were fleeing the Reconquista.
Spain began declining in the sixteenth century, and Andalusia suffered as a consequence, although the ports of Seville and Cádiz flourished as centers of trade with the New World. In 1713 Gibraltar was ceded to Great Britain. In 1833 Andalusia was divided into the present eight provinces.
Catalonia and Andalusia were strongholds of anarchism during the Spanish Republic, which was established in 1931. It fell to the Insurgents in the Spanish civil war of 1936–1939. Demonstrations against the national government of Francisco Franco were common. In 1981 Andalusia became an autonomous region and in 1982 it elected its first parliament.
Government
Andalusia began its own distinct political force in 1978, when the Spanish constitution established historical nationalities. Historical nationalities in Spain, like Andalusia, were granted a special, autonomous status that was based on the idea that the area contained a specific nationality. Another major idea behind historical nationalities was their supposed independence from Spain as a whole. Under this idea Historical Nationalities were areas that were considered culturally independent prior to the second Spanish War. Andalusia is one of only four such regions in Spain, with the other historical nationalities found in Catalonia, Basque, and Galicia. Many other communities in Spain were recognized as a result of the constitution, but other communities were not granted the political and cultural independence of historical nationalities.
Administrative divisions
| Province | Capital | Population | Density | Municipalities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Almería | Almería | 635.850 | 72,47 hab./km² | Municipalities |
| Cádiz | Cádiz | 1.180.817 | 158,80 hab./km² | Municipalities |
| Córdoba | Córdoba | 788.287 | 72,47 hab./km² | Municipalities |
| Granada | Granada | 882.184 | 68,70 hab./km² | Municipalities |
| Huelva | Huelva | 483.792 | 47,67 hab./km² | Municipalities |
| Jaén | Jaén | 662.751 | 49,09 hab./km² | Municipalities |
| Málaga | Málaga | 1.491.287 | 204,06 hab./km² | Municipalities |
| Seville | Seville | 1.813.908 | 129,23 hab./km² | Municipalities |
Other important Andalusian cities are:
- El Ejido, and Roquetas de Mar, Almería
- La Línea de la Concepción, Algeciras, Sanlúcar de Barrameda, Rota, San Fernando, Jerez, and El Puerto, Cádiz
- Almuñécar, Guadix, Loja and Motril, Granada
- Linares, Úbeda and Baeza, Jaén
- Antequera, Ronda and Marbella, Málaga
- Dos Hermanas, Lebrija, Osuna and Utrera, Sevilla
Economy
Andalusia is particularly rich in natural resources, but despite this fact, Andalusia continues to have one of the lowest GDP per capita in Spain and poverty is widespread. The economic difficulties of the region are commonly attributed to poor soil conditions. With rocky soil throughout the state and a subtropical climate, Andalusia is agriculturally comparable to North Africa. Major agricultural products of the region include olive oil and wine, whose production levels are gradually increasing with increased mechanization. The natural wealth of the region is found in its mineral deposits, particularly copper, iron, zinc, and lead. These minerals have been drawn from the region since Phoenician and Roman times.
While the agricultural portions of the economy continue to struggle, the service sector is becoming a significant part of the national product of Andalusia. Manufacturing and service sectors are growing exponentially, with the growth rates in Andalusia exceeding those found elsewhere in Spain. High growth rates in the service sector are expected to continue, especially as tourism becomes more prominent in the area.
Culture
The Moorish influx contributed most significantly to the distinctive Andalusian culture that is apparent today. Moorish influences were particularly strong in architecture, with prominent examples found at the Alhambra and the Giralda towers.
Andalusia is considered to be one of the most colorful regions of Spain, with ornamentation playing a large role in clothing. Dance and music are also vital to the culture of Andalusia, with the most popular performance dance being the flamenco. Flamenco, while most often performed by Roma gypsies has gained popularity around the globe. Two distinct types of flamenco exist in Andalusia, those which are choreographed, and those which are not. Unchoreographed flamenco dance is referred to as cante jondo, and has a less structured musical rhythm than choreographed flamenco.
Archaeological ruins include Medina Azahara, near Córdoba, and the Roman city of Itálica, near Seville, and at Palos, in the province of Huelva, the Andalusian port from which Columbus's expedition of discovery was launched.
The Spanish language spoken in The Americas today is largely descended from the Andalusian dialect of Spanish. The Spanish spoken at the Canary Islands resembles more the Spanish spoken in the Caribbean due to the role played by Seville as the gateway to Spain's American territories during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition. 2003. Andalusia Answers.com., Columbia University Press. Retrieved November 22, 2007.
- Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Andalusia Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- Lewis, Brenda Ralph. 2002. Great Civilizations. Bath, UK: Parragon Publishing. ISBN 0752561413
- Costantino, Maria. 2001. The Illustrated Flag Handbook. New York: Gramercy Books. ISBN 0517218100
- Noble, John. 2007. Lonely Planet Andalucia. Lonely Planet Publications. ISBN 174059973X
External links
All links retrieved July 26, 2023.
| |||||||||
| |||||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
- Andalusia history
- Historical_regions_in_Spain history
- Geography_of_Spain history
- Music_of_Andalusia history
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.