Difference between revisions of "Propylene glycol" - New World Encyclopedia
(added credit and category tags, deleted foreign language links) |
|||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
However, propylene glycol is not approved for use in cat food. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has determined that propylene glycol in or on cat food has not been shown by adequate scientific data to be safe for use. Use of propylene glycol in or on cat food causes the feed to be adulterated and in violation of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. 21CFR589.1001 | However, propylene glycol is not approved for use in cat food. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has determined that propylene glycol in or on cat food has not been shown by adequate scientific data to be safe for use. Use of propylene glycol in or on cat food causes the feed to be adulterated and in violation of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. 21CFR589.1001 | ||
| − | Prolonged contact with propylene glycol is essentially non-irritating to the skin. Undiluted propylene glycol is minimally irritating to the eye, and can produce slight transient conjunctivitis (the eye recovers after the exposure is removed). Exposure to mists may cause eye irritation, as well as upper respiratory tract irritation.<ref> | + | Prolonged contact with propylene glycol is essentially non-irritating to the skin. Undiluted propylene glycol is minimally irritating to the eye, and can produce slight transient conjunctivitis (the eye recovers after the exposure is removed). Exposure to mists may cause eye irritation, as well as upper respiratory tract irritation.<ref>[http://www.dow.com/PublishedLiterature/dh_0361/09002f1380361176.pdf?filepath=propyleneglycol/pdfs/noreg/117-01515.pdf&fromPage=GetDoc Dow Propylene Glycol Industrial Safety Data Sheet], No. 248, November 17, 2003, page 1.</ref> Inhalation of the propylene glycol vapors appears to present no significant hazard in ordinary applications. However, limited human experience indicates that inhalation of propylene glycol mists could be irritating to some individuals. Therefore inhalation exposure to mists of these materials should be avoided. Some research has suggested that propylene glycol not be used in applications where inhalation exposure or human eye contact with the spray mists of these materials is likely, such as fogs for theatrical productions or antifreeze solutions for emergency eye wash stations.<ref>[http://www.dow.com/PublishedLiterature/dh_02aa/09002f13802aaf25.pdf A Guide to Glycols], page 36.</ref> |
| − | </ref> Inhalation of the propylene glycol vapors appears to present no significant hazard in ordinary applications. However, limited human experience indicates that inhalation of propylene glycol mists could be irritating to some individuals. Therefore inhalation exposure to mists of these materials should be avoided. Some research has suggested that propylene glycol not be used in applications where inhalation exposure or human eye contact with the spray mists of these materials is likely, such as fogs for theatrical productions or antifreeze solutions for emergency eye wash stations.<ref> | ||
Propylene glycol does not cause sensitization and it shows no evidence of being a carcinogen or of being genotoxic.<ref>1,2-Dihydroxypropane SIDS Initial Assessment Profile (http://www.chem.unep.ch/irptc/sids/OECDSIDS/57-55-6.pdf), UNEP Publications, SIAM 11, U.S.A, January 23-26, 2001, page 21.</ref><ref>Title 21, U.S. Code of Federal Regulations. 1999. </ref> | Propylene glycol does not cause sensitization and it shows no evidence of being a carcinogen or of being genotoxic.<ref>1,2-Dihydroxypropane SIDS Initial Assessment Profile (http://www.chem.unep.ch/irptc/sids/OECDSIDS/57-55-6.pdf), UNEP Publications, SIAM 11, U.S.A, January 23-26, 2001, page 21.</ref><ref>Title 21, U.S. Code of Federal Regulations. 1999. </ref> | ||
| Line 107: | Line 106: | ||
Patients with [[vulvodynia]] and [[interstitial cystitis]] may be especially sensitive to propylene glycol. Women struggling with yeast infections may also notice that some OTC creams can cause intense burning.<ref>Elizabeth Vliet MD, Screaming To Be Heard: Hormonal Connections That Women Suspect and Doctors Ignore". M. Evans and Company, Inc. New York 1995</ref>Post menopausal women who require the use of an estrogen cream may notice that brand name creams made with propylene glycol often create extreme, uncomfortable burning along the vulva and perianal area. In these cases, patients can request that a local [[compounding|compounding pharmacy]] make a "propylene glycol free" cream. | Patients with [[vulvodynia]] and [[interstitial cystitis]] may be especially sensitive to propylene glycol. Women struggling with yeast infections may also notice that some OTC creams can cause intense burning.<ref>Elizabeth Vliet MD, Screaming To Be Heard: Hormonal Connections That Women Suspect and Doctors Ignore". M. Evans and Company, Inc. New York 1995</ref>Post menopausal women who require the use of an estrogen cream may notice that brand name creams made with propylene glycol often create extreme, uncomfortable burning along the vulva and perianal area. In these cases, patients can request that a local [[compounding|compounding pharmacy]] make a "propylene glycol free" cream. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Alcohol]] | ||
| + | * [[Ethylene glycol]] | ||
| + | * [[Glycerol]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Notes == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
Revision as of 22:20, 6 January 2009
| Propylene glycol[1] | |
|---|---|
| |
|
|
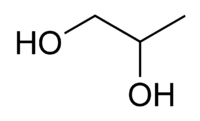
| IUPAC name | propane-1,2-diol |
| Other names | propylene glycol, 1,2-propanediol, 1,2-Dihydroxypropane, methyl ethyl glycol (MEG), methylethylene glycol, PG, Sirlene, Dowfrost |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | [] |
| RTECS number | TY6300000 |
| SMILES | CC(O)CO |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C3H8O2 |
| Molar mass | 76.09 g/mol |
| Density | 1.036 g/cm³ |
| Melting point |
-59 °C |
| Boiling point |
188.2 °C |
| Solubility in water | fully miscible |
| Solubility in ethanol | fully miscible |
| Solubility in diethyl ether | fully miscible |
| Solubility in acetone | fully miscible |
| Solubility in chloroform | fully miscible |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.34 W/m-K (50% H2O @ 90°C) |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS |
| NFPA 704 |
|
| S-phrases | S24 S25 |
| Related Compounds | |
| Related glycols | Ethylene glycol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Propylene glycol, known also by the systematic name propane-1,2-diol, is an organic compound (a diol alcohol), usually a faintly sweet, odorless, and colorless clear viscous liquid that is hygroscopic and miscible with water, acetone, and chloroform.
Chirality
Propylene glycol contains an asymmetrical carbon atom, so it exists in two stereoisomers. The commercial product is a racemic mixture. Pure optical isomers can be obtained by hydration of optically pure propylene oxide.[2]
Production
Industrially propylene glycol is produced by propylene oxide hydration. Different manufacturers use non-catalytic high-temperature process at 200-220 °C or catalytic route which proceeds at 150-180 °C in presence of ion exchange resin or small amounts of sulfuric acid or alkali. Final products contain 20% 1,2-propanediol, 1.5% of dipropylene glycol and small amount of other polypropylene glycol.[3] Propylene glycol can also be converted from glycerol, a biodiesel byproduct.
Applications
Propylene glycol is used:
- As a moisturizer in medicines, cosmetics, food, toothpaste, mouth wash, and tobacco products
- In electronic cigarettes to make the produced vapor better resemble cigarette smoke
- As a medical and sexual lubricant (A.K.A. "personal lubricant")
- As an emulsification agent in Angostura and orange bitters
- As a solvent for food colors and flavorings
- As a humectant food additive, labeled as E number E1520
- As a cooling agent for beer and wine glycol jacketed fermentation tanks
- As a carrier in fragrance oils
- As a less-toxic antifreeze
- As a solvent used in mixing photographic chemicals, such as film developers
- In smoke machines to make artificial smoke for use in firefighters' training and theatrical productions
- In hand sanitizers, antibacterial lotions, and saline solutions
- In cryonics
- As a working fluid in hydraulic presses
- As a coolant in liquid cooling systems
- To regulate humidity in a cigar humidor
- As the killing and preserving agent in pitfall traps, usually used to capture ground beetles
- To treat livestock ketosis
- As the main ingredient in deodorant sticks.
- To de-ice aircraft.[4]
Propylene glycol has properties similar to those of ethylene glycol (monoethylene glycol, or MEG). (Note: propylene glycol may also use the acronym MEG, but as an abbreviation of methyl ethyl glycol.) The industrial norm is to replace ethylene glycol by propylene glycol.
Safety
Cases of propylene glycol poisoning are related to either inappropriate intravenous use or accidental ingestion by children.[5] The oral toxicity of propylene glycol is very low. In one study, rats were provided with feed containing as much as 5% PG over a period of 104 weeks and they showed no apparent ill effects.[6] Because of its low chronic oral toxicity, propylene glycol is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for use as a direct food additive.
Serious toxicity will occur only at extremely high intakes over a relatively short period of time that result in plasma concentrations of over 4 g/L.[7] Such levels of ingestion would not be possible when consuming reasonable amounts of a food product or dietary supplements containing at most 1 g/kg propylene glycol.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has determined propylene glycol to be "generally recognized as safe" for use in food, cosmetics, and medicines. Like ethylene glycol, propylene glycol affects the body's chemistry by increasing the amount of acid. Propylene glycol is metabolized into pyruvic acid, which is a normal metabolite in the breakdown of glucose, while ethylene glycol is metabolized into oxalic acid, which is toxic.
However, propylene glycol is not approved for use in cat food. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has determined that propylene glycol in or on cat food has not been shown by adequate scientific data to be safe for use. Use of propylene glycol in or on cat food causes the feed to be adulterated and in violation of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. 21CFR589.1001
Prolonged contact with propylene glycol is essentially non-irritating to the skin. Undiluted propylene glycol is minimally irritating to the eye, and can produce slight transient conjunctivitis (the eye recovers after the exposure is removed). Exposure to mists may cause eye irritation, as well as upper respiratory tract irritation.[8] Inhalation of the propylene glycol vapors appears to present no significant hazard in ordinary applications. However, limited human experience indicates that inhalation of propylene glycol mists could be irritating to some individuals. Therefore inhalation exposure to mists of these materials should be avoided. Some research has suggested that propylene glycol not be used in applications where inhalation exposure or human eye contact with the spray mists of these materials is likely, such as fogs for theatrical productions or antifreeze solutions for emergency eye wash stations.[9]
Propylene glycol does not cause sensitization and it shows no evidence of being a carcinogen or of being genotoxic.[10][11]
Recent Clinical Journal of Medicine article states two cases of adult men experiencing psychosis from use of propylene glycol used in phenytoin injection USP. Both patients had to be switched to Cerebyx (Fosphenytoin Sodium) in order to avoid propylene glycol co-solvent.
Allergic reaction
Research has suggested that individuals who cannot tolerate propylene glycol probably experience a special form of irritation, but that they only rarely develop allergic contact dermatitis. Other investigators believe that the incidence of allergic contact dermatitis to propylene glycol may be greater than 2% in patients with eczema.[12]
Patients with vulvodynia and interstitial cystitis may be especially sensitive to propylene glycol. Women struggling with yeast infections may also notice that some OTC creams can cause intense burning.[13]Post menopausal women who require the use of an estrogen cream may notice that brand name creams made with propylene glycol often create extreme, uncomfortable burning along the vulva and perianal area. In these cases, patients can request that a local compounding pharmacy make a "propylene glycol free" cream.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 7868.
- ↑ 1,2-Propanediol. ChemIndustry.ru. Retrieved 2007-12-28.
- ↑ 1,2-propanediol: chemical product info at CHEMINDUSTRY.RU
- ↑ http://pubs.acs.org/cen/whatstuff/stuff/7901scit5.html
- ↑ National Library of Medicine;. Human Toxicity Excerpts: CAS Registry Number: 57-55-6 (1,2-Propylene Glycol). Selected toxicity information from HSDB. 2005.
- ↑ Gaunt, IF, Carpanini, FMB, Grasso, P and Lansdown, ABG, Long-term toxicity of propylene glycol in rats, Food and Cosmetics Toxicology, Apr. 1972, 10(2), pages 151 - 162.
- ↑ Flanagan RJ;Braithwaite RA;Brown SS;Widdop B;de Wolff FA;. The International Programme on Chemical Safety: Basic Analytical Toxicology. WHO, 1995.
- ↑ Dow Propylene Glycol Industrial Safety Data Sheet, No. 248, November 17, 2003, page 1.
- ↑ A Guide to Glycols, page 36.
- ↑ 1,2-Dihydroxypropane SIDS Initial Assessment Profile (http://www.chem.unep.ch/irptc/sids/OECDSIDS/57-55-6.pdf), UNEP Publications, SIAM 11, U.S.A, January 23-26, 2001, page 21.
- ↑ Title 21, U.S. Code of Federal Regulations. 1999.
- ↑ [American Medical Association, Council on Drugs. AMA Drug Evaluations Annual 1994. Chicago, IL: American Medical Association, 1994., p. 1224]
- ↑ Elizabeth Vliet MD, Screaming To Be Heard: Hormonal Connections That Women Suspect and Doctors Ignore". M. Evans and Company, Inc. New York 1995
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
External links
- WebBook page for C3H8O2
- ATSDR - Case Studies in Environmental Medicine: Ethylene Glycol and Propylene Glycol Toxicity U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (public domain)
- Propylene Glycol info at DOW Chemical
- Propylene Glycol at Lyondell Chemical
- Propylene Glycol info at Scorecard.com
- Propylene Glycol - chemical product info: properties, production, applications.
- Propylene Glycol Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) at J.T. Baker's website (via Mallinckrodt Baker's website MSDS listings)
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
