Difference between revisions of "Inuit" - New World Encyclopedia
| Line 303: | Line 303: | ||
* Kuhnlein, Harriet. ''Traditional Plant Foods of Canadian Indigenous Peoples: Nutrition, Botany and Use''. Taylor and Francis, 1991. ISBN 978-2881244650 | * Kuhnlein, Harriet. ''Traditional Plant Foods of Canadian Indigenous Peoples: Nutrition, Botany and Use''. Taylor and Francis, 1991. ISBN 978-2881244650 | ||
* McGrath, Melanie. ''The Long Exile: A Tale of Inuit Betrayal and Survival in the High Arctic''. Knopf, 2007. ISBN 978-1400040476 | * McGrath, Melanie. ''The Long Exile: A Tale of Inuit Betrayal and Survival in the High Arctic''. Knopf, 2007. ISBN 978-1400040476 | ||
| + | * Kleivan, Inge, and Birgitte Sonne. ''Eskimos, Greenland and Canada (Iconography of Religions Section 8 - Arctic Peoples)''. Leiden, The Netherlands: Brill Academic Publishers, 1997. ISBN 9004071601 | ||
| + | * Laugrand, Frédéric, Jarich Oosten, and François Trudel. ''Representing Tuurngait: Memory and History in Nunavut, Volume 1''. Nunavut Arctic College, 2000. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * Asatchaq, and Tom Lowenstein. ''The Things That Were Said of Them Shaman Stories and Oral Histories of the Tikiġaq People''. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 1992. ISBN 0520065697 | |
| − | * Asatchaq, and Tom Lowenstein. '' | + | * Blake, Dale. ''Inuit Life Writings and Oral Traditions Inuit Myths''. St. John's, Newfoundland: Educational Resource Development Co-operative, 2001. ISBN 0968880606 |
| − | * Blake, Dale. ''Inuit Life Writings and Oral Traditions Inuit Myths''. St. John's, | ||
* Christopher, Neil, Louise Flaherty, and Larry MacDougall. ''Stories of the Amautalik Fantastic Beings from Inuit Myths and Legends''. Iqaluit, Nunavut: Inhabit Media, 2007. ISBN 9780978218638 | * Christopher, Neil, Louise Flaherty, and Larry MacDougall. ''Stories of the Amautalik Fantastic Beings from Inuit Myths and Legends''. Iqaluit, Nunavut: Inhabit Media, 2007. ISBN 9780978218638 | ||
| − | * Fienup-Riordan, Ann. ''Boundaries and Passages Rule and Ritual in Yup'ik Eskimo Oral Tradition''. | + | * Fienup-Riordan, Ann. ''Boundaries and Passages Rule and Ritual in Yup'ik Eskimo Oral Tradition''. Norman, OK: University of Oklahoma Press, 1994. ISBN 0806126043 |
| − | * Hall, Edwin S. ''The Eskimo Storyteller: Folktales from Noatak, Alaska''. Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 1975. | + | * Hall, Edwin S. ''The Eskimo Storyteller: Folktales from Noatak, Alaska''. Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee Press, 1975. |
| − | * Himmelheber, Hans, and Ann Fienup-Riordan. ''Where the Echo Began And Other Oral Traditions from Southwestern Alaska''. Fairbanks: University of Alaska Press, 2000. ISBN 1889963038 | + | * Himmelheber, Hans, and Ann Fienup-Riordan. ''Where the Echo Began And Other Oral Traditions from Southwestern Alaska''. Fairbanks, AK: University of Alaska Press, 2000. ISBN 1889963038 |
| − | * | + | * Houston, James A. ''James Houston's Treasury of Inuit Legends''. Orlando, FL: Harcourt, 2006. ISBN 0152059245 |
* MacDonald, John. ''The Arctic Sky Inuit Astronomy, Star Lore, and Legend''. Toronto: Royal Ontario Museum/Nunavut Research Institute, 1998. ISBN 0888544278 | * MacDonald, John. ''The Arctic Sky Inuit Astronomy, Star Lore, and Legend''. Toronto: Royal Ontario Museum/Nunavut Research Institute, 1998. ISBN 0888544278 | ||
* Millman, Lawrence, and Timothy White. ''A Kayak Full of Ghosts Eskimo Tales''. Santa Barbara: Capra Press, 1987. ISBN 0884962679 | * Millman, Lawrence, and Timothy White. ''A Kayak Full of Ghosts Eskimo Tales''. Santa Barbara: Capra Press, 1987. ISBN 0884962679 | ||
| − | * Norman, Howard A., Leo Dillon, and Diane Dillon. '' | + | * Norman, Howard A., Leo Dillon, and Diane Dillon. ''The Girl Who Dreamed Only Geese, and Other Tales of the Far North''. New York, NY: Harcourt Brace, 1997. ISBN 0152309799 |
* Spalding, Alex. ''Eight Inuit Myths = Inuit Unipkaaqtuat Pingasuniarvinilit''. Ottawa: National Museums of Canada, 1979. | * Spalding, Alex. ''Eight Inuit Myths = Inuit Unipkaaqtuat Pingasuniarvinilit''. Ottawa: National Museums of Canada, 1979. | ||
| − | * Wolfson, Evelyn. ''Inuit Mythology''. Berkeley Heights, NJ: Enslow Pub, 2001. ISBN 0766015599 | + | * Wolfson, Evelyn. ''Inuit Mythology''. Berkeley Heights, NJ: Enslow Pub, 2001. ISBN 0766015599 |
| − | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
Revision as of 17:56, 17 July 2008
| Inuit |
|---|
 Inuit grandmother and grandchild, 1995 |
| Total population |
| 150,000 |
| Regions with significant populations |
| Greenland, Canada, United States, Russia |
| Languages |
| Inuit language, Eskimo-Aleut languages |
| Religions |
| Christianity, Shamanism |
| Related ethnic groups |
| Aleuts, Yupiks |
Inuit (plural: the singular, Inuk, means "man" or "person") is a general term for a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic regions of Alaska, Greenland, and Canada. Until fairly recent times, there has been a remarkable homogeneity in the culture throughout these areas, which have traditionally relied on fish, marine mammals, and land animals for food, pets, transport, heat, light, clothing, tools, and shelter. The Inuit language is grouped under Eskimo-Aleut languages.[1]
The Inuit people live throughout most of the Canadian Arctic and subarctic: in the territory of Nunavut ("our land"); the northern third of Quebec, in an area called Nunavik ("place to live"); the coastal region of Labrador, in an area called Nunatsiavut ("Our Beautiful Land"); in various parts of the Northwest Territories, mainly on the coast of the Arctic Ocean and the Yukon territory. Alaskan Inupiat live on the North Slope of Alaska and the Seward Peninsula. Greenland's Kalaallit are citizens of Denmark.
Nomenclature
In Canada and Greenland the term Eskimo has fallen out of favor, is considered pejorative,[2][3] and has been replaced by the term Inuit. However, while Inuit describes all of the Eskimo peoples in Canada and Greenland, that is not true in Alaska and Siberia. In Alaska the term Eskimo is commonly used, because it includes both Yupik and Inupiat, while Inuit is not accepted as a collective term or even specifically used for Inupiat (which technically is Inuit). No universal replacement term for Eskimo, inclusive of all Inuit and Yupik people, is accepted across the geographical area inhabited by the Inuit and Yupik peoples.[4]
Inuit, Yupik, and First Nations People
The Inuit Circumpolar Conference, a United Nations-recognised non-governmental organization (NGO), defines its constituency to include Canada's Inuit and Inuvialuit, Greenland's Kalaallit Inuit, Alaska's Inupiat and Yup'ik people, and the Siberian Yupik people of Russia.[5] However, the Yupik of Alaska and Siberia are not Inuit, and the Yupik languages are linguistically distinct from the Inuit languages.[4] Yupik people are not considered to be Inuit either by themselves or by ethnographers, and prefer to be called Yupik or Eskimo.
Canadian Inuit do not consider themselves, and are not usually considered by others, to be one of the First Nations, a term which normally applies to other indigenous peoples in Canada.[6] However, Inuit (and the Métis) are collectively recognised by the Constitution Act, 1982 as Aboriginal peoples in Canada.
The Inuit should not be confused with the Innu, a distinct First Nations people who live in northeastern Quebec and Labrador.
Some of the Inuit dialects were recorded in the 18th century, but until the latter half of the 20th century, most were not able to read and write in their own language. In the 1760s, Moravian missionaries arrived in Greenland, where they contributed to the development of a written system of language called Qaliujaaqpait, based on the Latin alphabet. The missionaries later brought this system to Labrador, from which it eventually spread as far as Alaska.[7]
Early history
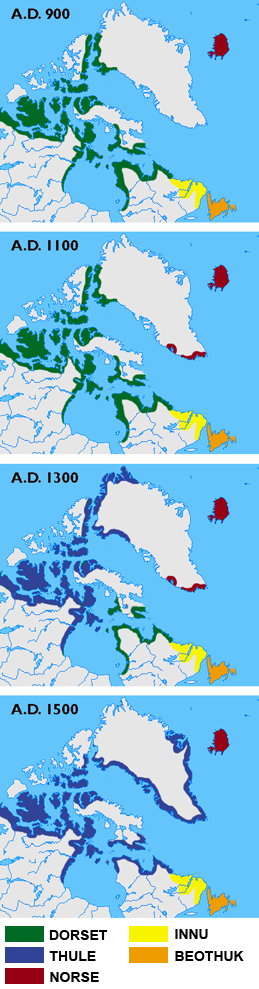
The Inuit are the descendants of what anthropologists call the Thule culture, who emerged from western Alaska around 1000 C.E. and spread eastwards across the Arctic, displacing the related Dorset culture (in Inuktitut, the Tuniit). Inuit legends speak of the Tuniit as "giants," people who were taller and stronger than the Inuit. Researchers believe that the Dorset culture lacked dogs, larger weapons and other technologies that gave the expanding Inuit society an advantage over them. By 1300, the Inuit had settled in west Greenland, and finally moved into east Greenland over the following century.
The Tuniit survived in Aivilik, Southampton and Coats Islands, until the beginning of the 20th century. They were known as Sadlermiut (Sallirmiut in the modern spelling). Their population had been ravaged by diseases brought by contact with Europeans, and the last of them fell in a flu epidemic caught from a passing whaler in 1902. The area has since been resettled by Inuit.
In Canada and Greenland the Inuit circulated almost exclusively north of the tree line, the de facto southern border of Inuit society. To the south, Native American Indian cultures were well established, and the culture and technology of Inuit society that served them so well in the Arctic was not suited to the subarctic, so they did not displace their southern neighbours. They had trade relations with more southern cultures, but as is the usual case boundary disputes were common and often a cause of aggressive actions.
Warfare, in general, was not uncommon among Inuit groups with sufficient population density. Inuit, such as the Nunatamiut (Uummarmiut), who inhabited the Mackenzie River delta area experienced common warfare whereas the Central Arctic Inuit lacked the population density to engage in warfare.
The first contact with Europeans came from the Vikings, who settled Greenland and explored the eastern Canadian coast. Norse literature speaks of skrælingar, most likely an undifferentiated label for all the native peoples of the Americas the Norse contacted, Tuniit, Inuit and Beothuks alike.
Sometime in the 13th century the Thule culture began arriving from what is now Canada. Norse accounts are scant. However, Norse made items have been found at Inuit campsites in Greenland. It is unclear whether they are the result of trade or plunder. One old account speaks of "small people" with whom the Norsemen fought. Ívar Bárðarson's[8] 14th century account mentions that one of the two Norse settlement areas, the western settlement, had been taken over by the skrælings. The reason why the Norse settlements failed is unclear, but the last record of them is from 1408, roughly the same period as the earliest Inuit settlements in east Greenland.
After roughly 1350, the climate grew colder during the Little Ice Age and the Inuit were forced to abandon hunting and whaling sites in the high Arctic. Bowhead whaling disappeared in Canada and Greenland (but continued in Alaska) and the Inuit had to subsist on a much poorer diet. Without whales, they lost access to essential raw materials for tools and architecture that were derived from whaling.
The changing climate forced the Inuit to also look south, pressuring them into the marginal niches along the edges of the tree line that Indians had not occupied, or where they were weak enough to coexist with. It is hard to say with any precision when the Inuit stopped their territorial expansion. There is evidence that they were still moving into new territory in southern Labrador in the 17th century, when they first began to interact with colonial North American civilisation.
Language
The Inuit mainly speak the traditional language, Inuktitut, but they also speak English, and French. Inuktitut is mainly spoken in the Yukon, Northwest Territories, and in some parts of Greenland.
The Inuktitut syllabary used in Canada is based on the Cree syllabary devised by the missionary James Evans. The present form of the syllabary for Canadian Inuktitut was adopted by the Inuit Cultural Institute in Canada in the 1970s. The Inuit in Alaska, the Inuvialuit, Inuinnaqtun speakers, and Inuit in Greenland and Labrador use the Roman alphabet, although it has been adapted for their use in different ways.
Though conventionally called a syllabary, the writing system has been classified by some observers as an abugida, since syllables starting with the same consonant have related glyphs rather than unrelated ones. All of the characters needed for the Inuktitut syllabary are available in the Unicode character repertoire. (See Unified Canadian Aboriginal Syllabics character table.) The territorial government of Nunavut, Canada has developed a TrueType font called Pigiarniq for computer displays. It was designed by Vancouver-based Tiro Typeworks.
Inuktitut is written in several different ways, depending on the dialect and region, but also on historical and political factors. Moravian missionaries, with the purpose of introducing the Inuit peoples to Christianity and the Bible, contributed to the development of an Inuktitut writing system in Greenland during the 1760s that was based on Roman orthography. They later travelled to Labrador in the 1800s, bringing the written Inuktitut with them. This roman alphabet writing scheme is distinguished by its inclusion of the letter kra. The Alaskan Yupik and Inupiat (who, in addition, developed their own system of hieroglyphics) and the Siberian Yupik also adopted the system of Roman orthography.
Eastern Canadian Inuit were the last to adopt the written word when, in the 1860s, missionaries imported the written system Qaniujaaqpait they had developed in their efforts to convert the Cree to Christianity. The very last Inuit peoples introduced to missionaries and writing were the Netsilik Inuit in Kugaaruk and north Baffin Island. The Netsilik adopted Qaniujaaqpait by the 1920s.
The "Greenlandic" system has been substantially reformed in recent years, making Labrador writing unique to Nunatsiavummiutut at this time. Most Inuktitut in Nunavut and Nunavik is written using a scheme called Qaniujaaqpait or Inuktitut syllabics, based on Canadian Aboriginal syllabics. The western part of Nunavut and the Northwest Territories use a Roman orthography (alphabet scheme) usually identified as Inuinnaqtun or Qaliujaaqpait, reflecting the predispositions of the missionaries who reached this area in the late 19th century and early 20th.
Cultural History

Diet
The Inuit have traditionally been hunters and fishers. They hunted, and still hunt, whales, walruses, caribou, seals, polar bears, muskoxen, birds, and at times other less commonly eaten animals such as foxes. The typical Inuit diet is high in protein and very high in fat - in their traditional diets, Inuit consumed an average of 75% of their daily energy intake from fat.[9] While it is not possible to cultivate plants for food in the Arctic, gathering those that are naturally available has always been typical. Grasses, tubers, roots, stems, berries, and seaweed were collected and preserved depending on the season and the location (kuanniq or edible seaweed).[10][11][12][13][14]
Lieb et al. (1926) published a case study of anthropologist Vilhjalmur Stefansson who lived with a group of Inuit.[15] The study focused on the fact that the Inuit's extremely low-carbohydrate diet had not had adverse effects on Stefansson's health, nor that of the Inuit. Stefansson (1946) also observed that the Inuit were able to get the necessary vitamins they needed from their traditional winter diet, which did not contain plant matter. In particular, he found that adequate vitamin C could be obtained from items in the Inuit's traditional diet of raw meat such as Ringed Seal liver and whale skin. While there was considerable skepticism when he reported these findings, they have been borne out in recent studies.[16]

Sea animals were hunted from single-passenger, covered seal-skin boats called qajaq[17] which were extraordinarily buoyant, and could easily be righted by a seated person, even if completely overturned. Because of this property, the Inuit design was copied, along with the Inuit word, by Europeans who still make and use them under the name kayak. They were originally the Inuit's design, but has been copied by people around the world. Kayaks have a special tube like design. Inuit also made umiak, larger, open boats made of wood frames covered with animal skins for transporting people, goods and dogs. They were 6 m (20 ft) - 12 m (39 ft) long. They also had a flat bottom so that it could come close to shore. In the winter, Inuit would also hunt sea mammals by patiently watching an aglu (breathing hole) in the ice and waiting for the air-breathing seals to use them, a technique also used by the polar bear, who hunts by seeking out holes in the ice and waiting nearby.
On land, the Inuit used dog sleds (qamutik) for transportation. The husky dog breed comes from Inuit breeding of dogs for transportation. A team of dogs in either a tandem/side-by-side or fan formation would pull a sled made of wood, animal bones, or the baleen from a whale's mouth, over the snow and ice. They used stars to navigate at sea and landmarks to navigate on land and possessed a comprehensive native system of toponymy. Where natural landmarks were insufficient, the Inuit would erect an inukshuk to compensate.
Dogs played an integral role in the annual routine of the Inuit. During the summer they became pack animals, sometimes dragging up to 20 kg (44 lb) of baggage. In the winter they pulled the sled and yearlong they assisted with hunting by sniffing out seal's holes and pestering polar bears. They loyally protected the Inuit villages by barking at bears and strangers. The Inuit generally favoured and tried to breed the most striking and handsome of dogs, especially ones with bright eyes and a healthy coat. Common husky dog breeds used by the Inuit were the Canadian Eskimo Dog (Qimmiq; Inuktitut for dog), the Greenland Dog, the Siberian Husky and the Alaskan Malamute. When the dog was newborn, the Inuit would perform rituals on the dog to give the pup favourable qualities. Its legs were pulled to make it grow strong and its nose was poked with a pin to enhance its sense of smell.
Industry, art, and clothing
Inuit industry relied almost exclusively on animal hides, driftwood, and bones, although some tools were also made out of worked stones, particularly the readily-worked soapstone. Walrus ivory was a particularly essential material, used to make knives. Art is a big part of Inuit history. Small sculptures of animals and human figures were made out of ivory and bone usually depicting everyday activities such as hunting and whaling.
Inuit made clothes and footwear from animal skins, sewn together using needles made from animal bones and threads made from other animal products such as sinew. The anorak (parka) is in essence made in a similar fashion by Arctic peoples from Europe through Asia and the Americas, including by the Inuit. In some groups of Inuit the hoods of women's parkas (amauti, plural amautiit) were traditionally made extra large, to protect the baby from the harsh wind when snuggled against the mother's back. Styles vary from region to region, from shape of the hood to length of the tails. Boots (kamik or mukluk) could be made of caribou or sealskin, and designs varied for men and women.
Certain Inuit also lived in temporary shelters made from snow in winter (the famous igloo), and during the few months of the year when temperatures were above freezing, they lived in tents made of animal skins and bones.
Gender roles, marriage, and community
The division of labour in traditional society had a strong gender component, but it was not absolute. The men were traditionally hunters and fishermen. The women took care of the children, cleaned huts, sewed, processed food, and cooked. However, there are numerous examples of women who hunted out of necessity or as a personal choice. At the same time, men who could be away from camp for several days, would be expected to know how to sew and cook.
The marital customs among the Inuit were not strictly monogamous: many Inuit relationships were implicitly or explicitly sexually open marriages; polygamy, divorce and remarriage were fairly common. Among some Inuit groups divorce required the approval of the community, if there were children, and particularly the agreement of the elders. Marriages were often arranged, sometimes in infancy, and occasionally forced on the couple by the community. Marriage was common for men when they became productive hunters, and for women at puberty. Family structure was flexible: a household might consist of a man and his wife or wives and children; it might include his parents or his wife's parents as well as adopted children; or it might be a larger formation of several siblings with their parents, wives and children; or even more than one family sharing dwellings and resources. Every household had its head, an elder or a particularly respected man.
There was also a larger notion of community, generally several families who shared a place where they wintered. Goods were shared within a household, and also to a significant extent within a whole community.
The Inuit were hunter-gatherers,[18] although it is commonly mistakenly believed that they were nomadic[citation needed], had no government, and had no conception of either private property or ownership of land. In fact they had very sophisticated concepts of private property and of land ownership that, as with their form of governance, was so drastically different than the Western concepts understood by European observers that the existence of such went entirely undocumented until well into the 20th century.[19]
Raiding
Virtually all Inuit cultures have oral traditions of raids by other indigenous peoples such as the Bloody Falls Massacre, even including fellow Inuit, and of taking vengeance on them in return. Western observers often regarded these tales as generally not entirely accurate historical accounts, but more as self-serving myths. But evidence shows that Inuit cultures had very accurate methods of teaching historical accounts to each new generation.[20]
The historic account of violence against outsiders does make clear that there was a history of hostile contact within the Inuit cultures and with other cultures.[21] It also makes it very clear that Inuit nations existed, and at times confederations of those nations too. The known confederations were usually formed for defensive purposes, generally to defend against a very prosperous, and thus very strong, nation. Alternately, people who lived in less productive geographical areas tended to be less warlike, having to spend more time producing food.
Justice with Inuit cultures was moderated by the form of governance that gave significant power to the elders in such decisions. But even then, as in most cultures around the world, it could be harsh and often included capital punishment for serious crimes against the community or even against an individual. It is also noted that during raids the Inuit, like their non-Inuit neighbors, tended to be merciless. [22]
Suicide, murder, and death
"A pervasive European myth about Inuit is that they killed elderly and unproductive people."[23] This is not generally true.[24][25][26] In a culture with an oral history, elders are the keepers of communal knowledge, effectively the community library[27], and there are cultural taboos against sacrificing elders because they are of extreme value as the repository of knowledge.[28][29]
When food is not sufficient there is little doubt that the elderly are the least likely to survive. It is also true that in an extreme case of famine the Inuit fully understood that a hunter was necessarily the one to feed on whatever food was left if there was to be any hope of obtaining more food.
However, a common response to desperate conditions and the threat of starvation was infanticide, which did sometimes entail abandoning an infant in hopes that someone less desperate might find and adopt him or her before the cold or the wildlife finished him or her off. All Inuit tribes practiced some form of infanticide.
It was long presumed by anthropologists that Inuit cultures routinely killed children born with physical defects. The type of presumption has been based mostly on theorizing by people educated in Western cultures about how an Inuit culture could survive and function, and had very little to do with science or archaeology. Between 1982 and 1994, however, a storm with high winds caused ocean waves to erode part of the bluffs near Barrow, Alaska, and a body was discovered to have been washed out of the mud. Unfortunately the storm claimed the body, which was not recovered. But examination of the eroded bank indicated that an ancient house, perhaps with other remains, was likely to be claimed by the next storm. The site (known as the "Ukkuqsi archaeological site") was excavated. Several frozen bodies (now known as the "frozen family") were recovered, autopsies were performed, and they were interred as the first burials in the then new Imaiqsaun Cemetery south of Barrow.[30] Years later another body washed out of the bluff - that of a female child, approximately 9 years old, who had clearly been born with a congenital birth defect.[31] This child had never been able to walk, but must have been cared for by family throughout her life.[32] That body, dated at about 1200 C.E., suggests that Inuit culture has long valued children, including those with birth defects.
During the 19th century, the Western Arctic suffered a population decline of close to 90% of their population resulting from foreign diseases including tuberculosis, measles, influenza, and smallpox. Autopsies near Greenland reveal that, more commonly pneumonia, kidney diseases, trichinosis, malnutrition, and degenerative disorders may have contributed to mass deaths among different Inuit tribes. The Inuit believed that the cause of the disease came from a spiritual origin, and cures were said to be possible through confession.[33]
Traditional law
Inuit traditional laws are anthropologically different to Western law concepts. 'Customary law' was thought nonexistent in Inuit society before the introduction of the Canadian legal system. Hoebel, in 1954, concluded that only 'rudimentary law' existed amongst the Inuit.
Indeed, prior to about 1970 it is impossible to find even one reference to a Western observer who was aware that any form of governance existed among any Inuit people. [19]
- maligait refers to what has to be followed
- piqujait refers to what has to be done
- tirigusuusiit refers to what has to be not done
If someone's action went against the tirigusuusiit, maligait or piqujait, the angakkuq might have to intervene, lest the consequences be dire to the individual or the community.[34]
- We are told today that Inuit never had laws or "maligait." Why? They say because they are not written on paper. When I think of paper, I think you can tear it up, and the laws are gone. The laws of the Inuit are not on paper.
—Mariano Aupilaarjuk, Rankin Inlet, Nunavut, "Perspectives on Traditional Law"[35]
- We are told today that Inuit never had laws or "maligait." Why? They say because they are not written on paper. When I think of paper, I think you can tear it up, and the laws are gone. The laws of the Inuit are not on paper.
Traditional beliefs
The Inuit people inhabit the land stretching from southeast Alaska to Greenland, an environment that heavily influenced a mythology filled with adventure tales of whale and walrus hunts. Long winter months of waiting for caribou herds or sitting near breathing holes hunting seals gave birth to stories of mysterious and sudden appearance of ghosts and fantastic creatures. Some Inuit looked into the aurora borealis, or northern lights, to find images of their family and friends dancing in the next life, and they relied upon the angakkuq (shaman), while the nearest thing to a central deity was the Old Woman (Sedna), who lived beneath the sea. The waters, a central food source, were believed to contain great gods.
The Inuit practiced a form of shamanism based on animist principles. They believed that all things had a form of spirit, just like humans, and that to some extent these spirits could be influenced by a pantheon of supernatural entities that could be appeased when one required some animal or inanimate thing to act in a certain way. The angakkuq of a community of Inuit was not the leader, but rather a sort of healer and psychotherapist, who tended wounds and offered advice, as well as invoking the spirits to assist people in their lives. His or her role was to see, interpret and exhort the subtle and unseen. Angakkuqs were not trained, they were held to be born with the ability.
Inuit religion was closely tied to a system of rituals that were integrated into the daily life of the people. These rituals were simple but held to be necessary. According to a customary Inuit saying, "The great peril of our existence lies in the fact that our diet consists entirely of souls." By believing that all things, including animals, have souls like those of humans, any hunt that failed to show appropriate respect and customary supplication would only give the liberated spirits cause to avenge themselves.
The harshness and randomness of life in the Arctic ensured that Inuit lived with concern for the uncontrollable, where a streak of bad luck could destroy an entire community. To offend a spirit was to risk its interference with an already marginal existence. The Inuit understand that they work in harmony with supernatural powers to provide the necessities of day-to-day survival.
Mythology
Inuit mythology has many similarities to the religions of other polar regions. Inuit traditional religious practices could be very briefly summarised as a form of shamanism based on animist principles.
In some respects, Inuit mythology stretches the common conception of what the term "mythology" means. Unlike Greek mythology, for example, at least a few people have believed in it, without interruption, from the distant past up to and including the present time. While the dominant religious system of the Inuit today is Christianity, many Inuit do still hold to at least some element of their traditional religious beliefs. Some see the Inuit as having adapted traditional beliefs to a greater or lesser degree to Christianity, while others would argue that it is rather the reverse that it true: The Inuit have adapted Christianity to their worldview.
Inuit traditional cosmology is not religion in the usual theological sense, and is similar to what most people think of as mythology only in that it is a narrative about the world and the place of people in it. In the words of Inuit writer Rachel Attituq Qitsualik:
The Inuit cosmos is ruled by no one. There are no divine mother and father figures. There are no wind gods and solar creators. There are no eternal punishments in the hereafter, as there are no punishments for children or adults in the here and now.
Indeed, the traditional stories, rituals and taboos of the Inuit are so tied into the fearful and precautionary culture required by their harsh environment that it raises the question as to whether they qualify as beliefs at all, much less religion. Knud Rasmussen asked his guide and friend Aua, an angakkuq (shaman), about Inuit religious beliefs among the Iglulingmiut (people of Igloolik) and was told: "We don't believe. We fear." Living in a varied and irregular world, the Inuit traditionally did not worship anything, but they feared much. Some authors debate the conclusions we might deduce from Aua's words, because the angakkuq was under the influence of missionaries, and later he even converted to Christianity—converted people often see the ideas in polarisation and contrasts, the authors say. Their study also analyses beliefs of several Inuit groups, concluding (among others) that fear was not diffuse.[36]
- Anirniit
The Inuit believed that all things had a form of spirit or soul (in Inuktitut: anirniq - breath; plural anirniit), just like humans. These spirits were held to persist after death - a common belief present in practically all human societies. However, the belief in the pervasiveness of spirits - the root of Inuit myth structure - has consequences. According to a customary Inuit saying "The great peril of our existence lies in the fact that our diet consists entirely of souls." By believing that all things - including animals - have souls like those of humans, killing an animal is little different from killing a person. Once the anirniq of the dead - animal or human - is liberated, it is free to take revenge. The spirit of the dead can only be placated by obedience to custom, avoiding taboos, and performing the right rituals.
The harshness and randomness of life in the Arctic ensured that Inuit lived constantly in fear of unseen forces. A run of bad luck could end an entire community, and begging potentially angry and vengeful but unseen powers for the necessities of day-to-day survival is a common consequence of a precarious existence even in modern society. For the Inuit, to offend an anirniq was to risk extinction. The principal role of the angakkuq in Inuit society was to advise and remind people of the rituals and taboos they needed to obey to placate the spirits, since he was held to be able to see and contact them.
The anirniit were seen to be a part of the sila - the sky or air around them - and were merely borrowed from it. Although each person's anirniq was individual, shaped by the life and body it inhabited, at the same time it was part of a larger whole. This enabled Inuit to borrow the powers or characteristics of an anirniq by taking its name. Furthermore, the spirits of a single class of thing - be it sea mammals, Polar Bears, or plants - were in some sense held to be the same, and could be invoked through a sort of keeper or master who was connected in some fashion with that class of thing. In some cases, it is the anirniq of a human or animal who became a figure of respect or influence over animals things through some action, recounted in a traditional tale. In other cases, it is a tuurngaq, as described below.
Since the arrival of Christianity among the Inuit, anirniq has become the accepted word for a soul in the Christian sense. This is the root word for a number of other Christian terms: anirnisiaq means angel and God is rendered as anirnialuk - the great spirit.
- Tuurngait
Some spirits were by nature unconnected to physical bodies. These figures were called tuurngait (singular tuurngaq) and were regarded as evil and monstruous, responsible for bad hunts and broken tools. They could also possess humans, as recounted in the story of Atanarjuat. The angakkuq could fight or exorcise them, or they could be held at bay by rituals; but they could also be caught and enslaved by an angakkuq, who could then turn them against free tuurngait.
Tuurngaq has, with Christianisation, taken on the additional meaning of demon in the Christian belief system.
- Angakuit
The angakkuq (Inuktitut syllabics ᐊᖓᑦᑯᖅ[37] or ᐊᖓᒃᑯᖅ[38], also angakuq; plural angakuit) of a community of Inuit was not the leader, but rather a sort of healer and psychotherapist, who tended wounds and offered advice, as well as invoking the spirits to assist people in their lives, or as often as not fighting them off. His or her role was to see, interpret and exhort the subtle and unseen. Angakkuq were not trained - they were held to be born with the ability and to show it as they matured. Rhythmic drums, chants and dances were often used in the performance of the duties of the angakkuq. Illumination (Inuktitut: qaumaniq) was often used by the angakkuq to describe a spiritual aura, the removal of which could, in their opinion, result in death.
The function of the angakkuq has largely disappeared in Christianized Inuit society.
- Other deities
A number of other Inuit myth figures were thought to hold power over some specific part of the Inuit world. These include such deities as Sedna (or Sanna), the master of sea animals, Nanook (or Nanuk) the master of polar bears, and Tekkeitsertok (or Tuktusiaqtuq), the master of caribou.
Shamanism
Among the Canadian Inuit, the shaman was known as an Angakkuq[39] (Inuktitut) or Angatkuq[17] (Inuvialuktun) (Inuktitut syllabics ᐊᖓᑦᑯᖅ).
Iglulik
According to Aua (an informant and friend of the anthropologist Rasmussen), one of the shaman's tasks among the Iglulik Inuit is to help the community in times when marine animals, which are kept by the Sea Woman (Takanaluk-arnaluk) in a pit in her house, are scarce. If taboo breaches that displease her lead to the failure of sea hunts, the shaman must visit her. Several barriers must be surmounted (such as a wall or a dog) and in some instances even the Sea Woman herself must be fought. If the shaman succeeds in appeasing her the animals will be released as normal.
The Iglulik variant of a myth explaining the Sea Woman’s origins involves a girl and her father. The girl did not want to marry. However, a bird managed to trick her into marriage and took her to an island. The girl's father managed to rescue his daughter, but the bird created a storm which threatened to sink their boat. Out of fear the father threw his daughter into the ocean, and cut her fingers as she tried to climb back into the boat. The cut joints became various sea mammals and the girl became a ruler of marine animals, living under the sea. Later on her remorseful father joined her.
This local variant differs from several others, like that of the Netsiliks, which is about an orphan girl mistreated by her community.
Aua also passed on information about the ability of an apprentice shaman to see themself as a skeleton,[40] naming each part using the specific shaman language.[40]
Inuit at Amitsoq Lake
For the Inuit at Amitsoq Lake (a rich fishing ground) sewing of many items was seasonally prohibited. Boot soles, for example could only be sewn far away from settlements in designated places.[41] Children at Amitsoq had a game called tunangusartut in which they imitated the adults behavior towards the spirits, including shamanizing, even reciting the same verbal formulae as shamans. This game was not considered offensive because a "spirit can understand the joke."[42]
Netsilik Inuit
The Netsilik Inuit (Netsilingmiut - People of the Seal) live in a region with an extremely long winter and stormy conditions in the spring, where starvation was a common danger.[43]
The cosmos of many other Eskimo cultures include protective guardian powers, but for the Netsilik the general hardship of life resulted in the extensive use of such measures, and even dogs could have amulets.[44] Unlike the Igluliks, the Netsilik used a large number of amulets. In one recorded instance, a young boy had eighty amulets, so many that he could hardly play.[45][43] In addition one man had seventeen names taken from his ancestors that were intended to protect him.[43][46]
Among the Netsilik, tattooing provided power that could affect which world a woman goes to after her death.[47]
The Sea Woman was known as Nuliayuk "the lubricous one".[48] If the people breached certain taboos, she would hold the marine animals in the tank of her lamp. When this happened the shaman had to visit her to beg for game. The Netsilik myth concerning her origin stated that she was an orphan girl who had been mistreated by her community.[49]
Another cosmic being known as Moon Man was thought to be friendly towards people and their souls as they arrive in celestial places.[50][51] This belief differs from that of the Greenland Eskimos, where the Moon’s anger was feared as a consequence of some taboo breaches.[50]
Sila was a sophisticated concept among Eskimo cultures (where its manifestation varied). Often associated with weather, it was conceived of as a power contained in people.[52] Among the Netsilik, Sila was imagined as male. The Netsilik (and Copper Eskimos) held that Sila originated as a giant baby whose parents were killed in combat between giants.[53]
Caribou Inuit
"Caribou Inuit" is a collective name for several inland groups (the Krenermiut, Aonarktormiut, Harvaktormiut, Padlermiut and Ahearmiut) living in an area bordered by the tree line and the west shore of Hudson Bay. They do not form a political unit and contacts between the groups are loose, but they share an inland lifestyle and exhibit some cultural unity. In the recent past, the Padlermiuts did have contact with the sea where they took part in seal hunts.[54]
The Caribou had a dualistic concept of the soul. The soul associated with respiration was called umaffia (place of life)[55] and the personal soul of a child was called tarneq (corresponding to the nappan of the Copper Eskimos). The tarneq was considered so weak that it needed the guardianship of a name-soul of a dead relative. The presence of the ancestor in the body of the child was felt to contribute to a more gentle behavior, especially among boys.[56] This belief amounted to a form of reincarnation.[55][57]
Because of their inland lifestyle, the Caribou had no belief concerning a Sea Woman. Other cosmic beings, variously named Sila or Pinga, take her place, controlling caribou instead of marine animals. Some groups made a distinction between the two figures, while others considered them the same. Sacrificial offerings to them could promote luck in hunting.[58]
Caribou shamans performed fortune-telling through qilaneq, a technique of asking a qila (spirit). The shaman placed his glove on the ground, and raised his staff and belt over it. The qila then entered the glove and drew the staff to itself. Qilaneq was practiced among several other Eskimo groups, where it was used to receive "yes" or "no" answers to questions.[59][60]
Copper Inuit
As mentioned, shamanhood among Eskimo peoples was a diverse phenomenon, just like the various Eskimo cultures themselves. Similar remarks apply for other beliefs: term silap inua / sila, hillap inua / hilla (among Inuit), ellam yua / ella (among Yup'ik) was used with some diversity among the groups.[61] In many instances it refers “outer space,” “intellect,” “weather,” “sky,” “universe”:[62][63][61][64][65] there may be some correspondence with the presocratic concept of logos.[66][62] In some other groups, this concept was more personified (/s l̥am juɣwa/ among Siberian Yupik).[67]
Among Copper Inuit, this “Wind Indweller” concept has some relatedness to their shamanhood: shamans were believed to obtain their power from this indweller, moreover, even their helping spirits were termed as silap inue.[68]
Since the arrival of Europeans
Canada
The lives of Paleo-Eskimos of the far north were largely unaffected by the arrival of visiting Norsemen except for mutual trade (McGhee 1992:194). Labrador Eskimo have had the longest continuous contact with Europeans (Kleivan 1966:9). After the disappearance of the Norse colonies in Greenland, the Inuit had no contact with Europeans for at least a century. By the mid 16th century, Basque fishermen were already working the Labrador coast and had established whaling stations on land, such as been excavated at Red Bay. The Inuit appear not to have interfered with their operations, but they raided the stations in winter for tools, and particularly worked iron, which they adapted to native needs.
Martin Frobisher's 1576 search for the Northwest Passage was the first well-documented post-Columbian contact between Europeans and Inuit. Frobisher's expedition landed on Baffin Island, not far from the town now called Iqaluit, but long known as Frobisher Bay. This first contact went poorly. Martin Frobisher, attempting to find the Northwest Passage, encountered Inuit on Resolution Island. Five sailors jumped ship and became part of Inuit mythology. The homesick sailors, tired of their adventure, attempted to leave in a small vessel and vanished. Frobisher brought an unwilling Inuk to England, doubtless the first Inuk ever to visit Europe. The Inuit oral tradition, in contrast, recounts the natives helping Frobisher's crewmen, whom they believed had been abandoned.
The semi-nomadic eco-centred Inuit were fishers and hunters harvesting lakes, seas, ice platforms and tundra. While there are some allegations that Inuit were hostile to early French and English explorers, fishers and whalers, more recent research suggests that the early relations with whaling stations along the Labrador coast and later James Bay were based on a mutual interest in trade (Mitchell 1996:49-62). In the final years of the 18th century, the Moravian Church began missionary activities in Labrador, supported by the British who were tired of the raids on their whaling stations. The Moravian missionaries could easily provide the Inuit with the iron and basic materials they had been stealing from whaling outposts, materials whose real cost to Europeans was almost nothing, but whose value to the Inuit was enormous and from then on contacts in Labrador were far more peaceful.
The European arrival tremendously damaged the Inuit way of life, causing mass death through new diseases introduced by whalers and explorers, and enormous social disruptions caused by the distorting effect of Europeans' material wealth. Nonetheless, Inuit society in the higher latitudes had largely persisted in isolation in the 19th century. The Hudson's Bay Company opened trading posts such as Great Whale River (1820), today the site of the twin villages of Whapmagoostui and Kuujjuarapik, where whale products of the commercial whale hunt were processed and furs traded. The British Naval Expedition (1821-3) led by Admiral William Edward Parry, which twice over wintered in Foxe Basin, provided the first informed, sympathetic and well-documented account of the economic, social and religious life of the Inuit. Parry stayed in what is now Igloolik over the second winter. Parry's writings with pen and ink illustrations of Inuit everyday life (1824) and those of Lyon (1824) were widely read (D'Anglure 2002:205). Captain George Comer's Inuit wife Shoofly known for her sewing skills and elegant attire (Driscoll 1980:6) was influential in convincing him to acquire more sewing accessories and beads for trade with Inuit. A few traders and missionaries circulated among the more accessible bands, and after 1904 they were accompanied by a handful of policemen. Unlike most Aboriginal peoples in Canada, however, the lands occupied by the Inuit were of little interest to European settlers—to the southerners, the homeland of the Inuit was a hostile hinterland. Southerners enjoyed lucrative careers as bureaucrats and service providers in the north, but very few southerners chose to retire there. In the early years of the 20th century, Canada, with its more hospitable lands largely settled, began to take a greater interest in its more peripheral territories, especially the fur and mineral rich hinterlands. By the late 1920s, there were no longer any Inuit who had not been contacted by traders, missionaries or government agents. In 1939, the Supreme Court of Canada found in Re Eskimos that the Inuit should be considered Indians and were thus under the jurisdiction of the federal government.
Native customs were worn down by the actions of the Royal Canadian Mounted Police, who enforced Canadian criminal law on Inuit who often could not understand what they had done wrong, and by missionaries who preached a moral code very different from the one they were used to. Many of the Inuit were systematically converted to Christianity in the 19th and 20th centuries, through rituals like the Siqqitiq.
World War II and the Cold War made Arctic Canada strategically important for the first time and, thanks to the development of modern aircraft, accessible year-round. The construction of air bases and the Distant Early Warning Line in the 1940s and 50s brought more intensive contacts with European society, particularly in the form of public education, which instilled and enforced foreign values disdainful of the traditional structure of Inuit society.
In the 1950s a process of relocation was undertaken by the Government of Canada for several reasons. These reasons were to include protecting Canada's sovereignty in the Arctic, lack of food in the area currently occupied and attempting to solve the "Eskimo problem," meaning the assimilation and end of the Inuit culture. One of the more notable relocations was undertaken in 1953, when 17 families were moved from Port Harrison (now Inukjuak, Quebec) to Resolute and Grise Fiord. They were dropped off in early September when winter had already arrived. The land they were sent to was very different from that in the Inukjuak area, being more barren, longer winters and polar night. They were told by the Royal Canadian Mounted Police they would be able to return within two years if conditions were not right. However, two years later more families were relocated to the High Arctic and it was to be thirty years before they were able to visit Inukjuak.[69][70][71]
By 1953, Canada's prime minister Louis St. Laurent publicly admitted, "Apparently we have administered the vast territories of the north in an almost continuing absence of mind." (Parker 1996:32) The government began to establish about forty permanent administrative centres to provide education, health and economic development services for Inuit (Parker 1996:32). Inuit from hundreds of smaller camps scattered across the north, began to congregate in these hamlets (Mitchell 1996:118).
Furthermore, regular visits from doctors and access to modern medical care raised the birth rate enormously. Before long, the Inuit population was beyond what traditional hunting and fishing could support. By the mid-1960s, encouraged first by missionaries, then by the prospect of paid jobs and government services, and finally forced by hunger and required by police, all Canadian Inuit lived year-round in permanent settlements. The nomadic migrations that were the central feature of Arctic life had for the most part disappeared. The Inuit, a once self-sufficient people in an extremely harsh environment, were in the span of perhaps two generations transformed into a small, impoverished minority lacking skills or resources to sell to the larger economy, but increasingly dependent on it for survival.
Although anthropologists like Diamond Jenness (1964) were quick to predict that Inuit culture was facing extinction, Inuit political activism was already emerging.
In the 1960s, the Canadian government funded the establishment of secular, government-operated high schools in the Northwest Territories (including what is now Nunavut) and Inuit areas in Quebec and Labrador along with the residential school system. The Inuit population was not large enough to support a full high school in every community, so this meant only a few schools were built, and students from across the territories were boarded there. These schools, in Aklavik, Iqaluit, Yellowknife, Inuvik and Kuujjuaq, brought together young Inuit from across the Arctic in one place for the first time, and exposed them to the rhetoric of civil and human rights that prevailed in Canada in the 1960s. This was a real wake-up call for Inuit, and it stimulated the emergence of a new generation of young Inuit activists in the late 1960s who came forward and pushed for respect for the Inuit and their territories.
The Inuit began to emerge as a political force in the late 1960s and early 1970s, shortly after the first graduates returned home. They formed new politically active associations in the early 1970s, starting with the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami in 1971, and more region specific organisations shortly afterwards, including the Northern Quebec Inuit Association (Makivik Corporation) and the Labrador Inuit Association. These activist movements began to change the direction of Inuit society in 1975 with the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement. This comprehensive land claims settlement for Quebec Inuit, along with a large cash settlement and substantial administrative autonomy in the new region of Nunavik, set the precedent for the settlements to follow. The Labrador Inuit submitted their land claim in 1977, although they had to wait until 2005 to have a signed land settlement establishing Nunatsiavut.
In 1982, the Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut (TFN) was incorporated, in order to take over negotiations for land claims on behalf of the Northwest Territories Inuit from the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, which became a joint association of the Inuit of Quebec, Labrador and the Northwest Territories.
The TFN worked for ten years and, in September 1992, came to a final agreement with the government of Canada. This agreement called for the separation of the Northwest Territories into an eastern territory whose aboriginal population would be predominately Inuit,[72] the future Nunavut, and a rump Northwest Territories in the west. It was the largest land claims agreement in Canadian history. In November 1992, the Nunavut Final Agreement was approved by nearly 85 percent of the Inuit of what would become Nunavut. As the final step in this long process, the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement was signed on May 25, 1993 in Iqaluit by Prime Minister Brian Mulroney and by Paul Quassa, the president of Nunavut Tunngavik Incorporated, which replaced the TFN with the ratification of the Nunavut Final Agreement. The Canadian Parliament passed the supporting legislation in June of the same year, enabling the 1999 establishment of Nunavut as a territorial entity.
The Inuvialuit are western Canadian Inuit who remained in the Northwest Territories when Nunavut split off. They live primarily in the Mackenzie River delta, on Banks Island, and in parts of Victoria Island in the Northwest Territories. They are officially represented by the Inuvialuit Regional Corporation and received a comprehensive land claims settlement in 1984, with the signing of the Inuvialuit Final Agreement.
With the establishment of Nunatsiavut in 2005, all the traditional Inuit lands in Canada are now covered by some sort of land claims agreement providing for regional autonomy.
Inuit communities in Canada continue to suffer under crushing unemployment, overcrowded housing, substance abuse, crime, violence and suicide. The problems Inuit face in the 21st century should not be underestimated. However, many Inuit are upbeat about the future. Arguably, their situation is better than it has been since the 14th century. Inuit arts, carving, print making, textiles and throat singing, are very popular, not only in Canada but globally, and Inuit artists are widely known. Indeed, Canada has, metaphorically, adopted some of the Inuit culture as a sort of national identity, using Inuit symbols like the inukshuk in unlikely places, such as its use as a symbol in the upcoming 2010 Winter Olympics in Vancouver. Respected art galleries display Inuit art, the largest collection of which is at the Winnipeg Art Gallery. Some Inuit languages such as Inuktitut, appears to have a more secure future in Quebec and Nunavut. There are a surprising number of Inuit, even those who now live in urban centres such as Ottawa, Montreal and Winnipeg, who have experienced living on the land in the traditional life style. People such as Legislative Assembly of Nunavut member, Levinia Brown and former Commissioner of Nunavut and the NWT, Helen Maksagak were born and lived the early part of their life "on the land." Inuit culture is alive and vibrant today in spite of the negative impacts of recent history.
Greenland
The Thule people arrived in Greenland in the 13th century. There they encountered the Norsemen, who had established colonies there since the late 10th century, as well as a later wave of the Dorset people.
Alaska
The Inuit people of Alaska are the Inupiat (from Inuit- people - and piaq/t real, i.e. 'real people') who live in the Northwest Arctic Borough, the North Slope Borough and the Bering Straits region. Barrow, the northernmost city in the United States, is in the Inupiat region. Their language is Iñupiaq (which is the singular form of Inupiat).
International issues
In recent years, circumpolar cultural and political groups like the Inuit Circumpolar Conference have come together to promote the Inuit and other northern people and to fight against ecological problems, such as global warming, which disproportionately affects the Inuit population. Global warming may cause Arctic mammal populations to decline. However, a recent study by Mitch Taylor shows that, contrary to the dire predictions, eleven of thirteen polar bear populations have remained stable or increased. The study also shows that the number of polar bears in western Hudson Bay is decreasing due to the effect of global warming, while the decrease of the population in Baffin Bay is directly associated with the over hunting of the bears by Greenland hunters.[73][74]
Modern culture
Well-known Inuit politicians include Premier of Nunavut, Paul Okalik, and Nancy Karetak-Lindell, MP for the riding of Nunavut.
An important biennial event, the Arctic Winter Games, is held in communities across the northern regions of the world, featuring traditional Inuit and northern sports as part of the events. A cultural event is also held. The games were first held in 1970, and while rotated usually among Alaska, Yukon and the Northwest Territories, they have also been held in Schefferville, Quebec in 1976, in Slave Lake, Alberta, and a joint Iqaluit, Nunavut-Nuuk, Greenland staging in 2002. In other sporting events, Jordin Tootoo became the first Inuk to play in the National Hockey League in the 2003-04 season, playing for the Nashville Predators.
Although Inuit life has changed significantly over the past century, many traditions continue. Traditional storytelling, mythology, and dancing remain important parts of the culture. Family and community are very important. The Inuktitut language is still spoken in many areas of the Arctic and is common on radio and in television programming.
Visual and performing arts are strong. In 2002 the first feature film in Inuktitut, Atanarjuat, was released worldwide to great critical and popular acclaim. It was directed by Zacharias Kunuk, and written, filmed, produced, directed, and acted almost entirely by Inuit of Igloolik. One of the most famous Inuit artists is Pitseolak Ashoona. Susan Aglukark is a popular singer. Mitiarjuk Attasie Nappaaluk works at preserving Inuktitut and has written the first novel published in that language.[75] In 2006, Cape Dorset was hailed as Canada's most artistic city, with 23% of the labour force employed in the arts.[76] Inuit art such as soapstone carvings is one of Nunavut's most important industries.
Recently, there has been an identity struggle among the younger generations of Inuit tribes between their traditional heritage and the modern society which their cultures have been forced to assimilate into in order to maintain a livelihood. With current dependence on modern society for necessities, (including governmental jobs, food, aid, medicine, etc), the Inuit people have had much interaction with and exposure to the societal norms outside their previous cultural boundaries. The stressors regarding the identity crisis among teenagers have led to disturbingly high numbers of suicide. The cases are so frequent that unfortunately suicide has become a sort of cultural norm.[citation needed]
A series of authors has focused upon increasing myopia in the youngest generations of Inuit. Myopia was almost unknown prior to the Inuit adoption of western culture. This phenomenon is also seen in other cultures (for example, Vanuatu). Principal theories are the change to a less nutritious western style diet, and exposure to over-illumination in intense early grade education.[77]
Economy today
Today, Inuit work in all sectors of the economy, including mining, oil and gas, construction, government and administrative services. Many Inuit still supplement their income through hunting. Tourism is a growing industry in the Inuit economy. Inuit guides take tourists on dogsled and hunting expeditions, and work with outfitting organizations. About 30 percent of Inuit derive part-time income from their sculpture, carving and print making. The Canadian Government has encouraged the Inuit to enter the broader Canadian life of business and trade through cooperative marketing.
The settlement of land claims in the Northwest Territories, Nunavut and Northern Quebec has given the Inuit money and a framework to develop and expand economic development activities. New emerging businesses include real estate, tourism, airlines and offshore fisheries.
Notes
- ↑ The Hunters of the Arctic. bambusspiele.de. Retrieved 2008-01-07.
- ↑ The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language: Fourth Edition
- ↑ Setting the Record Straight About Native Languages: What Does "Eskimo" Mean In Cree?
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lawrence Kaplan, "Inuit or Eskimo: Which names to use?". Alaska Native Language Center, University of Alaska Fairbanks. (2002) Retrieved June 5, 2008. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "kaplan" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Inuit Circumpolar Conference. (2006). "Charter." Inuit Circumpolar Conference (Canada). Retrieved on 2007-04-06.
- ↑ Native Groups. civilization.ca. Retrieved 2008-01-07.
- ↑ Project Naming, the identification of Inuit portrayed on photographic collections at Library and Archives Canada
- ↑ Ívar Bárðarson
- ↑ The Inuit Paradox. Retrieved 2008-03-25.
- ↑ Kuhnlein, Harriet [1991]. "Chapter 4. Descriptions and Uses of Plant Foods by Indigenous Peoples", Traditional Plant Foods of Canadian Indigenous Peoples: Nutrition, Botany and Use (Food and Nutrition in History and Anthropology), 1st edition, Taylor and Francis, pp. 26-29. ISBN 978-2881244650. Retrieved 2007-11-19.
- ↑ Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami. Arctic Wildlife. Retrieved 2007-11-20.
- ↑ Bennett, John and Rowley, Susan (2004). "Chapter 5. Gathering", Uqalurait: An Oral History of Nunavut. McGill-Queen's University Press, pp. 84-85. ISBN 978-0773523401. “...shorelines, Inuit gathered seaweed and shellfish. For some, these foods were a treat;...”
- ↑ kuanniq. Asuilaak Living Dictionary. Retrieved 2007-02-16.
- ↑ Bennett, John and Rowley, Susan (2004). "Chapter 5. Gathering", Uqalurait: An Oral History of Nunavut. McGill-Queen's University Press, pp. 78-85. ISBN 978-0773523401.
- ↑ Lieb et al. (1926). "The Effects of an Exclusive Long-Continued Meat Diet." JAMA, July 3, 1926
- ↑ Fediuk, Karen. 2000 Vitamin C in the Inuit diet: past and present. MA Thesis, School of Dietetics and Human Nutrition, McGill University 5-7; 95. Retrieved on: December 8, 2007.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 qajaq. Asuilaak Living Dictionary. Retrieved 2007-05-12. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "livingdict" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Snow, Dean R. "The first Americans and the differentiation of hunter-gatherer cultures." North America. Eds. Bruce G. Trigger and Wilcomb E. Washburn. Cambridge University Press, 1996. Cambridge Histories Online. Cambridge University Press. 05 May 2008 DOI:10.1017/CHOL9780521573924.004]
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Tirigusuusiit, Piqujait and Maligait: Inuit Perspectives on Traditional Law. Nunavut Arctic College. Retrieved 2007-10-17.
- ↑ Ernest S. Burch, Jr., PhD. From Skeptic to Believer.
- ↑ Fienup-Reordan, Ann (1990). "Eskimo Essays".
- ↑ War by Rachel Attituq Qitsualik
- ↑ Canadian Historical Review, Volume 79, Number 3, September 1998, University of Toronto Press, Page=591
- ↑ "Senilicide and Invalidicide among the Eskimos" by Rolf Kjellstrom in Folk: Dansk etnografisk tidsskrift, volume 16/17 (1974/75)
- ↑ "Notes on Eskimo Patterns of Suicide" by Alexander H. Leighton and Charles C. Hughes in Southwestern Journal of Anthropology, volume 11 (1955)
- ↑ Eskimos and Explorers, 2d ed., by Wendell H. Oswalt (1999)
- ↑ What is Traditional Knowledge?. Alaska Native Science Commission. Retrieved 2008-05-05.
- ↑ Kawagley, Angayuqaq (1995). A Yupiaq World View. ISBN 0881338591.
- ↑ Burch, Ernest S (1988). The Eskimos. University of Oklahoma Press, p21. ISBN 0806121262. “Given the importance that Eskimos attached to the aged, it is surprising that so many Westerners believe that they systematically eliminated elderly people as soon as they became incapable of performing the duties related to hunting or sewing.”
- ↑ Hess, Bill (2003). Gift of the Whale: The Inupiat Bowhead Hunt, A Sacred Tradition. Sasquatch Books. ISBN 1570613826.
- ↑ Barrow Visitors Guide 2006.
- ↑ Dear Young Girl.
- ↑ Information from "Inuit: Glimpses of an Arctic Past" by Morrison and Germain
- ↑ Tirigusuusiit and Maligait. Listening to our past. Retrieved 2007-10-17.
- ↑ Eileen, Travers (2003-01-01). When Survival Means Preserving Oral Traditions. voices-unabridged.org. Retrieved 2007-10-17.
- ↑ Kleivan & Sonne 1985:32
- ↑ Inuktitut Living Dictionary
- ↑ Inuktitut Living Dictionary
- ↑ angakkuq. Asuilaak Living Dictionary. Retrieved 2007-04-24.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 Merkur 1985:122
- ↑ Rasmussen 1965:244
- ↑ Rasmussen 1965:245
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 43.2 Rasmussen 1965:262
- ↑ Rasmussen 1965:268
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedK&S43 - ↑ Kleivan & Sonne 1985:15
- ↑ Rasmussen 1965:256,279
- ↑ Kleivan & Sonne 1985:27
- ↑ Rasmussen 1965:278
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 Kleivan & Sonne 1985:30
- ↑ Rasmussen 1965:279
- ↑ Rasmussen 1965:106
- ↑ Kleivan & Sonne 1985:31
- ↑ Gabus 1970:145
- ↑ 55.0 55.1 Kleivan & Sonne 1985:18
- ↑ Gabus 1970:111
- ↑ Gabus 1970:212
- ↑ Kleivan &Sonne 1985:31, 36
- ↑ Rasmussen 1965:108, Kleivan & Sonne 1985:26
- ↑ Gabus 1970:227–228
- ↑ 61.0 61.1 Kleivan & Sonne 1986: 31
- ↑ 62.0 62.1 Mousalimas 1997: 23–26
- ↑ Nuttall 1997: 75
- ↑ Merkur 1985: 235–240
- ↑ Gabus 1970: 230–234
- ↑ Saladin d'Anglure 1990
- ↑ Menovščikov 1968: 447
- ↑ Merkur 1985: 230
- ↑ 2.2 To Improve the Lives of Aboriginal People
- ↑
 PDF
PDF
- ↑ Broken Promises
- ↑ Aboriginal identity population in 2001
- ↑ Articnet, (May 1, 2006) Toronto Star (Dr. Mitchell Taylor)
- ↑ CBC News, Nunavut rethinks polar bear quotas as numbers drop, Last Updated: June 9, 2005
- ↑ Northern resident helps bridge the gap between cultures
- ↑ Cape Dorset named most 'artistic' municipality
- ↑ Short-sightedness may be tied to refined diet
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Bennett, John and Rowley, Susan. Uqalurait: An Oral History of Nunavut. McGill-Queen's University Press, 2004. ISBN 978-0773523401
- Briggs, Jean. Never in Anger: Portrait of an Eskimo Family. Harvard University Press, 2006. ISBN 0674608283
- Burch, Ernest S. The Eskimos. University of Oklahoma Press, 1988. ISBN 0806121262
- Gontran De Poncins. Kabloona: Among the Inuit. Graywolf Press, 1996. ISBN 1555972497
- Ruesch, Hans. Top Of The World. Pocket Books, 1973. ISBN 978-0671739287
- Hess, Bill. Gift of the Whale: The Inupiat Bowhead Hunt, A Sacred Tradition. Sasquatch Books, 2003. ISBN 1570613826
- Kawagley, Angayuqaq. A Yupiaq World View: A Pathway to Ecology and Spirit. Waveland Press, 1995. ISBN 0881338591
- Kuhnlein, Harriet. Traditional Plant Foods of Canadian Indigenous Peoples: Nutrition, Botany and Use. Taylor and Francis, 1991. ISBN 978-2881244650
- McGrath, Melanie. The Long Exile: A Tale of Inuit Betrayal and Survival in the High Arctic. Knopf, 2007. ISBN 978-1400040476
- Kleivan, Inge, and Birgitte Sonne. Eskimos, Greenland and Canada (Iconography of Religions Section 8 - Arctic Peoples). Leiden, The Netherlands: Brill Academic Publishers, 1997. ISBN 9004071601
- Laugrand, Frédéric, Jarich Oosten, and François Trudel. Representing Tuurngait: Memory and History in Nunavut, Volume 1. Nunavut Arctic College, 2000.
- Asatchaq, and Tom Lowenstein. The Things That Were Said of Them Shaman Stories and Oral Histories of the Tikiġaq People. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, 1992. ISBN 0520065697
- Blake, Dale. Inuit Life Writings and Oral Traditions Inuit Myths. St. John's, Newfoundland: Educational Resource Development Co-operative, 2001. ISBN 0968880606
- Christopher, Neil, Louise Flaherty, and Larry MacDougall. Stories of the Amautalik Fantastic Beings from Inuit Myths and Legends. Iqaluit, Nunavut: Inhabit Media, 2007. ISBN 9780978218638
- Fienup-Riordan, Ann. Boundaries and Passages Rule and Ritual in Yup'ik Eskimo Oral Tradition. Norman, OK: University of Oklahoma Press, 1994. ISBN 0806126043
- Hall, Edwin S. The Eskimo Storyteller: Folktales from Noatak, Alaska. Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee Press, 1975.
- Himmelheber, Hans, and Ann Fienup-Riordan. Where the Echo Began And Other Oral Traditions from Southwestern Alaska. Fairbanks, AK: University of Alaska Press, 2000. ISBN 1889963038
- Houston, James A. James Houston's Treasury of Inuit Legends. Orlando, FL: Harcourt, 2006. ISBN 0152059245
- MacDonald, John. The Arctic Sky Inuit Astronomy, Star Lore, and Legend. Toronto: Royal Ontario Museum/Nunavut Research Institute, 1998. ISBN 0888544278
- Millman, Lawrence, and Timothy White. A Kayak Full of Ghosts Eskimo Tales. Santa Barbara: Capra Press, 1987. ISBN 0884962679
- Norman, Howard A., Leo Dillon, and Diane Dillon. The Girl Who Dreamed Only Geese, and Other Tales of the Far North. New York, NY: Harcourt Brace, 1997. ISBN 0152309799
- Spalding, Alex. Eight Inuit Myths = Inuit Unipkaaqtuat Pingasuniarvinilit. Ottawa: National Museums of Canada, 1979.
- Wolfson, Evelyn. Inuit Mythology. Berkeley Heights, NJ: Enslow Pub, 2001. ISBN 0766015599
External links
- Aboriginal Perspectives View National Film Board of Canada films on Canada's Aboriginal Peoples.
- Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, Canada's National Inuit Organization
- The Inuvialuit of the Western Arctic
- CBC Digital Archives - An Inuit Education: Honouring a past, creating a future
- A History of Aboriginal Treaties and Relations in Canada This site includes contextual materials, links to digitized primary sources and summaries of primary source documents.
- Alaskool: Alaska Native Curriculum and Teacher Development Project
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.