Difference between revisions of "Belgium" - New World Encyclopedia
John Willis (talk | contribs) (created, categorized & credited) |
John Willis (talk | contribs) m (moved map) |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | The '''Kingdom of Belgium''' | + | The '''Kingdom of Belgium''' is a country in [[Western Europe|northwest Europe]] bordered by [[Netherlands|the Netherlands]], [[Germany]], [[Luxembourg]] and [[France]]. Belgium has a population of over ten million people in an area of thirty thousand square kilometres. Straddling the cultural boundary between [[Germanic language|Germanic]] and [[Romance language|Romance]] Europe, it is both linguistically and culturally divided. Two major languages are spoken in Belgium: Dutch—sometimes unofficially called [[Flemish (linguistics)|Flemish]]—spoken in [[Flanders]] to the north; and French, spoken in [[Walloon Region|Wallonia]] in the south. The capital, [[Brussels-Capital Region|Brussels]], is officially bilingual. In addition to the two, an officially recognized minority of [[German language|German]] speakers is present in the east. This linguistic diversity often leads to political conflict, and is reflected in Belgium's complex [[Communities, regions and provinces of Belgium|system of government]] and [[history of Belgium|political history]]. |
| + | |||
| + | Belgium derives its name from its first named inhabitants, the ''[[Belgae]]'', a group of mostly [[Celt|Celtic]] tribes, and from the [[Roman province]] in northern [[Gaul]], known as [[Gallia Belgica]]. Historically, Belgium has been a part of the [[Low Countries]], which also includes the Netherlands and Luxembourg. From the end of the [[Middle Ages]] until the seventeenth century, it was a prosperous center of commerce and culture. From the sixteenth century until independence in 1830, Belgium, called at that time [[Southern Netherlands |the Southern Netherlands]], was the site of many battles between the European powers, and has been dubbed "the Cockpit of Europe." More recently, Belgium was a founding member of the [[European Union]], hosting its headquarters, as well as those of other major international organisations, such as [[NATO]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Geography== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Belgium, with an area of 30,528 km², has three main geographical regions: the coastal plain in the north-west, the central plateau, and the [[Ardennes]] uplands in the south-east. The coastal plain consists mainly of sand dunes and [[polder]]s. Polders are areas of land, close to or below sea level that have been reclaimed from the sea, from which they are protected by [[Dike (construction)|dike]]s or, further inland, by fields that have been drained with canals. The second geographical region, the central plateau, lies further inland. This is a smooth, slowly rising area that has many fertile valleys and is irrigated by many waterways. Here one can also find rougher land, including caves and small [[gorge]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Hautes-Fagnes.jpg|thumb|left|200px|Landscape in the [[Hautes Fagnes]], in the Ardennes]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The third geographical region, called the Ardennes, is more rugged than the first two. It is a thickly forested plateau, very rocky and not very good for farming, which extends into northern France. This is where much of Belgium's wildlife can be found. Belgium's highest point, the [[Signal de Botrange]] is located in this region at only 694 metres. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The climate is maritime [[temperate]], with significant precipitation in all seasons ([[Köppen climate classification]]: ''Cfb''; the average temperature is 3°C in January, and 18°C in July; the average precipitation is 65 mm in January, and 78 mm in July). | ||
| − | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| − | + | ||
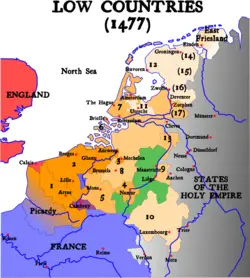
Over the past two millennia, the area that is now known as Belgium has seen significant demographic, political and cultural upheavals. The first well-documented population move was the conquest of the region by the [[Roman Republic]] in the 1st century B.C.E., followed in the 5th century by the [[Germanic people|Germanic]] [[Frank]]s. The Franks established the [[Merovingian]] kingdom, which became the [[Carolingian Empire]] in the 8th century. During the Middle Ages, the Low Countries were split into many small [[feudal]] states. Most of them were united in the course of the 14th and 15th centuries by the house of [[Burgundy]] as the [[Burgundian Netherlands]]. These states gained a degree of autonomy in the 15th century and were thereafter named the [[Seventeen Provinces]]. | Over the past two millennia, the area that is now known as Belgium has seen significant demographic, political and cultural upheavals. The first well-documented population move was the conquest of the region by the [[Roman Republic]] in the 1st century B.C.E., followed in the 5th century by the [[Germanic people|Germanic]] [[Frank]]s. The Franks established the [[Merovingian]] kingdom, which became the [[Carolingian Empire]] in the 8th century. During the Middle Ages, the Low Countries were split into many small [[feudal]] states. Most of them were united in the course of the 14th and 15th centuries by the house of [[Burgundy]] as the [[Burgundian Netherlands]]. These states gained a degree of autonomy in the 15th century and were thereafter named the [[Seventeen Provinces]]. | ||
{| align="left" border="0" | {| align="left" border="0" | ||
| Line 65: | Line 76: | ||
| [[Image:Wappers belgian revolution.jpg|left|thumb|250px|''Episode of the Belgian Revolution of 1830'', [[Egide Charles Gustave Wappers]] (1834), in the Musée d'Art Ancien, Brussels]] | | [[Image:Wappers belgian revolution.jpg|left|thumb|250px|''Episode of the Belgian Revolution of 1830'', [[Egide Charles Gustave Wappers]] (1834), in the Musée d'Art Ancien, Brussels]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | The history of Belgium can be distinguished from that of the Low Countries from the 16th century. A [[civil war]], the [[Eighty Years' War]] (1568 | + | The history of Belgium can be distinguished from that of the Low Countries from the 16th century. A [[civil war]], the [[Eighty Years' War]] (1568-1648), divided the Seventeen Provinces into the [[Republic of the Seven United Provinces of the Netherlands|United Provinces]] in the north and the [[Southern Netherlands]] in the south. The southern provinces were ruled successively by the [[Habsburg Spain|Spanish]] and the [[History of Austria#Charles VI and Maria Theresa (1711-80)|Austrian]] [[Habsburg]]s. Until independence, the Southern Netherlands were sought after by numerous French conquerors and were the theatre of most [[Early_Modern_France#France_in_the_17th_and_18th_centuries |Franco-Spanish and Franco-Austrian wars]] during the 17th and 18th centuries. Following the [[French Revolutionary Wars: Campaigns of 1794 | Campaigns of 1794 in the French Revolutionary Wars]], the Low Countries—including territories that were never under Habsburg rule, such the [[Bishopric of Liège]]—were overrun by France, ending Spanish-Austrian rule in the region. The reunification of the Low Countries as the [[United Kingdom of the Netherlands]] occurred at the end of the [[first French Empire|French Empire]] in 1815. |
The 1830 [[Belgian Revolution]] led to the establishment of an [[independence|independent]], [[Catholicism|Catholic]] and neutral Belgium under a provisional government. Since the installation of [[Leopold I]] as king in 1831, Belgium has been a [[constitutional monarchy]] and [[parliamentary democracy]]. Between independence and [[World War II]], the democratic system evolved from an [[oligarchy]] characterised by two main parties, the Catholics and the Liberals, to a [[universal suffrage]] system that has included a third party, the [[Belgian Labour Party]], and a strong role for the [[trade union]]s. Originally, French, which was the adopted language of the [[nobility]] and the [[bourgeoisie]] was the official language. The country has since developed a bilingual Dutch-French system. | The 1830 [[Belgian Revolution]] led to the establishment of an [[independence|independent]], [[Catholicism|Catholic]] and neutral Belgium under a provisional government. Since the installation of [[Leopold I]] as king in 1831, Belgium has been a [[constitutional monarchy]] and [[parliamentary democracy]]. Between independence and [[World War II]], the democratic system evolved from an [[oligarchy]] characterised by two main parties, the Catholics and the Liberals, to a [[universal suffrage]] system that has included a third party, the [[Belgian Labour Party]], and a strong role for the [[trade union]]s. Originally, French, which was the adopted language of the [[nobility]] and the [[bourgeoisie]] was the official language. The country has since developed a bilingual Dutch-French system. | ||
| − | The [[Berlin Conference]] of 1885 agreed to hand over [[Colonisation of the Congo|Congo]] to [[Léopold II of Belgium|King Leopold II]] as his private possession, called the [[Congo Free State]]. In 1908, it was ceded to Belgium as a colony, henceforth called the [[Belgian Congo]]. Belgium's neutrality was violated in 1914, when Germany invaded Belgium as part of the [[Schlieffen Plan]]. The former [[German colonies]] [[Ruanda-Urundi]]—now called [[Rwanda]] and [[Burundi]]—were occupied by the Belgian Congo in 1916. They were mandated in 1924 to Belgium by the [[League of Nations]]. Belgium was again invaded by Germany in 1940 during the [[blitzkrieg]] offensive. The Belgian Congo gained its independence on | + | The [[Berlin Conference]] of 1885 agreed to hand over [[Colonisation of the Congo|Congo]] to [[Léopold II of Belgium|King Leopold II]] as his private possession, called the [[Congo Free State]]. In 1908, it was ceded to Belgium as a colony, henceforth called the [[Belgian Congo]]. Belgium's neutrality was violated in 1914, when Germany invaded Belgium as part of the [[Schlieffen Plan]]. The former [[German colonies]] [[Ruanda-Urundi]]—now called [[Rwanda]] and [[Burundi]]—were occupied by the Belgian Congo in 1916. They were mandated in 1924 to Belgium by the [[League of Nations]]. Belgium was again invaded by Germany in 1940 during the [[blitzkrieg]] offensive. The Belgian Congo gained its independence on 30 July 1960 during the [[Congo Crisis]], and Ruanda-Urundi became independent in 1962. |
| + | |||
| + | After World War II, Belgium joined NATO and, together with the Netherlands and Luxembourg, formed the [[Benelux]] group of nations. Belgium was also one of the founding members of the [[European Economic Community]]. Belgium hosts the headquarters of NATO and a major part of the [[European Union]]'s institutions and administrations, including the [[European Commission]], the [[Council of the European Union]] and most of the sessions of the [[European Parliament]]. During the 20th century, and in particular since World War II, the history of Belgium has been increasingly dominated by the autonomy of its two main language communities. This period saw a rise in intercommunal tensions, and the unity of the Belgian state has come under scrutiny. Through constitutional reforms in the 1970s and 1980s, [[regionalisation]] of the unitary state had led to the establishment of a three-tiered system of [[federal]], linguistic-community and regional governments, a compromise designed to minimise linguistic tensions. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Be-map.gif|thumb|200px| [[Brussels]], [[Antwerp]], [[Ghent]], [[Charleroi]], [[Liège (city)|Liège]], [[Bruges]] and [[Namur (city)|Namur]] are the seven largest cities of Belgium, with populations above 100,000]] | |
== Politics== | == Politics== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Belgium is a [[constitutional monarchy |constitutional]] [[popular monarchy]] and [[parliamentary system|parliamentary democracy]] that evolved after World War II from a [[unitary state]] to a [[federation]]. The [[bicameralism|bicameral]] [[parliament]] is composed of a [[Senate]] and a [[Chamber of Representatives]]. The former is a mix of directly elected senior politicians and representatives of the communities and regions; while the latter represents all Belgians over the age of eighteen in a [[proportional representation|proportional voting]] system. Belgium is one of the few countries that has [[compulsory voting]], thus having one of the highest rates of [[voter turnout]] in the world. | + | Belgium is a [[constitutional monarchy |constitutional]] [[popular monarchy]] and [[parliamentary system|parliamentary democracy]] that evolved after World War II from a [[unitary state]] to a [[federation]]. The [[bicameralism|bicameral]] [[parliament]] is composed of a [[Senate]] and a [[Chamber of Representatives]]. The former is a mix of directly elected senior politicians and representatives of the communities and regions; while the latter represents all Belgians over the age of eighteen in a [[proportional representation|proportional voting]] system. Belgium is one of the few countries that has [[compulsory voting]], thus having one of the highest rates of [[voter turnout]] in the world. |
| − | The federal government, formally nominated by the king, must have the confidence of the Chamber of Representatives. It is led by the [[Prime Minister]]. The numbers of Dutch- and French-speaking ministers are equal as prescribed by the | + | The federal government, formally nominated by the king, must have the confidence of the Chamber of Representatives. It is led by the [[Prime Minister]]. The numbers of Dutch- and French-speaking ministers are equal as prescribed by the Constitution. The King or Queen is the [[head of state]], though he has limited [[Royal Prerogative |prerogative]]s. Actual power is vested in the Prime Minister and the [[list of Governments in Belgium |different governments]], who govern the country. The judicial system is based on [[Civil law (legal system)|civil law]] and originates from the [[Napoleonic code]]. The [[Court of Appeals]] is one level below the [[Court of Cassation (Belgium)|Court of Cassation]], an institution based on the [[Cour de cassation|French Court of Cassation]]. |
Belgium's political institutions are complex; most political power is organised around the need to represent the main language communities. Since around 1970, the significant national Belgian [[political party|political parties]] has split into distinct components that mainly represent the interests of these communities. The major parties in each community belong to three main political families: the [[right-wing politics|right-wing]] [[Liberal Party|Liberals]], the [[centrism|centrist]] [[Christian Democracy|Christian Democrats]], and the [[left-wing politics|left-wing]] [[Social Democracy|Social Democrats]]. Other important younger parties are the [[worldwide green parties|Green parties]] and, especially in Flanders, the [[nationalism|nationalist]] and [[far-right]] parties. Politics is strongly influenced by powerful lobby groups, such as [[trade union]]s and business interests in the form of the [[Federation of Enterprises in Belgium]], or the [[Roman Catholic Church]] and the [[Freemasonry]]. | Belgium's political institutions are complex; most political power is organised around the need to represent the main language communities. Since around 1970, the significant national Belgian [[political party|political parties]] has split into distinct components that mainly represent the interests of these communities. The major parties in each community belong to three main political families: the [[right-wing politics|right-wing]] [[Liberal Party|Liberals]], the [[centrism|centrist]] [[Christian Democracy|Christian Democrats]], and the [[left-wing politics|left-wing]] [[Social Democracy|Social Democrats]]. Other important younger parties are the [[worldwide green parties|Green parties]] and, especially in Flanders, the [[nationalism|nationalist]] and [[far-right]] parties. Politics is strongly influenced by powerful lobby groups, such as [[trade union]]s and business interests in the form of the [[Federation of Enterprises in Belgium]], or the [[Roman Catholic Church]] and the [[Freemasonry]]. | ||
| − | + | The current king, [[Albert II of Belgium|Albert II]], succeeded King [[Baudouin of Belgium|Baudouin]] in 1993. In 1999, Prime Minister [[Guy Verhofstadt]] from the [[Flemish Liberals and Democrats|VLD]] has led a six-party Liberal-Social Democrat-Greens [[coalition]], often referred to as 'the rainbow government'. This was the first government without the Christian Democrats since 1958. In the 2003 elections, Verhofstadt won a second term in office and has led a Liberal-Social Democrat coalition of four parties. More recently however, the steady rise of the Flemish ultra-right nationalist [[separatism|separatist]] party [[Vlaams Belang]], has superseded the [[Flemish Block|Vlaams Blok]] amidst concerns of racism promoted by the party. | |
| − | The current king, [[Albert II of Belgium|Albert II]], succeeded King [[Baudouin of Belgium|Baudouin]] in 1993. In 1999, Prime Minister [[Guy Verhofstadt]] from the [[Flemish Liberals and Democrats|VLD]] has led a six-party Liberal-Social Democrat-Greens [[coalition]], often referred to as 'the rainbow government'. This was the first government without the Christian Democrats since 1958. | + | |
| + | A significant achievement of the two successive Verhofstadt governments has been the achievement of a balanced budget; Belgium is one of the few member-states of the EU to have done so. This policy was applied by the successive governments during the 1990s under pressure from the [[European Council]]. The fall of the previous government was mainly due to the [[dioxin]] crisis, a major food intoxication scandal in 1999 that led to the establishment of the Belgian Food Agency. This event resulted in an atypically large representation by the Greens in parliament, and a greater emphasis on environmental politics during the first Verhofstadt government. One Green policy, for example, resulted in [[nuclear power phase-out#Belgium|nuclear phase-out]] legislation, which has been modified by the current government. The absence of Christian Democrats from the ranks of the government has enabled Verhofstadt to tackle social issues from a more [[liberalism|liberal]] point of view and to develop new legislation on the use of [[soft drug]]s, [[same-sex marriage in Belgium|same-sex marriage]] and [[euthanasia#Belgium|euthanasia]]. During the two most recent parliaments, the government has promoted active diplomacy in Africa, opposed a military intervention during the [[Iraq disarmament crisis]], and has passed legislation concerning [[War Crimes Law (Belgium)|war crimes]]. Both of Verhofstadt's terms have been marked by disputes between the Belgian communities. The major points of contention are the nocturnal air traffic routes at [[Brussels Airport]] and the status of the electoral district of [[Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde]]. | ||
| − | + | ==Communities and regions== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Image:350px-Belgium RegProv border.jpg|250px|right|thumbnail|Belgium is composed of the five northern Dutch-speaking provinces of [[Flanders]], the five southern French-speaking provinces of [[Wallonia]] (the [[German-speaking community of Belgium |German-speaking Community]] is located in the [[Liège (province) |province of Liège]] along the German border) and the bilingual [[Brussels-Capital Region|Capital Region of Brussels]]. The boundary between these regions is marked in red.]] | [[Image:350px-Belgium RegProv border.jpg|250px|right|thumbnail|Belgium is composed of the five northern Dutch-speaking provinces of [[Flanders]], the five southern French-speaking provinces of [[Wallonia]] (the [[German-speaking community of Belgium |German-speaking Community]] is located in the [[Liège (province) |province of Liège]] along the German border) and the bilingual [[Brussels-Capital Region|Capital Region of Brussels]]. The boundary between these regions is marked in red.]] | ||
| − | The country's constitution was revised on | + | The country's constitution was revised on July 14, 1993, to create a unique federal state, based on three levels: |
#The federal government, based in Brussels. | #The federal government, based in Brussels. | ||
#The three language communities: | #The three language communities: | ||
| Line 106: | Line 115: | ||
Conflicts between the bodies are resolved by the [[Court of Arbitration of Belgium|Court of Arbitration]]. The setup allows a compromise to distinctly different cultures live together peacefully. | Conflicts between the bodies are resolved by the [[Court of Arbitration of Belgium|Court of Arbitration]]. The setup allows a compromise to distinctly different cultures live together peacefully. | ||
| − | The Flemish Community absorbed the Flemish Region in 1980 to form the government of | + | The Flemish Community absorbed the Flemish Region in 1980 to form the government of Flanders. The overlapping boundaries of the Regions and Communities have created two notable peculiarities: the territory of the Brussels-Capital Region is included in both Flemish and French Communities, and the territory of the German-speaking Community lies wholly within the Walloon Region. Flemish and Walloon regions are furthermore subdivided in administrative entities, the provinces. |
At the highest level of this three-tiered setup is the [[Belgian federal government |federal government]] which manages [[foreign affairs]], [[development aid]], [[defence]], [[Belgium/Military|military]], police, economic management, [[social welfare]], [[social security]] transport, energy, telecommunications, and scientific research, limited competencies in education and culture, and the supervision of taxation by regional authorities. The federal government controls more than 90 per cent of all taxation. The community governments are responsible for the promotion of language, culture and education in mostly schools, libraries and theatres. The third tier is the Regional governments, who manage mostly land and property based issues such as housing, transportation etc. For example, a school building in Brussels belonging to the public school systemwould be regulated by the regional government of Brussels. However, the school as an institution would fall under the regulations of the Flemish government if the primary language of teaching is Dutch, but under the French Community government if the primary language is French. | At the highest level of this three-tiered setup is the [[Belgian federal government |federal government]] which manages [[foreign affairs]], [[development aid]], [[defence]], [[Belgium/Military|military]], police, economic management, [[social welfare]], [[social security]] transport, energy, telecommunications, and scientific research, limited competencies in education and culture, and the supervision of taxation by regional authorities. The federal government controls more than 90 per cent of all taxation. The community governments are responsible for the promotion of language, culture and education in mostly schools, libraries and theatres. The third tier is the Regional governments, who manage mostly land and property based issues such as housing, transportation etc. For example, a school building in Brussels belonging to the public school systemwould be regulated by the regional government of Brussels. However, the school as an institution would fall under the regulations of the Flemish government if the primary language of teaching is Dutch, but under the French Community government if the primary language is French. | ||
| − | == | + | == Economy== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Densely populated, Belgium is located at the heart of one of the world's most highly industrialised regions. | Densely populated, Belgium is located at the heart of one of the world's most highly industrialised regions. | ||
[[Image:Ougree_16.jpg|thumb|300px|Steelmaking along the [[Meuse]] at [[Ougrée]], near [[Liège (city) |Liège]].]] | [[Image:Ougree_16.jpg|thumb|300px|Steelmaking along the [[Meuse]] at [[Ougrée]], near [[Liège (city) |Liège]].]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | By the end of the 1980s, Belgian macroeconomic policies had resulted in a cumulative government debt of about 120% of [[GDP]]. Currently, although the government has recently succeeded in balancing its budget, public debt is nearly 100% of GDP. | + | Belgium was the first continental European country to undergo the [[Industrial Revolution]], in the early 1800s. [[Liège (city) |Liège]] and [[Charleroi]] rapidly developed mining and steelmaking, which flourished until the mid-20th century. However, by the 1840s the textile industry of Flanders was in severe crisis and there was famine in Flanders (1846-50). After World War II, [[Ghent]] and [[Antwerp]] experienced a fast expansion of the [[chemical]] and [[petroleum]] industries. The [[1973 oil crisis|1973]] and [[1979 oil crisis|1979 oil crises]] sent the economy into a prolonged recession. The Belgian steel industry has since experienced serious decline. This has been responsible for inhibiting the economic development of [[Wallonia]]. In the 1980s and 1990s, the economic centre of the country continued to shift northwards to Flanders. Nowadays, industry is concentrated in the populous Flemish area in the north. |
| + | |||
| + | By the end of the 1980s, Belgian macroeconomic policies had resulted in a cumulative government debt of about 120% of [[GDP]]. Currently, although the government has recently succeeded in balancing its budget, public debt is nearly 100% of GDP. In 2004, the real growth rate of GDP was estimated at 2.7% {{ref|nationalBank}} but is expected to fall to 1.3% in 2005. | ||
Belgium has a particularly [[open economy]]. It has developed an excellent [[transportation in Belgium|transportation infrastructure]] of ports, canals, [[Rail transport in Belgium|railways]] and highways to integrate its industry with that of its neighbours. Antwerp is the second-largest European port. One of the founding members of the European Union, Belgium strongly supports the extension of the powers of EU institutions to integrate the member economies. In 1999, Belgium adopted the [[euro]], the single European currency, which replaced the [[Belgian franc]] in 2002. The Belgian economy is strongly oriented towards foreign trade, in particular of high value-added goods. The main imports are food products, machinery, rough diamonds, petroleum and petroleum products, chemicals, clothing and accessories, and textiles. The main exports are automobiles, food and food products, iron and steel, finished diamonds, textiles, plastics, petroleum products, and nonferrous metals. Since 1922, Belgium and [[Luxembourg]] have been a single trade market within a [[customs union |customs]] and [[currency union]]—the [[Belgian-Luxembourgian Economic Union]]. Its main trading partners are Germany, the Netherlands, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, the United States and Spain. Belgium ranks ninth on the 2005 [[United Nations]] [[Human Development Index]]. | Belgium has a particularly [[open economy]]. It has developed an excellent [[transportation in Belgium|transportation infrastructure]] of ports, canals, [[Rail transport in Belgium|railways]] and highways to integrate its industry with that of its neighbours. Antwerp is the second-largest European port. One of the founding members of the European Union, Belgium strongly supports the extension of the powers of EU institutions to integrate the member economies. In 1999, Belgium adopted the [[euro]], the single European currency, which replaced the [[Belgian franc]] in 2002. The Belgian economy is strongly oriented towards foreign trade, in particular of high value-added goods. The main imports are food products, machinery, rough diamonds, petroleum and petroleum products, chemicals, clothing and accessories, and textiles. The main exports are automobiles, food and food products, iron and steel, finished diamonds, textiles, plastics, petroleum products, and nonferrous metals. Since 1922, Belgium and [[Luxembourg]] have been a single trade market within a [[customs union |customs]] and [[currency union]]—the [[Belgian-Luxembourgian Economic Union]]. Its main trading partners are Germany, the Netherlands, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, the United States and Spain. Belgium ranks ninth on the 2005 [[United Nations]] [[Human Development Index]]. | ||
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | The [[population density]] (342 per km²) is one of the highest in Europe, after the Netherlands and some smaller countries such as [[Monaco]]. The areas with the highest population density are around the Brussels-Antwerp-Ghent-[[Leuven]] agglomerations, as well as other important urban centres as Liège, [[Charleroi]], [[Kortrijk]], [[Bruges]], [[Hasselt]] and [[Namur (city) | Namur]]. The Ardennes have the lowest density. As of 2005, the Flemish Region has a population of about 6,043,161, Wallonia 3,395,942 and Brussels 1,006,749. | + | The [[population density]] (342 per km²) is one of the highest in Europe, after the Netherlands and some smaller countries such as [[Monaco]]. The areas with the highest population density are around the Brussels-Antwerp-Ghent-[[Leuven]] agglomerations, as well as other important urban centres as Liège, [[Charleroi]], [[Kortrijk]], [[Bruges]], [[Hasselt]] and [[Namur (city) | Namur]]. The Ardennes have the lowest density. As of 2005, the Flemish Region has a population of about 6,043,161, Wallonia 3,395,942 and Brussels 1,006,749. Almost all of the population is urban (97.3% in 1999). The main cities and their populations are Brussels (1,006,749), Antwerp (457,749), Ghent (230,951), Charleroi (201,373), and Liège (185,574). |
[[image:Basilica of the Sacred Heart in Belgium.jpg|thumb|right|250px|[[Basilica of the Sacred Heart, Belgium | Basilica of the Sacred Heart]], Brussels. The basilica is the National Basilica of Belgium. It stands as a symbol of the historical link between the [[List of Belgian monarchs |Belgian monarchy]] and the Catholic Church.]] | [[image:Basilica of the Sacred Heart in Belgium.jpg|thumb|right|250px|[[Basilica of the Sacred Heart, Belgium | Basilica of the Sacred Heart]], Brussels. The basilica is the National Basilica of Belgium. It stands as a symbol of the historical link between the [[List of Belgian monarchs |Belgian monarchy]] and the Catholic Church.]] | ||
| + | |||
About 60% of the country is Dutch-speaking, 40% French-speaking, and 1% German-speaking. However, these figures must be interpreted cautiously, because the most recent linguistic census was taken before 1960, and the mother tongue is not always the same as the language used in public or in official life. Brussels is officially French-Dutch bilingual, but mostly French speaking; it evolved from a Dutch-speaking place to its current dominantly French character when the Belgian state became independent in 1830. | About 60% of the country is Dutch-speaking, 40% French-speaking, and 1% German-speaking. However, these figures must be interpreted cautiously, because the most recent linguistic census was taken before 1960, and the mother tongue is not always the same as the language used in public or in official life. Brussels is officially French-Dutch bilingual, but mostly French speaking; it evolved from a Dutch-speaking place to its current dominantly French character when the Belgian state became independent in 1830. | ||
| − | Both the [[Dutch language|Dutch]] spoken in Belgium and the [[Belgian French]] have minor differences in [[vocabulary]] and [[semantic]] nuances from the varieties spoken in France and the Netherlands. Many people can still speak [[dialects]] of [[Flemish (linguistics)|Flemish]] and [[Walloon language|Walloon]]. These dialects, along with some other ones like [[Picard language |Picard]] or [[Limburgish]], | + | Both the [[Dutch language|Dutch]] spoken in Belgium and the [[Belgian French]] have minor differences in [[vocabulary]] and [[semantic]] nuances from the varieties spoken in France and the Netherlands. Many people can still speak [[dialects]] of [[Flemish (linguistics)|Flemish]] and [[Walloon language|Walloon]]. These dialects, along with some other ones like [[Picard language |Picard]] or [[Limburgish]], are not used in public life. |
| − | The ''[[laicite|laïque]]'' constitution provides for freedom of religion, and the government generally respects this right in practice. According to the ''2001 Survey and Study of Religion'', | + | The ''[[laicite|laïque]]'' constitution provides for freedom of religion, and the government generally respects this right in practice. According to the ''2001 Survey and Study of Religion'', about 47% of the population identify themselves as belonging to the Catholic Church. According to these figures, the Muslim population is the second largest religious community, at 3.5% (see [[Religion in Belgium]]). Since independence, Catholicism, counterbalanced by strong [[freethought]] movements, has had an important role in Belgium's politics, in particular via the Christian trade union ([[CSC/ACV]]) and the Christian Democrat parties ([[CD&V]], [[CDH]]). |
| − | 98% of the adult population is | + | 98% of the adult population is literate. Education is compulsory from the ages of six to 18, but many Belgians continue to study until the age of about 23. Among the [[OECD]] countries in 1999, Belgium had the third highest proportion of 18–21-year-olds enrolled in [[postsecondary education]], at 42%. Nevertheless, in recent years, concern is rising over certain forms of [[illiteracy]], such as [[functional illiteracy]]. In the period 1994–98, 18.4% of the population lacks functional literacy skills. Mirroring the historical political conflicts between the freethought and Catholic segments of the population, the Belgian educational system in each communities is split into a ''[[laicite|laïque]]'' branch controlled by the communities, the provinces, or the municipalities, and a [[subsidy|subsidised]] religious—mostly Catholic—branch controlled by both the communities and the religious authorities—usually the [[diocese]]s. |
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
| − | + | ||
Belgian cultural life has tended to concentrate within each community. The shared element is less important, because there are no bilingual universities, except the royal military academy, no common media, and no single, common large cultural or scientific organisation where both main communities are represented. Aside from these differences, Belgium is well-known for its fine art and architecture. | Belgian cultural life has tended to concentrate within each community. The shared element is less important, because there are no bilingual universities, except the royal military academy, no common media, and no single, common large cultural or scientific organisation where both main communities are represented. Aside from these differences, Belgium is well-known for its fine art and architecture. | ||
The region corresponding to today's Belgium has seen the flourishing of major artistic movements that have had tremendous influence over European art. The [[Mosan art]], the [[Early Netherlandish painting|Early Netherlandish]], the Flemish [[Renaissance]] and [[Baroque]] painting, and major examples of [[Romanesque architecture|Romanesque]], [[Gothic architecture|Gothic]], [[Renaissance architecture |Renaissance]] and [[Baroque architecture]], and the Renaissance [[vocal music]] of the [[Dutch School (music) |Dutch School]] developed in the southern part of the Low Countries, are milestones in the history of art. | The region corresponding to today's Belgium has seen the flourishing of major artistic movements that have had tremendous influence over European art. The [[Mosan art]], the [[Early Netherlandish painting|Early Netherlandish]], the Flemish [[Renaissance]] and [[Baroque]] painting, and major examples of [[Romanesque architecture|Romanesque]], [[Gothic architecture|Gothic]], [[Renaissance architecture |Renaissance]] and [[Baroque architecture]], and the Renaissance [[vocal music]] of the [[Dutch School (music) |Dutch School]] developed in the southern part of the Low Countries, are milestones in the history of art. | ||
| − | |||
This rich artistic production, often referred to as a whole as [[Flemish art]], gradually declined during the second half of the 17th century. However, in the 19th and 20th centuries, many original artists appeared. In music, [[Adolphe Sax]] invented the [[saxophone]] in 1846. [[Eugène Ysaÿe]] was a major 19th- and 20th-century Belgian violinist (See also [[Music of Belgium]]). In architecture, [[Victor Horta]] was a major initiator of the [[Art Nouveau]] style. Belgium has produced famous [[romanticism |romantic]], [[expressionism |expressionist]] and [[surrealism |surrealist]] painters; these include [[Egide Charles Gustave Wappers |Egide Wappers]], [[James Ensor]], [[Constant Permeke]] and [[René Magritte]]. In literature, Belgium has produced several well-known authors, such as the poets [[Emile Verhaeren]], [[Jacques Brel]] and novelists [[Hendrik Conscience]] and [[Georges Simenon]]. The poet and playwright [[Maurice Maeterlinck]] won the [[Nobel Prize in literature]] in 1911. The best known [[Franco-Belgian comics]] are ''[[The Adventures of Tintin]]'' by [[Hergé]] but many other major authors of comics have been Belgian, including [[Edgar P. Jacobs]] and [[André Franquin]]. | This rich artistic production, often referred to as a whole as [[Flemish art]], gradually declined during the second half of the 17th century. However, in the 19th and 20th centuries, many original artists appeared. In music, [[Adolphe Sax]] invented the [[saxophone]] in 1846. [[Eugène Ysaÿe]] was a major 19th- and 20th-century Belgian violinist (See also [[Music of Belgium]]). In architecture, [[Victor Horta]] was a major initiator of the [[Art Nouveau]] style. Belgium has produced famous [[romanticism |romantic]], [[expressionism |expressionist]] and [[surrealism |surrealist]] painters; these include [[Egide Charles Gustave Wappers |Egide Wappers]], [[James Ensor]], [[Constant Permeke]] and [[René Magritte]]. In literature, Belgium has produced several well-known authors, such as the poets [[Emile Verhaeren]], [[Jacques Brel]] and novelists [[Hendrik Conscience]] and [[Georges Simenon]]. The poet and playwright [[Maurice Maeterlinck]] won the [[Nobel Prize in literature]] in 1911. The best known [[Franco-Belgian comics]] are ''[[The Adventures of Tintin]]'' by [[Hergé]] but many other major authors of comics have been Belgian, including [[Edgar P. Jacobs]] and [[André Franquin]]. | ||
Revision as of 08:57, 12 December 2005
| Kingdom of Belgium Koninkrijk België Royaume de Belgique Königreich Belgien |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: Dutch: Eendracht maakt macht; French: L'union fait la force; German: Einigkeit macht stark (English: "Strength lies in unity") |
||||||
| Anthem: The Brabançonne |
||||||
| Capital (and largest city) | Brussels 50°54′N 4°32′E | |||||
| Official languages | Dutch, French, German | |||||
| Government | Constitutional Monarchy | |||||
| Independence | ||||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 30,528 km² (148th) Expression error: Unexpected div operator. sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 6.4 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2005 estimate | 10,445,852 (79th) | ||||
| - | 2005 census | 10,445,852 | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2004 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $316.2 billion (30th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $29,707 (14th) | ||||
| Currency | Euro (EUR) |
|||||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .be | |||||
| Calling code | +32 | |||||
The Kingdom of Belgium is a country in northwest Europe bordered by the Netherlands, Germany, Luxembourg and France. Belgium has a population of over ten million people in an area of thirty thousand square kilometres. Straddling the cultural boundary between Germanic and Romance Europe, it is both linguistically and culturally divided. Two major languages are spoken in Belgium: Dutch—sometimes unofficially called Flemish—spoken in Flanders to the north; and French, spoken in Wallonia in the south. The capital, Brussels, is officially bilingual. In addition to the two, an officially recognized minority of German speakers is present in the east. This linguistic diversity often leads to political conflict, and is reflected in Belgium's complex system of government and political history.
Belgium derives its name from its first named inhabitants, the Belgae, a group of mostly Celtic tribes, and from the Roman province in northern Gaul, known as Gallia Belgica. Historically, Belgium has been a part of the Low Countries, which also includes the Netherlands and Luxembourg. From the end of the Middle Ages until the seventeenth century, it was a prosperous center of commerce and culture. From the sixteenth century until independence in 1830, Belgium, called at that time the Southern Netherlands, was the site of many battles between the European powers, and has been dubbed "the Cockpit of Europe." More recently, Belgium was a founding member of the European Union, hosting its headquarters, as well as those of other major international organisations, such as NATO.
Geography
Belgium, with an area of 30,528 km², has three main geographical regions: the coastal plain in the north-west, the central plateau, and the Ardennes uplands in the south-east. The coastal plain consists mainly of sand dunes and polders. Polders are areas of land, close to or below sea level that have been reclaimed from the sea, from which they are protected by dikes or, further inland, by fields that have been drained with canals. The second geographical region, the central plateau, lies further inland. This is a smooth, slowly rising area that has many fertile valleys and is irrigated by many waterways. Here one can also find rougher land, including caves and small gorges.
The third geographical region, called the Ardennes, is more rugged than the first two. It is a thickly forested plateau, very rocky and not very good for farming, which extends into northern France. This is where much of Belgium's wildlife can be found. Belgium's highest point, the Signal de Botrange is located in this region at only 694 metres.
The climate is maritime temperate, with significant precipitation in all seasons (Köppen climate classification: Cfb; the average temperature is 3°C in January, and 18°C in July; the average precipitation is 65 mm in January, and 78 mm in July).
History
Over the past two millennia, the area that is now known as Belgium has seen significant demographic, political and cultural upheavals. The first well-documented population move was the conquest of the region by the Roman Republic in the 1st century B.C.E., followed in the 5th century by the Germanic Franks. The Franks established the Merovingian kingdom, which became the Carolingian Empire in the 8th century. During the Middle Ages, the Low Countries were split into many small feudal states. Most of them were united in the course of the 14th and 15th centuries by the house of Burgundy as the Burgundian Netherlands. These states gained a degree of autonomy in the 15th century and were thereafter named the Seventeen Provinces.
The history of Belgium can be distinguished from that of the Low Countries from the 16th century. A civil war, the Eighty Years' War (1568-1648), divided the Seventeen Provinces into the United Provinces in the north and the Southern Netherlands in the south. The southern provinces were ruled successively by the Spanish and the Austrian Habsburgs. Until independence, the Southern Netherlands were sought after by numerous French conquerors and were the theatre of most Franco-Spanish and Franco-Austrian wars during the 17th and 18th centuries. Following the Campaigns of 1794 in the French Revolutionary Wars, the Low Countries—including territories that were never under Habsburg rule, such the Bishopric of Liège—were overrun by France, ending Spanish-Austrian rule in the region. The reunification of the Low Countries as the United Kingdom of the Netherlands occurred at the end of the French Empire in 1815.
The 1830 Belgian Revolution led to the establishment of an independent, Catholic and neutral Belgium under a provisional government. Since the installation of Leopold I as king in 1831, Belgium has been a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy. Between independence and World War II, the democratic system evolved from an oligarchy characterised by two main parties, the Catholics and the Liberals, to a universal suffrage system that has included a third party, the Belgian Labour Party, and a strong role for the trade unions. Originally, French, which was the adopted language of the nobility and the bourgeoisie was the official language. The country has since developed a bilingual Dutch-French system.
The Berlin Conference of 1885 agreed to hand over Congo to King Leopold II as his private possession, called the Congo Free State. In 1908, it was ceded to Belgium as a colony, henceforth called the Belgian Congo. Belgium's neutrality was violated in 1914, when Germany invaded Belgium as part of the Schlieffen Plan. The former German colonies Ruanda-Urundi—now called Rwanda and Burundi—were occupied by the Belgian Congo in 1916. They were mandated in 1924 to Belgium by the League of Nations. Belgium was again invaded by Germany in 1940 during the blitzkrieg offensive. The Belgian Congo gained its independence on 30 July 1960 during the Congo Crisis, and Ruanda-Urundi became independent in 1962.
After World War II, Belgium joined NATO and, together with the Netherlands and Luxembourg, formed the Benelux group of nations. Belgium was also one of the founding members of the European Economic Community. Belgium hosts the headquarters of NATO and a major part of the European Union's institutions and administrations, including the European Commission, the Council of the European Union and most of the sessions of the European Parliament. During the 20th century, and in particular since World War II, the history of Belgium has been increasingly dominated by the autonomy of its two main language communities. This period saw a rise in intercommunal tensions, and the unity of the Belgian state has come under scrutiny. Through constitutional reforms in the 1970s and 1980s, regionalisation of the unitary state had led to the establishment of a three-tiered system of federal, linguistic-community and regional governments, a compromise designed to minimise linguistic tensions.
Politics
Belgium is a constitutional popular monarchy and parliamentary democracy that evolved after World War II from a unitary state to a federation. The bicameral parliament is composed of a Senate and a Chamber of Representatives. The former is a mix of directly elected senior politicians and representatives of the communities and regions; while the latter represents all Belgians over the age of eighteen in a proportional voting system. Belgium is one of the few countries that has compulsory voting, thus having one of the highest rates of voter turnout in the world.
The federal government, formally nominated by the king, must have the confidence of the Chamber of Representatives. It is led by the Prime Minister. The numbers of Dutch- and French-speaking ministers are equal as prescribed by the Constitution. The King or Queen is the head of state, though he has limited prerogatives. Actual power is vested in the Prime Minister and the different governments, who govern the country. The judicial system is based on civil law and originates from the Napoleonic code. The Court of Appeals is one level below the Court of Cassation, an institution based on the French Court of Cassation.
Belgium's political institutions are complex; most political power is organised around the need to represent the main language communities. Since around 1970, the significant national Belgian political parties has split into distinct components that mainly represent the interests of these communities. The major parties in each community belong to three main political families: the right-wing Liberals, the centrist Christian Democrats, and the left-wing Social Democrats. Other important younger parties are the Green parties and, especially in Flanders, the nationalist and far-right parties. Politics is strongly influenced by powerful lobby groups, such as trade unions and business interests in the form of the Federation of Enterprises in Belgium, or the Roman Catholic Church and the Freemasonry.
The current king, Albert II, succeeded King Baudouin in 1993. In 1999, Prime Minister Guy Verhofstadt from the VLD has led a six-party Liberal-Social Democrat-Greens coalition, often referred to as 'the rainbow government'. This was the first government without the Christian Democrats since 1958. In the 2003 elections, Verhofstadt won a second term in office and has led a Liberal-Social Democrat coalition of four parties. More recently however, the steady rise of the Flemish ultra-right nationalist separatist party Vlaams Belang, has superseded the Vlaams Blok amidst concerns of racism promoted by the party.
A significant achievement of the two successive Verhofstadt governments has been the achievement of a balanced budget; Belgium is one of the few member-states of the EU to have done so. This policy was applied by the successive governments during the 1990s under pressure from the European Council. The fall of the previous government was mainly due to the dioxin crisis, a major food intoxication scandal in 1999 that led to the establishment of the Belgian Food Agency. This event resulted in an atypically large representation by the Greens in parliament, and a greater emphasis on environmental politics during the first Verhofstadt government. One Green policy, for example, resulted in nuclear phase-out legislation, which has been modified by the current government. The absence of Christian Democrats from the ranks of the government has enabled Verhofstadt to tackle social issues from a more liberal point of view and to develop new legislation on the use of soft drugs, same-sex marriage and euthanasia. During the two most recent parliaments, the government has promoted active diplomacy in Africa, opposed a military intervention during the Iraq disarmament crisis, and has passed legislation concerning war crimes. Both of Verhofstadt's terms have been marked by disputes between the Belgian communities. The major points of contention are the nocturnal air traffic routes at Brussels Airport and the status of the electoral district of Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde.
Communities and regions
The country's constitution was revised on July 14, 1993, to create a unique federal state, based on three levels:
- The federal government, based in Brussels.
- The three language communities:
- the Flemish (i.e., Dutch-speaking) Community;
- the French (i.e., French-speaking) Community; and
- the German-speaking Community.
- The three regions (which differ from the language communities with respect to the German-speaking community and the Brussels region):
- the Flemish Region;
- the Walloon Region; and
- the Brussels-Capital Region.
Conflicts between the bodies are resolved by the Court of Arbitration. The setup allows a compromise to distinctly different cultures live together peacefully.
The Flemish Community absorbed the Flemish Region in 1980 to form the government of Flanders. The overlapping boundaries of the Regions and Communities have created two notable peculiarities: the territory of the Brussels-Capital Region is included in both Flemish and French Communities, and the territory of the German-speaking Community lies wholly within the Walloon Region. Flemish and Walloon regions are furthermore subdivided in administrative entities, the provinces.
At the highest level of this three-tiered setup is the federal government which manages foreign affairs, development aid, defence, military, police, economic management, social welfare, social security transport, energy, telecommunications, and scientific research, limited competencies in education and culture, and the supervision of taxation by regional authorities. The federal government controls more than 90 per cent of all taxation. The community governments are responsible for the promotion of language, culture and education in mostly schools, libraries and theatres. The third tier is the Regional governments, who manage mostly land and property based issues such as housing, transportation etc. For example, a school building in Brussels belonging to the public school systemwould be regulated by the regional government of Brussels. However, the school as an institution would fall under the regulations of the Flemish government if the primary language of teaching is Dutch, but under the French Community government if the primary language is French.
Economy
Densely populated, Belgium is located at the heart of one of the world's most highly industrialised regions.
Belgium was the first continental European country to undergo the Industrial Revolution, in the early 1800s. Liège and Charleroi rapidly developed mining and steelmaking, which flourished until the mid-20th century. However, by the 1840s the textile industry of Flanders was in severe crisis and there was famine in Flanders (1846-50). After World War II, Ghent and Antwerp experienced a fast expansion of the chemical and petroleum industries. The 1973 and 1979 oil crises sent the economy into a prolonged recession. The Belgian steel industry has since experienced serious decline. This has been responsible for inhibiting the economic development of Wallonia. In the 1980s and 1990s, the economic centre of the country continued to shift northwards to Flanders. Nowadays, industry is concentrated in the populous Flemish area in the north.
By the end of the 1980s, Belgian macroeconomic policies had resulted in a cumulative government debt of about 120% of GDP. Currently, although the government has recently succeeded in balancing its budget, public debt is nearly 100% of GDP. In 2004, the real growth rate of GDP was estimated at 2.7% [1] but is expected to fall to 1.3% in 2005.
Belgium has a particularly open economy. It has developed an excellent transportation infrastructure of ports, canals, railways and highways to integrate its industry with that of its neighbours. Antwerp is the second-largest European port. One of the founding members of the European Union, Belgium strongly supports the extension of the powers of EU institutions to integrate the member economies. In 1999, Belgium adopted the euro, the single European currency, which replaced the Belgian franc in 2002. The Belgian economy is strongly oriented towards foreign trade, in particular of high value-added goods. The main imports are food products, machinery, rough diamonds, petroleum and petroleum products, chemicals, clothing and accessories, and textiles. The main exports are automobiles, food and food products, iron and steel, finished diamonds, textiles, plastics, petroleum products, and nonferrous metals. Since 1922, Belgium and Luxembourg have been a single trade market within a customs and currency union—the Belgian-Luxembourgian Economic Union. Its main trading partners are Germany, the Netherlands, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, the United States and Spain. Belgium ranks ninth on the 2005 United Nations Human Development Index.
Demographics
The population density (342 per km²) is one of the highest in Europe, after the Netherlands and some smaller countries such as Monaco. The areas with the highest population density are around the Brussels-Antwerp-Ghent-Leuven agglomerations, as well as other important urban centres as Liège, Charleroi, Kortrijk, Bruges, Hasselt and Namur. The Ardennes have the lowest density. As of 2005, the Flemish Region has a population of about 6,043,161, Wallonia 3,395,942 and Brussels 1,006,749. Almost all of the population is urban (97.3% in 1999). The main cities and their populations are Brussels (1,006,749), Antwerp (457,749), Ghent (230,951), Charleroi (201,373), and Liège (185,574).
About 60% of the country is Dutch-speaking, 40% French-speaking, and 1% German-speaking. However, these figures must be interpreted cautiously, because the most recent linguistic census was taken before 1960, and the mother tongue is not always the same as the language used in public or in official life. Brussels is officially French-Dutch bilingual, but mostly French speaking; it evolved from a Dutch-speaking place to its current dominantly French character when the Belgian state became independent in 1830.
Both the Dutch spoken in Belgium and the Belgian French have minor differences in vocabulary and semantic nuances from the varieties spoken in France and the Netherlands. Many people can still speak dialects of Flemish and Walloon. These dialects, along with some other ones like Picard or Limburgish, are not used in public life.
The laïque constitution provides for freedom of religion, and the government generally respects this right in practice. According to the 2001 Survey and Study of Religion, about 47% of the population identify themselves as belonging to the Catholic Church. According to these figures, the Muslim population is the second largest religious community, at 3.5% (see Religion in Belgium). Since independence, Catholicism, counterbalanced by strong freethought movements, has had an important role in Belgium's politics, in particular via the Christian trade union (CSC/ACV) and the Christian Democrat parties (CD&V, CDH).
98% of the adult population is literate. Education is compulsory from the ages of six to 18, but many Belgians continue to study until the age of about 23. Among the OECD countries in 1999, Belgium had the third highest proportion of 18–21-year-olds enrolled in postsecondary education, at 42%. Nevertheless, in recent years, concern is rising over certain forms of illiteracy, such as functional illiteracy. In the period 1994–98, 18.4% of the population lacks functional literacy skills. Mirroring the historical political conflicts between the freethought and Catholic segments of the population, the Belgian educational system in each communities is split into a laïque branch controlled by the communities, the provinces, or the municipalities, and a subsidised religious—mostly Catholic—branch controlled by both the communities and the religious authorities—usually the dioceses.
Culture
Belgian cultural life has tended to concentrate within each community. The shared element is less important, because there are no bilingual universities, except the royal military academy, no common media, and no single, common large cultural or scientific organisation where both main communities are represented. Aside from these differences, Belgium is well-known for its fine art and architecture.
The region corresponding to today's Belgium has seen the flourishing of major artistic movements that have had tremendous influence over European art. The Mosan art, the Early Netherlandish, the Flemish Renaissance and Baroque painting, and major examples of Romanesque, Gothic, Renaissance and Baroque architecture, and the Renaissance vocal music of the Dutch School developed in the southern part of the Low Countries, are milestones in the history of art.
This rich artistic production, often referred to as a whole as Flemish art, gradually declined during the second half of the 17th century. However, in the 19th and 20th centuries, many original artists appeared. In music, Adolphe Sax invented the saxophone in 1846. Eugène Ysaÿe was a major 19th- and 20th-century Belgian violinist (See also Music of Belgium). In architecture, Victor Horta was a major initiator of the Art Nouveau style. Belgium has produced famous romantic, expressionist and surrealist painters; these include Egide Wappers, James Ensor, Constant Permeke and René Magritte. In literature, Belgium has produced several well-known authors, such as the poets Emile Verhaeren, Jacques Brel and novelists Hendrik Conscience and Georges Simenon. The poet and playwright Maurice Maeterlinck won the Nobel Prize in literature in 1911. The best known Franco-Belgian comics are The Adventures of Tintin by Hergé but many other major authors of comics have been Belgian, including Edgar P. Jacobs and André Franquin.
More recently, notable cinema directors have emerged, most of them strongly influenced by French cinema. The absence of a major Belgian cinema company has forced them to emigrate or participate in low-budget productions. Belgian directors include Stijn Coninx, Luc and Jean-Pierre Dardenne; actors include Jan Decleir, Marie Gillain; and films include Man Bites Dog and The Alzheimer Affair. In the 1980s, Antwerp's Royal Academy of Fine Arts has produced the important fashion trendsetters, the Antwerp Six.
Belgium has also contributed to the development of science and technology. The mathematician Simon Stevin, the anatomist Andreas Vesalius and the cartographer Gerardus Mercator are among the most influential scientists from the beginning of Early Modern in the Low Countries. More recently, at the end of the 19th century, in applied science, the chemist Ernest Solvay and the engineer Zenobe Gramme have given their names to the Solvay process and the Gramme dynamo. Georges Lemaître is a famous Belgian cosmologist credited with proposing the Big Bang theory of the origin of the universe in 1927. Three Nobel Prizes in Physiology or Medicine have been awarded to Belgians: Jules Bordet in 1919, Corneille Heymans in 1938, and Albert Claude and Christian De Duve in 1974. Ilya Prigogine was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1977.
One could not understand Belgian cultural life without considering the folk festivals, which play a major role in the country's cultural life. Examples are the Carnival of Binche, the Ducasse of Ath, the procession of the Holy Blood in Bruges, the 15th-of-August festival in Liège, and the Walloon festival in Namur. A major non-official holiday is the Saint Nicholas Day, which commemorates the festival of the children and, in Liège, of the students.
Belgium is well represented in the world of sport—football (soccer) and cycling are especially popular. The national football team is the Red Devils. Among the well known cyclists, Eddy Merckx, won five Tours de France. Belgium also has two current female tennis champions: Kim Clijsters and Justine Henin-Hardenne.
Many highly ranked restaurants can be found in the high-impact gastronomic guides, such as the Michelin Guide. Brands of Belgian chocolate, like Neuhaus, are world renowned and widely sold; even the cheapest and most popular brand, Leonidas, has earned a reputation for its quality. Belgium produces over 500 varieties of beer (ales, pils) (see Belgian beer). Belgians have a reputation for loving waffles and French fries, both originally from Belgium; the national food is steak (or mussels) with French fries.
External links
- Official site of the Belgian federal government
- Official site of Belgian tourist office in the Americas
- Telephone directory online
- Belgian Newspapers
- Wikitravel guide
- Belgium is celebrating the 175th anniversary of its independence and the 25th anniversary of the federal state
- bruessel-gui.de - Images: Brussels & Belgium
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- World history at KLMA
- L'aménagement linguistique dans le monde in French by Jacques Leclerc, University of Laval, Canada
- Portal of the INS to statisical publications about Belgium
- CIA World Fact Book
- Constitution of Belgium
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.