Difference between revisions of "Istanbul" - New World Encyclopedia
m (→Climate) |
m (→Administration) |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
[[Image:Istambul and Bosporus big.jpg|thumb|200px|Satellite photo over Istanbul and the [[Bosporus]]]] | [[Image:Istambul and Bosporus big.jpg|thumb|200px|Satellite photo over Istanbul and the [[Bosporus]]]] | ||
The city has a [[temperate]]-[[continental climate]], with hot and humid summers; and cold, rainy and often snowy winters. Humidity is generally rather high. Yearly precipitation for Istanbul averages 870 mm. Snowfall is quite common, snowing for a week or two during the winter season, but it can be heavy once it snows. It is most likely to occur between the months of December and March. The summer months between June and September bring average daytime temperatures of 28 °C (82 °F). The warmest month is July with an average temperature of 23.2 °C (74 °F), the coldest is January with 5.4 °C (42 °F). The weather becomes slightly cooler as one moves toward eastern Istanbul. Summer is by far the driest season. The city is quite windy, having an average wind speed of 17 km/h (11 mph). | The city has a [[temperate]]-[[continental climate]], with hot and humid summers; and cold, rainy and often snowy winters. Humidity is generally rather high. Yearly precipitation for Istanbul averages 870 mm. Snowfall is quite common, snowing for a week or two during the winter season, but it can be heavy once it snows. It is most likely to occur between the months of December and March. The summer months between June and September bring average daytime temperatures of 28 °C (82 °F). The warmest month is July with an average temperature of 23.2 °C (74 °F), the coldest is January with 5.4 °C (42 °F). The weather becomes slightly cooler as one moves toward eastern Istanbul. Summer is by far the driest season. The city is quite windy, having an average wind speed of 17 km/h (11 mph). | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Geology=== | ===Geology=== | ||
[[Image:Istanbul Bogazici Ulus view 3690-3699.jpg|thumb|200px|Panoramic view of the [[Bosporus]] from the hills of the Ulus neighborhood]] | [[Image:Istanbul Bogazici Ulus view 3690-3699.jpg|thumb|200px|Panoramic view of the [[Bosporus]] from the hills of the Ulus neighborhood]] | ||
| − | Istanbul is situated near the [[North Anatolian fault]] line, which runs from northern [[Anatolia]] to the [[Marmara Sea]]. Two [[tectonic plate]]s, the African and the Eurasian, push against each other here. This fault line has been responsible for several deadly [[earthquake]]s in the region throughout history. In 1509, a catastrophic earthquake caused a tsunami which broke over the sea-walls of the city, destroying over 100 [[mosque]]s and killing 10,000 people. | + | Istanbul is situated near the [[North Anatolian fault]] line, which runs from northern [[Anatolia]] to the [[Marmara Sea]]. Two [[tectonic plate]]s, the African and the Eurasian, push against each other here. This fault line has been responsible for several deadly [[earthquake]]s in the region throughout history. In 1509, a catastrophic earthquake caused a [[tsunami]] which broke over the sea-walls of the city, destroying over 100 [[mosque]]s and killing 10,000 people. An earthquake largely destroyed the [[Eyüp Sultan Mosque]] In 1766. The 1894 earthquake caused the collapse of many parts of the [[the Grand Bazaar, Istanbul|Grand Bazaar]]. A devastating earthquake in August 1999, left 18,000 dead and many more homeless.<ref>{{cite news|url=http://archives.cnn.com/2000/NATURE/04/28/istanbul.quake.enn/ |title=Istanbul advised to brace for major quake |publisher=Environmental News Network via CNN |accessdate=2006-08-20 |date=2000-04-28}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|url=http://atlas.cc.itu.edu.tr/~barka/pubs/ist_haz/istanbul.html |title=Heightened odds of large earthquakes near Istanbul: An interaction-based probability calculation |publisher=Science |date=2000}}</ref> In all of these earthquakes, the devastating effects are a result of the close settlement and poor construction of buildings. Seismologists predict another earthquake, possibly measuring 7.0 on the [[Richter scale]], occurring before 2025. |
| − | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 55: | ||
===Founding of Byzantium=== | ===Founding of Byzantium=== | ||
| − | [[Greeks|Greek]] settlers of [[Megara]] colonized | + | [[Greeks|Greek]] settlers of [[Megara]] colonized the area in 685 B.C.E. [[Byzantium]]—then known as Byzantion—takes its name from of King [[Byzas]] of Magara under whose leadership the site was reportedly settled in 667. The town became an important trading center due to its strategic location at the Black Sea's only entrance. It later conquered [[Chalcedon]], across the Bosporus. |
| − | The city was [[siege|besieged]] by [[Roman Empire|Rome]] and suffered extensive damage in | + | The city was [[siege|besieged]] by [[Roman Empire|Rome]] and suffered extensive damage in 196 CE. Byzantium was rebuilt by the Roman Emperor [[Septimius Severus]] and quickly regained its previous prosperity, being temporarily renamed as ''Augusta Antonina'' by the emperor, in honor of his son. |
| − | The location of Byzantium attracted [[Constantine I of the Roman Empire|Constantine the Great]] in 324 after a [[prophet]]ic [[dream]] was said to have identified the location of the city | + | The location of Byzantium attracted [[Constantine I of the Roman Empire|Constantine the Great]] in 324 after a [[prophet]]ic [[dream]] was said to have identified the location of the city. The practical reason behind his move was probably Constantine's final victory over [[Licinius]] at the [[Battle of Chrysopolis]] on the [[Bosporus]], on September 18, 324, which ended the civil war between the Roman co-emperors, and brought an end to the final vestiges of the system in which [[Nicomedia]] (present-day [[İzmit]], 100 km east of Istanbul) was the most senior Roman capital city. |
| − | Byzantium | + | Byzantium now called as ''[[New Rome|Nova Roma]]'' and eventually ''[[Constantinople|Constantinopolis]]'', was officially proclaimed the new capital of the [[Roman Empire]] six years later, in 330. Following the death of [[Theodosius I]] in 395 and the permanent partition of the Roman Empire between his two sons, Constantinople became the capital of the [[Byzantine Empire|Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire]]. The unique position of Constantinople at the center of two continents made the city a magnet for international [[commerce]], [[culture]] and [[diplomacy]]. The Byzantine Empire was distinctly Greek in culture and became the center of [[Eastern Orthodox Church|Greek Orthodox Christianity]]. The capital was adorned with many magnificent [[church]]es, including the [[Hagia Sophia]], once the world's largest [[cathedral]]. The seat of the [[Patriarch of Constantinople]], spiritual leader of the Eastern Orthodox Church, still remains in the [[Fener]] ([[Phanar]]) district of Istanbul. |
| − | In 1204, the [[Fourth Crusade]] was launched to capture [[Jerusalem]], but | + | Orthodox and Catholic Christianity permanently split from one another in 1054 amid serious animosity. In 1204, the [[Fourth Crusade]] was launched to capture [[Jerusalem]], but instead turned on Constantinople, which was sacked and desecrated. The city subsequently became the center of the Catholic [[Latin Empire]], created by the crusaders to replace the Orthodox [[Byzantine Empire]], which was divided into a number of splinter states. One of these, the [[Empire of Nicaea]] was to recapture Constantinople in 1261 under the command of [[Michael VIII Palaeologus]]. |
{{wide image|Constantinople Panoramic Normalised.png|1000px|Panoramic view of the city in the 1870s as seen from [[Galata Tower]] ([[:Image:Constantinople-Photo-Panoramic view2.png|full image]])}} | {{wide image|Constantinople Panoramic Normalised.png|1000px|Panoramic view of the city in the 1870s as seen from [[Galata Tower]] ([[:Image:Constantinople-Photo-Panoramic view2.png|full image]])}} | ||
| Line 73: | Line 70: | ||
Following centuries of decline, Constantinople became surrounded by more youthful and powerful empires, most notably that of the [[Ottoman Turks]]. On 29 May 1453, [[Mehmed II|Sultan Mehmed II]] "the Conqueror" entered [[Constantinople]] after a 53–day [[siege]] and the city was promptly made the new capital of the [[Ottoman Empire]]. The last Byzantine emperor, [[Constantine XI (Palaeologus)]], was killed in battle. For three days the city was abandoned to pillage and massacre, after which order was restored by the sultan. | Following centuries of decline, Constantinople became surrounded by more youthful and powerful empires, most notably that of the [[Ottoman Turks]]. On 29 May 1453, [[Mehmed II|Sultan Mehmed II]] "the Conqueror" entered [[Constantinople]] after a 53–day [[siege]] and the city was promptly made the new capital of the [[Ottoman Empire]]. The last Byzantine emperor, [[Constantine XI (Palaeologus)]], was killed in battle. For three days the city was abandoned to pillage and massacre, after which order was restored by the sultan. | ||
| − | In the last decades of the Byzantine Empire, the city had decayed as the Byzantine state became increasingly isolated and financially bankrupt, its population had dwindled to some | + | In the last decades of the Byzantine Empire, the city had decayed as the Byzantine state became increasingly isolated and financially bankrupt, its population had dwindled to some 30,000-40,000 people, while large sections remained uninhabited. Thus, Sultan Mehmed set out to rejuvenate the city economically, creating the [[Grand Bazaar]] and inviting the fleeing Orthodox and Catholic inhabitants to return back. Captured prisoners were freed to settle in the city while provincial governors in Rumelia and Anatolia were ordered to send 4,000 families to settle in the city, whether Muslim, Christian or Jew, to form a unique [[cosmopolitan]] [[society]].<ref>Kinross, P., 2002. The Ottoman Centuries: The Rise and Fall of the Turkish Empire. Perrenial p.117</ref> The Sultan also endowed the city with various architectural monuments, including the [[Topkapı Palace]] and the [[Eyüp Sultan Mosque]]. Religious foundations were established to fund the construction of grand imperial mosques, adjoined by their associated [[school]]s, [[hospital]]s and [[public bath]]s. |
| + | |||
[[Image:Golden Horn and Sultanahmet.jpg|thumb|300px|View of the [[Topkapı Palace|Seraglio]] Point (Sarayburnu) on the [[Golden Horn]] as seen from [[Galata Tower]], with the [[Sea of Marmara]] and the [[Princes' Islands]] in the background, and [[Kadıköy]] (ancient [[Chalcedon]]) at left, on the Asian side]] | [[Image:Golden Horn and Sultanahmet.jpg|thumb|300px|View of the [[Topkapı Palace|Seraglio]] Point (Sarayburnu) on the [[Golden Horn]] as seen from [[Galata Tower]], with the [[Sea of Marmara]] and the [[Princes' Islands]] in the background, and [[Kadıköy]] (ancient [[Chalcedon]]) at left, on the Asian side]] | ||
| − | [[Suleiman the Magnificent]]’s reign was a period of great [[artistic]] and [[architectural]] achievements. The famous architect [[Sinan]] designed many mosques and other grand [[building]]s in the city, while Ottoman arts of [[Ceramics (art)|ceramics]] and [[calligraphy]] also flourished. Many of these | + | [[Suleiman the Magnificent]]’s reign was a period of great [[artistic]] and [[architectural]] achievements. The famous architect [[Sinan]] designed many mosques and other grand [[building]]s in the city, while Ottoman arts of [[Ceramics (art)|ceramics]] and [[calligraphy]] also flourished. Many of these survive to this day; some in the form of mosques while others have become museums such as the [[Jerrahi|Cerrahi]] [[Tekke]] and the [[Sunbul Effendi|Sünbül Efendi]] and Ramazan Efendi [[Mosque]]s and [[Turbes|Türbes]]; the Galata Mevlevihanesi; the Yahya Efendi Tekke; and the [[Bektashi|Bektaşi]] Tekke, which now serves [[Alevi]] [[Muslims]] as a [[cemevi]] (gathering house). |
| − | The city was modernized from the 1870s onwards with the construction of bridges, the creation of | + | The city was modernized from the 1870s onwards with the construction of bridges, the creation of an updated water system, electric lights, and the introduction of [[streetcars]] and [[telephones]]. |
===Modern Istanbul=== | ===Modern Istanbul=== | ||
| − | When the Republic of [[Turkey]] was founded in 1923, the capital was moved from Istanbul to [[Ankara]]. In the early years of the republic, Istanbul was overlooked in favor of the new capital. However, in the 1950s, Istanbul underwent great structural change, as new roads and factories were constructed throughout the city. Wide modern boulevards, avenues and public squares were built | + | When the Republic of [[Turkey]] was founded in 1923, the capital was moved from Istanbul to [[Ankara]]. In the early years of the republic, Istanbul was overlooked in favor of the new capital. However, in the 1950s, Istanbul underwent great structural change, as new roads and factories were constructed throughout the city. Wide modern boulevards, avenues and public squares were built, sometimes at the expense of the demolition of historical buildings. The city's once numerous and prosperous [[Greece|Greek]] community, remnants of the city's Greek origins, dwindled in the aftermath of the 1955 [[Istanbul Pogrom]], with most Greeks in Turkey leaving their homes for Greece. |
| − | During the 1970s, the population of Istanbul began to rapidly increase as people from [[Anatolia]] migrated to the city in order to find employment in the many new factories that were constructed at the outskirts of the city. This sudden sharp increase in the population caused a rapid rise in housing development | + | During the 1970s, the population of Istanbul began to rapidly increase as people from [[Anatolia]] migrated to the city in order to find employment in the many new factories that were constructed at the outskirts of the city. This sudden sharp increase in the population caused a rapid rise in housing development, some of poor quality, and many previously outlying villages became engulfed into the greater metropolis of Istanbul. |
Today, as well as being the country's largest city, Istanbul is the financial, cultural, and economic center of modern [[Turkey]]. | Today, as well as being the country's largest city, Istanbul is the financial, cultural, and economic center of modern [[Turkey]]. | ||
| Line 88: | Line 86: | ||
==Cityscape== | ==Cityscape== | ||
===Architecture=== | ===Architecture=== | ||
| − | + | ||
[[Image:EgyptianObelisk.jpg|thumb|180px|Obelisk of [[Thutmosis III]] at the [[Hippodrome of Constantinople]] was brought from the [[Temple of Karnak]] in [[Egypt]] by [[Theodosius the Great]]]] | [[Image:EgyptianObelisk.jpg|thumb|180px|Obelisk of [[Thutmosis III]] at the [[Hippodrome of Constantinople]] was brought from the [[Temple of Karnak]] in [[Egypt]] by [[Theodosius the Great]]]] | ||
| − | + | Throughout its long history, Istanbul has acquired a reputation for being a cultural and ethnic melting pot. As a result, there are many historical [[mosque]]s, [[church]]es, [[synagogue]]s, [[palace]]s, [[castle]]s, and [[tower]]s to visit in the city. | |
| − | The most important monuments of Roman architecture | + | The most important monuments of Roman architecture include the Column of Constantine ([[Turkish language|Turkish]]: ''Çemberlitaş'') which was erected in 330 CE and reportedly contains several fragments of the [[Original Cross]] and the bowl with which [[Virgin Mary]] washed the feet of Jesus at its base; the Mazulkemer Aqueduct and [[Valens aqueduct|Valens Aqueduct]]; the Column of the Goths (''Gotlar Sütunu'') at the Seraglio Point; the ''Milion'' which served for calculating the distances between Constantinople and other cities of the Roman Empire; and the [[Hippodrome of Constantinople]], which was built following the model of the [[Circus Maximus]] in [[Rome]]. |
[[Image:Car bed kap deu2.jpg|thumb|left|200px|[[Walls of Constantinople]]]] | [[Image:Car bed kap deu2.jpg|thumb|left|200px|[[Walls of Constantinople]]]] | ||
| − | + | The city walls had 55 gates, the largest of which was the Porta Aurea (Golden Gate), the ceremonial entrance gate used by the emperors, at the southwestern end of the triple land walls, close to the Sea of Marmara. Unlike the city walls, which were built of brick and limestone, the Porta Aurea was built of large clean-cut white marble blocks in order to distinguish it from the rest, and a quadriga with elephant statues stood on its top. The doors of the Porta Aurea were made of gold, hence the name, which means ''Golden Gate'' in Latin. | |
| − | Early Byzantine architecture followed the classical Roman model of domes and arches, but further improved these architectural concepts, as evidenced with the [[Hagia Sophia]], which was designed by Isidorus and Anthemius | + | Early Byzantine architecture followed the classical Roman model of domes and arches, but further improved these architectural concepts, as evidenced with the [[Hagia Sophia]], which was designed by Isidorus and Anthemius between 532 and 537 during the reign of Justinian the Great. |
[[Image:Hagia Eirene.jpg|thumb|left|200px|[[Hagia Irene]] was one of the most important churches built by [[Justinian the Great|Justinian]]. The mosaics in its interior were removed during the [[iconoclasm|iconoclastic period]] and replaced with a simple cross]] | [[Image:Hagia Eirene.jpg|thumb|left|200px|[[Hagia Irene]] was one of the most important churches built by [[Justinian the Great|Justinian]]. The mosaics in its interior were removed during the [[iconoclasm|iconoclastic period]] and replaced with a simple cross]] | ||
| − | Many churches with magnificent golden | + | Many churches with magnificent golden [[icon]]s were built until the eighth century. Many of these were vandalized during the [[iconoclasm]] movement of (730-787) which began with the reign of [[Leo III the Isaurian]]. The [[iconoclasts]] of this period, like the [[Muslim]] counterparts, believed that the images of Christ and other saints on the walls of the churches constituted a sin, and they forcefully had them removed or destroyed. A second iconoclastic period followed in (814-842), initiated by [[Leo V the Armenian]]. |
[[Image:Dvor porf kap.jpg|thumb|200px|[[Palace of Porphyrogenitus]]]] | [[Image:Dvor porf kap.jpg|thumb|200px|[[Palace of Porphyrogenitus]]]] | ||
| − | During the [[Fourth Crusade]] in 1204, most of the city's important buildings were sacked, and numerous architectural and artistic treasures were shipped to [[Venice]], whose | + | During the [[Fourth Crusade]] in 1204, most of the city's important buildings were sacked by the forces of Western Christianity, and numerous architectural and artistic treasures were shipped to [[Venice]], whose ruler, [[Enrico Dandolo]], had organized the sack of Constantinople. These items include the famous Statue of the Tetrarchs and the four bronze horse statues that once stood at the top of the [[Hippodrome of Constantinople]], which today stand on the front facade of the [[Saint Mark's Basilica]] in Venice. |
The [[Palace of Porphyrogenitus]] ([[Turkish language|Turkish]]: ''Tekfur Sarayı''), which is the only surviving part of the [[Blachernae|Blachernae Palace]], dates from the period of the Fourth Crusade. In these years, on the northern side of the [[Golden Horn]], the Dominican priests of the Catholic Church built the [[Arap Mosque|Church of Saint Paul]] in 1233. | The [[Palace of Porphyrogenitus]] ([[Turkish language|Turkish]]: ''Tekfur Sarayı''), which is the only surviving part of the [[Blachernae|Blachernae Palace]], dates from the period of the Fourth Crusade. In these years, on the northern side of the [[Golden Horn]], the Dominican priests of the Catholic Church built the [[Arap Mosque|Church of Saint Paul]] in 1233. | ||
| Line 116: | Line 114: | ||
Following the Ottoman conquest of the city, Sultan [[Mehmed II]] initiated a wide scale reconstruction plan, which included the construction of grand buildings such as the [[Eyüp Sultan Mosque]], [[Fatih Mosque]], [[Topkapı Palace]], [[Grand Bazaar, Istanbul|The Grand Bazaar]] and the [[Yedikule|Yedikule (Seven Towers) Castle]] which guarded the main entrance gate of the city, the Porta Aurea (Golden Gate). In the centuries following Mehmed II, many new important buildings, such as the [[Süleymaniye Mosque]], [[Sultanahmet Mosque]], [[Yeni Mosque]] and numerous others were constructed. | Following the Ottoman conquest of the city, Sultan [[Mehmed II]] initiated a wide scale reconstruction plan, which included the construction of grand buildings such as the [[Eyüp Sultan Mosque]], [[Fatih Mosque]], [[Topkapı Palace]], [[Grand Bazaar, Istanbul|The Grand Bazaar]] and the [[Yedikule|Yedikule (Seven Towers) Castle]] which guarded the main entrance gate of the city, the Porta Aurea (Golden Gate). In the centuries following Mehmed II, many new important buildings, such as the [[Süleymaniye Mosque]], [[Sultanahmet Mosque]], [[Yeni Mosque]] and numerous others were constructed. | ||
| − | Traditionally, Ottoman buildings were built of ornate wood. Only "state buildings" such as palaces and mosques were built of stone. Starting from the | + | Traditionally, Ottoman buildings were built of ornate wood. Only "state buildings" such as palaces and mosques were built of stone. Starting from the eighteenth and nineteeth centuries, wood was gradually replaced with stone as the primary building material, while traditional Ottoman architectural styles were replaced with European architectural styles. New palaces and mosques were built in [[Neoclassical]], Baroque and [[Rococo]] styles, or a mixture of all three, such as the [[Dolmabahçe Palace]], [[Dolmabahçe Mosque]] and [[Ortaköy Mosque]]. Even [[Neo-Gothic]] mosques were built, such as the Pertevniyal Valide Sultan Mosque and Yıldız Mosque. Large state buildings like schools or military barracks were also built in various European styles. |
[[Image:DolmabahceMainGate.JPG|thumb|left|200px|[[Dolmabahçe Palace]]]] | [[Image:DolmabahceMainGate.JPG|thumb|left|200px|[[Dolmabahçe Palace]]]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Image:Arnavutkoy.jpg|thumb|200px|[[Yalı|Waterfront houses]] in [[Arnavutköy]]]] | [[Image:Arnavutkoy.jpg|thumb|200px|[[Yalı|Waterfront houses]] in [[Arnavutköy]]]] | ||
| Line 128: | Line 124: | ||
[[Image:Akmerkez1.jpg|thumb|200px|[[Akmerkez]] in the quarter of [[Etiler]] is the only shopping mall in the world which won both "Europe's Best" and "World's Best" awards by [[ICSC]]]] | [[Image:Akmerkez1.jpg|thumb|200px|[[Akmerkez]] in the quarter of [[Etiler]] is the only shopping mall in the world which won both "Europe's Best" and "World's Best" awards by [[ICSC]]]] | ||
[[Image:Bağdat Caddesi 5.jpg|thumb|200px|The 6 km long [[Baghdad Street|Bağdat Avenue]] has rows of shops, cafés, pubs and restaurants lining up its wide granite pavements on both flanks]] | [[Image:Bağdat Caddesi 5.jpg|thumb|200px|The 6 km long [[Baghdad Street|Bağdat Avenue]] has rows of shops, cafés, pubs and restaurants lining up its wide granite pavements on both flanks]] | ||
| − | |||
[[Image:Galata tower istanbul.jpg|thumb|left|200px|[[Galata Tower]] dominates the skyline of the medieval [[Republic of Genoa|Genoese]] citadel at the northern side of the [[Golden Horn]]]] | [[Image:Galata tower istanbul.jpg|thumb|left|200px|[[Galata Tower]] dominates the skyline of the medieval [[Republic of Genoa|Genoese]] citadel at the northern side of the [[Golden Horn]]]] | ||
| − | + | In the last decades, numerous tall structures were built around the city to accommodate a rapid growth in population. Surrounding towns were absorbed into Istanbul as the city rapidly expanded outwards. The tallest high-rise office and residential buildings are mostly located in the northern areas of the European side, which also have numerous upmarket shopping malls. | |
| − | |||
| − | In the last decades, numerous tall structures were built around the city to accommodate a rapid growth in population. Surrounding towns were absorbed into Istanbul as the city rapidly expanded outwards. The tallest | ||
| − | Starting from the second half of the | + | Starting from the second half of the twentieth century, the Asian side of Istanbul, which was originally a tranquil place full of seaside summer residences and elegant chalet mansions surrounded by lush and vast umbrella pine gardens, experienced massive urban growth. |
An improved transportation infrastructure, with both high speed highways and railways, encouraged this growth. Another important factor in the recent growth of the Asian side of the city has been migration from [[Anatolia]]. Today, more than one-third of the city's population live in the Asian side of Istanbul. | An improved transportation infrastructure, with both high speed highways and railways, encouraged this growth. Another important factor in the recent growth of the Asian side of the city has been migration from [[Anatolia]]. Today, more than one-third of the city's population live in the Asian side of Istanbul. | ||
| − | Due to Istanbul's exponential growth during the second half of the | + | Due to Istanbul's exponential growth during the second half of the twentieth century, a significant portion of the city's outskirts consist of ''[[gecekondu]]s'', a Turkish word created in the 1940s meaning "built overnight." These neighborhoods are typically built on abandoned land or on lands owned by others, without the permission of the landowner, and do not obey building codes and regulations. At present, ''gecekondu'' areas are being gradually demolished and replaced by modern mass-housing complexes. |
==Administration== | ==Administration== | ||
===Organization=== | ===Organization=== | ||
| + | The metropolitan model of governance has been used with the establishment of metropolitan administration in 1930. The metropolitan council is accepted as the competent authority for decision-making. The metropolitan government structure consists of three main organs: (1) The Metropolitan Mayor (elected every five years), (2) The Metropolitan Council (decision making body with the mayor, district Mayors, and one fifth of the district municipal councilors), (3) The metropolitan executive committee. There are three types of local authorities: municipalities, special provincial administrations, and village administrations. Among the local authorities, municipalities are gaining greater importance with the rise in urbanization. | ||
| − | + | Istanbul has 31 districts. These can be divided into three main areas: the historic peninsula, the areas north of the [[Golden Horn]], and the Asian side. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Istanbul has 31 districts. | ||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
Revision as of 15:53, 15 September 2007
| Hagia Sophia | |
Symbol of Istanbul Municipality | |
| Location in Turkey | |
| Overview | |
| Region | Marmara Region, Turkey |
| Province | Istanbul Province |
| Population | 10,291,102 (2007) |
| Area | 1,538,77 km² |
| Population density | 6521 inh./km² |
| Elevation | 100 m |
| Coordinates | Coordinates: |
| Postal code | 34010 to 34850 and 80000 to 81800 |
| Area code | (+90) 212 (European side) (+90) 216 (Asian side) |
| Mayor | Kadir Topbaş (Justice and Development Party) |
| Website | Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality |
| Governor | Muammer Güler |
| Governor website | Istanbul Portal |
Istanbul (Turkish: İstanbul, Greek: Κωνσταντινούπολη, historically Byzantium and later Constantinople; see other names) is Turkey's most populous city, and its cultural and financial center. The city covers 25 districts of the Istanbul province. It is located at 41° N 29° E, on the Bosporus strait, and encompasses the natural harbor known as the Golden Horn, in the northwest of the country. It extends both on the European (Thrace) and on the Asian (Anatolia) side of the Bosporus, and is thereby the only metropolis in the world which is situated on two continents. In its long history, Istanbul (Constantinople) served as the capital city of the Roman Empire (330-395), the Byzantine Empire (395-1204 and 1261-1453), the Latin Empire (1204-1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453-1922). The city was chosen as joint European Capital of Culture for 2010. The "Historic Areas of Istanbul" were added to the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1985.
Names
The city of Istanbul has had many names through its history. Byzantium, Constantinople, and Stamboul are examples that may still be found in active use. Among others, it has been called New Rome or Second Rome, since the Roman Emperor Constantine the Great founded it on the site of the ancient Greek city of Byzantium as a second, and decidedly Christian, capital of the Roman Empire, in contrast to the still largely pagan Rome.[2] It has also been nicknamed "The City on Seven Hills" because the historic peninsula, the oldest part of the city, was built by Constantine on seven hills to match the seven hills of Rome. The hills are represented in the city coat of arms with seven mosques, one at the top of each hill. Another old nickname of Istanbul is Vasileousa Polis (Queen of Cities) due to its importance and wealth throughout the Middle Ages.
In an edict of March 28, 1930, the Turkish authorities officially requested foreigners to cease referring to the city with their traditional non-Turkish names (such as Constantinople) and to adopt İstanbul as the sole name also in the foreign languages.[3]
Geography
Istanbul is located in the north-west Marmara Region of Turkey. It encloses the southern Bosporus which places the city on two continents – the western portion of Istanbul is in Europe, while the eastern portion is in Asia. The city boundaries cover a surface area of 1,539 square kilometers, while the metropolitan region, or the Province of Istanbul, covers 6,220 square kilometers.
Climate

The city has a temperate-continental climate, with hot and humid summers; and cold, rainy and often snowy winters. Humidity is generally rather high. Yearly precipitation for Istanbul averages 870 mm. Snowfall is quite common, snowing for a week or two during the winter season, but it can be heavy once it snows. It is most likely to occur between the months of December and March. The summer months between June and September bring average daytime temperatures of 28 °C (82 °F). The warmest month is July with an average temperature of 23.2 °C (74 °F), the coldest is January with 5.4 °C (42 °F). The weather becomes slightly cooler as one moves toward eastern Istanbul. Summer is by far the driest season. The city is quite windy, having an average wind speed of 17 km/h (11 mph).
Geology

Istanbul is situated near the North Anatolian fault line, which runs from northern Anatolia to the Marmara Sea. Two tectonic plates, the African and the Eurasian, push against each other here. This fault line has been responsible for several deadly earthquakes in the region throughout history. In 1509, a catastrophic earthquake caused a tsunami which broke over the sea-walls of the city, destroying over 100 mosques and killing 10,000 people. An earthquake largely destroyed the Eyüp Sultan Mosque In 1766. The 1894 earthquake caused the collapse of many parts of the Grand Bazaar. A devastating earthquake in August 1999, left 18,000 dead and many more homeless.[4][5] In all of these earthquakes, the devastating effects are a result of the close settlement and poor construction of buildings. Seismologists predict another earthquake, possibly measuring 7.0 on the Richter scale, occurring before 2025.
History
| “ | If the Earth was a single state, Istanbul would be its capital [1]. | ” |
Founding of Byzantium
Greek settlers of Megara colonized the area in 685 B.C.E. Byzantium—then known as Byzantion—takes its name from of King Byzas of Magara under whose leadership the site was reportedly settled in 667. The town became an important trading center due to its strategic location at the Black Sea's only entrance. It later conquered Chalcedon, across the Bosporus.
The city was besieged by Rome and suffered extensive damage in 196 C.E. Byzantium was rebuilt by the Roman Emperor Septimius Severus and quickly regained its previous prosperity, being temporarily renamed as Augusta Antonina by the emperor, in honor of his son.
The location of Byzantium attracted Constantine the Great in 324 after a prophetic dream was said to have identified the location of the city. The practical reason behind his move was probably Constantine's final victory over Licinius at the Battle of Chrysopolis on the Bosporus, on September 18, 324, which ended the civil war between the Roman co-emperors, and brought an end to the final vestiges of the system in which Nicomedia (present-day İzmit, 100 km east of Istanbul) was the most senior Roman capital city.
Byzantium now called as Nova Roma and eventually Constantinopolis, was officially proclaimed the new capital of the Roman Empire six years later, in 330. Following the death of Theodosius I in 395 and the permanent partition of the Roman Empire between his two sons, Constantinople became the capital of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire. The unique position of Constantinople at the center of two continents made the city a magnet for international commerce, culture and diplomacy. The Byzantine Empire was distinctly Greek in culture and became the center of Greek Orthodox Christianity. The capital was adorned with many magnificent churches, including the Hagia Sophia, once the world's largest cathedral. The seat of the Patriarch of Constantinople, spiritual leader of the Eastern Orthodox Church, still remains in the Fener (Phanar) district of Istanbul.
Orthodox and Catholic Christianity permanently split from one another in 1054 amid serious animosity. In 1204, the Fourth Crusade was launched to capture Jerusalem, but instead turned on Constantinople, which was sacked and desecrated. The city subsequently became the center of the Catholic Latin Empire, created by the crusaders to replace the Orthodox Byzantine Empire, which was divided into a number of splinter states. One of these, the Empire of Nicaea was to recapture Constantinople in 1261 under the command of Michael VIII Palaeologus.
Ottoman conquest
Following centuries of decline, Constantinople became surrounded by more youthful and powerful empires, most notably that of the Ottoman Turks. On 29 May 1453, Sultan Mehmed II "the Conqueror" entered Constantinople after a 53–day siege and the city was promptly made the new capital of the Ottoman Empire. The last Byzantine emperor, Constantine XI (Palaeologus), was killed in battle. For three days the city was abandoned to pillage and massacre, after which order was restored by the sultan.
In the last decades of the Byzantine Empire, the city had decayed as the Byzantine state became increasingly isolated and financially bankrupt, its population had dwindled to some 30,000-40,000 people, while large sections remained uninhabited. Thus, Sultan Mehmed set out to rejuvenate the city economically, creating the Grand Bazaar and inviting the fleeing Orthodox and Catholic inhabitants to return back. Captured prisoners were freed to settle in the city while provincial governors in Rumelia and Anatolia were ordered to send 4,000 families to settle in the city, whether Muslim, Christian or Jew, to form a unique cosmopolitan society.[6] The Sultan also endowed the city with various architectural monuments, including the Topkapı Palace and the Eyüp Sultan Mosque. Religious foundations were established to fund the construction of grand imperial mosques, adjoined by their associated schools, hospitals and public baths.
Suleiman the Magnificent’s reign was a period of great artistic and architectural achievements. The famous architect Sinan designed many mosques and other grand buildings in the city, while Ottoman arts of ceramics and calligraphy also flourished. Many of these survive to this day; some in the form of mosques while others have become museums such as the Cerrahi Tekke and the Sünbül Efendi and Ramazan Efendi Mosques and Türbes; the Galata Mevlevihanesi; the Yahya Efendi Tekke; and the Bektaşi Tekke, which now serves Alevi Muslims as a cemevi (gathering house).
The city was modernized from the 1870s onwards with the construction of bridges, the creation of an updated water system, electric lights, and the introduction of streetcars and telephones.
Modern Istanbul
When the Republic of Turkey was founded in 1923, the capital was moved from Istanbul to Ankara. In the early years of the republic, Istanbul was overlooked in favor of the new capital. However, in the 1950s, Istanbul underwent great structural change, as new roads and factories were constructed throughout the city. Wide modern boulevards, avenues and public squares were built, sometimes at the expense of the demolition of historical buildings. The city's once numerous and prosperous Greek community, remnants of the city's Greek origins, dwindled in the aftermath of the 1955 Istanbul Pogrom, with most Greeks in Turkey leaving their homes for Greece.
During the 1970s, the population of Istanbul began to rapidly increase as people from Anatolia migrated to the city in order to find employment in the many new factories that were constructed at the outskirts of the city. This sudden sharp increase in the population caused a rapid rise in housing development, some of poor quality, and many previously outlying villages became engulfed into the greater metropolis of Istanbul.
Today, as well as being the country's largest city, Istanbul is the financial, cultural, and economic center of modern Turkey.
Cityscape
Architecture

Throughout its long history, Istanbul has acquired a reputation for being a cultural and ethnic melting pot. As a result, there are many historical mosques, churches, synagogues, palaces, castles, and towers to visit in the city.
The most important monuments of Roman architecture include the Column of Constantine (Turkish: Çemberlitaş) which was erected in 330 C.E. and reportedly contains several fragments of the Original Cross and the bowl with which Virgin Mary washed the feet of Jesus at its base; the Mazulkemer Aqueduct and Valens Aqueduct; the Column of the Goths (Gotlar Sütunu) at the Seraglio Point; the Milion which served for calculating the distances between Constantinople and other cities of the Roman Empire; and the Hippodrome of Constantinople, which was built following the model of the Circus Maximus in Rome.
The city walls had 55 gates, the largest of which was the Porta Aurea (Golden Gate), the ceremonial entrance gate used by the emperors, at the southwestern end of the triple land walls, close to the Sea of Marmara. Unlike the city walls, which were built of brick and limestone, the Porta Aurea was built of large clean-cut white marble blocks in order to distinguish it from the rest, and a quadriga with elephant statues stood on its top. The doors of the Porta Aurea were made of gold, hence the name, which means Golden Gate in Latin.
Early Byzantine architecture followed the classical Roman model of domes and arches, but further improved these architectural concepts, as evidenced with the Hagia Sophia, which was designed by Isidorus and Anthemius between 532 and 537 during the reign of Justinian the Great.

Many churches with magnificent golden icons were built until the eighth century. Many of these were vandalized during the iconoclasm movement of (730-787) which began with the reign of Leo III the Isaurian. The iconoclasts of this period, like the Muslim counterparts, believed that the images of Christ and other saints on the walls of the churches constituted a sin, and they forcefully had them removed or destroyed. A second iconoclastic period followed in (814-842), initiated by Leo V the Armenian.
During the Fourth Crusade in 1204, most of the city's important buildings were sacked by the forces of Western Christianity, and numerous architectural and artistic treasures were shipped to Venice, whose ruler, Enrico Dandolo, had organized the sack of Constantinople. These items include the famous Statue of the Tetrarchs and the four bronze horse statues that once stood at the top of the Hippodrome of Constantinople, which today stand on the front facade of the Saint Mark's Basilica in Venice.
The Palace of Porphyrogenitus (Turkish: Tekfur Sarayı), which is the only surviving part of the Blachernae Palace, dates from the period of the Fourth Crusade. In these years, on the northern side of the Golden Horn, the Dominican priests of the Catholic Church built the Church of Saint Paul in 1233.
Following the Ottoman conquest of the city, Sultan Mehmed II initiated a wide scale reconstruction plan, which included the construction of grand buildings such as the Eyüp Sultan Mosque, Fatih Mosque, Topkapı Palace, The Grand Bazaar and the Yedikule (Seven Towers) Castle which guarded the main entrance gate of the city, the Porta Aurea (Golden Gate). In the centuries following Mehmed II, many new important buildings, such as the Süleymaniye Mosque, Sultanahmet Mosque, Yeni Mosque and numerous others were constructed.
Traditionally, Ottoman buildings were built of ornate wood. Only "state buildings" such as palaces and mosques were built of stone. Starting from the eighteenth and nineteeth centuries, wood was gradually replaced with stone as the primary building material, while traditional Ottoman architectural styles were replaced with European architectural styles. New palaces and mosques were built in Neoclassical, Baroque and Rococo styles, or a mixture of all three, such as the Dolmabahçe Palace, Dolmabahçe Mosque and Ortaköy Mosque. Even Neo-Gothic mosques were built, such as the Pertevniyal Valide Sultan Mosque and Yıldız Mosque. Large state buildings like schools or military barracks were also built in various European styles.
Urbanism
In the last decades, numerous tall structures were built around the city to accommodate a rapid growth in population. Surrounding towns were absorbed into Istanbul as the city rapidly expanded outwards. The tallest high-rise office and residential buildings are mostly located in the northern areas of the European side, which also have numerous upmarket shopping malls.
Starting from the second half of the twentieth century, the Asian side of Istanbul, which was originally a tranquil place full of seaside summer residences and elegant chalet mansions surrounded by lush and vast umbrella pine gardens, experienced massive urban growth.
An improved transportation infrastructure, with both high speed highways and railways, encouraged this growth. Another important factor in the recent growth of the Asian side of the city has been migration from Anatolia. Today, more than one-third of the city's population live in the Asian side of Istanbul.
Due to Istanbul's exponential growth during the second half of the twentieth century, a significant portion of the city's outskirts consist of gecekondus, a Turkish word created in the 1940s meaning "built overnight." These neighborhoods are typically built on abandoned land or on lands owned by others, without the permission of the landowner, and do not obey building codes and regulations. At present, gecekondu areas are being gradually demolished and replaced by modern mass-housing complexes.
Administration
Organization
The metropolitan model of governance has been used with the establishment of metropolitan administration in 1930. The metropolitan council is accepted as the competent authority for decision-making. The metropolitan government structure consists of three main organs: (1) The Metropolitan Mayor (elected every five years), (2) The Metropolitan Council (decision making body with the mayor, district Mayors, and one fifth of the district municipal councilors), (3) The metropolitan executive committee. There are three types of local authorities: municipalities, special provincial administrations, and village administrations. Among the local authorities, municipalities are gaining greater importance with the rise in urbanization.
Istanbul has 31 districts. These can be divided into three main areas: the historic peninsula, the areas north of the Golden Horn, and the Asian side.
Demographics
- Further information: Historical population values and Demographics of Turkey
The population of the metropolis has more than tripled during the 25 years between 1980 and 2005. Roughly 70 percent of all Istanbulers live in the European section and around 30 percent live in the Asian section. The graph shows the numbers of inhabitants by year. The doubling of the population of Istanbul between 1980 and 1985 is due to a natural increase in population as well as the expansion of municipal limits.[citation needed]
According to the 2000 census, the population was 8,803,468 (city proper) and 10,018,735 (metro area). The census bureau estimate for July 20, 2005 was 11,322,000 for the province, which is generally considered as the metropolitan area, making it one of the twenty largest metropolitan areas in the world.[citation needed]
Religion
- Further information: Mosques, Churches, Synagogues
The urban landscape of Istanbul is shaped by many communities. The most important and most populous major religion is Islam. The first mosque in Istanbul was built in Kadıköy (ancient Chalcedon) on the Asian side of the city, which was conquered by the Ottoman Turks in 1353, a full century before the conquest of Constantinople across the Bosporus, on the European side. The first mosque on the European side of Istanbul was built inside the Rumeli Castle in 1452. The first grand mosque which was built in the city proper is the Eyüp Sultan Mosque (1458), while the first imperial mosque inside the city walls was the Fatih Mosque (1470) which was built on the site of the Church of the Holy Apostles, an important Byzantine church which was originally edificed in the time of Constantine the Great. Many other imperial mosques were built in the following centuries, such as the famous Süleymaniye Mosque (1557) which was ordered by Suleiman the Magnificent and designed by the great Ottoman architect Sinan, and the famous Sultan Ahmet Mosque (1616) which is also known as the Blue Mosque for the blue tiles which adorn its interior.
Istanbul was the final seat of the Islamic Caliphate, between 1517 and 1924. The personal belongings of the Prophet Mohammed and the earliest Caliphs who followed him are today preserved in the Topkapı Palace, the Eyüp Sultan Mosque and in several other prominent mosques of Istanbul.
Religious minorities include Greek Orthodox Christians, Armenian Christians, Catholic Levantines and Sephardic Jews. Some districts have sizable populations of these ethnic groups, such as the Kumkapı district which has a sizable Armenian population, the Balat district which has a sizable Jewish population, the Fener district which has a sizable Greek population, and some neighborhoods in the Nişantaşı and Beyoğlu districts which have sizable Levantine populations. In some quarters, such as Kuzguncuk, an Armenian church sits next to a synagogue, and on the other side of the road a Greek Orthodox church is found beside a mosque.
The seat of the Patriarch of Constantinople, spiritual leader of the Greek Orthodox Church is located in the Fener (Phanar) district. Also based in Istanbul are the archbishop of the Turkish-Orthodox community, an Armenian archbishop, and the Turkish Grand-Rabbi.
Following the Turkish conquest of Constantinople in 1453, the Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II established the Millet System, according to which the different ethnic groups within Constantinople and the rest of the Ottoman Empire were to be governed by a group of institutions based on faith. With the Millet System, a great deal of the internal affairs regarding these communities were assigned to the administration of these religious authorities; such as the Ecumenical Patriarchate for the affairs of all Orthodox Christians, the Armenian Patriarchate for the affairs of the Armenian (and for some time also the Syriac) Christians, and later the Grand Rabbi for the affairs of the Jews.
The population of the Armenian and Greek minorities in Istanbul greatly declined beginning in the late nineteenth century. The city's Greek Orthodox community were exempted from the population exchange between Greece and Turkey of 1923. However, a series of special restrictions and taxes beginning in the 1930s (see, e.g., Varlık Vergisi), finally culminating in the Istanbul Pogrom of 1955, greatly increased emigration, and in 1964, all Greeks without Turkish citizenship residing in Turkey (around 100,000) were deported. Today, most of Turkey's remaining Greek and Armenian minorities live in or near Istanbul.
The Sephardic Jews have lived in the city for over 500 years, see the history of the Jews in Turkey. Together with the Arabs, the Sephardic Jews fled the Iberian Peninsula during the Spanish Inquisition of 1492, when they were forced to convert to Christianity after the fall of the Moorish Kingdom of Andalucia. The Ottoman Sultan Bayezid II (1481-1512) sent a sizable fleet to Spain under the command of Kemal Reis in order to save the Arabs and Sephardic Jews who were tortured and killed because of their faith. More than 200,000 Spanish Jews fled first to Tangier, Algiers, Genova and Marseille, later to Salonica and finally to Istanbul. The Sultan granted Ottoman citizenship to over 93,000 of these Spanish Jews. Another large group of Sephardic Jews came from southern Italy which was under Spanish control. The Sephardic Jews of Iberia and Italy contributed much to the rising power of the Ottoman Empire by introducing new ideas, methods and craftsmanship. The first Gutenberg press in Istanbul was established by the Sephardic Jews in 1493, who excelled in many areas, particularly medicine, trade and banking. More than 20,000 Sephardic Jews still remain in Istanbul today.
There is also a relatively smaller and more recent community of Ashkenazi Jews in Istanbul who continue to live in the city since the nineteenth century. A second large wave of Ashkenazi Jews came to Istanbul during the 1930s and 1940s following the rise of Nazism in Germany which persecuted the Ashkenazi Jews of central and eastern Europe.
During the Byzantine period, the Genoese Podestà ruled over the Italian community of Galata, which was mostly made up of the Genoese, Venetians, Tuscans and Ragusans. Following the Turkish siege of Constantinople in 1453, during which the Genoese sided with the Byzantines and defended the city together with them, the Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II allowed the Genoese (who had fled to their colonies in the Aegean Sea such as Lesbos and Chios) to return back to the city.
There were more than 40,000 Catholic Italians in Istanbul at the turn of the 20th century, a figure which not only included the descendants of the local Genoese and Venetian merchants who lived here since the Byzantine and early Ottoman periods, but also the numerous Italian workers and artisans who came to the city from southern Italy during the nineteenth century. The number of Istanbul's Italians decreased after the end of the Ottoman Empire for several reasons. The Turkish Republic no longer recognized the trade privileges that were given to the descendants of the Genoese and Venetian merchants, and foreigners were no longer allowed to work in Turkey in a wide number of sectors, including many artisanships, in which numerous Istanbulite Italians used to work. The Varlık Vergisi (Wealth Tax) of the World War II years, which imposed higher tariffs on non-Muslims and foreigners in Turkey, also played an important role in the migration of Istanbul's Italians to Italy - who still live in the city, but in far fewer numbers when compared with the early twentieth century. The influence of the Italian community of Istanbul, however, is still visible in the architecture of many quarters, particularly Galata, Beyoğlu and Nişantaşı.
Crime
The overwhelming majority of crime is non-violent in nature. There are remarkably few assaults or robberies in which guns or knives are used.[7] Pickpockets work in tourist areas, particularly around Taksim Square.
In November 2003 al Qaida-affiliated suicide bombers blew up the British Consulate, the HSBC Bank, and two synagogues, killing dozens and wounding hundreds of people. These incidents represent a significant change from prior attacks in Turkey and show an increased willingness on the part of terrorists to attack Western targets.[8] While the threat of terrorism remains high in Istanbul as in most Western cities, the most significant threat to safety comes from vehicular accidents.[9]
Economy
Historically, Istanbul has been the center of the country's economic life due to its location as an international junction of land and sea trade routes. In 2005 the City of Istanbul had a GDP of $133 billion, outranking many prominent cities in the world including Singapore, Mumbai, Rome, Montreal, Milan, Beijing, Cairo, Jakarta, Vienna, Delhi, Bangkok, Tehran, St. Petersburg, Johannesburg, Stockholm, Cape Town, Berlin, Athens, Birmingham, Manchester, Hamburg, Turin, Lyon, Munich, Warsaw, Naples, Ankara, Amsterdam, Rotterdam, Brussels and many others, according to a research conducted by PriceWaterhouseCoopers (PWC).[10][11][12]
In 2005 companies based in Istanbul made exports worth $41,397,000,000 and imports worth $69,883,000,000; which corresponded to 56.6 percent and 60.2 percent of Turkey's exports and imports, respectively, in that year.[13] In 2006 Turkey's exports grew a further +16.1 percent while imports grew +17.6 percent due to a rising demand of energy resources and raw materials by the industrial manufacturers in the country.[14]
Income distribution is not fairly balanced in Istanbul, such that 20 percent of the highest income group uses 64 percent of the resources and 20 percent of the lowest income group uses 4 percent of the resources (based on 1994 statistics).[15] The change in Istanbul's living standards is a direct reflection of the nation's statistics as the 27.5 percent share of the total consumption in Turkey is performed by the population of Istanbul.
In the late 1990s, the economy of Turkey, and Istanbul in particular, suffered several major depressions. The Asian financial crisis between July 1997 and the beginning of 1998, as well as the crisis in Russia between August 1998 and the middle of 1999 had negative effects in all areas of the economy, particularly on exports. Following this setback, a slow reorganization of the economy of Istanbul was observed in 1999.
The major earthquake which was epicentered in nearby Kocaeli on August 17, 1999, triggered one of the largest economic shocks for the city. Apart from the capital and human losses caused by the disaster, a decrease in GDP of approximately two percent occurred. Despite these downturns, Istanbul's economy has strongly improved and recovered in the recent years.
Financial Sector
Istanbul has always been the "financial capital" of Turkey, even after Ankara became the new political capital in 1923. The opening of specific markets in the city during the 1980s further strengthened this status. Inaugurated at the beginning of 1986, the Istanbul Stock Exchange (ISE) is the sole securities market of Turkey, established to provide trading in equities, right coupons, Government bonds, Treasury bills, revenue sharing certificates, bonds issued by the Privatization Administration and corporate bonds, and to carry out overnight transactions.[16]
In 1993 the ISE decided on gold market liberalization, and in 1995 the Istanbul Gold Exchange was established, which ended the gold bullion imports monopoly of the Turkish Central Bank and transferred it to the private sector members of the gold exchange.[17]
Levent and Maslak financial districts are home to the headquarters of Turkey's largest companies and banks, as well as the local headquarters of global giants of the financial sector such as Citibank, Merrill Lynch, J. P. Morgan, HSBC, ABN Amro, Fortis, ING Bank, BNP Paribas, Société Générale, Banca di Roma, UniCredit, WestLB, Deutsche Bank, Commerzbank, and many others. Both Levent and Maslak have a constantly growing and changing dynamic skyline with several new skyscraper projects being proposed, approved and initiated every year.
Industry
Istanbul is the "industrial center" of Turkey. It employs approximately 20 percent of Turkey's industrial labor and contributes 38 percent of Turkey's industrial workspace. In addition, the city generates 55 percent of Turkey's trade and 45 percent of the country's wholesale trade, and generates 21.2 percent of Turkey's gross national product. Istanbul contributes 40 percent of all taxes collected in Turkey and produces 27.5 percent of Turkey's national product.
Many of Turkey's major manufacturing plants are located in the city. Istanbul and its surrounding province produce cotton, fruit, olive oil, silk, and tobacco. Food processing, textile production, oil products, rubber, metal ware, leather, chemicals, electronics, glass, machinery, paper and paper products, and alcoholic drinks are among the city's major industrial products. The city also has plants that assemble automobiles and trucks.
Pharmaceutical industry started in 1952 with the establishment of "Eczacıbaşı Pharmaceuticals Factory" in Levent, Istanbul.[18] Today, 134 companies operate in the Turkish pharmaceutical industry, a significant part of which is based within or near Istanbul.[19]
Tourism
Istanbul is one of the most important tourism spots of Turkey. There are thousands of hotels and other tourist oriented industries in the city, catering to both vacationers and visiting professionals. In 2006 a total of 23,148,669 tourists visited Turkey, most of whom entered the country through the airports and seaports of Istanbul and Antalya.[20] The total number of tourists who entered Turkey through Atatürk International Airport and Sabiha Gökçen International Airport in Istanbul reached 5,346,658, rising from 4,849,353 in 2005.[21]
Istanbul is also one of the world’s most exciting conference destinations and is an increasingly popular choice for the world’s leading international associations.[22] Istanbul’s conference appeal developed with three separate conference and exhibition areas: The Conference Valley (Istanbul Convention & Exhibition Center, Istanbul Hilton Convention & Exhibition Center, the Military Museum Cultural Center and the Cemal Reşit Rey Concert Hall); The Airport & Exhibition District (150,000 m2 (1.6 m sq ft) of exhibition space around the CNR International Expo Center); and the Business & Financial District (with many distributed centers). These cluster areas feature a combination of accommodations, meeting facilities, and exhibition space. They can be used individually, or collectively through transportation with the Istanbul metro, and are linked together for accommodating events with 10,000 or more participants.
Infrastructure
Health and medicine
- See also: Hospitals
The city has many public and private hospitals, clinics and laboratories within its bounds and numerous medical research centers. Many of these facilities have high technology equipment, which has contributed to the recent upsurge in "medical tourism" to Istanbul,[23] particularly from West European countries like the United Kingdom and Germany where governments send patients with lower income to the city for the relatively inexpensive service of high-tech medical treatment and operations.[24] Istanbul has particularly become a global destination for laser eye surgery and plastic surgery.[25][26][27] The city also has an Army Veterans Hospital in the military medical center.
Pollution-related health problems increase especially in the winter, when the combustion of heating fuels increase. The rising number of new cars in the city and the slow development of public transportation often cause urban smog conditions. Mandatory use of unleaded gas was scheduled to begin only in January 2006.[28]
Nevertheless, air and water pollution created by the numerous factories, motor vehicles and private households as well as noise pollution generated by the immense traffic continue to concern the population of Istanbul. Diseases such as bronchitis and asthma are far more common among the inhabitants of the city's gecekondu areas largely because of the proximity of these poorer, densely populated areas to industry.[citation needed]
Utilities
The first water supply systems which were built in Istanbul date back to the foundation of the city. Two of the greatest aqueducts built in the Roman period are the Mazulkemer Aqueduct and the Valens Aqueduct. These aqueducts were built in order to channel water from the Halkalı area in the western edge of the city to the Beyazıt district in the city center, which was known as the Forum Tauri in the Roman period.[29] After reaching the city center, the water was later collected in the city's numerous cisterns, such as the famous Philoxenos (Binbirdirek) Cistern and the Basilica (Yerebatan) Cistern. Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent commissioned Sinan, his engineer and architect-in-chief, to improve the water needs of the city. Sinan constructed the Kırkçeşme Water Supply System in 1555.[30] In later years, with the aim of responding to the ever-increasing public demand, water from various springs was channeled to the public fountains by means of small supply lines; see German Fountain.
Today, Istanbul has a chlorinated and filtered water supply and a sewage disposal system managed by the government agency ISKI.[31] The current level of facilities are not sufficient enough to meet the rising demand of the growing city. Water supply sometimes becomes a problem, particularly in the summer.
Electricity distribution services are covered by the state-owned TEK. The first electricity production plant in the city, Silahtarağa Termik Santrali, was established in 1914 and continued to supply electricity until 1983.[32]
The Ottoman Ministry of Post and Telegraph was established in the city on October 23, 1840.[33] The first post office was the Postahane-i Amire near the courtyard of Yeni Mosque.[34] In 1876 the first international postal network between Istanbul and the lands beyond the vast Ottoman Empire — which, in that year, stretched from the borders with Austria-Hungary and Russia at north to the Ottoman provinces of Yemen and Sudan at south and Tunisia at west — was established.[35]
Samuel Morse received his first ever patent for the telegraph in 1847, at the old Beylerbeyi Palace (the present Beylerbeyi Palace was built in 1861-1865 on the same location) in Istanbul, which was issued by Sultan Abdülmecid who personally tested the new invention.[36] Following this successful test, installation works of the first telegraph line between Istanbul and Edirne began on August 9, 1847.[37] In 1855 the Telegraph Administration was established.[38] In July 1881 the first telephone circuit in Istanbul was established between the Ministry of Post and Telegraph in Soğukçeşme and the Postahane-i Amire in Yenicami.[39] On October 23, 1986, mobile telephone and paging systems were put into service in Istanbul, Ankara and İzmir. On February 23, 1994, GSM technology was established in the city.[40] A nationwide Internet network and connection with the World Wide Web was established in 1996.[41]
Infrastructure improvements since the mid 1990s include the resolution of the garbage problem, improved traffic conditions and improved air quality due to the increased use of natural gas.[citation needed]
Transportation
Istanbul has two international airports: The larger one is the Atatürk International Airport located in the Yeşilköy district on the European side, about 24 kilometers west from the city center. When it was first built, the airport used to be at the western edge of the metropolitan area but now lies within the city bounds.
The smaller one is the Sabiha Gökçen International Airport located in the Kurtköy district on the Asian side, close to the Istanbul Park GP Racing Circuit. It is situated approximately 20 kilometers east of the Asian side and 45 kilometers east of the European city center.
The Sirkeci Terminal of the Turkish State Railways (TCDD) is the terminus of all the lines on the European side and the main connection node of the Turkish railway network with the rest of Europe. Currently, international connections are provided by the line running between Istanbul and Thessaloniki, Greece, and the Bosporus Express serving daily between Sirkeci and Gara de Nord in Bucharest, Romania. Lines to Sofia, Belgrade, Budapest, and Chişinău are established over the Bosporus Express connection to Bucharest. Sirkeci Terminal was originally opened as the terminus of the Orient Express.
Beyond the Bosporus, the Haydarpaşa Terminal on the Asian side serves lines running several times daily to Ankara, and less frequently to other destinations in Anatolia. The railway networks on the European and Asian sides are currently connected by the train ferry across the Bosporus, which will be replaced by an underwater tunnel connection with the completion of the Marmaray project, scheduled for 2009. Marmaray (Bosporus Rail Tunnel) will also connect the metro lines on the European and Asian parts of the city. Haydarpaşa Terminal was originally opened as the terminus of the Istanbul-Baghdad and Istanbul-Damascus-Medina railways.
Sea transport is vital for Istanbul, as the city is practically surrounded by sea on all sides: the Sea of Marmara, the Golden Horn, the Bosporus and the Black Sea. Many Istanbulers live on the Asian side of the city but work on the European side (or vice-versa) and the city's famous commuter ferries form the backbone of the daily transition between the two parts of the city - even more so than the two suspension bridges which span the Bosporus.
The port of Istanbul is the most important one in the country. The old port on the Golden Horn serves primarily for personal navigation, while Karaköy port in Galata is used by the large cruise liners. Istanbul Modern, the city's largest museum and gallery of modern arts, is located close to Karaköy port. Regular services as well as cruises from both Karaköy and Eminönü exist to several ports such as Pireaus (Greece) and the Greek islands, Dubrovnik (Croatia), Venice, Naples (Italy), Marseille (France), and Haifa (Israel) in the Mediterranean Sea, and also Odessa (Ukraine) in the Black Sea.
- Tünel Istanbul.jpg
Istanbul's Tünel (1875) is the world's second-oldest subway line after London's Underground
- Sirkeci-station Orient Express.JPG
Sirkeci Terminal was opened in 1890 as the terminus of the Orient Express
- Haydarpasha train station istanbul.jpg
Haydarpaşa Terminal was opened in 1908 as the terminus of the Istanbul-Baghdad and Istanbul-Medina railways
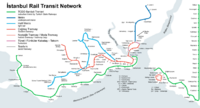
- Istanbulmetros.jpg
Istanbul Metro
Life in the city
Cultural activity, tourism and commerce are expected to remain important in the life of the city. However, major challenges loom ahead, such as demographic growth, traffic congestion, disorganized housing construction, the restoration of historic buildings and the planning of a 3rd motorway transition through the Bosporus. Daily life in Istanbul is colorful and vibrant and continues to bustle side by side with many carefully protected Roman, Byzantine and Ottoman monuments. Istanbul is often considered the capital of Turkey in terms of commerce, entertainment, culture, education, shopping, tourism and art. More than half of the population lives and works on the European side. The large number of people living in the residential areas on the Anatolian side use bridges and ferries to commute to work in a city that has been one of the most popular destinations for voyagers throughout history.
Art & Culture
Istanbul is becoming increasingly colorful in terms of its rich social, cultural, and commercial activities. While world famous pop stars fill stadiums, activities like opera, ballet and theater continue throughout the year. During seasonal festivals, world famous orchestras, chorale ensembles, concerts and jazz legends can be found often playing to a full house.

Istanbul Archaeology Museum, established in 1881, is one of the largest and most famous museums of its kind in the world. The museum contains more than 1,000,000 archaeological pieces from the Mediterranean basin, the Balkans, the Middle East, North Africa and Central Asia.
A significant culture has been developed around what is known as a Turkish Bath (Hamam), the origins of which can be traced back to the ancient Roman Bath, which was a part of the Byzantine lifestyle and customs that were inherited first by the Seljuk Turks and later the Ottomans, who developed it into something more elaborate.
Media
The first Turkish newspaper, Takvim-i Vekayi, was printed on 1 August 1831 in the Bâbıâli (Bâb-ı Âli, meaning The Sublime Porte) district. Bâbıâli became the main center for print media. Istanbul is also the printing capital of Turkey with a wide variety of domestic and foreign periodicals expressing diverse views, and domestic newspapers are extremely competitive. Most nationwide newspapers are based in Istanbul, with simultaneous Ankara and İzmir editions.[42] There are also numerous local and national TV and radio stations located in Istanbul.
Education
- Further information: Education in Turkey
Universities
Istanbul holds some of the finest institutions of higher education in Turkey, including a number of public and private universities. Most of the reputable universities are public, but in recent years there has also been an upsurge in the number of private universities. Istanbul University (1453) is the oldest Turkish educational institution in the city, while Istanbul Technical University (1773) is the world's second-oldest technical university dedicated entirely to engineering sciences. Other prominent state universities in Istanbul are the Boğaziçi University (1863), Mimar Sinan University of Fine Arts (1882), Marmara University (1883), Yıldız Technical University (1911) and Galatasaray University (1992).
Almost all Turkish private high schools and universities in Istanbul teach in English, German or French as the primary foreign language, usually accompanied by a secondary foreign language.
Libraries
There are many libraries in Istanbul. For the complete list, see the list of libraries in Istanbul.
Sports
The first modern sports club established during the late Ottoman period was Beşiktaş Jimnastik Kulübü (1903). Beşiktaş JK was followed by Galatasaray SK (1905) and Fenerbahçe SK (1907). Galatasaray became the first Turkish football club to win European titles (the UEFA Cup and UEFA Super Cup of 2000). At present, Galatasaray is also the Turkish team with the most Turkish Super League titles (16) along with Fenerbahçe (16); followed by Beşiktaş (12) and Trabzonspor (6).
The Atatürk Olympic Stadium is a five-star UEFA stadium and a first-class venue for track and field, having reached the highest required standards set by the International Olympic Committee and sports federations such as the IAAF, FIFA and UEFA. The stadium hosted the 2005 UEFA Champions League Final. The Şükrü Saracoğlu Stadium will host the 2009 UEFA Cup Final.
Sports like football, basketball and volleyball are very popular in the city. In addition to Fenerbahçe, Galatasaray and Beşiktaş, which field teams in multiple sports, several other clubs have also excelled in particular team sports; such as Efes Pilsen and Fenerbahçe Ülker in basketball; or Eczacıbaşı and Vakıfbank in volleyball. Efes Pilsen basketball team won the first ever European title by a Turkish club in any team sport (Korac Cup of 1996).
Istanbul hosts several annual motorsports events, such as the Formula One Turkish Grand Prix, the MotoGP Grand Prix of Turkey, the FIA World Touring Car Championship, the GP2 and the Le Mans Series 1000 km races at the Istanbul Park GP Racing Circuit.
Notes
- ↑ World Gazetteer - Istanbul
- ↑ R. Krautheimer, "Three Christian Capitals: Topography and Politics." Berkeley, 1983
- ↑ Stanford and Ezel Shaw (1977): History of the Ottoman Empire and Modern Turkey. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Vol II, p. 386; Robinson (1965), The First Turkish Republic, p. 298
- ↑ "Istanbul advised to brace for major quake", Environmental News Network via CNN, 2000-04-28. Retrieved 2006-08-20.
- ↑ Heightened odds of large earthquakes near Istanbul: An interaction-based probability calculation. Science (2000).
- ↑ Kinross, P., 2002. The Ottoman Centuries: The Rise and Fall of the Turkish Empire. Perrenial p.117
- ↑ Crime Takes a Vacation (Yours); Istanbul: Plenty of pickpockets, and sobering bar bills. The New York Times Company. Retrieved 2007-01-16.
- ↑ Travel to Turkey. U.S. Department of State Bureau of Consular Affairs. Retrieved 2007-01-16.
- ↑ 2004 OSAC Crime and Safety Report for Istanbul. Overseas Security Advisory Council • Bureau of Diplomatic Security U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 2007-01-16.
- ↑ PriceWaterhouseCoopers: U.K. Economic Outlook and Global City GDP Ranking 2005-2020 Full Report (PDF)
- ↑ PriceWaterhouseCoopers: Global City GDP Rankings 2005-2020 Press Release
- ↑ Hürriyet: İstanbul 133 milyar dolarlık oldu dünyanın 34’üncü zengini çıktı
- ↑ CNN Türk: Dış ticaretin lokomotifi İstanbul (Istanbul is the locomotive of foreign trade)
- ↑ State Statistics Institute of the Republic of Turkey: Statistics of Foreign Trade (1923-2006)
- ↑ İstanbul Büyükşehir Belediyesi Resmi Web Sitesi. Istanbul Metropolitan Municipality (IMMWEBl). Retrieved 2007-01-01.
- ↑ Financial sector (PDF). Foreign Economic Relations Board Turkey DEIK. Retrieved 2007-01-01.
- ↑ World Gold Council > jewellery:Turkey. World Gold Council. Retrieved 2007-01-01.
- ↑ Baytop T. Türk Eczacılık Tarihi Araştırmaları (History of Turkish Pharmacy Researches) Istanbul. 2000:12-75.
- ↑ Dogan UVEY*, Ayse Nur GOKCE*, Ibrahim BASAGAOGLU (2004) "Pharmaceutical Industry in Turkey" in 38th International Medical History Congress in Istanbul
- ↑ Hürriyet: 2006’da Türkiye’ye gelen turist başına harcama 728 dolara indi
- ↑ Sabah: Turist sayısı genelde düştü İstanbul'da arttı
- ↑ EIBTM 2007 - The Global Meetings & Incentive Exhibition for the MICE Industry. Reed Exhibitions Limited (member of the Association of Event Organisers (AEO)). Retrieved 2006-03-11.
- ↑ Med Retreat - Medical Tourism: Turkey
- ↑ BBC News - Health - Personal story: IVF in Istanbul
- ↑ LASIK: Laser Eye Surgery in Istanbul
- ↑ Med-Istanbul: Laser Eye Surgery in Istanbul
- ↑ Plastic Surgery in Turkey
- ↑ CIA — The World Factbook. CIA. Retrieved 2006-03-11.
- ↑ İSKİ İstanbul Su ve Kanalizasyon İdaresi: Tarihce. Istanbul water and sewerage administration (history). Retrieved 2006-03-11.
- ↑ İSKİ İstanbul Su ve Kanalizasyon İdaresi: Tarihce. Istanbul water and sewerage administration (history). Retrieved 2006-03-11.
- ↑ İSKİ Administration. Istanbul water and sewerage administration. Retrieved 2006-03-11.
- ↑ Vikipedi: Türkiye'nin Elektriği
- ↑ Vikipedi: PTT
- ↑ Vikipedi: PTT
- ↑ Vikipedi: PTT
- ↑ Istanbul City Guide: Beylerbeyi Palace
- ↑ Türk Telekom: History
- ↑ Vikipedi: PTT
- ↑ Türk Telekom: History
- ↑ Türk Telekom: History
- ↑ Türk Telekom: History
- ↑ CIA — The World Factbook. CIA. Retrieved 2006-03-11.
External links
- İstanbul City Camera
- Istanbul Governor's Office
- Municipality of Greater Istanbul
- Where to go in Istanbul
- Travel guide to Istanbul from Wikitravel
- WikiSatellite view of Istanbul at WikiMapia
- Emporis: Istanbul image gallery
- Emporis: Famous buildings of Istanbul
- Emporis: Highrise buildings of Istanbul
- Emporis: Other important structures of Istanbul
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.