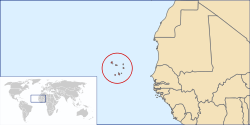
Cape Verde
| Rep√ļblica de Cabo Verde ¬†(Portuguese) Republic of Cape Verde |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Anthem:¬†C√Ęntico da Liberdade¬†(Portuguese) Song of Freedom |
||||||
| Capital (and largest city) | Praia 14¬į55‚Ä≤N 23¬į31‚Ä≤W | |||||
| Official languages | Portuguese | |||||
| Recognized regional languages | Cape Verdean Creole | |||||
| Ethnic groups  | Creole (mulatto) 71% African 28% European 1%[1] |
|||||
| Demonym | Cape Verdean | |||||
| Government | Parliamentary republic | |||||
|  -  | President | José Maria Neves | ||||
|  -  | Prime Minister | Ulisses Correia e Silva | ||||
| Independence | ||||||
|  -  | from Portugal | July 5, 1975  | ||||
| Area | ||||||
|  -  | Total | 4,033 km² (172nd) 1,557 sq mi  |
||||
|  -  | Water (%) | negligible | ||||
| Population | ||||||
|  -  | 2021 estimate | 589,451[1] (172nd) | ||||
|  -  | 2010 census | 491,875 (172nd) | ||||
|  -  | Density | 123.7/km² (89th) 325.0/sq mi |
||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2019 estimate | |||||
|  -  | Total | $4.323 billion  | ||||
|  -  | Per capita | $7,728[2]  | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate | |||||
|  -  | Total | $2.042 billion  | ||||
|  -  | Per capita | $3,651[2]  | ||||
| Currency | Cape Verdean escudo (CVE) |
|||||
| Time zone | CVT (UTC-1) | |||||
|  -  | Summer (DST) | not observed (UTC-1) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .cv | |||||
| Calling code | [[++238]] | |||||
The Republic of Cape Verde or Cape Verde is a republic located on an archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean, off the western coast of Africa. The previously uninhabited islands were discovered and colonized by the Portuguese in the fifteenth century; they subsequently became a trading center for African slaves. The Cape Verde islands experienced the longest period of European colonization of any African nation. The Portuguese remained in direct control from 1456 to 1975. Most Cape Verdeans descend from both groups, and their culture reflects this.
After independence, Cape Verde was led initially, along with Guinea-Bissau, by a Marxist party that imposed strict controls on the economy and politics of the nation. But a multiparty democracy emerged in 1991, and the government is liberalizing the economy to attract investment and donors. With few natural resources other than its beaches and mountains, Cape Verde is hoping to bring a growing number of tourists. Because of the lack of employment opportunities at home, more Cape Verdeans live in the United States and other countries than on the islands themselves, and their remittances home are a major boost to the economy.
Geography
Cape Verde is an archipelago off the coast of Africa. It is formed by ten main islands and eight islets. The main islands are:
- Barlaventos (northern island group)
- Santo Ant√£o
- S√£o Vicente
- Santa Luzia
- S√£o Nicolau
- Sal
- Boa Vista
- Sotaventos (southern island group)
- Maio
- Santiago
- Fogo
- Brava
Of these, only Santa Luzia is uninhabited. Presently it is a Natural Reserve. The island chain is of volcanic origin, but only Fogo has an active volcano, Mount Fogo, which reaches 9,281 ft (2,829 m) above sea level. Peaks on Santo Ant√£o and S√£o Tiago reach 6,493 ft (1,979 m) and 4,567 ft (1,392 m), respectively. All but three of the islands are quite mountainous, with prominent cliffs and deep ravines. High ground and southwestern slopes support lush vegetation because of moisture condensation. Only four islands have year-round running streams. Mindelo on S√£o Vicente is the principal port, but there are several other fine harbors.
Climate
A cold Atlantic current produces an arid atmosphere around the archipelago. From December to June it is cool and dry, with temperatures at sea level averaging 70¬įF (21¬įC); from July to November is warmer, with temperatures averaging 81¬įF (27¬įC).
Rainfall is sparse, around 5 in (13 cm) annually in the northern islands and 12 in (30 cm) in the south. The archipelago is subject to cyclical droughts.
History
Cape Verde was uninhabited when the Portuguese arrived in 1456, and the islands were thus made part of the Portuguese empire. Plantations were established and slaves imported from Africa to work on them. Due to its location off the coast of Africa, Cape Verde became an important port as well as a major center of the slave trade with Europe and the Americas.
Periodic droughts, made worse by deforestation and overgrazing, lead to the deaths of hundreds of thousands from starvation. In the mid-nineteenth century, as the slave trade came to an end, the colony's importance declined. Yet the population rebounded as a result of intermarriage between Africans and Portuguese. As the number of mixed people grew, more opportunities opened up for Cape Verdeans than in other Portuguese colonies. A quarter of the population could read at the time of independence, compared to 5 percent in Guinea-Bissau. It was these educated Cape Verdeans, particularly Amilcar Cabral, who provided the leadership for the long struggle for independence from Portugal.
In 1975, after Salazar's death, the islands finally achieved independence, partially due to the efforts of the African Party for the Independence of Guinea-Bissau and Cape Verde (PAIGC). After independence, the PAIGC attempted to unite Cape Verde and Guinea-Bissau into one nation, with the PAIGC controlling both governments, but a coup in the latter nation in 1980 resulted in strains that ended these plans. In Cape Verde itself the PAICV (affiliated with the PAIGC) governed until elections were held in 1991 that resulted in a change of government. The PAICV was re-elected in 2001 and 2006, but has largely abandoned its initial Marxist leanings and embraced the market economy.
Politics
The government of Cape Verde is a republic with a president who is head of state and a prime minister who heads the government, based on a constitution that was established in 1980. Elections are held for both the prime minister and president, who both govern for five-year terms. Members of the General Assembly are elected as well, and they appoint the Supreme Tribunal of Justice.
Prior to independence, Cape Verde was subject to Portuguese civil and criminal codes, and most of those provisions remain in effect. A Supreme Tribunal of Justice hears appeals from subregional and regional tribunals. Informal popular tribunals serve as courts of the first instance for minor disputes. The 1992 constitution provides for a judiciary independent from the executive branch.
The African Party for the Independence of Cape Verde (Partido Africano da Independência do Cabo Verde, or PAICV) was the sole legal political party from 1975 until 1990. In 1990, the constitution was amended to legalize opposition parties.
Economy
Cape Verde is a small nation that lacks resources and experiences severe droughts as well as water shortages. Agriculture is somewhat stymied by lack of rain and is restricted to only four islands for most of the year. Only 20 percent of the land can be used for crops. Torrential rains and floods erode the usable land. Beans and maize are the important crops. Others include bananas, yams, manioc, pumpkins, sugarcane, coffee, and groundnuts (peanuts). Although 70 percent of the people live in rural areas, the lack of rainfall means the country must import most of its food and depends on international aid during droughts. It must also import all its petroleum products, so it has been hurt by the rise in oil prices.
During its ten years in power, the Movement for Democracy reversed the previous socialist policies of the PAICV and liberalized the economy. Freeing prices and exchange rates from government control and a privatization program encouraged foreign investors and donors. The investors are eager to take advantage of Cape Verde's low wages and high unemployment rate. The Chinese have financed several major development projects, such as a dam, a stadium, and a cement factory, and have also invested in the ceramics and fishing industries. The fishing potential, mostly lobster and tuna, is not fully exploited. Industries are food and beverages, fish processing, shoes and garments, salt mining, and ship repair.
The nation's GDP is largely from the services industry. Cape Verde's economy has largely grown since the late 1990s and is now considered a country of average human development. Cape Verde has significant cooperation with Portugal at every level of the economy, leading it to fix its currency first to the Portuguese escudo, then the euro since 1999. Most of the recent growth has been in tourism, which has good potential due to its white beaches and sunny weather.
Former Portuguese Prime Minister José Manuel Durão Barroso promised to help integrate Cape Verde within the European Union sphere of influence via greater cooperation with Portugal. In March 2005, former Portuguese President Mário Soares launched a petition urging the European Union to start membership talks with Cape Verde.
Cape Verde annually runs a high trade deficit, financed by foreign aid and remittances from emigrants.
Cape Verde is used as a transshipment point for Latin American cocaine destined for Western Europe; however, the lack of a well-developed financial system limits the country's utility as a money-laundering center.
Demographics
Most inhabitants of Cape Verde are descendants of the white Portuguese settlers and black African slaves. More Cape Verdeans live abroad than in Cape Verde, with significant emigrant communities in the United States, Portugal, and Angola. There are also significant numbers of Cape Verdeans in São Tomé and Príncipe, Senegal, France, and the Netherlands.
Housing on the islands varies greatly, from the elegant, Mediterranean-style homes of Europeans and middle-class Cape Verdeans to the simple timber and mud-block houses of peasants. At last estimate, approximately 95 percent of all housing units were one-floor dwellings with external walls mostly of stone and clay, stone and cement, or all stone.
Water is delivered by pipes, wells, tanks and cisterns, and other sources.
Violence and discrimination against women and abuse of children were serious problems. Domestic violence against women, including wife beating, was widespread. There were police and judicial delays in acting on abuse cases. Violence against women was the subject of extensive public service media coverage. Rape, including spousal rape, is a criminal offense, but the government generally did not effectively enforce the law. Sexual harassment is very common but not culturally perceived as a crime.
Under the law women enjoy the same rights as men, including rights under family law, property law, and in the judicial system. Despite legal prohibitions against sex discrimination and provisions for full equality, including equal pay for equal work, discrimination against women continues. Although often paid less than men for comparable work, women are making inroads in various professions, especially in the private sector.
The government provided free primary health care for children, and boys and girls had equal access.
Child abuse and mistreatment and sexual violence against children were serious problems. The media reported cases of sexual abuse against children and adolescents. Government efforts to address these problems were inadequate. Child labor is a problem. In the cities, children wash cars on the streets, and in the countryside, within low-income families, children do domestic work.
Education
The government provides free and universal education for all children aged 6 to 12. Education is compulsory until age 11; secondary education is free only for children whose families with a low annual income.
Culture
The culture of Cape Verde reflects its mixed Portuguese and African roots. It is well known for its diverse forms of music such as morna (the Cape Verdian fado, often expressing homesickness and nostalgia) and the urban Cape Verdean kizomba, and a wide variety of dances: the soft morna, the funana (a sensual mixed Portuguese and African dance), the extreme sensuality of coladeira, and the African batuko. These indicate the diverse origins of Cape Verde's residents, which is also reflected in the cuisine and the arts. Indigenously, the term "Cabo" is used to refer to residents as well as the culture of Cape Verde. The best-known singer is Cesario Evora, whose recordings are near the top of World Music charts.
The national food is cachupa, a stew combining several kinds of meat (often sausage or bacon) or fish with various beans and corn. Another common dish is pastel de milho, a mixture of meat or fish and some vegetables, wrapped in a pastry made from boiled potatoes and corn flour, then deep-fried.
Traditional crafts include weaving, ceramics, basketry, mat making, and batik.
Religion
Over 90 percent of the population is Roman Catholic. Protestant churches account for a small percentage, with the largest denomination being the Church of the Nazarene. There are also groups of Muslims and Baha'i. Several African traditional religions are practiced, especially on S√£o Tiago, with some traditional elements infused in other religions. Though there is no state religion, Catholic religious holidays are officially observed.
Literature
Cape Verdean literature is one of the richest of Lusitanian Africa. Prior to independence, a major theme was the longing for liberation. Other themes are slavery, racial discrimination, and the sea.
- Poets: Frusoni Sergio, Tavares Eug√©nio, B. L√©za, Jo√£o Cleofas Martins, Lu√≠s Romano de Madeira Melo, Ov√≠dio Martins, Barbosa Jorge, Fortes Corsino Ant√≥nio, Baltasar Lopes (Osvaldo Alc√Ęntara), Jo√£o V√°rio, Oswaldo Os√≥rio, Arm√©nio Vieira, Vadinho Velhinho, Jos√© Lu√≠s Tavares, etc.
- Authors: Manuel Lopes - Movimento Claridade, Almeida Germano, Luís Romano de Madeira Melo, Germano de Almeida, Orlanda Amarilis, Jorge Vera Cruz Barbosa, Pedro Cardoso, Mário José Domingues, Daniel Filipe, Mário Alberto Fonseca de Almeida, Corsino António Fortes, Arnaldo Carlos de Vasconcelos França, António Aurélio Gonçalves, Aguinaldo Brito Fonseca, Ovídio de Sousa Martins, Osvaldo Osório, Dulce Almada Duarte, Manuel Veiga
- Composers: Manuel de Novas, Vasco Martins
Media
There are three independent newspapers and one state‚ÄĎowned newspaper; six independent radio stations and one state‚ÄĎowned radio station; and one state‚ÄĎowned television station and two foreign‚ÄĎowned stations. Foreign broadcasts are permitted. The independent media were active and expressed a wide variety of views without restriction. Journalists are independent of government control and not required to reveal their sources.
The law requires a formal licensing mechanism for mass media, including government authorization to broadcast; however, there were no reports in 2006 that licenses were denied or revoked or that the government refused to authorize broadcasts.
There are no government restrictions on access to the Internet or reports that the government monitored e‚ÄĎmail or Internet chat rooms. Individuals and groups could engage in the peaceful expression of views via the Internet, including electronic mail.
Language
Cape Verde's official language is Portuguese, but Portuguese Creoles (Crioulo, Criol, Krioulo, Caboverdiano), which vary considerably from island to island, are widely used. Each of the nine inhabited islands has its own creole, with the greatest differences between the creole of Santiago and that of Santo Ant√£o.
Notes
- ‚ÜĎ 1.0 1.1 CIA, Cape Verde The World Factbook. Retrieved January 21, 2022.
- ‚ÜĎ 2.0 2.1 Report for Selected Countries and Subjects International Monetary Fund. Retrieved January 21, 2022.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Balla, Marcel Gomes. Antonio's Island. Braiswick, 2002. ISBN 1898030480
- Cutter, Charles Hickman. Africa, 2006. World Today series. Harpers Ferry, WV: Stryker-Post Publications, 2006. ISBN 1887985727
- Gailey, Harry A. History of Africa: Volume III, From 1945 to present. Malabar, FL: Robert E. Krieger Publishing Company, 1989. ISBN 0894642960
- Fitzpatrick, Mary. West Africa. Victoria, Australia: Lonely Planet Publications, 2002. ISBN 1740592492
External Links
All links retrieved November 25, 2023.
- Cabo Verde CIA The World Factbook.
- Cape Verde African Studies Center.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.