Harare, Zimbabwe
Mike Butler (talk | contribs) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (44 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Images OK}}{{epname|Harare, Zimbabwe}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}}{{copyedited}} | ||
{{Infobox Settlement | {{Infobox Settlement | ||
| − | <!--See Template:Infobox | + | <!--See Template:Infobox settlement for additional fields that may be available—> |
| − | <!--See the Table at Infobox | + | <!--See the Table at Infobox settlement for all fields and descriptions of usage—> |
<!-- Basic info —> | <!-- Basic info —> | ||
| − | |official_name =Harare | + | |official_name =Harare |
| − | + | |native_name =(Salisbury) | |
| − | |native_name = | + | |nickname =<br />Sunshine City, H Town |
| − | |nickname =H Town | ||
|settlement_type =City | |settlement_type =City | ||
| − | |motto =Pamberi | + | |motto =Pamberi Nekushandira Vanhu ''(Forward with Service to the People)'' |
|translit_lang1= | |translit_lang1= | ||
|translit_lang1_type= | |translit_lang1_type= | ||
|translit_lang1_info= | |translit_lang1_info= | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<!-- images and maps -----------> | <!-- images and maps -----------> | ||
|image_skyline =Harare from the Kopje.jpg | |image_skyline =Harare from the Kopje.jpg | ||
| Line 63: | Line 35: | ||
|dot_map_caption = | |dot_map_caption = | ||
|dot_x = |dot_y = | |dot_x = |dot_y = | ||
| + | |pushpin_map = | ||
| + | |pushpin_map_caption = | ||
| + | |pushpin_label_position = none <!-- the position of the pushpin label: left, right, top, bottom, none —> | ||
<!-- Location ------------------> | <!-- Location ------------------> | ||
| + | |coordinates_region =ZW | ||
|subdivision_type =Country | |subdivision_type =Country | ||
|subdivision_name =[[Zimbabwe]] | |subdivision_name =[[Zimbabwe]] | ||
|subdivision_type1 =[[Provinces of Zimbabwe|Province]] | |subdivision_type1 =[[Provinces of Zimbabwe|Province]] | ||
| − | |subdivision_name1 = | + | |subdivision_name1 =Harare |
|subdivision_type2 = | |subdivision_type2 = | ||
|subdivision_name2 = | |subdivision_name2 = | ||
| Line 78: | Line 54: | ||
|government_type = | |government_type = | ||
|leader_title =[[Mayor of Harare|Mayor]] | |leader_title =[[Mayor of Harare|Mayor]] | ||
| − | |leader_name =[[Muchadeyi Masunda]] | + | |leader_name =[[Muchadeyi Masunda]] |
|leader_title1 =<!-- for places with, say, both a mayor and a city manager —> | |leader_title1 =<!-- for places with, say, both a mayor and a city manager —> | ||
|leader_name1 = | |leader_name1 = | ||
| Line 87: | Line 63: | ||
|leader_title4 = | |leader_title4 = | ||
|leader_name4 = | |leader_name4 = | ||
| − | |established_title =Founded | + | |established_title =Founded as Fort Salisbury |
|established_date =1890 | |established_date =1890 | ||
| − | |established_title2 =<!-- | + | |established_title2 =<!-- was never incorporated as a town —>Incorporated (city) |
| − | |established_date2 = | + | |established_date2 =1935 |
| − | |established_title3 = | + | |established_title3 =Renamed to Harare |
| − | |established_date3 = | + | |established_date3 =1982 |
<!-- Area ---------------------> | <!-- Area ---------------------> | ||
|area_magnitude = | |area_magnitude = | ||
|unit_pref =<!--Enter: Imperial, if Imperial (metric) is desired—> | |unit_pref =<!--Enter: Imperial, if Imperial (metric) is desired—> | ||
|area_footnotes = | |area_footnotes = | ||
| − | |area_total_km2 | + | |area_total_km2 =960.6 |
| − | |area_land_km2 =<!--See table @ Template:Infobox | + | |area_land_km2 =<!--See table @ Template:Infobox settlement for details on automatic unit conversion—> |
|area_water_km2 = | |area_water_km2 = | ||
|area_total_sq_mi = | |area_total_sq_mi = | ||
| Line 112: | Line 88: | ||
|area_blank1_sq_mi = | |area_blank1_sq_mi = | ||
<!-- Population -----------------------> | <!-- Population -----------------------> | ||
| − | |population_as_of = | + | |population_as_of =2009 |
|population_footnotes = | |population_footnotes = | ||
|population_note =estimated | |population_note =estimated | ||
| − | |population_total = | + | |population_total =1,606,000 |
| − | |population_density_km2 = | + | |population_density_km2 =2540 |
| − | |population_density_sq_mi = | + | |population_density_sq_mi =4330 |
|population_metro = | |population_metro = | ||
|population_density_metro_km2 = | |population_density_metro_km2 = | ||
|population_density_metro_sq_mi = | |population_density_metro_sq_mi = | ||
| − | |population_urban = | + | |population_urban =2,800,111 |
|population_density_urban_km2 = | |population_density_urban_km2 = | ||
|population_density_urban_sq_mi = | |population_density_urban_sq_mi = | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<!-- General information —> | <!-- General information —> | ||
| − | |timezone=[[Central African Time|CAT]] | + | |timezone=[[Central African Time|CAT]] |
|utc_offset=+2 | |utc_offset=+2 | ||
| − | |timezone_DST= | + | |timezone_DST= |
| − | |utc_offset_DST= | + | |utc_offset_DST= |
| − | |latd= 17|latm= | + | |latd= 17|latm=52|latNS=S |
| − | |longd= 31|longm= | + | |longd= 31|longm= 2|longEW=E|coordinates_display=d |
| − | |elevation_footnotes = | + | |elevation_footnotes = |
|elevation_m =1490 | |elevation_m =1490 | ||
|elevation_ft = | |elevation_ft = | ||
| Line 141: | Line 113: | ||
|postal_code_type =<!-- enter ZIP code, Postcode, Post code, Postal code... —> | |postal_code_type =<!-- enter ZIP code, Postcode, Post code, Postal code... —> | ||
|postal_code = | |postal_code = | ||
| − | |area_code = | + | |area_code =4 |
|twin1 =[[Nottingham]] | |twin1 =[[Nottingham]] | ||
|twin1_country =[[United Kingdom]] | |twin1_country =[[United Kingdom]] | ||
| Line 150: | Line 122: | ||
|twin4 =[[Prato]] | |twin4 =[[Prato]] | ||
|twin4_country =[[Italy]] | |twin4_country =[[Italy]] | ||
| − | |twin5 =[[Lago]] | + | |twin5 =[[Lago, Calabria|Lago]] |
|twin5_country =[[Italy]] | |twin5_country =[[Italy]] | ||
|twin6 = | |twin6 = | ||
| Line 158: | Line 130: | ||
|blank_name = | |blank_name = | ||
|blank_info = | |blank_info = | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|website =http://www.hararecity.co.zw | |website =http://www.hararecity.co.zw | ||
| − | |footnotes = | + | |footnotes =Dialling code 4 (or 04 from within Zimbabwe) |
| − | }} | + | }} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Harare''' (formerly '''Salisbury''') is the [[Capital (political)|capital]] of [[Zimbabwe]]. It lies in the northeastern part of the country at an elevation of 1,483 meters (4,865 feet), and has a warm temperate climate. Administratively, Harare is an independent city equivalent to a province. | |
| − | Numerous suburbs surround the city, retaining the names colonial administrators gave them during the | + | A modern, well-planned [[city]] with multi-storied buildings and tree-lined avenues, Harare is Zimbabwe's largest city, as well as its administrative, commercial, manufacturing, [[communications]], and [[education]] center. It serves as a distribution point for the surrounding [[agriculture|agricultural]] and [[gold]]-mining areas. Numerous suburbs surround the city, retaining the same names colonial administrators gave them during the nineteenth century, such as Warren Park "D," Borrowdale, Mount Pleasant, Marlborough, Tynwald, and Avondale. |
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | While Harare is modern and well-planned and plays an essential role within Zimbabwe, it must also resolve the problems found within the nation. These include the highest mortality rate among all [[Africa]]n nations and very high incidences of [[HIV]]/[[AIDS]] infection. Zimbabwe has the highest literacy rate of all African nations with a strong foundation of [[education]] and abundance of [[natural resource]]s, all of which are assets that can be used toward the nation's progress and prosperity. | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| − | [[Image:Harare district.png|thumb|left| | + | [[Image:Harare district.png|thumb|left|225px|Harare district]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
The name ''Harare'' derives from the [[Shona people|Shona]] chieftain Neharawa, who with his people occupied the area known as the Kopje (pronounced "Koppie"), near where the commercial area developed. Before independence, "Harare" was the name of the Black residential area now known as Mbare. | The name ''Harare'' derives from the [[Shona people|Shona]] chieftain Neharawa, who with his people occupied the area known as the Kopje (pronounced "Koppie"), near where the commercial area developed. Before independence, "Harare" was the name of the Black residential area now known as Mbare. | ||
| − | Harare is situated in the northeastern part of [[Zimbabwe]] in the uplands at an elevation of | + | Harare is situated in the northeastern part of [[Zimbabwe]] in the uplands at an elevation of 1,483 meters (4,865 feet). |
| − | Harare has a warm temperate climate. | + | Harare has a warm temperate [[climate]]. Its high altitude and the prevalence of a cool south-easterly airflow maintains temperatures that are rather low for the tropics. The average maximum daytime temperature in January (midsummer) is 77°F (25°C), dropping to an average maximum of around 68°F (20°C) in July. There are three main seasons--a warm, wet season from November to March/April; a cool, dry season from May to August (corresponding to the [[Southern Hemisphere]] winter); and a hot, dry season in September/October. The average annual rainfall is about 32.4 inches (825 mm) in the southwest rising to 33.6 inches (855 mm) on the higher land in the northeast. |
| − | The climate supports a natural vegetation of open woodland. The most common tree of the local region is the Msasa [[Brachystegia spiciformis]] that | + | The climate supports a natural vegetation of open woodland. The most common [[tree]] of the local region is the Msasa [[Brachystegia spiciformis]] that colors the landscape wine-red with its new leaves in late August. An introduced tree that contributes most to the town's atmosphere is the [[Jacaranda]] (a South American species) that produces a burst of lilac when it blooms in September. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
[[Image:Matabeleland.png|thumb|right|250px|[[Matabeleland]] in the 1800s.]] | [[Image:Matabeleland.png|thumb|right|250px|[[Matabeleland]] in the 1800s.]] | ||
[[Image:Salisbury in 1930.jpg|right|thumb|250px|Salisbury in 1930.]] | [[Image:Salisbury in 1930.jpg|right|thumb|250px|Salisbury in 1930.]] | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Jacaranda trees in Montagu Ave, Harare, Zimbabwe in 1975.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Jacaranda trees in Montagu Ave, Harare, in 1975.]] |
[[Image:Mugabecloseup2008.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Robert Mugabe in 2008.]] | [[Image:Mugabecloseup2008.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Robert Mugabe in 2008.]] | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Harare.jpg|thumb|250px|Downtown Harare.]] | |
| + | [[Iron Age]] [[Bantu]]-speaking peoples began migrating into the area known as [[Zimbabwe]] perhaps as far back as two thousand years ago, including the ancestors of the [[Shona]], who account for roughly four-fifths of the country's population today. | ||
| − | From | + | From 1250 to 1629, the [[Mutapa Empire]], which stretched between the [[Zambezi River|Zambezi]] and [[Limpopo River]]s of [[Southern Africa]] in the modern states of Zimbabwe and [[Mozambique]], traded [[gold]], [[ivory]], and [[copper]] for [[cloth]] and [[glass]] with [[Islam|Muslim]] merchants on the [[Indian Ocean]] coast. |
| − | In 1834, the [[Ndebele people (Zimbabwe)|Ndebele people]] arrived while fleeing from the [[Zulu]] leader [[Shaka]], making the area their new empire, [[Matabeleland]]. In 1837- | + | From c. 1250–1629, the area that was to became Zimbabwe was ruled under the [[Mutapa Empire]], which was renowned for its gold trade with the [[Arab]]s. The Mutapa Empire founders were culturally and politically related to the builders who constructed Great Zimbabwe, the name given to hundreds of great stone ruins spread out over a 200 square mile (500 km²) area within the modern-day country of Zimbabwe. |
| + | |||
| + | The [[Portugal|Portuguese]] dominated much of southeast [[Africa]]'s coast by 1515, seeking to dominate the trade with [[India]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 1834, the [[Ndebele people (Zimbabwe)|Ndebele people]] arrived from south of the Limpopo River while fleeing from the [[Zulu]] leader [[Shaka]] (1787–1828), making the area their new empire, [[Matabeleland]]. In 1837-1838, the Ndebele conquered the Shona, and forced them to pay tribute and to concentrate in northern Zimbabwe. | ||
In the 1880s, the [[British South Africa Company]], owned by English-born businessman, mining magnate, and politician [[Cecil Rhodes]] (1853–1902), arrived in the area. | In the 1880s, the [[British South Africa Company]], owned by English-born businessman, mining magnate, and politician [[Cecil Rhodes]] (1853–1902), arrived in the area. | ||
| − | In 1890, the city was founded as a fort at the spot where the British South Africa Company’s Pioneer Column, a military volunteer force of settlers | + | In 1890, the city was founded as a fort at the spot where the British South Africa Company’s Pioneer Column, a military volunteer force of settlers organized by Rhodes, halted its march into [[Mashonaland]], a region in northern [[Zimbabwe]], the home of the Shona people. |
| − | The city was originally named Fort Salisbury after | + | The city was originally named Fort Salisbury after [[Robert Arthur Talbot Gascoyne-Cecil]], the Third Marquess of Salisbury, who was then [[British prime minister]], and it subsequently became known simply as Salisbury. |
| − | At that time, the area was poorly drained and earliest development was on sloping ground along the left bank of a stream that became | + | At that time, the area was poorly drained and its earliest development was on sloping ground along the left bank of a [[stream]] that became a trunk road (Julius Nyerere Way). The first area to be drained, near the head of the stream, was named Causeway, and became the site of the most important Government buildings, including the Senate House and the Office of the Prime Minister (renamed for the use of President Mugabe.) |
| − | In 1898, the name Southern Rhodesia was adopted. <ref name="conquered">[http://www.worldtrek.org/odyssey/africa/062699/062699monicabula.html So Who Was Shaka Zulu- Really?] | + | Salisbury was declared a municipality in 1897. In 1898, the name Southern Rhodesia was adopted for the territory.<ref name="conquered">Africa Stage, [http://www.worldtrek.org/odyssey/africa/062699/062699monicabula.html So Who Was Shaka Zulu--Really?] Retrieved November 30, 2008.</ref> When the [[railway]] arrived from Beira (Mozambique) in 1899, the town developed as a trading center. |
| − | + | The [[United Kingdom]] annexed Southern Rhodesia from the British South Africa Company in 1923, and Salisbury became the capital of the British colony. It became a city in 1935. | |
| − | + | Industrialization during [[World War II]] and after attracted an influx of migrants. | |
| − | + | The city was the capital of the [[Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland]] from 1953 to 1963, and from then was the capital of [[Southern Rhodesia]]. | |
| − | + | A 1961 constitution was formulated that favored whites in power. The government of [[Ian Smith]] (1919–2007) declared [[Rhodesia]] independent of [[Great Britain]] on November 11, 1965. The [[United Kingdom]] did not recognize the act and demanded more complete voting rights for the black African majority in the country. | |
| + | |||
| + | [[United Nations]] sanctions and a [[guerrilla war|guerrilla]] uprising led to free elections in 1979, and independence as the [[Republic of Zimbabwe]] in 1980. [[Robert Mugabe]] (b. 1924), a former schoolteacher whose goal was to replace white minority-rule with a one-party [[Marxism|Marxist]] regime, became the nation's first prime minister, and remained the country's only ruler, as president since 1987. | ||
The capital city retained the name Salisbury until April 18, 1982, the second anniversary of Zimbabwean independence, when it was changed to Harare. | The capital city retained the name Salisbury until April 18, 1982, the second anniversary of Zimbabwean independence, when it was changed to Harare. | ||
| Line 229: | Line 191: | ||
Mugabe's chaotic land redistribution campaign, which began in 2000, caused an exodus of white farmers, crippled the economy, and ushered in widespread shortages of basic commodities. | Mugabe's chaotic land redistribution campaign, which began in 2000, caused an exodus of white farmers, crippled the economy, and ushered in widespread shortages of basic commodities. | ||
| − | Ignoring international condemnation, Mugabe rigged the 2002 presidential election to ensure his | + | Ignoring international condemnation, Mugabe rigged the 2002 presidential election to ensure his re-election. The ruling ZANU-PF party used fraud and intimidation to win a two-thirds majority in the March 2005 parliamentary election, allowing it to amend the constitution at will and recreate the Senate, which had been abolished in the late 1980s. |
| − | In April 2005, Harare embarked on Operation Restore Order, ostensibly an urban rationalization program, which resulted in the destruction of the homes or businesses of 700,000 mostly poor supporters of the opposition. This caused a sharp reaction in the international community because it took place without | + | In April 2005, Harare embarked on Operation Restore Order, ostensibly an urban rationalization program, which resulted in the destruction of the homes or businesses of 700,000 mostly poor supporters of the opposition. This caused a sharp reaction in the international community because it took place without warning and no plans were made to provide alternative housing. |
| − | This was followed by [[Operation Chikerema]] (Operation "Better Living") a year later which consisted of building concrete housing. Critics | + | This was followed by [[Operation Chikerema]] (Operation "Better Living") a year later which consisted of building concrete housing. Critics stated that these were inadequate citing the lack of [[electricity]], [[plumbing]] or other [[infrastructure]] in poorly accessible areas. |
| − | Mugabe in June 2007 instituted price controls on all basic commodities causing panic buying and leaving store shelves empty for months. | + | Mugabe, in June 2007, instituted price controls on all basic commodities causing panic buying and leaving store shelves empty for months. |
| − | + | The political and economic crisis plaguing [[Zimbabwe]] has harmed Harare. A government-appointed commission replaced the elected council for alleged inefficiency, although essential services such as rubbish collection and street repairs have rapidly worsened, and are now virtually non-existent. In May 2006, the Zimbabwean newspaper the Financial Gazette described the city as a "sunshine city-turned-sewage farm."<ref>Charles Rukuni Bulawayo, May 17, 2006, [http://www.zimbabwesituation.com/may19_2006.html#Z13 Zimbabwe: It's Chombo's Fault,] ''Financial Gazette.'' Retrieved November 30, 2008.</ref> | |
| + | |||
| + | General elections held in March 2008 contained irregularities but still amounted to a censure of the ZANU-PF-led government with significant gains in opposition seats in parliament. Movement For Democratic Change opposition leader [[Morgan Tsvangirai]] (b. 1952) won the presidential polls, and may have won an outright majority, but official results did not reflect this. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the lead up to a run-off election in late June 2008, considerable violence enacted against opposition party members led to the withdrawal of Tsvangirai from the ballot. Extensive evidence of vote tampering and ballot-box stuffing resulted in international condemnation of the process, and calls for the creation of a power-sharing government have been ignored. | ||
==Government== | ==Government== | ||
[[Image:Harare Downtown1.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Along parliament buildings.]] | [[Image:Harare Downtown1.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Along parliament buildings.]] | ||
| − | [[Zimbabwe]] is a parliamentary democracy in which the president, who is both the chief of state and head of government, is elected by popular vote for a five-year term, and has no term limits. The bicameral parliament consists of a Senate of 93 members | + | [[Zimbabwe]] is a parliamentary democracy in which the president, who is both the chief of state and head of government, is elected by popular vote for a five-year term, and has no term limits. The bicameral parliament consists of a Senate of 93 members, and a House of Assembly of 210 members. |
| − | Zimbabwe is divided into eight provinces and two cities with provincial status. | + | Zimbabwe is divided into eight provinces and two cities with provincial status. These are territorial divisions for the purposes of administrative, political and geographical demarcation. The provinces are subdivided into 59 districts and 1200 municipalities. |
Administratively, Harare is an independent city equivalent to a province. | Administratively, Harare is an independent city equivalent to a province. | ||
| − | Harare has been the location of several international summits such as the Eighth Summit of the Non-Aligned Movement (1986) and [[Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting]] (1991). The latter produced the [[Harare Declaration]], dictating the membership criteria of the Commonwealth. In 1995, Harare hosted most of the Sixth [[All-Africa Games]], sharing the event with other Zimbabwean cities such as [[Bulawayo]] and [[Chitungwiza]]. | + | Harare has been the location of several international summits such as the Eighth Summit of the [[Non-Aligned Movement]] (1986) and [[Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting]] (1991). The latter produced the [[Harare Declaration]], dictating the membership criteria of the Commonwealth. In 1995, Harare hosted most of the Sixth [[All-Africa Games]], sharing the event with other Zimbabwean cities such as [[Bulawayo]] and [[Chitungwiza]]. |
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
| Line 253: | Line 219: | ||
[[Image:Harare International Ariport.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Harare International Airport.]] | [[Image:Harare International Ariport.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Harare International Airport.]] | ||
[[Image:Harare anglicanchurch.JPG|thumb|right|250px|Anglican cathedral.]] | [[Image:Harare anglicanchurch.JPG|thumb|right|250px|Anglican cathedral.]] | ||
| − | The government of Zimbabwe in 2008 struggled with an unsustainable fiscal deficit, an overvalued official exchange rate, hyperinflation, and bare store shelves. Its 1998-2002 involvement in the war in the [[Democratic Republic of the Congo]] drained hundreds of millions of dollars from the economy. The government's land reform program, characterized by chaos and violence, has badly damaged the commercial farming sector, the traditional source of exports and foreign exchange and the provider of 400,000 jobs, turning Zimbabwe into a net importer of food products. | + | The government of Zimbabwe in 2008 struggled with an unsustainable fiscal deficit, an overvalued official exchange rate, hyperinflation, and bare store shelves. Its 1998-2002, involvement in the war in the [[Democratic Republic of the Congo]] drained hundreds of millions of dollars from the economy. The government's land reform program, characterized by chaos and violence, has badly damaged the commercial [[agriculture|farming]] sector, the traditional source of exports and foreign exchange and the provider of 400,000 jobs, turning [[Zimbabwe]] into a net importer of food products. |
| − | The [[European Union]] and the [[United States]] provide food aid on humanitarian grounds. Badly needed support from the International Monetary Fund had been suspended because of the government's arrears on past loans and the government's unwillingness to enact reforms that would stabilize the economy | + | The [[European Union]] and the [[United States]] provide food aid on humanitarian grounds. Badly needed support from the [[International Monetary Fund]] had been suspended because of the government's arrears on past loans and the government's unwillingness to enact reforms that would stabilize the economy. |
| − | Due to the unstable economic conditions and failure to control inflation, economists have suggested that the Reserve Bank be reformed | + | The Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe routinely prints money to fund the budget deficit, causing the official annual inflation rate to rise from 32 percent in 1998, to 133 percent in 2004, 585 percent in 2005, passed 1,000 percent in 2006, and 26,000 percent in November 2007. Due to the unstable economic conditions and failure to control inflation, economists have suggested that the Reserve Bank be reformed. |
Zimbabwe's per capita GDP was estimated at $200 in 2007. | Zimbabwe's per capita GDP was estimated at $200 in 2007. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Harare is Zimbabwe's largest [[city]], as well as its administrative, commercial, manufacturing, [[communications]], and [[education]]al center, and serves as a distribution point for the surrounding agricultural and [[gold]]-mining areas. | ||
| − | + | The city is a trade center for [[tobacco]], [[maize]], [[cotton]], and [[citrus]] [[fruit]]s. Manufactures include [[textile]]s, [[steel]], and [[chemical industry|chemicals]]. Factories produce processed food, beverages, [[clothing]], [[cigarette]]s, building materials, and [[plastic]]s. Gold is [[Mining|mined]] in the area. | |
| − | Harare is a hub of rail, road, and air transport in [[Zimbabwe]]. The public transport system of buses, run by [[ZUPCO]] crumbled in the first decade of the | + | Harare is a hub of rail, road, and air transport in [[Zimbabwe]]. The public transport system of buses, run by [[ZUPCO]] crumbled in the first decade of the twenty-first century. Privately owned companies that operate commuter omnibuses proliferated. With a fuel crisis, the government introduced commuter trains in order to ease transport shortages. The [[National Railways of Zimbabwe]] operates a daily overnight passenger train service from Harare to [[Mutare]] and another one to [[Bulawayo]]. [[Harare International Airport]] is Zimbabwe's main airport. |
| − | With | ||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
| − | + | Harare had an estimated population of 1,600,000, with 2,800,000 in its [[metropolitan area]] in 2006. There has been an increasing flow of Zimbabweans into [[South Africa]] and [[Botswana]] in search of better economic opportunities. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Black Africans make up 98 percent of Zimbabwe's population. [[Shona]] comprise 82 percent; [[Ndebele]] 14 percent; other two percent; mixed and [[Asia]]n one percent; and white, fewer than one percent. | |
| − | + | [[English language|English]] is the official [[language]], while [[Shona]], [[Sindebele]] (the language of the [[Ndebele]]), and numerous but minor tribal dialects, are spoken. | |
| − | + | About half of Zimbabwe's population follow syncretic [[religion]]s which are part [[Christian]], part indigenous beliefs. Christians make up 25 percent, those following indigenous beliefs 24 percent, [[Muslim]] and other, one percent. | |
| − | + | Harare is the site of the [[University of Zimbabwe]], the largest and most complete institution of higher learning in the nation, about three miles (five kilometers) north of the city. It was founded through a special relationship with the [[University of London]] and it opened its doors to its first students in 1952. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Places of interest== | |
| + | [[Image:Eastgate Centre, Harare, Zimbabwe.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The pink-hued Eastgate Centre, with its distinctive chimneys.]] | ||
| + | Places of interest include the Queen Victoria Museum, which has zoological and historical exhibits, the Anglican and Roman Catholic cathedrals, as well as: | ||
| + | * The Eastgate Centre, which is a shopping center and office block in central Harare, that is designed to be ventilated and cooled by entirely natural means, it was probably the first building in the world to use natural cooling to this level of sophistication. It opened in 1996 on Rubert Mugabe Ave and Second Street. | ||
* The National Gallery of Zimbabwe, which has a collection of European paintings as well as traditional and contemporary African art. | * The National Gallery of Zimbabwe, which has a collection of European paintings as well as traditional and contemporary African art. | ||
| − | * Mushandirapamwe Hotel, which is a hotel at [[Machipisa Shopping Centre]] in | + | * Mushandirapamwe Hotel, which is a hotel at [[Machipisa Shopping Centre]] in the Highfield district. It is owned by the Tawengwa family, sons of [[George Tawengwa]], a prominent Zimbabwean businessman who was the first black person to buy a farm in 1960. |
| − | * Rufaro Stadium, which is a multi-use [[stadium | + | * Harvest House, which is a six story building in Harare, located at 44 Nelson Mandela Ave and Angwa Street, and serves as the National Headquarters of the Movement for Democratic Change party. |
| − | + | * Sam Nujoma Street, which is one of the main streets of the city, was originally called Second Street, but this was changed to Sam Nujoma Street after [[Sam Nujoma]], a former president of [[Namibia]]. | |
| − | + | * Rufaro Stadium, which is a multi-use [[stadium]], used mostly for [[football (soccer)|football]] matches, and has a capacity of 35,000 people. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Looking to the future== |
| − | + | Harare is [[Zimbabwe]]'s capital and largest [[city]], as well as its administrative, commercial, manufacturing, [[communications]], and [[education]]al center. Along with the country, Harare's fortunes rise and fall with the successes and failures of its government. In 2008, Zimbabwe had an unpopular government that seemed powerless when dealing with the nation's problems. However, there is a strong foundation in education as well as abundant [[natural resources]], both of which can propel future prosperity. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Notes== | |
| − | + | <references/> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | ||
| − | < | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | + | * "Commentary—Suicidal Violence—Daily News, Harare." 2003. ''World Press Review.'' 50 (6): 46. ISSN 0195-8895 | |
| − | + | * Horn, Nancy E. 1994. ''Cultivating Customers: Market Women in Harare, Zimbabwe. Women and Change in the Developing World.'' Boulder, CC: Lynne Rienner Publishers. ISBN 9781555874728. | |
| − | + | * Kamete, Amin Y. 2002. ''Governing the Poor in Harare, Zimbabwe: Shifting Perceptions and Changing Responses''. Uppsala: Nordiska Afrikainstitutet. ISBN 9789171065032. | |
| − | * Horn, Nancy E. 1994. Cultivating | + | * Rakodi, Carole. 1995. ''Harare: Inheriting a Settler-Colonial City, Change or Continuity?'' World cities series. Chichester: J. Wiley. ISBN 9780471949510. |
| − | * Kamete, Amin Y. 2002. ''Governing the | + | * Tingay, Paul, and Roger de la Harpe. 1997. ''Harare''. London: New Holland. ISBN 9781868258901. |
| − | * Rakodi, Carole. 1995. ''Harare: | + | * ''World Fact Book''. 2008. Zimbabwe. |
| − | * Tingay, Paul, and Roger de la Harpe. 1997. ''Harare''. London: New Holland. ISBN 9781868258901 | + | * Yoshikuni, Tsuneo. 2007. ''African Urban Experiences in Colonial Zimbabwe: A Social History of Harare Before 1925''. Harare: Weaver Press. ISBN 9781779220547. |
| − | * Yoshikuni, Tsuneo. 2007. ''African | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{List of African capitals}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Geography]] | [[Category:Geography]] | ||
[[Category:Cities]] | [[Category:Cities]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Africa]] | ||
{{credit|Harare|250095438|Zimbabwe|254093470|}} | {{credit|Harare|250095438|Zimbabwe|254093470|}} | ||
Latest revision as of 13:29, 24 January 2023
| Harare (Salisbury) |
|||
| Harare, Zimbabwe from the Kopje | |||
|
|||
| Nickname: Sunshine City, H Town |
|||
| Motto: Pamberi Nekushandira Vanhu (Forward with Service to the People) | |||
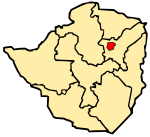
| Map of Zimbabwe showing the location of Harare. | |||
| Coordinates: 17°52′S 31°2′E | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Zimbabwe | ||
| Province | Harare | ||
| Founded as Fort Salisbury | 1890 | ||
| Incorporated (city) | 1935 | ||
| Renamed to Harare | 1982 | ||
| Government | |||
| - Mayor | Muchadeyi Masunda | ||
| Area | |||
| - City | 960.6 km² (370.9 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 1,490 m (4,888 ft) | ||
| Population (2009) | |||
| - City | 1,606,000 | ||
| - Density | 2,540/km² (4,330/sq mi) | ||
| - Urban | 2,800,111 | ||
| estimated | |||
| Time zone | CAT (UTC+2) | ||
| Area code(s) | 4 | ||
| Twin Cities | |||
| - Nottingham | United Kingdom | ||
| - Munich | Germany | ||
| - Cincinnati | United States | ||
| - Prato | Italy | ||
| - Lago | Italy | ||
| Dialling code 4 (or 04 from within Zimbabwe) | |||
| Website: http://www.hararecity.co.zw | |||
Harare (formerly Salisbury) is the capital of Zimbabwe. It lies in the northeastern part of the country at an elevation of 1,483 meters (4,865 feet), and has a warm temperate climate. Administratively, Harare is an independent city equivalent to a province.
A modern, well-planned city with multi-storied buildings and tree-lined avenues, Harare is Zimbabwe's largest city, as well as its administrative, commercial, manufacturing, communications, and education center. It serves as a distribution point for the surrounding agricultural and gold-mining areas. Numerous suburbs surround the city, retaining the same names colonial administrators gave them during the nineteenth century, such as Warren Park "D," Borrowdale, Mount Pleasant, Marlborough, Tynwald, and Avondale.
While Harare is modern and well-planned and plays an essential role within Zimbabwe, it must also resolve the problems found within the nation. These include the highest mortality rate among all African nations and very high incidences of HIV/AIDS infection. Zimbabwe has the highest literacy rate of all African nations with a strong foundation of education and abundance of natural resources, all of which are assets that can be used toward the nation's progress and prosperity.
Geography
The name Harare derives from the Shona chieftain Neharawa, who with his people occupied the area known as the Kopje (pronounced "Koppie"), near where the commercial area developed. Before independence, "Harare" was the name of the Black residential area now known as Mbare.
Harare is situated in the northeastern part of Zimbabwe in the uplands at an elevation of 1,483 meters (4,865 feet).
Harare has a warm temperate climate. Its high altitude and the prevalence of a cool south-easterly airflow maintains temperatures that are rather low for the tropics. The average maximum daytime temperature in January (midsummer) is 77°F (25°C), dropping to an average maximum of around 68°F (20°C) in July. There are three main seasons—a warm, wet season from November to March/April; a cool, dry season from May to August (corresponding to the Southern Hemisphere winter); and a hot, dry season in September/October. The average annual rainfall is about 32.4 inches (825 mm) in the southwest rising to 33.6 inches (855 mm) on the higher land in the northeast.
The climate supports a natural vegetation of open woodland. The most common tree of the local region is the Msasa Brachystegia spiciformis that colors the landscape wine-red with its new leaves in late August. An introduced tree that contributes most to the town's atmosphere is the Jacaranda (a South American species) that produces a burst of lilac when it blooms in September.
History
Iron Age Bantu-speaking peoples began migrating into the area known as Zimbabwe perhaps as far back as two thousand years ago, including the ancestors of the Shona, who account for roughly four-fifths of the country's population today.
From 1250 to 1629, the Mutapa Empire, which stretched between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers of Southern Africa in the modern states of Zimbabwe and Mozambique, traded gold, ivory, and copper for cloth and glass with Muslim merchants on the Indian Ocean coast.
From c. 1250–1629, the area that was to became Zimbabwe was ruled under the Mutapa Empire, which was renowned for its gold trade with the Arabs. The Mutapa Empire founders were culturally and politically related to the builders who constructed Great Zimbabwe, the name given to hundreds of great stone ruins spread out over a 200 square mile (500 km²) area within the modern-day country of Zimbabwe.
The Portuguese dominated much of southeast Africa's coast by 1515, seeking to dominate the trade with India.
In 1834, the Ndebele people arrived from south of the Limpopo River while fleeing from the Zulu leader Shaka (1787–1828), making the area their new empire, Matabeleland. In 1837-1838, the Ndebele conquered the Shona, and forced them to pay tribute and to concentrate in northern Zimbabwe.
In the 1880s, the British South Africa Company, owned by English-born businessman, mining magnate, and politician Cecil Rhodes (1853–1902), arrived in the area.
In 1890, the city was founded as a fort at the spot where the British South Africa Company’s Pioneer Column, a military volunteer force of settlers organized by Rhodes, halted its march into Mashonaland, a region in northern Zimbabwe, the home of the Shona people.
The city was originally named Fort Salisbury after Robert Arthur Talbot Gascoyne-Cecil, the Third Marquess of Salisbury, who was then British prime minister, and it subsequently became known simply as Salisbury.
At that time, the area was poorly drained and its earliest development was on sloping ground along the left bank of a stream that became a trunk road (Julius Nyerere Way). The first area to be drained, near the head of the stream, was named Causeway, and became the site of the most important Government buildings, including the Senate House and the Office of the Prime Minister (renamed for the use of President Mugabe.)
Salisbury was declared a municipality in 1897. In 1898, the name Southern Rhodesia was adopted for the territory.[1] When the railway arrived from Beira (Mozambique) in 1899, the town developed as a trading center.
The United Kingdom annexed Southern Rhodesia from the British South Africa Company in 1923, and Salisbury became the capital of the British colony. It became a city in 1935.
Industrialization during World War II and after attracted an influx of migrants.
The city was the capital of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland from 1953 to 1963, and from then was the capital of Southern Rhodesia.
A 1961 constitution was formulated that favored whites in power. The government of Ian Smith (1919–2007) declared Rhodesia independent of Great Britain on November 11, 1965. The United Kingdom did not recognize the act and demanded more complete voting rights for the black African majority in the country.
United Nations sanctions and a guerrilla uprising led to free elections in 1979, and independence as the Republic of Zimbabwe in 1980. Robert Mugabe (b. 1924), a former schoolteacher whose goal was to replace white minority-rule with a one-party Marxist regime, became the nation's first prime minister, and remained the country's only ruler, as president since 1987.
The capital city retained the name Salisbury until April 18, 1982, the second anniversary of Zimbabwean independence, when it was changed to Harare.
Mugabe's chaotic land redistribution campaign, which began in 2000, caused an exodus of white farmers, crippled the economy, and ushered in widespread shortages of basic commodities.
Ignoring international condemnation, Mugabe rigged the 2002 presidential election to ensure his re-election. The ruling ZANU-PF party used fraud and intimidation to win a two-thirds majority in the March 2005 parliamentary election, allowing it to amend the constitution at will and recreate the Senate, which had been abolished in the late 1980s.
In April 2005, Harare embarked on Operation Restore Order, ostensibly an urban rationalization program, which resulted in the destruction of the homes or businesses of 700,000 mostly poor supporters of the opposition. This caused a sharp reaction in the international community because it took place without warning and no plans were made to provide alternative housing.
This was followed by Operation Chikerema (Operation "Better Living") a year later which consisted of building concrete housing. Critics stated that these were inadequate citing the lack of electricity, plumbing or other infrastructure in poorly accessible areas.
Mugabe, in June 2007, instituted price controls on all basic commodities causing panic buying and leaving store shelves empty for months.
The political and economic crisis plaguing Zimbabwe has harmed Harare. A government-appointed commission replaced the elected council for alleged inefficiency, although essential services such as rubbish collection and street repairs have rapidly worsened, and are now virtually non-existent. In May 2006, the Zimbabwean newspaper the Financial Gazette described the city as a "sunshine city-turned-sewage farm."[2]
General elections held in March 2008 contained irregularities but still amounted to a censure of the ZANU-PF-led government with significant gains in opposition seats in parliament. Movement For Democratic Change opposition leader Morgan Tsvangirai (b. 1952) won the presidential polls, and may have won an outright majority, but official results did not reflect this.
In the lead up to a run-off election in late June 2008, considerable violence enacted against opposition party members led to the withdrawal of Tsvangirai from the ballot. Extensive evidence of vote tampering and ballot-box stuffing resulted in international condemnation of the process, and calls for the creation of a power-sharing government have been ignored.
Government
Zimbabwe is a parliamentary democracy in which the president, who is both the chief of state and head of government, is elected by popular vote for a five-year term, and has no term limits. The bicameral parliament consists of a Senate of 93 members, and a House of Assembly of 210 members.
Zimbabwe is divided into eight provinces and two cities with provincial status. These are territorial divisions for the purposes of administrative, political and geographical demarcation. The provinces are subdivided into 59 districts and 1200 municipalities.
Administratively, Harare is an independent city equivalent to a province.
Harare has been the location of several international summits such as the Eighth Summit of the Non-Aligned Movement (1986) and Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting (1991). The latter produced the Harare Declaration, dictating the membership criteria of the Commonwealth. In 1995, Harare hosted most of the Sixth All-Africa Games, sharing the event with other Zimbabwean cities such as Bulawayo and Chitungwiza.
Economy
The government of Zimbabwe in 2008 struggled with an unsustainable fiscal deficit, an overvalued official exchange rate, hyperinflation, and bare store shelves. Its 1998-2002, involvement in the war in the Democratic Republic of the Congo drained hundreds of millions of dollars from the economy. The government's land reform program, characterized by chaos and violence, has badly damaged the commercial farming sector, the traditional source of exports and foreign exchange and the provider of 400,000 jobs, turning Zimbabwe into a net importer of food products.
The European Union and the United States provide food aid on humanitarian grounds. Badly needed support from the International Monetary Fund had been suspended because of the government's arrears on past loans and the government's unwillingness to enact reforms that would stabilize the economy.
The Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe routinely prints money to fund the budget deficit, causing the official annual inflation rate to rise from 32 percent in 1998, to 133 percent in 2004, 585 percent in 2005, passed 1,000 percent in 2006, and 26,000 percent in November 2007. Due to the unstable economic conditions and failure to control inflation, economists have suggested that the Reserve Bank be reformed.
Zimbabwe's per capita GDP was estimated at $200 in 2007.
Harare is Zimbabwe's largest city, as well as its administrative, commercial, manufacturing, communications, and educational center, and serves as a distribution point for the surrounding agricultural and gold-mining areas.
The city is a trade center for tobacco, maize, cotton, and citrus fruits. Manufactures include textiles, steel, and chemicals. Factories produce processed food, beverages, clothing, cigarettes, building materials, and plastics. Gold is mined in the area.
Harare is a hub of rail, road, and air transport in Zimbabwe. The public transport system of buses, run by ZUPCO crumbled in the first decade of the twenty-first century. Privately owned companies that operate commuter omnibuses proliferated. With a fuel crisis, the government introduced commuter trains in order to ease transport shortages. The National Railways of Zimbabwe operates a daily overnight passenger train service from Harare to Mutare and another one to Bulawayo. Harare International Airport is Zimbabwe's main airport.
Demographics
Harare had an estimated population of 1,600,000, with 2,800,000 in its metropolitan area in 2006. There has been an increasing flow of Zimbabweans into South Africa and Botswana in search of better economic opportunities.
Black Africans make up 98 percent of Zimbabwe's population. Shona comprise 82 percent; Ndebele 14 percent; other two percent; mixed and Asian one percent; and white, fewer than one percent.
English is the official language, while Shona, Sindebele (the language of the Ndebele), and numerous but minor tribal dialects, are spoken.
About half of Zimbabwe's population follow syncretic religions which are part Christian, part indigenous beliefs. Christians make up 25 percent, those following indigenous beliefs 24 percent, Muslim and other, one percent.
Harare is the site of the University of Zimbabwe, the largest and most complete institution of higher learning in the nation, about three miles (five kilometers) north of the city. It was founded through a special relationship with the University of London and it opened its doors to its first students in 1952.
Places of interest
Places of interest include the Queen Victoria Museum, which has zoological and historical exhibits, the Anglican and Roman Catholic cathedrals, as well as:
- The Eastgate Centre, which is a shopping center and office block in central Harare, that is designed to be ventilated and cooled by entirely natural means, it was probably the first building in the world to use natural cooling to this level of sophistication. It opened in 1996 on Rubert Mugabe Ave and Second Street.
- The National Gallery of Zimbabwe, which has a collection of European paintings as well as traditional and contemporary African art.
- Mushandirapamwe Hotel, which is a hotel at Machipisa Shopping Centre in the Highfield district. It is owned by the Tawengwa family, sons of George Tawengwa, a prominent Zimbabwean businessman who was the first black person to buy a farm in 1960.
- Harvest House, which is a six story building in Harare, located at 44 Nelson Mandela Ave and Angwa Street, and serves as the National Headquarters of the Movement for Democratic Change party.
- Sam Nujoma Street, which is one of the main streets of the city, was originally called Second Street, but this was changed to Sam Nujoma Street after Sam Nujoma, a former president of Namibia.
- Rufaro Stadium, which is a multi-use stadium, used mostly for football matches, and has a capacity of 35,000 people.
Looking to the future
Harare is Zimbabwe's capital and largest city, as well as its administrative, commercial, manufacturing, communications, and educational center. Along with the country, Harare's fortunes rise and fall with the successes and failures of its government. In 2008, Zimbabwe had an unpopular government that seemed powerless when dealing with the nation's problems. However, there is a strong foundation in education as well as abundant natural resources, both of which can propel future prosperity.
Notes
- ↑ Africa Stage, So Who Was Shaka Zulu—Really? Retrieved November 30, 2008.
- ↑ Charles Rukuni Bulawayo, May 17, 2006, Zimbabwe: It's Chombo's Fault, Financial Gazette. Retrieved November 30, 2008.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- "Commentary—Suicidal Violence—Daily News, Harare." 2003. World Press Review. 50 (6): 46. ISSN 0195-8895
- Horn, Nancy E. 1994. Cultivating Customers: Market Women in Harare, Zimbabwe. Women and Change in the Developing World. Boulder, CC: Lynne Rienner Publishers. ISBN 9781555874728.
- Kamete, Amin Y. 2002. Governing the Poor in Harare, Zimbabwe: Shifting Perceptions and Changing Responses. Uppsala: Nordiska Afrikainstitutet. ISBN 9789171065032.
- Rakodi, Carole. 1995. Harare: Inheriting a Settler-Colonial City, Change or Continuity? World cities series. Chichester: J. Wiley. ISBN 9780471949510.
- Tingay, Paul, and Roger de la Harpe. 1997. Harare. London: New Holland. ISBN 9781868258901.
- World Fact Book. 2008. Zimbabwe.
- Yoshikuni, Tsuneo. 2007. African Urban Experiences in Colonial Zimbabwe: A Social History of Harare Before 1925. Harare: Weaver Press. ISBN 9781779220547.
| |||||||||||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.