Difference between revisions of "Great Rift Valley" - New World Encyclopedia
({{Paid}}) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) m |
||
| (20 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Ebapproved}}{{Copyedited}}{{Paid}}{{Approved}}{{Submitted}}{{Images OK}} |
| − | [[Image:Africa6 006.jpg|right|300px|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:Africa6 006.jpg|right|300px|thumb|right|The '''Great Rift Valley''' as it is visible near Eldoret, Kenya]] |
| − | The '''Great Rift Valley''' is a | + | The '''Great Rift Valley''' is a [[geography|geographical]] and [[geology|geological]] feature running north to south for around 4,000 miles (6,400 kilometers), from northern [[Syria]] to central [[Mozambique]] in [[East Africa]]. Astronauts say it is the most significant physical detail on the planet that is visible from space. In [[Africa]], the terrain ranges from salt flats more than 500 feet (152 meters) below sea level to towering, snow-capped [[mountain]]s. The Rift is known for its spectacular scenery and abundant, sometimes unique, wildlife. A series of some thirty [[lake]]s lies along its length; the three largest in Africa are known as the Great Lakes and include [[Lake Tanganyika]], the second deepest lake in the world, and [[Lake Victoria]], the second-largest freshwater lake by surface area in the world. Some of the oldest remains of ancestral humans have been found in in the African segment of the valley. |
| − | + | {{toc}} | |
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
[[Image:Aerial jordan.jpg|thumb|200|right|The Jordan Rift Valley from space]] | [[Image:Aerial jordan.jpg|thumb|200|right|The Jordan Rift Valley from space]] | ||
| − | [[Image:Greatrift.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Northern section of the Great Rift Valley | + | [[Image:Greatrift.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Northern section of the Great Rift Valley: the [[Sinai Peninsula]] is in the center and the [[Dead Sea]] and [[Jordan River]] valley are above]] |
| − | The Great Rift Valley varies in width from twenty to sixty miles (thirty to one hundred kilometers), and in depth from a few hundred to several thousand meters. The northernmost part of the Rift forms the Beqaa Valley in [[Lebanon]]. To the south, in [[Israel]], it is known as the Hula Valley separating the Galilee mountains and the [[Golan Heights]]. Farther south, the valley | + | The Great Rift Valley varies in width from twenty to sixty miles (thirty to one hundred kilometers), and in depth from a few hundred to several thousand meters. The northernmost part of the Rift forms the Beqaa Valley in [[Lebanon]]. To the south, in [[Israel]], it is known as the Hula Valley separating the Galilee mountains and the [[Golan Heights]]. Farther south, the valley is the home of the [[Jordan River]], which flows southward through Lake Hula into the [[Sea of Galilee]] in Israel and then continues south through the Jordan Valley into the [[Dead Sea]] on the Israeli-[[Jordan]]ian border. From the Dead Sea southward, the Rift is occupied by the Wadi Arabah and then the [[Gulf of Aqaba]] and the [[Red Sea]]. |
| − | + | {{readout||left|250px|The Great Rift Valley is such a significant physical feature on the [[earth]] that it is clearly visible from space}} | |
| − | The southern end of the Red Sea marks a fork in the rift. The Afar Triangle or Danakil Depression of [[Ethiopia]] and [[Eritrea]] is the probable location of a triple junction, which is possibly underlain by a [[mantle plume]]. | + | The southern end of the Red Sea marks a fork in the rift. The Afar Triangle or Danakil Depression of [[Ethiopia]] and [[Eritrea]] is the probable location of a [[triple junction]], which is possibly underlain by a [[mantle plume]] (an upwelling of abnormally hot rock within the earth's mantle that helps the earth to lose heat). The [[Gulf of Aden]] is an eastward continuation of the rift—before the rift opened, the Arabian Peninsula was attached to the Horn of Africa—and from this point the rift extends southeastward as part of the mid-oceanic ridge of the [[Indian Ocean]]. In a southwest direction the fault continues as the Great Rift Valley, which split the older Ethiopian highlands into two halves. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | In | + | In eastern Africa the valley divides into the '''Eastern Rift''' and the '''Western Rift'''. The Western Rift, also called the Albertine Rift, is edged by some of the highest mountains in Africa, including the Virunga Mountains, Mitumba Mountains, and Ruwenzori Range, and contains the Rift Valley lakes, which include some of the deepest lakes in the world (up to 1,470 meters deep at [[Lake Tanganyika]]). Many sites in the Albertine Rift are protected as national parks, wildlife reserves, or forest reserves. But there are several other sites important for conservation that require legal protection in the future, mainly in the [[Democratic Republic of Congo]]. |
| − | + | In [[Kenya]], the valley is deepest to the north of [[Nairobi]]. As the lakes in the Eastern Rift have no outlet to the sea, these lakes tend to be shallow and have a high [[mineral]] content as the evaporation of water leaves the salts behind. For example, Lake Magadi is almost solid [[sodium carbonate]], and Lakes Elmenteita, Baringo, Bogoria, and Nakuru are all strongly alkaline, while Lake Naivasha needs to be supplied by freshwater springs to support its biological variety. | |
| + | Sodium carbonate, however, creates an ideal breeding ground for [[algae]]. Several species of [[fish]], [[tilapia]] in particular, thrive in this environment. As a result, millions of [[bird]]s flock to these soda lakes to feast on the abundant food supply of algae and fish. Each of the lakes in the Rift Valley string has a slightly different water composition ranging from freshwater to extremely alkaline, highly saline to brackish. | ||
==Geothermal activity== | ==Geothermal activity== | ||
| − | + | Subterranean movement is common today as the Rift Valley is home to thirty active and semi-active [[volcano]]es and countless [[hot springs]] along its length. The formation of the Rift Valley continues, probably driven by [[mantle plume]]s. The associated geothermal activity and spreading at the rift has caused the lithosphere to thin from the typical sixty-mile (100-kilometer) thickness for continents to a mere 20 kilometers. If spreading continues, the lithosphere may rupture several million years from now, splitting eastern Africa off to form a new landmass. This would lead to the formation of a new mid-ocean ridge. | |
| − | Subterranean movement is common today as the Rift Valley is home to thirty active and semi-active [[volcano]]es and countless [[hot springs]] along its length. The formation of the Rift Valley continues, probably driven by [[mantle plume]]s | ||
The volcanic activity at this site and unusual concentration of hotspots has produced the volcanic mountains [[Mount Kilimanjaro]], Mount Kenya, Mount Karisimbi, Mount Nyiragongo, Mount Meru, and Mount Elgon, as well as the Crater Highlands in [[Tanzania]]. The Ol Doinyo Lengai volcano remains active and is currently the only [[carbonatite|natrocarbonatite]] volcano in the world. | The volcanic activity at this site and unusual concentration of hotspots has produced the volcanic mountains [[Mount Kilimanjaro]], Mount Kenya, Mount Karisimbi, Mount Nyiragongo, Mount Meru, and Mount Elgon, as well as the Crater Highlands in [[Tanzania]]. The Ol Doinyo Lengai volcano remains active and is currently the only [[carbonatite|natrocarbonatite]] volcano in the world. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 25: | ||
==History of exploration== | ==History of exploration== | ||
| − | The first [[Europe]]ans to penetrate Central and East Africa reported [[snow]] at the [[equator]] but were not initially believed. The Royal Geographical Society sent an expedition to the region in search of the Nile's source. The detailed reports of that trip helped [[Austria|Austrian]] geologist [[Eduard Suess]] formulate his theory that the system of valleys and lakes that crossed [[Arabia]] and [[Africa]] was part of a continuous trough. In 1891 he published a paper attributing the geology and structural geography between [[Syria]] and [[Malawi]] to interconnected movements | + | The first [[Europe]]ans to penetrate Central and East Africa reported [[snow]] at the [[equator]] but were not initially believed. The Royal Geographical Society sent an expedition to the region in search of the [[Nile River|Nile]]'s source. The detailed reports of that trip helped [[Austria|Austrian]] geologist [[Eduard Suess]] formulate his theory that the system of valleys and lakes that crossed [[Arabia]] and [[Africa]] was part of a continuous trough. In 1891 he published a paper attributing the geology and structural geography between [[Syria]] and [[Malawi]] to interconnected movements within the [[Earth]]. The following year, British explorer [[John Walter Gregory]] began his explorations of East Africa. His comparisons of geological strata led him to conclude that faulting, not erosion, had formed the valley to which he gave the name "Great Rift Valley," the name still used for the entire African Rift. |
==Discoveries in human evolution== | ==Discoveries in human evolution== | ||
| − | The Rift Valley has been a rich source of [[fossil]]s that allow study of [[human evolution]]. Richard Leakey has speculated that the diversity of environments resulting from the creation of the Rift Valley provided "an ideal setting for evolutionary change." The presence of multiple lakes in the region would have drawn animals, including [[hominid]]s. Furthermore, the rise and fall of lake levels and seasonal flooding of [[river]]s aided in burying and preserving [[bone]]s. The numerous active [[volcano]]es in the region provided volcanic ash that would later allow dating of the fossils that were found. | + | The Rift Valley has been a rich source of [[fossil]]s that allow study of [[human evolution]]. [[Richard Leakey]] has speculated that the diversity of environments resulting from the creation of the Rift Valley provided "an ideal setting for evolutionary change." The presence of multiple lakes in the region would have drawn animals, including [[hominid]]s. Furthermore, the rise and fall of lake levels and seasonal flooding of [[river]]s aided in burying and preserving [[bone]]s. The numerous active [[volcano]]es in the region provided volcanic ash that would later allow dating of the fossils that were found. |
| − | There is no reason to conclude that early hominids were confined to East Africa, but because the rapidly eroding highlands filled the valley with sediments, a favorable environment for the preservation of remains was created. The bones of several hominid ancestors of modern humans have been found there, including those of "Lucy" | + | There is no reason to conclude that early hominids were confined to East Africa, but because the rapidly eroding highlands filled the valley with sediments, a favorable environment for the preservation of remains was created. The bones of several hominid ancestors of modern humans have been found there, including those of "Lucy," a nearly complete [[Australopithecus]] skeleton that was discovered by [[anthropology|anthropologist]] [[Donald Johanson]]. The husband and wife team of [[Richard Leakey|Richard]] and [[Mary Leakey]] has also done significant work in this region. |
It has been suggested by scientists that the Rift's trough may have been an important route for human dispersal. | It has been suggested by scientists that the Rift's trough may have been an important route for human dispersal. | ||
==Great Lakes== | ==Great Lakes== | ||
| − | [[Image:EAfrica.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Map of East Africa showing some of the historically active volcanoes (red triangles) and the Afar Triangle (shaded, center) — a triple junction where three plates are pulling away from one another: the Arabian Plate, and the two parts of the African Plate (the Nubian and the Somalian) splitting along the East African Rift Zone (USGS) | + | [[Image:EAfrica.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Map of East Africa showing some of the historically active volcanoes (red triangles) and the Afar Triangle (shaded, center)—a triple junction where three plates are pulling away from one another: the Arabian Plate, and the two parts of the African Plate (the Nubian and the Somalian) splitting along the East African Rift Zone (USGS)]] |
| − | + | The African Rift Valley lakes include some of the oldest, largest, and deepest lakes in the world, and many are freshwater ecoregions of great [[biodiversity]], while others are alkaline or soda lakes supporting highly specialized organisms. | |
Two major lakes are located in [[Asia]]: The [[Dead Sea]] and the [[Sea of Galilee]] (Lake Tiberias). | Two major lakes are located in [[Asia]]: The [[Dead Sea]] and the [[Sea of Galilee]] (Lake Tiberias). | ||
| Line 45: | Line 43: | ||
The '''Ethiopian Rift Valley''' lakes are the northernmost of the African Rift Valley lakes. In central [[Ethiopia]] the Great Rift Valley splits the Ethiopian highlands into northern and southern halves, and the Ethiopian Rift Valley lakes occupy the floor of the rift valley between the two highlands. Most of the Ethiopian Rift Valley lakes do not have an outlet, and most are alkaline. The major ones are: | The '''Ethiopian Rift Valley''' lakes are the northernmost of the African Rift Valley lakes. In central [[Ethiopia]] the Great Rift Valley splits the Ethiopian highlands into northern and southern halves, and the Ethiopian Rift Valley lakes occupy the floor of the rift valley between the two highlands. Most of the Ethiopian Rift Valley lakes do not have an outlet, and most are alkaline. The major ones are: | ||
| − | * Lake Abaya ( | + | * Lake Abaya (1,160 square kilometers; elevation 1,285 meters) (447.8 square miles; elevation 4,215 feet), the largest lake of the Ethiopian Rift Valley |
| − | * Lake Chamo (551 | + | * Lake Chamo (551 square kilometers; 1,235 meters) (212.7 square miles; elevation 4,051 feet) |
| − | * Lake Awasa (129 | + | * Lake Awasa (129 square kilometers; elevation 1,708 meters) (49.8 square miles; elevation 5,602 feet) |
| − | * Lake Zway (485 | + | * Lake Zway (485 square kilometers; elevation 1,636 meters) (187.2 square miles; elevation 5,366 feet) |
| − | * Lake Abijatta (205 | + | * Lake Abijatta (205 square kilometers; elevation 1,573 meters) (79.1 square miles; elevation 5,159 feet) |
| − | * Lake Koka (250 | + | * Lake Koka (250 square kilometers; elevation 1,590 meters) (96.5 square miles; elevation 5,215 feet) |
| − | * Lake Tana ( | + | * Lake Tana (3,600 square kilometers; elevation 1,788 meters) (1390 square miles; elevation 5,865 feet)—the source of the Blue Nile—is not a Rift Valley lake, but lies in the Ethiopian highlands north of the Rift Valley. |
South of the Ethiopian highlands, where the Rift Valley splits in two, the '''Eastern Rift''' is home to the [[Kenya]]n lakes, while most of the Central African Rift Valley lakes lie in the Western Rift. The Kenyan section is home to eight lakes, of which two are freshwater and the rest alkaline. Of the latter, the shallow soda lakes of the Eastern Rift Valley have crystallized [[salt]] turning the shores white, and are famous for the large flocks of [[flamingo]] that feed on [[crustacean]]s. | South of the Ethiopian highlands, where the Rift Valley splits in two, the '''Eastern Rift''' is home to the [[Kenya]]n lakes, while most of the Central African Rift Valley lakes lie in the Western Rift. The Kenyan section is home to eight lakes, of which two are freshwater and the rest alkaline. Of the latter, the shallow soda lakes of the Eastern Rift Valley have crystallized [[salt]] turning the shores white, and are famous for the large flocks of [[flamingo]] that feed on [[crustacean]]s. | ||
| − | * Lake Turkana ( | + | * Lake Turkana (6,405 square kilometers; elevation 360 meters) (2,473 square miles; elevation 1,180 feet)—alkaline, is the largest of the Kenyan lakes, on the border of Kenya and Ethiopia. |
* Lake Logipi is a seasonal, shallow hot-spring fed soda lake in the Suguta Valley just south of Lake Turkana | * Lake Logipi is a seasonal, shallow hot-spring fed soda lake in the Suguta Valley just south of Lake Turkana | ||
| − | * Lake Baringo ( | + | * Lake Baringo (130 square kilometers; elevation 1,000 meters) (50.2 square miles; elevation 3,280 feet)—freshwater, second largest of the Kenyan Rift Valley lakes |
| − | * Lake Bogoria(34 | + | * Lake Bogoria (34 square kilometers; elevation 990 meters) (13.1 square miles; elevation 3,247 feet)—shallow soda lake, a national preserve |
| − | * Lake Nakuru (40 | + | * Lake Nakuru (40 square kilometers; elevation 1,759 meters) (15.4 square miles; elevation 5,769 feet)—shallow soda lake, has been a national park since 1968 |
* Lake Elmenteita, shallow soda lake | * Lake Elmenteita, shallow soda lake | ||
| − | * Lake Naivasha (160 | + | * Lake Naivasha (160 square kilometers, varies somewhat with rainfall; elevation 1,890 meters) (61.8 square miles; elevation 6,199 feet)—freshwater lake, is the highest in this group |
* Lake Magadi, shallow soda lake | * Lake Magadi, shallow soda lake | ||
| − | The | + | The [[Tanzania]]n section of this group has two alkaline lakes: |
* Lake Natron, shallow soda lake | * Lake Natron, shallow soda lake | ||
* Lake Eyasi, shallow soda lake | * Lake Eyasi, shallow soda lake | ||
| − | The lakes of the '''Western''' or Albertine Rift, together with Lake Victoria, include the largest, deepest, and oldest of the Rift Valley lakes. They are also referred | + | The lakes of the '''Western''' or Albertine Rift, together with [[Lake Victoria]], include the largest, deepest, and oldest of the Rift Valley lakes. They are also referred to as the Central African lakes. Lakes Albert, Victoria, and Edward are part of the [[Nile River]] basin. |
| − | Lake Victoria (elevation | + | Lake Victoria (elevation 1,134 meters (3,719 feet)), with an area of 68,800 square kilometers (26,563 square miles), is the largest lake in Africa, but is not actually within the Rift Valley; it occupies a depression between the Eastern and Western Rifts, formed by the uplift of the rifts to either side. Lakes Victoria, Tanganyika, and Malawi are sometimes collectively known as the African Great Lakes. |
The Western Rift Valley Lakes are freshwater and home to an extraordinary number of endemic species. Approximately 1,500 cichlid [[fish]] species live in the lakes, as well as other fish families. The lakes are also important habitats for a number of [[amphibian]] species. | The Western Rift Valley Lakes are freshwater and home to an extraordinary number of endemic species. Approximately 1,500 cichlid [[fish]] species live in the lakes, as well as other fish families. The lakes are also important habitats for a number of [[amphibian]] species. | ||
| − | * Lake Albert ( | + | * Lake Albert (5,300 square kilometers; elevation 615 meters) (2,045 square miles; elevation 2,017 feet) is the northernmost lake in the Western Rift |
| − | * Lake Edward ( | + | * Lake Edward (2,325 square kilometers; elevation 912 meters) (898 square miles; elevation 2,991 feet) drains north into Lake Albert |
| − | * Lake Kivu ( | + | * Lake Kivu (2,220 square kilometers; elevation 1,460 meters) (857 square miles; elevation 4,788 feet) empties into Lake Tanganyika via the Ruzizi River |
| − | * Lake Tanganyika (32,000 | + | * [[Lake Tanganyika]] (32,000 square kilometers; elevation 773 meters) (12,355 square miles; elevation 2,535 feet) is the largest and deepest of the Rift Valley lakes (more than 1,400 meters (4,592 feet)), and is thought to be the second-oldest lake on the planet (after [[Lake Baikal]]); part of the [[Congo River]] basin, it feeds into it via the Lukuga River |
The '''Southern Rift Valley''' lakes are like the Western Rift Valley lakes in that, with one exception, they are freshwater lakes. | The '''Southern Rift Valley''' lakes are like the Western Rift Valley lakes in that, with one exception, they are freshwater lakes. | ||
| − | * Lake Rukwa (about | + | * Lake Rukwa (about 5,670 square kilometers (2,189 square miles), but quite variable) in Tanzania is the alkaline exception, lying southeast of Tanganyika, and has no outlet |
| − | * Lake Malawi (30,000 | + | * [[Lake Malawi]] (30,000 square kilometers; elevation 500 meters) (11,583 square miles; elevation 1640 feet), the second largest and second deepest of the Rift Valley lakes at over 700 meters (2,296 feet), is drained by the Shire River, a tributary of the [[Zambezi River]] |
| − | * Lake Malombe (450 | + | * Lake Malombe (450 square kilometers) (174 square miles) is on the Shire River |
| − | * Lake Chilwa ( | + | * Lake Chilwa (1,750 square kilometers; elevation 622 meters) (676 square miles; elevation 2,040 feet) has no outlet but extensive wetlands; it is the southernmost of the Rift Valley lakes |
==Flora and fauna== | ==Flora and fauna== | ||
| − | A wide variety of fauna inhabit the Rift Valley. Those parts that are | + | A wide variety of fauna inhabit the Rift Valley. Those parts that are [[grassland]]s contain a greater concentration of wild [[animal]]s than any other area of comparable size. Species unique to the Rift Valley include the mountain [[gorilla]] that is found on the forested slopes of the Virunga volcanoes and fish that dwell in the alkaline springs. |
| − | The wide variety of | + | The wide variety of terrains—from desert to mountain—results in adaptation of flora to altitude, temperature, and rainfall totals. |
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | * Donald | + | * Gregory, John Walter. 1896. ''The Great Rift Valley''. University of Michigan Library. {{ASIN|B0037CEM5M}} |
| − | * | + | * Johanson, Donald and Blake Edgar. 1996. ''From Lucy to Language''. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0684810239 |
| − | + | * Leakey, Richard E. 1981. ''The Making of Mankind''. New York: E.P. Dutton. ISBN 0525150552 | |
| + | * Pavitt, Nigel. 2001. ''Africa's Great Rift Valley''. New York: Harry N. Abrams. ISBN 0810906023 | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| − | + | All links retrieved July 13, 2017. | |
| − | * [http://www.cotf.edu/ete/modules/rift/rvwhatisriftvalley.html What Is the Rift Valley?] | + | * [http://www.cotf.edu/ete/modules/rift/rvwhatisriftvalley.html What Is the Rift Valley?] – Wheeling Jesuit University, Classroom of the Future |
| − | |||
| + | {{credit|104427077}} | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Geography]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Global regions]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 16:42, 13 July 2017
The Great Rift Valley is a geographical and geological feature running north to south for around 4,000 miles (6,400 kilometers), from northern Syria to central Mozambique in East Africa. Astronauts say it is the most significant physical detail on the planet that is visible from space. In Africa, the terrain ranges from salt flats more than 500 feet (152 meters) below sea level to towering, snow-capped mountains. The Rift is known for its spectacular scenery and abundant, sometimes unique, wildlife. A series of some thirty lakes lies along its length; the three largest in Africa are known as the Great Lakes and include Lake Tanganyika, the second deepest lake in the world, and Lake Victoria, the second-largest freshwater lake by surface area in the world. Some of the oldest remains of ancestral humans have been found in in the African segment of the valley.
Geography

The Great Rift Valley varies in width from twenty to sixty miles (thirty to one hundred kilometers), and in depth from a few hundred to several thousand meters. The northernmost part of the Rift forms the Beqaa Valley in Lebanon. To the south, in Israel, it is known as the Hula Valley separating the Galilee mountains and the Golan Heights. Farther south, the valley is the home of the Jordan River, which flows southward through Lake Hula into the Sea of Galilee in Israel and then continues south through the Jordan Valley into the Dead Sea on the Israeli-Jordanian border. From the Dead Sea southward, the Rift is occupied by the Wadi Arabah and then the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea.
The southern end of the Red Sea marks a fork in the rift. The Afar Triangle or Danakil Depression of Ethiopia and Eritrea is the probable location of a triple junction, which is possibly underlain by a mantle plume (an upwelling of abnormally hot rock within the earth's mantle that helps the earth to lose heat). The Gulf of Aden is an eastward continuation of the rift—before the rift opened, the Arabian Peninsula was attached to the Horn of Africa—and from this point the rift extends southeastward as part of the mid-oceanic ridge of the Indian Ocean. In a southwest direction the fault continues as the Great Rift Valley, which split the older Ethiopian highlands into two halves.
In eastern Africa the valley divides into the Eastern Rift and the Western Rift. The Western Rift, also called the Albertine Rift, is edged by some of the highest mountains in Africa, including the Virunga Mountains, Mitumba Mountains, and Ruwenzori Range, and contains the Rift Valley lakes, which include some of the deepest lakes in the world (up to 1,470 meters deep at Lake Tanganyika). Many sites in the Albertine Rift are protected as national parks, wildlife reserves, or forest reserves. But there are several other sites important for conservation that require legal protection in the future, mainly in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
In Kenya, the valley is deepest to the north of Nairobi. As the lakes in the Eastern Rift have no outlet to the sea, these lakes tend to be shallow and have a high mineral content as the evaporation of water leaves the salts behind. For example, Lake Magadi is almost solid sodium carbonate, and Lakes Elmenteita, Baringo, Bogoria, and Nakuru are all strongly alkaline, while Lake Naivasha needs to be supplied by freshwater springs to support its biological variety.
Sodium carbonate, however, creates an ideal breeding ground for algae. Several species of fish, tilapia in particular, thrive in this environment. As a result, millions of birds flock to these soda lakes to feast on the abundant food supply of algae and fish. Each of the lakes in the Rift Valley string has a slightly different water composition ranging from freshwater to extremely alkaline, highly saline to brackish.
Geothermal activity
Subterranean movement is common today as the Rift Valley is home to thirty active and semi-active volcanoes and countless hot springs along its length. The formation of the Rift Valley continues, probably driven by mantle plumes. The associated geothermal activity and spreading at the rift has caused the lithosphere to thin from the typical sixty-mile (100-kilometer) thickness for continents to a mere 20 kilometers. If spreading continues, the lithosphere may rupture several million years from now, splitting eastern Africa off to form a new landmass. This would lead to the formation of a new mid-ocean ridge.
The volcanic activity at this site and unusual concentration of hotspots has produced the volcanic mountains Mount Kilimanjaro, Mount Kenya, Mount Karisimbi, Mount Nyiragongo, Mount Meru, and Mount Elgon, as well as the Crater Highlands in Tanzania. The Ol Doinyo Lengai volcano remains active and is currently the only natrocarbonatite volcano in the world.
Pre-colonial history
When the Bantu peoples left West Africa about five thousand years ago, one branch moved east and reached the Great Lakes region two thousand years later. The descendants of the groups that remained established the Buganda, Bunyoro, and Karagwe Kingdoms, while others continued on to the Indian Ocean coast or moved south to Lake Malawi.
History of exploration
The first Europeans to penetrate Central and East Africa reported snow at the equator but were not initially believed. The Royal Geographical Society sent an expedition to the region in search of the Nile's source. The detailed reports of that trip helped Austrian geologist Eduard Suess formulate his theory that the system of valleys and lakes that crossed Arabia and Africa was part of a continuous trough. In 1891 he published a paper attributing the geology and structural geography between Syria and Malawi to interconnected movements within the Earth. The following year, British explorer John Walter Gregory began his explorations of East Africa. His comparisons of geological strata led him to conclude that faulting, not erosion, had formed the valley to which he gave the name "Great Rift Valley," the name still used for the entire African Rift.
Discoveries in human evolution
The Rift Valley has been a rich source of fossils that allow study of human evolution. Richard Leakey has speculated that the diversity of environments resulting from the creation of the Rift Valley provided "an ideal setting for evolutionary change." The presence of multiple lakes in the region would have drawn animals, including hominids. Furthermore, the rise and fall of lake levels and seasonal flooding of rivers aided in burying and preserving bones. The numerous active volcanoes in the region provided volcanic ash that would later allow dating of the fossils that were found.
There is no reason to conclude that early hominids were confined to East Africa, but because the rapidly eroding highlands filled the valley with sediments, a favorable environment for the preservation of remains was created. The bones of several hominid ancestors of modern humans have been found there, including those of "Lucy," a nearly complete Australopithecus skeleton that was discovered by anthropologist Donald Johanson. The husband and wife team of Richard and Mary Leakey has also done significant work in this region.
It has been suggested by scientists that the Rift's trough may have been an important route for human dispersal.
Great Lakes
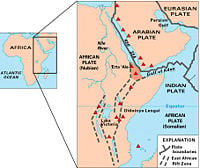
The African Rift Valley lakes include some of the oldest, largest, and deepest lakes in the world, and many are freshwater ecoregions of great biodiversity, while others are alkaline or soda lakes supporting highly specialized organisms.
Two major lakes are located in Asia: The Dead Sea and the Sea of Galilee (Lake Tiberias).
The Ethiopian Rift Valley lakes are the northernmost of the African Rift Valley lakes. In central Ethiopia the Great Rift Valley splits the Ethiopian highlands into northern and southern halves, and the Ethiopian Rift Valley lakes occupy the floor of the rift valley between the two highlands. Most of the Ethiopian Rift Valley lakes do not have an outlet, and most are alkaline. The major ones are:
- Lake Abaya (1,160 square kilometers; elevation 1,285 meters) (447.8 square miles; elevation 4,215 feet), the largest lake of the Ethiopian Rift Valley
- Lake Chamo (551 square kilometers; 1,235 meters) (212.7 square miles; elevation 4,051 feet)
- Lake Awasa (129 square kilometers; elevation 1,708 meters) (49.8 square miles; elevation 5,602 feet)
- Lake Zway (485 square kilometers; elevation 1,636 meters) (187.2 square miles; elevation 5,366 feet)
- Lake Abijatta (205 square kilometers; elevation 1,573 meters) (79.1 square miles; elevation 5,159 feet)
- Lake Koka (250 square kilometers; elevation 1,590 meters) (96.5 square miles; elevation 5,215 feet)
- Lake Tana (3,600 square kilometers; elevation 1,788 meters) (1390 square miles; elevation 5,865 feet)—the source of the Blue Nile—is not a Rift Valley lake, but lies in the Ethiopian highlands north of the Rift Valley.
South of the Ethiopian highlands, where the Rift Valley splits in two, the Eastern Rift is home to the Kenyan lakes, while most of the Central African Rift Valley lakes lie in the Western Rift. The Kenyan section is home to eight lakes, of which two are freshwater and the rest alkaline. Of the latter, the shallow soda lakes of the Eastern Rift Valley have crystallized salt turning the shores white, and are famous for the large flocks of flamingo that feed on crustaceans.
- Lake Turkana (6,405 square kilometers; elevation 360 meters) (2,473 square miles; elevation 1,180 feet)—alkaline, is the largest of the Kenyan lakes, on the border of Kenya and Ethiopia.
- Lake Logipi is a seasonal, shallow hot-spring fed soda lake in the Suguta Valley just south of Lake Turkana
- Lake Baringo (130 square kilometers; elevation 1,000 meters) (50.2 square miles; elevation 3,280 feet)—freshwater, second largest of the Kenyan Rift Valley lakes
- Lake Bogoria (34 square kilometers; elevation 990 meters) (13.1 square miles; elevation 3,247 feet)—shallow soda lake, a national preserve
- Lake Nakuru (40 square kilometers; elevation 1,759 meters) (15.4 square miles; elevation 5,769 feet)—shallow soda lake, has been a national park since 1968
- Lake Elmenteita, shallow soda lake
- Lake Naivasha (160 square kilometers, varies somewhat with rainfall; elevation 1,890 meters) (61.8 square miles; elevation 6,199 feet)—freshwater lake, is the highest in this group
- Lake Magadi, shallow soda lake
The Tanzanian section of this group has two alkaline lakes:
- Lake Natron, shallow soda lake
- Lake Eyasi, shallow soda lake
The lakes of the Western or Albertine Rift, together with Lake Victoria, include the largest, deepest, and oldest of the Rift Valley lakes. They are also referred to as the Central African lakes. Lakes Albert, Victoria, and Edward are part of the Nile River basin.
Lake Victoria (elevation 1,134 meters (3,719 feet)), with an area of 68,800 square kilometers (26,563 square miles), is the largest lake in Africa, but is not actually within the Rift Valley; it occupies a depression between the Eastern and Western Rifts, formed by the uplift of the rifts to either side. Lakes Victoria, Tanganyika, and Malawi are sometimes collectively known as the African Great Lakes.
The Western Rift Valley Lakes are freshwater and home to an extraordinary number of endemic species. Approximately 1,500 cichlid fish species live in the lakes, as well as other fish families. The lakes are also important habitats for a number of amphibian species.
- Lake Albert (5,300 square kilometers; elevation 615 meters) (2,045 square miles; elevation 2,017 feet) is the northernmost lake in the Western Rift
- Lake Edward (2,325 square kilometers; elevation 912 meters) (898 square miles; elevation 2,991 feet) drains north into Lake Albert
- Lake Kivu (2,220 square kilometers; elevation 1,460 meters) (857 square miles; elevation 4,788 feet) empties into Lake Tanganyika via the Ruzizi River
- Lake Tanganyika (32,000 square kilometers; elevation 773 meters) (12,355 square miles; elevation 2,535 feet) is the largest and deepest of the Rift Valley lakes (more than 1,400 meters (4,592 feet)), and is thought to be the second-oldest lake on the planet (after Lake Baikal); part of the Congo River basin, it feeds into it via the Lukuga River
The Southern Rift Valley lakes are like the Western Rift Valley lakes in that, with one exception, they are freshwater lakes.
- Lake Rukwa (about 5,670 square kilometers (2,189 square miles), but quite variable) in Tanzania is the alkaline exception, lying southeast of Tanganyika, and has no outlet
- Lake Malawi (30,000 square kilometers; elevation 500 meters) (11,583 square miles; elevation 1640 feet), the second largest and second deepest of the Rift Valley lakes at over 700 meters (2,296 feet), is drained by the Shire River, a tributary of the Zambezi River
- Lake Malombe (450 square kilometers) (174 square miles) is on the Shire River
- Lake Chilwa (1,750 square kilometers; elevation 622 meters) (676 square miles; elevation 2,040 feet) has no outlet but extensive wetlands; it is the southernmost of the Rift Valley lakes
Flora and fauna
A wide variety of fauna inhabit the Rift Valley. Those parts that are grasslands contain a greater concentration of wild animals than any other area of comparable size. Species unique to the Rift Valley include the mountain gorilla that is found on the forested slopes of the Virunga volcanoes and fish that dwell in the alkaline springs.
The wide variety of terrains—from desert to mountain—results in adaptation of flora to altitude, temperature, and rainfall totals.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Gregory, John Walter. 1896. The Great Rift Valley. University of Michigan Library. ASIN B0037CEM5M
- Johanson, Donald and Blake Edgar. 1996. From Lucy to Language. New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0684810239
- Leakey, Richard E. 1981. The Making of Mankind. New York: E.P. Dutton. ISBN 0525150552
- Pavitt, Nigel. 2001. Africa's Great Rift Valley. New York: Harry N. Abrams. ISBN 0810906023
External links
All links retrieved July 13, 2017.
- What Is the Rift Valley? – Wheeling Jesuit University, Classroom of the Future
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.

