Difference between revisions of "Georgetown, Guyana" - New World Encyclopedia
Mike Butler (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (75 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}}{{copyedited}} | ||
{{Infobox Settlement | {{Infobox Settlement | ||
<!--See the Table at Infobox Settlement for all fields and descriptions of usage—> | <!--See the Table at Infobox Settlement for all fields and descriptions of usage—> | ||
<!-- Basic info ----------------> | <!-- Basic info ----------------> | ||
| − | |official_name = Georgetown | + | |official_name = City of Georgetown |
| − | |other_name = | + | |other_name = |
| − | |native_name = | + | |native_name = |
| − | |nickname = Garden | + | |nickname = GT, The Garden City |
| − | |settlement_type = | + | |settlement_type = |
|motto = | |motto = | ||
| − | |||
|image_skyline = Governmental administration.jpg | |image_skyline = Governmental administration.jpg | ||
| − | |imagesize = | + | |imagesize = 250px |
|image_caption = Parliament Building, Georgetown | |image_caption = Parliament Building, Georgetown | ||
| − | |image_flag = | + | |image_flag = |
|flag_size = | |flag_size = | ||
| − | |image_seal = | + | |image_seal = |
|seal_size = | |seal_size = | ||
| − | |image_shield = | + | |image_shield = |
|shield_size = | |shield_size = | ||
|image_blank_emblem = | |image_blank_emblem = | ||
|blank_emblem_type = | |blank_emblem_type = | ||
|blank_emblem_size = | |blank_emblem_size = | ||
| − | |image_map = | + | |image_map = |
| − | |mapsize = | + | |mapsize = |
| − | |map_caption = | + | |map_caption = |
| − | |image_map1 = | + | |image_map1 = |
| − | |mapsize1 = | + | |mapsize1 = |
| − | |map_caption1 = | + | |map_caption1 = |
|image_dot_map = | |image_dot_map = | ||
|dot_mapsize = | |dot_mapsize = | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
|pushpin_map_caption =Location in Guyana | |pushpin_map_caption =Location in Guyana | ||
<!-- Location ------------------> | <!-- Location ------------------> | ||
| + | |coordinates_region = GY | ||
|subdivision_type = Country | |subdivision_type = Country | ||
|subdivision_name = [[Image:Flag of Guyana.svg|25px]] [[Guyana]] | |subdivision_name = [[Image:Flag of Guyana.svg|25px]] [[Guyana]] | ||
|subdivision_type1 = Admin. division | |subdivision_type1 = Admin. division | ||
|subdivision_name1 = [[Demerara-Mahaica]] | |subdivision_name1 = [[Demerara-Mahaica]] | ||
| − | |subdivision_type2 = | + | |subdivision_type2 = |
| − | |subdivision_name2 = | + | |subdivision_name2 = |
| − | |subdivision_type3 = | + | |subdivision_type3 = |
| − | |subdivision_name3 = | + | |subdivision_name3 = |
| − | |subdivision_type4 = | + | |subdivision_type4 = |
|subdivision_name4 = | |subdivision_name4 = | ||
<!-- Politics -----------------> | <!-- Politics -----------------> | ||
|government_footnotes = | |government_footnotes = | ||
| − | |government_type = | + | |government_type = Mayor-Council |
| − | |leader_title = | + | |leader_title = Mayor |
| − | |leader_name = | + | |leader_name = Hamilton Greene |
|leader_title1 = <!-- for places with, say, both a mayor and a city manager —> | |leader_title1 = <!-- for places with, say, both a mayor and a city manager —> | ||
|leader_name1 = | |leader_name1 = | ||
| Line 58: | Line 59: | ||
|leader_title4 = | |leader_title4 = | ||
|leader_name4 = | |leader_name4 = | ||
| − | |established_title = | + | |established_title = Established |
| − | |established_date = | + | |established_date = 1781 |
| − | |established_title2 = | + | |established_title2 = Named |
| − | |established_date2 = | + | |established_date2 = 29 April 1812 |
|established_title3 = <!-- Incorporated (city) —> | |established_title3 = <!-- Incorporated (city) —> | ||
|established_date3 = | |established_date3 = | ||
<!-- Area ---------------------> | <!-- Area ---------------------> | ||
| − | |area_magnitude = | + | |area_magnitude = 87 |
|unit_pref =Imperial <!--Enter: Imperial, if Imperial (metric) is desired—> | |unit_pref =Imperial <!--Enter: Imperial, if Imperial (metric) is desired—> | ||
|area_footnotes = | |area_footnotes = | ||
| Line 73: | Line 74: | ||
|area_total_sq_mi = | |area_total_sq_mi = | ||
|area_land_sq_mi = | |area_land_sq_mi = | ||
| − | |area_water_sq_mi = | + | |area_water_sq_mi = 10 |
|area_water_percent = | |area_water_percent = | ||
|area_urban_km2 = | |area_urban_km2 = | ||
| − | |area_urban_sq_mi = | + | |area_urban_sq_mi = 20 |
|area_metro_km2 = | |area_metro_km2 = | ||
| − | |area_metro_sq_mi = | + | |area_metro_sq_mi = 57 |
|area_blank1_title = | |area_blank1_title = | ||
|area_blank1_km2 = | |area_blank1_km2 = | ||
|area_blank1_sq_mi = | |area_blank1_sq_mi = | ||
<!-- Population -----------------------> | <!-- Population -----------------------> | ||
| − | |population_as_of = | + | |population_as_of =2009 |
|population_footnotes = | |population_footnotes = | ||
|population_note = | |population_note = | ||
| − | |population_total = | + | |population_total =239,227 |
|population_density_km2 = | |population_density_km2 = | ||
|population_density_sq_mi = | |population_density_sq_mi = | ||
| − | |population_metro = | + | |population_metro =354,964 |
|population_density_metro_km2 = | |population_density_metro_km2 = | ||
|population_density_metro_sq_mi = | |population_density_metro_sq_mi = | ||
| Line 99: | Line 100: | ||
|population_blank2_title =Religions | |population_blank2_title =Religions | ||
|population_blank2 = | |population_blank2 = | ||
| − | |population_density_blank1_km2 = | + | |population_density_blank1_km2 = |
|population_density_blank1_sq_mi = | |population_density_blank1_sq_mi = | ||
<!-- General information ---------------> | <!-- General information ---------------> | ||
| − | |timezone = | + | |timezone = [[UTC-4]] |
| − | |utc_offset = | + | |utc_offset = |
| − | |timezone_DST = | + | |timezone_DST = |
| − | |utc_offset_DST = | + | |utc_offset_DST = |
|latd=6 |latm=48 |lats= |latNS=N | |latd=6 |latm=48 |lats= |latNS=N | ||
| − | |longd=58|longm=10 |longs= |longEW=W | + | |longd=58|longm=10 |longs= | longEW=W|coordinates_display=d |
|elevation_footnotes = <!--for references: use <ref> tags—> | |elevation_footnotes = <!--for references: use <ref> tags—> | ||
| − | |elevation_m = | + | |elevation_m = 0 |
| − | |elevation_ft = | + | |elevation_ft = -6 |
<!-- Area/postal codes & others --------> | <!-- Area/postal codes & others --------> | ||
|postal_code_type = <!-- enter ZIP code, Postcode, Post code, Postal code... —> | |postal_code_type = <!-- enter ZIP code, Postcode, Post code, Postal code... —> | ||
|postal_code = | |postal_code = | ||
| − | |area_code = | + | |area_code = 231, 233, 225, 226, 227 |
|blank_name = | |blank_name = | ||
|blank_info = | |blank_info = | ||
|blank1_name = | |blank1_name = | ||
|blank1_info = | |blank1_info = | ||
| − | |website = | + | |website = |
| − | |footnotes = | + | |footnotes = |
| − | }} | + | }} |
| − | '''Georgetown''' | + | '''Georgetown''' is the [[Capital (political)|capital]] and largest city of [[Guyana]] on the mainland of [[South America]]. The city is located on the [[Atlantic Ocean]] at the mouth of the [[Demerara River]], in the region known as Demerara-Mahaica. A retail and administrative center, and a financial services center, Georgetown is Guyana's chief seaport. The city's existence and survival from the elements depends on a sea wall, drainage canals, and sluice gates as it is situated three feet, about one meter, below the high tide level. |
| + | |||
| + | Founded by the British in 1781 and named for King [[George III of the United Kingdom]], Georgetown long served as the capital of [[British Guiana]]. The city also came under both French and Dutch rule. It was largely rebuilt by the French by 1784. A devastating [[fire]], in 1945, ruined the commercial heart of the capital, and destroyed historical and [[architecture|architectural]] gems which lent greatly to the city's character. | ||
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | Guyana is the third smallest country on the mainland of South America and is one of the poorest countries in the [[Western Hemisphere]]. Following its independence from the [[United Kingdom]] in 1966, the country was subject to [[socialism|socialist]] policies that resulted in a deteriorating [[economics|economy]]. A reform program began in 1989 and reduced the government's role in the country's economics and encouraged foreign investment. However, city leadership lacked accountability, exacerbating many of the city's problems. This issue was being addressed in 2008 by Georgetown's mayor, [[Hamilton Green]]—a possible important first step in instituting good governance and ensuring equitable prosperity. | ||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| − | [[Image:Dwelling in city.jpg|left|thumb| | + | [[Image:Dwelling in city.jpg|left|thumb|225px|A colonial era building.]] |
| − | [[Image:Laluni St panorama.jpg|thumb|left| | + | [[Image:Laluni St panorama.jpg|thumb|left|225px|Laluni St, Queenstown, Georgetown, 2006.]] |
| − | Georgetown was named after King [[George III]] when the city was | + | Georgetown was named after King [[George III]] when the city was recaptured by the British in 1812. It is situated on the [[Atlantic Ocean]] coast at the mouth of the [[Demerara River]] and was nicknamed "Garden City of the Caribbean." |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The local [[climate]] is tropical, hot and humid, and moderated by northeast trade winds. The average maximum daytime [[temperature]] year-round is 86°F (30°C). Mean annual precipitation is 40 inches (1004 mm). | |
| − | + | Georgetown, which is laid out in a north-south, east-west grid, is interlaced with [[canal]]s protected by [[kokers]], or sluices. The city was built by the [[Netherlands|Dutch]] and later the [[Great Britain|British]] provided drainage to the city that lies three feet (one meter) below high-tide level. A long sea wall helps prevent flooding. The city covers an area of 15 square miles (38.8 square kilometers). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | Georgetown has expanded dramatically through the years and may be divided into three regions: Central Georgetown that includes the business district as well as the seat of the federal Government; Greater Georgetown, that contains some of the most expensive and luxurious metropolitan neighborhoods; and South Georgetown, a poor area along the eastern bank of the Demerara River. | ||
| + | The city has an abundance of tree-lined streets and avenues and contains many wooden colonial buildings and markets. Regent Street is Georgetown's premier shopping district, while Sheriff Street is Guyana's popular entertainment center. | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
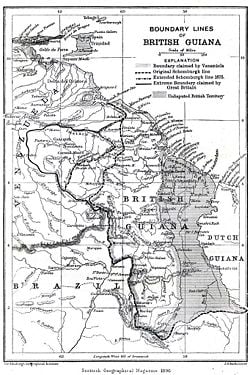
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Boundary lines of British Guiana 1896.jpg|right|thumb|250 px|Boundary lines of British Guiana in 1896.]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The history of Guyana began before the arrival of [[Europe]]ans, when the region of present-day [[Guyana]] was inhabited by [[Carib]], [[Arawak]], and [[Warao]] peoples. Guyana's first sighting by Europeans was by [[Alonzo de Ojeda]] and [[Amerigo Vespucci]] in 1499. In 1595, [[Sir Walter Raleigh]] explored the area for [[England]]. The [[Dutch]] began exploring and settling in Guyana in the late sixteenth century, followed by the [[British]]. Both began trading with the Amerindian peoples upriver. | |
| − | + | The first Dutch settlement was established on the [[Pomeroon River]] in 1581. The settlers were evicted by Spaniards and [[Amerindian|Indians]], probably in 1596. Until 1804, there were estates, now forgotten, at Sandy Point and Kierfield, on the seaward side of the present seawall of Georgetown. | |
| − | + | Georgetown began as a small town in the eighteenth century. Originally, the capital of the [[Demerara-Essequibo]] colony was located on [[Borselen Island]] in the Demerara River under the administration of the [[Netherlands|Dutch]]. When the [[British]] captured the colony in 1781, Lieutenant-Colonel [[Robert Kingston]] chose the mouth of the Demerara River for the establishment of a town which was situated between Plantations Werk-en-rust and Vlissengen. | |
| − | + | The [[France|French]] captured the colony in 1782 and developed this town, making it their capital city, [[La Nouvelle Ville]]. To guard against the dangers of flood and fire, buildings were required to have brick foundations, tiled, separate kitchens, and no thatch was to be used. | |
| − | + | At that time, the small town was bordered by two canals, the Croal Street Canal and the Hadfield Street Canal. There was one main [[dam]] known as Brickdam. | |
| − | + | When the town was taken by the Dutch in 1784, it was renamed [[Stabroek]] after [[Nicolaas Geelvinck]] (1732—1787), Lord of Stabroek, and President of the [[Dutch West India Company]]. The Dutch settlers soon built walls similar to those used in their homeland to keep the [[Atlantic Ocean]] out from the north, and divert water coming from the higher ground to the south. Eventually the town expanded and covered the estates of Vlissengen, La Bourgade, and Eve Leary to the North, and La Repentir to the South. | |
| − | + | When the British regained control in 1812, it was renamed Georgetown, in honor of [[King George III]]. The town began to expand and develop, and Robbstown, Cummingsburg, Kingston, and Werk-en-Rust were added. | |
| − | + | The abolition of [[slavery]] in 1834 led to black settlement of urban areas and the importation of indentured servants from [[India]] to work the [[sugar]] plantations. | |
| + | |||
| + | Under the English administration, the town was controlled by a Board of Police. However with the abolition of slavery, the powers of the Board of Police proved ineffective and on March 1, 1837, an ordinance established a mayor and town council. | ||
| − | + | Georgetown gained official city status on August 24, 1842, during the reign of [[Queen Victoria]]. In 1848, the British built a railroad, five miles (eight kilometers) long, from Georgetown to Plaisance, which was the first railroad on the [[South America]]n continent. | |
| − | + | In 1928, British Guiana was made a crown colony, a move that reasserted British control at a time when political and labor unrest was rising. | |
| − | + | On February 23, 1945, the Great Fire, as it came to be known, devastated the commercial heart of the capital, and consumed a host of historical and architectural gems which had given the city its character. Most buildings in the business district were rebuilt in reinforced concrete. | |
| − | + | Guyana achieved independence from the [[United Kingdom]] in 1966, and became a republic on February 23, 1970, though remaining a member of the Commonwealth. Forbes Burnham (1923-1985) became the first prime minister and nationalized foreign companies that dominated the [[bauxite]] and sugar industries. Greater Georgetown came into being on April 29, 1970. | |
| − | + | In 1992, Cheddi Jagan (1918–1997) was elected president in what is considered the country's first free and fair election since independence. After his death five years later, his wife, Janet Jagan (b. 1920), became president but resigned in 1999 due to poor health. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Government== | ==Government== | ||
[[Image:Cottage of city Georgetown.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Victoria Law Courts.]] | [[Image:Cottage of city Georgetown.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Victoria Law Courts.]] | ||
| − | Guyana is a republic in which the chief of state president is elected as leader of a party list in parliamentary elections, every five years. The head of government is the prime minister, who is appointed by the president. The unicameral National Assembly comprises 65 members elected every five years. A cabinet of ministers is appointed by the president. | + | [[Guyana]] is a republic in which the chief of state is the president, who is elected as leader of a party list in parliamentary elections, every five years. The head of government is the prime minister, who is appointed by the president. The unicameral National Assembly comprises 65 members elected every five years. A cabinet of ministers is appointed by the president. |
| − | + | Guyana is divided into 10 regions, each headed by a chairman who presides over a regional democratic council. The regions are divided into 27 neighborhood councils. Local communities are administered by village or city councils. | |
| − | Georgetown is | + | As the capital of Guyana, Georgetown is the location of Parliament Building, the Court of Appeals, the official residence of the Head of State as well as the Head of Government. Georgetown is the seat of the Caribbean Community ([[Caricom|CARICOM]]) Secretariat, which is the the administrative Arm of the Caribbean Regional Integration Organisation. |
| − | + | Georgetown is governed by a mayor, whose office includes the deputy mayor, city clerk, and city engineer, and supervises the city constables. The city council is the legislative branch of the city government. The Georgetown Magistrate Court has judicial responsibility for the Georgetown Magisterial District. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Guyana]] is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children [[Slave trade|trafficked]] for the purposes of commercial sexual exploitation and forced labor. The nation is also a trans shipment point for [[narcotics]] from [[South America]]—primarily [[Venezuela]]—to [[Europe]] and the [[United States]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | == Economy == | ||
| + | [[Image:Stabroek Market Clock by Khirsah1.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Stabroek Market Clock]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Bourda-market.jpg|thumb|right|250 px|A section of Bourda Market, Georgetown.]] | ||
| + | The Guyanese economy showed moderate economic growth in the first decade of the twenty-first century, based on expansion in the [[agriculture|agricultural]] and [[mining]] sectors, a more favorable atmosphere for business initiatives, a more realistic exchange rate, fairly low inflation, and the continued support of international organizations. Chronic problems include a shortage of skilled labor and a deficient [[infrastructure]]. The government, in 2008, was juggling a sizable external debt against the urgent need for expanded public investment. The [[bauxite]] mining sector was expected to benefit from restructuring and partial privatization, and the state-owned [[sugar]] industry was to conduct efficiency increasing modernizations. | ||
| − | Georgetown is Guyana's largest city and | + | Georgetown is Guyana's largest [[city]] and is the country's chief commercial and manufacturing center. Large sugar refineries are located in the city. Businesses include: Demerara [[sugar]], [[timber]], [[bauxite]], [[gold]], and [[diamond]]s, which are exported through Georgetown's harbor. |
| − | + | This city accounts for a large portion of Guyana's GDP, estimated at $2.819-billion in 2007. Guyana's per capital GDP was estimated at $3700 in that year. | |
| − | + | Georgetown is serviced by a ferry, the [[Demerara Harbour Bridge]] and the four-lane East Coast Highway that was completed in 2005. Numerous buses and taxis serve Georgetown. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The [[Cheddi Jagan International Airport]] is located on the right bank of the [[Demerara River]], 41 kilometers south of Georgetown. Closer to the city is the newly-expanded [[Ogle Airport]], with a new terminal to handle regional international and inter-Caricom flights. Georgetown hosts Guyana's only seaport. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Demographics== | |
| − | + | Georgetown had an estimated [[population]] of 310,320 in 2002. The population of [[Guyana]] (769,000) is racially and ethnically heterogeneous, composed chiefly of the descendants of immigrants who came to the country either as slaves or as indentured laborers. East Indians made up 43.5 percent of Guyana's population, black (Africans) 30.2 percent, mixed 16.7 percent, Amerindians 9.1 percent, and others 0.5 percent in 2002. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Guyana's [[culture]] is very similar to that of the [[English language|English]]-speaking [[Caribbean]], to the extent that Guyana is included and accepted as a Caribbean nation. [[Language]]s spoken are English, Amerindian dialects, Creole, Caribbean Hindustani (a dialect of Hindi), and [[Urdu]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Religion]]s, according to the 2002 census, include [[Hinduism|Hindu]] 28.4 percent, [[Pentecostalism|Pentecostal]] 16.9 percent, [[Roman Catholic]] 8.1 percent, [[Anglican]] 6.9 percent, [[Seventh Day Adventist]] 5 percent, [[Methodism|Methodist]] 1.7 percent, [[Jehovah Witness]] 1.1 percent, other [[Christian]] 17.7 percent, [[Muslim]] 7.2 percent, other 4.3 percent, none 4.3 percent. | |
| − | |||
| + | Georgetown is the seat of the [[University of Guyana]], and the Cyril Potter College. | ||
| − | + | Georgetown's population is racially and ethnically heterogeneous, and its culture is more closely associated with the [[Caribbean]] than with [[Latin America]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Places of interest== | |
| − | + | [[Image:Umana Yana by Khirsah1.jpg|thumb|right|250 px|Umana Yana, built by Wai-Wai [[Amerindian]]s using traditional techniques.]] | |
| + | [[Image:Smaller Providence Stadium inside.jpg|right|thumb|250px|[[Providence Stadium]] hosted several [[2007 Cricket World Cup]], replacing [[Bourda]] as the national stadium and [[cricket test]] venue.]] | ||
| − | + | Most of the city's main buildings are centered around the western part of Georgetown, which is the location of Independence Square and Promenade Gardens, the Walter Roth Museum of Anthropology, the National Library of Guyana (built by [[Andrew Carnegie]]), the Bank of Guyana, the National Museum of Guyana, and State House (built 1852) where the president resides, and [[St. George's Anglican Cathedral]]. There are numerous [[church]]es, [[mosque]]s and Hindu [[mandir]]s. | |
| − | [[ | ||
| − | + | To the south is where the neo-[[Gothic]] Georgetown City Hall (1889) is to be found, as well as the Victoria Law Courts (1887), the Roman Catholic Brickdam Cathedral, City Engineer House, the Magistrate's Court, St. Andrew's Kirk (1818), and Independence Arch. | |
| + | The northern area of the city near the Atlantic coast contains Fort William Frederick, a park, and the [[Umana Yana]], a conical thatched building built by Wai-Wai [[Amerindian]]s using traditional techniques for the 1972 [[Non-Aligned Foreign Ministers Conference]]. The [[Georgetown Light House]] is a landmark. | ||
| − | + | The city also has an extensive [[botanical garden]], a [[zoo]], and a seaside promenade. Places of interest include: | |
| − | + | * [[Guyana]]'s Parliament Building, designed by [[Joseph Hadfield]], was built on a foundation of [[Chlorocardium|greenheart]] logs. The foundation stone was laid in 1829 and, in April 1834, the structure, [[stucco]]ed to resemble stone blocks, was completed. The Parliament Building is an example of 19th century [[Renaissance architecture]] and is one of two domed buildings in the city. Within its compound are two [[cannon]]s that were used in the [[Crimean War]] and a statue of [[Hubert Nathaniel Critchlow]], OBE (1884-1958) who is regarded as the father of [[Trade Union]]ism in Guyana. | |
| − | The | + | * The National Art Gallery, Castellani House, is a large wooden building that was designed by Cesar Castellani. It served as the residence of the Director of Agriculture, then the Prime Minister. In 1993, it was inaugurated as the Art Gallery. |
| − | + | * The Stabroek Market, which sells [[fruit]]s, [[vegetable]]s, [[livestock]], [[meat]], [[fish]], [[furniture]], manufactured household goods, tools, [[jewelry]], and more, has a prominent cast-iron clock tower that dominates the city sky line. The market extends from Water Street to the bank of the [[Demerara River]]. | |
| − | + | ==Looking to the future== | |
| + | Georgetown, the [[capital]] and largest [[city]] of [[Guyana]], serves as a retail and administrative center, a financial services center, and is the country’s chief port. The nationalization of foreign companies operating in Guyana in the late 1970s caused an exodus of skilled people and capital, from which the nation has yet to recover. Run-down buildings, a shortage of skilled labor and a deficient infrastructure were evident in the capital city in 2008, as the government juggled a sizable external debt against the urgent need for expanded public investment. | ||
| − | + | [[Hamilton Green]], Georgetown's mayor and the former prime minister of Guyana, has called for governmental accountability. Green describes true democracy thus: "The test of a modern Democracy is a form of governance in which political and economic power is shared, and where these truly reside in the people and exercised by them through time honoured institutions, their representatives and protocol."<ref>Hamilton Green, [http://propagandapress.org/2008/10/11/guyana-has-a-facade-of-democracy-hamilton-green/ Guyana has a facade of democracy,] ''Propaganda Press! Freedom in Guyana''. Retrieved December 13, 2008.</ref> He has gone on to declare that the city can prosper only when those in charge are held accountable. When financial corruption ceases, funds can be used more equitably and wisely in solving many of Georgetown's problems. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==Notes== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | {{ | + | * De Barros, Juanita. ''Order and Place in a Colonial City: Patterns of Struggle and Resistance in Georgetown, British Guiana, 1889-1924.'' Montréal: McGill-Queen's University Press, 2003. ISBN 978-0773524552. |
| + | * Edwards, R., S. C. Wu, and J. Mensah. "Georgetown, Guyana." ''Cities.'' 22 (6) (2005): 446-454. ISSN 0264-2751. | ||
| + | * Guyana Lands and Surveys Commission. 2006. ''The City of Georgetown.'' Georgetown: Guyana Lands and Surveys Commission. {{OCLC|162107765}}. | ||
| + | * ''Historical Georgetown Guyana''. Georgetown, Guyana: Sheik M. Hassan, 1997. {{OCLC|45069045}}. | ||
| + | * Temple, Bob. ''Guyana. Discovering South America''. Philadelphia, PA: Mason Crest Publishers, 2004. ISBN 1590843002. | ||
| + | * ''World Fact Book,'' 2008. | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | + | All links retrieved June 19, 2017. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | * Guyana On-line Tourist Guide [http://www.turq.com/guyana/georgetown.html Georgetown tour] | ||
| + | * [http://www.galenfrysinger.com/guyana.htm Georgetown photo gallery] | ||
| + | * [http://www.tramz.com/gy/g.html The Tramways of Georgetown] | ||
| + | * [http://www.guyana.org/special/great_fire.html The Great Fire of 1945] | ||
| + | * [http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?sec=travel&res=9901E7D8163FF935A35751C0A9669C8B63 Article: Guyana's Capital, Tropical Victorian] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{South American capitals}} | ||
[[Category:Geography]] | [[Category:Geography]] | ||
[[Category:Cities]] | [[Category:Cities]] | ||
| − | + | [[Category:South America]] | |
| − | {{credit | + | {{credit|Georgetown,_Guyana|252471957|History_of_Guyana|252133798|}} |
Latest revision as of 20:14, 13 December 2023
| City of Georgetown | |
| Parliament Building, Georgetown | |
| Nickname: GT, The Garden City | |
| Location in Guyana | |
| Coordinates: 6°48′N 58°10′W | |
|---|---|
| Country | |
| Admin. division | Demerara-Mahaica |
| Established | 1781 |
| Named | 29 April 1812 |
| Government | |
| - Type | Mayor-Council |
| - Mayor | Hamilton Greene |
| Area | |
| - Water | 10 sq mi (25.9 km²) |
| - Urban | 20 sq mi (51.8 km²) |
| - Metro | 57 sq mi (147.6 km²) |
| Elevation | -6 ft (0 m) |
| Population (2009) | |
| - City | 239,227 |
| - Metro | 354,964 |
| Time zone | UTC-4 (UTC) |
| Area code(s) | 231, 233, 225, 226, 227 |
Georgetown is the capital and largest city of Guyana on the mainland of South America. The city is located on the Atlantic Ocean at the mouth of the Demerara River, in the region known as Demerara-Mahaica. A retail and administrative center, and a financial services center, Georgetown is Guyana's chief seaport. The city's existence and survival from the elements depends on a sea wall, drainage canals, and sluice gates as it is situated three feet, about one meter, below the high tide level.
Founded by the British in 1781 and named for King George III of the United Kingdom, Georgetown long served as the capital of British Guiana. The city also came under both French and Dutch rule. It was largely rebuilt by the French by 1784. A devastating fire, in 1945, ruined the commercial heart of the capital, and destroyed historical and architectural gems which lent greatly to the city's character.
Guyana is the third smallest country on the mainland of South America and is one of the poorest countries in the Western Hemisphere. Following its independence from the United Kingdom in 1966, the country was subject to socialist policies that resulted in a deteriorating economy. A reform program began in 1989 and reduced the government's role in the country's economics and encouraged foreign investment. However, city leadership lacked accountability, exacerbating many of the city's problems. This issue was being addressed in 2008 by Georgetown's mayor, Hamilton Green—a possible important first step in instituting good governance and ensuring equitable prosperity.
Geography
Georgetown was named after King George III when the city was recaptured by the British in 1812. It is situated on the Atlantic Ocean coast at the mouth of the Demerara River and was nicknamed "Garden City of the Caribbean."
The local climate is tropical, hot and humid, and moderated by northeast trade winds. The average maximum daytime temperature year-round is 86°F (30°C). Mean annual precipitation is 40 inches (1004 mm).
Georgetown, which is laid out in a north-south, east-west grid, is interlaced with canals protected by kokers, or sluices. The city was built by the Dutch and later the British provided drainage to the city that lies three feet (one meter) below high-tide level. A long sea wall helps prevent flooding. The city covers an area of 15 square miles (38.8 square kilometers).
Georgetown has expanded dramatically through the years and may be divided into three regions: Central Georgetown that includes the business district as well as the seat of the federal Government; Greater Georgetown, that contains some of the most expensive and luxurious metropolitan neighborhoods; and South Georgetown, a poor area along the eastern bank of the Demerara River.
The city has an abundance of tree-lined streets and avenues and contains many wooden colonial buildings and markets. Regent Street is Georgetown's premier shopping district, while Sheriff Street is Guyana's popular entertainment center.
History
The history of Guyana began before the arrival of Europeans, when the region of present-day Guyana was inhabited by Carib, Arawak, and Warao peoples. Guyana's first sighting by Europeans was by Alonzo de Ojeda and Amerigo Vespucci in 1499. In 1595, Sir Walter Raleigh explored the area for England. The Dutch began exploring and settling in Guyana in the late sixteenth century, followed by the British. Both began trading with the Amerindian peoples upriver.
The first Dutch settlement was established on the Pomeroon River in 1581. The settlers were evicted by Spaniards and Indians, probably in 1596. Until 1804, there were estates, now forgotten, at Sandy Point and Kierfield, on the seaward side of the present seawall of Georgetown.
Georgetown began as a small town in the eighteenth century. Originally, the capital of the Demerara-Essequibo colony was located on Borselen Island in the Demerara River under the administration of the Dutch. When the British captured the colony in 1781, Lieutenant-Colonel Robert Kingston chose the mouth of the Demerara River for the establishment of a town which was situated between Plantations Werk-en-rust and Vlissengen.
The French captured the colony in 1782 and developed this town, making it their capital city, La Nouvelle Ville. To guard against the dangers of flood and fire, buildings were required to have brick foundations, tiled, separate kitchens, and no thatch was to be used.
At that time, the small town was bordered by two canals, the Croal Street Canal and the Hadfield Street Canal. There was one main dam known as Brickdam.
When the town was taken by the Dutch in 1784, it was renamed Stabroek after Nicolaas Geelvinck (1732—1787), Lord of Stabroek, and President of the Dutch West India Company. The Dutch settlers soon built walls similar to those used in their homeland to keep the Atlantic Ocean out from the north, and divert water coming from the higher ground to the south. Eventually the town expanded and covered the estates of Vlissengen, La Bourgade, and Eve Leary to the North, and La Repentir to the South.
When the British regained control in 1812, it was renamed Georgetown, in honor of King George III. The town began to expand and develop, and Robbstown, Cummingsburg, Kingston, and Werk-en-Rust were added.
The abolition of slavery in 1834 led to black settlement of urban areas and the importation of indentured servants from India to work the sugar plantations.
Under the English administration, the town was controlled by a Board of Police. However with the abolition of slavery, the powers of the Board of Police proved ineffective and on March 1, 1837, an ordinance established a mayor and town council.
Georgetown gained official city status on August 24, 1842, during the reign of Queen Victoria. In 1848, the British built a railroad, five miles (eight kilometers) long, from Georgetown to Plaisance, which was the first railroad on the South American continent.
In 1928, British Guiana was made a crown colony, a move that reasserted British control at a time when political and labor unrest was rising.
On February 23, 1945, the Great Fire, as it came to be known, devastated the commercial heart of the capital, and consumed a host of historical and architectural gems which had given the city its character. Most buildings in the business district were rebuilt in reinforced concrete.
Guyana achieved independence from the United Kingdom in 1966, and became a republic on February 23, 1970, though remaining a member of the Commonwealth. Forbes Burnham (1923-1985) became the first prime minister and nationalized foreign companies that dominated the bauxite and sugar industries. Greater Georgetown came into being on April 29, 1970.
In 1992, Cheddi Jagan (1918–1997) was elected president in what is considered the country's first free and fair election since independence. After his death five years later, his wife, Janet Jagan (b. 1920), became president but resigned in 1999 due to poor health.
Government
Guyana is a republic in which the chief of state is the president, who is elected as leader of a party list in parliamentary elections, every five years. The head of government is the prime minister, who is appointed by the president. The unicameral National Assembly comprises 65 members elected every five years. A cabinet of ministers is appointed by the president.
Guyana is divided into 10 regions, each headed by a chairman who presides over a regional democratic council. The regions are divided into 27 neighborhood councils. Local communities are administered by village or city councils.
As the capital of Guyana, Georgetown is the location of Parliament Building, the Court of Appeals, the official residence of the Head of State as well as the Head of Government. Georgetown is the seat of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) Secretariat, which is the the administrative Arm of the Caribbean Regional Integration Organisation.
Georgetown is governed by a mayor, whose office includes the deputy mayor, city clerk, and city engineer, and supervises the city constables. The city council is the legislative branch of the city government. The Georgetown Magistrate Court has judicial responsibility for the Georgetown Magisterial District.
Guyana is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children trafficked for the purposes of commercial sexual exploitation and forced labor. The nation is also a trans shipment point for narcotics from South America—primarily Venezuela—to Europe and the United States.
Economy
The Guyanese economy showed moderate economic growth in the first decade of the twenty-first century, based on expansion in the agricultural and mining sectors, a more favorable atmosphere for business initiatives, a more realistic exchange rate, fairly low inflation, and the continued support of international organizations. Chronic problems include a shortage of skilled labor and a deficient infrastructure. The government, in 2008, was juggling a sizable external debt against the urgent need for expanded public investment. The bauxite mining sector was expected to benefit from restructuring and partial privatization, and the state-owned sugar industry was to conduct efficiency increasing modernizations.
Georgetown is Guyana's largest city and is the country's chief commercial and manufacturing center. Large sugar refineries are located in the city. Businesses include: Demerara sugar, timber, bauxite, gold, and diamonds, which are exported through Georgetown's harbor.
This city accounts for a large portion of Guyana's GDP, estimated at $2.819-billion in 2007. Guyana's per capital GDP was estimated at $3700 in that year.
Georgetown is serviced by a ferry, the Demerara Harbour Bridge and the four-lane East Coast Highway that was completed in 2005. Numerous buses and taxis serve Georgetown.
The Cheddi Jagan International Airport is located on the right bank of the Demerara River, 41 kilometers south of Georgetown. Closer to the city is the newly-expanded Ogle Airport, with a new terminal to handle regional international and inter-Caricom flights. Georgetown hosts Guyana's only seaport.
Demographics
Georgetown had an estimated population of 310,320 in 2002. The population of Guyana (769,000) is racially and ethnically heterogeneous, composed chiefly of the descendants of immigrants who came to the country either as slaves or as indentured laborers. East Indians made up 43.5 percent of Guyana's population, black (Africans) 30.2 percent, mixed 16.7 percent, Amerindians 9.1 percent, and others 0.5 percent in 2002.
Guyana's culture is very similar to that of the English-speaking Caribbean, to the extent that Guyana is included and accepted as a Caribbean nation. Languages spoken are English, Amerindian dialects, Creole, Caribbean Hindustani (a dialect of Hindi), and Urdu.
Religions, according to the 2002 census, include Hindu 28.4 percent, Pentecostal 16.9 percent, Roman Catholic 8.1 percent, Anglican 6.9 percent, Seventh Day Adventist 5 percent, Methodist 1.7 percent, Jehovah Witness 1.1 percent, other Christian 17.7 percent, Muslim 7.2 percent, other 4.3 percent, none 4.3 percent.
Georgetown is the seat of the University of Guyana, and the Cyril Potter College.
Georgetown's population is racially and ethnically heterogeneous, and its culture is more closely associated with the Caribbean than with Latin America.
Places of interest

Most of the city's main buildings are centered around the western part of Georgetown, which is the location of Independence Square and Promenade Gardens, the Walter Roth Museum of Anthropology, the National Library of Guyana (built by Andrew Carnegie), the Bank of Guyana, the National Museum of Guyana, and State House (built 1852) where the president resides, and St. George's Anglican Cathedral. There are numerous churches, mosques and Hindu mandirs.
To the south is where the neo-Gothic Georgetown City Hall (1889) is to be found, as well as the Victoria Law Courts (1887), the Roman Catholic Brickdam Cathedral, City Engineer House, the Magistrate's Court, St. Andrew's Kirk (1818), and Independence Arch.
The northern area of the city near the Atlantic coast contains Fort William Frederick, a park, and the Umana Yana, a conical thatched building built by Wai-Wai Amerindians using traditional techniques for the 1972 Non-Aligned Foreign Ministers Conference. The Georgetown Light House is a landmark.
The city also has an extensive botanical garden, a zoo, and a seaside promenade. Places of interest include:
- Guyana's Parliament Building, designed by Joseph Hadfield, was built on a foundation of greenheart logs. The foundation stone was laid in 1829 and, in April 1834, the structure, stuccoed to resemble stone blocks, was completed. The Parliament Building is an example of 19th century Renaissance architecture and is one of two domed buildings in the city. Within its compound are two cannons that were used in the Crimean War and a statue of Hubert Nathaniel Critchlow, OBE (1884-1958) who is regarded as the father of Trade Unionism in Guyana.
- The National Art Gallery, Castellani House, is a large wooden building that was designed by Cesar Castellani. It served as the residence of the Director of Agriculture, then the Prime Minister. In 1993, it was inaugurated as the Art Gallery.
- The Stabroek Market, which sells fruits, vegetables, livestock, meat, fish, furniture, manufactured household goods, tools, jewelry, and more, has a prominent cast-iron clock tower that dominates the city sky line. The market extends from Water Street to the bank of the Demerara River.
Looking to the future
Georgetown, the capital and largest city of Guyana, serves as a retail and administrative center, a financial services center, and is the country’s chief port. The nationalization of foreign companies operating in Guyana in the late 1970s caused an exodus of skilled people and capital, from which the nation has yet to recover. Run-down buildings, a shortage of skilled labor and a deficient infrastructure were evident in the capital city in 2008, as the government juggled a sizable external debt against the urgent need for expanded public investment.
Hamilton Green, Georgetown's mayor and the former prime minister of Guyana, has called for governmental accountability. Green describes true democracy thus: "The test of a modern Democracy is a form of governance in which political and economic power is shared, and where these truly reside in the people and exercised by them through time honoured institutions, their representatives and protocol."[1] He has gone on to declare that the city can prosper only when those in charge are held accountable. When financial corruption ceases, funds can be used more equitably and wisely in solving many of Georgetown's problems.
Notes
- ↑ Hamilton Green, Guyana has a facade of democracy, Propaganda Press! Freedom in Guyana. Retrieved December 13, 2008.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- De Barros, Juanita. Order and Place in a Colonial City: Patterns of Struggle and Resistance in Georgetown, British Guiana, 1889-1924. Montréal: McGill-Queen's University Press, 2003. ISBN 978-0773524552.
- Edwards, R., S. C. Wu, and J. Mensah. "Georgetown, Guyana." Cities. 22 (6) (2005): 446-454. ISSN 0264-2751.
- Guyana Lands and Surveys Commission. 2006. The City of Georgetown. Georgetown: Guyana Lands and Surveys Commission. OCLC 162107765.
- Historical Georgetown Guyana. Georgetown, Guyana: Sheik M. Hassan, 1997. OCLC 45069045.
- Temple, Bob. Guyana. Discovering South America. Philadelphia, PA: Mason Crest Publishers, 2004. ISBN 1590843002.
- World Fact Book, 2008.
External links
All links retrieved June 19, 2017.
- Guyana On-line Tourist Guide Georgetown tour
- Georgetown photo gallery
- The Tramways of Georgetown
- The Great Fire of 1945
- Article: Guyana's Capital, Tropical Victorian
Asunción, Paraguay · Bogotá, Colombia · Brasília, Brasil · Buenos Aires, Argentina · Caracas, Venezuela · Cayenne, French Guiana · Georgetown, Guyana · Grytviken, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands · La Paz, Bolivia · Lima, Peru · Montevideo, Uruguay · Paramaribo, Suriname · Quito, Ecuador · Santiago, Chile · Sucre, Bolivia · Stanley, Falkland Islands
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.