Mayotte
| Collectivité départementale de Mayotte | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| Anthem: La Marseillaise |
||||
| Capital (and largest city) | Mamoudzou | |||
| Official languages | French | |||
| Government | overseas collectivity of France | |||
| - | President of France | Nicolas Sarkozy | ||
| - | President of the General Council | Saïd Omar Oili | ||
| Independence | overseas collectivity of France | |||
| - | Voted to remain a territory of France | 1974 | ||
| Area | ||||
| - | Total | 374 km² (~185th) 144 sq mi |
||
| - | Water (%) | 0.4 | ||
| Population | ||||
| - | July 2006 estimate | 201,234 (187th) | ||
| - | July 2002 census | 160,265 | ||
| GDP (PPP) | 2003 estimate | |||
| - | Total | $466.8 million (208th) | ||
| - | Per capita | $2,600 (2003 est.) (129th) | ||
| Currency | Euro (EUR) |
|||
| Time zone | (UTC+3) | |||
| Internet TLD | .yt | |||
| Calling code | +262 | |||
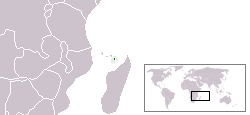
Mayotte (pronounced /majɔt/ in French), officially the Departmental Collectivity of Mayotte (French: Collectivité départementale de Mayotte), is an overseas collectivity of France consisting of a main island, Grande-Terre (or Mahoré), a smaller island, Petite-Terre (or Pamanzi), and several islets around these two.
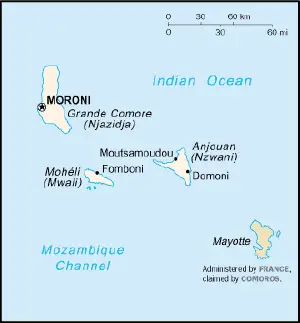
Mayotte is located at the northern end of the Mozambique Channel in the Indian Ocean, between northern Madagascar and northern Mozambique. The territory is geographically part of the Comoro islands, but has been politically separate since the 1970s. The territory is also known as Mahoré, the native name of its main island, especially by advocates of its inclusion in the Union of Comoros.
 Wikimedia Atlas of Mayotte, holding maps related to Mayotte.
Wikimedia Atlas of Mayotte, holding maps related to Mayotte.
Geography
The main island, Grande-Terre (or Mahoré), geologically the oldest of the Comoros, is 39 kilometres (24 mi) long and 22 kilometres (13½ mi) wide, and its highest point is Mount Benara (French: Mont Bénara; Shimaore: Mlima Bénara) at 660 meters (2,165 ft) above sea level. Because of the volcanic rock, the soil is relatively rich in some areas. A coral reef encircling much of the island ensures protection for ships and a habitat for fish.
Dzaoudzi was the capital of Comoros until 1977. It is situated on Petite-Terre (or Pamanzi), which at 10 square kilometers (3.9 sq mi) is the largest of several islets adjacent to Mahoré. Mayotte is a member of the Indian Ocean Commission, with a separate membership rather than as part of the Comoros.
History
- For the history of Mayotte before 1974 see also History of the Comoros.
In 1500 the Maore or Mawuti (contraction of the Arabic جزيرة الموت and corrupted to Mayotte in French) sultanate was established on the island.
In 1503, Mayotte was observed by Portuguese explorers, but not colonized.
In 1832, it was conquered by Andriantsoly, former king of Iboina on Madagascar; in 1833 conquered by the neighbouring sultanate of Mwali (Mohéli island in French); on 19 November 1835 again conquered by Ndzuwani sultanate (Anjouan sultanate in French; a governor was installed with the unusual islamic style of Qadi (from the Arabic قاض which means judge), sort of a 'Resident Magistrate' in British terms), but in 1836 regained its independence under a last local Sultan.
Mayotte was ceded to France along with the other Comoros in 1843. It was the only island in the archipelago that voted in referendums in 1974 and 1976 to retain its link with France and forgo independence (with 63.8% and 99.4% of votes respectively). The Comoros continue to claim the island, and a draft 1976 United Nations Security Council resolution supported by 11 of the 15 members of the Council would have recognized Comoros sovereignty over Mayotte, but France vetoed the resolution (the last time, as of 2004, France cast a lone veto in the Council). The United Nations General Assembly has adopted a series of resolutions on the issues, whose tenor can be gauged from their title: "Question of the Comorian Island of Mayotte" up to 1995. Since 1995, the subject of Mayotte has no more been evocated by the General Assembly.
The situation of Mayotte proved to be unwieldy for France: while the local population very largely did not want to be independent from France and join the Comoros, some international criticism from post-colonial leftist regimes was heard about Mayotte's ongoing ties to France. Furthermore, the peculiar local administration of Mayotte, largely ruled by customary Muslim law, would be difficult to integrate into the legal structures of France, not to mention the costs of bringing the standards of living to levels close to those of metropolitan France. For these reasons, the laws passed by the national parliament must state specifically that they apply to Mayotte for them to be applicable on Mayotte.
The status of Mayotte was changed in 2001 towards one very close to the status of the departments of mainland France, with the particular designation of departmental community, although the island is still claimed by the Comoros. This change was approved by 73% at a referendum on Mayotte. After the constitutional reform of 2003 it became an overseas community while retaining the title departmental community of Mayotte.
Politics
Template:Politics of Mayotte
Politics of Mayotte takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic French overseas community, whereby the President of the General Council is the head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government.
Mayotte also sends one deputy to the French National Assembly and two senators to the French Senate.
Administrative divisions
Mayotte is divided into 17 communes. There also exist 19 cantons (not shown here) which match exactly the communes except in the case of the commune of Mamoudzou which is divided into three cantons. There are no arrondissements.
|
Transport
- No railways or waterways.
- Highways:
- total: 93 kilometres (58 mi)
- paved : 72 kilometres (45 mi)
- unpaved : 21 kilometres (13 mi)
- total: 93 kilometres (58 mi)
- Ports and harbours:
- Dzaoudzi
- "Longoni" (Koungou)
- Airports:
- with paved runways: 1 (2002)
Demographics
At the 2002 census there were 160,301 people living in Mayotte. 64.7% of these were born in Mayotte, 3.9% were born in the rest of the French Republic (either metropolitan France or overseas France except Mayotte), 28.1% were immigrants from the Comoros, 2.8% were immigrants from Madagascar, and the remaining 0.5% came from other countries.[1]
Historical population
| 1958 | 1966 | 1978 | 1985 | 1991 | 1997 | 2002 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23,364 | 32,607 | 47,246 | 67,205 | 94,410 | 131,320 | 160,265 | ||||||
| Official figures from past censuses. | ||||||||||||
Languages
The native languages of Mayotte are:
- Shimaore, a dialect of the Comorian language (a close relative of Swahili)
- Kibushi, a western dialect of the Malagasy language (the language of Madagascar) heavily influenced by Shimaore and Arabic
- Kiantalaotsi, another western dialect of the Malagasy language also heavily influenced by Shimaore and Arabic
- Arabic, essentially learnt in the Koranic schools
Kibushi is spoken in the south and north-west of Mayotte, while Shimaore is spoken elsewhere.
Other non-native languages are also present in Mayotte:
- French, the language imported by the French colonizers
- various dialects of the Comorian language essentially imported by immigrants who have arrived in Mayotte since 1974: Shindzwani (the dialect of Anjouan), Shingazidza (the dialect of Grande Comore), and Shimwali (the dialect of Mohéli).
Shingazidza and Shimwali on the one hand and Shimaore on the other hand are hardly mutually intelligible. Shindzwani and Shimaore are perfectly mutually intelligible.
A survey was conducted by the French Ministry of National Education in 2006 among pupils registered in CM2 (equivalent to fifth grade in the US and Year 6 in England and Wales). Questions were asked regarding the languages spoken by the pupils as well as the languages spoken by their parents. According to the survey, the ranking of mother tongues is the following (ranked by number of first language speakers in the total population; note that percentages add up to more than 100% because some people are natively bilingual):[2]
- Shimaore: 55.1%
- Shindzwani: 22.3%
- Kibushi: 13.6%
- Shingazidza: 7.9%
- French: 1.4%
- Shimwali: 0.8%
- Arabic: 0.4%
- Kiantalaotsi: 0.2%
- Other: 0.4%
However, when also counting second language speakers (e.g. someone whose mother tongue is Shimaore but who also speaks French as a second language) then the ranking becomes:
- Shimaore: 88.3%
- French: 56.9%
- Shindzwani: 35.2%
- Kibushi: 28.8%
- Shingazidza: 13.9%
- Arabic: 10.8%
- Shimwali: 2.6%
- Kiantalaotsi: 0.9%
- Other: 1.2%
French is the only official language of Mayotte. It is the language used by the administrations and the school system. It is the language most used by televisions and radios as well as in commercial announcements and billboards. In spite of this, Mayotte is one of the French overseas territories where the knowledge of French is the least developed, as showed by the figures above. At the 2002 census, only 55% of people older than 15 y/o declared they could read and write French, although this figure is higher than those who can read and write Shimaore (41%) or Arabic (33%).
With the mandatory schooling of children and the economic development both implemented by the French central state, the French language has progressed significantly on Mayotte in recent years. The survey conducted by the Ministry of National Education showed that while first and second language speakers of French represented 56.9% of the population in general, this figure was only 37.7% for the parents of CM2 pupils, but reached 97.0% for the CM2 pupils themselves (whose age is between 10 and 14 in general).
Already there are instances of families speaking only French to their children in the hope of helping their social advancement. With French schooling and French language television, many young people turn to French or use many French words when speaking Shimaore and Kibushi, leading some to fear that these native languages of Mayotte could either disappear or become some sort of French-based creole.[3]
See also
- Geography of Mayotte
- Demographics of Mayotte
- Politics of Mayotte
- Economy of Mayotte
- Communications in Mayotte
- French overseas departments and territories
- Administrative divisions of France
- Islands controlled by France in the Indian and Pacific oceans
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- ↑ (French) INSEE, Government of France. MIG 1 DET - POPULATION SELON LE LIEU DE NAISSANCE (XLS). Retrieved 2007-05-17.
- ↑ (French) Daniel Barreteau. Premiers résultats d'une enquête sociolinguistique auprès des élèves de CM2 de Mayotte (PDF). Retrieved 2007-05-17.
- ↑ (French) Mayotte Hebdo (June 18, 2004). Le shimaoré fout le camp!. Retrieved 2007-05-17.
External links
- CIA World Factbook - Mayotte
- {{{2}}} at the Open Directory Project
- WorldStatesmen- Mayotte
- Travel guide to Mayotte from Wikitravel
- (French) Analysis of the linguistic situation on Mayotte
- "Voyages...Visages" - Another way of travelling and seeing
- Comité du tourisme de Mayotte Official tourism website (French)
| Overseas departments and territories of France | |
|---|---|
| Overseas departments1 | French Guiana · Guadeloupe · Martinique · Réunion |
| Overseas collectivities | French Polynesia · Mayotte2 · Saint Barthelemy · Saint Martin · Saint Pierre and Miquelon · Wallis and Futuna |
| Special status | New Caledonia |
| Uninhabited lands | Clipperton Island French Southern and Antarctic Lands (Amsterdam Island • Saint-Paul Island • Crozet Islands • Kerguelen Islands • Adélie Land |
Sovereign states
Algeria ·
Angola ·
Benin ·
Botswana ·
Burkina Faso ·
Burundi ·
Cameroon ·
Cape Verde ·
Central African Republic ·
Chad ·
Democratic Republic of the Congo ·
Republic of the Congo ·
Comoros ·
Côte d'Ivoire ·
Djibouti ·
Egypt1 ·
Equatorial Guinea ·
Eritrea ·
Ethiopia ·
Gabon ·
The Gambia ·
Ghana ·
Guinea-Bissau ·
Guinea ·
Kenya ·
Lesotho ·
Liberia ·
Libya ·
Madagascar ·
Malawi ·
Mali ·
Mauritania ·
Mauritius ·
Morocco ·
Mozambique ·
Namibia ·
Niger ·
Nigeria ·
Rwanda ·
Senegal ·
Seychelles ·
Sierra Leone ·
Somalia ·
South Africa ·
Spain2 ·
Sudan ·
Swaziland ·
São Tomé and Príncipe ·
Tanzania ·
Togo ·
Tunisia ·
Uganda ·
Zambia ·
Zimbabwe
Dependencies | Unrecognized
British Indian Ocean Territory (UK) ·
French Southern and Antarctic Lands (France) ·
Mayotte (France) ·
Réunion (France) ·
St. Helena3 (UK)
|
Puntland ·
Somaliland ·
Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
1 Partly in Asia. 2 Mostly in Europe. 3 Includes the dependencies of Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha.
| Outlying territories of European countries | |
|---|---|
| Denmark | Greenland |
| France | Clipperton Island · French Guiana · French Polynesia · French Southern and Antarctic Lands (Amsterdam • Saint-Paul • Crozet • Kerguelen • Adélie Land1 • Scattered islands in the Indian Ocean: Bassas da India • Europa Island • Glorioso Islands • Juan de Nova Island • Tromelin Island) · Guadeloupe · Martinique · Mayotte · New Caledonia · Réunion · Saint-Barthélemy · Saint Martin · Saint Pierre and Miquelon · Wallis and Futuna |
| Italy | Pantelleria · Pelagie Islands (Lampedusa • Lampione • Linosa) |
| Netherlands | Aruba · Netherlands Antilles (Bonaire • Curaçao • Saba • Sint Maarten • Sint Eustatius) |
| Norway | Bouvet Island · Peter I Island1 · Queen Maud Land1 |
| Portugal | Azores · Madeira |
| Russia | Khabomai · Ratmanov Island · Shikotan |
| Spain | Canary Islands · Plazas de soberanía (Ceuta • Melilla) |
| United Kingdom | Anguilla · Ascension Island · Bermuda · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Falkland Islands · Montserrat · Saint Helena · Tristan da Cunha · Turks and Caicos Islands · British Antarctic Territory1 · British Indian Ocean Territory · Pitcairn Islands · South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands |
Template:Indian Ocean
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.