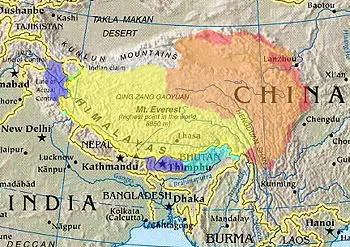
Tibet
| Tibetan areas designated by the PRC.[1] | |||||||||
| Tibet Autonomous Region (actual control).[2] | |||||||||
| Claimed by India as part of Aksai Chin.[3] | |||||||||
| Claimed (not controlled) by the PRC as part of the TAR.[4] | |||||||||
| Other historically/culturally-Tibetan areas.[5] | |||||||||
Tibet, called “Bod” by Tibetans, or 西藏 (Xīzàng) by the Chinese, is a plateau region in Central Asia and the indigenous home to the Tibetan people. With an average elevation of 16,000 feet, (4900 meters) it is the highest region on Earth and is commonly referred to as the "Roof of the World."
The Tibetan Empire came into existence in the seventh century when Emperor Songtsän Gampo united many areas and tribes of the region. From the early 1600s the Dalai Lamas, whose succession is based on the doctrine of reincarnation, are known as spiritual leaders, whose historical status as actual rulers is disputed.
Tibet has been controlled by the People's Republic of China (PRC) since 1950. As an exclusive mandate, Tibet is also officially claimed by the Republic of China (Taiwan). The government of the People's Republic of China, and the Government of Tibet in Exile, disagree over when Tibet became a part of China, and whether this incorporation into China is legitimate according to international law.
Definitions

When the Government of Tibet in Exile and the Tibetan refugee community abroad refer to Tibet, they mean the areas consisting of the traditional provinces of Amdo, Kham, and Ü-Tsang, but excluding Sikkim, Bhutan, and Ladakh that have also formed part of the Tibetan cultural sphere.
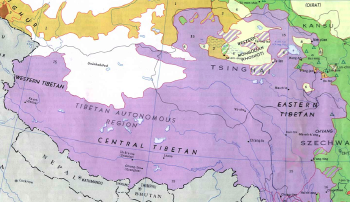
When the People's Republic of China (PRC) refers to Tibet, it means the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR): a province-level entity which includes Arunachal Pradesh (which used to be part of Tibet but is an Indian state set up by India after Indian occupation). The TAR covers the Dalai Lama's former domain, consisting of Ü-Tsang and western Kham, while Amdo and eastern Kham are part of Qinghai, Gansu, Yunnan, and Sichuan.
The difference in definition is a major source of dispute. The distribution of Amdo and eastern Kham into surrounding provinces was initiated by the Yongzheng Emperor of Qing Dynasty of China which exercised complete sovereignty over Tibet during the eighteenth century and has been continuously maintained by successive Chinese governments. Tibetan exiles, in turn, consider the maintenance of this arrangement from the eighteenth century as part of a divide-and-rule policy.
The original name in Sanskrit is "Divat", the "Divine Region". Many less literate people pronounced this as "Tibat". The British, later spelt it as "Tibet". The modern Chinese name for Tibet, 西藏 (Xīzàng), is a phonetic transliteration derived from the region called Tsang (western Ü-Tsang). The name originated during the Qing Dynasty of China, ca. 1700.
The English word Tibet, is derived from the Arabic word Tubbat, which. Comes via Persian from the Turkic word Töbäd (plural of Töbän), meaning "the heights". The word for Tibet in Medieval Chinese, 吐蕃 (Pinyin Tǔfān, often given as Tubo), is derived from the same Turkic word.
Geography
Located on the Tibetan Plateau, the world's highest region, Tibet is bordered on the north and east by China, on the west by the Kashmir Region of India and on the south by Nepal, Bangladesh and Bhutan.
Tibet occupies about 471,700 square miles (1,221,600 square kilometers) on the high Plateau of Tibet surrounded by enormous mountains. Historic Tibet consists of several regions:
- Amdo (A mdo) in the northeast, incorporated by China into the provinces of Qinghai, Gansu and Sichuan.
- Kham (Khams) in the east, divided between Sichuan, northern Yunnan and Qinghai.
- Western Kham, part of the Tibetan Autonomous Region
- Ü-Tsang (dBus gTsang) (Ü in the center, Tsang in the center-west, and Ngari (mNga' ris) in the far west), part of the Tibetan Autonomous Region
Tibetan cultural influences extend to the neighboring states of Bhutan, Nepal, adjacent regions of India such as Sikkim and Ladakh, and adjacent provinces of China where Tibetan Buddhism is the predominant religion.
The Ch’iang-t’ang plateau in the north extends more than 800 miles (1300 km) across with an average elevation of 15,000 feet (4500 meters) above sea level. It has brackish lakes and no river systems there. The plateau descends in elevation towards the east. Mountain ranges in the south-east create a north- south barrier to travel and communication.
The Kunlun Mountains, with its highest peak Mu-tzu-t’a-ko reaching 25,338 feet (7723 meters) form a border to the north. The Himalaya mountains, one of the youngest mountain ranges in the world at only four million years old, form the western and southern border — the highest peak is Mount Everest, which rises to 29,035 feet (8850 meters) on the Tibet–Nepal border. North of Ma-fa-mu Lake and stretching east is the Kang-ti-ssu Range, with several peaks, exceeding 20,000 feet. The Brahmaputra River, which flows across southern Tibet to India, separates this range from the Himalayas.
The Indus River, known in Tibet as the Shih-ch'üan Ho, has its source in western Tibet near the sacred Mount Kailas, and flows west across Kashmir to Pakistan. The Hsiang-ch'üan River flows west to become the Sutlej River in western India, the K'ung-ch'üeh River eventually join the Ganges River, and the Ma-ch'üan River flows east and, after joining the Lhasa River, forms the Brahmaputra River. The Salween River flows from east-central Tibet, through Yunnan to Myanmar. The Mekong River has its source in southern Tsinghai as two rivers—the Ang and Cha—which join near the Tibet border to flow through eastern Tibet and western Yunnan to Laos and Thailand. The Yangtze River arises in southern Tsinghai.
Lakes T'ang-ku-la-yu-mu, Na-mu, and Ch'i-lin are the three largest lakes and are located in central Tibet. In western Tibet are two adjoining lakes, Ma-fa-mu Lake, sacred to Buddhists and Hindus, and Lake La-ang.
The climate is dry nine months of the year, and average snowfall is only 18 inches, due to the rain shadow effect whereby mountain ranges prevent moisture from the ocean from reaching the plateaus. Western passes receive small amounts of fresh snow each year but remain traversable all year round. Low temperatures are prevalent throughout these western regions, where bleak desolation is unrelieved by any vegetation beyond the size of low bushes, and where wind sweeps unchecked across vast expanses of arid plain. The cool dry air means grain can be stored for 50 to 60 years, dried meat will last for a year, and epidemics are rare.
Northern Tibet is subject to high temperatures in the summer and intense cold in the winter. The seasonal temperature variation is minimal, with the greatest temperature differences occurring during a 24-hour period. Lhasa, at an elevation of 11,830 feet, has a maximum daily temperature of 85°F (30°C) and a minimum of -2°F (-19°C).
The arid climate of the windswept Ch'iang-t'ang supports little except grasses. Plant life in the river valleys and in the south and southeast includes willows, poplars, conifers, teak, rhododendrons, oaks, birches, elms, bamboo, sugarcane, babul trees, thorn trees, and tea bushes. The leaves of the lca-wa, khumag, and sre-ral, which grow in the low, wet regions, are used for food. Wildflowers include the blue poppy, lotus, wild pansy, oleander, and orchid.
The forests have tigers, leopards, bears, wild boars, wild goats, stone martens (a kind of cat), langurs, lynx, jackals, wild buffaloes, pha-ra (a small jackal), and gsa' (a small leopard). The high grasslands and dry bush areas have brown bears, wild and bighorn sheep, mountain antelope, musk deer, wild asses, wild yaks, snakes, scorpions, lizards, and wolves. Water life includes types of fish, frog, crab, otter, and turtle. Birds include the jungle fowl, mynah, hawk, the gull, crane, sheldrake, cinnamon teal, and owls. Natural hazards include earthquakes, landslides, and snow.
Lhasa is Tibet's traditional capital and the capital of the Tibet Autonomous Region. Lhasa contains the world heritage site the Potala Palace and Norbulingka, the residences of the Dalai Lama, and a number of significant temples and monasteries which are deeply engrained in its history including Jokhang and Ramoche Temple.Shigatse is the country's second largest city, west of Lhasa. Gyantse, Chamdo are also amongst the largest. Other cities in historic Tibet include, Nagchu, Nyingchi, Nedong, Barkam, Sakya, Gartse, Pelbar, and Tingri; in Sichuan, Kangding (Dartsedo); in Qinghai, Jyekundo or Yushu, Machen, Lhatse, and Golmud.
History
Chinese and the "proto-Tibeto-Burman" language may have split sometime before 4000 B.C.E., when the Chinese began growing millet in the Yellow River valley while the Tibeto-Burmans remained nomads. Tibetan split from Burman around 500 C.E.
Zhang Zhung culture
Prehistoric Iron Age hill forts and burial complexes have been found on the Chang Tang plateau but the remoteness of the location is hampering archaeological research. The initial identification of this culture is as the Zhang Zhung culture which is described in ancient Tibetan texts and is known as the original culture of the Bön religion. According to Annals of Lake Manasarowar, at one point the Zhang Zhung civilization, which started sometime before 1500 B.C.E., comprised 18 kingdoms in the west and northwest portion of Tibet, centered around sacred Mount Kailash. At that time the region was warmer.
The Tibetan Empire
.
Tibet first enters history in the Geography of Ptolemy under the name batai (βαται), a Greek transcription of the indigenous name Bod. Tibet next appears in history in a Chinese text where it is referred to as fa. The first incident from recorded Tibetan history which is confirmed externally occurred when King Namri Lontsen sent an ambassador to China in the early seventh century.
Early Tibet was divided into princedoms, which in the sixth century were consolidated under a king, Gnam-ri srong-brtsan (570 — 619 C.E.), who commanded 100,000 warriors. His son Songtsän Gampo (604–650 C.E.), the 33rd King of Tibet, united parts of the Yarlung River Valley and is credited with expanding Tibet's power and with inviting Buddhism to Tibet. In 640 he married Princess Wencheng, the niece of the powerful Chinese Emperor Taizong of Tang China. Songtsen Gampo, defeated the Zhang Zhung in 644 C.E.
Tibet divided
The reign of Langdarma (838-842) was plagued by external troubles. The Uyghur state to the North collapsed under pressure from the Kirghiz in 840, and many displaced persons fled to Tibet. Langdarma was assassinated in 842. The Tibetan empire collapsed, either as the result of war of succession, or war between rival generals. Allies of one posthumous heir controlled Lhasa, while allies of the other went to Yalung. Nyima-Gon, a representative of the ancient Tibetan royal house founded the first Ladakh dynasty, in the Kashmir region, to the east of present day Ladakh. Central rule was largely nonexistent over the Tibetan region from 842 to 1247, and Buddhism declined in central Tibet, surviving surreptitiously in the region of Kham.
A son of the king of the western Tibet Kingdom of Guge became a Buddhist monk and was responsible for inviting the renowned Indian pandit Atisha to Tibet in 1042 thus ushering in the Chidar (Phyi dar) phase of Buddhism there. Tibetan scholar Dkon-mchog rgyal-po established the Sakya Monastery in Lhokha in 1073. Over the next two centuries Sakya monastery grew to a position of prominence in Tibetan life and culture. At this time, some monasteries began practising a tradition whereby a deceased lama (head of the monastery) was succeeded by a boy judged to be his reincarnation.
Mongol sovereignty
The Mongol khans had ruled northern China by conquest since 1215, as emperors of the Yuan Dynasty. In 1240, the Mongols, investigating an option to attack China from the west, marched into central Tibet and attacked several monasteries. Köden, younger brother of Mongol ruler Güyük Khan, invited the leader of the Sakya sect, to come to his capital and formally surrender Tibet to the Mongols. The Sakya lama arrived in Kokonor with his two nephews, Drogön Chögyal Phagpa (1235-80) and Chana Dorje (1239-1267) (Phyag-na Rdo-rje) (1239-67) in 1246. Köden recognized the Sakya lama as temporal ruler of Tibet in 1247. This event marks the incorporation of Tibet into China, according to modern Chinese historians. Pro-Tibetan historians argue that China and Tibet remained two separate units within the Mongol Empire..
Kublai Khan, who was elected Qaghan in 1260 following the death of his brother Möngke, named Drogön Chögyal Phagpa “state preceptor” his chief religious official, in Tibet. In 1265, Drogön Chögyal Phagpa returned to Tibet and tried to impose Sakya hegemony with the appointment of Shakya Bzang-po (a long time servant and ally of the Sakyas) as the Dpon-chen ('great administrator') over Tibet in 1267. A census was conducted in 1268 and Tibet was divided into 13 myriarchies. In 1270, Phagpa was named Dishi ('imperial preceptor'), and his position as ruler of Tibet was reconfirmed.
Sakya rule continued into the middle of the fourteenth century, although it was challenged by a revolt of the Drikung Kagyu sect with the assistance of Hülegü Khan of the Ilkhanate in 1285. The revolt was suppressed in 1290 when the Sakyas and eastern Mongols burned Drikung Monastery and killed 10,000 people.
Phag-mo-gru-pa dynasty
The collapse of the Mongol Yuan dynasty in 1368 led to the overthrow of the Sakya in Tibet. When the native Chinese Ming dynasty evicted the Mongols, Tibet regained its independence, and for more than 100 years the Phag-mo-gru-pa line governed in its own right. Buddhism revived. Literary activity was intense. Monasteries were built and decorated by Chinese craftsmen. In 1435, the lay princes of Rin-spungs, ministers of Gong-ma, and patrons of the Karma-pa sect, rebelled and by 1481 had seized control of the Phag-mo-gru court.
Yellow Hat sect
The rigorous Buddhist reformist Tsong-kha-pa, who had studied with the leading teachers of the day, formulated his own doctrine, emphasizing the moral and philosophical teachings of Atisha over the magic and mysticism of Sakya. In 1409, he founded a monastery at Dga'-ldan, noted for strict monastic discipline, which appealed to people weary of rivalry and strife between wealthy monasteries. After his death, devoted and ambitious followers built around his teaching and prestige what became the Dge-lugs-pa, or Yellow Hat sect.
The Dalai Lama lineage
The Mongolian ruler Altan Khan bestowed the title of “Dalai Lama” upon Sonam Gyatso, the third head of the Gelugpa Buddhist sect, in 1578, thus reviving the patron-priest relationship that had existed between Kublai Khan and 'Phags-pa.
"Dalai" means "ocean" in Mongolian, and "Lama" is the Tibetan equivalent of the Sanskrit word "guru", and is commonly translated to mean "spiritual teacher". Gyatso was an abbot at the Drepung monastery who was widely considered the most eminent lama of his time. Although Sonam Gyatso became the first lama to hold the title "Dalai Lama", due to the fact that he was the third member of his lineage, he became known as the "third Dalai Lama". The previous two titles were conferred posthumously upon his earlier incarnations. The Dalai Lama is believed to be the embodiment of a spiritual emanation of the bodhisattva—Avalokitesvara, the mythic progenitor of Tibetans. Succession passes to a child, born soon after the death of a Dalai Lama, believed to have received the spirit of the deceased.
Fifth Dalai Lama
The fourth Dalai Lama supposedly reincarnated in Mongol Altan Khan's family. Mongol forces entered Tibet to push this claim, opposed by the Karma-pa sect and Tibet's secular aristocracy. The fourth Dalai Lama died in 1616. New Oyrat Mongol leader Güüshi Khan invaded Tibet in 1640. In 1642, Güüshi enthroned the Fifth Dalai Lama as ruler of Tibet.
Lobsang Gyatso, the fifth Dalai Lama, (1617-1682) was the first Dalai Lama to wield effective political power over central Tibet. He is known for unifying Tibet under the control of the Geluk school of Tibetan Buddhism, after defeating the rival Kagyu and Jonang sects, and the secular ruler, the prince of Shang, in a prolonged civil war. His efforts were successful in part because of aid from Gushi Khan. The Jonang monasteries were either closed or forcibly converted, and that school remained in hiding until the latter part of the twentieth century. The fifth Dalai Lama initiated the construction of the Potala Palace in Lhasa, and moved the center of government there from Drepung.
Manchu sovereignty
The Ch'ing, or Manchu dynasty was installed in China in 1644. The Manchu wanted good relations with Tibet because of the Dalai Lama's prestige among the Mongols. Meanwhile, Tibet clashed with Bhutan in 1646 and 1657, and with Ladakh up to 1684.
The Manchus did not find out about the death of the Fifth Dalai Lama (in 1682), and the appearance of his supposed reincarnation, until 1696. Infuriated, Manchu Emperor K’ang-hsi (who reigned 1661–1722) found an ally in Mongol Lha-bzang Khan, the fourth successor of Güüshi, who sought to assert rights as king in Tibet. The behaviour of the sixth Dalai Lama (1683-1706), a poetry-writing libertine, provided an excuse for Lha-bzang Khan, in 1705, to kill minister regent Sangs-rgyas rgya-mtsho and depose the Dalai Lama as a spurious reincarnation. Fearing Mongol control of Tibet, in 1720 Manchu troops drove out the Mongols, thus gaining a titular sovereignty over Tibet, leaving representatives and a small garrison in Lhasa, and government in the hands of the Dalai Lamas. Manchu troops quelled a civil war in Tibet in 1728, restored order after the assassination of a political leader in 1750, and drove out Gurkhas, who had invaded from Nepal in 1792. Chinese contact helped shape the Tibetan bureaucracy, army, and mail service. Chinese customs influenced dress, food, and manners.
British interest
The first Europeans to arrive in Tibet were Portuguese missionaries in 1624, who built a church. Two Jesuit missionaries, Johannes Gruber and Albert D'Orville, reached Lhasa in 1661, and. The eighteenth century brought more Jesuits and Capuchins from Europe who gradually met opposition from Tibetan lamas who finally expelled them from Tibet in 1745. In 1774, a Scottish nobleman George Bogle came to Shigatse to investigate trade for the British East India Company, introducing the first potato crop into Tibet. All foreigners except Chinese were excluded from Tibet after 1792.
In 1865 Great Britain began secretly mapping Tibet. Trained Indian surveyor-spies disguised as pilgrims or traders counted their strides on their travels across Tibet and took readings at night.
British colonial officials in India attempted to secure a foothold in Tibet, who saw the region as a trade route to China, then as a way to counter Russian advances towards India. In 1904, a British diplomatic mission, led by Colonel Francis Younghusband and accompanied by a large military escort, forced its way through to Lhasa. But on his way to Lhasa, Younghusband killed 1300 Tibetans in Gyangzê because the natives were in fear of what kind of unequal treaty the British would offer the Tibetans. The 13th Dalai Lama fled to China. A treaty was concluded between Britain and Tibet, and then between Britain and China in 1906, that recognized Chinese sovereignty over Tibet.
Chinese sovereignty resisted
The Anglo-Chinese convention encouraged China to invade Tibet in 1910. The 13th Dalai Lama fled again, this time to India. But after the Chinese Revolution in 1911–12, the Tibetans expelled all the Chinese and declared their independence. All Chinese officials and troops were expelled from the country by 1913.
A convention at Simla in 1914 provided for an autonomous Tibet, and for Chinese sovereignty in the region called Inner Tibet. The Chinese government repudiated the agreement, and in 1918, strained relations between Tibet and China exploded into armed conflict. Efforts to conciliate the dispute have failed, and fighting flared up in 1931. The Dalai Lamas continued to govern Tibet as an independent state.
The subsequent outbreak of World War I and Chinese Civil War caused the Western powers and the infighting factions of China proper to lose interest in Tibet, and the 13th Dalai Lama ruled undisturbed until his death in 1933.
In 1935, the 14th Dalai Lama, Tenzin Gyatso was born in Amdo in eastern Tibet and was recognized as the latest reincarnation. He was taken to Lhasa in 1937 where he was later given an official ceremony in 1939. During the 1940s during World War II, two Austrian mountaineers, Heinrich Harrer and Peter Aufschnaider came to Lhasa, where Harrer became tutor and consort to the young Dalai Lama giving him a sound knowledge of western culture and modern society, until he was forced to leave with the Chinese invasion in 1950.
Chinese invade
In October 1950, Communist Chinese troops invaded Tibet. The regency invested the 14th Dalai Lama, although he was only 15 years old. Poorly equipped Tibetan troops were soon crushed. An appeal by the Dalai Lama to the United Nations was denied, while Great Britain and India offered no help. A Tibetan delegation was summoned to China. In May 1951, they signed a dictated treaty that gave the Dalai Lama authority in domestic affairs, Chinese control of Tibetan foreign and military affairs, and for the return from China of the Tibetan Buddhist spiritual leader, the Panchen Lama, allegedly a communist partisan. The Communist Chinese military entered Lhasa in October, and the Panchen Lama arrived there in April 1952.
Chinese rule
During 1952 the Chinese built airfields and military roads. A purge of anti-Communists was reportedly carried out early in 1953. India recognized Tibet as part of China in 1954 and withdrew its troops from two Tibetan frontier trading posts. The Dalai Lama was elected a vice-president of the National People's Congress, the Chinese legislative body.. A committee was set up in 1956 to prepare a constitution, the Dalai Lama was named chairman, and the Panchen Lama first vice-chairman.
An uprising broke out in Amdo and eastern Kham in June 1956. The resistance, supported by the US-American CIA, eventually spread to Lhasa. It was crushed by 1959. During this campaign, tens of thousands of Tibetans were killed. The 14th Dalai Lama and other government principals fled to exile in India, but isolated resistance continued in Tibet until 1969 when the CIA abruptly withdrew its support.
Although the Panchen Lama remained a virtual prisoner, the Chinese set him as a figurehead in Lhasa, claiming that he headed the legitimate Government of Tibet since the Dalai Lama had fled to India. In 1965, the area that had been under the control of the Dalai Lama's government from the 1910s to 1959 (U-Tsang and western Kham) was set up as an Autonomous Region. The monastic estates were broken up and secular education introduced.
During the Cultural Revolution, the Chinese Red Guards inflicted a campaign of organized vandalism against cultural sites in the entire PRC, including Tibet's Buddhist heritage. Some young Tibetans joined in the campaign of destruction, voluntarily due to the ideological fervour that was sweeping the entire PRC and involuntarily due to the fear of being denounced as enemies of the people. Of the several thousand monasteries in Tibet, over 6500 were destroyed, only a handful of the most important, religiously or culturally, monasteries remained without major damage according to the Chinese source. And hundreds of thousands of Buddhist monks and nuns were forced to return to secular life.
In 1989, the Panchen Lama was finally allowed to return to Shigatse, where he addressed a crowd of 30,000 and described what he saw as the suffering of Tibet and the harm being done to his country in the name of socialist reform under the rule of the PRC in terms reminiscent of the petition he had presented to Chinese Premier Zhou Enlai in 1962.. Five days later, he mysteriously died of a massive heart attack at the age of 50.
In 1995 the Dalai Lama named six-year-old Gedhun Choekyi Nyima as the 11th Panchen Lama without Chinese approval, while the PRC named another child, Gyancain Norbu in conflict. Gyancain Norbu was raised in Beijing and has appeared occasionally on state media. Tibetans reject the PRC-selected Panchen Lama. Gedhun Choekyi Nyima and his family have gone missing - widely believed to be imprisoned by China - and under a hidden identity for protection and privacy according to the PRC.
The PRC continues to portray its rule over Tibet as an unalloyed improvement, but foreign governments continue to make occasional protests about aspects of PRC rule in Tibet because of frequent reports of human rights violation in Tibet by groups such as Human Rights Watch. All governments, however, recognize the PRC's sovereignty over Tibet today, and none have recognized the Government of Tibet in Exile in India.
Government and politics
Before the Chinese occupied Tibet in 1951, the country had a theocratic government with the Dalai Lama the religious and temporal head. From 1951, the Chinese relied on military control working towards regional autonomy, which was granted in 1965. Since then, Tibet has been one of the People’s Republic of China’s five autonomous regions.
An autonomous region has its own local government, but with more legislative rights. It is a minority entity and has a higher population of a particular minority ethnic group. Following Soviet practice, the chief executive is typically a member of the local ethnic group while the party general secretary is non-local and usually Han Chinese.
The region is divided into the municipality of Lhasa, directly under the jurisdiction of the regional government, and prefectures (Qamdo, Shannan, Xigazê, Nagqu, Ngari, and Nyingchi), which are subdivided into counties.
The army comprises regular Chinese troops under a Chinese commander, stationed at Lhasa. There are military cantonments in major towns along the borders with India, Nepal, and Bhutan. Tibetans have been forcibly recruited into regular, security, and militia regiments.
The Central Tibetan Administration (CTA), officially the Central Tibetan Administration of His Holiness the Dalai Lama, is a government in exile headed by Tenzin Gyatso, the 14th Dalai Lama, which claims to be the rightful and legitimate government of Tibet. It is commonly referred to as the Tibetan Government in Exile.
The CTA is headquartered in Dharamsala, India, where the Dalai Lama settled after fleeing Tibet in 1959 after a failed uprising against Chinese rule. It claims jurisdiction over the entirety of the Tibet Autonomous Region and Qinghai province, as well as parts of the neighboring provinces of Gansu, Sichuan and Yunnan - all of which is termed "Historic Tibet" by CTA.
The CTA exercises many governmental functions in relation to the Tibetan exile community in India, which numbers around 100,000. The administration runs schools, health services, cultural activities and economic development projects for the Tibetan community. It also provides welfare services for the hundreds of Tibetans who continue to arrive in India each month as refugees after having crossed from China, usually via Nepal, on foot. The government of India allows the CTA to exercise effective jurisdiction in these matters over the Tibetan communities in northern India. The CTA is not recognized as a government by any country, but it receives financial aid from governments and international organisations for its welfare work among the Tibetan exile community in India. This does not imply recognition of the CTA as a government.
Disputed territory — exile view
The government of Tibet in exile says that the issue is that of the right to self-determination of the Tibetan people. It says that:
- Approximately 1.2 million have died as a result of the Chinese occupation since 1950, and up to 10 percent of the Tibetan population was interned, with few survivors.
- Despite the central government's claim to have granted most religious freedoms, Tibetan monasteries are under stringent government control, and in 1998, three monks and five nuns died while in custody, after suffering beatings and torture for having shouted slogans supporting the Dalai Lama and Tibetan independence.
- Projects that the PRC claims to have benefited Tibet, such as the China Western Development economic plan or the Qinghai-Tibet Railway, are actually politically-motivated actions to consolidate central control over Tibet by facilitating militarization and Han migration while benefit only a few Tibetans
People's Republic of China view
The government of the PRC maintains that the Tibetan Government did almost nothing to improve the Tibetans' material and political standard of life during its rule from 1913-1959, and that they opposed any reforms proposed by the Chinese government. The government of the PRC claims that the lives of Tibetans have improved immensely compared to self-rule before 1950:
- Gross domestic product of the TAR in 2007 was 30 times that of before 1950
- Workers in Tibet have the second highest wages in China
- The TAR has 22,500 km of highways, as opposed to none in 1950
- All secular education in the TAR was created after the revolution, the TAR now has 25 scientific research institutes as opposed to none in 1950
- Infant mortality has dropped from 43 percent in 1950 to 0.661 percent in 2000
- Life expectancy]] has risen from 35.5 years in 1950 to 67 in 2000
- The traditional Epic of King Gesar, which is the longest epic poem in the world and which had only been handed down orally, has been collected and published
- 300 million renminbi have been allocated since the 1980s for the maintenance and protection of Tibetan monasteries.
The Cultural Revolution and the cultural damage it wrought upon the entire PRC has been condemned as a nationwide catastrophe. Its main instigators, the Gang of Four, have been brought to justice, and a reoccurrence is unthinkable in an increasingly modernized China. The China Western Development plan is viewed by the PRC as a massive, benevolent, and patriotic undertaking by the wealthier eastern coast to help the western parts of China, including Tibet, catch up in prosperity and living standards.
Economy
Tibet is rich in mineral resources, but its economy has remained underdeveloped. Surveys of western Tibet in the 1930s and 1940s discovered goldfields, deposits of borax, as well as radium, iron, titanium, lead, and arsenic. There is a 25-mile belt of iron ore along the Mekong River, plentiful coal, and oil-bearing formations. Other mineral resources include oil shale, manganese, lead, zinc, quartz, and graphite. Precious and semi-precious stones include jade, lapis lazuli, among others. The forest timber resource in the Khams area alone was estimated at 3.5-billion cubic feet. The swift-flowing rivers provide enormous hydroelectric power potential, possibly contributing one-third of China's potential resources. Because of the inaccessibility of Tibet's forests, forestry is developing.
The economy of Tibet is dominated by subsistence agriculture. Livestock raising is the primary occupation mainly on the Tibetan Plateau, including sheep, cattle, goats, camels, yaks (large, long-haired oxen) and horses. However the main crops grown are barley, wheat, buckwheat, rye, potatoes and assorted fruits and vegetables. Butter from the yak and the mdzo-mo (a crossbreed of the yak and the cow) is the main dairy product.
Under Chinese control, the small hydroelectric power station at Lhasa was repaired, a new thermal station was installed in Jih-k'a-tse. Hydrographic stations were established to determine hydroelectric potential. An experimental geothermal power station was commissioned in the early 1980s, with the transmitting line terminating in Lhasa. Emphasis was placed on agricultural-processing industries and tourism. The PRC government exempts Tibet from all taxation and provides 90 percent of Tibet's government expenditures. Tibet's economy depends on Beijing.

Qinghai-Tibet railway
The Qinghai-Tibet Railway which links the region to Qinghai in China proper was opened in 2006. The Chinese government claims that the line will promote the development of impoverished Tibet. But opponents argue the railway will harm Tibet since it would bring in more Han Chinese residents, the country's dominant ethnic group, who have been migrating steadily to Tibet over the last decade, bringing with them their popular culture. Opponents say the large influx of Han Chinese will ultimately extinguish the local culture. Others argue that the railway will damage Tibet's fragile ecology.
Tourism
Tibet's tourism has grown., especially after the finish of Qingzang Railway in July 2006, Tibet received 2.5 million tourists in 2006, including 150 thousands foreigners. Increased interest in Tibetan Buddhism has helped make tourism an increasingly important sector, and this is actively promoted by the authorities. Tourists buy handicrafts — hats, jewelry (silver and gold), wooden items, clothing, quilts, fabrics, Tibetan rugs and carpets.
Limited data
As an autonomous region of China, data on imports and exports is not readily available, and any that is derives from state publications issued for publicity purposes. According to PRC figures, Tibet's GDP in 2001 was 13.9 billion yuan (US$1.8-billion). Tibet's economy has had an average growth of 12 percent per year from 2000 to 2006, a figure that corresponded to the five-year goal issued at the start of the period.
The per capita GDP reached 10,000 renminbi (mainland China unit of currency) in 2006 for the first time. That would convert to $1233, which would place Tibet between Mali (164th) and Nigeria (165th) on the International Monetary Fund list. By comparison, the PRC per capita GDP is $7598, or 87th. Tibet is a poor part of China.
Demographics
The population of the Tibet Autonomous Region was 2,616,329 in 2000. The population for the greater Tibet region, including Xining and Haidong, was 10,523,432, and without Xining and Haidong was 7,282,154. Since the 1980s, increasing economic liberalization and internal mobility has also resulted in the influx of many Han Chinese into Tibet for work or settlement, though the actual number of this floating population remains disputed. The issue of the proportion of the Han Chinese population in Tibet is a politically sensitive one. The Central Tibetan Administration says that the People's Republic of China has actively swamped Tibet with Han Chinese migrants in order to alter Tibet's demographic makeup. Life expectancy for the total population was 67 in 2000.
Ethnicity
Historically, the population of Tibet consisted of primarily ethnic Tibetans. Other ethnic groups in Tibet include Menba (Monpa), Lhoba, Mongols and Hui Chinese. According to tradition the original ancestors of the Tibetan people, as represented by the six red bands in the Tibetan flag, are: the Se, Mu, Dong, Tong, Dru and Ra.
The Tibet Autonomous Region in 2000 had 2,427,168 Tibetans (92.8 percent), 158,570 Han Chinese (6.1 percent) and 30,595 others (1.2 percent) according to PRC Department of Population figures. In the TAR itself, much of the Han population is to be found in Lhasa. Chinese figures for Greater Tibet without Xining and Haidong were: Tibetans 5,021,231 (69 percent), Han 1,470,209 (20.2 percent) and others 790,714 (10.9 percent).
The Government of Tibet in Exile gives the number of non-Tibetans in Greater Tibet as 7.5 million (as opposed to six million Tibetans), and claims this is as a result of an active policy of demographically swamping the Tibetan people and further diminishing any chances of Tibetan political independence, and as such, to be in violation of the Geneva Convention of 1946 that prohibits settlement by occupying powers.
The Government of Tibet in Exile questions all statistics given by the PRC government, since they do not include members of the People's Liberation Army garrisoned in Tibet, or the large floating population of unregistered migrants. The Qinghai-Tibet Railway (Xining to Lhasa) is also a major concern, as it is believed to further facilitate the influx of migrants.
The PRC government does not view itself as an occupying power and has vehemently denied allegations of demographic swamping. The PRC also does not recognize Greater Tibet as claimed by the Government of Tibet in Exile, saying that those areas outside the TAR were not controlled by the Tibetan government before 1959 in the first place, having been administered instead by other surrounding provinces for centuries.
Jampa Phuntsok, chairman of the TAR, has also said that the central government has no policy of migration into Tibet due to its harsh high-altitude conditions, that the six percent Han in the TAR is a very fluid group mainly doing business or working, and that there is no immigration problem. Population control policies like the one-child policy only apply to Han Chinese, not to Tibetans.
Religion
Religion is extremely important to the Tibetans. Tibetan Buddhism is a subset of Tantric Buddhism, also known as Vajrayana Buddhism, which is also related to the Shingon Buddhist tradition in Japan. Tibetan Buddhism is also practiced in Mongolia, the Buryat Republic, the Tuva Republic, and in the Republic of Kalmykia. Tibet is also home to the original spiritual tradition called Bön, the indigenous shamanistic religion of the Himalayas. Notable monasteries: Ani Tsankhung Nunnery, Changzhu Temple, Dorje Drak, Drepung, Drigung, Dzogchen, Ganden Monastery, Jokhang, Kumbum (Kham), Labrang, Menri, Namgyal, Narthang, Palcho, Ralung , Ramoche Temple, Sakya, Sanga , Sera, Shalu, Shechen, Surmang, Tashilhunpo, Tsurphu, and Yerpa.
In Tibetan cities, there are also small communities of Muslims, known as Kachee (Kache), who trace their origin to immigrants from three main regions: Kashmir (Kachee Yul in ancient Tibetan), Ladakh and the Central Asian Turkic countries. Islamic influence in Tibet also came from Persia. After 1959 a group of Tibetan Muslims made a case for Indian nationality based on their historic roots to Kashmir and the Indian government declared all Tibetan Muslims Indian citizens later on that year. There is also a well established Chinese Muslim community (gya kachee), which traces its ancestry back to the Hui ethnic group of China. It is said that Muslim migrants from Kashmir and Ladakh first entered Tibet around the rwelfth century. Marriages and social interaction gradually led to an increase in the population until a sizable community grew up around Lhasa.
The Potala Palace, former residence of the Dalai Lamas, is a World Heritage Site, as is Norbulingka, former summer residence of the Dalai Lama.
During the suppression of pro-independence forces in the 1950s, and during the Cultural Revolution in the 1960s, most historically significant sites in Tibet were vandalized or totally destroyed.
Since 2002, Tibetans in exile have allowed a Miss Tibet beauty contest in spite of concerns that this event is considered a Western influence. The beauty contest is condemned by the Tibetan government in exile.
Language
The Tibetan language is generally classified as a Tibeto-Burman language of the Sino-Tibetan language family. Spoken Tibetan includes numerous regional dialects which, in many cases, are not mutually intelligible. Moreover, the boundaries between Tibetan and certain other Himalayan languages are sometimes unclear. In general, the dialects of central Tibet (including Lhasa), Kham, Amdo, and some smaller nearby areas are considered Tibetan dialects, while other forms, particularly Dzongkha, Sikkimese, Sherpa, and Ladakhi, are considered for political reasons by their speakers to be separate languages. Ultimately, taking into consideration this wider understanding of Tibetan dialects and forms, "greater Tibetan" is spoken by approximately six million people across the Tibetan Plateau. Tibetan is also spoken by approximately 150,000 exile speakers who have fled from modern-day Tibet to India and other countries.
Men and women
Traditionally, Tibetan women not only did far more physical labor than men in the fields and shouldered household tasks, but also engaged in traditional handicraft and commercial activities. Tibetan men have been described as idle and lazy, while Tibetan women are strong and healthy. There are conflicting reports of the status of women in Tibetan society. Some accounts claim Tibetan women had equal rights with men and enjoyed a higher status than women in India and Burma.
Nuns have taken a leading role in resisting Chinese authorities. Since the late 1980s, the Chinese crackdown on the resistance has become increasingly centred on nunneries, which have had strict rules imposed on them, informers planted. Nuns convicted of political offenses are not allowed to return to their worship
Family and class
Marriage in Tibet, which involved both monogamy and polyandry, was traditionally related to the system of social stratification and land tenure, according to Melvyn C. Goldstein, who studied the issue on a field trip to Tibet in 1965-1967. Tibetan laymen traditionally were divided into two classes – the gerba (lords) and mi-sey (serfs). Membership of these classes was hereditary, and linkage was passed on through parallel descent – daughters were linked to the lord of the mother, and sons to the lord of the father. There were two categories of serfs – tre-ba (taxpayer) and du-jung (small householder). Tre-ba were superior in terms of status and wealth, and were organized into family units which held sizable plots of land (up to 300 acres) from their lord. They held a written title to the land, and could not be evicted so long as they fulfilled their obligations, which were quite onerous, and involved providing human and animal labor, caring for animals on behalf of the lord, and paying tax. Du-jung existed in two varieties —the bound du-jung held smaller (one or two acre), non-inheritable plots, wheras the non-bound du-jung leased his services.
The system of marriage in tre-ba families meant that for purposes of inheritance, only one marriage could occur in each generation, to produce with full rights of inheritance (jural), thus keeping the corporate family intact. Two conjugal families in a generation, with two sets of heirs, were thought likely to lead to partition of the land inheritance. To solve this problem, for example, in a family with two sons and one daughter, the daughter would move to the home of her husband, following the patrilineal pattern, and the two sons would marry one woman, establishing a polyandrous marriage, thus keeping the inherited land and obligations intact. Since Tibetans believed that marriages involving three of four brothers to one wife were too difficult, surplus brothers would become celibate monks, and surplus daughters could become nuns.
Perpetuation of the corporate family across the generations was the prime concern for tre-ba families. The traditional Tibetan solution for a situation when a mother died before her son married, was to have the son and father share a new wife. If a family had two daughters and no sons, the daughters could enter into a polygynous marriage, sharing a husband.
Since du-jung gained access to land as individuals rather than corporate families, the importance of the family unit was diminished. Couples married for love, married monogamously, and established their own households, without pressure to maintain an extended family. Sometimes aged parents lived with one of their children. The only instances on polyandry found among du-jung occurred when family wealth was involved.
Polyandry continued to be practised by some people in 2007, but was not common.
Education
Before 1950, there were a few secular schools in Tibet. Monasteries provided education, and some larger ones operated along the lines of theological universities. In the 1950s, government-run primary schools, community primary schools, and secondary technical and tertiary schools including Tibet University were established. A 10-year doctoral degree program in Buddhism is available at the state-run Tibet Buddhist College.
Culture
Tibet has a rich culture that shows a pervasive influence of Mahayana Buddhism, Tantric Buddhism, also known as Vajrayana Buddhism, as well as the indigenous shamanistic religion of the Himalayas is known as Bön. Greek statuary inspired both bronze and stone statues of the Buddha to be created for temple use.
Art
Tibetan art is deeply religious in nature, a form of sacred art. From the exquistely detailed statues found in Gompas to wooden carvings to the intricate designs of the Thangka paintings, the over-riding influence of Tibetan Buddhism on culture and art can be found in almost every object and every aspect of daily life.
The Greek skill in statuary, brought to neighbouring India in the fourth century B.C.E. by Alexander the Great, led to a Greco-Buddhist synthesis. Whereas the Buddha did not previously have a standardized statuary representation, the Greek models inspired both bronze and stone statues of the Buddha to be created for temple use.
Thangka paintings, a syncrestism of Chinese scroll-painting with Nepalese and Kashmiri painting, appeared in Tibet around the tenth century. Rectangular and painted on cotton or linen, they are usually traditional motifs depicting religious, astrological, and theological subjects, and sometimes the Mandala. To ensure that the image will not fade, organic and mineral pigments are added, and the painting is framed in colorful silk broadcades.
Tibetan rugs are primarily made from tibetan highland sheep's virgin wool. The Tibetan uses rugs for almost any domestic use from flooring to wall hanging to horse saddles. Tibetan rugs were traditionally hand-made, but with the introduction of modern technology, a few aspects of the rug making processes have been taken over by machine primarily because of cost, and the disappearance of knowledge.
With Tibet's occupation by Chinese communists in early 1950, Tibetan refugees took their knowledge of rug making to India and Nepal. Nepal’s rug business is one of the largest industries in the country and there are many rug exporters.
Architecture
Tibetan architecture contains Oriental and Indian influences, and reflects a deeply Buddhist approach. The Buddhist wheel, along with two dragons, can be seen on nearly every Gompa in Tibet. The design of the Tibetan Chörtens can vary, from roundish walls in Kham to squarish, four-sided walls in Ladakh.
The most unusual feature of Tibetan architecture is that many of the houses and monasteries are built on elevated, sunny sites facing the south, and are often constructed using a mixture of rocks, wood, cement and earth. Little fuel is available for heat or lighting, so flat roofs are built to conserve heat, and multiple windows are constructed to let in sunlight. Walls are usually sloped inwards at 10 degrees as a precaution against frequent earthquakes in the mountainous area.
Standing at 117 meters in height and 360 meters in width, the Potala Palace is considered as the most important example of Tibetan architecture. Formerly the residence of the Dalai Lama, it contains over a thousand rooms within thirteen stories, and houses portraits of the past Dalai Lamas and statues of the Buddha. It is divided between the outer White Palace, which serves as the administrative quarters, and the inner Red Quarters, which houses the assembly hall of the Lamas, chapels, 10,000 shrines, and a vast library of Buddhist scriptures.
Clothing


Tibetans are conservative in their dress, and though some have taken to wearing Western clothes, traditional styles abound. Women wear dark-colored wrap dresses over a blouse, and a colorful striped, woven wool apron signals that she is married. Men and women both wear long sleeves even in the hot summer months.
A Khata is a traditional ceremonious scarf given in Tibet. It symbolizes goodwill, auspiciousness and compassion. It is usually made of silk and white symbolising the pure heart of the giver. The khata is a highly versatile gift. It can be presented at any festive occasions to a host or at weddings, funerals, births, graduations, arrivals and departure of guests etc. The Tibetans commonly give a kind acknowledgment of “Tashi Delek” (meaning good luck) at the time of presenting.
Cuisine
The most important crop in Tibet is barley, and dough made from barley flour called tsampa, is the staple food of Tibet. This is either rolled into noodles or made into steamed dumplings called momos. Meat dishes are likely to be yak, goat, or mutton, often dried, or cooked into a spicy stew with potatoes. Mustard seed is cultivated in Tibet, and therefore features heavily in its cuisine. Yak yoghurt, butter and cheese are frequently eaten, and well-prepared yoghurt is considered something of a prestige item. Butter tea is very popular to drink and many Tibetans drink up to 100 cups a day.
Other Tibetan foods include:
- Balep korkun - a central Tibetan flatbread that is made on a skillet.
- Thenthuk - a type of cold-weather soup made with noodles and various vegetables.
Jasmine tea and yak butter tea are drunk. Alcoholic beverages include:
- Chhaang, a beer usually made from barley
- Raksi, a rice wine
In larger Tibetan towns and cities many restaurants now serve Sichuan-style Chinese food. Western imports and fusion dishes, such as fried yak and chips, are also popular. Nevertheless, many small restaurants serving traditional Tibetan dishes persist in both cities and the countryside.
Drama
The Tibetan folk opera, known as Ache Lhamo, which literally means "sister goddess", is a combination of dances, chants and songs. The repertoire is drawn from Buddhist stories and Tibetan history.
The Tibetan opera was founded in the 14th century by Thangthong Gyalpo, a Lama and a bridge builder. Gyalpo and seven recruited girls organized the first performance to raise funds for building bridges, which would facilitate transportation in Tibet. The tradition continued, and llhamo is held on various festive occasions such as the Linka and Shoton festival.
The performance is usually a drama, held on a barren stage, that combines dances, chants and songs. Colorful masks are sometimes worn to identify a character, with red symbolizing a king and yellow indicating deities and lamas.
The performance starts with a stage purification and blessings. A narrator then sings a summary of the story, and the performance begins. Another ritual blessing is conducted at the end of the play.
Music
The music of Tibet reflects the cultural heritage of the trans-Himalayan region, centered in Tibet but also known wherever ethnic Tibetan groups are found in India, Bhutan, Nepal and further abroad. First and foremost Tibetan music is religious music, reflecting the profound influence of Tibetan Buddhism on the culture.
Tibetan music often involves chanting in Tibetan or Sanskrit, as an integral part of the religion. These chants are complex, often recitations of sacred texts or in celebration of various festivals. Yang chanting, performed without metrical timing, is accompanied by resonant drums and low, sustained syllables. Other styles include those unique to the various schools of Tibetan Buddhism, such as the classical music of the popular Gelugpa school, and the romantic music of the Nyingmapa, Sakyapa and Kagyupa schools.
Secular Tibetan music has been promoted by organizations like the Dalai Lama's Tibetan Institute of Performing Arts. This organization specialized in the lhamo, an operatic style, before branching out into other styles, including dance music like toeshey and nangma. Nangma is especially popular in the karaoke bars of the urban center of Tibet, Lhasa. Another form of popular music is the classical gar style, which is performed at rituals and ceremonies. Lu are a type of songs that feature glottal vibrations and high pitches. There are also epic bards who sing of Tibet's national hero Gesar.
Nangma dance music is especially popular in the karaoke bars of the urban center of Tibet, Lhasa. Another form of popular music is the classical gar style, which is performed at rituals and ceremonies. Lu are a type of songs that feature glottal vibrations and high pitches. There are also epic bards who sing of Tibet's national hero Gesar.
Tibetan music has had a profound effect on some styles of Western music, especially New Age. Composers like Philip Glass and Henry Eichheim are most well-known for their use of Tibetan elements in their music.[citation needed] The first such fusion was Tibetan Bells, a 1971 release by Nancy Hennings and Henry Wolff. The soundtrack to Kundun, by Philip Glass, has helped to popularize Tibetan music.
Foreign styles of popular music have also had a major impact within Tibet. Indian ghazal and filmi are very popular, as is rock and roll, an American style which has produced Tibetan performers like Rangzen Shonu. Since the relaxation of some laws in the 1980s, Tibetan pop, popularized by the likes of Yadong, Jampa Tsering, 3-member group AJIA, 4-member group Gao Yuan Hong, 5-member group Gao Yuan Feng, and Dechen Shak-Dagsay are well-known, as are the sometimes politicized lyrics of nangma. Gaoyuan Hong in particular has introduced elements of Tibetan language rapping into their singles.
Cinema
In recent years there have been a number of films produced about Tibet, mostly notably Hollywood films such as Seven Years in Tibet, starring Brad Pitt, and Kundun, a biography of the Dalai Lama, directed by Martin Scorsese. Both of these films were banned by the Chinese government because of Tibetan nationalist overtones. Other films include Samsara, The Cup and the 1999 Himalaya, a French-American produced film with a Tibetan cast set in Nepal and Tibet. In 2005, exile Tibetan filmmaker Tenzing Sonam and his partner Ritu Sarin made Dreaming Lhasa, the first internationally recognized feature film to come out of the diaspora to explore the contemporary reality of Tibet. In 2006, Sherwood Hu made Prince of the Himalayas, an adaptation of Shakespeare's Hamlet, set in ancient Tibet and featuring an all-Tibetan cast. Seen also briefly in the 1994 movie The Shadow, starring Alec Baldwin. Kekexili , or Mountain Patrol, is a film made by National Geographic about a Chinese reporter that goes to Tibet to report on the issue involving the endangerment of Tibetan Antelope.
Festivals
Tibet has various festivals which commonly are performed to worship Buddha throughout the year. Losar is the Tibetan New Year Festival, and involves a week of drama and carnivals, horse races and archery. The Monlam Prayer Festival follows it in the first month of the Tibetan calendar which involves many Tibetans dancing and participating in sports events and sharing picnics. On the 15th day of the fourth month, Saka dawa celebrates the birth and enlightenment of Sakyamuni and his entry to Nirvana. An outdoor opera is held and captured animals released. Worshippers flock to the Jokhang in Lhasa to pray. The Golden Star Festival held in the seventh to eighth month is to wash away passion, greed and jealousy and to abandon ego. Ritual bathing in rivers takes place and picnics are held. There are numerous other festivals.
The Tibetan calendar lags approximately four to six weeks behind the solar calendar. For example the Tibetan First Month usually falls in February, the Fifth Month June or early July and the Eight Month in September.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Allen, Charles (2004). Duel in the Snows: The True Story of the Younghusband Mission to Lhasa. London: John Murray, 2004. ISBN 0-7195-5427-6.
- Bell, Charles (1924). Tibet: Past & Present. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- Dowman, Keith (1988). The Power-Places of Central Tibet: The Pilgrim's Guide. Routledge & Kegan Paul. London, ISBN 0-7102-1370-0. New York, ISBN 0-14-019118-6.
- Goldstein, Melvyn C.; with the help of Gelek Rimpoche. A History of Modern Tibet, 1913-1951: The Demise of the Lamaist State. Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers (1993), ISBN 81-215-0582-8. University of California (1991), ISBN 0-520-07590-0.
- Grunfeld, Tom (1996). The Making of Modern Tibet. ISBN 1-56324-713-5.
- Gyatso, Palden (1997). "The Autobiography of a Tibetan Monk". Grove Press. NY, NY. ISBN 0-8021-3574-9
- Human Rights in China: China, Minority Exclusion, Marginalization and Rising Tensions, London, Minority Rights Group International, 2007
- McKay, Alex (1997). Tibet and the British Raj: The Frontier Cadre 1904-1947. London: Curzon. ISBN 0-7007-0627-5.
- Norbu, Thubten Jigme; Turnbull, Colin (1968). Tibet: Its History, Religion and People. Reprint: Penguin Books (1987).
- Pachen, Ani; Donnely, Adelaide (2000). Sorrow Mountain: The Journey of a Tibetan Warrior Nun. Kodansha America, Inc. ISBN 1-56836-294-3.
- Parenti, Michael (2004)."Friendly Feudalism: The Tibet Myth".
- Petech, Luciano (1997). China and Tibet in the Early XVIIIth Century: History of the Establishment of Chinese Protectorate in Tibet. T'oung Pao Monographies, Brill Academic Publishers, ISBN 9-00403-442-0.
- Samuel, Geoffrey (1993). Civilized Shamans: Buddhism in Tibetan Societies. Smithsonian ISBN 1-56098-231-4.
- Schell, Orville (2000). Virtual Tibet: Searching for Shangri-La from the Himalayas to Hollywood. Henry Holt. ISBN 0-8050-4381-0.
- Shakya, Tsering (1999). The Dragon in the Land of Snows: A History of Modern Tibet Since 1947. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 0-231-11814-7.
- Smith, Warren W. (Jr.) (1996). Tibetan Nation: A History of Tibetan Nationalism and Sino-Tibetan Relations. Boulder, CO: Westview Press. ISBN 0-8133-3155-2.
- Stein, R. A. (1962). Tibetan Civilization. First published in French; English translation by J. E. Stapelton Driver. Reprint: Stanford University Press (with minor revisions from 1977 Faber & Faber edition), 1995. ISBN 0-8047-0806-1.
- Thurman, Robert (2002). Robert Thurman on Tibet. DVD. ASIN B00005Y722.
- Wilby, Sorrel (1988). Journey Across Tibet: A Young Woman's 1900-Mile Trek Across the Rooftop of the World. Contemporary Books. ISBN 0-8092-4608-2.
- Wilson, Brandon (2004). Yak Butter Blues: A Tibetan Trek of Faith. Heliographica. An Imprint of Pilgrim's Tales. ISBN 1-933037-23-7, ISBN 1-933037-24-5.
- Jiawei, Wang (2000). "The Historical Status of China's Tibet". ISBN-7-80113-304-8.
- Tibet wasn't always ours, says Chinese scholar by Venkatesan Vembu, Daily News & Analysis, 22 February 2007
External links
- Ukraine U.S. Department of State, accessed July 23, 2007.
- Ukraine BBC News Country Profile, accessed July 23, 2007.
- Ukraine Economist.com, accessed July 23, 2007.
Against PRC rule and policies in Tibet
- Tibetan Government in Exile's main web site
- Tibetan Government in Exile's government site
- Students for a Free Tibet's website
For PRC rule and policies in Tibet
- Tibetan History on the China Tibet Information Center of the PRC
- White Paper on Tibetan Culture and Homayk
Apolitical
- Travel guide to Tibet from Wikitravel
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
- ↑ 西藏自治区; 青海省; 四川省; 云南省; 甘肃省 (行政区划网).
- ↑ Tibet at a glance (The Office of Tibet, London; 30 September 1996);
Official web page of Arunachal Pradesh;
China-India Border: Eastern Sector (map produced by the United States Central Intelligence Agency; Perry-Castañeda Library Map Collection, University of Texas at Austin). - ↑ China-India Border: Western Sector (map produced by the United States Central Intelligence Agency; Perry-Castañeda Library Map Collection, University of Texas at Austin);
Official Website of Jammu and Kasmir (Directorate of Information, Jammu and Kashmir Government). - ↑ China-India Border: Eastern Sector (map produced by the United States Central Intelligence Agency; Perry-Castañeda Library Map Collection, University of Texas at Austin);
China Tibet Information Center. - ↑ Kingdom of Bhutan (Bhutan Tourism Corporation Limited);
About Sikkim (Government of Sikkim, Department of Information Technology);
History of Leh (Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council).