Cascade Range
| Cascade Range | |
| The Cascades | |
| Range | |
Mount Rainier in Washington state
| |
| Countries | United States, Canada |
|---|---|
| Provinces/States | Oregon, Washington, California, British Columbia |
| Highest point | Mount Rainier |
| - elevation | 14,410 feet (4,392 meters) |
| - coordinates | |
| Length | 700 miles (1,100 km), north-south |
| Period | Pliocene |
The Cascade Range is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from Canada's British Columbia through the U.S. states of Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, including the rugged spires of the North Cascades, and the notable volcanoes known as the High Cascades. The small part of the range in British Columbia is called the Canadian Cascades or Cascade Mountains; the latter term is also sometimes used by Washington residents to refer to the Washington section of the Cascades in addition to North Cascades, the more usual American term, as in North Cascades National Park.
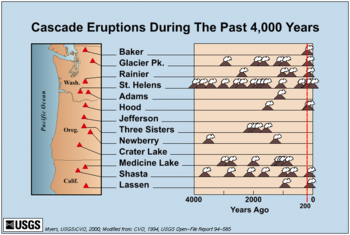
The Cascades are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, the ring of volcanoes and associated mountains around the Pacific Ocean. All of the known historic eruptions in the contiguous United States have been from Cascade volcanoes. The two most recent were Lassen Peak in 1914 through 1921 and a major eruption of Mount Saint Helens in 1980. According to monitoring systems of the U.S. Geological Survey, minor eruptions of Mount Saint Helens have also occurred, most recently in 2006.
The Range has had a major influence on the climate, agriculture, economics, population spread, and settlement patterns of the Northwestern United States and the Pacific Northwest region of North America, and have been a major facet of life for generations of Native Americans. Its approximate 700 mile (1,127 km) length is home to a great diversity of plant and animal life, as well as to majestic mountain scenery.
Geography
The southern end of the Cascade Range is about 30 to 50 miles (50 to 80 km) wide and 4,500 to 5,000 feet (1,370 to 1,520 m) high. It is 80 miles (130 km) wide in northern Washington, while at its northern apex at Lytton Mountain (2,049 m) in Canada, near the confluence of the Fraser and Thompson Rivers, the range is only 10 miles (16 km) wide.
The tallest volcanoes of the Cascades are called the High Cascades and dominate their surroundings, often standing twice the height of the nearby mountains. They often have a visual height (above nearby crestlines) of one mile (1.6 km) or more. The tallest peaks, such as the 14,411 foot (4,392 m) high Mount Rainier, dominate their surroundings for 50 to 100 miles (80 to 160 km).
The northern part of the range, north of Mount Rainier, is known as the North Cascades. It is extremely rugged, with many of the lesser peaks steep and glaciated. The valleys are quite low, resulting in great local relief, and major passes are only about 1,000 m (3,300 ft) high. The southern part of the Canadian Cascades are included in the North Cascades, and have the same geography and geology. Opinions differs as to whether to include the Coquihalla Range within the Cascades, which reaches up to the confluence of the Fraser and Thompson Rivers. Its northern reaches have very different terrain and geology, more resembling the plateau country which extends north and east from the range's terminus at Lytton Mountain.
Because of the range's proximity to the Pacific Ocean, precipitation is substantial, especially on the western slopes, with annual accumulations of up to 150 inches (3,800 mm) in some areas—Mount Baker, for instance, recorded the largest single-season snowfall on record in the world in 1999—and heavy snowfall as low as 2,000 feet (600 m). It is not uncommon for some places in the Cascades to have over 200 inches (5,500 mm) of snow accumulation, such as at Lake Helen (near Lassen Peak), one of the snowiest places in the world. Most of the High Cascades are therefore white with snow and ice year-round. The western slopes are densely covered with Douglas-fir, Western Hemlock, and Red alder, while the drier eastern slopes are mostly Ponderosa Pine, with Western Larch at higher elevations. Annual rainfall drops to 9 inches (200 mm) on the eastern foothills due to a rainshadow effect.
Beyond the foothills is an arid plateau that was created 16 million years ago as a coalescing series of layered flood basalt flows. Together, these sequences of fluid volcanic rock form a 200,000 square mile (520,000 km²) region of eastern Washington, Oregon, and parts of Northern California and Idaho called the Columbia River Plateau.
The Columbia River Gorge is the only major break in the American part of the Cascades. When the Cascades began to rise 7 million years ago in the Pliocene, the Columbia River drained the relatively low Columbia River Plateau. As the range grew, the Columbia was able to keep pace, creating the gorge and major pass seen today. The gorge also exposes uplifted and warped layers of basalt from the plateau.
History
Native history
Native Americans have inhabited the area for thousands of years and developed their own myths and legends concerning the Cascades. According to some of these tales, Mounts Baker, Jefferson, and Shasta were used as refuge from a great flood. Other stories, such as the Bridge of the Gods tale, had various High Cascades such as Mount Hood and Mount Adams, act as god-like chiefs who made war by throwing fire and stone at each other. Mount St. Helens with its pre-1980 graceful appearance, was regaled as a beautiful maiden for whom Hood and Adams feuded. Among the many stories concerning Mount Baker, one tells that the mountain was formerly married to Mount Rainier and lived in that vicinity. Then, because of a marital dispute, she picked herself up and marched north to her present position. Native tribes also developed their own names for the High Cascades and many of the smaller peaks, the most well-known to non-natives being Tahoma, the Lushootseed name for Mount Rainier.
The legendary and diverse ethnographic history of the Cascade Range is too complex to recount, except to say that the spine of the range forms the divide between the Interior Salish and Coast Salish language groupings, and mythographically between the realm of Coyote on the east and that of the Transformers and the spirit-world of the Coast on the west.
Legends associated with the great volcanoes are many, as well as with other peaks and geographical features of the range, including its many hot springs and waterfalls and rock towers and other formations. Stories of Tahoma—today Mount Rainier and the namesake of Tacoma, Washington—allude to great, hidden grottos with sleeping giants, apparitions and other marvels in the volcanoes of Washington, and Mount Shasta in California has long been well-known for its associations with everything from Lemurians to aliens to elves and, as everywhere in the Cascades, Sasquatch or Bigfoot.
European and American exploration
In the spring of 1792 British navigator George Vancouver entered Puget Sound and began giving English names to the high mountains he saw. Mount Baker was named for Vancouver's third lieutenant, Mount St. Helens for a famous diplomat, Mount Hood was named in honor of Samuel Hood, 1st Viscount Hood (an admiral of the Royal Navy) and the tallest Cascade, Mount Rainier, is the namesake of Admiral Peter Rainier. Vancouver's expedition did not, however, name the range these peaks belonged to. As marine trade in the Strait of Georgia and Puget Sound proceeded in the 1790s and beyond, the summits of Rainier and Baker became familiar to captains and crews (mostly British and American over all others, but not exclusively).
In 1805, the Lewis and Clark Expedition passed through the Cascades by using the Columbia River, which for many years was the only practical way to pass that section of the range. Trade on the lower Columbia River, which skirts the southern end of the range, did not occur until after Lewis and Clark in 1806, more specifically as a result of David Thompson's visit on behalf of the North West Company shortly afterward, and Simon Fraser's journey down the Fraser River in 1808.
The Lewis and Clark expedition, and the many settlers and traders that followed, met their last obstacle to their journey at the Cascades Rapids in the Columbia River Gorge, a feature on the river now submerged beneath the Bonneville Reservoir. Before long, the great white-capped mountains that loomed above the rapids were called the "mountains by the cascades" and later simply as the "Cascades" (the earliest attested use of this name is in the writings of botanist David Douglas). On their return trip Lewis and Clark's group spotted a high but distant snowy pinnacle that they named for the sponsor of the expedition, U.S. President Thomas Jefferson.
Exploration and settlement of the Cascades region by Europeans and Americans was accelerated by the establishment of a major trading post of the Hudson's Bay Company at Fort Vancouver near today's Portland, Oregon. From this base, Hudson's Bay Company trapping parties traveled throughout the Cascades in search of beaver and other fur-bearing animals. Using what became known as the Siskiyou Trail, Hudson's Bay Company trappers were the first non-natives to explore the southern Cascades in the 1820s and 1830s, establishing trails which passed near Crater Lake, Mount McLoughlin, Medicine Lake Volcano, Mount Shasta, and Lassen Peak.
The course of political history in the Pacific Northwest saw the spine of the Cascade Range being proposed as a boundary settlement during the Oregon Dispute of 1846. The United States rejected the proposal and insisted on the 49th Parallel, which cuts across the range just north of Mount Baker. Throughout the period of dispute and up to the creation of the Crown Colony of British Columbia in 1858, the edge of the range along the Columbia and Okanogan Rivers formed the main express route of the Hudson's Bay Company's busy traffic, and passes across the range were used by Hudson's Bay Company staff at Fort Nisqually. The vast majority of non-native residents of the Cascade Range region until about 1840 were British subjects, most of mixed French-native blood and some Hawaiians and blacks as well as Scots who were the backbone of Hudson's Bay Company administration.
Settlement
American settlement of the flanks of the Coast Range did not occur until the early 1840s, at first only marginally. Following the Oregon Treaty, the inward flux of migration from the Oregon Trail intensified and the passes and back-valleys of what is now the state of Washington were explored and populated, and it was not long after that railways followed. Despite its being traversed by several major freeways and rail lines, and its lower flanks subjected to major logging in recent decades, large parts of the range remain intense and forbidding alpine wilderness. Most of the northern half of the High Cascades, from Rainier north, have been preserved as U.S. National Parks or British Columbia provincial parks, or other forms of protected area.

The Canadian side of the range has a history that includes the Fraser Canyon Gold Rush of 1858-1860 and its famous Cariboo Road, as well as the older Hudson's Bay Company Brigade Trail from the Canyon to the Interior, the Dewdney Trail, and older routes which connected east to the Similkameen and Okanagan valleys.
The southern mainline of the Canadian Pacific Railway penetrated the range via the passes of the Coquihalla River, along one of the steepest and snowiest routes in the entire Pacific Cordillera. Near Hope, British Columbia, the railway roadbed and the Othello Tunnels, now decommissioned, are popular tourist recreation destinations for hiking and bicycling. The pass is used by the Coquihalla Highway, a government megaproject built as part of the Expo 86 spending boom of the 1980s, which is now the main route from the Coast to the British Columbia interior. Traffic formerly went via the Fraser Canyon, to the west, or via Allison Pass and Manning Park along Highway 3 to the south, near the border.
The Barlow Road was the first established land path for U.S. settlers through the Cascade Range in 1845, and formed the final overland link for the Oregon Trail (previously, settlers had to raft down the treacherous rapids of the Columbia River). The Barlow Road left the Columbia at Hood River and passed along the south side of Mount Hood at Government Camp, terminating in Oregon City. There is an interpretive site there now at "The End of The Oregon Trail." The road was constructed as a toll road—$5/wagon—and was very successful.
In addition, the Applegate Trail was created to allow settlers to avoid rafting down the Columbia River. The Applegate Trail used the path of the California Trail to north-central Nevada. From there, the Applegate Trail headed northwest into northern California, and continued northwest towards today's Ashland, Oregon. From there, settlers would head north along the established Siskiyou Trail into the Willamette Valley.
With the exception of the 1915 eruption of remote Lassen Peak in Northern California, the range was quiet for more than a century. Then, on May 18, 1980, the dramatic eruption of little-known Mount St. Helens shattered the quiet and brought the world's attention to the range. Geologists were also concerned that the St. Helens eruption was a sign that long-dormant Cascade volcanoes might become active once more, as in the period from 1800 to 1857 when a total of eight erupted. None have erupted since St. Helens, but precautions are being taken nevertheless, such as the Mount Rainier Volcano Lahar Warning System in Pierce County, Washington.
Cascade Range volcanoes
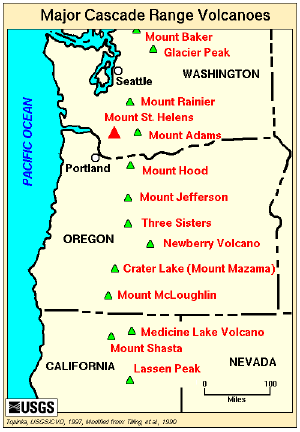
Volcanoes south of the Fraser River in the Cascade Volcanic Belt (a geological term) belong to the Cascade Range (a geographic term). Peaks are listed north to south.
North Cascades and Canadian Cascades
- Mount Slesse (British Columbia, near the United States-Canada border) is an ancient volcanic plug, long extinct.
- Mount Baker (Near the United States-Canada border)—highest peak in northern Washington. It still shows some steam activity from its crater, though it is considered dormant. Mount Baker is one of the snowiest places on Earth; in 1999 the ski area (on a subsidiary peak) recorded the world's greatest single-season snowfall: 1,140 inches (95 feet or 2,896 cm).
- Glacier Peak (northern Washington)—secluded and relatively inaccessible peak. Contrary to its name, its glacial cover is not so extensive. The volcano is surprisingly small in volume, and gets most of its height by having grown atop a non-volcanic ridge.
High Cascades
- Mount Rainier (southeast of Tacoma, Washington)—highest peak in the Cascades, it dominates the surrounding landscape. There is no other higher peak northward until the Yukon-Alaska-BC border apex beyond the Alsek River.
- Mount St. Helens (southern Washington)—Erupted in 1980, leveling forests to the north of the mountain and sending ash across the northwest. The northern part of the mountain was destroyed in the blast (1980 Mount St. Helens eruption).
- Mount Adams (east of Mount St. Helens) — the second highest peak in Washington and third highest in the Cascade Range.
- Mount Hood (northern Oregon)—the highest peak in Oregon and arguably the most frequently climbed major peak in the Cascades.
- Mount Jefferson (north-central Oregon)—the second highest peak in Oregon.
- Three Fingered Jack (north-central Oregon)—Highly eroded Pleistocene volcano.
- Mount Washington (between Santiam and McKenzie passes)—a highly eroded shield volcano.
- Three Sisters (near the city of Bend, Oregon)—South Sister is the highest and youngest, with a well defined crater. Middle Sister is more pyramidal and eroded. North Sister is the oldest and has a crumbling rock pinnacle.

- Broken Top (to the southeast of South Sister)—a highly eroded extinct stratovolcano. Contains Bend Glacier.
- Newberry Volcano and Newberry Caldera—isolated caldera with two crater lakes. Very variable lavas. Flows from here have reached the city of Bend.
- Mount Bachelor (near Three Sisters)—a geologically young (less than 15,000 years) shield-to-stratovolcano which is now the site of a popular ski resort.
- Mount Bailey (north of Mount Mazama)
- Mount Thielsen (east of Mount Bailey)—highly eroded volcano with a prominent spire, making it the Lightning Rod of the Cascades.
- Mount Mazama (southern Oregon)—better known for its Crater Lake, which is a caldera formed by a catastrophic eruption which took out most of the summit roughly 6,900 years ago. Mount Mazama is estimated to have been about 11,000 ft. (3,350 m) elevation prior to the blast.
- Mount Scott (southern Oregon)—on the southeastern flank of Crater Lake. At 8,929 feet (2,721 m) elevation, this small stratovolcano is the highest peak in Crater Lake National Park.
- Mount McLoughlin (near Klamath Falls, Oregon)—presents a symmetrical appearance when viewed from Klamath Lake.
- Medicine Lake Volcano—a shield volcano in northern California which is the largest volcano by volume in the Cascades.
- Mount Shasta (northern California)—second highest peak in the Cascades. Can be seen in the Sacramento Valley as far as 140 miles (225 km) away, as it is a dominating feature of the region.
- Lassen Peak (south of Mount Shasta)—southernmost volcano in the Cascades and the most easily climbed peak in the range. It erupted from 1914 to 1921, and like Mount Shasta, it too can be seen in the Sacramento Valley, up to 120 miles (193 km) away.
Protected areas
There are four U.S. National Parks in the Cascade Range and many U.S. National Monuments, U.S. Wilderness Areas, and U.S. National Forests. Each classification protects the various glaciers, volcanoes, geothermal fields, rivers, lakes, forests, and wildlife to varying degrees.
National parks
- Lassen Volcanic National Park was established in 1916 while its namesake peak was erupting. The park includes the most extensive and active thermal areas in the United States outside Yellowstone National Park.
- Crater Lake National Park preserves the remains of Mount Mazama, a large volcano that imploded thousands of years ago, forming a caldera that was later filled with rain and ground water, later to be known as Crater Lake.
- Mount Rainier National Park surrounds the Cascades' tallest volcano, Mount Rainier, which in turn is shrouded in the largest glacier system in the United States south of Alaska.
- North Cascades National Park was carved out of a primitive part of the range composed of ancient metamorphic and sedimentary rock. Mount Baker and Glacier Peak are nearby.
National monuments
- Mount St. Helens National Volcanic Monument was formed following the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens in order to preserve the devastated area and give scientists a chance to study its recovery.
- Newberry National Volcanic Monument includes the area around Newberry Volcano in central Oregon.
- Cascade-Siskiyou National Monument is located in southern Oregon at the junction of the Cascades and the Siskiyou Mountains.
- Lava Beds National Monument in California lies on the northeast flank of the Medicine Lake Volcano and is the site of the largest concentration of lava tube caves in the United States.
Wilderness areas

- Wenatchee National Forest Wilderness Areas
- Alpine Lakes Wilderness
- Glacier Peak Wilderness
- Henry M. Jackson Wilderness
- Lake Chelan-Sawtooth Wilderness
- Norse Peak Wilderness
- William O. Douglas Wilderness
- Goat Rocks Wilderness
- Gifford Pinchot National Forest Wilderness Areas
- Goat Rocks Wilderness
- Tatoosh Wilderness
- Mount Adams Wilderness
- Indian Heaven Wilderness
- Trapper Creek Wilderness
- William O. Douglas Wilderness
- Mount Baker-Snoqualmie National Forest Wilderness Areas
- Alpine Lakes Wilderness
- Boulder River Wilderness
- Clearwater Wilderness
- Glacier Peak Wilderness
- Henry M. Jackson Wilderness
- Mount Baker Wilderness
- Noisy-Diobsud Wilderness
- Norse Peak Wilderness
- Mount Hood National Forest Wilderness Areas
- Badger Creek Wilderness
- Bull of the Woods Wilderness
- Mark O. Hatfield Wilderness
- Mount Hood Wilderness
- Salmon-Huckleberry Wilderness
- Deschutes National Forest Wilderness Areas
- Diamond Peak Wilderness
- Mount Jefferson Wilderness
- Mount Thielsen Wilderness
- Mount Washington Wilderness
- Three Sisters Wilderness
- Willamette National Forest Wilderness Areas
- Opal Creek Wilderness
- Middle Santiam Wilderness
- Menagerie Wilderness
- Waldo Lake Wilderness
- Umpqua National Forest Wilderness Areas
- Boulder Creek Wilderness
- Rogue River-Siskiyou National Forest Wilderness Areas
- Sky Lakes Wilderness
- Rogue-Umpqua Divide Wilderness
- Fremont-Winema National Forests Wilderness Areas
- Mountain Lakes Wilderness
- Shasta-Trinity National Forest Wilderness Areas
- Mount Shasta Wilderness
- Lassen National Forest Wilderness Areas
- Caribou Wilderness
- Ishi Wilderness
- Thousand Lakes Wilderness
Provincial Parks
- Garibaldi Provincial Park includes Mount Garibaldi and the southern part of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt (although not technically part of the Cascade Range).
- Skagit Valley Provincial Park
- E.C. Manning Provincial Park
- Cascade Recreation Area
- Cathedral Provincial Park and Protected Area
- Coquihalla Canyon Provincial Park
Human uses
Soil conditions for farming in the area are generally excellent, especially downwind of volcanoes. This is largely due to the fact that volcanic rocks are often rich in minerals such as potassium and decay easily. Volcanic debris, especially lahars, also have a leveling effect, while the storage of water in the form of snow and ice is also important. Much of that water eventually flows into reservoirs where it is used for recreation before its potential energy is captured to generate hydroelectric power before being used to irrigate crops.
Because of the abundance of powerful streams, many of the major westward rivers off the Cascades have been dammed to provide hydroelectric power. One of these, Ross Dam on the Skagit River, created a reservoir which spans the border southeast of Hope, British Columbia, extending into Canada two miles. At the foot of the southeast flank of Mount Baker, at Concrete, Washington, the Baker River is dammed to form Shannon and Baker Lakes.
In addition, there is a largely untapped amount of geothermal power that can be generated from the Cascades. The United States Geological Survey's Geothermal Research Program has been investigating this potential. Some of this energy is already being used in places such as Klamath Falls, Oregon where volcanic steam is used to heat public buildings. The highest recorded temperature found in the range is 510 °F (265 °C) at 3,075 feet (937 m) below Newberry Caldera's floor.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Beckey, Fred W. 1987. Cascade Alpine Guide: Climbing and High Routes. Seattle, Wash: Mountaineers. ISBN 9780898864236.
- Dzurisin, Dan and Peter H. Stauffer, and James W. Hendley II. 1997. Living With Volcanic Risk in the Cascades. U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved October 13, 2008.
- Harris, Stephen L. 1976. Fire and Ice: The Cascade Volcanoes. Seattle: The Mountaineers.
- Harris, Stephen L., and Stephen L. Harris. 1988. Fire Mountains of the West: The Cascade and Mono Lake Volcanoes. Roadside geology series. Missoula, MT: Mountain Press Pub. Co. ISBN 087842220X.
- Holland, Stuart S. 1976. Landforms of British Columbia: A Physiographic Outline. Victoria, B.C.: Dept. of Mines and Petroleum Resources.
- Wood, Charles Arthur, and Juergen Kienle. 1990. Volcanoes of North America: United States and Canada. Cambridge [England]: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521364690.
External links
All links retrieved November 29, 2023.
- Central and Southern Cascades Forests images at bioimages.vanderbilt.edu
- Eastern Cascades Forests images at bioimages.vanderbilt.edu
- Cascade Mountains Leeward Forests images at bioimages.vanderbilt.edu
- British Columbia Mainland Coastal Forests images at bioimages.vanderbilt.edu
- University of Washington Libraries Digital Collections – Dwight Watson Photographs Photographs taken by mountaineer and amateur photographer Dwight Watson of hiking and skiing expeditions in the Cascade and Olympic Mountain ranges of Washington State, ca. 1920s-1960s. Includes, among others, scenic images of Mounts Rainier, Baker, Adams, and Glacier Peak.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.