Difference between revisions of "Phosgene" - New World Encyclopedia
({{Paid}}) |
m (Protected "Phosgene": copyedited [edit=sysop:move=sysop]) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Claimed}}{{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}}{{Contracted}}{{Paid}} | + | {{Claimed}}{{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}}{{Contracted}}{{Paid}}{{copyedited}} |
{| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | {| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | ||
! {{chembox header}} | Phosgene | ! {{chembox header}} | Phosgene | ||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | '''Phosgene''' is the [[chemical compound]] with the [[chemical formula|formula]] COCl<sub>2</sub>. This highly [[toxic]] gas gained infamy as a [[chemical weapon]] during [[World War I]], but it is also a valuable industrial reagent and building block in [[organic synthesis]]. It is | + | '''Phosgene''' is the [[chemical compound]] with the [[chemical formula|formula]] COCl<sub>2</sub>. This highly [[toxic]] gas gained infamy as a [[chemical weapon]] during [[World War I]], but it is also a valuable industrial reagent and building block in [[organic synthesis]]. It is colorless, but can appear as a white or yellowish haze when released into air, due to refraction of light. In low concentrations, its odor resembles recently cut [[hay]] or green corn ([[maize]]), while at higher concentrations it may be strongly unpleasant. In addition to its industrial production, small amounts occur naturally from the breakdown of chlorinated compounds and the [[combustion]] of [[chlorine]]-containing [[organic chemistry|organic]] compounds. |
==History== | ==History== | ||
| − | Phosgene was synthesized by the chemist [[John Davy (chemist)|John Davy]] (1790-1868) in 1812 by exposing a mixture of carbon monoxide and chlorine to [[sunlight]]. He named it in reference to use of light to promote the reaction; from [[Greek language|Greek]], ''phos'' (light) and ''gene'' (born).<ref> | + | Phosgene was synthesized by the chemist [[John Davy (chemist)|John Davy]] (1790-1868) in 1812, by exposing a mixture of carbon monoxide and chlorine to [[sunlight]]. He named it in reference to use of light to promote the reaction; from [[Greek language|Greek]], ''phos'' (light) and ''gene'' (born).<ref>John Davy, On a gaseous compound of carbonic oxide and chlorine, ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London'' (1814)102: 144-151.</ref> It gradually became important in the chemical industry as the [[19th century]] progressed, particularly in dye manufacturing. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Phosgene was stockpiled as part of U.S. military arsenals until well after [[World War II]] in the form of aerial bombs and mortar rounds. | + | Phosgene was stockpiled as part of U.S. military arsenals until well after [[World War II]], in the form of aerial bombs and mortar rounds. The United States began disposing of its stockpiles in 1969. Even before then, the importance of phosgene as a weapon had declined as more lethal [[nerve agent]]s were developed. |
==Structure and basic properties== | ==Structure and basic properties== | ||
| − | Phosgene is a planar molecule. The C=O distance is 1.18 [[angstrom (unit)|Å]], the C---CL distance is 1.74 Å and the Cl---C---Cl angle is 111.8°.<ref>Nakata, | + | Phosgene is a planar molecule. The C=O distance is 1.18 [[angstrom (unit)|Å]], the C---CL distance is 1.74 Å and the Cl---C---Cl angle is 111.8°.<ref>M. Nakata, K. Kohata, T. Fukuyama, K. Kuchitsu, Molecular structure of Phosgene as studied by gas electron diffraction and microwave spectroscopy. The r<sub>z</sub> Structure and Isotope Effect, ''Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy'' (1980) Volume 83: 105-117.</ref> |
Phosgene is the simplest and one of the most [[electrophilic]] [[acid chloride]]s. This high electrophilicity is manifested in the tendency of phosgene to react with [[water]], that is, hydrolyze. This hydrolysis reaction releases [[hydrogen chloride]] and [[carbon dioxide]]: | Phosgene is the simplest and one of the most [[electrophilic]] [[acid chloride]]s. This high electrophilicity is manifested in the tendency of phosgene to react with [[water]], that is, hydrolyze. This hydrolysis reaction releases [[hydrogen chloride]] and [[carbon dioxide]]: | ||
| Line 116: | Line 109: | ||
==Production== | ==Production== | ||
| − | Around 2 million tons are produced annually<ref | + | Around 2 million tons of phosgene are produced annually<ref>CBWInfo.com, [http://cbwinfo.com/Chemical/Pulmonary/CG.shtml Choking Agent: CG.] Retrieved July 24, 2007.</ref> for use in the synthesis of fine chemicals and polymers. Industrially, phosgene is produced by passing purified [[carbon monoxide]] and [[chlorine]] gas through a bed of highly porous [[carbon]], which acts as a [[catalyst]]. The [[chemical equation]] for this [[chemical reaction|reaction]] follows: |
:CO + Cl<sub>2</sub> → COCl<sub>2</sub> | :CO + Cl<sub>2</sub> → COCl<sub>2</sub> | ||
The reaction is exothermic, therefore the reactor must be cooled to carry away the heat it produces. Typically, the reaction is conducted between 50 and 150 °C. Above 200 °C, phosgene decomposes back into carbon monoxide and chlorine. | The reaction is exothermic, therefore the reactor must be cooled to carry away the heat it produces. Typically, the reaction is conducted between 50 and 150 °C. Above 200 °C, phosgene decomposes back into carbon monoxide and chlorine. | ||
| Line 122: | Line 115: | ||
Upon [[ultraviolet]] radiation in the presence of [[oxygen]], [[chloroform]] slowly converts into phosgene via a [[radical reaction]]. To suppress this photodegradation, chloroform is often stored in brown-tinted glass containers. | Upon [[ultraviolet]] radiation in the presence of [[oxygen]], [[chloroform]] slowly converts into phosgene via a [[radical reaction]]. To suppress this photodegradation, chloroform is often stored in brown-tinted glass containers. | ||
| − | Because of safety issues, phosgene is almost always produced and consumed within the same plant. It is listed on [[List of Schedule 3 substances (CWC)|schedule 3]] of the [[Chemical Weapons Convention]]: | + | Because of safety issues, phosgene is almost always produced and consumed within the same plant. It is listed on [[List of Schedule 3 substances (CWC)|schedule 3]] of the [[Chemical Weapons Convention]]: All production sites manufacturing more than 30 tonnes per year must be declared to the [[OPCW]].<ref>Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons, [http://www.opcw.org/html/db/cwc/eng/cwc_annex_verification_part_VIII.html Regime for Schedule 3 Chemicals and Facilities Related to Such Chemicals.] Retrieved December 3, 2007.</ref> Although much less dangerous than [[nerve agent]]s, phosgene is still regarded as a viable chemical warfare agent. |
==Uses== | ==Uses== | ||
| − | Phosgene is used chiefly in the production of [[polymer]]s including [[polyurethane]]s, [[polycarbonate]]s, and [[polyurea]]s. It is also valuable in the preparation of fine chemicals.<ref> Hamley, | + | Phosgene is used chiefly in the production of [[polymer]]s including [[polyurethane]]s, [[polycarbonate]]s, and [[polyurea]]s. It is also valuable in the preparation of fine chemicals.<ref>P. Hamley, "Phosgene," ''Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis,'' (New York: John Wiley, 2001).</ref> In the laboratory for small-scale reactions, gaseous phosgene has increasingly been supplanted by more easily handled [[reagent]]s that effect comparable transformations: [[Diphosgene]] (chloroformic acid ester), which is a liquid at room temperature, or [[triphosgene]], a crystalline substance. Following are three of many useful reactions involving phosgene. |
====Synthesis of carbonates==== | ====Synthesis of carbonates==== | ||
[[Diol]]s react with phosgene to give either linear or cyclic carbonates (R = H, alkyl, aryl): | [[Diol]]s react with phosgene to give either linear or cyclic carbonates (R = H, alkyl, aryl): | ||
:HOCR<sub>2</sub>-X-CR<sub>2</sub>OH + COCl<sub>2</sub> → 1/n [OCR<sub>2</sub>-X-CR<sub>2</sub>OC(O)-]<sub>n</sub> + 2 HCl | :HOCR<sub>2</sub>-X-CR<sub>2</sub>OH + COCl<sub>2</sub> → 1/n [OCR<sub>2</sub>-X-CR<sub>2</sub>OC(O)-]<sub>n</sub> + 2 HCl | ||
| − | [[Polycarbonate]]s are an important class of engineering [[thermoplastic]], found for example in lenses in eye glasses. | + | [[Polycarbonate]]s are an important class of engineering [[thermoplastic]], found, for example, in lenses in eye glasses. |
====Synthesis of isocyanates==== | ====Synthesis of isocyanates==== | ||
| Line 141: | Line 134: | ||
It is also used to produce [[acid chloride]]s: | It is also used to produce [[acid chloride]]s: | ||
:RCO<sub>2</sub>H + COCl<sub>2</sub> → RC(O)Cl + HCl + [[Carbon dioxide|CO<sub>2</sub>]] | :RCO<sub>2</sub>H + COCl<sub>2</sub> → RC(O)Cl + HCl + [[Carbon dioxide|CO<sub>2</sub>]] | ||
| − | Such acid chlorides react with amines and | + | Such acid chlorides react with amines and [[alcohol]]s to give, respectively, [[amide]]s and [[ester]]s, which are common intermediates in the [[dye]], [[pesticide]], and [[pharmaceutical]] industries. Despite being an efficient method of synthesizing acyl chloride from carboxylic acids, laboratory safety issues led to the use of the less toxic [[thionyl chloride]]. |
==Safety== | ==Safety== | ||
| − | Phosgene is an insidious poison as the odor may not be noticed and symptoms may be slow to appear.<ref> | + | Phosgene is an insidious poison, as the odor may not be noticed and symptoms may be slow to appear.<ref>J. Borak and W.F. Diller, Phosgene exposure: mechanisms of injury and treatment strategies, ''Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine'' (2001) 42,2: 110-119.</ref> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Like many reactive chlorides, phosgene combines with water in the tissues of the respiratory tract to form [[hydrochloric acid]]. Phosgene is stable when stored in dry steel containers. Phosgene is a member of a class of organic chemicals known as [[alkylating agent]]s. These agents can react with both DNA and with enzymes ([[polymerase]]s) that are responsible for replication of DNA in cells. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Like many reactive chlorides, phosgene combines with water in the tissues of the respiratory tract to form [[hydrochloric acid]]. | ||
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
| Line 162: | Line 147: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | * Chang, Raymond. 2006. ''Chemistry'' | + | * Chang, Raymond. 2006. ''Chemistry,'' 9th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math. ISBN 0073221031 |
| − | + | * Cotton, F. Albert, and Geoffrey Wilkinson. 1980. ''Advanced Inorganic Chemistry,'' 4th ed. New York: Wiley. ISBN 0471027758 | |
| − | * Cotton, F. Albert, and Geoffrey Wilkinson. 1980. ''Advanced Inorganic Chemistry'' | + | * McMurry, J., and R.C. Fay. 2004. ''Chemistry,'' 4th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. ISBN 0131402080 |
| − | |||
| − | * McMurry, J., and R.C. Fay. 2004. ''Chemistry'' | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
Revision as of 21:29, 3 December 2007
| Phosgene | |
|---|---|
| |
| General | |
| Systematic name | Carbonyl chloride |
| Other names | Phosgene CG Carbonic acid dichloride Carbon dichloride oxide Carbon oxychloride Carbonyl dichloride Chloroformyl chloride Dichloroformaldehyde |
| Molecular formula | CCl2O |
| SMILES | O=C(Cl)Cl |
| Molar mass | 98.9 g mol-1 |
| Appearance | colorless gas |
| CAS number | [75-44-5] |
| Properties | |
| Density and phase | 4.248 g dm-3, gas (15 °C) |
| Solubility in water | hydrolysis |
| Other solvents | chlorocarbons |
| Melting point | −118 °C (155 K) |
| Boiling point | 8 °C (281 K) |
| Structure | |
| Molecular shape | Planar |
| Dipole moment | 1.17 D |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | http://www.vngas.com/pdf/g67.pdf |
| EU classification | Very toxic (T+) |
| NFPA 704 | |
| R-phrases | R26, R34 |
| S-phrases | S1/2, S9, S26, S36/37/39, S45 |
| Flash point | non-flammable |
| RTECS number | SY5600000 |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Carbonyl fluoride |
| Other cations | Nitrosyl chloride |
| Related compounds | Carbonic acid Urea Carbon monoxide Chloroformic acid |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | |
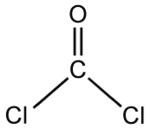
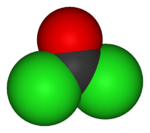
Phosgene is the chemical compound with the formula COCl2. This highly toxic gas gained infamy as a chemical weapon during World War I, but it is also a valuable industrial reagent and building block in organic synthesis. It is colorless, but can appear as a white or yellowish haze when released into air, due to refraction of light. In low concentrations, its odor resembles recently cut hay or green corn (maize), while at higher concentrations it may be strongly unpleasant. In addition to its industrial production, small amounts occur naturally from the breakdown of chlorinated compounds and the combustion of chlorine-containing organic compounds.
History
Phosgene was synthesized by the chemist John Davy (1790-1868) in 1812, by exposing a mixture of carbon monoxide and chlorine to sunlight. He named it in reference to use of light to promote the reaction; from Greek, phos (light) and gene (born).[1] It gradually became important in the chemical industry as the 19th century progressed, particularly in dye manufacturing.
Phosgene was stockpiled as part of U.S. military arsenals until well after World War II, in the form of aerial bombs and mortar rounds. The United States began disposing of its stockpiles in 1969. Even before then, the importance of phosgene as a weapon had declined as more lethal nerve agents were developed.
Structure and basic properties
Phosgene is a planar molecule. The C=O distance is 1.18 Å, the C---CL distance is 1.74 Å and the Cl---C---Cl angle is 111.8°.[2]
Phosgene is the simplest and one of the most electrophilic acid chlorides. This high electrophilicity is manifested in the tendency of phosgene to react with water, that is, hydrolyze. This hydrolysis reaction releases hydrogen chloride and carbon dioxide:
- COCl2 + H2O → CO2 + 2 HCl
The toxicity of phosgene is mainly due to the HCl that is released in this hydrolysis reaction.
Production
Around 2 million tons of phosgene are produced annually[3] for use in the synthesis of fine chemicals and polymers. Industrially, phosgene is produced by passing purified carbon monoxide and chlorine gas through a bed of highly porous carbon, which acts as a catalyst. The chemical equation for this reaction follows:
- CO + Cl2 → COCl2
The reaction is exothermic, therefore the reactor must be cooled to carry away the heat it produces. Typically, the reaction is conducted between 50 and 150 °C. Above 200 °C, phosgene decomposes back into carbon monoxide and chlorine.
Upon ultraviolet radiation in the presence of oxygen, chloroform slowly converts into phosgene via a radical reaction. To suppress this photodegradation, chloroform is often stored in brown-tinted glass containers.
Because of safety issues, phosgene is almost always produced and consumed within the same plant. It is listed on schedule 3 of the Chemical Weapons Convention: All production sites manufacturing more than 30 tonnes per year must be declared to the OPCW.[4] Although much less dangerous than nerve agents, phosgene is still regarded as a viable chemical warfare agent.
Uses
Phosgene is used chiefly in the production of polymers including polyurethanes, polycarbonates, and polyureas. It is also valuable in the preparation of fine chemicals.[5] In the laboratory for small-scale reactions, gaseous phosgene has increasingly been supplanted by more easily handled reagents that effect comparable transformations: Diphosgene (chloroformic acid ester), which is a liquid at room temperature, or triphosgene, a crystalline substance. Following are three of many useful reactions involving phosgene.
Synthesis of carbonates
Diols react with phosgene to give either linear or cyclic carbonates (R = H, alkyl, aryl):
- HOCR2-X-CR2OH + COCl2 → 1/n [OCR2-X-CR2OC(O)-]n + 2 HCl
Polycarbonates are an important class of engineering thermoplastic, found, for example, in lenses in eye glasses.
Synthesis of isocyanates
The synthesis of isocyanates from amines illustrates the electrophilic character of this reagent and its use in introducing the equivalent of "CO2+" (R = alkyl, aryl):
- RNH2 + COCl2 → RN=C=O + 2 HCl
Such reactions are conducted in the presence of a base such as pyridine that absorbs the hydrogen chloride.
Synthesis of acid chlorides and esters
It is also used to produce acid chlorides:
- RCO2H + COCl2 → RC(O)Cl + HCl + CO2
Such acid chlorides react with amines and alcohols to give, respectively, amides and esters, which are common intermediates in the dye, pesticide, and pharmaceutical industries. Despite being an efficient method of synthesizing acyl chloride from carboxylic acids, laboratory safety issues led to the use of the less toxic thionyl chloride.
Safety
Phosgene is an insidious poison, as the odor may not be noticed and symptoms may be slow to appear.[6]
Like many reactive chlorides, phosgene combines with water in the tissues of the respiratory tract to form hydrochloric acid. Phosgene is stable when stored in dry steel containers. Phosgene is a member of a class of organic chemicals known as alkylating agents. These agents can react with both DNA and with enzymes (polymerases) that are responsible for replication of DNA in cells.
Notes
- ↑ John Davy, On a gaseous compound of carbonic oxide and chlorine, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London (1814)102: 144-151.
- ↑ M. Nakata, K. Kohata, T. Fukuyama, K. Kuchitsu, Molecular structure of Phosgene as studied by gas electron diffraction and microwave spectroscopy. The rz Structure and Isotope Effect, Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy (1980) Volume 83: 105-117.
- ↑ CBWInfo.com, Choking Agent: CG. Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- ↑ Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons, Regime for Schedule 3 Chemicals and Facilities Related to Such Chemicals. Retrieved December 3, 2007.
- ↑ P. Hamley, "Phosgene," Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, (New York: John Wiley, 2001).
- ↑ J. Borak and W.F. Diller, Phosgene exposure: mechanisms of injury and treatment strategies, Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine (2001) 42,2: 110-119.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Chang, Raymond. 2006. Chemistry, 9th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math. ISBN 0073221031
- Cotton, F. Albert, and Geoffrey Wilkinson. 1980. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry, 4th ed. New York: Wiley. ISBN 0471027758
- McMurry, J., and R.C. Fay. 2004. Chemistry, 4th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. ISBN 0131402080
External links
- Davy's account of his discovery of phosgene Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- International Chemical Safety Card 0007 Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- U.S. CDC Emergency Preparedness & Response Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- U.S. EPA Acute Exposure Guideline Levels Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- CBWInfo website Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- History of chemical warfare during World War I Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- Use of Phosgene in WWII and in modern-day warfare (Refer to Section 4.C of the article) Retrieved July 24, 2007.
| Agents of Chemical Warfare | ||
|---|---|---|
| Blood agents: | Cyanogen chloride (CK) – Hydrogen cyanide (AC) | |
| Blister agents: | Lewisite (L) – Sulfur mustard gas (HD, H, HT, HL, HQ) – Nitrogen mustard gas (HN1, HN2, HN3) | |
| Nerve agents: | G-Agents: Tabun (GA) – Sarin (GB) – Soman (GD) – Cyclosarin (GF) | V-Agents: VE – VG – VM – VX | |
| Pulmonary agents: | Chlorine – Chloropicrin (PS) – Phosgene (CG) – Diphosgene (DP) | |
| Incapacitating agents: | Agent 15 (BZ) – KOLOKOL-1 | |
| Riot control agents: | Pepper spray (OC) – CS gas – CN gas (mace) – CR gas | |
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
