Difference between revisions of "Serbia" - New World Encyclopedia
({{Contracted}}) |
Mike Butler (talk | contribs) (Serbia - importing) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Claimed}}{{Contracted}} | {{Claimed}}{{Contracted}} | ||
| − | '''This article is | + | {{Infobox Country or territory |
| + | |native_name = Република Србија<br/>''Republika Srbija'' | ||
| + | |conventional_long_name = Republic of Serbia | ||
| + | |common_name = Serbia | ||
| + | |image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg | ||
| + | |image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg | ||
| + | |image_map = Europe location SRB.png | ||
| + | |map_caption = {{map_caption |region=on the [[Europe|European continent]]}} | ||
| + | <!--*NATIONAL MOTTO* OF SERBIA IS **NOT** SAMO SLOGA SRBINA SPASAVA. THANKS FOR YOUR UNDERSTANDING.—> | ||
| + | |national_anthem = <span style="line-height:1.25em;">''[[Bože pravde]]''<small><br/>''God of Justice''</small></span> | ||
| + | |official_languages = [[Serbian language]] {{smallsup|1}} | ||
| + | |regional_languages = [[Hungarian language|Hungarian]], [[Croatian language|Croatian]], [[Slovak language|Slovak]], [[Romanian language|Romanian]], <br>[[Rusyn language|Rusyn]] {{smallsup|2}} [[Albanian language|Albanian]] {{smallsup|3}} | ||
| + | |capital = [[Belgrade]] | ||
| + | |latd=44 |latm=48 |latNS=N |longd=20 |longm=28 |longEW=E | ||
| + | |largest_city = capital | ||
| + | |government_type = [[Semi-presidential system|Semi-presidential]] [[Republic|republic]] | ||
| + | |leader_title1 = [[President of Serbia|President]] | ||
| + | |leader_title2 = [[Prime Minister of Serbia|Prime Minister]] | ||
| + | |leader_name1 = [[Boris Tadić]] | ||
| + | |leader_name2 = [[Vojislav Koštunica]] | ||
| + | |area_rank = 113th | ||
| + | |area_magnitude = 1 E10 | ||
| + | |area = 88,361 | ||
| + | |areami² = 34,116 | ||
| + | |percent_water = 0.13 | ||
| + | |population_estimate = 10,147,398 | ||
| + | |population_estimate_rank = 80th | ||
| + | |population_estimate_year = 2007 | ||
| + | |population_census = 7,498,001{{smallsup|4}} | ||
| + | |population_census_year = 2002 | ||
| + | |population_density = 115 | ||
| + | |population_densitymi² = 297 | ||
| + | |population_density_rank = 94th | ||
| + | |GDP_PPP_year = 2007 | ||
| + | |GDP_PPP = $54.310 billion | ||
| + | |GDP_PPP_rank = 72th | ||
| + | |GDP_PPP_per_capita = $7,234 | ||
| + | |GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 89th | ||
| + | |Gini = 24 | ||
| + | |Gini_year = 2007 | ||
| + | |Gini_category = <font color="#009900">low</font> | ||
| + | |sovereignty_type = Establishment | ||
| + | |sovereignty_note = | ||
| + | |established_event1 = Formation | ||
| + | |established_event2 = First unified state | ||
| + | |established_event3 = Independence | ||
| + | |established_event4 = Kingdom established | ||
| + | |established_event5 = Empire established | ||
| + | |established_event6 = Independence lost<br/>{{spaces|3}}to [[Ottoman Empire]] | ||
| + | |established_event7 = {{nowrap|[[First Serbian Uprising]]}} | ||
| + | |established_event8 = First Constitution | ||
| + | |established_event9 = [[Congress of Berlin|Recognized]] | ||
| + | |established_event10 = [[Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenians|Kingdom of SCS]] | ||
| + | |established_event11 = [[Serbia and Montenegro|SCG]] [[Montenegrin independence referendum, 2006|dissolved]] | ||
| + | |established_date1 = [[9th century]] | ||
| + | |established_date2 = [[Circa|c.]][[960]] | ||
| + | |established_date3 = [[1185]] | ||
| + | |established_date4 = [[1077]] (''[[Duklja|Dioclea]]'')<br/>[[1217]] (''[[Raška (state)|Rascia]]'') | ||
| + | |established_date5 = [[1346]] | ||
| + | |established_date6 = <br/>[[1459]] | ||
| + | |established_date7 = [[February 15|Feb 15]], [[1804]] | ||
| + | |established_date8 = [[February 15|Feb 15]], [[1835]] | ||
| + | |established_date9 = [[1878]] | ||
| + | |established_date10 = [[1918]] | ||
| + | |established_date11 = [[June 5]], [[2006]] | ||
| + | |HDI_year = n/a. | ||
| + | |currency = [[Serbian dinar]]{{smallsup|5}} | ||
| + | |currency_code = RSD | ||
| + | |country_code = RS | ||
| + | |time_zone = [[Central European Time|CET]] | ||
| + | |utc_offset = +1 | ||
| + | |time_zone_DST = [[Central European Summer Time|CEST]] | ||
| + | |utc_offset_DST = +2 | ||
| + | |cctld = [[.yu]] ([[.rs]]){{smallsup|6}} | ||
| + | |calling_code = 381 | ||
| + | |ISO_3166-1_alpha2 = RS | ||
| + | |ISO_3166-1_alpha3 = SRB | ||
| + | |ISO_3166-1_num = 688 | ||
| + | |alt_sport_code = SRB | ||
| + | |vehicle_code = SRB | ||
| + | |footnotes = <sup>1</sup> Following the adoption of the new [[Constitution of Serbia|Constitution]], <br>[[Gaj's Latin alphabet|Serbian Latin]] script is awaiting parliamentary <br>approval alongside the official [[Serbian Cyrillic alphabet|Serbian Cyrillic]] script. <br><sup>2</sup> Official languages of [[Vojvodina]]. <br><sup>3</sup> Official languages of [[Kosovo]]. <br><sup>4</sup> does not include the figures for [[Kosovo]] <br><sup>5</sup> The [[euro]] is used in Kosovo alongside the dinar. <br><sup>6</sup> The [[.rs]] was reserved in September 2006, <br>should be available in 2007. [[.yu]] is still in use<br> until the current active leases expire. | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | '''Serbia''', officially the '''Republic of Serbia''' ({{lang-sr|Република Србија or ''Republika Srbija''}}, {{Audio|Republika Srbija.ogg|listen}}), is a [[landlocked]] [[country]] in [[Central Europe|Central]] and [[Balkans|Southeastern]] [[Europe]], covering the southern part of the [[Pannonian Plain]] and the central part of the [[Balkans|Balkan Peninsula]]. It is bordered by [[Hungary]] on the north; [[Romania]] and [[Bulgaria]] on the east; [[Albania]] and [[Republic of Macedonia|Macedonia]] on the south; and [[Montenegro]], [[Croatia]] and [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]] on the west. The capital is [[Belgrade]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The modern state of Serbia emerged in 1817 following the [[Second Serbian Uprising]]. Later, it expanded its territory further south to include [[Kosovo and Metohija]] and the regions of [[Raška (region)|Raška]] and [[Macedonia (region)|Macedonia]] (in 1912). Finally, [[Vojvodina]] (formerly an autonomous Habsburg crownland named [[Voivodship of Serbia and Tamiš Banat]]) proclaimed its secession from [[Austria-Hungary]], and joined Serbia in 1918. The current borders of the country were established following the end of [[World War II]], when Serbia became a federal unit within the [[Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia]]. Serbia became an independent state again in 2006, after [[Montenegro]] left the [[Serbia and Montenegro|union]] which was formed after the [[Breakup of Yugoslavia|dissolution of Yugoslavia]] in 1990s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Name== | ||
| + | In 17th and early 20th century English works, the country was often referred to as ''Servia''.<ref name="B1911">[http://www.1911encyclopedia.org/Servia 1911 Encyclopedia Britannica:Servia]</ref><ref>[http://www.newadvent.org/cathen/13732a.htm Catholic Encyclopedia] used the name "Servia"</ref> The usage was often resented by Serbs, who felt that the use of "Servia" linked the Serbs to the Latin ''servus'', a slave or servant.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://clcwebjournal.lib.purdue.edu/clcweb99-2/deltcheva99.html|title=East Central Europe as a Politically Correct Scapegoat: The Case of Bulgaria}}</ref><ref name="B1911"/> The British press stopped using the term by the 1930s, allegedly due to the efforts of ''Vojislav M. Petrovich'', publisher of the Serbian grammar in London.<ref>[http://www.croatianhistory.net/etf/et112.html The period of Croatia within ex-Yugoslavia]</ref> However, scholars today agree that Serbian name did not derive from word ''servus''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The basic name, [[Serboi]], originates in the works of [[Tacitus]], [[Plinius]] and [[Ptolemy]] in the 1st and 2nd centuries, describing a people living north of the [[Caucasus]]. Following the migration into [[Central Europe]], [[White Serbs]] established a state called [[Sorbia]] ([[White Serbia]]) in the 5th century. Their arrival in the [[Balkans]] is thought to have happened in 630, when Serbs settled among the other Slavic tribes that settled there a century earlier and mixed with them forming a medieval Serbian nation. Serbian kings were crowned as ''Kings of all Serbs'' rather than ''Kings of Serbia'', and were using the terms ''Serb lands'' rather than ''Serbia'' itself. This is due to the fact that the [[Serbs]] mostly lived in several different tribal denominations such as [[Dioclea]] and [[Travunija]], rather than in one unified state; however, the first unified state was achieved under the [[Vlastimirovic dynasty]] in the 9th century and has reemerged several times during [[History of Serbia|Serbian history]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Geography== | ||
| + | {{main|Geography of Serbia}} | ||
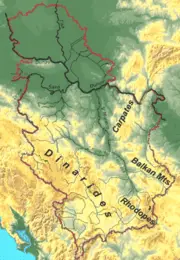
| + | [[Image:Serbia mountain ranges.png|thumb|left|180px|Serbia's geographic components]] | ||
| + | Serbia is located in Europe, on the Balkan peninsula and in the [[Pannonian Plain]]. It is placed at the crossroads between [[Central Europe|Central]], [[Southern Europe|Southern]] and [[Eastern Europe]]. The [[Danube]] river (2850 km) flows through the northern third of the country; it is 588 km long and forms the border with [[Croatia]] and part of [[Romania]]. The [[Sava River|Sava]] river forms the southern border of the [[Vojvodina]] province, flows into the Danube in central [[Belgrade]], and bypasses the hills of the [[Fruška Gora]] in the west. Sixty kilometers to the northeast of Belgrade, the [[Tisza|Tisa]] river flows into the Danube and ends its 1350 km long journey from [[Ukraine]], and the partially navigable [[Timiş River]] (60 km/350 km) flows into the Danube near [[Pancevo]]. The [[Begej]] river (254 km) flows into Tisa near [[Titel]]. All five rivers are navigable, connecting the country with ''Northern'' and ''Western Europe'' (through the [[Rhine-Main-Danube Canal]]–[[North Sea]] route), to ''Eastern Europe'' (via the Tisa–, [[Timiş River|Timiş]]–, [[Begej]]– and Danube–[[Black sea]] routes) and to ''Southern Europe'' (via the Sava river). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The eastern border of the country is determined by the [[Carpathian Mountain range]], which runs through the whole of [[Central Europe]]. The [[Carpathian Mountains|Carpathians]] meet the [[Balkan Mountains]], following the course of [[Velika Morava]], a 500 km long (partially navigable) river. [[Midzor]] peak is the highest point in Eastern Serbia at 2156 m. In the southeast, the [[Balkan Mountains]] meet the [[Rhodope Mountains]], connecting the country with [[Greece]]. The [[Sar Mountains]] of Kosovo form the border with [[Albania]], with one of the highest peaks in the region, [[Djeravica]] (2656 m). [[Dinaric Alps]] of Serbia follow the flow of the [[Drina river]] (at 350 km navigable for smaller vessels only) overlooking the Dinaric peaks on the other side of the shore in [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Sr-map.png|250px|thumb|right|Map of Serbia]] | ||
| + | ===Climate=== | ||
| + | The Serbian [[climate]] varies between a continental climate in the north, with cold winters, and hot, humid summers with well distributed rainfall patterns, and a more Adriatic climate in the south with hot, dry summers and autumns and relatively cold winters with heavy inland snowfall. Differences in elevation, proximity to the [[Adriatic sea]] and large river basins, as well as the exposure to the winds account for climate differences.<ref>[http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-92892/Serbia Serbia], ''[[Encyclopedia Britannica]]'' Online</ref> [[Vojvodina]] possesses typical continental climate, with airmasses from [[Northern Europe|Northern]] and [[Western Europe]] which shape its climatic profile. South and Southwest Serbia is subject to Mediterranean influences, however the [[Dinaric Alps]] and other mountain ranges contribute cooling down the biggest part of warm air masses. Winters are quite harsh in [[Sandžak]] due to the mountains which encircle that plateau.<ref>Radovanović, M and Dučić, V, 2002, [http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2002EGSGA..27.2283R Variability of Climate in Serbia in the Second Half of the 20th Century], EGS XXVII General Assembly, Nice, [[21 April]] to [[26 April]] [[2002]], abstract #2283, '''27''':2283–, provided by the [[Smithsonian]] / [[NASA]] Astrophysics Data System</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Average annual air temperature for the period [[1961]]–[[1990|90]] for the area with the altitude of up to 300 m amounts to 10.9 [[°C]]. The areas with the altitudes of 300 to 500 m have average annual temperature of around 10.0 °C, and over 1000 m of altitude around 6.0 °C.<ref name="RHMZ">[http://www.hidmet.sr.gov.yu/eng/meteorologija/klimatologija_srbije.php Basic Climate Characteristics for the Territory of Serbia], Hydrometeorologic Service of Serbia</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Cities=== | ||
| + | {{main|List of cities in Serbia}} | ||
| + | [[Image:NoviBG Nov30 2005.jpg|thumb|right|250px|[[Belgrade]], the capital city]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Tvrdjava1.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The [[Niš]] Fortress]] | ||
| + | Major cities (over 100,000 inhabitants) — 2002 census data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |colspan="4" align="center"| '''Largest Serbian cities and municipalities''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !rowspan="2"|City|| colspan="2"|Population | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !Urban || Municipality | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Belgrade]] || align="right"| 1,273,651 || align="right"|1,576,124 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Novi Sad]] || align="right"|215,659 || align="right"|299,294 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Niš]] || align="right"|194,790 || align="right"|250,518 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Kragujevac]] || align="right"|145,980 || align="right"|211,580 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Leskovac]] || align="right"|78,030 || align="right"|156,252 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Subotica]] || align="right"|99,471 || align="right"|147,758 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Zrenjanin]] || align="right"|79,545 || align="right"|131,509 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Kruševac]] || align="right"|75,256 || align="right"|131,368 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Pančevo]] || align="right"|77,087 || align="right"|127,162 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Kraljevo]] || align="right"|57,411 || align="right"|121,707 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Čačak]] || align="right"|73,217 || align="right"|117,012 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Smederevo]] || align="right"|77,808 || align="right"|109,867 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Sombor]] || align="right"|51,471 || align="right"|97,263 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Valjevo]] || align="right"|61,035 || align="right"|96,761 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | * The following cities in [[Kosovo and Metohija]], according to [http://www.world-gazetteer.com/wg.php?x=1150378054&men=gcis&lng=en&dat=32&geo=-244&srt=npan&col=aohdq&geo=-3985 World Gazetteer] estimates, surpass the 100,000 mark: [[Priština]], [[Prizren]], [[Djakovica]], [[Peć]] and [[Kosovska Mitrovica]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===National parks=== | ||
| + | Serbia has five [[national park]]s: | ||
| + | *[[Fruška Gora]] (250 km²) | ||
| + | *[[Kopaonik]] (120 km²) | ||
| + | *[[Tara National Park|Tara]] (220 km²) | ||
| + | *[[Đerdap]] ([[Iron Gate (Danube)|Iron Gate]]) (640 km²) | ||
| + | *[[Šar mountain|Šar-planina]] (390 km²) | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==History== | ||
| + | {{main|History of Serbia}} | ||
| + | {{see also|List of Serbian monarchs|History of Yugoslavia|}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Upon arrival to [[Balkans]] in the 5th and 6th century, [[Serbs]] formed their first unified state under the [[Vlastimirovic dynasty]] by [[812]]. The state would achieve full independence, evolving into the [[Serbian Kingdom]] and the [[Serbian Empire]] under the rule of the prominent [[House of Nemanjic]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:CarDusan.jpg|250px|thumb|right|Medieval Serbian Emperor [[Stefan Uroš IV Dušan of Serbia|Stefan Uroš IV Dušan]]]] | ||
| + | Serbia reached an apogee in economy, law, military, and religion during the rule of the [[House of Nemanjic]], especially during [[Emperor Dusan]]. As a result of internal struggle between the rival noble families, it succumbed fully to the [[Ottoman Empire]] in the 16th century. The first Serbia was formed in 1217, and modern Serbia reemerged in the 19th century, when it became an independent principality and then a kingdom. In the 20th century, Serbia was a backbone of various [[Yugoslavia|South Slavic states]], including the [[Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes]] from 1918 to 1941 (renamed the [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia]] in 1929), the [[Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia]] from 1945 to 1992, the [[Federal Republic of Yugoslavia]] from 1992 to 2003, and the State Union of [[Serbia and Montenegro]] from 2003 to 2006.<ref>[http://www.lahana.org/blog/Second%20Balkan%20War.htm Second Balkan War 1913], Lahana.org</ref><ref>[http://www.germannotes.com/hist_ww1_opening.shtml Outbreak and Opening of WW1], GermanNotes.com</ref><ref>[http://www.infoplease.com/spot/yugotimeline1.html Timeline: The Former Yugoslavia], InfoPlease.com</ref> After [[Montenegro]] [[Montenegrin independence referendum, 2006|voted]] for independence from the State Union, Serbia officially proclaimed its independence on [[June 7]], [[2006]], as the [[successor state]] to the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Early history=== | ||
| + | [[Serbs]] settled the region by 630 C.E., having been invited by the [[Byzantine Empire|Byzantine]] [[List of Byzantine Emperors|emperor]] [[Heraclius]]. They were fully converted to [[Christianity]] by 865 C.E.<ref>[http://www.njegos.org/medieval/zeta.htm Serb Medieval State of Zeta], Serb Land of Montenegro website</ref><ref>[http://www.snaga.org.yu/ilustrovana_istorija_srba/tekst/engleski/01/01-06-doseljavanje-slovena.html The Arrival of Slavs, the Adoption of Christianity and the Serbian State of Stefan Nemanja], Illlustrated History of the Serbs</ref> The roots of the Serbian state date back to the [[7th century]] and the [[House of Vlastimirović]]. A Serbian kingdom (centered around [[Duklja]]) was established in the [[11th century]]. It lasted until the end of the [[12th century]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Medieval=== | ||
| + | Serbs formed four distinct independent kingdoms by the 14th century — [[Duklja|Dioclea]], [[Raška (state)|Rascia]], [[Syrmia]] and [[Bosnia (region)|Bosnia]].<ref>[http://www.njegos.org/medieval/mihailo.htm Fresco of King Mihailo], Serb Land of Montenegro website</ref><ref>[http://www.suc.org/culture/history/Serb_History/nemanjici.html Serbian Medieval History: Balkan Power (1168–1321)], Serbian Unity Congress</ref><ref>[http://www.blinkbits.com/en_wikifeeds/Szerem]</ref><ref>{{sr icon}} [http://www.rastko.org.yu/rastko-bo/istorija/srednjivek/nserovic-tvrtko_l.html Stefan Tvrtko I Kotromanić], Projekat Rastko-Boka</ref> Of those, the most viable was [[Raška (state)|Raška]], formed in the 12th century by the Serbian [[Župan|Grand Župan]] [[Stefan Nemanja]]. In [[1220]], under [[Stefan the First Crowned]], Serbia became a kingdom, and rose from [[Byzantine]], [[Second Bulgarian Empire|Bulgaria]]n and [[Kingdom of Hungary|Hungarian]] patronage.<ref>[http://wnd.com/news/article.asp?ARTICLE_ID=22926]</ref> In [[1346]], [[Stefan Dušan]] established the [[Serbian Empire]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Under Dušan's rule, Serbia reached its [[territory (country subdivision)|territorial]] peak, becoming one of the larger states in [[Europe]]. In [[1349]] and [[1354]], Dušan also made and enforced [[Dušan's Code]], a universal system of laws. By nature a soldier and a conqueror, Dušan did not make any systematic effort to stabilize or administer his gains, and the Empire began to dissolve soon after his death. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Golubac.JPG|thumb|right|250px|[[Golubac fortress]] overlooking the [[Danube]] river]] | ||
| + | The Empire had disintegrated by the historic [[Battle of Kosovo]] in [[1389]]. The northern Serbian territories (the [[Serbian Despotate]]) were conquered in [[1459]] following the siege of the "temporary" capital [[Smederevo]]. [[Bosnia (region)|Bosnia]] fell a few years after Smederevo, and [[Herzegovina]] in [[1482]]. [[Belgrade]] was the last major Balkan city to endure Ottoman onslaughts, as it joined Catholic [[Kingdom of Hungary]], following heavy Turkish defeat in [[Siege of Belgrade]] of [[1456]]. It held out for another 70 years, succumbing to the Ottomans in [[1521]], alongside the greater part of the Kingdom of Hungary that was soon conquered. Another shortlasting incarnation of the Serbian state was the one of [[Emperor Jovan Nenad]] in the 16th-century [[Vojvodina]], however it also collapsed and its territory was conquered by the [[Ottoman Empire]], before finally passing to the [[Habsburg Empire]], under which it would remain for about two centuries. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Ottoman/Austrian rule=== | ||
| + | Following the collapse of [[Serbian Empire]] before historic [[Battle of Kosovo]], most of Serbia was under [[Ottoman Empire|Ottoman]] occupation between [[1459]] and [[1804]], despite three [[Austrian Empire|Austrian]] invasions and numerous rebellions (such as the [[Banat Uprising]]). [[Islam]] was in a period of expansion during this time, especially in [[Raška (region)|Raška]], Kosovo and [[Bosnia Province, Ottoman Empire|Bosnia]]. The Ottoman period was a defining one in the history of the country; Slavic, Byzantine, Arabic and Turkish cultures suffused. Many contemporary cultural traits can be traced back to Ottoman period. However the majority of the Serbs managed to keep their culture and religion through the long period of Ottoman rule. The northern third of the modern country, [[Vojvodina]], endured a century long Ottoman occupation before passing to [[Habsburg Empire]] in the end of the 17th century and beginning of the 18th century, only to proclaim secession from [[Austria-Hungary]] in 1918. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Kara-Djordje Petrovic.jpg|thumb|left|220px|[[Karađorđe Petrović]], leader of the [[First Serbian uprising]] in 1804]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Principality of Serbia/Crownland of Vojvodina=== | ||
| + | The [[First Serbian Uprising]] of [[1804]]–[[1813|13]], led by [[Đorđe Petrović]] (also known as ''Karađorđe'' or "Black George"), and the [[Second Serbian Uprising]] of [[1815]] resulted in autonomy and self-governance of the new [[Principality of Serbia]] (previously [[Pashaluk of Belgrade]]) from the [[Porte]]. As it was semi-independent from the Ottoman Empire, it is considered to be the precursor of the formation of [[History of Modern Serbia|modern Serbia]]. After the Ottomans were definitely expelled in 1867, Serbia de facto secured its sovereignty, which was formally recognised internationally at the [[Congress of Berlin]] in 1878.<ref>[http://www.royalfamily.org/ustanak/USTANAK_ENG.htm The First Serbian Uprising], website of the Royal Family of Serbia and Yugoslavia</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | From [[1815]] to [[1903]], the Serbian state was ruled by the [[House of Obrenović]], except from [[1842]] to [[1858]], when Serbia was ruled by Prince [[Alexander Karađorđević, Prince of Serbia|Aleksandar Karađorđević]]. In 1903, the House of Obrenović was replaced by the [[House of Karađorđević]], who were descendants of Đorđe Petrović. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Serbia02.png|220px|thumb|right|Austrian and Ottoman Serbia in 1849]] | ||
| + | In 1848, Serbs in the northern part of present-day Serbia, which was ruled by the [[Austrian Empire]], established an autonomous region known as the [[Serbian Vojvodina]]. As of 1849, the region was transformed into a new Austrian crownland known as the [[Vojvodina of Serbia and Tamiš Banat]]. Although the crownland was abolished in 1860, the Serbs from the Vojvodina region gained another opportunity to achieve their political demands in 1918. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Independent Kingdom=== | ||
| + | The struggle for liberty, modern society and a [[nation-state]] in Serbia lasted almost three decades and was completed with the adoption of the constitution on [[15 February]] [[1835]]. In 1876, [[Montenegro]], Serbia, and [[Bosnia and Herzegovina|Bosnia]] declared war against the Ottoman Empire and proclaimed their unification. However, the [[Treaty of Berlin, 1878|1878 Treaty of Berlin]], which was signed at the [[Congress of Berlin]] by the [[Great Powers]], granted complete independence only to Serbia and Montenegro, leaving Bosnia and [[Sanjak of Novi Pazar]] to [[Austria-Hungary]], who blocked their unification until the [[Balkan Wars]] of 1912 and 1913 and [[World War I]]. | ||
| + | [[Image:Kralj Petar I Karadjordjevic.jpg|220px|thumb|left| King [[Peter I of Yugoslavia|Petar I Karađorđević]], Serbian leader in the [[First World War]]]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | On [[28 June]] [[1914]] the [[Assassination in Sarajevo|assassination]] of [[Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria]] at [[Sarajevo]] in [[Austria-Hungary]] by [[Gavrilo Princip]], a South Slav unionist, Austrian citizen and member of [[Young Bosnia]], led to Austria-Hungary declaring war on Serbia. The [[Russian Empire]] started to mobilize its troops in defence of its ally Serbia, which resulted in the [[German Empire]] declaring war on Russia in support of its ally Austria-Hungary. However, as German military planners [[Schlieffen Plan#The Schlieffen Plan In Action.2C And Its Failure|wished to avoid a war on two fronts]] against both Russia and [[France]], they attacked France first. This eventually culminated in all the major [[European Powers]] being drawn into the war. The Serbian Army won several major victories against Austria-Hungary at the beginning of [[World War I]], but it was overpowered by the joint forces of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary and Bulgaria in 1915. Most of its army and some people went to exile to [[Greece]] and [[Corfu]] where it healed, regrouped and returned to [[Macedonian front (World War I)]] to lead a final breakthrough through enemy lines on [[15 September]] [[1918]], freeing Serbia again and ending the World War I on [[11 November]].<ref>[http://www.archives.org.yu/ Archive of Serbia]</ref> In World War I, Serbia had 1,264,000 casualties — 28% of its total population, and 58% of its male population.[http://www.serbia-info.com/enc/history/modern.html] | ||
| + | {{History of Serbia}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The Yugoslav era=== | ||
| + | After 1918, Serbia, along with [[Montenegro]], was a founding member of the [[Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes]], later known as the [[Kingdom of Yugoslavia]]. During [[World War II]], Serbia was a German-occupied puppet state that included present-day Central Serbia and Banat, popularly called [[Nedić's Serbia]]. However, parts of the present-day territory of Serbia were occupied by Croatian, Hungarian, Bulgarian, Albanian, and Italian armies. The occupying powers committed numerous crimes against the civilian population, especially against Serbs and Jews.{{Fact|date=January 2007}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 1945, Serbia was established as one of the federal units of the [[SFRJ|second Yugoslavia]], the Socialist Federative Republic of Yugoslavia, led by [[Josip Broz Tito]] until his death in 1980. In 1989, the [[League of Communists of Serbia]] selected [[Slobodan Milošević]] to become the republic's President. Milošević was controversial in Yugoslavia because he opposed Kosovo's autonomy and that his rise to power through the [[Anti-bureaucratic revolution]] was done through mass protests which pushed out the leadership of the autonomous provinces and also the republic of Montenegro. He also aggravated the situation in post-Tito Yugoslavia by alleging that certain politicians in Yugoslavia were anti-Serb. Milošević's nationalist stand on Kosovo and desire to strengthen Serbia's position in Yugoslavia. The republics of Yugoslavia including Serbia all adopted multi-party systems in 1990. Milosevic and the Communist establishment were elected under the [[Socialist Party of Serbia]]. In the other republics, except for Montenegro, secessionist governments were elected. | ||
| + | |||
| + | By 1992, Slovenia, Croatia, Macedonia, and Bosnia & Herzegovina had all declared independence from Yugoslavia, resulting in the collapse of the Socialist Federal Republic and the outbreak of war. Serbia, together with Montenegro, formed the [[Federal Republic of Yugoslavia]] in 1992. Serbian government supported Croatian and Bosnian Serbs in the [[Yugoslav wars]] from 1991 to 1995. As a result, [[sanctions]] were imposed by the UN, which led to political isolation and economic decline.[http://www.srpska-mreza.com/bookstore/voices/voices6.htm] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serbia's official peace was broken between 1998 and 1999, when the situation in Kosovo worsened with continued clashes in Kosovo between the Serbian and Yugoslav security forces and the ethnic Albanian [[Kosovo Liberation Army]] (KLA). The Serbian actions in Kosovo prompted a [[Operation Allied Force|NATO aerial bombardment]] which lasted for 78 days. The attacks were ended following a negotiation on the [[Republic of Macedonia|Macedonian]]-[[Yugoslavia|FR Yugoslav]] border between Nato spokesperson [[Mike Jackson]] and officials on behalf of Milošević, in which Milošević would withdraw all security forces, including the military and the police, and have them replaced by a body of international police. The agreement upheld Yugoslav (later Serbian) sovereignty over Kosovo but replaced Serbian government of the province with a UN administration (See: [[Kosovo War]] and [[UNMIK]]). NATO also surrendered its bid to station NATO troops across the whole Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, which had been one of its demands at the Rambouillet negotiations prior to the bombing campaign.[http://www.commondreams.org/views/031400-107.htm] | ||
| + | |||
| + | In September 2000, opposition parties claimed that Milošević committed fraud in routine federal elections. Street protests and rallies throughout Serbia eventually forced Milošević to concede and hand over power to the recently formed Democratic Opposition of Serbia (DOS), a broad coalition of anti-Milošević parties. [[5th October Overthrow|The fall of Milošević]] led to end of the international isolation Serbia suffered during the Milošević years. Serbia's new leaders announced that Serbia would seek to join the [[European Union]] and [[NATO]]. In October 2005, the EU opened negotiations with Serbia for a [[Stabilization and Association Agreement]] ([[SAA]]), a preliminary step towards joining the [[EU]].Negotiations were continued after short break. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Serbia and Montenegro=== | ||
| + | From 2003 to 2006, Serbia was part of the [[Serbia and Montenegro|State Union of Serbia and Montenegro]], into which the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia had been transformed. On [[21 May]] [[2006]] Montenegro held a [[Montenegrin independence referendum, 2006|referendum]] to determine whether or not to end the union with Serbia. The next day, state-certified results showed 55.5% of voters in favor of independence, which was just above the 55% required by the referendum.[http://edition.cnn.com/2006/WORLD/europe/05/22/montenegro.independence/] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Republic of Serbia=== | ||
| + | On [[5 June]] [[2006]] [[National Assembly of Serbia]] declared Serbia the legal successor to the State Union, following the decision of the people of [[Montenegro]] expressed at the independence referendum. [http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/europe/5083690.stm] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Government and politics== | ||
| + | {{main|Politics of Serbia}} | ||
| + | {{see also|Politics of Vojvodina|Elections in Serbia|Human rights in Serbia|Constitutional status of Kosovo}} | ||
| + | [[Image:BorisTadicPress.jpg|thumb|[[Boris Tadić]], president of Serbia]] | ||
| + | On [[4 February]] [[2003]] the [[Parliament of Serbia and Montenegro|parliament of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia]] agreed to a weaker form of cooperation between Serbia and Montenegro within a [[confederal]] state called Serbia and Montenegro. The Union ceased to exist following Montenegrin and Serbian declarations of independence in June 2006. | ||
| + | |||
| + | After the ousting of [[Slobodan Milošević]] on [[5 October]] [[2000]], the country was governed by the [[Democratic Opposition of Serbia]]. Tensions gradually increased within the coalition until the [[Democratic Party of Serbia]] (DSS) left the government, leaving the [[Democratic Party (Serbia)|Democratic Party]] (DS) in overall control. Nevertheless, in March [[2004]] the DSS gathered enough support to form the new [[Government of Serbia]], together with [[G17 Plus]] and coalition [[Serbian Renewal Movement|SPO]]–[[New Serbia|NS]], and the support of the [[Socialist Party of Serbia]], who do not take part in the government, but in exchange for the support hold minor government and justice positions and influence policies. The [[Prime Minister of Serbia]] is [[Vojislav Koštunica]], leader of the [[Democratic Party of Serbia]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The current [[President of Serbia]] is [[Boris Tadić]], leader of the [[Democratic Party (Serbia)|Democratic Party]] (DS). He was elected with 53% of the vote in the second round of the [[Serbian presidential election, 2004|Serbian presidential election]] held on [[27 June]] [[2004]], following several unsuccessful elections since [[2002]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serbia held a two-day [[Serbian constitutional referendum, 2006|referendum]] on [[October 28]] and [[October 29]], [[2006]], that ratified a new constitution to replace the Milošević-era constitution. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serbia held Parliamentary elections on [[21 January]] [[2007]]. The [[Serbian Radical Party]] claimed victory, but no party has won an absolute majority. | ||
| + | |||
| + | On 8 May 2007, [[Tomislav Nikolić]] was elected Speaker of the Serbian Parliament, which sparked a great deal of speculation about Serbia's political future, particularly from the [[European Union]], the [[United States]] and international media. [http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/europe/6636199.stm] Following last-minute negotiations on the part of the DS and DSS political parties, an agreement was reached on the make-up of the country's new government on 11 May 2007 between DS, DSS and G17 Plus.[http://www.b92.net/eng/news/politics-article.php?yyyy=2007&mm=05&dd=11&nav_category=93&nav_id=41168] This led to Nikolić's resignation two days later on 13 May 2007. [http://www.mercurynews.com/nationworld/ci_5890049] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Administrative subdivisions=== | ||
| + | {{main|Subdivisions of Serbia}} | ||
| + | [[Image:Srbija okruzi.png|thumb|200px|right|Political map of Serbia]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serbia is divided into 29 [[districts of Serbia|districts]] plus the [[City of Belgrade]]. The districts and the city of Belgrade are further divided into [[municipalities of Serbia|municipalities]]. Serbia has two autonomous provinces: [[Kosovo and Metohija]] in the south (5 districts, 30 municipalities), which is presently under the administration of the [[UNMIK|United Nations Mission in Kosovo]], and [[Vojvodina]] in the north (7 districts, 46 municipalities). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The part of Serbia that is neither in Kosovo nor in Vojvodina is called [[Central Serbia]]. Central Serbia is not an administrative division, unlike the two autonomous provinces, and it has no regional government of its own. In [[English language|English]] this region is often called "[[Serbia proper]]" to denote "the part of the Republic of Serbia not including the provinces of Vojvodina and Kosovo", as the [[Library of Congress]] puts it.<ref>[http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/yugoslavia/yu_glos.html Glossary — Yugoslavia], [[Library of Congress]]</ref> This usage was also employed in [[Serbo-Croatian]] during the Yugoslav era (in the form of "uža Srbija", literally: "narrow Serbia"). Its use in English is purely geographical, without any particular political meaning being implied. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Negotiations are currently underway to determine the final status of [[Kosovo]]. The [[Contact Group]] has postponed the completing of the status process until after Serbian parliamentary elections in January 2007. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Demographics== | ||
| + | {{main|Demographics of Serbia}} | ||
| + | {{see also|Demographic history of Serbia|Demographic history of Vojvodina|Demographic history of Kosovo|Ethnic groups of Vojvodina}} | ||
| + | [[Image:Slovaci u Srbiji.jpg|150px|thumb|right|[[Slovaks]] in Serbia]] | ||
| + | ;Population statistics of Serbia (Estimate May 2005): | ||
| + | *Serbia (total): 9,396,411 | ||
| + | **[[Vojvodina]]: 2,116,725 | ||
| + | **[[Central Serbia]]: 5,479,686 | ||
| + | **Kosovo: 1,800,000 | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{bar box | ||
| + | |width=300px | ||
| + | |title=Serbia <small>(excluding Kosovo)</small> in 2002 | ||
| + | |titlebar=#ddd | ||
| + | |bars= | ||
| + | {{bar percent|Serbs|red|82.86}} | ||
| + | {{bar percent|Hungarians|green|3.91}} | ||
| + | {{bar percent|Bosniaks|lightgreen|1.82}} | ||
| + | {{bar percent|Roma|yellow|1.44}} | ||
| + | {{bar percent|Yugoslavs|blue|1.08}} | ||
| + | {{bar percent|other|gray|9.79}} | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serbia is populated mostly by [[Serbs]]. Significant [[minority|minorities]] include [[Albanians]] (who are a majority in the province of Kosovo), [[Magyars|Hungarians]], [[Bosniaks]], [[Roma (people)|Roma]], [[Croats]], [[Slovaks]], [[Montenegrins]], [[Macedonians (ethnic group)|Macedonians]], [[Bulgarians]], [[Romanians]], etc. The two provinces, Vojvodina and Kosovo, are ethnically and religiously diverse. | ||
| + | |||
| + | According to the last official census<ref>[http://www.statserb.sr.gov.yu/ Statistical office of the Republic of Serbia]</ref> data collected in 2002, ethnic composition of Serbia is: | ||
| + | *Total: 7,498,001 | ||
| + | **Serbs: 6,212,844 (82.86%) | ||
| + | **Hungarians: 293,172 (3.91%) | ||
| + | **Bosniaks: 136,464 (1.82%) | ||
| + | **Roma: 107,971 (1.44%) | ||
| + | **Yugoslavs: 80,978 (1.08%) | ||
| + | **Others (each less than 1%): 666,572 (8.89%) | ||
| + | |||
| + | The census was not conducted in Serbia's southern province of Kosovo, which is under administration by the United Nations. Its population is estimated to 2,100,000 inhabitants, of whom 92% are Albanians, 5.3% Serbs and others form 2.7% of its population.{{fact|date=June 2007}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Refugees]] and IDPs in Serbia form between 7% and 7.5% of its population. With over half a million refugees (from [[Croatia]] mainly, to an extent [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]] too and internally displaced personal from [[Kosovo]]), Serbia takes the first place in Europe with the largest refugee crisis, as a result of the [[Yugoslav]] wars.{{fact|date=June 2007}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Religion== | ||
| + | {{main|Religion in Serbia}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{bar box | ||
| + | |title=Serbia <small>(excluding Kosovo)</small> in 2002 | ||
| + | |titlebar=#ddd | ||
| + | |left1=religion | ||
| + | |right1=percent | ||
| + | |bars= | ||
| + | {{bar percent|Eastern Orthodoxy|violet|84.1}} | ||
| + | {{bar percent|Roman Catholicism|red|6.24}} | ||
| + | {{bar percent|Islam|green|4.82}} | ||
| + | {{bar percent|Protestantism|blue|1.44}} | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | According to the 2002 Census [http://www.statserb.sr.gov.yu/], 82% of the population of Serbia (excluding [[Kosovo]]) or 6,2 million people declared their nationality as [[Serbs|Serbian]], who are overwhelmingly adherents of the '''[[Serbian Orthodox Church]]'''. Other '''[[Orthodox Christian]]''' communities in Serbia include [[Montenegrins]], [[Romanians]], [[Macedonians (ethnic group)|Macedonians]], [[Bulgarians]], [[Vlachs]] etc. Together they comprise about 84% of the entire population. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Catholicism]]''' is mostly present in [[Vojvodina]] (mainly in its northern part), where almost 20% of the regional population (belonging to different ethnic groups such as the [[Hungarians]], [[Slovaks]], [[Croats]], [[Bunjevci]], [[Czechs]], etc) belong to this [[Christian]] denomination. There are an estimated 433,000 baptised [[Catholics]] in Serbia, roughly 6,2% of the population, mostly bounded to the northern province and [[Belgrade]] area. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Protestantism]]''' accounts for about 1,5 % of the country's population. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Islam]]''' has a strong historic populous in the southern regions of Serbia - [[Sandzak|Raska region]], several municipalities in the south-east, and especially in the southern province of [[Kosovo]]. [[Bosniaks]] are the largest [[Muslim]] community in Serbia (excluding Kosovo) at about 140,000 (2%), followed by [[Albanians]] (1%), [[Turks]], [[Arabs]] etc. | ||
| + | |||
| + | With the Exile of '''[[Judaism|Jews]]''' from Spain during the infamous Inquisition era thousands of both individuals and families escaping that horror made their way through Europe to the Balkans. A goodly number settled in Serbia and became part of the general population. They were well accepted and during the ensuing generations the majority assimilated or became traditional or secular rather than remain orthodox Jews as had been the original immigrants. Later on the wars that ravaged the region resulted in a great part of the Serbian Jewish population either being killed or escaping to other regions for hopefully safer abodes in Yugoslavia and Austria-Hungary. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Economy== | ||
| + | {{main|Economy of Serbia}} | ||
| + | Serbia has an economy based mostly on various [[services]], [[industry]] and [[agriculture]]. In the late 1980s, at the beginning of the process of economic transition, its position was favorable, but it was gravely impacted by [[UN]] [[economic sanctions]] [[1992]]–[[1995|95]], the damage to infrastructure and industry during the [[NATO]] air strikes in [[1999]], as well as having problems from losing the markets of ex-[[Yugoslavia]] and [[Comecon]]. Main economic problems include high unemployment and an insufficient amount of economic reforms. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serbia grows about one-third of the world's [[raspberry|raspberries]] and is the leading frozen fruit exporter.<ref>[http://www.invest-in-serbia.com/modules.php?name=Content&pa=showpage&pid=66 Rebranding Serbia: A Hobby Shortly to Become a Full-Time Job?!]</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:100RSD front.jpg|right|thumb|[[Nikola Tesla]] on 100 [[Serbian dinar]] banknote]] | ||
| + | After the ousting of former Federal Yugoslav President Milošević in October [[2000]], the country experienced faster economic growth (the amount of economic growth in [[2006]] was 6.3 percent<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ebrd.com/new/pressrel/2006/152nov14.htm |title=Domestic consumption drives growth in Eastern Europe |accessdate=2006-11-16 |format=HTML|work=EBRD Transition Report 2006 }}</ref>), and has been preparing for membership in the [[European Union]], its most important trading partner. Serbia suffers from high export/import trade deficit and considerable national debt. The country expects some major economic impulses and high growth rates in the next years. Serbia has been occasionally called a "Balkan tiger" due to its recent high economic growth rates, a reference to the [[East Asian Tigers]].<!-- Page no longer exists: ref>[http://www.chron.com/disp/story.mpl/ap/world/4346608.html]</ref —> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serbia has been very successful in economic reforms since the 2000 revolution, especially in the past three years in which growth has averaged 6 – 7 percent, and foreign direct investment is at record levels. | ||
| + | The nation is expected to reach its pre-1990 level of GDP within a short time frame.{{fact|date=June 2007}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Estimated GDP of Serbia for [[2006]] is $50.688 billion which is $6 771 per capita [[Purchasing Power Parity]] (PPP), $4 220 (nominal). GDP growth rate in [[2006]] is 5.8%.<ref>[http://webrzs.statserb.sr.gov.yu/axd/en/index1.php?SifraV=157&Link= Economic Trends in the Republic of Serbia 2006], Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia</ref> Growth in 2005 was 6.3%<ref>[http://webrzs.statserb.sr.gov.yu/axd/en/drugastrana.php?Sifra=0001&izbor=odel&tab=30 Gross Domestic Product of the Republic of Serbia 1997–2005], Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia</ref> | ||
| + | FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) in 2006 was [[US dollar|$]]5.85 billion or [[€]]4.5 billion. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Culture== | ||
| + | {{main|Serbian culture}} | ||
| + | [[Image:Meister von Mileseva 001.jpg|155px|thumb|right|The White Angel in [[Mileševa monastery]]]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serbia is one of [[Europe|Europe's]] most culturally diverse countries. The borders between large empires ran through the territory of today's Serbia for long periods in history: between the [[Byzantine Empire|Eastern]] and [[Western Roman Empire|Western]] halves of the [[Roman Empire]]; between [[Kingdom of Hungary]], [[Bulgarian Empire]] and [[Byzantium]]; and between the [[Ottoman Empire]] and the [[Austrian Empire]] (later [[Austria-Hungary]]). As a result, while the north is culturally "[[Mitteleuropa|Central European]]", the south is rather more "[[Oriental]]". Of course, both regions have influenced each other, and so the distinction between north and south is artificial to some extent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[Byzantine Empire]]'s influence on Serbia was perhaps the greatest. Serbs are [[Eastern Orthodox Christianity|Orthodox Christians]] with their own national church — the [[Serbian Orthodox Church]]. They use both the [[Cyrillic]] and [[Latin]] alphabets, as a result of both Eastern and Western influences. The [[List of Serb Orthodox monasteries|monasteries of Serbia]], built largely in the [[Middle Ages]], are one of the most valuable and visible traces of [[History of Medieval Serbia|medieval Serbia's]] association with the Byzantium and the Orthodox World, but also with the Romanic (Western) Europe that Serbia had close ties with back in Middle Ages. Most of Serbia's queens still remembered today in [[History of Serbia|Serbian history]] were mostly of foreign origin: [[Helen d'Anjou]] (a cousin of [[Charles I of Sicily]]), [[Anna Dondolo]] (daughter of the [[Doge of Venice|Doge]] of [[Republic of Venice|Venice]], [[Enrico Dandolo]]), [[Catherine]] of [[Kingdom of Hungary|Hungary]], [[Symonide]] of [[Byzantine Empire|Byzantium]].<!-- who are all these queens? can they be wikilinked? —> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Education=== | ||
| + | {{main|Education in Serbia}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Education in Serbia is regulated by the [[Serbian Ministry of Education and Sports]]. Education starts in either pre-schools or elementary schools. Children enroll in elementary schools ({{lang-sr|''Osnovna škola'' / Основна школа}}) at age of 7 and it lasts for eight years. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Tourism=== | ||
| + | [[Image:HramSvetogSave.jpg|thumb|right|250px|[[Temple of Saint Sava]], the largest Orthodox church in the world.]] | ||
| + | {{main|Tourism in Serbia}} | ||
| + | {{seealso|Agrotourism in Serbia}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Tourism in Serbia is mostly based in mountains and villages. The most famous mountain resorts are [[Zlatibor]], [[Kopaonik]], and the [[Tara Mountain|Tara]]. There also are a lot of spas in Serbia, one the biggest of which is the [[Vrnjačka Banja]]. There is significant tourism in [[Belgrade]], [[Novi Sad]] and [[Niš]]. There are also two very popular festival called the [[EXIT (festival)|Exit Festival]] and the [[Guča|Guča trumpet festival]]. In 2006, there have been over 2 million tourists arrivals in Serbia. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Music=== | ||
| + | {{main|Music of Serbia}} | ||
| + | Serbia won the [[Eurovision Song Contest 2007|2007 Eurovision Song Contest]] in [[Helsinki]] and will host the [[Eurovision Song Contest 2008|2008 Eurovision Song Contest]]. The winning song was "[[Molitva]]" ("Prayer" in English) sung by [[Marija Šerifović]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Serbian holidays=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | ! Date | ||
| + | ! Name | ||
| + | ! Notes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[January 7]] | ||
| + | | [[Eastern Orthodox Church|Orthodox]] [[Christmas]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[January 13]] / [[January 14]] | ||
| + | | {{lang|sr|''Pravoslavna Nova Godina'' (Православна Нова Година)}} | ||
| + | | Orthodox [[New Year]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[February 15]] | ||
| + | | {{lang|sr|''Dan državnosti Srbije'' (Дан државности Србије)}} | ||
| + | | Serbian [[National Day]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[April 6]] | ||
| + | | Orthodox [[Good Friday]] | ||
| + | | Date for 2007 only | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[April 8]] | ||
| + | | Orthodox [[Easter]] | ||
| + | | Date for 2007 only | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[April 9]] | ||
| + | | Orthodox [[Easter Monday]] | ||
| + | | Date for 2007 only | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[May 1]] / [[May 2]] | ||
| + | | [[Labour Day]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[May 9]] | ||
| + | | [[Victory Day]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[June 28]] | ||
| + | | [[Vidovdan]] | ||
| + | | See linked page | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Infrastructure== | ||
| + | ===Communications=== | ||
| + | {{main|Communications in Serbia}} | ||
| + | 89% of households in Serbia have static telephone lines, 49% have computers, 27% use the internet, 42% have cable TV and 90% of the population have cell phones.[http://www.novosti.co.yu/code/navigate.php?Id=5&status=jedna&vest=103744&datum=2007-05-15],[http://webrzs.statserb.sr.gov.yu/axd/drugastrana.php?Sifra=0005&izbor=odel&tab=47],[http://www.poslovnimagazin.biz/magazin/u-srbiji-27-odsto-gradjana-koristi-internet-33-279]. | ||
| + | {{Expand|date=January 2007}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Transportation=== | ||
| + | {{main|Transportation in Serbia}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Serbia, in particular the valley of the [[Morava]], is often described as "the crossroads between East and West", which is one of the primary reasons for its turbulent history. The Morava valley route, which avoids mountainous regions, is by far the easiest way of traveling overland from continental [[Europe]] to [[Greece]] and [[Asia Minor]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[European routes]] E65, E70, E75 and E80, as well as the E662, E761, E762, E763, E771, and E851 pass through the country. The E70 westwards from Belgrade and most of the E75 are modern highways of [[motorway]] / [[autobahn]] standard or close to that. As of 2005, Serbia has 1,481,498 registrated cars, 16,042 motocycles, 9,626 buses, 116,440 trucks, 28,222 special transport vehicles, 126,816 tractors, and 101,465 trailers.[http://webrzs.statserb.sr.gov.yu/axd/drugastrana.php?Sifra=0005&izbor=odel&tab=46] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Danube River, [[central Europe]]'s connection to the [[Black Sea]], flows through Serbia. | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are four international airports in Serbia: [[Belgrade Nikola Tesla Airport]], [[Niš Constantine the Great Airport]], [[Vršac International Airport]] and [[Priština International Airport]] (located in Kosovo, under Serbian sovereignty but under UN administration since 1999). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The national airline carrier is [[Jat Airways]] and the railway system is operated by [[Beovoz]] in [[Belgrade]] and by [[Serbian Railways]] on the national level. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | {{portal|Serbia|Flag of Serbia (state) (bordered).svg}} | ||
| + | *[[Military of Serbia]] | ||
| + | *[[List of Serbs]] | ||
| + | *[[List of computer systems from Serbia]] | ||
| + | *[[Radio Television of Serbia]] | ||
| + | *[[Serbian Campaign (World War I)]] | ||
| + | *[[Serbian law]] | ||
| + | *[[Timeline of Serbian history]] | ||
| + | *[[Foreign relations of Serbia]] | ||
| + | *[[Serbian passport]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <!-- ---------------------------------------------------------- | ||
| + | See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Footnotes for a | ||
| + | discussion of different citation methods and how to generate | ||
| + | footnotes using the<ref>, </ref> and <reference /> tags | ||
| + | ----------------------------------------------------------- —> | ||
| + | *{{loc}} | ||
| + | *{{factbook}} | ||
| + | <div class="references-small"> | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | {{commonscat|Serbia}} | ||
| + | {{sisterlinks|Serbia}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Government links=== | ||
| + | <small>(In alphabetical order of domain name.)</small> | ||
| + | * [http://www.narodnakancelarija.srbija.yu/eng/ People's Office of Serbian President] | ||
| + | * [http://www.nbs.yu/export/internet/english/ National Bank of Serbia] | ||
| + | * [http://www.parlament.sr.gov.yu/content/eng/index.asp National Assembly of Serbia] | ||
| + | * [http://www.predsednik.yu/default.asp?lng=eng President of the Republic of Serbia] | ||
| + | * [http://www.seio.sr.gov.yu/code/navigate.asp?Id=20 The EU integration Office of Serbian Government] | ||
| + | * [http://www.serbia-tourism.org/index_e.php/ National Tourism Organisation of Serbia] | ||
| + | * [http://www.srbija.sr.gov.yu/?change_lang=en Serbian Government] | ||
| + | * [http://webrzs.statserb.sr.gov.yu/axd/en/index.php Republic of Serbia Statistical Office] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Other links=== | ||
| + | *[https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/rb.html CIA World Factbook profile on Serbia] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{credit|142073601}} | ||
Revision as of 22:19, 2 July 2007
| Република Србија Republika Srbija Republic of Serbia | |||||
| |||||
| Anthem: Bože pravde God of Justice | |||||
| Capital | Belgrade 44°48′N 20°28′E | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Largest city | capital | ||||
| Official languages | Serbian language 1 | ||||
| Government | Semi-presidential republic | ||||
| - President | Boris Tadić | ||||
| - Prime Minister | Vojislav Koštunica | ||||
| Establishment | |||||
| - Formation | 9th century | ||||
| - First unified state | c.960 | ||||
| - Independence | 1185 | ||||
| - Kingdom established | 1077 (Dioclea) 1217 (Rascia) | ||||
| - Empire established | 1346 | ||||
| - Independence lost to Ottoman Empire |
1459 | ||||
| - First Serbian Uprising | Feb 15, 1804 | ||||
| - First Constitution | Feb 15, 1835 | ||||
| - Recognized | 1878 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 88,361 km² (113th) 34,116 sq mi | ||||
| - Water (%) | 0.13 | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - 2007 estimate | 10,147,398 | ||||
| - 2002 census | 7,498,0014 | ||||
| - Density | 115/km² 297/sq mi | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2007 estimate | ||||
| - Total | $54.310 billion | ||||
| - Per capita | $7,234 | ||||
| Currency | Serbian dinar5 (RSD)
| ||||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||||
| - Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .yu (.rs)6 | ||||
| Calling code | +381 | ||||
| 1 Following the adoption of the new Constitution, Serbian Latin script is awaiting parliamentary approval alongside the official Serbian Cyrillic script. 2 Official languages of Vojvodina. 3 Official languages of Kosovo. 4 does not include the figures for Kosovo 5 The euro is used in Kosovo alongside the dinar. 6 The .rs was reserved in September 2006, should be available in 2007. .yu is still in use until the current active leases expire. | |||||
Serbia, officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: Република Србија or Republika Srbija, listen ▶), is a landlocked country in Central and Southeastern Europe, covering the southern part of the Pannonian Plain and the central part of the Balkan Peninsula. It is bordered by Hungary on the north; Romania and Bulgaria on the east; Albania and Macedonia on the south; and Montenegro, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina on the west. The capital is Belgrade.
The modern state of Serbia emerged in 1817 following the Second Serbian Uprising. Later, it expanded its territory further south to include Kosovo and Metohija and the regions of Raška and Macedonia (in 1912). Finally, Vojvodina (formerly an autonomous Habsburg crownland named Voivodship of Serbia and Tamiš Banat) proclaimed its secession from Austria-Hungary, and joined Serbia in 1918. The current borders of the country were established following the end of World War II, when Serbia became a federal unit within the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Serbia became an independent state again in 2006, after Montenegro left the union which was formed after the dissolution of Yugoslavia in 1990s.
Name
In 17th and early 20th century English works, the country was often referred to as Servia.[1][2] The usage was often resented by Serbs, who felt that the use of "Servia" linked the Serbs to the Latin servus, a slave or servant.[3][1] The British press stopped using the term by the 1930s, allegedly due to the efforts of Vojislav M. Petrovich, publisher of the Serbian grammar in London.[4] However, scholars today agree that Serbian name did not derive from word servus.
The basic name, Serboi, originates in the works of Tacitus, Plinius and Ptolemy in the 1st and 2nd centuries, describing a people living north of the Caucasus. Following the migration into Central Europe, White Serbs established a state called Sorbia (White Serbia) in the 5th century. Their arrival in the Balkans is thought to have happened in 630, when Serbs settled among the other Slavic tribes that settled there a century earlier and mixed with them forming a medieval Serbian nation. Serbian kings were crowned as Kings of all Serbs rather than Kings of Serbia, and were using the terms Serb lands rather than Serbia itself. This is due to the fact that the Serbs mostly lived in several different tribal denominations such as Dioclea and Travunija, rather than in one unified state; however, the first unified state was achieved under the Vlastimirovic dynasty in the 9th century and has reemerged several times during Serbian history.
Geography
Serbia is located in Europe, on the Balkan peninsula and in the Pannonian Plain. It is placed at the crossroads between Central, Southern and Eastern Europe. The Danube river (2850 km) flows through the northern third of the country; it is 588 km long and forms the border with Croatia and part of Romania. The Sava river forms the southern border of the Vojvodina province, flows into the Danube in central Belgrade, and bypasses the hills of the Fruška Gora in the west. Sixty kilometers to the northeast of Belgrade, the Tisa river flows into the Danube and ends its 1350 km long journey from Ukraine, and the partially navigable Timiş River (60 km/350 km) flows into the Danube near Pancevo. The Begej river (254 km) flows into Tisa near Titel. All five rivers are navigable, connecting the country with Northern and Western Europe (through the Rhine-Main-Danube Canal–North Sea route), to Eastern Europe (via the Tisa–, Timiş–, Begej– and Danube–Black sea routes) and to Southern Europe (via the Sava river).
The eastern border of the country is determined by the Carpathian Mountain range, which runs through the whole of Central Europe. The Carpathians meet the Balkan Mountains, following the course of Velika Morava, a 500 km long (partially navigable) river. Midzor peak is the highest point in Eastern Serbia at 2156 m. In the southeast, the Balkan Mountains meet the Rhodope Mountains, connecting the country with Greece. The Sar Mountains of Kosovo form the border with Albania, with one of the highest peaks in the region, Djeravica (2656 m). Dinaric Alps of Serbia follow the flow of the Drina river (at 350 km navigable for smaller vessels only) overlooking the Dinaric peaks on the other side of the shore in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Climate
The Serbian climate varies between a continental climate in the north, with cold winters, and hot, humid summers with well distributed rainfall patterns, and a more Adriatic climate in the south with hot, dry summers and autumns and relatively cold winters with heavy inland snowfall. Differences in elevation, proximity to the Adriatic sea and large river basins, as well as the exposure to the winds account for climate differences.[5] Vojvodina possesses typical continental climate, with airmasses from Northern and Western Europe which shape its climatic profile. South and Southwest Serbia is subject to Mediterranean influences, however the Dinaric Alps and other mountain ranges contribute cooling down the biggest part of warm air masses. Winters are quite harsh in Sandžak due to the mountains which encircle that plateau.[6]
Average annual air temperature for the period 1961–90 for the area with the altitude of up to 300 m amounts to 10.9 °C. The areas with the altitudes of 300 to 500 m have average annual temperature of around 10.0 °C, and over 1000 m of altitude around 6.0 °C.[7]
Cities

Major cities (over 100,000 inhabitants) — 2002 census data.
| Largest Serbian cities and municipalities | |||
| City | Population | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | Municipality | ||
| Belgrade | 1,273,651 | 1,576,124 | |
| Novi Sad | 215,659 | 299,294 | |
| Niš | 194,790 | 250,518 | |
| Kragujevac | 145,980 | 211,580 | |
| Leskovac | 78,030 | 156,252 | |
| Subotica | 99,471 | 147,758 | |
| Zrenjanin | 79,545 | 131,509 | |
| Kruševac | 75,256 | 131,368 | |
| Pančevo | 77,087 | 127,162 | |
| Kraljevo | 57,411 | 121,707 | |
| Čačak | 73,217 | 117,012 | |
| Smederevo | 77,808 | 109,867 | |
| Sombor | 51,471 | 97,263 | |
| Valjevo | 61,035 | 96,761 | |
- The following cities in Kosovo and Metohija, according to World Gazetteer estimates, surpass the 100,000 mark: Priština, Prizren, Djakovica, Peć and Kosovska Mitrovica.
National parks
Serbia has five national parks:
- Fruška Gora (250 km²)
- Kopaonik (120 km²)
- Tara (220 km²)
- Đerdap (Iron Gate) (640 km²)
- Šar-planina (390 km²)
History
Upon arrival to Balkans in the 5th and 6th century, Serbs formed their first unified state under the Vlastimirovic dynasty by 812. The state would achieve full independence, evolving into the Serbian Kingdom and the Serbian Empire under the rule of the prominent House of Nemanjic.
Serbia reached an apogee in economy, law, military, and religion during the rule of the House of Nemanjic, especially during Emperor Dusan. As a result of internal struggle between the rival noble families, it succumbed fully to the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century. The first Serbia was formed in 1217, and modern Serbia reemerged in the 19th century, when it became an independent principality and then a kingdom. In the 20th century, Serbia was a backbone of various South Slavic states, including the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes from 1918 to 1941 (renamed the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in 1929), the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia from 1945 to 1992, the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia from 1992 to 2003, and the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro from 2003 to 2006.[8][9][10] After Montenegro voted for independence from the State Union, Serbia officially proclaimed its independence on June 7, 2006, as the successor state to the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro.
Early history
Serbs settled the region by 630 C.E., having been invited by the Byzantine emperor Heraclius. They were fully converted to Christianity by 865 C.E.[11][12] The roots of the Serbian state date back to the 7th century and the House of Vlastimirović. A Serbian kingdom (centered around Duklja) was established in the 11th century. It lasted until the end of the 12th century.
Medieval
Serbs formed four distinct independent kingdoms by the 14th century — Dioclea, Rascia, Syrmia and Bosnia.[13][14][15][16] Of those, the most viable was Raška, formed in the 12th century by the Serbian Grand Župan Stefan Nemanja. In 1220, under Stefan the First Crowned, Serbia became a kingdom, and rose from Byzantine, Bulgarian and Hungarian patronage.[17] In 1346, Stefan Dušan established the Serbian Empire.
Under Dušan's rule, Serbia reached its territorial peak, becoming one of the larger states in Europe. In 1349 and 1354, Dušan also made and enforced Dušan's Code, a universal system of laws. By nature a soldier and a conqueror, Dušan did not make any systematic effort to stabilize or administer his gains, and the Empire began to dissolve soon after his death.

The Empire had disintegrated by the historic Battle of Kosovo in 1389. The northern Serbian territories (the Serbian Despotate) were conquered in 1459 following the siege of the "temporary" capital Smederevo. Bosnia fell a few years after Smederevo, and Herzegovina in 1482. Belgrade was the last major Balkan city to endure Ottoman onslaughts, as it joined Catholic Kingdom of Hungary, following heavy Turkish defeat in Siege of Belgrade of 1456. It held out for another 70 years, succumbing to the Ottomans in 1521, alongside the greater part of the Kingdom of Hungary that was soon conquered. Another shortlasting incarnation of the Serbian state was the one of Emperor Jovan Nenad in the 16th-century Vojvodina, however it also collapsed and its territory was conquered by the Ottoman Empire, before finally passing to the Habsburg Empire, under which it would remain for about two centuries.
Ottoman/Austrian rule
Following the collapse of Serbian Empire before historic Battle of Kosovo, most of Serbia was under Ottoman occupation between 1459 and 1804, despite three Austrian invasions and numerous rebellions (such as the Banat Uprising). Islam was in a period of expansion during this time, especially in Raška, Kosovo and Bosnia. The Ottoman period was a defining one in the history of the country; Slavic, Byzantine, Arabic and Turkish cultures suffused. Many contemporary cultural traits can be traced back to Ottoman period. However the majority of the Serbs managed to keep their culture and religion through the long period of Ottoman rule. The northern third of the modern country, Vojvodina, endured a century long Ottoman occupation before passing to Habsburg Empire in the end of the 17th century and beginning of the 18th century, only to proclaim secession from Austria-Hungary in 1918.
Principality of Serbia/Crownland of Vojvodina
The First Serbian Uprising of 1804–13, led by Đorđe Petrović (also known as Karađorđe or "Black George"), and the Second Serbian Uprising of 1815 resulted in autonomy and self-governance of the new Principality of Serbia (previously Pashaluk of Belgrade) from the Porte. As it was semi-independent from the Ottoman Empire, it is considered to be the precursor of the formation of modern Serbia. After the Ottomans were definitely expelled in 1867, Serbia de facto secured its sovereignty, which was formally recognised internationally at the Congress of Berlin in 1878.[18]
From 1815 to 1903, the Serbian state was ruled by the House of Obrenović, except from 1842 to 1858, when Serbia was ruled by Prince Aleksandar Karađorđević. In 1903, the House of Obrenović was replaced by the House of Karađorđević, who were descendants of Đorđe Petrović.
In 1848, Serbs in the northern part of present-day Serbia, which was ruled by the Austrian Empire, established an autonomous region known as the Serbian Vojvodina. As of 1849, the region was transformed into a new Austrian crownland known as the Vojvodina of Serbia and Tamiš Banat. Although the crownland was abolished in 1860, the Serbs from the Vojvodina region gained another opportunity to achieve their political demands in 1918.
Independent Kingdom
The struggle for liberty, modern society and a nation-state in Serbia lasted almost three decades and was completed with the adoption of the constitution on 15 February 1835. In 1876, Montenegro, Serbia, and Bosnia declared war against the Ottoman Empire and proclaimed their unification. However, the 1878 Treaty of Berlin, which was signed at the Congress of Berlin by the Great Powers, granted complete independence only to Serbia and Montenegro, leaving Bosnia and Sanjak of Novi Pazar to Austria-Hungary, who blocked their unification until the Balkan Wars of 1912 and 1913 and World War I.
On 28 June 1914 the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria at Sarajevo in Austria-Hungary by Gavrilo Princip, a South Slav unionist, Austrian citizen and member of Young Bosnia, led to Austria-Hungary declaring war on Serbia. The Russian Empire started to mobilize its troops in defence of its ally Serbia, which resulted in the German Empire declaring war on Russia in support of its ally Austria-Hungary. However, as German military planners wished to avoid a war on two fronts against both Russia and France, they attacked France first. This eventually culminated in all the major European Powers being drawn into the war. The Serbian Army won several major victories against Austria-Hungary at the beginning of World War I, but it was overpowered by the joint forces of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary and Bulgaria in 1915. Most of its army and some people went to exile to Greece and Corfu where it healed, regrouped and returned to Macedonian front (World War I) to lead a final breakthrough through enemy lines on 15 September 1918, freeing Serbia again and ending the World War I on 11 November.[19] In World War I, Serbia had 1,264,000 casualties — 28% of its total population, and 58% of its male population.[3] Template:History of Serbia
The Yugoslav era
After 1918, Serbia, along with Montenegro, was a founding member of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, later known as the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. During World War II, Serbia was a German-occupied puppet state that included present-day Central Serbia and Banat, popularly called Nedić's Serbia. However, parts of the present-day territory of Serbia were occupied by Croatian, Hungarian, Bulgarian, Albanian, and Italian armies. The occupying powers committed numerous crimes against the civilian population, especially against Serbs and Jews.[citation needed]
In 1945, Serbia was established as one of the federal units of the second Yugoslavia, the Socialist Federative Republic of Yugoslavia, led by Josip Broz Tito until his death in 1980. In 1989, the League of Communists of Serbia selected Slobodan Milošević to become the republic's President. Milošević was controversial in Yugoslavia because he opposed Kosovo's autonomy and that his rise to power through the Anti-bureaucratic revolution was done through mass protests which pushed out the leadership of the autonomous provinces and also the republic of Montenegro. He also aggravated the situation in post-Tito Yugoslavia by alleging that certain politicians in Yugoslavia were anti-Serb. Milošević's nationalist stand on Kosovo and desire to strengthen Serbia's position in Yugoslavia. The republics of Yugoslavia including Serbia all adopted multi-party systems in 1990. Milosevic and the Communist establishment were elected under the Socialist Party of Serbia. In the other republics, except for Montenegro, secessionist governments were elected.
By 1992, Slovenia, Croatia, Macedonia, and Bosnia & Herzegovina had all declared independence from Yugoslavia, resulting in the collapse of the Socialist Federal Republic and the outbreak of war. Serbia, together with Montenegro, formed the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in 1992. Serbian government supported Croatian and Bosnian Serbs in the Yugoslav wars from 1991 to 1995. As a result, sanctions were imposed by the UN, which led to political isolation and economic decline.[4]
Serbia's official peace was broken between 1998 and 1999, when the situation in Kosovo worsened with continued clashes in Kosovo between the Serbian and Yugoslav security forces and the ethnic Albanian Kosovo Liberation Army (KLA). The Serbian actions in Kosovo prompted a NATO aerial bombardment which lasted for 78 days. The attacks were ended following a negotiation on the Macedonian-FR Yugoslav border between Nato spokesperson Mike Jackson and officials on behalf of Milošević, in which Milošević would withdraw all security forces, including the military and the police, and have them replaced by a body of international police. The agreement upheld Yugoslav (later Serbian) sovereignty over Kosovo but replaced Serbian government of the province with a UN administration (See: Kosovo War and UNMIK). NATO also surrendered its bid to station NATO troops across the whole Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, which had been one of its demands at the Rambouillet negotiations prior to the bombing campaign.[5]
In September 2000, opposition parties claimed that Milošević committed fraud in routine federal elections. Street protests and rallies throughout Serbia eventually forced Milošević to concede and hand over power to the recently formed Democratic Opposition of Serbia (DOS), a broad coalition of anti-Milošević parties. The fall of Milošević led to end of the international isolation Serbia suffered during the Milošević years. Serbia's new leaders announced that Serbia would seek to join the European Union and NATO. In October 2005, the EU opened negotiations with Serbia for a Stabilization and Association Agreement (SAA), a preliminary step towards joining the EU.Negotiations were continued after short break.
Serbia and Montenegro
From 2003 to 2006, Serbia was part of the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro, into which the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia had been transformed. On 21 May 2006 Montenegro held a referendum to determine whether or not to end the union with Serbia. The next day, state-certified results showed 55.5% of voters in favor of independence, which was just above the 55% required by the referendum.[6]
Republic of Serbia
On 5 June 2006 National Assembly of Serbia declared Serbia the legal successor to the State Union, following the decision of the people of Montenegro expressed at the independence referendum. [7]
Government and politics
On 4 February 2003 the parliament of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia agreed to a weaker form of cooperation between Serbia and Montenegro within a confederal state called Serbia and Montenegro. The Union ceased to exist following Montenegrin and Serbian declarations of independence in June 2006.
After the ousting of Slobodan Milošević on 5 October 2000, the country was governed by the Democratic Opposition of Serbia. Tensions gradually increased within the coalition until the Democratic Party of Serbia (DSS) left the government, leaving the Democratic Party (DS) in overall control. Nevertheless, in March 2004 the DSS gathered enough support to form the new Government of Serbia, together with G17 Plus and coalition SPO–NS, and the support of the Socialist Party of Serbia, who do not take part in the government, but in exchange for the support hold minor government and justice positions and influence policies. The Prime Minister of Serbia is Vojislav Koštunica, leader of the Democratic Party of Serbia.
The current President of Serbia is Boris Tadić, leader of the Democratic Party (DS). He was elected with 53% of the vote in the second round of the Serbian presidential election held on 27 June 2004, following several unsuccessful elections since 2002.
Serbia held a two-day referendum on October 28 and October 29, 2006, that ratified a new constitution to replace the Milošević-era constitution.
Serbia held Parliamentary elections on 21 January 2007. The Serbian Radical Party claimed victory, but no party has won an absolute majority.
On 8 May 2007, Tomislav Nikolić was elected Speaker of the Serbian Parliament, which sparked a great deal of speculation about Serbia's political future, particularly from the European Union, the United States and international media. [8] Following last-minute negotiations on the part of the DS and DSS political parties, an agreement was reached on the make-up of the country's new government on 11 May 2007 between DS, DSS and G17 Plus.[9] This led to Nikolić's resignation two days later on 13 May 2007. [10]
Administrative subdivisions
Serbia is divided into 29 districts plus the City of Belgrade. The districts and the city of Belgrade are further divided into municipalities. Serbia has two autonomous provinces: Kosovo and Metohija in the south (5 districts, 30 municipalities), which is presently under the administration of the United Nations Mission in Kosovo, and Vojvodina in the north (7 districts, 46 municipalities).
The part of Serbia that is neither in Kosovo nor in Vojvodina is called Central Serbia. Central Serbia is not an administrative division, unlike the two autonomous provinces, and it has no regional government of its own. In English this region is often called "Serbia proper" to denote "the part of the Republic of Serbia not including the provinces of Vojvodina and Kosovo", as the Library of Congress puts it.[20] This usage was also employed in Serbo-Croatian during the Yugoslav era (in the form of "uža Srbija", literally: "narrow Serbia"). Its use in English is purely geographical, without any particular political meaning being implied.
Negotiations are currently underway to determine the final status of Kosovo. The Contact Group has postponed the completing of the status process until after Serbian parliamentary elections in January 2007.
Demographics
- Population statistics of Serbia (Estimate May 2005)
- Serbia (total): 9,396,411
- Vojvodina: 2,116,725
- Central Serbia: 5,479,686
- Kosovo: 1,800,000
| Serbia (excluding Kosovo) in 2002 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serbs | 82.86% | |||
| Hungarians | 3.91% | |||
| Bosniaks | 1.82% | |||
| Roma | 1.44% | |||
| Yugoslavs | 1.08% | |||
| other | 9.79% | |||
Serbia is populated mostly by Serbs. Significant minorities include Albanians (who are a majority in the province of Kosovo), Hungarians, Bosniaks, Roma, Croats, Slovaks, Montenegrins, Macedonians, Bulgarians, Romanians, etc. The two provinces, Vojvodina and Kosovo, are ethnically and religiously diverse.
According to the last official census[21] data collected in 2002, ethnic composition of Serbia is:
- Total: 7,498,001
- Serbs: 6,212,844 (82.86%)
- Hungarians: 293,172 (3.91%)
- Bosniaks: 136,464 (1.82%)
- Roma: 107,971 (1.44%)
- Yugoslavs: 80,978 (1.08%)
- Others (each less than 1%): 666,572 (8.89%)
The census was not conducted in Serbia's southern province of Kosovo, which is under administration by the United Nations. Its population is estimated to 2,100,000 inhabitants, of whom 92% are Albanians, 5.3% Serbs and others form 2.7% of its population.[citation needed]
Refugees and IDPs in Serbia form between 7% and 7.5% of its population. With over half a million refugees (from Croatia mainly, to an extent Bosnia and Herzegovina too and internally displaced personal from Kosovo), Serbia takes the first place in Europe with the largest refugee crisis, as a result of the Yugoslav wars.[citation needed]
Religion
| Serbia (excluding Kosovo) in 2002 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| religion | percent | |||
| Eastern Orthodoxy | 84.1% | |||
| Roman Catholicism | 6.24% | |||
| Islam | 4.82% | |||
| Protestantism | 1.44% | |||
According to the 2002 Census [11], 82% of the population of Serbia (excluding Kosovo) or 6,2 million people declared their nationality as Serbian, who are overwhelmingly adherents of the Serbian Orthodox Church. Other Orthodox Christian communities in Serbia include Montenegrins, Romanians, Macedonians, Bulgarians, Vlachs etc. Together they comprise about 84% of the entire population.
Catholicism is mostly present in Vojvodina (mainly in its northern part), where almost 20% of the regional population (belonging to different ethnic groups such as the Hungarians, Slovaks, Croats, Bunjevci, Czechs, etc) belong to this Christian denomination. There are an estimated 433,000 baptised Catholics in Serbia, roughly 6,2% of the population, mostly bounded to the northern province and Belgrade area.
Protestantism accounts for about 1,5 % of the country's population.
Islam has a strong historic populous in the southern regions of Serbia - Raska region, several municipalities in the south-east, and especially in the southern province of Kosovo. Bosniaks are the largest Muslim community in Serbia (excluding Kosovo) at about 140,000 (2%), followed by Albanians (1%), Turks, Arabs etc.
With the Exile of Jews from Spain during the infamous Inquisition era thousands of both individuals and families escaping that horror made their way through Europe to the Balkans. A goodly number settled in Serbia and became part of the general population. They were well accepted and during the ensuing generations the majority assimilated or became traditional or secular rather than remain orthodox Jews as had been the original immigrants. Later on the wars that ravaged the region resulted in a great part of the Serbian Jewish population either being killed or escaping to other regions for hopefully safer abodes in Yugoslavia and Austria-Hungary.
Economy
Serbia has an economy based mostly on various services, industry and agriculture. In the late 1980s, at the beginning of the process of economic transition, its position was favorable, but it was gravely impacted by UN economic sanctions 1992–95, the damage to infrastructure and industry during the NATO air strikes in 1999, as well as having problems from losing the markets of ex-Yugoslavia and Comecon. Main economic problems include high unemployment and an insufficient amount of economic reforms.
Serbia grows about one-third of the world's raspberries and is the leading frozen fruit exporter.[22]
After the ousting of former Federal Yugoslav President Milošević in October 2000, the country experienced faster economic growth (the amount of economic growth in 2006 was 6.3 percent[23]), and has been preparing for membership in the European Union, its most important trading partner. Serbia suffers from high export/import trade deficit and considerable national debt. The country expects some major economic impulses and high growth rates in the next years. Serbia has been occasionally called a "Balkan tiger" due to its recent high economic growth rates, a reference to the East Asian Tigers.
Serbia has been very successful in economic reforms since the 2000 revolution, especially in the past three years in which growth has averaged 6 – 7 percent, and foreign direct investment is at record levels. The nation is expected to reach its pre-1990 level of GDP within a short time frame.[citation needed]
Estimated GDP of Serbia for 2006 is $50.688 billion which is $6 771 per capita Purchasing Power Parity (PPP), $4 220 (nominal). GDP growth rate in 2006 is 5.8%.[24] Growth in 2005 was 6.3%[25] FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) in 2006 was $5.85 billion or €4.5 billion.
Culture
Serbia is one of Europe's most culturally diverse countries. The borders between large empires ran through the territory of today's Serbia for long periods in history: between the Eastern and Western halves of the Roman Empire; between Kingdom of Hungary, Bulgarian Empire and Byzantium; and between the Ottoman Empire and the Austrian Empire (later Austria-Hungary). As a result, while the north is culturally "Central European", the south is rather more "Oriental". Of course, both regions have influenced each other, and so the distinction between north and south is artificial to some extent.
The Byzantine Empire's influence on Serbia was perhaps the greatest. Serbs are Orthodox Christians with their own national church — the Serbian Orthodox Church. They use both the Cyrillic and Latin alphabets, as a result of both Eastern and Western influences. The monasteries of Serbia, built largely in the Middle Ages, are one of the most valuable and visible traces of medieval Serbia's association with the Byzantium and the Orthodox World, but also with the Romanic (Western) Europe that Serbia had close ties with back in Middle Ages. Most of Serbia's queens still remembered today in Serbian history were mostly of foreign origin: Helen d'Anjou (a cousin of Charles I of Sicily), Anna Dondolo (daughter of the Doge of Venice, Enrico Dandolo), Catherine of Hungary, Symonide of Byzantium.
Education
Education in Serbia is regulated by the Serbian Ministry of Education and Sports. Education starts in either pre-schools or elementary schools. Children enroll in elementary schools (Serbian: Osnovna škola / Основна школа) at age of 7 and it lasts for eight years.
Tourism
Tourism in Serbia is mostly based in mountains and villages. The most famous mountain resorts are Zlatibor, Kopaonik, and the Tara. There also are a lot of spas in Serbia, one the biggest of which is the Vrnjačka Banja. There is significant tourism in Belgrade, Novi Sad and Niš. There are also two very popular festival called the Exit Festival and the Guča trumpet festival. In 2006, there have been over 2 million tourists arrivals in Serbia.
Music
Serbia won the 2007 Eurovision Song Contest in Helsinki and will host the 2008 Eurovision Song Contest. The winning song was "Molitva" ("Prayer" in English) sung by Marija Šerifović.
Serbian holidays
| Date | Name | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| January 7 | Orthodox Christmas | |
| January 13 / January 14 | Pravoslavna Nova Godina (Православна Нова Година) | Orthodox New Year |
| February 15 | Dan državnosti Srbije (Дан државности Србије) | Serbian National Day |
| April 6 | Orthodox Good Friday | Date for 2007 only |
| April 8 | Orthodox Easter | Date for 2007 only |
| April 9 | Orthodox Easter Monday | Date for 2007 only |
| May 1 / May 2 | Labour Day | |
| May 9 | Victory Day | |
| June 28 | Vidovdan | See linked page |
Infrastructure
Communications
89% of households in Serbia have static telephone lines, 49% have computers, 27% use the internet, 42% have cable TV and 90% of the population have cell phones.[12],[13],[14].