Difference between revisions of "Kuril Islands" - New World Encyclopedia
Mary Anglin (talk | contribs) m |
Erin Kratt (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[Image:matua.jpg|290px|right|thumb|[[Matua]] Island as seen from [[Raikoke]].]] | [[Image:matua.jpg|290px|right|thumb|[[Matua]] Island as seen from [[Raikoke]].]] | ||
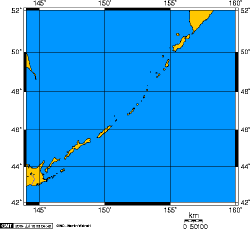
| − | The '''Kuril Islands''' or '''Kurile Islands''' in [[Russia]]'s [[Sakhalin Oblast]] region, are a volcanic island archipelago that stretches approximately 1,300 km (700 miles) northeast from [[Hokkaidō]], [[Japan]], to [[Kamchatka Peninsula|Kamchatka]], [[Russia]], separating the [[Sea of Okhotsk]] from the North [[Pacific]] Ocean. | + | The '''Kuril Islands''' or '''Kurile Islands''' in [[Russia]]'s [[Sakhalin Oblast]] region, are a volcanic island archipelago that stretches approximately 1,300 km (700 miles) northeast from [[Hokkaidō]], [[Japan]], to [[Kamchatka Peninsula|Kamchatka]], [[Russia]], separating the [[Sea of Okhotsk]] from the North [[Pacific]] Ocean. The chain consists of 22 main islands (most of which are volcanically active) and around 30 smaller islets with a total area of 15,600 km². |
| + | The islands are divided into three sub-groups that are separated by deep (up to 2,000 m) straits: the Northern Kuril Islands (Shumshu to Shiashkotan) are separated from the Central Kuril Islands (Matua to Simushir) by the Krusentern Strait. The Central Kuril Isalnds are, in turn, separated from the Southern Kuril Islands (Chirpoy to Kunashir) by the Boussole Strait<ref>[http://www.oceandots.com/pacific/kuril/ Kuril Islands], ''Kuril Islands''. Retrieved April 18, 2007</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Nomenclature == | == Nomenclature == | ||
| Line 166: | Line 169: | ||
*[[Organization of Karafuto Fortress]] | *[[Organization of Karafuto Fortress]] | ||
*[[Evacuation of Karafuto and Kuriles]] | *[[Evacuation of Karafuto and Kuriles]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Notes == | ||
| + | <References/> | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
Revision as of 17:59, 18 April 2007
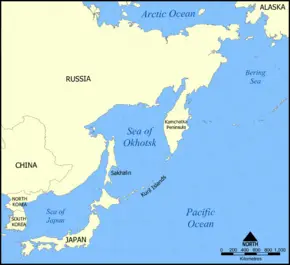
The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, are a volcanic island archipelago that stretches approximately 1,300 km (700 miles) northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. The chain consists of 22 main islands (most of which are volcanically active) and around 30 smaller islets with a total area of 15,600 km². The islands are divided into three sub-groups that are separated by deep (up to 2,000 m) straits: the Northern Kuril Islands (Shumshu to Shiashkotan) are separated from the Central Kuril Islands (Matua to Simushir) by the Krusentern Strait. The Central Kuril Isalnds are, in turn, separated from the Southern Kuril Islands (Chirpoy to Kunashir) by the Boussole Strait[1].
Nomenclature
The Kuril Islands are known in Japanese as the Chishima Islands (Kanji: 千島列島 / Hepburn Romaji: Chishima rettō [tɕiɕiːmaretːoː], literally, Thousand Islands Archipelago), also known as the Kuriru Islands (Kanji: クリル列島 / Hepburn Romaji: Kuriru rettō [kɯrirɯretːoː], literally, Kuril Archipelago). The name Kuril originates from the autonym of the aboriginal Ainu: "kur", meaning man. It may also be related to names for other islands that have traditionally been inhabited by the Ainu people, such as Kuyi or Kuye for Sakhalin and Kai for Hokkaidō.
Geography
The Kuril Islands form part of the ring of tectonic instability encircling the Pacific ocean referred to as the Ring of Fire. The islands themselves are summits of stratovolcanoes that are a direct result of the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Okhotsk Plate, which forms the Kuril Trench some 200 km east of the islands. The chain has around 100 volcanoes, some 40 of which are active, and many hot springs and fumaroles. There is frequent seismic activity, including an earthquake of magnitude 8.3 recorded on November 15, 2006, which resulted in tsunami waves up to 5 ft reaching the California coast.
The climate on the islands is generally severe, with long, cold, stormy winters and short and notoriously foggy summers. The average annual precipitation is 30–40 inches (760–1,000 mm), most of which falls as snow.
The chain ranges from temperate to sub-arctic climate types, and the vegatative cover consequently ranges from tundra in the north to dense spruce and larch forests on the larger southern islands. The highest elevations on the island are Alaid volcano (highest point 2339 m) on Atlasov Island at the northern end of the chain and Tyatya volcano (1819 m) on Kunashir Island at the southern end.
Landscape types and habitats on the island include many kinds of beach and rocky shores, cliffs, wide rivers and fast gravelly streams, forests, grasslands, alpine tundra, crater lakes and peat bogs. The soils are generally productive, due to the periodic influxes of volcanic ash and, in certain places, due to significant enrichment by seabird excrements. However, many of the steep, unconsolidated slopes are susceptible to landslides and newer volcanic activity can entirely denude a landscape.
Marine ecology
Due to their location along the Pacific shelf edge and the confluence of Okhotsk Sea gyre and the southward Oyashio current, the waters around the Kuril islands are among the most productive in the North Pacific, supporting a wide range and high abundance of marine life.
Invertebrates: Extensive kelp beds surrounding almost every island provide crucial habitat for sea urchins, various mollusks and countless other invertebrates and their associated predators. Many species of squid provide a principle component of the diet of many of the smaller marine mammals and birds along the chain.
Fish: Further offshore, walleye pollock, Pacific cod, several species of flatfish are of the greatest commercial importance. During the 1980's, migratory Japanese sardine was one of the most abundant fish in the summer and the main commercial species, but the fishery collapsed and by 1993 no sardines were reported caught leading to significant economic contraction in the few settlements on the islands. Several salmon species, notably pink and sockeye, spawn on some of the larger islands.
Pinnipeds: The Kuril islands are home to two species of eared seal, the Steller sea lion and northern fur seal, both of which aggregate on several smaller islands along the chain in the summer to form several of the largest reproductive rookeries in Russia. A distinct Kuril island subspecies of the common seal (Phoca vitulina stejnegeri) and Largha are also abundant.
Pinnipeds were a significant object of harvest for the indigenous populations of the Kuril islands, both for food and materials such as skin and bone. The long term fluctuations in the range and distribution of human settlements along the Kuril island presumably tracked the pinniped ranges. In historical times, fur seals were heavily exploited for their fur in the 19th and early 20th centuries and several of the largest reproductive rookeries, as on Raykoke island, were extirpated. In contrast, commercial harvest of the true seals and Steller sea lions has been relatively insignificant on the Kuril islands proper. Since the 1960's there has been essentially no additional harvest and the pinniped populations in the Kuril islands appear to be fairly healthy and in some cases expanding. The notable exception is the now extinct Japanese sea lion which was known to occasionally haul out on the Kuril islands.
Sea otters were exploited very heavily for their pelts in the 19th century. Indeed, the pursuit of the valuable otter pelts drove the expansion of the Russians onto the islands and much of the Japanese interest. Their numbers consequently dwindled rapidly. A near total ban on harvest since the mid 20th century has allowed the species to recover and they are now reasonably abundant throughout the chain.
Cetaceans: The most abundant cetaceans include orcas, harbor and Dall's porpoises. Baird's and Cuvier's beaked whales, fin whales, and sperm whales are also observed.
Seabirds: The Kuril islands are home to many millions of seabirds, including northern fulmars, tufted puffins, murres, kittiwakes, guillemots, auklets, petrels, gulls, cormorants. On many of the smaller islands in summer, where terrestrial predators are absent, virtually every possibly hummock, cliff niche or underneath of boulder is occupied by a nesting bird.
Terrestrial ecology
The composition of terrestrial species on the Kuril islands is dominated by Asian mainland taxa via migration from Hokkaido and Sakhalin Islands and by Kamchatkan taxa from the North. While highly diverse, there is a relatively low level of endemism.
Because of the generally smaller size and isolation of the central islands, few major terrestrial mammals have colonized these, though red and arctic foxes were introduced for the sake of the fur trade in the 1880's. The bulk of the terrestrial mammal biomass is taken up by rodents, many introduced in historical times. The largest southernmost and northernmost islands are inhabited by brown bear, foxes, martens. Some species of deer are found on the more southerly islands.
Among terrestrial birds, ravens, peregrine falcons, some wrens and wagtails are common.
History
The Kuril Islands first came under Japanese administration in the Edo period of Japan, in the form of claims by the Matsumae clan. It is claimed that the Japanese knew of the northern islands 370 years ago. (see "The Kuril Islands", John J Stephan, Clarendon Press, Oxford 1974, pp. 50–56). Trade between these islands and Ezo (Hokkaidō) existed long before then. On "Shōhō Onkuko Ezu", a map of Japan made by the Tokugawa shogunate, in 1644, there are 39 large and small islands shown northeast of the Shiretoko peninsula and Cape Nosappu.
Russia began to advance into the Kurils in the early 18th century. Although the Russians often sent expedition parties for research and hunted sea otters, they never went south of Urup island. This was because the Edo Shogunate controlled islands south of Iturup and had guards stationed on those islands to prevent incursions by foreigners.
In 1811, Captain Golovnin and his crew, who stopped at Kunashir during their hydrographic survey, were captured by retainers of the Nambu clan, and sent to the Matsumae authorities. Because a Japanese seaman, Takataya Kahei, was also captured by a Russian vessel near Kunashir, Japan and Russia entered into negotiations to establish the border between the two countries (1813).
The Treaty of Commerce, Navigation and Delimitation was concluded in 1855, and the border was established between Iturup and Urup. This border confirmed that Japanese territory stretched south from Iturup and Russian territory stretched north of Urup. Sakhalin remained a place where people from both countries could live. In 1875 (Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1875)) Japan relinquished all its rights in Sakhalin in exchange for Russian cession of all its rights in the Kuriles to Japan.
During the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905, Gunji, a retired Japanese military man and local settler in Shumshu, led an invading party to the Kamchatka coast. Russia sent reinforcements to the area to capture and intern this group. After the war was over, Japan received fishing rights in Russian waters as part of the Russo-Japanese fisheries agreement (until 1945).
During their armed intervention in Siberia 1918–1925, Japanese forces from the northern Kurils, along with United States and European forces, occupied southern Kamchatka. Japanese vessels made naval strikes against Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky.
The Soviet Union reclaimed the South of Sakhalin and the Kuriles by force at the end of World War II (Treaty of San Francisco), but Japan maintains a claim to the four southernmost islands of Kunashir, Iturup, Shikotan, and the Habomai rocks, together called the Northern Territories (see Kuril Islands dispute).
Japanese Administration in Kurile Archipelago
In 1869, the new, Meiji government established the Colonization Commission in Sapporo to aid in the development of the northern area. Ezo was renamed Hokkaidō and Kita Ezo later received the name of Karafuto. Eleven provinces and 86 districts were founded by Meiji government and were put under the control of feudal clans. Because the new Meiji government could not sufficiently cope with Russians moving to south Sakhalin, the Treaty for exchange of Sakhalin for the Kuril Island was concluded in 1875 and 18 islands to the north of Uruppu, which had belonged to Russia, were transferred to Japan.
Road networks and post offices were established on Kunashiri and Etorofu. Life on the islands became more stable when a regular sea route connecting islands with Hokkaidō was opened and a telegraphic system began. At the end of the Taisho era, towns and villages were organized in the northern territories and village offices were established on each island. The Habomai island were all part of Habomai Village for example. In other cases the town and village system was not adopted on islands north of Uruppu, which were under direct control of Nemuro Subprefectural office of the Hokkaidō government.
Each village had a district forestry system, a marine product examination center, a salmon hatchery, a post office, a police station, elementary school, Shinto temple, and other public facilities. In 1930, 8,300 people lived on Kunashiri island and 6,000 on Etorofu island, and most of them were engaged in coastal and high sea fishing.
Kuril during WW2
- Admiral Yamamoto Isoroku ordered the meeting of the Imperial Japanese Navy Strike force for the Hawaii Operation (Pearl Harbor Attack), during November 22, 1941 in Tankan or Hittokappu Bay, in Etorofu Island, South Kurils. The territory was chosen for its sparse population, lack of foreigners, and constant fog coverage. The Admiral ordered the move to Hawaii on the morning of November 26.
- During July 10, 1943, occurred the first bombardment against Shumushu and Paramushiro Japanese bases. From Alexai airfield 8 B-25 Mitchell from 77th Bomb. Sqdn. took off led by Capt. James L. Hudelson. This mission struck Paramushiro bases principally.
- Another mission, was flown during September 11, 1943, when Eleventh Air Force dispatched eight B-24 Liberators and 12 B-25s. But now the Japanese were alert and reinforced their defenses. 74 crew members in three B-24s and seven B-25 failed to return. Twenty two men were killed in action, one taken prisoner and 51 interned in Kamchatka, Russia.
- 11th Air Force implement other bombing mission against northern Kurils in February 5, 1944, when envoyed six B-24 from 404th Bomber Sqdn. and 16 P-38 from 54th Fighter Sqdn.
- Japanese report why in Matsuwa, military installations were subject of American air strikes between 1943–44.
- The Americans' "Operation Wedlock", diverted Japanese attention north and misled them about U.S. strategy in the Pacific. The plan included air strikes by USAAF and US Navy Bombers and U.S. Navy shore bombardment and submarine operations. Japanese increased their garrison in north Kurils from 8,000 in 1943 to 41,000 in 1944 and maintained more than 400 aircraft in Kurils and Hokkaidō area in anticipation that the Americans might invade from Alaska.
- Americans planners had briefly contemplated an invasion of northern Japan from Aleutians during fall of 1943, but rejected that idea as too risky and impractical. They considered the use of Boeing B-29 Superfortresses, on Amchitka and Shemya Bases, but rejected that idea too. U.S. military maintained interest in these plans when they ordered the expansion of bases in the western Aleutians, and major construction began on Shemya. Plans were put on the shelf for a possible invasion of Japan via the Northern route in 1945.
- In August 18–31, Soviet forces invaded the North and South Kurils.
- Eleventh Air Force, sent between August 24 and September 4, 1945, two B-24 in reconnaissance mission over North Kuril Islands to take photos of the Soviet occupation in the area. Soviet fighters intercepted and forced them away, a foretaste of the Cold war that lay ahead.
Kuril Islands dispute
The Kuril Island dispute is a dispute between Japan and Russia over sovereignty over the southernmost Kuril Islands. The disputed islands are currently under Russian administration as part of the Sakhalin Oblast, but are also claimed by Japan, which refers to them as the Northern Territories (北方領土 Hoppō Ryōdo) or Southern Chishima (南千島 Minami Chishima). The disputed islands are:
- Kunashir in Russian (Кунашир) or Kunashiri in Japanese (国後島)
- Iturup in Russian (Итуруп), or Etorofu in Japanese (択捉島)
- Shikotan in both Russian (Шикотан) and Japanese (色丹島)
- the Habomai rocks in both Russian (Хабомай) and Japanese (歯舞群島)
The dispute results from an ambiguity over the Treaty of San Francisco (1951). Under Article 2c, Japan renounces all right, title, and claim to the Kuril Islands, and to that portion of Sakhalin and the islands adjacent to it over which Japan acquired sovereignty as a consequence of the Treaty of Portsmouth signed on 5 September 1905. It was in accord with earlier agreements between Allied powers and one of the conditions of the USSR to enter in war with Japan.
However, the Soviet Union chose not to be a signatory to the San Francisco Treaty. And Article 2 of an earlier (1855) Russo-Japanese Treaty of Commerce, Navigation and Delimitation (the Treaty of Shimoda), which provided for an agreement on borders, states "Henceforth the boundary between the two nations shall lie between the islands of Etorofu and Uruppu. The whole of Etorofu shall belong to Japan; and the Kurile Islands, lying to the north of and including Uruppu, shall belong to Russia." Note that Kunashiri, Shikotan and Habomais Islands are not explicitly mentioned in the treaty.
Since the Soviet Union era, the occupation has been taught there that "the punishment to Japan"[citation needed] to rationalize the war trophy. There was practically no hostile activity between the USSR and Japan before the USSR renounced the Soviet-Japanese Neutrality Pact and declared war on Japan (Operation August Storm) on August 8, 1945.
On July 7, 2005, the European Parliament issued an official statement recommending the return of the territories in dispute[2], to which Russia protested immediately.
As of 2006, Russia's Putin administration has offered Japan the return of Shikotan and the Habomais (about 6% of the disputed area) if Japan renounce its claims to the other two islands. The Soviet-Japanese joint declaration of 1956 signed by the USSR and Japan promised at least Shikotan and the Habomais to be returned to Japan before a peace agreement could be made.
On 16 August 2006, a Russian border patrol boat found a Japanese vessel fishing near the disputed islands. The Japanese vessel allegedly defied several orders to stop, and made dangerous maneuvers. A Russian patrol opened preventive fire on the Japanese vessel to stop it. A Japanese 35-year-old crab fisherman, Mitsuhiro Morita,[3] was wounded in the head unintentionally and died later. It was the first fatality related to this dispute in 50 years.[4] However, the diplomatic fallout from this incident was minimal.[5]
Today
Today, roughly 30,000 people (ethnic Russians, Ukrainians, Belarusians, Tatars, Koreans, Nivkhs, Oroch, and Ainu) inhabit the Kuril Islands. About half of the population lives below the poverty line, according to the regional administration. Fishing is the primary occupation. The islands have strategic and economic value, in terms of fisheries and also mineral deposits of pyrite, sulfur, and various polymetallic ores.
Atlasov Island
The second northernmost, Atlasov Island (Oyakoba to the Japanese), is an almost perfect volcanic cone rising sheer out of the sea, and has led to many Japanese eulogies in haiku, wood-block prints, etc., extolling its beauty, much as they do the more well-known Mt. Fuji.
On January 13, 2007, an earthquake of magnitude 8.3 generated an alert of tsunami.
Islands
While in Russian sources the islands are mentioned for the first time in 1646, the earliest detailed information about them was provided by the explorer Vladimir Atlasov in 1697. In the 18th and early 19th centuries, the Kuril Islands were explored by Danila Antsiferov, I.Kozyrevsky, Ivan Yevreinov, Fyodor Luzhin, Martin Shpanberg, Adam Johann von Krusenstern, Vasily Golovnin, and Henry James Snow.
From north to south, the main islands are (alternative names given in parentheses are mainly Japanese):
- Shumshu (Shimushu)
- Atlasov Island (Oyakoba, Alaid or Araito)
- Paramushir (Paramushiro or Poromushiri)
- Antsiferov Island (Shirinki)
- Makanrushi (Makanrushiri)
- Onekotan (Onnekotan)
- Kharimkotan (Kharimukotan, Harumokotan)
- Ekarma (Ekaruma)
- Chirinkotan
- Shiashkotan (Shashukotan)
- Raikoke (Raykoke)
- Matua (Matsuwa)
- Rasshua (Rasuwa)
- Ushishir (Ushishiri or Ushichi)
- Ketoy (Ketoe or Ketoi)
- Simushir (Shimushiro or Shinshiru)
- Broutona (Buroton or Makanruru)
- Chirpoy (Chirinhoi)
- Brat Chirpoyev (Burato-Chiripoi)
- Urup (Uruppu)
- Iturup (Etorofu)
- Kunashir (Kunashiri)
- And the Lesser Kurils:
- Shikotan
- Habomai Rocks, including Seleni (Shibotsu), Taraku, Yuri, Akiyuri, Suisho, Zelioni (Kaigara), Oodoke and Moeshiri
See also
- Chishima Province
- Karafuto
- Organization of Hokkai(North) Army
- Organization of Kita and Minami Fortresses
- Governor-General of Karafuto
- Political Division of Karafuto Province(1905-1945)
- Organization of Karafuto Fortress
- Evacuation of Karafuto and Kuriles
Notes
- ↑ Kuril Islands, Kuril Islands. Retrieved April 18, 2007
- ↑ European Parliament resolution on relations between the EU, China and Taiwan and security in the Far East #15 [1]
- ↑ (August 28, 2006) Milestones. Time 168 (10): 12.
- ↑ Japan fisherman killed by Russia. BBC news (16 August 2006).
- ↑ Russia-Japan Island Row Intensifies with Killing of Fisherman. PINR (01 September 2006).
External links
- http://depts.washington.edu/ikip/index.shtml (Kuril Island Biocomplexity Project)
- Kuril Islands at Ocean Dots.com (includes space imagery)
- http://artedi.fish.washington.edu/okhotskia/ikip/index.htm
- http://www.mofa.go.jp/region/europe/russia/territory/index.html
- USGS Map showing location of Magnitude 8.3 Earthquake 46.616°N, 153.224°E Kuril Islands region, 2006 November 15 11:14:16 UTC
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.