Difference between revisions of "Nitroglycerin" - New World Encyclopedia
(imported latest version of article from Wikipedia) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}}{{Paid}}{{Copyedited}} | ||
{{explosivebox | | {{explosivebox | | ||
| − | |IUPAC_name = | + | |IUPAC_name = propane-1,2,3-triyl trinitrate |
|image=Nitroglycerin-2D-skeletal.png | |image=Nitroglycerin-2D-skeletal.png | ||
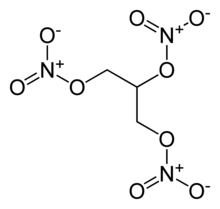
| − | |chemical_formula = | + | |chemical_formula = C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>5</sub>(NO<sub>3</sub>)<sub>3</sub> |
|molecular_weight = 227.0872 [[gram|g]]/[[mole (unit)|mol]] | |molecular_weight = 227.0872 [[gram|g]]/[[mole (unit)|mol]] | ||
| − | |shock_sensitivity = Very | + | |shock_sensitivity = Very High |
|friction_sensitivity = Very high | |friction_sensitivity = Very high | ||
|density = 1.13 [[kilogram|kg]]/[[cubic metre|dm³]] at 15 [[Celsius|°C]] | |density = 1.13 [[kilogram|kg]]/[[cubic metre|dm³]] at 15 [[Celsius|°C]] | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
|CAS_number = 55-63-0 | |CAS_number = 55-63-0 | ||
|PubChem = 4510 | |PubChem = 4510 | ||
| − | |SMILES = C(C(CO[N+](=O)[O-])O<br>[N+](=O)[O-])O[N+](=O)[O-] | + | |SMILES = C(C(CO[N+](=O)[O-])O<br/>[N+](=O)[O-])O[N+](=O)[O-] |
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Nitroglycerin''' ('''NG''') | + | '''Nitroglycerin''' ('''NG''')—also known as '''nitroglycerine''', '''trinitroglycerin''', and '''glyceryl trinitrate'''—is a heavy, colorless, oily liquid obtained by [[nitration|nitrating]] [[glycerol]]. It is a powerful [[explosive]] and is used in the manufacture of [[dynamite]], which in turn is employed in the [[construction]] and [[demolition]] industries. It is also a [[plasticizer]] in some solid [[propellant]]s for [[rocket]]s. In medicine, nitroglycerin serves as a [[vasodilator]] (an agent that dilates blood vessels) and is therefore used to treat [[heart]] conditions. |
| − | + | {{toc}} | |
== History == | == History == | ||
| − | Nitroglycerin was discovered by chemist [[Ascanio Sobrero]] in | + | Nitroglycerin was discovered by chemist [[Ascanio Sobrero]] in 1847, working under [[T.J. Pelouze]] at the [[University of Torino]]. The best manufacturing process was developed by [[Alfred Nobel]] in the 1860s. His company exported a liquid combination of nitroglycerin and [[gunpowder]] as 'Swedish Blasting Oil', but it was extremely unstable and dangerous, resulting in numerous catastrophes, including an explosion that destroyed a [[Wells Fargo]] office in [[San Francisco]] in 1866.<ref>[http://CPRR.org/Museum/Newspapers/Nitroglycerine.html Nitroglycerine! Terrible Explosion and Loss of Lives in San Francisco.] ''Central Pacific Railroad Photographic History Museum.'' (1866 newspaper article). Retrieved September 20, 2007.</ref> The liquid was widely banned, and Nobel developed [[dynamite]], a less sensitive explosive, by mixing nitroglycerin with the inert [[absorbent]] ''[[kieselguhr]]'' ([[diatomaceous earth]]). Other similar mixtures, such as ''dualine'' and ''lithofracteur,'' were also prepared by mixing nitroglycerin with inert materials such as [[nitrocellulose|nitrocellulose gel]] or [[blasting gelatin]]. |
== Instability and desensitization == | == Instability and desensitization == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | In its pure form, nitroglycerin is a [[contact explosive]]—that is, physical shock can cause it to explode. It degrades over time to even more unstable forms, making it highly dangerous to transport or use. In its undiluted form, it is one of the most powerful high explosives, comparable to the military explosives [[RDX]] and [[PETN]] (which are not used in munitions at full concentration because of their sensitivity) as well as the [[plastic explosive]] [[C-4 (explosive)|C-4]]. | |
| − | + | Early in the history of this explosive it was discovered that liquid nitroglycerin can be "desensitized" by cooling to 5 to 10 [[Celsius|°C]] (40 to 50 [[Fahrenheit|°F]]), at which temperature it freezes, contracting upon solidification. However, later thawing can be extremely sensitizing, especially if impurities are present or if warming is too rapid. | |
| − | + | It is possible to chemically "desensitize" nitroglycerin to a point where it can be considered approximately as "safe" as modern [[Explosive material|high explosive]] formulations, by the addition of approximately 10-30 percent [[ethanol]], [[acetone]], or [[dinitrotoluene]]. (The percentage varies with the desensitizing agent used.) Desensitization requires extra effort to reconstitute the "pure" product. Failing this, it must be assumed that desensitized nitroglycerin is substantially more difficult to detonate, possibly rendering it useless as an explosive for practical applications. | |
| − | + | A serious problem in the use of nitroglycerin is associated with its high freezing point 13 [[Celsius|°C]] (55 [[Fahrenheit|°F]]). Solid nitroglycerin is much less sensitive to shock than the liquid form, a feature common in explosives. In the past, it was often shipped in the frozen state, but this resulted in many accidents during the thawing process by the end user, just prior to use. This disadvantage can be overcome by using mixtures of nitroglycerin with other polynitrates; for example, a mixture of nitroglycerin and [[ethylene glycol dinitrate]] freezes at -29 °C (-20 °F). | |
| − | |||
| − | + | == Detonation versus deflagration == | |
| − | + | Nitroglycerin and any or all of the diluents used can certainly [[deflagration|deflagrate]] or burn. However, the explosive power of nitroglycerin is derived from [[detonation]]: energy from the initial decomposition causes a pressure gradient that detonates the surrounding fuel. This can generate a self-sustained shock-wave that propagates through the fuel-rich medium at or above the [[speed of sound]], as a cascade of near-instantaneous, pressure-induced decomposition of the fuel into gas. This is quite unlike deflagration, which depends solely upon available fuel, regardless of pressure differences or shock. | |
| − | == | + | == Manufacture == |
| − | The industrial manufacturing process often uses a nearly 50:50 mixture of [[sulfuric acid]] and [[nitric acid]]. | + | The industrial manufacturing process often uses a nearly 50:50 mixture of [[sulfuric acid]] and [[nitric acid]]. This can be produced by mixing white fuming nitric acid (pure nitric acid from which oxides of nitrogen have been removed, as opposed to red fuming nitric acid) and concentrated sulfuric acid. This mixture is often attained by the cheaper method of mixing fuming sulfuric acid (sulfuric acid containing excess [[sulfur trioxide]]) and azeotropic nitric acid (consisting of around 70 percent nitric acid, the rest being water). |
| − | The sulfuric acid produces protonated nitric acid species, which are attacked by glycerin's [[Nucleophile|nucleophilic]] [[oxygen]] atoms. The [[nitro]] [[functional group|group]] is thus added as an ester C-O-NO<sub>2</sub> and water is produced. | + | The sulfuric acid produces protonated nitric acid species, which are attacked by glycerin's [[Nucleophile|nucleophilic]] [[oxygen]] atoms. The [[nitro]] [[functional group|group]] is thus added as an ester (C-O-NO<sub>2</sub>), and water is produced.<ref>This is different from an aromatic nitration reaction in which [[nitronium ion]]s are the active species in an electrophilic attack of the molecule's ring system.</ref> |
| − | The addition of glycerin results in an [[chemical reaction|exothermic reaction]] ( | + | The addition of glycerin results in an [[chemical reaction|exothermic reaction]] (that is, heat is released). However, if the mixture becomes too hot, it results in runaway reaction—a state of accelerated nitration accompanied by the destructive oxidizing of organic materials of nitric acid and the release of very poisonous brown [[nitrogen dioxide]] gas at high risk of an explosion. Thus, the glycerin mixture is added slowly to the reaction [[Container|vessel]] containing the mixed acid (not acid to glycerin). The nitrator is cooled with cold water or some other coolant mixture and maintained throughout the glycerin addition at about 22 °C. The nitrator vessel, often constructed of iron or lead and generally stirred with compressed air, has an emergency trap door at its base, which hangs over a large pool of very cold water and into which the whole reaction mixture (called the charge) can be dumped to prevent an explosion, a process referred to as "drowning." If the temperature of the charge exceeds about 10 °C (actual value varies by country), or brown fumes are seen in the nitrators vent, then it is immediately drowned. |
| − | + | Because of the great dangers associated with its production, most nitroglycerin production facilities are in offshore rigs or remote locations. | |
| − | == Medical | + | == Medical uses == |
{{main|Glyceryl trinitrate (pharmacology)}} | {{main|Glyceryl trinitrate (pharmacology)}} | ||
| − | In [[medicine]], nitroglycerin | + | In [[medicine]], nitroglycerin is generally called glyceryl trinitrate and is used as a [[heart]] medication (under the trade names '''Nitrospan®''', '''Nitrostat®''', and '''Tridil®''', amongst others). Used as a treatment for [[angina pectoris]] ([[coronary heart disease|ischemic heart disease]]), it is available in the form of tablets, ointment, solution (for intravenous use), transdermal patches ('''Transderm Nitro®''', '''Nitro-Dur®'''), or sprays administered [[sublingual]]ly ('''Nitrolingual Pump Spray®''', '''Natispray®'''). |
| − | The principal action of nitroglycerin is [[vasodilation]] | + | The principal action of nitroglycerin is [[vasodilation]]—widening of the [[blood vessel]]s. Nitroglycerin will dilate veins more than arteries, decreasing cardiac preload and leading to the following therapeutic effects during episodes of [[angina pectoris]]: |
* subsiding of chest pain | * subsiding of chest pain | ||
* decrease of [[blood pressure]] | * decrease of [[blood pressure]] | ||
* increase of heart rate. | * increase of heart rate. | ||
| + | * [[orthostatic hypotension]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | These effects arise because nitroglycerin is converted to [[nitric oxide]] in the body (by a mechanism that is not completely understood), and nitric oxide is a natural vasodilator. Recently, it has also become popular in an [[off-label]] use at reduced (0.2 percent) concentration in ointment form, as an effective treatment for [[anal fissure]]. | ||
| + | == Adverse health effects == | ||
| − | These | + | Infrequent exposure to high doses of nitroglycerin can cause severe headaches—a condition known as "NG head." The headaches can be severe enough to incapacitate some people. It appears, however, that many people develop a tolerance for and dependence on nitroglycerin after long-term exposure. Withdrawal symptoms include headaches and heart problems. These symptoms may disappear with re-exposure to nitroglycerin. For workers regularly exposed to this substance in the workplace (such as in nitroglycerin manufacturing facilities), this can result in a "Monday Morning Headache"—they develop they develop symptoms of withdrawal over the weekend, which are countered by reexposure on the next working day. In rare cases, withdrawal has been found to be fatal. |
| − | + | == See also == | |
| + | |||
| + | * [[Alfred Nobel]] | ||
| + | * [[Dynamite]] | ||
| + | * [[Explosive]] | ||
| + | * [[Glycerol]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Notes == | ||
| + | <references /> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| − | * | + | * Akhavan, Jacqueline. 2004. ''The Chemistry of Explosives.'' RSC Paperbacks. Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 0854046402. |
| − | + | ||
| + | * Davis, Tenney Lombard. 1984. ''The Chemistry of Powder and Explosives.'' Hollywood, CA: Angriff Press. ISBN 0913022004. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Meyer, Edith Patterson. 1958. ''Dynamite and Peace; the Story of Alfred Nobel.'' Boston: Little, Brown. OCLC 1252824. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Meyer, Rudolf, Josef Köhler, and Axel Homburg. 2007. ''Explosives.'' Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. ISBN 978-3527316564. | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | * [http:// | + | All links retrieved November 15, 2022. |
| − | * [http:// | + | * [http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=4510 PubChem: Nitroglycerin.] ''NCBI''. |
| − | * [http://www.logwell.com/tales/menu/index.html The Tallini Tales of Destruction] Detailed and horrific stories of the historical use of nitroglycerin-filled torpedoes to restart petroleum wells. | + | * [http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C55630 1,2,3-Propanetriol, trinitrate (Nitroglycerin)] ''NIST''. |
| − | + | * [http://www.logwell.com/tales/menu/index.html The Tallini Tales of Destruction.] ''logwell.com''. (Detailed and horrific stories of the historical use of nitroglycerin-filled torpedoes to restart petroleum wells.) | |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Physical sciences]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Chemistry]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Organic chemistry]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Construction technology]] |
| + | [[Category:Military technology]] | ||
| − | + | {{credit|157827466}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 02:27, 16 November 2022
| propane-1,2,3-triyl trinitrate IUPAC name | |
| Chemical formula | C3H5(NO3)3 |
| Molecular mass | 227.0872 g/mol |
| Shock sensitivity | Very High |
| Friction sensitivity | Very high |
| Density | 1.13 kg/dm³ at 15 °C |
| Explosive velocity | 7700 m/s |
| RE factor | 1.50 |
| Melting point | 13.2 °C (55.76 °F) |
| Autoignition temperature | Decomposes at 50 to 60 °C (122 to 140 °F) |
| Appearance | Clear yellow/colorless oily liquid |
| CAS number | 55-63-0 |
| PubChem | 4510 |
| SMILES | C(C(CO[N+](=O)[O-])O [N+](=O)[O-])O[N+](=O)[O-] |
Nitroglycerin (NG)—also known as nitroglycerine, trinitroglycerin, and glyceryl trinitrate—is a heavy, colorless, oily liquid obtained by nitrating glycerol. It is a powerful explosive and is used in the manufacture of dynamite, which in turn is employed in the construction and demolition industries. It is also a plasticizer in some solid propellants for rockets. In medicine, nitroglycerin serves as a vasodilator (an agent that dilates blood vessels) and is therefore used to treat heart conditions.
History
Nitroglycerin was discovered by chemist Ascanio Sobrero in 1847, working under T.J. Pelouze at the University of Torino. The best manufacturing process was developed by Alfred Nobel in the 1860s. His company exported a liquid combination of nitroglycerin and gunpowder as 'Swedish Blasting Oil', but it was extremely unstable and dangerous, resulting in numerous catastrophes, including an explosion that destroyed a Wells Fargo office in San Francisco in 1866.[1] The liquid was widely banned, and Nobel developed dynamite, a less sensitive explosive, by mixing nitroglycerin with the inert absorbent kieselguhr (diatomaceous earth). Other similar mixtures, such as dualine and lithofracteur, were also prepared by mixing nitroglycerin with inert materials such as nitrocellulose gel or blasting gelatin.
Instability and desensitization
In its pure form, nitroglycerin is a contact explosive—that is, physical shock can cause it to explode. It degrades over time to even more unstable forms, making it highly dangerous to transport or use. In its undiluted form, it is one of the most powerful high explosives, comparable to the military explosives RDX and PETN (which are not used in munitions at full concentration because of their sensitivity) as well as the plastic explosive C-4.
Early in the history of this explosive it was discovered that liquid nitroglycerin can be "desensitized" by cooling to 5 to 10 °C (40 to 50 °F), at which temperature it freezes, contracting upon solidification. However, later thawing can be extremely sensitizing, especially if impurities are present or if warming is too rapid.
It is possible to chemically "desensitize" nitroglycerin to a point where it can be considered approximately as "safe" as modern high explosive formulations, by the addition of approximately 10-30 percent ethanol, acetone, or dinitrotoluene. (The percentage varies with the desensitizing agent used.) Desensitization requires extra effort to reconstitute the "pure" product. Failing this, it must be assumed that desensitized nitroglycerin is substantially more difficult to detonate, possibly rendering it useless as an explosive for practical applications.
A serious problem in the use of nitroglycerin is associated with its high freezing point 13 °C (55 °F). Solid nitroglycerin is much less sensitive to shock than the liquid form, a feature common in explosives. In the past, it was often shipped in the frozen state, but this resulted in many accidents during the thawing process by the end user, just prior to use. This disadvantage can be overcome by using mixtures of nitroglycerin with other polynitrates; for example, a mixture of nitroglycerin and ethylene glycol dinitrate freezes at -29 °C (-20 °F).
Detonation versus deflagration
Nitroglycerin and any or all of the diluents used can certainly deflagrate or burn. However, the explosive power of nitroglycerin is derived from detonation: energy from the initial decomposition causes a pressure gradient that detonates the surrounding fuel. This can generate a self-sustained shock-wave that propagates through the fuel-rich medium at or above the speed of sound, as a cascade of near-instantaneous, pressure-induced decomposition of the fuel into gas. This is quite unlike deflagration, which depends solely upon available fuel, regardless of pressure differences or shock.
Manufacture
The industrial manufacturing process often uses a nearly 50:50 mixture of sulfuric acid and nitric acid. This can be produced by mixing white fuming nitric acid (pure nitric acid from which oxides of nitrogen have been removed, as opposed to red fuming nitric acid) and concentrated sulfuric acid. This mixture is often attained by the cheaper method of mixing fuming sulfuric acid (sulfuric acid containing excess sulfur trioxide) and azeotropic nitric acid (consisting of around 70 percent nitric acid, the rest being water).
The sulfuric acid produces protonated nitric acid species, which are attacked by glycerin's nucleophilic oxygen atoms. The nitro group is thus added as an ester (C-O-NO2), and water is produced.[2]
The addition of glycerin results in an exothermic reaction (that is, heat is released). However, if the mixture becomes too hot, it results in runaway reaction—a state of accelerated nitration accompanied by the destructive oxidizing of organic materials of nitric acid and the release of very poisonous brown nitrogen dioxide gas at high risk of an explosion. Thus, the glycerin mixture is added slowly to the reaction vessel containing the mixed acid (not acid to glycerin). The nitrator is cooled with cold water or some other coolant mixture and maintained throughout the glycerin addition at about 22 °C. The nitrator vessel, often constructed of iron or lead and generally stirred with compressed air, has an emergency trap door at its base, which hangs over a large pool of very cold water and into which the whole reaction mixture (called the charge) can be dumped to prevent an explosion, a process referred to as "drowning." If the temperature of the charge exceeds about 10 °C (actual value varies by country), or brown fumes are seen in the nitrators vent, then it is immediately drowned.
Because of the great dangers associated with its production, most nitroglycerin production facilities are in offshore rigs or remote locations.
Medical uses
In medicine, nitroglycerin is generally called glyceryl trinitrate and is used as a heart medication (under the trade names Nitrospan®, Nitrostat®, and Tridil®, amongst others). Used as a treatment for angina pectoris (ischemic heart disease), it is available in the form of tablets, ointment, solution (for intravenous use), transdermal patches (Transderm Nitro®, Nitro-Dur®), or sprays administered sublingually (Nitrolingual Pump Spray®, Natispray®).
The principal action of nitroglycerin is vasodilation—widening of the blood vessels. Nitroglycerin will dilate veins more than arteries, decreasing cardiac preload and leading to the following therapeutic effects during episodes of angina pectoris:
- subsiding of chest pain
- decrease of blood pressure
- increase of heart rate.
- orthostatic hypotension
These effects arise because nitroglycerin is converted to nitric oxide in the body (by a mechanism that is not completely understood), and nitric oxide is a natural vasodilator. Recently, it has also become popular in an off-label use at reduced (0.2 percent) concentration in ointment form, as an effective treatment for anal fissure.
Adverse health effects
Infrequent exposure to high doses of nitroglycerin can cause severe headaches—a condition known as "NG head." The headaches can be severe enough to incapacitate some people. It appears, however, that many people develop a tolerance for and dependence on nitroglycerin after long-term exposure. Withdrawal symptoms include headaches and heart problems. These symptoms may disappear with re-exposure to nitroglycerin. For workers regularly exposed to this substance in the workplace (such as in nitroglycerin manufacturing facilities), this can result in a "Monday Morning Headache"—they develop they develop symptoms of withdrawal over the weekend, which are countered by reexposure on the next working day. In rare cases, withdrawal has been found to be fatal.
See also
Notes
- ↑ Nitroglycerine! Terrible Explosion and Loss of Lives in San Francisco. Central Pacific Railroad Photographic History Museum. (1866 newspaper article). Retrieved September 20, 2007.
- ↑ This is different from an aromatic nitration reaction in which nitronium ions are the active species in an electrophilic attack of the molecule's ring system.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Akhavan, Jacqueline. 2004. The Chemistry of Explosives. RSC Paperbacks. Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 0854046402.
- Davis, Tenney Lombard. 1984. The Chemistry of Powder and Explosives. Hollywood, CA: Angriff Press. ISBN 0913022004.
- Meyer, Edith Patterson. 1958. Dynamite and Peace; the Story of Alfred Nobel. Boston: Little, Brown. OCLC 1252824.
- Meyer, Rudolf, Josef Köhler, and Axel Homburg. 2007. Explosives. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. ISBN 978-3527316564.
External links
All links retrieved November 15, 2022.
- PubChem: Nitroglycerin. NCBI.
- 1,2,3-Propanetriol, trinitrate (Nitroglycerin) NIST.
- The Tallini Tales of Destruction. logwell.com. (Detailed and horrific stories of the historical use of nitroglycerin-filled torpedoes to restart petroleum wells.)
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.