Difference between revisions of "Edom" - New World Encyclopedia
| (24 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{2Copyedited}}{{Copyedited}}{{Ebcompleted}}{{Paid}}{{Approved}}{{submitted}}{{Images OK}} |
| − | {{ | ||
| − | |||
| − | The Edomite people were a [[Semitic languages|Semitic]]-speaking tribal group inhabiting the [[Negev Desert]] and the Aravah valley of what is now southern [[Israel]] and adjacent [[Jordan]]. | + | [[Image:Edom.PNG|thumb|right|250 px|'''Edom''', shown in red, c. 600 B.C.E.]] |
| + | '''Edom''' (אֱדוֹם, ʾĔḏôm, "red") was a nation in the southern [[Levant]] from the eleventh century <small>B.C.E</small> until [[Roman Empire|Roman]] times. The region has much reddish [[sandstone]], which may have given rise to the name. The nation's name in [[Assyrian language|Assyrian]] was ''Udumi''; in [[Greek language|Greek]], ''Ἰδουμαία'' (Idoumaía); in [[Latin]], ''Idumæa'' or ''Idumea''. The Edomite people were a [[Semitic languages|Semitic]]-speaking tribal group inhabiting the [[Negev Desert]] and the Aravah valley of what is now southern [[Israel]] and adjacent [[Jordan]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the [[Hebrew Bible]], Edom is a name given to [[Esau]] in the as well as to the nation purportedly descended from him. Esau was the brother of [[Jacob]], the ancestor of the [[Israelite]] nation, with whom he struggled throughout his life. The struggle between these eponymous ancestors—as both brothers and foes—continued in the histories of these two neighboring nations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jacob and Esau fought but in the end were reconciled. Memory of that brotherly reconciliation continues in later Israelite legislation: "You shall not detest an Edomite, for he is your brother... The sons of the third generation who are born to them may enter the assembly of the Lord ([[Deuteronomy|Deut.]] 23:7-8). Occasionally they would form an alliance (Deut. 2:23), and there is some evidence that the early Edomites worshiped [[Yahweh]] ([[Judges, Book of|Judg.]] 5:4). Nevertheless, from the time the Edomites refused the Israelites passage on their [[Exodus]] from Egypt ([[Numbers, Book of|Num.]] 20:14-21), relations deteriorated, and for the most part, these two peoples remained enemies. During the biblical period of the kings, Edom was a vassal state of the [[Kingdom of Judah]]. During the [[Babylonian Exile]], the Edomites took advantage of the situation to plunder [[Jerusalem]] and expropriate large portions of Judah's land. This led to particularly bitter feelings on the part of the Jews, so much so that in the [[Talmud]]ic period "Edom" became a symbol for the [[Roman Empire]], the Jews' arch-oppressors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In Roman times, Idumea accepted [[Judaism]] and produced a particularly famous native son in King [[Herod the Great]] and his royal line. Idumeans fought side-by-side with Jews against [[Roman Empire|Rome]]. Possibilities for further reconciliation were dashed with the Jews' defeat in the [[Jewish-Roman Wars]], after which Edom also ceased to exist. | ||
==The Edomites== | ==The Edomites== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 14: | ||
===Origins=== | ===Origins=== | ||
| − | The Edomites may have been connected with the [[Shasu]] and [[Shutu]], nomadic raiders mentioned in [[Ancient Egypt|Egypt]]ian sources. | + | The Edomites may have been connected with the [[Shasu]] and [[Shutu]], nomadic raiders mentioned in [[Ancient Egypt|Egypt]]ian sources. A letter from an Egyptian scribe at a border fortress in the Wadi Tumilat during the reign of [[Mernepta]] reports movement of nomadic "shasu-tribes of Edom" to watering holes in Egyptian territory.<ref>Donald B. Redford, ''Egypt, Canaan and Israel in Ancient Times'' (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1993, ISBN 978-0691000862), 228; 318.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | In the biblical narrative, the Edomites are descended from Esau, the twin brother of the patriarch [[Jacob]], father of the Israelites. Jacob had fled from Esau after deceiving their father [[Isaac]] into giving Jacob his blessing, which was meant for Esau. After 21 years in exile, Jacob returned and the two brothers were reconciled. Esau lived near Mount Seir, commonly thought to be the Jebel esh-Shera range of today's southern Jordan. Jacob settled in the hill country of [[Canaan]], at [[Shechem]]. Earlier, their mother, [[Rebekah]], had received a prophecy from God predicting that the twins represented two nations, and that "the elder will serve the younger." | ||
| − | + | Esau and his descendants prospered, becoming the nation known in later times as the Edomites. Although the Bible does not mention the reddish sandstone which characterizes the region, the [[Book of Genesis]] mentions "red" a number of times in describing Esau and explaining his alternate name of Edom (red). "The first one [Esau] came out reddish ''admoni'' in [[Hebrew language|Hebrew]]], as hairy as a fur coat. They named him Esau" (Genesis 25:25). Years later, "[[Jacob]] was once simmering a stew, when Esau came home exhausted from the field. Esau said to Jacob, "Give me a swallow of that red stuff.’ He was therefore given the name ''Edom''" (Genesis 25:29-30). | |
| − | === | + | ===Early biblical history=== |
| − | The Edomites' original country, according to the [[Bible]], stretched from the [[Sinai Peninsula | + | The Edomites' original country, according to the [[Bible]], stretched from the [[Sinai Peninsula]] as far as [[Kadesh Barnea]]. Southward it reached as far as [[Aqaba|Eilat]], which was the [[seaport]] of Edom ([[Deuteronomy|Deut.]] 1:2; 2:1-8). On the north of Edom was the territory of [[Moab]] ([[Book of Judges|Judg.]] 11:17-18; [[Books of Kings|2 Kings]] 3:8-9). The boundary between Moab and Edom was the Wadi Zered (Deut. 2:13-18). The ancient capital of Edom was Bozrah ([[Genesis|Gen.]] 36:33; [[Book of Isaiah|Isa.]] 34:6, 63:1). According to Genesis, Esau's descendants settled in this land after displacing the [[Horites]]. It was also called the land of Seir. |
| − | : | + | |
| + | [[Mount Seir]] appears to have been strongly identified with the Edomites and may have been a cultic site associated with the god [[Yahweh]], conceived of as a deity of rain and storm. The ancient "Song of Deborah" (Judges 5:4) states: | ||
| + | :Yahweh, when You went out from Seir, | ||
:When You marched from the field of Edom, | :When You marched from the field of Edom, | ||
:The earth quaked, the heavens also dripped, | :The earth quaked, the heavens also dripped, | ||
:Even the clouds dripped water. | :Even the clouds dripped water. | ||
| − | Elsewhere, God is depicted doing "the same for the descendants of Esau" as he had done for Israel, by fighting on the side of the Edomites | + | Elsewhere, God is depicted doing "the same for the descendants of Esau" as he had done for Israel, by fighting on the side of the Edomites against their enemies, the Horites (Deut. 2:22). |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Genesis]] 36 chronicles Esau's family and the kings of Edom. If the account may be taken at face value, the kingship of Edom was, at least in early times, not [[hereditary kingship|hereditary]],<ref>Bruce R. Gordon, [http://ellone-loire.net/obsidian/Holyland.html#Edom Edom (Idumaea),] Regnal Chronologies. Retrieved August 30, 2007.</ref> but perhaps elective. | |
| − | + | ==Relations with Israel== | |
| − | + | During the [[Exodus]], when the king of Edom refused to allow the [[Israelites]] ([[Book of Numbers|Num.]] 20:19) to pass through his land on their way to [[Canaan]], they detoured around the country because of his show of force (Num. 20:14-21). The Book of Deuteronomy adds that God ordered Israel to avoid confrontation rather than wage war against the Edomites (Deut. 2:4-6). It also declares: "You shall not detest an Edomite, for he is your brother... The sons of the third generation who are born to them may enter the assembly of the Lord" (23:7-8). | |
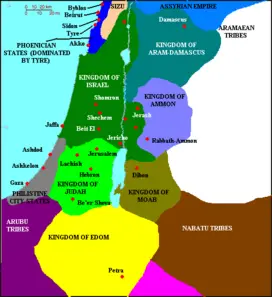
| − | + | [[Image:Levant 830.png|thumb|right|272px|Map of the southern [[Levant]], c. 830s B.C.E. | |
| − | [[Image:Levant 830.png|thumb|right|272px|Map of the southern [[Levant]], c. | ||
{{legend|#00ff00|Kingdom of Judah}} | {{legend|#00ff00|Kingdom of Judah}} | ||
{{legend|#008000|Kingdom of Israel}} | {{legend|#008000|Kingdom of Israel}} | ||
| Line 46: | Line 52: | ||
{{legend|#808040|Kingdom of Moab}}]] | {{legend|#808040|Kingdom of Moab}}]] | ||
| − | Nothing further is recorded of the Edomites in the | + | Nothing further is recorded of the Edomites in the Bible until a brief mention of warfare between the Edomites and King [[Saul]] of Israel in the late 1000s B.C.E. (1 Sam. 14:47). An Edomite named Doeg is later described as Saul's chief shepherd. Doeg is also the villain in story of the hideous murder of the priests of Nob, which had been ordered by Saul in retaliation for their sheltering of the renegade [[David]] (1 Sam. 21-22). |
| − | + | Later, King [[David]] and his general [[Joab]] defeated the Edomites in the "valley of salt," (probably near the [[Dead Sea]]), occupying the country for six months and reportedly slaughtering thousands in a policy clearly aimed at [[genocide]] (2 Sam. 8:13-14; 1 Kings 9:15-16), Deuteronomy's advice notwithstanding. An Edomite prince named Hadad escaped and fled to [[Egypt]], and Edom became a vassal state of David's kingdom. After David's death, Hadad returned and tried to start a rebellion, but failed and went to Syria.<ref>[[Josephus]], ''Jewish Antiquities'' viii. 7, S 6.</ref> David placed Israelite governors over the Edomites (2 Sam. 8:14), and this form of government seems to have continued under [[Solomon]]. | |
| − | + | When Israel divided into two kingdoms, Edom became a dependency of the [[Kingdom of Judah]]. In the time of [[Jehoshaphat]] (c. 914 B.C.E..) the Bible mentions a king of Edom (2 Kings 3:9-26), who made common cause with Israel and Judah against [[Moab]] and met with the prophet [[Elisha]]. A miracle ensued, relieving their drought-stricken armies with a flood of water "the color of blood" flowing from "the direction of Edom." | |
| − | + | However, 2 Chronicles 20:10-23 reports significant rebellion against Jehoshaphat, consisting of forces from Edom, [[Ammon]], and [[Moab]]. Through God's intervention, the invaders eventually turned against one another, thus failing in their plan. Edom also revolted in the time of King [[Jehoram]] of Judah (mid-ninth century B.C.E.) and elected a king of its own (2 Kings 8:20-22; 2 Chron. 21:8). The writer of [[Books of Kings|Kings]] reports that "To this day Edom has been in rebellion against Judah." Jehoram's son [[Amaziah]] attacked and defeated the Edomites, seizing Selah (2 Kings 14:7; [[Books of Chronicles|2 Chron.]] 25:11-1). However, it would not be until the second century B.C.E. that Edom came completely under Jewish rule (see below). | |
| − | + | In the time of [[Nebuchadrezzar II]], Edomites helped plunder Jerusalem and slaughter the Jews ([[Psalms]] 137:7; [[Obadiah, Book of|Obad.]] 11-14). For this reason the later [[prophet]]s denounced Edom violently (Isa. 34:5-8; [[Book of Jeremiah|Jer.]] 49:7-22; Obad. ''passim''). The Edomites were held in contempt by many [[Israelite]]s. Hence the [[Book of Psalms]] takes a very different view than does Deuteronomy toward the Edomites, portraying God as saying: "Moab is my washpot: over Edom will I cast out my shoe" (Psalms 60:8 and 108:9). | |
| − | + | ===Economy=== | |
| − | + | The Kingdom of Edom drew much of its livelihood from the caravan trade between Egypt, the [[Levant]], [[Mesopotamia]], and southern [[Arabia]], along the [[Incense]] Route. Astride the [[King's Highway (ancient)|King's Highway]], the Edomites were one of several states in the region for whom trade was vital due to the scarcity of arable land. Edom's location on the southern highlands left it with only a small strip of land that received sufficient rain for farming, a fact consistent with the Song of [[Deborah]]'s emphasis on [[Yahweh]]'s role in providing rain from Seir. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Edom probably exported [[salt]] and [[balsam]] (used for perfume and [[temple]] incense in the ancient world) from the [[Dead Sea]] region. In the time of Amaziah (838 B.C.E.), Selah (Petra) was its principal stronghold (2 Kings 14:7), while Eilat and Ezion-geber were its seaports (1 Kings 9:26). | |
| − | + | ==Post-biblical times== | |
| + | [[Image:Prise de Jérusalem par Hérode le Grand.jpg|thumb|200px|[[Herod the Great]], an Idumean, was the Roman client king of Judea in the late first century B.C.E..]] | ||
| + | Edom is mentioned in [[Assyria]]n [[Cuneiform script|cuneiform]] inscriptions in the form ''"Udumi"'' or ''"Udumu"''; three of its kings are known from the same source: [[Ḳaus-malaka]] at the time of [[Tiglath-pileser III]] (c. 745 B.C.E.), [[Malik-rammu]] at the time of [[Sennacherib]] (c. 705 B.C.E..), and [[Ḳaus-gabri]] at the time of [[Esarhaddon]] (c. 680 B.C.E.). According to the Egyptian inscriptions, the "Aduma" at times extended their possessions to the borders of Egypt. After the conquest of Judah by the [[Babylonian Empire|Babylonians]], the Edomites were allowed to settle in the region south of [[Hebron]]. They prospered in this new country, called by the Greeks and Romans "Idumaea" or "Idumea," for more than four centuries.<ref>[[Gospel of Mark|Mark]] 3:8; Ptolemy, "Geography," v. 16.</ref> At the same time they were driven by the [[Nabataeans]] from their ancestral lands to the south and east. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | During the revolt of the [[Maccabees]] against the [[Seleucid]] kingdom, a Seleucid general named [[Gorgias (general)|Gorgias]] reportedly ruled as "governor of Idumaea"; whether he was a Greek or a [[Hellenistic civilization|Hellenized]] Edomite is unknown (2 Maccabees 12:32). However, some scholars maintain that the reference to Idumaea in that passage is an error. The Jewish independence leader [[Judas Maccabeus]] conquered their territory for a time around 163 B.C.E.<ref>Josephus, "Jewish Antiquities" xii. 8, §§ 1, 6.</ref> Idumea was again subdued by [[John Hyrcanus]] (c. 125 B.C.E.), who forced the Idumeans to observe [[Jewish]] [[halakha|rites and laws]].<ref>''Ibid''. xiii. 9, § 1; xiv. 4, § 4.</ref> They were then incorporated with the Jewish nation, though as second class citizens. | |
| − | + | The [[Hasmonean]] official [[Antipater the Idumaean]] was of Edomite origin. He was the progenitor of the [[Herodian Dynasty]] that ruled [[Judea]] after the Roman conquest. Under [[Herod the Great]] Idumaea was ruled on Herod's behalf by a series of governors, among whom were his brother [[Joseph ben Antipater]] and his brother-in-law [[Kostobar]]. Herod's lack of popularity in Judea was in large part due to his Edomite origins, as well as the tyrannical nature of his reign. | |
| − | + | Immediately before the siege of [[Jerusalem]] by [[Titus]], 20,000 Idumaeans, reportedly came to Jerusalem to fight on behalf of the [[Zealotry|Zealots]] who were besieged in the [[Temple of Jerusalem|Temple]].<ref>Josephus, ''Jewish Wars'' iv. 4, § 5.</ref> After the Jewish Wars, the Idumaeans ceased to maintain a historically distinct existence, although the geographical name "Idumea" still existed at the time of [[Jerome]]. | |
| − | == | + | ==Edomite religion== |
| − | + | The nature of Edomite religion is uncertain. [[Yahweh]]-worship, apparently associated with Mount Seir and the [[Shashu]] tribes, does not appear to have predominated among the Edomites in their early history. As close relatives of other [[Canaan|Levantine Semites]], they may have worshiped such gods as [[El]], [[Baal]], [[Asherah]], and also Yahweh. A national deity named [[Kaus]] (possibly analogous to the [[Moab]]ite god [[Chemosh]]) is known from personal names and from an altar inscription discovered near [[Mamre]]. However, their relatively kind treatment by the [[Deuteronomy|Deuteronomist]]—who detested nations given to the worship of "foreign gods"—indicates that he did not consider the Edomites a major spiritual threat. By the later second century B.C.E., whether by force or choice, the Idumeans had largely adopted Judaism. | |
==Controversy== | ==Controversy== | ||
| + | A number of points of controversy exist over the biblical story of the Edomites. One has to do with their origins and the story of [[Jacob]] and [[Esau]]. The other has to do with the age of the Edomite nation. | ||
| − | + | Bible critics see Jacob and Esau as ''eponyms'', legendary characters who serve to explain the origins and character of later tribes and nations. In this view, the story of Jacob and Esau serves to explain the reason why the Edomites were destined to remain a vassal state of Judah: it was prophesied by God while the twins struggled in their mother's womb. Their treatment by Israel/Jacob is recognized as unfair to them—the Israelites being newcomers to the area—but predestined by God. Yet, because they are brothers to the [[Israelite]]s, the Edomites are not to be despised. They may intermarry with [[Jew]]s, and are to be recognized as members of the Israelite congregation after three generations. | |
| − | + | Whether or not the story of Jacob and Esau is historically accurate, it is clear that it exactly parallels the story of the relations between Israel/Judah and Edom. Just as Esau was born first but destined to losing his birthright and blessing to Jacob, so the Edomites were there first, but their destiny was to serve Israel as a vassal. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Regarding the age of the historical Edomites, the question is whether their nation already existed as described in the Bible in the time of [[David]], or not. For that matter, even David's kingdom is doubted by many scholars as existing at anything beyond the tribal level in [[tribe of Judah|Judah]]. For over a century, archaeologists specializing in the [[Middle East]] maintained that there was no evidence of an organized state society in Edom earlier than the 800s or 700s B.C.E.<ref>Redford 305.</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Recently, however, excavations such as the 2004 dig at [[Khirbat an-Nahas]] in Jordan have shed new light on the history of Edom, unearthing artifacts and evidence of settled society as early as the tenth century B.C.E.<ref>Barry Jagoda, [http://ucsdnews.ucsd.edu/newsrel/soc/EDOM.asp “Controversial Dates Of Biblical Edom Reassessed In Results From New Archeological Research,”] University of California, San Diego (Press Release) (February 17, 2005). Retrieved August 30, 2007.</ref> Whether and to what extent these sites reflect Edomite statehood is debated. Thomas E. Levy, among other scholars, concluded from a survey of the an-Nahas site that Edom was a sophisticated, [[urbanization|urbanized]] society as early as the eleventh century B.C.E., (the date of the first Israelite monarchy, according to the Bible) which even had its own [[copper]] works.<ref>Thomas E. Levy and Mohammed Najjar, "Edom and Copper," ''Biblical Archeology Review'' (July/August 2006).</ref> Radiocarbon tests from the site have confirmed that the industrial areas of the site date to the eleventh and tenth centuries B.C.E.<ref>''Ibid''.</ref> | |
| − | < | ||
| − | == | + | ==Notes== |
| + | <div class="references-small"> | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| − | + | ==Rererences== | |
| − | + | * Cross, Frank Moore. ''Canaanite Myth and Hebrew Epic''. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1973. ISBN 978-0674091764 | |
| − | : | + | * Dicou, Bert. ''Edom, Israel's Brother and Antagonist: The Role of Edom in Biblical Prophecy and Story''. Sheffield Academic Press, 1994. ISBN 978-1850754589 |
| − | + | * Grant, Michael. ''The History of Ancient Israel''. New York: Scribner, 1984. ISBN 0684180812 | |
| − | : | + | * Redford, Donald B. ''Egypt, Canaan and Israel in Ancient Times''. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1993. ISBN 978-0691000862 |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | {{ | + | {{credit|107121481}} |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | [[Category:Geography]] |
| − | + | [[Category:History]] | |
| − | + | [[Category:Philosophy and religion]] | |
Latest revision as of 21:09, 8 August 2023
Edom (אֱדוֹם, ʾĔḏôm, "red") was a nation in the southern Levant from the eleventh century B.C.E until Roman times. The region has much reddish sandstone, which may have given rise to the name. The nation's name in Assyrian was Udumi; in Greek, Ἰδουμαία (Idoumaía); in Latin, Idumæa or Idumea. The Edomite people were a Semitic-speaking tribal group inhabiting the Negev Desert and the Aravah valley of what is now southern Israel and adjacent Jordan.
In the Hebrew Bible, Edom is a name given to Esau in the as well as to the nation purportedly descended from him. Esau was the brother of Jacob, the ancestor of the Israelite nation, with whom he struggled throughout his life. The struggle between these eponymous ancestors—as both brothers and foes—continued in the histories of these two neighboring nations.
Jacob and Esau fought but in the end were reconciled. Memory of that brotherly reconciliation continues in later Israelite legislation: "You shall not detest an Edomite, for he is your brother... The sons of the third generation who are born to them may enter the assembly of the Lord (Deut. 23:7-8). Occasionally they would form an alliance (Deut. 2:23), and there is some evidence that the early Edomites worshiped Yahweh (Judg. 5:4). Nevertheless, from the time the Edomites refused the Israelites passage on their Exodus from Egypt (Num. 20:14-21), relations deteriorated, and for the most part, these two peoples remained enemies. During the biblical period of the kings, Edom was a vassal state of the Kingdom of Judah. During the Babylonian Exile, the Edomites took advantage of the situation to plunder Jerusalem and expropriate large portions of Judah's land. This led to particularly bitter feelings on the part of the Jews, so much so that in the Talmudic period "Edom" became a symbol for the Roman Empire, the Jews' arch-oppressors.
In Roman times, Idumea accepted Judaism and produced a particularly famous native son in King Herod the Great and his royal line. Idumeans fought side-by-side with Jews against Rome. Possibilities for further reconciliation were dashed with the Jews' defeat in the Jewish-Roman Wars, after which Edom also ceased to exist.
The Edomites
Origins
The Edomites may have been connected with the Shasu and Shutu, nomadic raiders mentioned in Egyptian sources. A letter from an Egyptian scribe at a border fortress in the Wadi Tumilat during the reign of Mernepta reports movement of nomadic "shasu-tribes of Edom" to watering holes in Egyptian territory.[1]
In the biblical narrative, the Edomites are descended from Esau, the twin brother of the patriarch Jacob, father of the Israelites. Jacob had fled from Esau after deceiving their father Isaac into giving Jacob his blessing, which was meant for Esau. After 21 years in exile, Jacob returned and the two brothers were reconciled. Esau lived near Mount Seir, commonly thought to be the Jebel esh-Shera range of today's southern Jordan. Jacob settled in the hill country of Canaan, at Shechem. Earlier, their mother, Rebekah, had received a prophecy from God predicting that the twins represented two nations, and that "the elder will serve the younger."
Esau and his descendants prospered, becoming the nation known in later times as the Edomites. Although the Bible does not mention the reddish sandstone which characterizes the region, the Book of Genesis mentions "red" a number of times in describing Esau and explaining his alternate name of Edom (red). "The first one [Esau] came out reddish admoni in Hebrew], as hairy as a fur coat. They named him Esau" (Genesis 25:25). Years later, "Jacob was once simmering a stew, when Esau came home exhausted from the field. Esau said to Jacob, "Give me a swallow of that red stuff.’ He was therefore given the name Edom" (Genesis 25:29-30).
Early biblical history
The Edomites' original country, according to the Bible, stretched from the Sinai Peninsula as far as Kadesh Barnea. Southward it reached as far as Eilat, which was the seaport of Edom (Deut. 1:2; 2:1-8). On the north of Edom was the territory of Moab (Judg. 11:17-18; 2 Kings 3:8-9). The boundary between Moab and Edom was the Wadi Zered (Deut. 2:13-18). The ancient capital of Edom was Bozrah (Gen. 36:33; Isa. 34:6, 63:1). According to Genesis, Esau's descendants settled in this land after displacing the Horites. It was also called the land of Seir.
Mount Seir appears to have been strongly identified with the Edomites and may have been a cultic site associated with the god Yahweh, conceived of as a deity of rain and storm. The ancient "Song of Deborah" (Judges 5:4) states:
- Yahweh, when You went out from Seir,
- When You marched from the field of Edom,
- The earth quaked, the heavens also dripped,
- Even the clouds dripped water.
Elsewhere, God is depicted doing "the same for the descendants of Esau" as he had done for Israel, by fighting on the side of the Edomites against their enemies, the Horites (Deut. 2:22).
Genesis 36 chronicles Esau's family and the kings of Edom. If the account may be taken at face value, the kingship of Edom was, at least in early times, not hereditary,[2] but perhaps elective.
Relations with Israel
During the Exodus, when the king of Edom refused to allow the Israelites (Num. 20:19) to pass through his land on their way to Canaan, they detoured around the country because of his show of force (Num. 20:14-21). The Book of Deuteronomy adds that God ordered Israel to avoid confrontation rather than wage war against the Edomites (Deut. 2:4-6). It also declares: "You shall not detest an Edomite, for he is your brother... The sons of the third generation who are born to them may enter the assembly of the Lord" (23:7-8).
Nothing further is recorded of the Edomites in the Bible until a brief mention of warfare between the Edomites and King Saul of Israel in the late 1000s B.C.E. (1 Sam. 14:47). An Edomite named Doeg is later described as Saul's chief shepherd. Doeg is also the villain in story of the hideous murder of the priests of Nob, which had been ordered by Saul in retaliation for their sheltering of the renegade David (1 Sam. 21-22).
Later, King David and his general Joab defeated the Edomites in the "valley of salt," (probably near the Dead Sea), occupying the country for six months and reportedly slaughtering thousands in a policy clearly aimed at genocide (2 Sam. 8:13-14; 1 Kings 9:15-16), Deuteronomy's advice notwithstanding. An Edomite prince named Hadad escaped and fled to Egypt, and Edom became a vassal state of David's kingdom. After David's death, Hadad returned and tried to start a rebellion, but failed and went to Syria.[3] David placed Israelite governors over the Edomites (2 Sam. 8:14), and this form of government seems to have continued under Solomon.
When Israel divided into two kingdoms, Edom became a dependency of the Kingdom of Judah. In the time of Jehoshaphat (c. 914 B.C.E.) the Bible mentions a king of Edom (2 Kings 3:9-26), who made common cause with Israel and Judah against Moab and met with the prophet Elisha. A miracle ensued, relieving their drought-stricken armies with a flood of water "the color of blood" flowing from "the direction of Edom."
However, 2 Chronicles 20:10-23 reports significant rebellion against Jehoshaphat, consisting of forces from Edom, Ammon, and Moab. Through God's intervention, the invaders eventually turned against one another, thus failing in their plan. Edom also revolted in the time of King Jehoram of Judah (mid-ninth century B.C.E.) and elected a king of its own (2 Kings 8:20-22; 2 Chron. 21:8). The writer of Kings reports that "To this day Edom has been in rebellion against Judah." Jehoram's son Amaziah attacked and defeated the Edomites, seizing Selah (2 Kings 14:7; 2 Chron. 25:11-1). However, it would not be until the second century B.C.E. that Edom came completely under Jewish rule (see below).
In the time of Nebuchadrezzar II, Edomites helped plunder Jerusalem and slaughter the Jews (Psalms 137:7; Obad. 11-14). For this reason the later prophets denounced Edom violently (Isa. 34:5-8; Jer. 49:7-22; Obad. passim). The Edomites were held in contempt by many Israelites. Hence the Book of Psalms takes a very different view than does Deuteronomy toward the Edomites, portraying God as saying: "Moab is my washpot: over Edom will I cast out my shoe" (Psalms 60:8 and 108:9).
Economy
The Kingdom of Edom drew much of its livelihood from the caravan trade between Egypt, the Levant, Mesopotamia, and southern Arabia, along the Incense Route. Astride the King's Highway, the Edomites were one of several states in the region for whom trade was vital due to the scarcity of arable land. Edom's location on the southern highlands left it with only a small strip of land that received sufficient rain for farming, a fact consistent with the Song of Deborah's emphasis on Yahweh's role in providing rain from Seir.
Edom probably exported salt and balsam (used for perfume and temple incense in the ancient world) from the Dead Sea region. In the time of Amaziah (838 B.C.E.), Selah (Petra) was its principal stronghold (2 Kings 14:7), while Eilat and Ezion-geber were its seaports (1 Kings 9:26).
Post-biblical times

Edom is mentioned in Assyrian cuneiform inscriptions in the form "Udumi" or "Udumu"; three of its kings are known from the same source: Ḳaus-malaka at the time of Tiglath-pileser III (c. 745 B.C.E.), Malik-rammu at the time of Sennacherib (c. 705 B.C.E.), and Ḳaus-gabri at the time of Esarhaddon (c. 680 B.C.E.). According to the Egyptian inscriptions, the "Aduma" at times extended their possessions to the borders of Egypt. After the conquest of Judah by the Babylonians, the Edomites were allowed to settle in the region south of Hebron. They prospered in this new country, called by the Greeks and Romans "Idumaea" or "Idumea," for more than four centuries.[4] At the same time they were driven by the Nabataeans from their ancestral lands to the south and east.
During the revolt of the Maccabees against the Seleucid kingdom, a Seleucid general named Gorgias reportedly ruled as "governor of Idumaea"; whether he was a Greek or a Hellenized Edomite is unknown (2 Maccabees 12:32). However, some scholars maintain that the reference to Idumaea in that passage is an error. The Jewish independence leader Judas Maccabeus conquered their territory for a time around 163 B.C.E.[5] Idumea was again subdued by John Hyrcanus (c. 125 B.C.E.), who forced the Idumeans to observe Jewish rites and laws.[6] They were then incorporated with the Jewish nation, though as second class citizens.
The Hasmonean official Antipater the Idumaean was of Edomite origin. He was the progenitor of the Herodian Dynasty that ruled Judea after the Roman conquest. Under Herod the Great Idumaea was ruled on Herod's behalf by a series of governors, among whom were his brother Joseph ben Antipater and his brother-in-law Kostobar. Herod's lack of popularity in Judea was in large part due to his Edomite origins, as well as the tyrannical nature of his reign.
Immediately before the siege of Jerusalem by Titus, 20,000 Idumaeans, reportedly came to Jerusalem to fight on behalf of the Zealots who were besieged in the Temple.[7] After the Jewish Wars, the Idumaeans ceased to maintain a historically distinct existence, although the geographical name "Idumea" still existed at the time of Jerome.
Edomite religion
The nature of Edomite religion is uncertain. Yahweh-worship, apparently associated with Mount Seir and the Shashu tribes, does not appear to have predominated among the Edomites in their early history. As close relatives of other Levantine Semites, they may have worshiped such gods as El, Baal, Asherah, and also Yahweh. A national deity named Kaus (possibly analogous to the Moabite god Chemosh) is known from personal names and from an altar inscription discovered near Mamre. However, their relatively kind treatment by the Deuteronomist—who detested nations given to the worship of "foreign gods"—indicates that he did not consider the Edomites a major spiritual threat. By the later second century B.C.E., whether by force or choice, the Idumeans had largely adopted Judaism.
Controversy
A number of points of controversy exist over the biblical story of the Edomites. One has to do with their origins and the story of Jacob and Esau. The other has to do with the age of the Edomite nation.
Bible critics see Jacob and Esau as eponyms, legendary characters who serve to explain the origins and character of later tribes and nations. In this view, the story of Jacob and Esau serves to explain the reason why the Edomites were destined to remain a vassal state of Judah: it was prophesied by God while the twins struggled in their mother's womb. Their treatment by Israel/Jacob is recognized as unfair to them—the Israelites being newcomers to the area—but predestined by God. Yet, because they are brothers to the Israelites, the Edomites are not to be despised. They may intermarry with Jews, and are to be recognized as members of the Israelite congregation after three generations.
Whether or not the story of Jacob and Esau is historically accurate, it is clear that it exactly parallels the story of the relations between Israel/Judah and Edom. Just as Esau was born first but destined to losing his birthright and blessing to Jacob, so the Edomites were there first, but their destiny was to serve Israel as a vassal.
Regarding the age of the historical Edomites, the question is whether their nation already existed as described in the Bible in the time of David, or not. For that matter, even David's kingdom is doubted by many scholars as existing at anything beyond the tribal level in Judah. For over a century, archaeologists specializing in the Middle East maintained that there was no evidence of an organized state society in Edom earlier than the 800s or 700s B.C.E.[8]
Recently, however, excavations such as the 2004 dig at Khirbat an-Nahas in Jordan have shed new light on the history of Edom, unearthing artifacts and evidence of settled society as early as the tenth century B.C.E.[9] Whether and to what extent these sites reflect Edomite statehood is debated. Thomas E. Levy, among other scholars, concluded from a survey of the an-Nahas site that Edom was a sophisticated, urbanized society as early as the eleventh century B.C.E., (the date of the first Israelite monarchy, according to the Bible) which even had its own copper works.[10] Radiocarbon tests from the site have confirmed that the industrial areas of the site date to the eleventh and tenth centuries B.C.E.[11]
Notes
- ↑ Donald B. Redford, Egypt, Canaan and Israel in Ancient Times (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1993, ISBN 978-0691000862), 228; 318.
- ↑ Bruce R. Gordon, Edom (Idumaea), Regnal Chronologies. Retrieved August 30, 2007.
- ↑ Josephus, Jewish Antiquities viii. 7, S 6.
- ↑ Mark 3:8; Ptolemy, "Geography," v. 16.
- ↑ Josephus, "Jewish Antiquities" xii. 8, §§ 1, 6.
- ↑ Ibid. xiii. 9, § 1; xiv. 4, § 4.
- ↑ Josephus, Jewish Wars iv. 4, § 5.
- ↑ Redford 305.
- ↑ Barry Jagoda, “Controversial Dates Of Biblical Edom Reassessed In Results From New Archeological Research,” University of California, San Diego (Press Release) (February 17, 2005). Retrieved August 30, 2007.
- ↑ Thomas E. Levy and Mohammed Najjar, "Edom and Copper," Biblical Archeology Review (July/August 2006).
- ↑ Ibid.
Rererences
- Cross, Frank Moore. Canaanite Myth and Hebrew Epic. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1973. ISBN 978-0674091764
- Dicou, Bert. Edom, Israel's Brother and Antagonist: The Role of Edom in Biblical Prophecy and Story. Sheffield Academic Press, 1994. ISBN 978-1850754589
- Grant, Michael. The History of Ancient Israel. New York: Scribner, 1984. ISBN 0684180812
- Redford, Donald B. Egypt, Canaan and Israel in Ancient Times. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1993. ISBN 978-0691000862
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.