Difference between revisions of "Luxembourg" - New World Encyclopedia
Mike Butler (talk | contribs) |
Mike Butler (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
The border between Luxembourg and Germany is formed by three [[river]]s: the [[Moselle River|Moselle]], the [[Sauer]], and the [[Our River|Our]]. Other major rivers are the [[Alzette]], the [[Attert River|Attert]], the [[Clerve]], and the [[Wiltz River|Wiltz]]. The [[valley]]s of the mid-Sauer and Attert form the border between the [[Gutland]] and the [[Oesling]]. | The border between Luxembourg and Germany is formed by three [[river]]s: the [[Moselle River|Moselle]], the [[Sauer]], and the [[Our River|Our]]. Other major rivers are the [[Alzette]], the [[Attert River|Attert]], the [[Clerve]], and the [[Wiltz River|Wiltz]]. The [[valley]]s of the mid-Sauer and Attert form the border between the [[Gutland]] and the [[Oesling]]. | ||
| − | + | The Upper Sûre lake is the largest stretch of water in the Grandy Duchy. Surrounded by luxuriant vegetation and peaceful creeks, the lake is a centre for water sports, such as sailing, canoeing, and kayaking. Such outdoor activities, which has made it an attractive spot for tourists, have led to the growth of a local crafts industry. | |
| + | |||
| + | The town of [[Esch-sur-Sûre]] nestles at one end of the lake. Immediately above it, the river has been dammed to form a hydroelectric reservoir extending some six miles (10km) up the valley. The Upper Sûre dam was built in the 1960s to meet the country's drinking water requirements. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Luxembourg is part of the [[West European Continental]] climatic region, and enjoys a temperate climate without extremes. Winters are mild, summers fairly cool, and rainfall is high. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Rainfall reaches 49 inches (1.2 meters) a year in some areas. In the summer, excessive heat is rare and temperatures drop noticeably at night. Low temperatures and humidity make for what those living in this part of the country call, optimistically, an "invigorating climate". | ||
Trees include pine, chestnut, spruce, oak, linden, elm, and beech, as well as fruit trees. Shrubs include blueberry and genista, and ferns. There are numerous vineyards. The few wild animal species remaining include deer, roe deer, and wild boar, while birds are plentiful, and the rivers have perch, carp, bream, trout, pike, and eel. | Trees include pine, chestnut, spruce, oak, linden, elm, and beech, as well as fruit trees. Shrubs include blueberry and genista, and ferns. There are numerous vineyards. The few wild animal species remaining include deer, roe deer, and wild boar, while birds are plentiful, and the rivers have perch, carp, bream, trout, pike, and eel. | ||
Revision as of 00:49, 21 November 2007
| Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg Grand-Duché de Luxembourg Großherzogtum Luxemburg Grand Duchy of Luxembourg |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: "Mir wëlle bleiwe wat mir sinn" (Luxembourgish) "We wish to remain what we are" |
||||||
| Anthem: Ons Hémécht "Our Homeland" Royal anthem: De Wilhelmus 1 |
||||||
| Capital (and largest city) | Luxembourg 49°36′N 6°7′E | |||||
| Official languages | French, German, Luxembourgish (de jure since 1984) |
|||||
| Demonym | Luxembourger(s) | |||||
| Government | Constitutional grand duchy | |||||
| - | Grand Duke | Grand Duke Henri (List) | ||||
| - | Prime minister | Jean-Claude Juncker (List) | ||||
| History | ||||||
| - | Independence | 9 June 1815 | ||||
| - | 1st Treaty of London | 19 April 1839 | ||||
| - | 2nd Treaty of London | 11 May 1867 | ||||
| - | End of personal union | 23 November 1890 | ||||
| EU accession | March 25 1957 | |||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 2,586.4 km² (176th) 999 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | negligible | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2007 estimate | 480,222 (171st) | ||||
| - | 2001 census | 439,539 | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2006 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $32.6 billion (97th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $68,800 (2006) (1st) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2006 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $40.577 billion (65th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $87,995 (1st) | ||||
| Currency | Euro (€)2 (EUR) |
|||||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .lu3 | |||||
| Calling code | +352 | |||||
| 1 | Not the same as the Het Wilhelmus of the Netherlands. | |||||
| 2 | Prior to 1999: Luxembourgian franc. | |||||
| 3 | The .eu domain is also used, as it is shared with other European Union member states. | |||||
The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg (Luxembourgish: Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg, French: Grand-Duché de Luxembourg, German: Großherzogtum Luxemburg), archaically spelled Luxemburg, is a small landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany.
The world's only sovereign Grand Duchy, Luxembourg is a parliamentary representative democracy with a constitutional monarchy, ruled by a Grand Duke.
Luxembourg lies on the cultural divide between Romance Europe and Germanic Europe, borrowing customs from each of the distinct traditions. Although a secular state, Luxembourg is predominantly Roman Catholic.
The country has a highly developed economy, with the highest Gross Domestic Product per capita in the world. For many people in other parts of Europe, Luxembourg is best known for its radio and television stations, Radio Luxembourg and RTL.
Geography
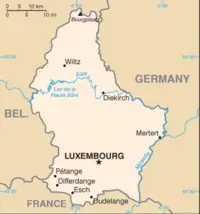
Luxembourg is one of the smallest countries in Europe, and ranked 175th in size of all the 194 independent countries of the world; the country is about 999 square miles (2586 square kilometers) in size, and measures 51 miles long (82km) and 35 miles (57km) wide. It is slightly smaller than Rhode Island in the United States.
To the east, Luxembourg borders the German states of Rhineland-Palatinate and Saarland, and, to the south, it borders the French région of Lorraine. The Grand Duchy borders the Belgian Walloon Region, in particular the latter's provinces of Luxembourg and Liège to the west and to the north respectively.
The northern third of the country is known as the ''Oesling'', and forms part of the Ardennes. It is dominated by hills and low mountains, including the Kneiff, which is the highest point, at 1837 feet (560 meters).
The southern two-thirds of the country is called the ''Gutland'', and is more densely populated than the Oesling. It is also more diverse, and can be divided into five geographic sub-regions. The Luxembourg plateau, in south-central Luxembourg, is a large, flat, sandstone formation, and the site of the city of Luxembourg. Little Switzerland, in the east of Luxembourg, has craggy terrain and thick forests. The Moselle valley is the lowest-lying region, running along the south-eastern border. The Red Lands, in the far south and southwest, are Luxembourg's industrial heartland and home to many of Luxembourg's largest towns.
The border between Luxembourg and Germany is formed by three rivers: the Moselle, the Sauer, and the Our. Other major rivers are the Alzette, the Attert, the Clerve, and the Wiltz. The valleys of the mid-Sauer and Attert form the border between the Gutland and the Oesling.
The Upper Sûre lake is the largest stretch of water in the Grandy Duchy. Surrounded by luxuriant vegetation and peaceful creeks, the lake is a centre for water sports, such as sailing, canoeing, and kayaking. Such outdoor activities, which has made it an attractive spot for tourists, have led to the growth of a local crafts industry.
The town of Esch-sur-Sûre nestles at one end of the lake. Immediately above it, the river has been dammed to form a hydroelectric reservoir extending some six miles (10km) up the valley. The Upper Sûre dam was built in the 1960s to meet the country's drinking water requirements.
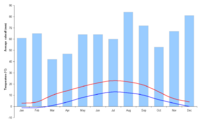
Luxembourg is part of the West European Continental climatic region, and enjoys a temperate climate without extremes. Winters are mild, summers fairly cool, and rainfall is high.
Rainfall reaches 49 inches (1.2 meters) a year in some areas. In the summer, excessive heat is rare and temperatures drop noticeably at night. Low temperatures and humidity make for what those living in this part of the country call, optimistically, an "invigorating climate".
Trees include pine, chestnut, spruce, oak, linden, elm, and beech, as well as fruit trees. Shrubs include blueberry and genista, and ferns. There are numerous vineyards. The few wild animal species remaining include deer, roe deer, and wild boar, while birds are plentiful, and the rivers have perch, carp, bream, trout, pike, and eel.
The city of Luxembourg, the capital and largest city, is the seat of several institutions and agencies of the European Union.
History
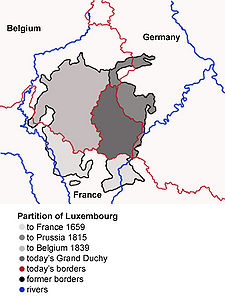
The recorded history of Luxembourg begins with the acquisition of Lucilinburhuc (today Luxembourg Castle) by Siegfried, Count of Ardennes in 963. The current name of Luxembourg comes from the former name Lucilinburhuc. Around this fort, a town gradually developed, which became the centre of a small, but important, state of great strategic value. In 1437, the House of Luxembourg suffered a succession crisis, precipitated by the lack of a male heir to assume the throne. In the following centuries, Luxembourg's fortress was steadily enlarged and strengthened by its successive occupants, the Bourbons, Habsburgs, Hohenzollerns, and the French, among others. After the defeat of Napoleon in 1815, Luxembourg was disputed between Prussia and the Netherlands. The Congress of Vienna formed Luxembourg as a Grand Duchy in personal union with the Netherlands. Luxembourg also became a member of the German Confederation, with a Confederate fortress manned by Prussian troops.
The Belgian Revolution of 1830–1839 reduced Luxembourg's territory by more than half, as the predominantly francophone western part of the country was transferred to Belgium. Luxembourg's independence was reaffirmed by the 1839 First Treaty of London. In the same year, Luxembourg joined the Zollverein. Luxembourg's independence and neutrality were again affirmed by the 1867 Second Treaty of London, after the Luxembourg Crisis nearly led to war between Prussia and France. After the latter conflict, the Confederate fortress was dismantled.
The King of the Netherlands remained Head of State as Grand Duke of Luxembourg, maintaining personal union between the two countries until 1890. At the death of William III, the Dutch throne passed to his daughter Wilhelmina, while Luxembourg (at that time restricted to male heirs; see Salic Law) passed to Adolph of Nassau-Weilburg.
Luxembourg was invaded and occupied by Germany during the First World War, but was allowed to maintain its independence and political mechanisms. It was again invaded and subject to German occupation in the Second World War in 1940, and was formally annexed into the Third Reich in 1942.
During World War II, Luxembourg abandoned its policy of neutrality, when it joined the Allies in fighting Germany. Its government, exiled to London, set up a small group of volunteers who participated in the Normandy invasion. It became a founding member of the United Nations in 1946, and of NATO in 1949. In 1957, Luxembourg became one of the six founding countries of the European Economic Community (later the European Union), and, in 1999, it joined the euro currency area. In 2005, a referendum on the EU treaty establishing a constitution for Europe was held in Luxembourg.[1]
Government and politics
Luxembourg has a parliamentary form of government with a constitutional monarchy inherited by male-preference primogeniture. Under the constitution of 1868, executive power is exercised by the Grand Duke or Grand Duchess and the cabinet, which consists of a Prime Minister and several other ministers. The Grand Duke has the power to dissolve the legislature and reinstate a new one. However, since 1919, sovereignty has resided with the country.[2]
Legislative power is vested in the Chamber of Deputies, a unicameral legislature of sixty members, who are directly elected to five-year terms from four constituencies. A second body, the Council of State (Conseil d'État), composed of twenty-one ordinary citizens appointed by the Grand Duke, advises the Chamber of Deputies in the drafting of legislation.[3]
The Grand Duchy has three lower tribunals (justices de paix; in Esch-sur-Alzette, the city of Luxembourg, and Diekirch), two district tribunals (Luxembourg and Diekirch) and a Superior Court of Justice (Luxembourg), which includes the Court of Appeal and the Court of Cassation. There is also an Administrative Tribunal and an Administrative Court, as well as a Constitutional Court, all of which are located in the capital.
Luxembourg is divided into three districts, which are further divided into twelve cantons and then 116 communes. Twelve of the communes have city status, of which the city of Luxembourg is the largest.
Luxembourg's contribution to its defence and to NATO consists of a small army. As a landlocked country, it has no navy, and it has no air force, except for the fact that the eighteen NATO AWACS airplanes were registered as aircraft of Luxembourg for convenience.[4] In a joint agreement with Belgium, both countries have put forth funding for one A400M military cargo plane, now currently on order. Luxembourg still maintains three Boeing 707 model TCAs for cargo and training purposes based in NATO Air Base Geilenkirchen.[4]
Luxembourg is a founding member of the European Union, NATO, the United Nations, Benelux, and the Western European Union, reflecting the political consensus in favour of economic, political, and military integration.
Economy
Luxembourg's stable, high-income economy features moderate growth, low inflation, and low unemployment. The industrial sector, which was dominated until the 1960s by steel, has become increasingly more diversified to include chemicals, rubber, and other products. During the past decades, growth in the financial sector has more than compensated for the decline in steel. Services, especially banking and other financial exports, account for the majority of economic output. Agriculture is based on small, family-owned farms. Luxembourg has especially close trade and financial ties to Belgium and the Netherlands (see Benelux), and as a member of the EU it enjoys the advantages of the open European market. Luxembourg possesses the highest GDP per capita in the world (US$68,800 as of 2006),[5] the twelfth highest Human Development Index, and the fourth highest quality of life.[6] As of March 2006, unemployment is 4.8% of the labour force.[7] For the fiscal year of 2005 and 2006, Luxembourg has run a budget deficit for the first time in many years, mostly because of slower international economic growth.[8]
Demographics
Luxembourg has a population of under half a million people in an area of approximately 2,585 square kilometres (998 sq mi).
The people of Luxembourg are called Luxembourgers.[9] The native population is ethnically a French and Germanic blend. The indigenous population was augmented by immigrants from Belgium, France, Germany, Italy, and Portugal throughout the twentieth century. Since the beginning of the Yugoslav wars, Luxembourg has seen many immigrants from war-torn and politically unstable Balkan states, such as Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, and Serbia. Annually, over 10,000 new immigrants arrive in Luxembourg, mostly from EU states, as well as Eastern Europe. As of 2000, there were 162,000 immigrants in Luxembourg, accounting for 37% of the total population. There are an estimated 5,000 illegal immigrants in Luxembourg.[10]
Language
Luxembourg is a trilingual country; French, German, and Luxembourgish are official languages.
Three languages are recognised as official in Luxembourg: French, German, and Luxembourgish, a Franconian language of the Moselle region very similar to the local German dialect spoken in the neighbouring part of Germany, except that it includes more borrowings from French. Apart from being one of the three official languages, Luxembourgish is also considered the national language of the Grand Duchy; it is the mother tongue or "language of the hearth" for nearly all Luxembourgers.
Each of the three languages is used as the primary language in certain spheres. Luxembourgish is the language that Luxembourgers generally speak to each other, but it is not much written. Most official (written) business is carried out in French. German is usually the first language taught in school and is the language of much of the media and of the church.[11]
Luxembourg's education system is trilingual: the first years of primary school are in Luxembourgish, before changing to German, while secondary school, the language of instruction changes to French. [12] However, as proficiency in all three languages is required for graduation from secondary school, half the students leave school without a certified qualification, with the children of immigrants being particularly disadvantaged.[13]
In addition to the three official languages, English is taught in the compulsory schooling (mostly from the eighth grade, i.e. at the age of 13 to 14 years) and much of the population of Luxembourg can speak some simple English, at any rate in Luxembourg City. Portuguese and Italian, the languages of the two largest immigrant communities, are also spoken by large parts of the population, but by relatively few from outside their respective communities.
Religion
Since 1979, it has been illegal for the government to collect statistics on religious beliefs or practices.[14] It is estimated that 87% of Luxembourgers are Roman Catholics, and the other 13% are mostly Protestants, Orthodox Christians, Jews, and Muslims.[5] Luxembourg is a secular state, but the state recognises certain religions as officially-mandated religions. This gives the state a hand in religious administration and appointment of clergy, in exchange for which the state pays certain running costs and wages. Currently, religions covered by such arrangements are Roman Catholicism, Judaism, Greek and Russian Orthodoxy, and Protestantism.
Culture
Luxembourg has been overshadowed by the culture of its neighbours, although, having been for much of its history a profoundly rural country, it retains a number of folk traditions. There are several notable museums, mostly located in the capital; these include the National Museum of History and Art (MNHA), the History Museum of the City of Luxembourg, and the new Grand Duke Jean Museum of Modern Art (Mudam). The National Museum of Military History (MNHM) in Diekirch is especially known for its representations of the Battle of the Bulge. The city of Luxembourg itself is on the UNESCO World Heritage List, on account of the historical importance of its fortifications.
The country has produced some internationally known artists, including the painters Joseph Kutter and Michel Majerus, as well as the photographer Edward Steichen. Steichen's The Family of Man exhibition is now permanently housed in Clervaux, and it has been placed on UNESCO's Memory of the World register.
Luxembourg is the first European city to be named "Capital of Culture" for the second time. The first time was in 1995. In 2007, the European Capital of Culture will be a cross-border area consisting of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, the Rheinland-Pfalz and Saarland in Germany, the Walloon Region and the German-speaking part of Belgium, and the Lorraine area in France. The event will promote mobility and the exchange of ideas, crossing borders in all areas, physical, psychological, artistic and emotional.
See also
- Foreign relations of Luxembourg
- Radio Luxembourg
- Grand Ducal Family of Luxembourg
- Communications in Luxembourg
- Military of Luxembourg
- Transportation in Luxembourg
- Luxembourg Boy Scouts Association
Notes
- ↑ Timeline: Luxembourg - A chronology of key events BBC News Online, 9 September 2006. Retrieved 8 October 2006.
- ↑ Constitution of Luxembourg (PDF). Service central de législation (2005). Retrieved 2006-07-23.
- ↑ Structure of the Conseil d'Etat. Conseil d'Etat. Retrieved 2006-07-23.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Luxembourg. Aeroflight.co.uk (8 September 2005). Retrieved 2006-07-23.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 World Factbook - Luxembourg. Central Intelligence Agency (19 December 2006). Retrieved 2007-01-13.
- ↑ World Life Quality Index 2005 (PDF). Economist Intelligence Unit (2005). Retrieved 2006-07-23.
- ↑ Euro-zone unemployment down to 8.1%. Eurostat (3 May 2006). Retrieved 2006-07-23.
- ↑ Economic Survey of Luxembourg 2006. OECD (2006). Retrieved 2006-07-23.
- ↑ http://www.eu2005.lu/en/savoir_lux/societe_tradition/lux_type/index.php
- ↑ Amanda Levinson. The Regularisation of Unauthorised Migrants: Literature Survey and Country Case Studies - Regularisation programmes in Luxembourg (PDF). Centre on Migration, Policy and Society, University of Oxford. Retrieved 2006-09-02.
- ↑ (French) À propos des langues (PDF) pp. pp.3-4. Service Information et Presse. Retrieved 2006-08-01.
- ↑ The Trilingual Education system in Luxembourg. Tel2l - Teacher Education by Learning through two languages, University of Navarra. Retrieved 2007-06-09.
- ↑ Immigration in Luxembourg: New Challenges for an Old Country. Migration Information Source. Retrieved 2007-06-09.
- ↑ (French) Mémorial A, 1979, No. 29 (PDF). Service central de législation. Retrieved 2006-08-01.
External links
- Governments on the WWW: Luxembourg
- History of Luxembourg: Primary Documents
- Official Governmental Site
- Official Website for Luxembourg
- Luxembourg National Tourist Office
- Luxembourg Tourist Office - London
- Luxembourg Geography
- Luxembourg European Capital of Culture 2007
- World Factbook: Information on Luxembourg
Albania · Andorra · Armenia2 · Austria · Azerbaijan1 · Belarus · Belgium · Bosnia and Herzegovina · Bulgaria · Croatia · Cyprus2 · Czech Republic · Denmark3 · Estonia · Finland · France3 · Georgia1 · Germany · Greece · Hungary · Iceland · Ireland · Italy · Kazakhstan1 · Latvia · Liechtenstein · Lithuania · Luxembourg · Republic of Macedonia · Malta · Moldova · Monaco · Montenegro · Netherlands3 · Norway3 · Poland · Portugal · Romania · Russia1 · San Marino · Serbia · Slovakia · Slovenia · Spain3 · Sweden · Switzerland · Turkey1 · Ukraine · United Kingdom3 · Vatican City
1 Has majority of its territory in Asia. 2 Entirely in Asia but having socio-political connections with Europe. 3 Has dependencies or similar territories outside Europe.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.