Difference between revisions of "Carotene" - New World Encyclopedia
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Copyedited}}{{Approved}}{{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Paid}} |
| − | [[Image:BetaCarotene-3d.png|thumb|300px|right|β-Carotene represented by a 3- | + | |
| − | + | [[Image:BetaCarotene-3d.png|thumb|300px|right|β-Carotene represented by a 3-dimensional stick diagram.]] | |
| − | + | ||
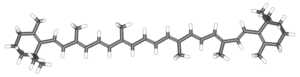
| + | The term '''carotene''' refers to a class of related organic [[chemical compounds|compounds]] with the formula C<sub>40</sub>H<sub>56</sub>. Carotenes exist in several [[isomer]]s that have the same formula but different [[molecule|molecular]] structures. These yellow-orange [[pigment]]s are synthesized by [[plant]]s and photosynthetic [[bacteria]], while [[animal]]s must obtain them as a nutrient from the diet. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Along with [[chlorophyll]] and other pigments found in specialized [[chloroplast]]s, carotenes absorb energy from sunlight to be used in [[photosynthesis]], a process in which [[solar energy]] is converted into potential chemical energy in the form of [[glucose]]. The carotene molecules transmit the absorbed [[light]] [[energy]] to chlorophyll to be funneled into the reactions of photosynthesis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Carotene is also the precursor to [[vitamin A]] in [[animal]]s. Although several carotenes are capable of producing vitamin A, the most active form is the isomer ''beta-carotene''. Vitamin A plays an important role in vision. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:CarrotDiversityLg.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Carotene is a pigment responsible for the orange color of [[carrot]]s.]] | ||
| + | In all living organisms, carotenes function as [[antioxidant]]s, which work by making themselves available for energetically favorable ''oxidation'' (donation of electrons). As such, they can be useful for curbing the excesses of damaging [[free radical]]s, which contain an unpaired [[electron]] and thus are highly reactive. Free radicals oxidize the molecules that make up [[cell membrane]]s and other vital tissues, altering their function. Antioxidants like the carotenes react readily with these free radicals before they can react with other compounds in the [[organism]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Carotenes contribute a yellow or orange pigmentation to [[fruit]]s such as [[apricot]]s, root [[vegetable]]s like [[carrot]]s and [[sweet potatoe]]s, and [[flower]]s such as dandelions and marigolds. The leafy greens [[broccoli]] and [[spinach]] are also good dietary sources, though the presence of carotene is visually masked by the green of chlorophyll molecules. Carotenes also give color to [[milk]] fat and egg yolks, and contribute to the ornamental hue of [[lobster]] shells. | ||
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | Carotenes (and their parent group, the [[carotenoid]]s) are examples of ubiquitous compounds called [[isoprenoid]]s, which may be thought of as the “sensual molecules” that contribute diverse colors and fragrances to the natural world (Stryer 1995). They attest to nature’s ability to use simple building blocks to create an array of compounds. The carotenes and other isoprenoids also demonstrate the functional role of beauty in the perpetuation of life. | ||
==Chemical structure and properties== | ==Chemical structure and properties== | ||
| − | + | Chemically, carotene is a [[terpene]], one of a large class of hydrocarbons derived biosynthetically from units of [[isoprene]], which has the molecular formula C<sub>5</sub>H<sub>8</sub>. Carotenes are synthesized from eight units of isoprene, which may be considered one of nature's preferred building blocks. | |
| − | + | ||
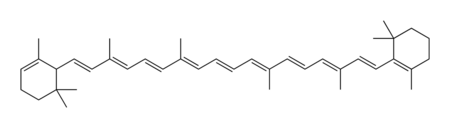
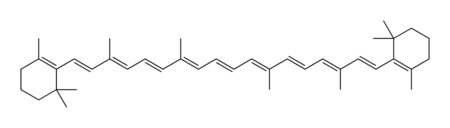
| − | Chemically, carotene is a [[terpene]], | + | Carotene naturally occurs in a variety of isomeric forms, which are designated by characters from the [[Greek alphabet]]. Although alpha-carotene (α-carotene) and beta-carotene (β-carotene) are the two primary forms of carotene, gamma, delta, and epsilon (γ, δ and ε-carotene) configurations also exist. |
| − | |||
[[Image:Alpha-carotene-2D-skeletal.png|thumb|450px|right|α-carotene]] | [[Image:Alpha-carotene-2D-skeletal.png|thumb|450px|right|α-carotene]] | ||
[[Image:Beta-carotene-2D-skeletal.png|thumb|450px|right|β-carotene]] | [[Image:Beta-carotene-2D-skeletal.png|thumb|450px|right|β-carotene]] | ||
| − | The two primary | + | The two primary isomers of carotene, α-carotene and β-carotene, differ in the position of [[double bond]]s in the cyclic group at the end of the molecule. |
| − | + | Carotenes absorb light because they contain extended networks of alternating single and double bonds (i.e., they are ''polyenes''). These double carbon-carbon bonds interact in a process known as [[Conjugated system|conjugation]], which results in an overall lower energy state. Normally, carbon-carbon double bonds that are not conjugated or only partially conjugated absorb light in the [[ultraviolet]] region of a [[Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy|spectrum]]; however, the absorption energy state of polyenes with numerous conjugated double bonds can be lowered such that they enter the visible region of the spectrum, resulting in compounds that are colored yellow and orange. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Synthesis== | |
| + | In [[plant]]s and photosynthetic [[bacteria]], carotenes are synthesized from ''isopentenyl pyrophosphate'', the basic 5-carbon building block. Their 40-carbon skeletons are built by the successive addition of five-carbon units to form a 20-carbon intermediate, which is then joined tail-to-tail with a second 20-carbon molecule. ''Phytoene'', a 40-carbon molecule, condenses to yield ''lycopene''. ''Cyclization'' of both ends of lycopene produces the characteristic ring structure of beta-carotene. | ||
| − | + | ==Functions in living organisms== | |
| + | ===Carotenes are light-harvesting pigments in photosynthesis=== | ||
| + | Carotenoids are present in plants and photosynthetic bacteria. They absorb light at other wavelengths than those absorbed by the two types of [[chlorophyll]] pigments (called ''chlorophyll a'' and ''b''), thus extending the range of light that can be absorbed from sunlight and used for [[photosynthesis]]. Carotenes and other light-absorbing pigments present in the antennas of chloroplasts funnel the energy of absorbed light to the two chlorophyll molecules at the ''reaction center'', where high-energy molecules such as [[ATP]] and [[NADPH]] are ultimately generated. | ||
| − | + | ===Beta-carotene is a precursor to vitamin A in animals=== | |
| + | Beta-carotene can be stored in the [[liver]] and converted to vitamin A as needed, thus making it a [[provitamin]] (i.e., a precursor to the vitamin). Vitamin A (also known as ''retinol'') is a fat-soluble alcohol that plays a crucial role in vision; it is converted to a component of the light-sensitive pigment [[rodopsin]] present in the [[retina]] of the eye. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Carotenes serve as antioxidants=== | ||
| + | Along with vitamins C and E, and a group of related compounds called coenzyme Q, carotones also act as antioxidants in a variety of organisms. They shelter [[prokaryote]]s from the deleterious effects of light, and protect vital cell functions in plants against the destructive effects of ultraviolet light, acting in a sense like the plant’s [[sunscreen]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===The color of carotene plays a role in reproduction=== | ||
| + | A wide range of carotenoids and other colorful compounds abound in the plant kingdom. The benefits for the plant in expending resources to produce these compounds are visible in their role in attracting [[insect]]s for pollination and luring animals for [[seed]] distribution. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Carotenoids are also common in animals, which cannot synthesize these molecules and must obtain them through the diet; in animals, they often function as ornamental features. For example, the red coloring of [[lobster]]s’ shells is created by carotene pigments. It has been proposed that carotenoids are used in ornamental traits because, given their physiological and chemical properties, they can be taken as honest indicators of individual health; hence, they are useful signposts when selecting potential mates. | ||
==Sources== | ==Sources== | ||
===Dietary sources=== | ===Dietary sources=== | ||
| − | + | Beta-carotene is the most common [[isomer]] and can be found in a variety of [[plant]]s, including certain [[flower]]s (e.g., dandelions and marigolds), [[fruit]]s (e.g., pumpkin, apricot, and cantaloupe), root [[vegetable]]s (e.g. carrots and sweet potatoes), and leafy greens (e.g., [[broccoli]] and spinach). β-carotene is also responsible for the coloration of yellow-orange bell peppers. | |
| − | + | Pigmentation caused by carotenes is also manifested in certain animals and animal products, such as egg yolks, the shells of lobsters, and the yellow-colored milk of Guernsey cows, noted for its high beta-carotene content. | |
| − | |||
===Carotene supplements=== | ===Carotene supplements=== | ||
| − | + | Beta-carotene was isolated from carrots early in the twentieth century, and first synthesized by scientists around 1950. Today, most of the world's synthetic supply of carotene comes from a manufacturing complex located in Freeport, Texas and owned by DSM. In [[Spain]], Vitatene produces natural beta-carotene from ''Blakeslea trispora'', a plant pathogen. In [[Australia]], organic beta-carotene is produced by Aquacarotene Limited from dried marine algae ''([[Dunaliella salina]])'' grown in harvesting ponds. | |
== Beta-carotene and human health== | == Beta-carotene and human health== | ||
===Carotenemia=== | ===Carotenemia=== | ||
| − | + | The [[RDA]] (Recommended Daily Allowance) for beta-carotene is rather low: 1000 mg for males and 800 mg for females, with slightly higher amounts for pregnant or lactating women. Although touted as a beneficial nutrient, too much vitamin A can actually be harmful to the body. ''Carotenemia'' or ''hypercarotenemia'' refers to a disorder caused by excess carotene. Unlike excess vitamin A, carotene is non-toxic. Although hypercarotenemia is not particularly dangerous, it can lead to a yellow-orange discoloration of the skin ''(carotenodermia)'', most often appearing around the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. It is most commonly associated with over-consumption of carrots, but it also can be a medical sign of more serious conditions such as [[diabetes mellitus]], [[anorexia nervosa]], and [[porphyria]]. | |
| − | Carotenemia or hypercarotenemia | ||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===Beta-carotene and cancer=== |
| − | + | Carotenoids are efficient free-radical scavengers that enhance the vertebrate [[immune system]]. Consequently, [[epidemiology|epidemiological]] studies have shown that people with high beta-carotene intake and high plasma levels of beta-carotene have a significantly reduced risk of lung [[cancer]]. | |
| − | + | However, studies of supplementation with large doses of synthetic beta-carotene in smokers or those with [[asbestos]] exposure have shown an increase in cancer risk. One explanation for this finding is that excessive beta-carotene leads to breakdown products that reduce plasma vitamin A and worsen the lung [[cell growth|cell proliferation]] induced by smoke (Omenn 1996; American Cancer Society 2000; Bjelavokic et al. 2007). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | + | * American Cancer Society. 2000. [http://www.cancer.org/docroot/NWS/content/NWS_1_1x_Warning_Labels_on_Beta_Carotene_Called_For.asp British cancer organization calls for warning labels on beta-carotene] ''American Cancer Society News''. Retrieved December 5, 2007. | |
| − | * Lodish, | + | * Bjelakovic et al. 2007. Mortality in randomized trials of antioxidant supplements for primary and secondary prevention: Systematic review and meta-analysis. ''JAMA.'' 297: 842. |
| + | * Lodish, H., D. Baltimore, A., Berk, S. L. Zipursky, P. Matsudaira, and J. Darnell. 1995. ''Molecular Cell Biology'', 3rd ed. New York,: Scientific American Books. ISBN 0716723808. | ||
| + | * Omenn, G. S. et al. 1996. [http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/abstract/334/18/1150 Effects of a combination of beta carotene and vitamin A on lung cancer and cardiovascular disease] ''The New England Journal of Medicine''. 334: 1150-5. Retrieved December 5, 2007. | ||
| + | * Stryer, L. 1995. ''Biochemistry'', 4th ed. New York: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0716720094. | ||
| − | + | ==External links== | |
| + | All links retrieved November 28, 2023. | ||
| + | *[http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/carotene/beta-carotene_home.html Beta-carotene website by Martha Evens, School of Chemistry, University of Bristol] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{credit|Carotene|130817648}} | |
| − | {{credit|Carotene|130817648 | ||
[[Category:Life sciences]] | [[Category:Life sciences]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Chemistry]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Biochemistry]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:37, 29 November 2023
The term carotene refers to a class of related organic compounds with the formula C40H56. Carotenes exist in several isomers that have the same formula but different molecular structures. These yellow-orange pigments are synthesized by plants and photosynthetic bacteria, while animals must obtain them as a nutrient from the diet.
Along with chlorophyll and other pigments found in specialized chloroplasts, carotenes absorb energy from sunlight to be used in photosynthesis, a process in which solar energy is converted into potential chemical energy in the form of glucose. The carotene molecules transmit the absorbed light energy to chlorophyll to be funneled into the reactions of photosynthesis.
Carotene is also the precursor to vitamin A in animals. Although several carotenes are capable of producing vitamin A, the most active form is the isomer beta-carotene. Vitamin A plays an important role in vision.

In all living organisms, carotenes function as antioxidants, which work by making themselves available for energetically favorable oxidation (donation of electrons). As such, they can be useful for curbing the excesses of damaging free radicals, which contain an unpaired electron and thus are highly reactive. Free radicals oxidize the molecules that make up cell membranes and other vital tissues, altering their function. Antioxidants like the carotenes react readily with these free radicals before they can react with other compounds in the organism.
Carotenes contribute a yellow or orange pigmentation to fruits such as apricots, root vegetables like carrots and sweet potatoes, and flowers such as dandelions and marigolds. The leafy greens broccoli and spinach are also good dietary sources, though the presence of carotene is visually masked by the green of chlorophyll molecules. Carotenes also give color to milk fat and egg yolks, and contribute to the ornamental hue of lobster shells.
Carotenes (and their parent group, the carotenoids) are examples of ubiquitous compounds called isoprenoids, which may be thought of as the “sensual molecules” that contribute diverse colors and fragrances to the natural world (Stryer 1995). They attest to nature’s ability to use simple building blocks to create an array of compounds. The carotenes and other isoprenoids also demonstrate the functional role of beauty in the perpetuation of life.
Chemical structure and properties
Chemically, carotene is a terpene, one of a large class of hydrocarbons derived biosynthetically from units of isoprene, which has the molecular formula C5H8. Carotenes are synthesized from eight units of isoprene, which may be considered one of nature's preferred building blocks.
Carotene naturally occurs in a variety of isomeric forms, which are designated by characters from the Greek alphabet. Although alpha-carotene (α-carotene) and beta-carotene (β-carotene) are the two primary forms of carotene, gamma, delta, and epsilon (γ, δ and ε-carotene) configurations also exist.
The two primary isomers of carotene, α-carotene and β-carotene, differ in the position of double bonds in the cyclic group at the end of the molecule.
Carotenes absorb light because they contain extended networks of alternating single and double bonds (i.e., they are polyenes). These double carbon-carbon bonds interact in a process known as conjugation, which results in an overall lower energy state. Normally, carbon-carbon double bonds that are not conjugated or only partially conjugated absorb light in the ultraviolet region of a spectrum; however, the absorption energy state of polyenes with numerous conjugated double bonds can be lowered such that they enter the visible region of the spectrum, resulting in compounds that are colored yellow and orange.
Synthesis
In plants and photosynthetic bacteria, carotenes are synthesized from isopentenyl pyrophosphate, the basic 5-carbon building block. Their 40-carbon skeletons are built by the successive addition of five-carbon units to form a 20-carbon intermediate, which is then joined tail-to-tail with a second 20-carbon molecule. Phytoene, a 40-carbon molecule, condenses to yield lycopene. Cyclization of both ends of lycopene produces the characteristic ring structure of beta-carotene.
Functions in living organisms
Carotenes are light-harvesting pigments in photosynthesis
Carotenoids are present in plants and photosynthetic bacteria. They absorb light at other wavelengths than those absorbed by the two types of chlorophyll pigments (called chlorophyll a and b), thus extending the range of light that can be absorbed from sunlight and used for photosynthesis. Carotenes and other light-absorbing pigments present in the antennas of chloroplasts funnel the energy of absorbed light to the two chlorophyll molecules at the reaction center, where high-energy molecules such as ATP and NADPH are ultimately generated.
Beta-carotene is a precursor to vitamin A in animals
Beta-carotene can be stored in the liver and converted to vitamin A as needed, thus making it a provitamin (i.e., a precursor to the vitamin). Vitamin A (also known as retinol) is a fat-soluble alcohol that plays a crucial role in vision; it is converted to a component of the light-sensitive pigment rodopsin present in the retina of the eye.
Carotenes serve as antioxidants
Along with vitamins C and E, and a group of related compounds called coenzyme Q, carotones also act as antioxidants in a variety of organisms. They shelter prokaryotes from the deleterious effects of light, and protect vital cell functions in plants against the destructive effects of ultraviolet light, acting in a sense like the plant’s sunscreen.
The color of carotene plays a role in reproduction
A wide range of carotenoids and other colorful compounds abound in the plant kingdom. The benefits for the plant in expending resources to produce these compounds are visible in their role in attracting insects for pollination and luring animals for seed distribution.
Carotenoids are also common in animals, which cannot synthesize these molecules and must obtain them through the diet; in animals, they often function as ornamental features. For example, the red coloring of lobsters’ shells is created by carotene pigments. It has been proposed that carotenoids are used in ornamental traits because, given their physiological and chemical properties, they can be taken as honest indicators of individual health; hence, they are useful signposts when selecting potential mates.
Sources
Dietary sources
Beta-carotene is the most common isomer and can be found in a variety of plants, including certain flowers (e.g., dandelions and marigolds), fruits (e.g., pumpkin, apricot, and cantaloupe), root vegetables (e.g. carrots and sweet potatoes), and leafy greens (e.g., broccoli and spinach). β-carotene is also responsible for the coloration of yellow-orange bell peppers.
Pigmentation caused by carotenes is also manifested in certain animals and animal products, such as egg yolks, the shells of lobsters, and the yellow-colored milk of Guernsey cows, noted for its high beta-carotene content.
Carotene supplements
Beta-carotene was isolated from carrots early in the twentieth century, and first synthesized by scientists around 1950. Today, most of the world's synthetic supply of carotene comes from a manufacturing complex located in Freeport, Texas and owned by DSM. In Spain, Vitatene produces natural beta-carotene from Blakeslea trispora, a plant pathogen. In Australia, organic beta-carotene is produced by Aquacarotene Limited from dried marine algae (Dunaliella salina) grown in harvesting ponds.
Beta-carotene and human health
Carotenemia
The RDA (Recommended Daily Allowance) for beta-carotene is rather low: 1000 mg for males and 800 mg for females, with slightly higher amounts for pregnant or lactating women. Although touted as a beneficial nutrient, too much vitamin A can actually be harmful to the body. Carotenemia or hypercarotenemia refers to a disorder caused by excess carotene. Unlike excess vitamin A, carotene is non-toxic. Although hypercarotenemia is not particularly dangerous, it can lead to a yellow-orange discoloration of the skin (carotenodermia), most often appearing around the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. It is most commonly associated with over-consumption of carrots, but it also can be a medical sign of more serious conditions such as diabetes mellitus, anorexia nervosa, and porphyria.
Beta-carotene and cancer
Carotenoids are efficient free-radical scavengers that enhance the vertebrate immune system. Consequently, epidemiological studies have shown that people with high beta-carotene intake and high plasma levels of beta-carotene have a significantly reduced risk of lung cancer.
However, studies of supplementation with large doses of synthetic beta-carotene in smokers or those with asbestos exposure have shown an increase in cancer risk. One explanation for this finding is that excessive beta-carotene leads to breakdown products that reduce plasma vitamin A and worsen the lung cell proliferation induced by smoke (Omenn 1996; American Cancer Society 2000; Bjelavokic et al. 2007).
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- American Cancer Society. 2000. British cancer organization calls for warning labels on beta-carotene American Cancer Society News. Retrieved December 5, 2007.
- Bjelakovic et al. 2007. Mortality in randomized trials of antioxidant supplements for primary and secondary prevention: Systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 297: 842.
- Lodish, H., D. Baltimore, A., Berk, S. L. Zipursky, P. Matsudaira, and J. Darnell. 1995. Molecular Cell Biology, 3rd ed. New York,: Scientific American Books. ISBN 0716723808.
- Omenn, G. S. et al. 1996. Effects of a combination of beta carotene and vitamin A on lung cancer and cardiovascular disease The New England Journal of Medicine. 334: 1150-5. Retrieved December 5, 2007.
- Stryer, L. 1995. Biochemistry, 4th ed. New York: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0716720094.
External links
All links retrieved November 28, 2023.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.