Difference between revisions of "Sonoran Desert" - New World Encyclopedia
Mary Anglin (talk | contribs) m (→Yuma Desert) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Approved}}{{Submitted}}{{Images OK}}{{Paid}}{{Copyedited}} |
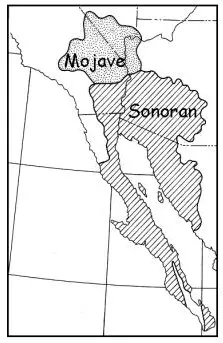
[[Image:Mojave-sonoran_deserts.png|thumb|Map of the Mojave and Sonoran deserts.]] | [[Image:Mojave-sonoran_deserts.png|thumb|Map of the Mojave and Sonoran deserts.]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | The '''Sonoran Desert''' | + | The '''Sonoran Desert''' is a [[North America]]n [[desert]] which straddles part of the [[United States-Mexico border]] and covers large parts of the [[U.S.]] states of [[Arizona]] and [[California]] and the [[Mexico|Mexican state]] of [[Sonora]]. It is one of the largest and hottest deserts in North America, with an area of 120,000 square miles (311,000 km²). The desert contains an incredible array of unique plants and animals, such as the [[saguaro]] cactus that can live to be 250 years old and the kangaroo rat that never needs to drink water. On January 17, 2001, 496,337 acres (2,008 km²) of the Sonoran Desert was set aside as the [[Sonoran Desert National Monument]] for the purpose of enhancing resource protection. |
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | The Sonoran is well known for its beauty and spectacular cacti. In spite of the harsh climate of this desert, there is diverse plant and animal life. This desert, in fact, has the greatest diversity of vegetative growth of any desert in the world. | ||
| − | + | == Geography == | |
| + | [[image:sonoran_desert_mountains.jpg|thumb|250px|Mountains in the Sonoran Desert]] | ||
| + | The desert's subregions include the Colorado Desert and [[Yuma Desert]]. In the 1951 publication, ''Vegetation of the Sonoran Desert,'' Forrest Shreve divided the Sonoran Desert into seven regions according to characteristic vegetation: Lower Colorado Valley, Arizona Upland, Plains of Sonora, Foothills of Sonora, Central Gulf Coast, Vizcaino Region, and Magdalena Region. Many [[Ecology|ecologists]] now consider Shreve's Vizcaino and Magdalena regions, which lie on the western side of the Baja California Peninsula, to be a separate [[ecoregion]], the [[Baja California]] desert. | ||
| − | The | + | === Flora and fauna === |
| + | The Sonoran Desert includes 60 [[mammal]] species, 350 [[bird]] species, 20 [[amphibian]] species, over 100 [[reptile]] species, 30 native [[fish]] species, and more than 2,000 native [[plant]] species. The desert is also home to many cultures including seventeen [[Native American]] cultures, as well as Latino, Chinese, Anglo, Arabic, and African immigrant cultures. | ||
| − | + | The Sonoran Desert includes such plants from the [[agave]] family, [[palm]] family, cactus family, legume family, and many others. Most plants not only survive the harsh conditions of the Sonoran Desert, but they actually thrive. Many have evolved to have specialized adaptations to the desert climate. To endure the intense sun and scarce rainfall, cacti have thick, waterproof skins to prevent water loss, as well as shallow roots that sprawl horizontally attaining a depth of just three inches, capturing moisture over a greater surface area. Both the [[saguaro]] and the world’s largest cacti, the [[cardon]], have expandable trunks to store as much as is available. When water is scarce, their trunks then contract. | |
| − | The Sonoran Desert includes | ||
| − | === | + | === Gila River === |
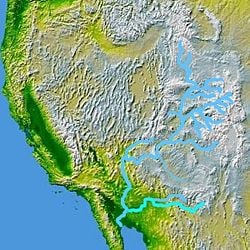
| − | The | + | [[Image:Wpdms nasa topo gila river.jpg|250px|thumb|left|The Gila River, a tributary of the Colorado, is shown highlighted on a map of the southwestern United States]] |
| + | |||
| + | The most significant river in the Yuma Desert is the Gila River of Arizona. It is a 630-mile- (1,014-km)-long tributary of the [[Colorado River]]. It rises in southwestern New Mexico, in the Elk Mountains, near the '''Gila Cliff Dwellings National Monument''' and the '''Gila National Forest'''. It flows westward into [[Arizona]], emerging from the Gila Mountains into the valley southeast of [[Phoenix, Arizona|Phoenix]]. It eventually joins the Colorado River near Yuma, Arizona. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Gila is one of the largest desert rivers in the world. It and its chief tributary, the [[Salt River]], would both be perennial streams carrying large volumes of water, but irrigation and municipal water diversions have turned both into largely dry rivers. Below the city of Phoenix to the [[Colorado River]], the Gila is largely a trickle or dry, as is the lower Salt River from Granite Reef Diversion Dam downstream to the Gila. The Gila used to be navigable by small craft from its mouth to near the Arizona-New Mexico border. The width varied from 150 to 1,200 feet with a depth from 2 to 40 feet. | ||
| + | |||
| + | After the Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo in 1848, the river served as the border between the [[United States]] and [[Mexico]] until the 1853 Gadsden Purchase extended U.S. territory south of the Gila. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A band of [[Pima]] (autonym "Akimel O'odham," river people), the Hila Akimel O'odham (Gila River People), have lived on the banks of the Gila River since before the arrival of Spanish explorers. Their traditional way of life (''himdagĭ,'' sometimes rendered in English as [[Him-dak]]) was and is centered at the river, which is considered sacred. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the Gila River Indian Community, the traditional way of life has generally been better preserved than in the Salt River [[Pima-Maricopa]] Indian Community. Some speculate this may be due to the fact that the Gila River, a central aspect of the traditional way of life, still flows through the reservation year-round (although at times as an intermittent stream), while the Salt River does not. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 32: | ||
=== Colorado Desert === | === Colorado Desert === | ||
| − | The '''Colorado Desert''' is a part of the larger | + | The '''Colorado Desert''' is a part of the larger Sonoran Desert extending southeastward for 164 miles (264 km) from the San Gorgonio Pass in southeastern California, (U.S.), to the [[Colorado River]] delta in northern [[Mexico]]. It encompasses approximately 2,500 sq mi (40,000 km²) east of Los Angeles and San Diego, extending from the [[San Bernardino Mountains]] east and southeast to the Colorado River, from which it takes its name. |
| + | |||
| + | The region is essentially the northwest extension of the Sonoran Desert to the southeast. It includes the heavily-irrigated Coachella and Imperial valleys on the north and south side of the Salton Sea respectively. It is crossed by several mountain ranges, including the [[San Jacinto Mountains|San Jacinto]], [[Santa Rosa Mountains (California)|Santa Rosa]], [[Little San Bernardino Mountains|Little San Bernardino]], and [[Chocolate Mountains|Chocolate]] mountains. It is also dominated by the [[San Andreas Transform Fault System]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Joshua Tree National Park''' is located on the northern edge of the region and includes many of the unique species and habitats of the region. The Colorado Desert encompasses the eastern part of the park and features natural gardens of [[creosote bush]], [[ocotillo]], and [[cholla]] [[cactus]]. The Little San Bernardino Mountains run through the southwest edge of the park. There are over 250 species of [[bird]] in the park including resident desert birds such as the [[Greater Roadrunner]] and [[Cactus Wren]] as well as [[Mockingbird]]s, [[Le Conte's Thrasher]], [[Verdin]], and [[Gambel's Quail]]. | ||
| − | + | '''Santa Rosa and San Jacinto National Monument''', created in October 2,000, covers an area of 272,000 acres encompassing much of the San Jacinto and Santa Rosa mountains along the western side of the region. Five different climate zones exist here, from desert to pine forest and to arctic pine at the highest elevation. It is home to more than 500 [[plant]] and [[animal]] species including the Peninsular [[bighorn sheep]]. | |
| − | [[ | + | '''Anza-Borrego Desert State Park''' is the largest state park in [[California]] and second largest state park in the [[United States]], (after [[Adirondack State Park]] in [[New York]]). It covers 600,000 acres (2,400 km²) from the edge of the coastal mountains east of San Diego to the Salton Sea and south almost to the US-Mexico border. The park is named after [[Spain|Spanish]] explorer [[Juan Bautista de Anza]] and the [[Spanish language|Spanish]] word ''borrego,'' or [[Bighorn Sheep]]. The park features washes, wildflowers, palm groves, [[cacti]], [[ocotillo]], and sweeping vistas. There are also the greater roadrunner, [[golden eagle]]s, [[kit fox]]es, [[mule deer]], and bighorn sheep as well as [[iguana]]s, [[chuckwalla]]s, and the red diamond [[rattlesnake]]. |
| − | [[Santa Rosa | + | With mountains all around, the highest are to the north—the [[Santa Rosa Mountains]]. The mountains are a wilderness, with no paved roads in, out or through. They have the only all-year-flowing watercourse in the park and are the home of the peninsular bighorn sheep, often called the Desert Bighorn. |
| − | |||
=== Yuma Desert === | === Yuma Desert === | ||
[[Image:400px-Organ pipe cactus 11.jpg|230px|thumb|right|Organ Pipe Cactus]] | [[Image:400px-Organ pipe cactus 11.jpg|230px|thumb|right|Organ Pipe Cactus]] | ||
| − | The '''Yuma Desert''' is a lower-elevation section of the Sonoran Desert in the Salton basin. The desert contains areas of sparse vegetation and has notable areas of sand dunes. With an average rainfall less than 8 inches each year, this is among the harshest deserts in North America. Human presence is sparse throughout, the largest town being Yuma, Arizona. | + | The '''Yuma Desert''' is a lower-elevation section of the Sonoran Desert in the Salton basin. The desert contains areas of sparse vegetation and has notable areas of sand dunes. With an average rainfall of less than 8 inches each year, this is among the harshest deserts in [[North America]]. Human presence is sparse throughout, the largest town being [[Yuma, Arizona]]. |
| + | |||
| + | The desert includes the lower-elevation areas of the southwestern corner of [[Arizona]], extending west to the [[Colorado River]]. On the other side of the river, in [[California]], is the Low Desert region of the Sonoran Desert, also referred to as the Colorado Desert. Though the two regions are separated only by the Colorado River, there are numerous species of plant and animals that live only on one side or the other, such as the [[saguaro]] cactus, which occurs only east of the river. The Yuma Desert also includes the sandy plains of western Sonora, going all the way to the head of the Gulf of California, then an inland strip reaching into the central Sonoran interior. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vegetation in the Yuma Desert is dominated by the [[Creosote]] bush ''(Larrea tridentata)'', which is widespread. The [[saguaro]] cactus ''Carnegiea gigantea'' and the [[ocotillo]] ''Fouquieria splendens'' are common on the bajadas, while many of the desert trees found are restricted to dry watercourses; these include palo verdes ''Parkinsonia,'' the desert willow ''Chilopsis linearis,'' ironwood ''Olneya tesota,'' and smoke trees ''Psorothamnus spinosus.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument''' is located in this desert and is the only place in the United States where the organ pipe cactus grows wild. Also found here are the '''Kofa National Wildlife Refuge''' and '''Cabeza Prieta National Wildlife Refuge'''. The Cabeza Prieta National Wildlife Refuge, established in 1939 to protect bighorn sheep, is located along 56 miles of the U.S. - Mexican border, and covers 860,010 acres, which is larger than the land area of the state of [[Rhode Island]]. There are 803,418 acres preserved as the Cabeza Prieta Refuge Wilderness. | ||
| − | + | == Additional Public Lands == | |
| + | [[Image:Casagrande1.jpg|thumb|255px|left| Shelter built in the 1930s to protect what remains of the National Monument.]] | ||
| − | + | '''Sonoran Desert National Monument''' is located in the state of [[Arizona]]. Created by Presidential proclamation on January 17, 2001, the 496,337 acre (2,008 km²) monument is managed by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management, an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. The U.S. Bureau of Land Management already managed the lands, however under monument status, the level of protection and preservation of resources is enhanced. The North Maricopa Mountains, South Maricopa Mountains, and the Table Top Wildernesses protect the richest regions of desert habitat from any future development. | |
| − | ''' | + | The '''Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum''' is one of the most visited attractions in Tucson, Arizona. Founded in 1952, it combines the attractions of a [[zoo]], [[museum]], and [[botanical garden]]. Its focus is the plants and animals that live in the Sonoran Desert, and it was a pioneer in the creation of naturalistic enclosures for its animals. The [[Center for Sonoran Desert Studies]], founded in 2005, conducts the educational and scientific functions of the Museum and is a hub for research, education and conservation of the Sonoran Desert. Over 500,000 people visit the museum each year. |
| − | + | '''Casa Grande Ruins National Monument''', in [[Coolidge, Arizona]] just northeast of the city of Casa Grande, preserves a group of [[Hohokam]] structures. | |
| − | |||
| − | The | + | The national monument consists of the ruins of multiple structures surrounded by a compound wall constructed by the [[Hohokam]], who farmed the Gila Valley in the early 1200s. "Casa grande" is [[Spanish language|Spanish]] for "big house" and the name refers to the largest structure on the site, which is what remains of a four-story structure that may have been abandoned by the mid-1400s. The structure is made of [[caliche]], and has managed to survive the extreme weather conditions for about seven centuries. Casa Grande now has a distinctive modern roof covering built in 1932. |
| − | + | Proclaimed '''Casa Grande Reservation''' by an order of President [[Benjamin Harrison]] on June 22, 1892, it was redesignated a national monument by [[Woodrow Wilson]] on August 3, 1918. As with all historical areas administered by the National Park Service, Casa Grande was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on October 15, 1966. | |
| − | + | '''Saguaro National Park''' is divided into two sections, lying approximately 20 miles (32 km) east and 15 miles (24 km) west of the center of the city of Tucson, Arizona. Total area in 2002 was 143 square miles (91,327 acres) (370 km²) of which 111 square miles (289 km²) is designated wilderness. Both sections conserve fine tracts of the Sonoran Desert, including ranges of significant hills, the [[Tucson Mountains]] in the west and the [[Rincon Mountains]] in the east. The park gets its name from the [[saguaro]] [[cactus]] which is native to the region. Many other kinds of cactus, including barrel cactus, cholla cactus, and prickly pear, are also abundant in the park. One endangered species of animals lives in the park part of the year during its migration, the Lesser Long-nosed [[Bat]], as does the threatened [[Mexican Spotted Owl]]. | |
| − | + | The park was established as [[Saguaro National Monument]] on March 1, 1933 and changed to a national park on October 14, 1994. | |
| − | == | + | == Proposals for greater national park system == |
| − | '''Sonoran Desert National | + | A proposal was made in 1935 for a '''Sonoran Desert National Park''', but was defeated due to mining and grazing interests in the area. In 1965, Secretary of Interior [[Stewart Udall]] and his brother [[Morris K. Udall]], U.S. Representative from [[Arizona]], raised the idea again; again it went nowhere. |
| − | + | The purpose and mission of this park would be to "protect significant desert features that provide world-class scenic, scientific, ecological, and educational opportunities." | |
| − | The | + | |
| + | The goals in the creation of this park, as stated by those making the proposal, would be to: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Preserve the unrivaled scenic, natural, biologic, wildlife, and geologic resources of these unique natural landscapes, while perpetuating significant and diverse ecosystems of the Sonoran Desert in their natural state and processes. Ensure the maximum protection of wilderness values provided by law. | ||
| + | *Preserve the cultural and archaeological resources of the Sonoran Desert associated with the prehistoric, historic, and contemporary Native American, Hispanic, Anglo, and other cultures. | ||
| + | *Retain and enhance opportunities for scientific research in undisturbed ecosystems. Serve as a baseline station for environmental, biological, and climatic changes. | ||
| + | *Promote understanding and appreciation for the Sonoran Desert, and provide opportunities for compatible recreation. | ||
== Spanish missions in the Sonoran Desert == | == Spanish missions in the Sonoran Desert == | ||
| − | [[Image:StXavier.jpg|left| | + | [[Image:StXavier.jpg|left|275px|thumb|San Xavier del Bac]] |
| − | The '''Spanish missions in the Sonoran Desert''' are a series of | + | The '''Spanish missions in the Sonoran Desert''' are a series of religious outposts established by [[Spain|Spanish]] [[Roman Catholic|Catholic]] [[Jesuit]]s and other orders to spread the [[Christian]] doctrine among the local [[Native American]]s, but with the added benefit of giving Spain a toehold in the frontier lands of its colony of New Spain. The missions are in an area of the Sonoran Desert called "[[Pimería Alta]]," or "Upper Pima Country." It is now divided between the [[Mexico|Mexican state]] of [[Sonora]] and the [[U.S.]] state of [[Arizona]]. |
| − | |||
=== Father Kino === | === Father Kino === | ||
| − | From 1493, the Kingdom of [[Spain]] had maintained a number of missions throughout ''Nueva España'' ([[New Spain]], consisting of [[Mexico]] and portions of what today are the | + | From 1493, the Kingdom of [[Spain]] had maintained a number of missions throughout ''Nueva España'' ([[New Spain]], consisting of [[Mexico]] and portions of what today are the Southwestern United States in order to facilitate colonization of these lands. |
| − | In the | + | In the spring of 1687, a Jesuit missionary from Italy named [[Eusebio Francisco Kino|Father Kino]] lived and worked with the Native Americans ([[Pima]]) in the area called the "Pimería Alta," after ten unsuccessful years trying to make a mission in Baja, California. During Father Kino's stay in the Pimería Alta, he founded over 20 missions in eight mission districts, and introduced cattle raising and wheat to the local people. Some missions were destroyed in 1751 during the [[Pima Rebellion]]. |
| − | It was rumored that the Jesuit priests had amassed fortunes | + | It was rumored that the Jesuit priests had amassed fortunes in the new land and were becoming very powerful. On February 3, 1768, King [[Carlos III]] ordered the Jesuits forcibly expelled from New Spain and returned to the home country. |
=== The missions === | === The missions === | ||
| − | * | + | *Mission Nuestra Señora de los Dolores: founded on March 13, 1687. This was the first mission founded by Father Kino. By 1744, the mission was abandoned. The cemetery remains on the site of the [[Tumacácori National Historical Park]] in Southern Arizona. |
*[http://www.nps.gov/tuma/Remedios.html Nuestra Señora de los Remedios] was founded in 1687 and was abandoned by 1730. Nothing remains of this mission. | *[http://www.nps.gov/tuma/Remedios.html Nuestra Señora de los Remedios] was founded in 1687 and was abandoned by 1730. Nothing remains of this mission. | ||
| − | *[http://www.nps.gov/archive/tuma/SanIgnacio.html San Ignacio de Cabórica] was founded in 1687 and is located in | + | *[http://www.nps.gov/archive/tuma/SanIgnacio.html San Ignacio de Cabórica] was founded in 1687 and is located in San Ignacio, Sonora. |
*[http://www.nps.gov/archive/tuma/Tubutama.html San Pedro y San Pablo del Tubutama] was founded in 1687. | *[http://www.nps.gov/archive/tuma/Tubutama.html San Pedro y San Pablo del Tubutama] was founded in 1687. | ||
| − | * | + | *Santa Teresa de Atil was founded in 1687. |
| − | *[http://parentseyes.arizona.edu/missions/Magdalena.html Santa Maria Magdalena] was founded in 1687, located in Sonora. | + | *[http://parentseyes.arizona.edu/missions/Magdalena.html Santa Maria Magdalena] was founded in 1687, located in Sonora. In 1966 Father Kino's bones were found buried beneath area where the chapel had been. |
| − | *[http://www.nps.gov/archive/tuma/Imuris.html San José de Imuris] was founded in 1687. | + | *[http://www.nps.gov/archive/tuma/Imuris.html San José de Imuris] was founded in 1687. |
| − | *[http://parentseyes.arizona.edu/missions/Cocospera.html Nuestra Señora del Pilar y Santiago de Cocóspera] was founded in 1689. It is located in | + | *[http://parentseyes.arizona.edu/missions/Cocospera.html Nuestra Señora del Pilar y Santiago de Cocóspera] was founded in 1689. It is located in Cocóspera, Sonora. |
| − | *[http://parentseyes.arizona.edu/missions/Oquitoa.html San Antonio Paduano del Oquitoa] was founded in 1689. It is located in | + | *[http://parentseyes.arizona.edu/missions/Oquitoa.html San Antonio Paduano del Oquitoa] was founded in 1689. It is located in Oquitoa, Sonora. |
| − | *[http://parentseyes.arizona.edu/missions/Pitiquito.html San Diego del Pitiquito] was founded in 1689. It is located in | + | *[http://parentseyes.arizona.edu/missions/Pitiquito.html San Diego del Pitiquito] was founded in 1689. It is located in Pitiquito, Sonora. |
*San Luis Bacoancos was founded in 1691. | *San Luis Bacoancos was founded in 1691. | ||
| − | * | + | *San Cayetano de Tumacácori Mission was built in 1732, but construction stopped in 1822 due to lack of funds. The farming land around the mission was sold at auction in 1834 and the mission was abandoned by 1840. It is now a National Monument in Tumacácori National Historical Park in Southern Arizona. |
*Los Santos Ángeles de Guevavi was founded in 1691. | *Los Santos Ángeles de Guevavi was founded in 1691. | ||
| Line 99: | Line 125: | ||
*San Lázaro was founded in 1691. | *San Lázaro was founded in 1691. | ||
| − | * | + | *San Xavier del Bac, now in Tucson, Arizona, founded in 1692, the present building dates from 1785. The interior is richly decorated with ornaments showing a mixture of New Spain and Native American artistic motifs. It is still used by [[Tohono O'odham]] and [[Yaqui]] tribal members. |
*San Cosme y Damián de Tucson: 1692 | *San Cosme y Damián de Tucson: 1692 | ||
| Line 115: | Line 141: | ||
*[http://www.nps.gov/archive/tuma/sonoitac.html Los Santos Reyes de Sonoita/San Ignacio de Sonoitac]: a rancheria near Tumacacori, 1692 | *[http://www.nps.gov/archive/tuma/sonoitac.html Los Santos Reyes de Sonoita/San Ignacio de Sonoitac]: a rancheria near Tumacacori, 1692 | ||
| − | == | + | == References == |
| − | |||
| − | + | * Abbey, Edward. 1973. ''Cactus country.'' New York: Time-Life Books. ASIN: B000X6J9E4 | |
| − | * Abbey, Edward. 1973. ''Cactus country'' | + | * Alcock, John. 1985. ''Sonoran Desert spring.'' Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0226012581 |
| − | * Alcock, John. | + | * Alcock, John. 1990. ''Sonoran Desert summer.'' Tucson: University of Arizona Press. ISBN 0816511500 |
| − | + | * Dykinga, Jack W., and Charles Bowden. 1992. ''The Sonoran Desert.'' New York: H.N. Abrams. ISBN 0810938243 | |
| − | * Alcock, John. | + | * Jaeger, Edmund C. ''The North American Deserts.'' Stanford University Press, 1967. 73-83 |
| − | * Dykinga, Jack W., and Charles Bowden. 1992. ''The Sonoran Desert'' | + | * ''The Pimeria Alt: missions & more.'' Tucson, Ariz.: Southwestern Mission Research Center, 1996. |
| − | * Edmund C. | + | * Phillips, Steven, and Patricia Wentworth Comus. 2000. ''A natural history of the Sonoran Desert.'' Tucson: Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum. ISBN 0520220293 |
| − | * ''The Pimeria Alt : missions & more'' | + | * Pickens, Buford L. [http://www.uapress.arizona.edu/BOOKS/bid356.htm The Missions of Northern Sonora, A 1935 Field Documentation], Tucson, ''University of Arizona Press''. 1993 reprint. Retrieved May 19, 2007. |
| − | * Buford L. | + | * Polzer, Charles. ''The Jesuit Missions of Northern Mexico.'' (The Spanish Borderlands Sourcebooks, Vol. 19) London: Routledge, 1991. ISBN 0824020960 |
| + | * [http://www.nps.gov/jotr/ Joshua Tree National Park], ''National Park Service''. Retrieved May 25, 2007. | ||
| + | * [http://www.desertmuseum.org/ Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum], ''Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum''. Retrieved May 25, 2007. | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | + | All links retrieved February 3, 2023. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | * Plagens, Michael J. [http://arizonensis.org/sonoran/ Sonoran Desert Naturalist]. ''Arizonensis''. | ||
| + | * [http://www.cas.vanderbilt.edu/bioimages/ecoregions/51310frame.htm Sonoran Desert]. ''Bio Images''. | ||
| + | * [http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9078145/Yuma-Desert Britannica.com Yuma Desert]. ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. | ||
| + | * [http://parentseyes.arizona.edu/missions/ Kino Missions]. ''Mission Churches of the Sonoran Desert''. | ||
| + | * [http://www.nps.gov/sagu/ Saguaro National Park]. ''National Park Service''. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{Deserts}} | {{Deserts}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | {{ | + | {{credit|Sonoran_Desert|125406587|Sonoran_Desert_National_Monument|117791373|Yuma_Desert|127226930|Colorado_Desert|119758703|Spanish_missions_in_the_Sonoran_Desert|114961994|Casa_Grande_Ruins_National_Monument|123332203|Saguaro_National_Park|129162188|Anza-Borrego_Desert_State_Park|125239428|Joshua_Tree_National_Park|132864789|Gila_River|125562519|Cabeza_Prieta_National_Wildlife_Refuge|118073025|Arizona-Sonora_Desert_Museum|116081463}} |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Geography]] |
[[Category:United States]] | [[Category:United States]] | ||
[[Category:Deserts]] | [[Category:Deserts]] | ||
| − | + | [[Category:National Parks]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:National monuments]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 01:16, 4 February 2023
The Sonoran Desert is a North American desert which straddles part of the United States-Mexico border and covers large parts of the U.S. states of Arizona and California and the Mexican state of Sonora. It is one of the largest and hottest deserts in North America, with an area of 120,000 square miles (311,000 km²). The desert contains an incredible array of unique plants and animals, such as the saguaro cactus that can live to be 250 years old and the kangaroo rat that never needs to drink water. On January 17, 2001, 496,337 acres (2,008 km²) of the Sonoran Desert was set aside as the Sonoran Desert National Monument for the purpose of enhancing resource protection.
The Sonoran is well known for its beauty and spectacular cacti. In spite of the harsh climate of this desert, there is diverse plant and animal life. This desert, in fact, has the greatest diversity of vegetative growth of any desert in the world.
Geography
The desert's subregions include the Colorado Desert and Yuma Desert. In the 1951 publication, Vegetation of the Sonoran Desert, Forrest Shreve divided the Sonoran Desert into seven regions according to characteristic vegetation: Lower Colorado Valley, Arizona Upland, Plains of Sonora, Foothills of Sonora, Central Gulf Coast, Vizcaino Region, and Magdalena Region. Many ecologists now consider Shreve's Vizcaino and Magdalena regions, which lie on the western side of the Baja California Peninsula, to be a separate ecoregion, the Baja California desert.
Flora and fauna
The Sonoran Desert includes 60 mammal species, 350 bird species, 20 amphibian species, over 100 reptile species, 30 native fish species, and more than 2,000 native plant species. The desert is also home to many cultures including seventeen Native American cultures, as well as Latino, Chinese, Anglo, Arabic, and African immigrant cultures.
The Sonoran Desert includes such plants from the agave family, palm family, cactus family, legume family, and many others. Most plants not only survive the harsh conditions of the Sonoran Desert, but they actually thrive. Many have evolved to have specialized adaptations to the desert climate. To endure the intense sun and scarce rainfall, cacti have thick, waterproof skins to prevent water loss, as well as shallow roots that sprawl horizontally attaining a depth of just three inches, capturing moisture over a greater surface area. Both the saguaro and the world’s largest cacti, the cardon, have expandable trunks to store as much as is available. When water is scarce, their trunks then contract.
Gila River
The most significant river in the Yuma Desert is the Gila River of Arizona. It is a 630-mile- (1,014-km)-long tributary of the Colorado River. It rises in southwestern New Mexico, in the Elk Mountains, near the Gila Cliff Dwellings National Monument and the Gila National Forest. It flows westward into Arizona, emerging from the Gila Mountains into the valley southeast of Phoenix. It eventually joins the Colorado River near Yuma, Arizona.
The Gila is one of the largest desert rivers in the world. It and its chief tributary, the Salt River, would both be perennial streams carrying large volumes of water, but irrigation and municipal water diversions have turned both into largely dry rivers. Below the city of Phoenix to the Colorado River, the Gila is largely a trickle or dry, as is the lower Salt River from Granite Reef Diversion Dam downstream to the Gila. The Gila used to be navigable by small craft from its mouth to near the Arizona-New Mexico border. The width varied from 150 to 1,200 feet with a depth from 2 to 40 feet.
After the Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo in 1848, the river served as the border between the United States and Mexico until the 1853 Gadsden Purchase extended U.S. territory south of the Gila.
A band of Pima (autonym "Akimel O'odham," river people), the Hila Akimel O'odham (Gila River People), have lived on the banks of the Gila River since before the arrival of Spanish explorers. Their traditional way of life (himdagĭ, sometimes rendered in English as Him-dak) was and is centered at the river, which is considered sacred.
In the Gila River Indian Community, the traditional way of life has generally been better preserved than in the Salt River Pima-Maricopa Indian Community. Some speculate this may be due to the fact that the Gila River, a central aspect of the traditional way of life, still flows through the reservation year-round (although at times as an intermittent stream), while the Salt River does not.
Deserts within the Sonoran
Colorado Desert
The Colorado Desert is a part of the larger Sonoran Desert extending southeastward for 164 miles (264 km) from the San Gorgonio Pass in southeastern California, (U.S.), to the Colorado River delta in northern Mexico. It encompasses approximately 2,500 sq mi (40,000 km²) east of Los Angeles and San Diego, extending from the San Bernardino Mountains east and southeast to the Colorado River, from which it takes its name.
The region is essentially the northwest extension of the Sonoran Desert to the southeast. It includes the heavily-irrigated Coachella and Imperial valleys on the north and south side of the Salton Sea respectively. It is crossed by several mountain ranges, including the San Jacinto, Santa Rosa, Little San Bernardino, and Chocolate mountains. It is also dominated by the San Andreas Transform Fault System.
Joshua Tree National Park is located on the northern edge of the region and includes many of the unique species and habitats of the region. The Colorado Desert encompasses the eastern part of the park and features natural gardens of creosote bush, ocotillo, and cholla cactus. The Little San Bernardino Mountains run through the southwest edge of the park. There are over 250 species of bird in the park including resident desert birds such as the Greater Roadrunner and Cactus Wren as well as Mockingbirds, Le Conte's Thrasher, Verdin, and Gambel's Quail.
Santa Rosa and San Jacinto National Monument, created in October 2,000, covers an area of 272,000 acres encompassing much of the San Jacinto and Santa Rosa mountains along the western side of the region. Five different climate zones exist here, from desert to pine forest and to arctic pine at the highest elevation. It is home to more than 500 plant and animal species including the Peninsular bighorn sheep.
Anza-Borrego Desert State Park is the largest state park in California and second largest state park in the United States, (after Adirondack State Park in New York). It covers 600,000 acres (2,400 km²) from the edge of the coastal mountains east of San Diego to the Salton Sea and south almost to the US-Mexico border. The park is named after Spanish explorer Juan Bautista de Anza and the Spanish word borrego, or Bighorn Sheep. The park features washes, wildflowers, palm groves, cacti, ocotillo, and sweeping vistas. There are also the greater roadrunner, golden eagles, kit foxes, mule deer, and bighorn sheep as well as iguanas, chuckwallas, and the red diamond rattlesnake.
With mountains all around, the highest are to the north—the Santa Rosa Mountains. The mountains are a wilderness, with no paved roads in, out or through. They have the only all-year-flowing watercourse in the park and are the home of the peninsular bighorn sheep, often called the Desert Bighorn.
Yuma Desert
The Yuma Desert is a lower-elevation section of the Sonoran Desert in the Salton basin. The desert contains areas of sparse vegetation and has notable areas of sand dunes. With an average rainfall of less than 8 inches each year, this is among the harshest deserts in North America. Human presence is sparse throughout, the largest town being Yuma, Arizona.
The desert includes the lower-elevation areas of the southwestern corner of Arizona, extending west to the Colorado River. On the other side of the river, in California, is the Low Desert region of the Sonoran Desert, also referred to as the Colorado Desert. Though the two regions are separated only by the Colorado River, there are numerous species of plant and animals that live only on one side or the other, such as the saguaro cactus, which occurs only east of the river. The Yuma Desert also includes the sandy plains of western Sonora, going all the way to the head of the Gulf of California, then an inland strip reaching into the central Sonoran interior.
Vegetation in the Yuma Desert is dominated by the Creosote bush (Larrea tridentata), which is widespread. The saguaro cactus Carnegiea gigantea and the ocotillo Fouquieria splendens are common on the bajadas, while many of the desert trees found are restricted to dry watercourses; these include palo verdes Parkinsonia, the desert willow Chilopsis linearis, ironwood Olneya tesota, and smoke trees Psorothamnus spinosus.
Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument is located in this desert and is the only place in the United States where the organ pipe cactus grows wild. Also found here are the Kofa National Wildlife Refuge and Cabeza Prieta National Wildlife Refuge. The Cabeza Prieta National Wildlife Refuge, established in 1939 to protect bighorn sheep, is located along 56 miles of the U.S. - Mexican border, and covers 860,010 acres, which is larger than the land area of the state of Rhode Island. There are 803,418 acres preserved as the Cabeza Prieta Refuge Wilderness.
Additional Public Lands
Sonoran Desert National Monument is located in the state of Arizona. Created by Presidential proclamation on January 17, 2001, the 496,337 acre (2,008 km²) monument is managed by the U.S. Bureau of Land Management, an agency within the U.S. Department of the Interior. The U.S. Bureau of Land Management already managed the lands, however under monument status, the level of protection and preservation of resources is enhanced. The North Maricopa Mountains, South Maricopa Mountains, and the Table Top Wildernesses protect the richest regions of desert habitat from any future development.
The Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum is one of the most visited attractions in Tucson, Arizona. Founded in 1952, it combines the attractions of a zoo, museum, and botanical garden. Its focus is the plants and animals that live in the Sonoran Desert, and it was a pioneer in the creation of naturalistic enclosures for its animals. The Center for Sonoran Desert Studies, founded in 2005, conducts the educational and scientific functions of the Museum and is a hub for research, education and conservation of the Sonoran Desert. Over 500,000 people visit the museum each year.
Casa Grande Ruins National Monument, in Coolidge, Arizona just northeast of the city of Casa Grande, preserves a group of Hohokam structures.
The national monument consists of the ruins of multiple structures surrounded by a compound wall constructed by the Hohokam, who farmed the Gila Valley in the early 1200s. "Casa grande" is Spanish for "big house" and the name refers to the largest structure on the site, which is what remains of a four-story structure that may have been abandoned by the mid-1400s. The structure is made of caliche, and has managed to survive the extreme weather conditions for about seven centuries. Casa Grande now has a distinctive modern roof covering built in 1932.
Proclaimed Casa Grande Reservation by an order of President Benjamin Harrison on June 22, 1892, it was redesignated a national monument by Woodrow Wilson on August 3, 1918. As with all historical areas administered by the National Park Service, Casa Grande was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on October 15, 1966.
Saguaro National Park is divided into two sections, lying approximately 20 miles (32 km) east and 15 miles (24 km) west of the center of the city of Tucson, Arizona. Total area in 2002 was 143 square miles (91,327 acres) (370 km²) of which 111 square miles (289 km²) is designated wilderness. Both sections conserve fine tracts of the Sonoran Desert, including ranges of significant hills, the Tucson Mountains in the west and the Rincon Mountains in the east. The park gets its name from the saguaro cactus which is native to the region. Many other kinds of cactus, including barrel cactus, cholla cactus, and prickly pear, are also abundant in the park. One endangered species of animals lives in the park part of the year during its migration, the Lesser Long-nosed Bat, as does the threatened Mexican Spotted Owl.
The park was established as Saguaro National Monument on March 1, 1933 and changed to a national park on October 14, 1994.
Proposals for greater national park system
A proposal was made in 1935 for a Sonoran Desert National Park, but was defeated due to mining and grazing interests in the area. In 1965, Secretary of Interior Stewart Udall and his brother Morris K. Udall, U.S. Representative from Arizona, raised the idea again; again it went nowhere.
The purpose and mission of this park would be to "protect significant desert features that provide world-class scenic, scientific, ecological, and educational opportunities."
The goals in the creation of this park, as stated by those making the proposal, would be to:
- Preserve the unrivaled scenic, natural, biologic, wildlife, and geologic resources of these unique natural landscapes, while perpetuating significant and diverse ecosystems of the Sonoran Desert in their natural state and processes. Ensure the maximum protection of wilderness values provided by law.
- Preserve the cultural and archaeological resources of the Sonoran Desert associated with the prehistoric, historic, and contemporary Native American, Hispanic, Anglo, and other cultures.
- Retain and enhance opportunities for scientific research in undisturbed ecosystems. Serve as a baseline station for environmental, biological, and climatic changes.
- Promote understanding and appreciation for the Sonoran Desert, and provide opportunities for compatible recreation.
Spanish missions in the Sonoran Desert
The Spanish missions in the Sonoran Desert are a series of religious outposts established by Spanish Catholic Jesuits and other orders to spread the Christian doctrine among the local Native Americans, but with the added benefit of giving Spain a toehold in the frontier lands of its colony of New Spain. The missions are in an area of the Sonoran Desert called "Pimería Alta," or "Upper Pima Country." It is now divided between the Mexican state of Sonora and the U.S. state of Arizona.
Father Kino
From 1493, the Kingdom of Spain had maintained a number of missions throughout Nueva España (New Spain, consisting of Mexico and portions of what today are the Southwestern United States in order to facilitate colonization of these lands.
In the spring of 1687, a Jesuit missionary from Italy named Father Kino lived and worked with the Native Americans (Pima) in the area called the "Pimería Alta," after ten unsuccessful years trying to make a mission in Baja, California. During Father Kino's stay in the Pimería Alta, he founded over 20 missions in eight mission districts, and introduced cattle raising and wheat to the local people. Some missions were destroyed in 1751 during the Pima Rebellion.
It was rumored that the Jesuit priests had amassed fortunes in the new land and were becoming very powerful. On February 3, 1768, King Carlos III ordered the Jesuits forcibly expelled from New Spain and returned to the home country.
The missions
- Mission Nuestra Señora de los Dolores: founded on March 13, 1687. This was the first mission founded by Father Kino. By 1744, the mission was abandoned. The cemetery remains on the site of the Tumacácori National Historical Park in Southern Arizona.
- Nuestra Señora de los Remedios was founded in 1687 and was abandoned by 1730. Nothing remains of this mission.
- San Ignacio de Cabórica was founded in 1687 and is located in San Ignacio, Sonora.
- San Pedro y San Pablo del Tubutama was founded in 1687.
- Santa Teresa de Atil was founded in 1687.
- Santa Maria Magdalena was founded in 1687, located in Sonora. In 1966 Father Kino's bones were found buried beneath area where the chapel had been.
- San José de Imuris was founded in 1687.
- Nuestra Señora del Pilar y Santiago de Cocóspera was founded in 1689. It is located in Cocóspera, Sonora.
- San Antonio Paduano del Oquitoa was founded in 1689. It is located in Oquitoa, Sonora.
- San Diego del Pitiquito was founded in 1689. It is located in Pitiquito, Sonora.
- San Luis Bacoancos was founded in 1691.
- San Cayetano de Tumacácori Mission was built in 1732, but construction stopped in 1822 due to lack of funds. The farming land around the mission was sold at auction in 1834 and the mission was abandoned by 1840. It is now a National Monument in Tumacácori National Historical Park in Southern Arizona.
- Los Santos Ángeles de Guevavi was founded in 1691.
- San Lázaro was founded in 1691.
- San Xavier del Bac, now in Tucson, Arizona, founded in 1692, the present building dates from 1785. The interior is richly decorated with ornaments showing a mixture of New Spain and Native American artistic motifs. It is still used by Tohono O'odham and Yaqui tribal members.
- San Cosme y Damián de Tucson: 1692
- Santa María Suamca: 1693
- Nuestra Señora de Loreto y San Marcelo de Sonoyta: 1693
- Nuestra Señora de la Ascención de Opodepe: 1704
- Los Santos Reyes de Sonoita/San Ignacio de Sonoitac: a rancheria near Tumacacori, 1692
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Abbey, Edward. 1973. Cactus country. New York: Time-Life Books. ASIN: B000X6J9E4
- Alcock, John. 1985. Sonoran Desert spring. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0226012581
- Alcock, John. 1990. Sonoran Desert summer. Tucson: University of Arizona Press. ISBN 0816511500
- Dykinga, Jack W., and Charles Bowden. 1992. The Sonoran Desert. New York: H.N. Abrams. ISBN 0810938243
- Jaeger, Edmund C. The North American Deserts. Stanford University Press, 1967. 73-83
- The Pimeria Alt: missions & more. Tucson, Ariz.: Southwestern Mission Research Center, 1996.
- Phillips, Steven, and Patricia Wentworth Comus. 2000. A natural history of the Sonoran Desert. Tucson: Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum. ISBN 0520220293
- Pickens, Buford L. The Missions of Northern Sonora, A 1935 Field Documentation, Tucson, University of Arizona Press. 1993 reprint. Retrieved May 19, 2007.
- Polzer, Charles. The Jesuit Missions of Northern Mexico. (The Spanish Borderlands Sourcebooks, Vol. 19) London: Routledge, 1991. ISBN 0824020960
- Joshua Tree National Park, National Park Service. Retrieved May 25, 2007.
- Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum, Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum. Retrieved May 25, 2007.
External links
All links retrieved February 3, 2023.
- Plagens, Michael J. Sonoran Desert Naturalist. Arizonensis.
- Sonoran Desert. Bio Images.
- Britannica.com Yuma Desert. Encyclopedia Britannica.
- Kino Missions. Mission Churches of the Sonoran Desert.
- Saguaro National Park. National Park Service.
| Deserts |
|---|
| Ad-Dahna | Alvord | Arabian | Aral Karakum | Atacama | Baja California | Barsuki | Betpak-Dala | Chalbi | Chihuahuan | Dasht-e Kavir | Dasht-e Lut | Dasht-e Margoh | Dasht-e Naomid | Gibson | Gobi | Great Basin | Great Sandy Desert | Great Victoria Desert | Kalahari | Karakum | Kyzylkum | Little Sandy Desert | Mojave | Namib | Nefud | Negev | Nubian | Ordos | Owyhee | Qaidam | Registan | Rub' al Khali | Ryn-Peski | Sahara | Saryesik-Atyrau | Sechura | Simpson | Sonoran | Strzelecki | Syrian | Taklamakan | Tanami | Thar | Tihamah | Ustyurt |
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
- Sonoran_Desert history
- Sonoran_Desert_National_Monument history
- Yuma_Desert history
- Colorado_Desert history
- Spanish_missions_in_the_Sonoran_Desert history
- Casa_Grande_Ruins_National_Monument history
- Saguaro_National_Park history
- Anza-Borrego_Desert_State_Park history
- Joshua_Tree_National_Park history
- Gila_River history
- Cabeza_Prieta_National_Wildlife_Refuge history
- Arizona-Sonora_Desert_Museum history
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.