Difference between revisions of "Auckland, New Zealand" - New World Encyclopedia
Mary Anglin (talk | contribs) (move image) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (32 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Approved}}{{Submitted | + | {{Approved}}{{Submitted}}{{Images OK}}{{Paid}}{{Copyedited}} |
| − | {{ | + | {{Infobox Settlement |
| − | { | + | <!--See Template:Infobox Settlement for additional fields that may be available—> |
| − | + | <!--See the Table at Infobox Settlement for all fields and descriptions of usage--> | |
| − | | | + | <!-- Basic info ----------------> |
| − | |- | + | |name = Auckland |
| − | + | |official_name = | |
| − | [[ | + | |other_name = |
| − | |- | + | |native_name = <small>Tāmaki Makaurau ([[Māori language|Māori]])</small> |
| − | | | + | |nickname = City of Sails,<br /> SuperCity (sometimes ironically), <br />Queen City (archaic)<!-- http://www.nzherald.co.nz/search/search.cfm?kw1=%22Queen%20city%22&kw2=&op=all&searchorder=2&display=20&start=0&thepage=1 —> |
| − | + | |settlement_type = [[Urban areas of New Zealand|Main urban area]] <!-- e.g. Town, Village, City, etc.—> | |
| − | | | + | |total_type = <!-- to set a non-standard label for total area and population rows —> |
| − | | | + | |motto = |
| − | | | + | <!-- images and maps -----------> |
| − | | | + | |image_skyline = AucklandMontage24032011.jpg |
| − | | | + | |imagesize = |
| − | | | + | |image_caption = |
| − | | | + | <br> |
| − | |- | + | * top: [[Auckland CBD|Downtown Auckland]] |
| − | + | * upper left: [[Piha]] | |
| − | | | + | * bottom left: [[Auckland Town Hall]] |
| − | | | + | * upper right: [[Auckland War Memorial Museum|Auckland Museum]] |
| − | | | + | * centre right: [[Viaduct Harbour]] |
| − | + | * bottom right: [[Waitakere Ranges]] | |
| − | |- | + | |image_flag = |
| − | | | + | |flag_size = |
| − | + | |image_seal = | |
| − | [[ | + | |seal_size = |
| − | + | |image_shield = | |
| − | |- | + | |shield_size = |
| − | | | + | |image_blank_emblem = |
| − | | | + | |blank_emblem_type = |
| − | + | |blank_emblem_size = | |
| − | |- | + | |image_map = |
| − | |} | + | |mapsize = |
| + | |map_caption = | ||
| + | |image_map1 = | ||
| + | |mapsize1 = | ||
| + | |map_caption1 = | ||
| + | |image_dot_map = | ||
| + | |dot_mapsize = | ||
| + | |dot_map_caption = | ||
| + | |dot_x = |dot_y = | ||
| + | <!-- Location ------------------> | ||
| + | |coordinates_display = inline,title | ||
| + | |coordinates_region = NZ | ||
| + | |subdivision_type = Country | ||
| + | |subdivision_name = {{NZ}} | ||
| + | |subdivision_type1 = [[Islands of New Zealand|Island]] | ||
| + | |subdivision_name1 = [[North Island]] | ||
| + | |subdivision_type2 = [[Regions of New Zealand|Region]] | ||
| + | |subdivision_name2 = [[Auckland Region|Auckland]] | ||
| + | |subdivision_type3 = [[Territorial authorities of New Zealand|Territorial authority]] | ||
| + | |subdivision_name3 = [[Auckland Council|Auckland]] | ||
| + | <!-- Local Boards --------------> | ||
| + | |parts_type=Local boards | ||
| + | |p1= [[Hibiscus and Bays Local Board|Hibiscus and Bays]] | ||
| + | |p2= [[Upper Harbour Local Board|Upper Harbour]] | ||
| + | |p3= [[Kaipatiki Local Board|Kaipatiki]] | ||
| + | |p4= [[Devonport-Takapuna Local Board|Devonport-Takapuna]] | ||
| + | |p5= [[Waitakere Ranges Local Board|Waitakere Ranges]] | ||
| + | |p6= [[Henderson-Massey Local Board|Henderson-Massey]] | ||
| + | |p7= [[Whau Local Board|Whau]] | ||
| + | |p8= [[Albert-Eden Local Board|Albert-Eden]] | ||
| + | |p9= [[Puketapapa Local Board|Puketapapa]] | ||
| + | |p10= [[Waitemata Local Board|Waitemata]] | ||
| + | |p11= [[Orakei Local Board|Orakei]] | ||
| + | |p12= [[Maungakiekie-Tamaki Local Board|Maungakiekie-Tamaki]] | ||
| + | |p13= [[Mangere-Otahuhu Local Board|Mangere-Otahuhu]] | ||
| + | |p14= [[Otara-Papatoetoe Local Board|Otara-Papatoetoe]] | ||
| + | |p15= [[Howick Local Board|Howick]] | ||
| + | |p16= [[Manurewa Local Board|Manurewa]] | ||
| + | |p17= [[Papakura Local Board|Papakura]] | ||
| + | <!-- Politics -----------------> | ||
| + | |government_footnotes = | ||
| + | |government_type = | ||
| + | |leader_title1 = Mayor | ||
| + | |leader_name1 = [[Len Brown]] | ||
| + | |established_title = Settled by Māori | ||
| + | |established_date = c. 1350 | ||
| + | |established_title1 = Settled by Europeans | ||
| + | |established_date1 = 1840 | ||
| + | <!-- Area ---------------------> | ||
| + | |area_magnitude = | ||
| + | |unit_pref = <!--Enter: Imperial, to display imperial before metric—> | ||
| + | |area_footnotes = | ||
| + | |area_urban_km2 = 1086 | ||
| + | |area_metro_km2 = 560 | ||
| + | |area_metro_footnotes = <ref name="mrq">[http://www.aucklandcouncil.govt.nz/SiteCollectionDocuments/aboutcouncil/planspoliciespublications/technicalpublications/mrq20110303.pdf Monitoring Research Quarterly], March 2011 Volume 4 Issue 1, page 4 (from the Auckland council website)</ref> | ||
| + | |area_land_km2 = <!--See table @ Template:Infobox Settlement for details on unit conversion—> | ||
| + | |area_water_km2 = | ||
| + | |area_total_sq_mi = | ||
| + | |area_land_sq_mi = | ||
| + | |area_water_sq_mi = | ||
| + | |area_water_percent = | ||
| + | <!-- Elevation --------------------------> | ||
| + | |elevation_footnotes = <!--for references: use <ref> </ref> tags—> | ||
| + | |elevation_m = | ||
| + | |elevation_ft = | ||
| + | |elevation_max_m = 196 | ||
| + | |elevation_max_ft = | ||
| + | |elevation_min_m = 0 | ||
| + | |elevation_min_ft = | ||
| + | <!-- Population -----------------------> | ||
| + | |population_as_of = June 2011 estimate | ||
| + | |population_footnotes = <ref>Statistics New Zealand, [http://www.stats.govt.nz/browse_for_stats/population/estimates_and_projections/subnational-pop-estimates-tables.aspx Subnational population estimates at 30 June 2011 (boundaries at 1 July 2011)]. Retrieved March 10, 2012.</ref> | ||
| + | |population_note = | ||
| + | |population_urban = 1,377,200 | ||
| + | |population_density_urban_km2 = | ||
| + | |population_metro = 1,486,000 | ||
| + | |population_density_metro_km2 = | ||
| + | |population_blank1_title = [[Demonym]] | ||
| + | |population_blank1 = Aucklander, [[Jafa]] (often derogatory) | ||
| + | <!-- General information -------------—> | ||
| + | |timezone = [[Time in New Zealand|NZST]] | ||
| + | |utc_offset = +12 | ||
| + | |timezone_DST = NZDT | ||
| + | |utc_offset_DST = +13 | ||
| + | |coor_pinpoint = <ref name="coor">{{Cite web|url=http://earth-info.nga.mil/gns/html/cntry_files.html| accessdate =August 2006|title=GEOnet Names Server (GNS)}}</ref> | ||
| + | |latd=36 |latm=50 |lats=25.50 |latNS=S | ||
| + | |longd=174 |longm=44 |longs=23.53 |longEW=E | ||
| + | <!-- Area/postal codes & others --------> | ||
| + | |blank_name = Local [[iwi]] | ||
| + | |blank_info = [[Ngāti Whātua]], [[Tainui]] | ||
| + | |postal_code_type = Postcode(s) | ||
| + | |postal_code = 0500-2999 | ||
| + | |area_code = 09 | ||
| + | |website = [http://www.aucklandcouncil.govt.nz/EN/Pages/default.aspx www.aucklandcouncil.govt.nz] | ||
| + | |footnotes = | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | The '''Auckland metropolitan area''' or '''Greater Auckland''', in the [[North Island]] of [[New Zealand]], is the largest urban area of the country. With over 1.3 million people, it is home to nearly one-third of the country's population. Demographic trends indicate that it will continue growing faster than the rest of the country. It is an extensive urban area consisting of Auckland City (excluding the Hauraki Gulf islands), North Shore City, and the urban parts of Waitakere and Manukau cities, along with Papakura District and some nearby urban parts of Rodney and Franklin Districts. | ||
| − | + | Auckland has the largest [[Polynesia]]n population of any city in the world <ref> ''The Rough guides to New Zealand''.[http://www.roughguides.com/website/travel/destination/content/?titleid=83&xid=idh185804920_0099 Auckland and around]. Retrieved October 14, 2007. </ref> as well as its country's greatest concentration of indigenous [[Maori]]. | |
| − | + | Auckland lies between the [[Hauraki Gulf]] of the [[Pacific Ocean]] to the east, the low [[Hunua Ranges]] to the south-east, the [[Manukau Harbour]] to the south-west, and the [[Waitakere Ranges]] and smaller ranges to the west and north-west. The central part of the urban area occupies a narrow [[isthmus]] between the Manukau Harbour on the [[Tasman Sea]] and the [[Waitemata Harbour]] on the Pacific Ocean. It is one of the few cities in the world to have harbors on two separate major bodies of water. Known as the "City of Sails," Auckland has more yachts per capita than any other city in the world. | |
| − | + | {{toc}} | |
| − | Auckland lies between the [[Hauraki Gulf]] of the [[Pacific Ocean]] to the east, the low [[Hunua Ranges]] to the south-east, the [[Manukau Harbour]] to the south-west, and the [[Waitakere Ranges]] and smaller ranges to the west and north-west. The central part of the urban area occupies a narrow [[isthmus]] between the Manukau Harbour on the [[Tasman Sea]] and the [[Waitemata Harbour]] on the Pacific Ocean. It is one of the few cities in the world to have harbors on two separate major bodies of water. | + | Auckland is known in the Maori tongue as ''Tamaki-Makau-Rau,'' meaning "the maiden with a hundred lovers." It earned this name because it was a coveted area, fought over by many tribes due to its incredible [[forest]]ed hills, rich [[soil]]s, beautiful beaches and abundance of seafood. Its temperate climate adds to its idyllic setting. The surrounding hills are covered in [[rainforest]] and the landscape is dotted with dozens of dormant volcanic cones. Considered a [[Polynesia]]n paradise, Auckland is a melting pot of [[South Pacific]] and [[Asia]]n cultures, strongly influenced by its own native Maori traditions. |
==History== | ==History== | ||
| − | The isthmus on which Auckland resides was first settled around 1350 and was valued for its rich and fertile [[soil|land]]. Ngati Whatua of Orakei are a hapu (Māori language for social division or subtribe) of the Ngati Whatua tribe, based at Kaipara. They lived in the area for hundreds of years. The subtribe owned the land communally and worked it together, tending crops and gathering food from the surrounding coastline and countryside. The basis of their identity stemmed from the land, which provided both economic and spiritual resources. <ref | + | The isthmus on which Auckland resides was first settled around 1350 and was valued for its rich and fertile [[soil|land]]. Ngati Whatua of Orakei are a hapu (Māori language for social division or subtribe) of the Ngati Whatua tribe, based at Kaipara. They lived in the area for hundreds of years. The subtribe owned the land communally and worked it together, tending crops and gathering food from the surrounding coastline and countryside. The basis of their identity stemmed from the land, which provided both economic and spiritual resources. <ref> ''Auckland City Council''. Ngati Whatua history of Auckland.</ref> |
On February 6, 1840, [[Great Britain]] and a number of New Zealand [[Maori]] tribes of North Island, including the Whatua of Orakei, signed an historic pact. This pact, the [[Treaty of Waitangi]], purported to protect Maori rights and was the basis of the British annexation of [[New Zealand]]. The treaty provided for | On February 6, 1840, [[Great Britain]] and a number of New Zealand [[Maori]] tribes of North Island, including the Whatua of Orakei, signed an historic pact. This pact, the [[Treaty of Waitangi]], purported to protect Maori rights and was the basis of the British annexation of [[New Zealand]]. The treaty provided for | ||
:(1) acceptance of the British queen's sovereignty in their lands, | :(1) acceptance of the British queen's sovereignty in their lands, | ||
:(2) the crown's protection of Maori possessions, with the exclusive right of the queen to purchase Maori land, and | :(2) the crown's protection of Maori possessions, with the exclusive right of the queen to purchase Maori land, and | ||
| − | :(3) full rights of British subjects for the Maori signatories. <ref> ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. [http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9075886/Treaty-of-Waitangi Treaty of Waitangi] Retrieved October 19, 2007.</ref> | + | :(3) full rights of British subjects for the Maori signatories. <ref> ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. [http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9075886/Treaty-of-Waitangi Treaty of Waitangi]. Retrieved October 19, 2007.</ref> |
| − | [[Image:moari.jpg|thumb|270px|right|The feather cloak he wears is only worn by the noble class of warrior kings, the moko or facial | + | [[Image:moari.jpg|thumb|270px|right|The feather cloak he wears is only worn by the noble class of warrior kings, the moko or facial tattoos told the story of his life, including his family heritage, his battles and his skills. The Green stone earrings and Tiki pendant are sources of power, authority and protection.]] |
| − | Approximately 3,000 acres (1214 hectares) of land was handed over to the Crown by Ngati Whatua of Orakei for a township to be established. The Crown paid £341 for the 3,000 acres and six months later, resold just 44 acres (17 hectares) of that land to settlers for £24,275. They used the money to build roads, [[bridge]]s, [[hospital]]s, and other services for the new town. Ngati Whatua of Orakei had effectively funded the early development of Auckland from the sale of their tribal land. <ref | + | Approximately 3,000 acres (1214 hectares) of land was handed over to the Crown by Ngati Whatua of Orakei for a township to be established. The Crown paid £341 for the 3,000 acres and six months later, resold just 44 acres (17 hectares) of that land to settlers for £24,275. They used the money to build roads, [[bridge]]s, [[hospital]]s, and other services for the new town. Ngati Whatua of Orakei had effectively funded the early development of Auckland from the sale of their tribal land. <ref>''Auckland City Council''.[http://www.aucklandcity.govt.nz/auckland/introduction/ngatiwhatua/default.asp Ngati Whatua history of Auckland]. Retrieved October 19, 2007.</ref> |
Māori population in the area is estimated to have peaked at 20,000 before the arrival of [[Europe]]ans. This event - and the guns which they traded to local [[iwi]] - upset the local power balances. This resulted in extensive inter-tribal warfare, which together with some introduced [[plague]]s resulted in the area having relatively low numbers of Māori when European settlement in New Zealand began in earnest. | Māori population in the area is estimated to have peaked at 20,000 before the arrival of [[Europe]]ans. This event - and the guns which they traded to local [[iwi]] - upset the local power balances. This resulted in extensive inter-tribal warfare, which together with some introduced [[plague]]s resulted in the area having relatively low numbers of Māori when European settlement in New Zealand began in earnest. | ||
| − | After the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi the new Governor of New Zealand, [[William Hobson]] chose the area as his new capital. He named the area "Auckland" for '''''George Eden, earl of Auckland''''', British first lord of the Admiralty and later governor-general of [[India]]. | + | After the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi the new Governor of New Zealand, [[William Hobson]] chose the area as his new capital. He named the area "Auckland" for '''''George Eden, earl of Auckland''''', British first lord of the Admiralty and later governor-general of [[India]]. Hobson founded the town of Auckland on September 18, 1840.<ref> ''Encyclopedia of New Zealand''. [http://www.teara.govt.nz/1966/A/AucklandCity/FoundationAndGrowth/en AUCKLAND CITY-Foundation and Growth]. Retrieved October 19, 2007.</ref> However, even in 1840, [[Port Nicholson]] (later [[Wellington]]), was seen as a better choice for an administrative capital, due to its proximity to the [[South Island]], which was being settled much more rapidly. At the same time, Auckland was the capital and principal city of the [[Auckland Province]], until the provincial system was abolished in 1876. Nonetheless, even after losing its status as the national capital in 1865, immigration to the new city stayed strong. |
| − | The present boroughs of Newmarket, Onehunga, Tamaki, Howick, and Drury were developed between 1850–1900 in the shape of villages and small-farming centers. The first 20 years of the | + | The present boroughs of Newmarket, Onehunga, Tamaki, Howick, and Drury were developed between 1850–1900 in the shape of villages and small-farming centers. The first 20 years of the twentieth century was a period of consolidation and development of the suburbs along main routes out of the city. These included Remuera, Epsom, Ellerslie, Mission Bay, Orakei, St. Heliers, Grey Lynn, Point Chevalier, Mount Albert, Devonport, Northcote, and Birkenhead. From 1918 to 1945 the population growth was centered in these already established settlements, while industries and industrial areas were established and expanded, particularly on the south-east perimeter. Since then Papatoetoe, Papakura, Manurewa, Henderson, and North Shore have shown a marked expansion. Auckland was declared a borough on July 29, 1851 and a city on April 24, 1871. <ref>Ibid.</ref> |
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| − | [[Image:Rangitoto Island North Head.jpg|thumb| | + | [[Image:Rangitoto Island North Head.jpg|thumb|275px|[[Rangitoto]] island as seen from [[North Head, New Zealand|North Head]].]] |
| − | Auckland is located at 36’ 51” South and 174’ 47” East. The Greater Auckland area lies on and around an [[isthmus]], less than | + | Auckland is located at 36’ 51” South and 174’ 47” East. The Greater Auckland area lies on and around an [[isthmus]], less than 1.2 miles (2 km) wide at its narrowest point, between [[Mangere Inlet]] and the [[Tamaki River]]. There are two harbors in the Auckland urban area surrounding this isthmus, [[Waitemata Harbour]] to the north, which opens east to the [[Hauraki Gulf]], and [[Manukau Harbour]] to the south, which opens west to the [[Tasman Sea]]. |
| − | The Auckland region experiences infrequent earthquake activity although it lies in one of the lowest earthquake activity regions of New Zealand. Earthquakes that register an intensity greater than VII on the Modified Mercalli scale are likely to cause widespread damage (The Modified | + | The Auckland region experiences infrequent [[earthquake]] activity although it lies in one of the lowest earthquake activity regions of New Zealand. Earthquakes that register an intensity greater than VII on the Modified Mercalli scale are likely to cause widespread damage (The Modified Mercalli scale lists "VII" as "Frightens everyone, damage to weak buildings, difficult to stand up"). <ref> ''Auckland Regional Council''. Earthquakes.</ref> |
===Volcanoes=== | ===Volcanoes=== | ||
| − | Auckland straddles the [[volcano]]es of the [[Auckland Volcanic Field]]. The approximately 50 volcanic vents in the field take the form of cones, lakes, lagoons, islands and depressions, and several have produced extensive lava flows. Most of the cones have been partly or completely [[quarry|quarried]] away. The individual volcanoes are all considered extinct, although the volcanic field itself is merely [[dormant volcano|dormant]]. | + | Auckland straddles the [[volcano]]es of the [[Auckland Volcanic Field]]. The approximately 50 volcanic vents in the field take the form of cones, lakes, lagoons, islands and depressions, and several have produced extensive [[lava]] flows. Most of the cones have been partly or completely [[quarry|quarried]] away. The individual volcanoes are all considered extinct, although the volcanic field itself is merely [[dormant volcano|dormant]]. |
| − | The most recent and by far the largest volcano, [[Rangitoto Island]], was formed within the last 1000 years, and its eruptions destroyed the Māori settlements on neighboring [[Motutapu Island]] some 700 years ago. Rangitoto's size, symmetry, and its position guarding the entrance to [[Waitemata Harbour]] and its visibility from many parts of the Auckland region make it Auckland's most iconic natural feature. It is eerily quiet as almost no birds | + | The most recent and by far the largest volcano, [[Rangitoto Island]], was formed within the last 1000 years, and its eruptions destroyed the Māori settlements on neighboring [[Motutapu Island]] some 700 years ago. Rangitoto's size, symmetry, and its position guarding the entrance to [[Waitemata Harbour]] and its visibility from many parts of the Auckland region make it Auckland's most iconic natural feature. It is eerily quiet as almost no birds or insects have settled on the island due to the rich acidity of its soil and type of flora that has adapted to grow out of the black broken rocky soil. |
===Harbors and Gulf=== | ===Harbors and Gulf=== | ||
| − | + | Bridges span parts of both the city's harbors, notably the [[Auckland Harbour Bridge]] crossing the Waitemata Harbour west of the Auckland CBD. The upper reaches of the Manukau and Waitemata Harbours are spanned by [[Mangere Bridge]] and the [[Upper Harbour Bridge]] respectively. In earlier times, [[portage]] paths crossed the narrowest sections of the isthmus. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Bridges span parts of both | ||
| − | |||
===Climate=== | ===Climate=== | ||
| + | Auckland has a warm, temperate climate, with warm, humid [[summer]]s and mild, damp [[winter]]s. The average daily maximum [[temperature]] is 23.7°C (74.7°F) in February, and 14.5°C (58.1°F) in July, the absolute maximum recorded temperature is 30.5°C (86.9°F), while the absolute minimum is -2.5°C (27.5°F). High levels of [[rain]]fall occur almost year-round with an average of 1240 mm per year spread over 137 'rain days'. <ref>''National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research (NIWA).'' [http://www.niwascience.co.nz/edu/resources/climate/summary/summary.prn Climate information for selected New Zealand locations]. Retrieved October 14, 2007 </ref> Climatic conditions vary in different parts of the city owing to geography such as hills, land cover and distance from the sea, hence unofficial Auckland temperature records exist, such as a maximum of 32.4°C (90.3°F) in Henderson during February 1998. <ref>''The Supramics Company''. [http://www.supramics.com/climate/chapter2.html Hot weather changes]. Retrieved October 14, 2007. </ref> On July 27, 1939 Auckland received its only [[snow]] fall in recorded history. <ref>Erick Brenstrum. June 2003. [http://www.civildefence.govt.nz/memwebsite.NSF/Files/Tephra2003-Snowstorms/$file/Tephra2003-Snowstorms.pdf Snowstorms]. ''Ministry of Civil Defence & Emergency Management''. Retrieved November 4, 2007. </ref> | ||
| − | + | Auckland also occasionally experiences cyclonic activity with five [[tropical cyclone]]s passing within 137 miles (220km) of Auckland City between 1970 and 2001. A severe cyclone with winds up to 170 km/hr (106 mph) and rainfall up to 85mm/hr (3.3" per hour) is expected every one hundred years. On average, 1-2 [[tornado]]es or waterspouts (tornadoes over water) are reported in Auckland every year. New Zealand's tornadoes are much smaller than those occurring in the [[United States|American]] Midwest with a damage path usually only 10-20 meters (33-66 feet) wide and 1-5 km (0.6-3.1 miles) long. They have an average life of only 15 minutes. <ref> Auckland Regional Council Tornado.</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | Auckland also occasionally experiences cyclonic activity with five tropical | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="width: 90%; margin: 0 auto 0 auto; font-size:80%;" | {| class="wikitable" style="width: 90%; margin: 0 auto 0 auto; font-size:80%;" | ||
| Line 166: | Line 257: | ||
==Governance== | ==Governance== | ||
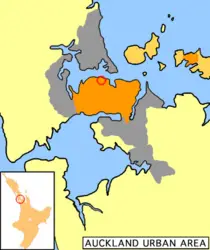
| − | [[Image:AucklandCity+Region.png|thumb| | + | [[Image:AucklandCity+Region.png|thumb|210px|Schematic map of Auckland showing Auckland City in orange, the Greater Auckland Area in gray and the City Center located by the red circle.]] |
The Auckland Regional Council (ARC) is one of the elected local government authorities of the Auckland Region. It consists of a chairman and 12 councilors. The ARC was created as the successor of the Auckland Regional Authority. Unlike the territorial authorities of Greater Auckland, it has an umbrella function covering all the various cities and districts making up the region, but its regulatory power and funding abilities are in turn restricted to several areas including public transport, environmental protection and regional parks. The ARC is an elected body, and collects its own revenue mainly by property taxes (or rates). | The Auckland Regional Council (ARC) is one of the elected local government authorities of the Auckland Region. It consists of a chairman and 12 councilors. The ARC was created as the successor of the Auckland Regional Authority. Unlike the territorial authorities of Greater Auckland, it has an umbrella function covering all the various cities and districts making up the region, but its regulatory power and funding abilities are in turn restricted to several areas including public transport, environmental protection and regional parks. The ARC is an elected body, and collects its own revenue mainly by property taxes (or rates). | ||
| − | Territorial authorities are the second tier of local government in New Zealand, below regional councils. In November 1989, central government restructured local authorities throughout | + | Territorial authorities are the second tier of local government in New Zealand, below regional councils. In November 1989, central government restructured local authorities throughout the country. Auckland City was merged with eight smaller local authorities to form a new Auckland City Council. The new city had double the population of the old and the amalgamation set the present-day boundaries of the city. |
| + | |||
| + | Auckland City Council consists of a mayor and 19 councilors with elections held every three years. Several islands of the [[Hauraki Gulf]] are administered as part of Auckland City, though they are not officially part of the Auckland metropolitan area. Parts of [[Waiheke Island]] effectively function as [[Suburbs of Auckland, New Zealand|Auckland suburbs]], while various smaller islands near Auckland are mostly recreational open space or nature sanctuaries. | ||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
| + | [[Image:Auckland City From the Sky Tower.png|thumb|275px|Auckland Central Business District.]] | ||
| + | Many major international corporations have an Auckland office, as the city is seen as the economic capital of the nation. Financial and business services are located here, making up a large percentage of the Central Business District (CBD) economy. <ref> ''Auckland City Council''. Auckland's CBD at a glance.</ref> A large proportion of the technical and trades workforce is based in the industrial zones of South Auckland. The largest commercial and industrial areas of Greater Auckland are in the southeast of Auckland City as well as in the western parts of Manukau City, mostly in the areas oriented towards the [[Manukau Harbour]] and the [[Tamaki River]] estuary. | ||
| − | + | One of Auckland’s most important economic features is Waitemata Harbour. Overseas and intercoastal shipping utilizes the harbor for Auckland’s internal and export trade. The ports of Auckland are responsible for NZ$11 billion a year flowing into the regional economy, including 173,000 jobs in the Auckland region. <ref> ''Ports of Auckland''. [http://www.poal.co.nz/about/economicimpact.htm Economic Impact] Retrieved October 16, 2007.</ref> | |
| − | + | The principal exports through Auckland’s ports include [[iron]], [[steel]], [[wool]], dairy products, and meat and hides. Its imports include [[petroleum]], iron and steel products, [[sugar]], [[wheat]], and [[phosphate]]s. <ref> ''The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition''. [http://www.answers.com/topic/auckland?cat=travel Auckland.] Retrieved October 16, 2007. </ref> The Greater Auckland area also supports engineering, publishing, and metal trades; the manufacture of paint, glass, plastics, chemicals, cement, and a variety of consumer goods; vehicle assembly and boatbuilding; and food processing, brewing, and sugar refining.<ref> ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. Auckland.</ref> | |
| − | + | In 1969, a large iron and steel mill was opened at Glenbrook (20 miles [32 km] south), and in 1977 construction was completed of a natural-gas pipeline running from the Maui field to Auckland. | |
==Demographics== | ==Demographics== | ||
| − | The Greater Auckland area has a population of 1,303,068 or 32.4 | + | The Greater Auckland area has a population of 1,303,068 (2006 census) or 32.4 percent of New Zealand’s population. However, it has a very low population density because it sprawls over more than 400 square miles. It is expected to grow to an estimated two million inhabitants by the year 2040. <ref> ''Auckland Regional Council''. Auckland's growth.</ref> |
| − | Auckland is home to many cultures. The majority of inhabitants claim [[ | + | Auckland is home to many cultures. The majority of inhabitants claim [[Europe]]an - predominantly [[Briton|British]] - descent, but substantial [[Māori]], [[Pacific Islander]] and [[Asia]]n communities exist as well. The 2006 Census by ''Statistics New Zealand'' listed 137,133 (or 11.1 percent of the Auckland population) persons that stated Māori as being either their sole ethnic group or one of several ethnic groups they belong to. |
| − | Auckland has the largest [[Polynesia]]n population of any city in the world and a higher proportion of people of Asian origin than the rest of New Zealand. Pacific Peoples accounts for 14.3 | + | Auckland has the largest [[Polynesia]]n population of any city in the world and a higher proportion of people of Asian origin than the rest of New Zealand. Pacific Peoples accounts for 14.3 percent of the Auckland population while 18.8 percent claim Asian heritage. <ref>''Statistics New Zealand''</ref> Ethnic groups from all corners of the world have a presence in Auckland, making it by far the country's most cosmopolitan city. |
| − | The 2006 Census also provides information about the | + | The 2006 Census also provides information about the multilinguality of the region. Accordingly, 867,825 people in the Auckland Region spoke one language only, while 274,863 spoke two, and 57,051 could converse in three or more languages. <ref> ''Statistics New Zealand''. [http://www.stats.govt.nz/census/2006-census-data/regional-summary-tables.htm Regional Summary Tables]. Retrieved October 16, 2007. </ref> |
==Education== | ==Education== | ||
| − | Auckland's population has one of the highest levels of education in New Zealand with 17.7 | + | [[Image:Devonport Wharf Kea Ferry.jpg|thumb|right|270px|Ferry travel is a popular type of public transport for some Auckland destinations.]] |
| + | Auckland's population has one of the highest levels of [[education]] in New Zealand with 17.7 percent of the population having earned a bachelor's degree or higher compared to a national average of only 14.2 percent. Only the national capital of Wellington, with 21.1 percent claiming a bachelor's degree or higher exceeds Auckland education level. <ref>Ibid. </ref> | ||
| − | Auckland has a number of important educational institutions, including some of the largest universities in the country. | + | Auckland has a number of important educational institutions, including some of the largest universities in the country. It is also known to be a major center of overseas language education, with large numbers of foreign students (particularly [[East Asia]]ns) coming to the city for several months or years to learn [[English language|English]] or study at universities. <ref> ''Statistics New Zealand''. [http://www2.stats.govt.nz/domino/external/pasfull/pasfull.nsf/4c2567ef00247c6a4c2567be0008d2f8/4c2567ef00247c6acc2571b900127ca3?OpenDocument Survey of English Language Providers - Year ended March 2006]. Retrieved October 20, 2007. </ref> There are approximately 50 "NZQA" certified schools and institutes teaching English in the Auckland area. |
| − | + | Among the most important tertiary educational institutes are the [[University of Auckland]], [[Unitec New Zealand]], [[Auckland University of Technology]], [[Massey University]], the [[Manukau Institute of Technology]] and AIS St. Helens that specializes in international students. | |
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Auckland is an ethnically diverse city containing 181 different ethnic groups<ref>Auckland City Council | + | Auckland is an ethnically diverse city containing 181 different ethnic groups. <ref> ''Auckland City Council'' Our People.</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | + | The city is home to 60 galleries, the largest of which are the Auckland Art Gallery and the New Gallery that contain more than 100,000 works, housing the county's most significant collection of New Zealand and European art. [[Live theater]], comedy, [[music]] and [[drama]] performances take place year-round at Auckland's many theaters and entertainment centers. | |
| − | The magnificent 'Pou Kapua' (a significant Maori and Pacific Island arts show-piece and the largest totem of its type in the world) is on display in Manukau. Daily Maori cultural performances are held at the Auckland War Memorial Museum, featuring Maori mythology, genealogy (Whakapapa) and spirituality (taha wairua). | + | The magnificent 'Pou Kapua' (a significant Maori and Pacific Island arts show-piece and the largest totem of its type in the world) is on display in Manukau. Daily [[Maori]] cultural performances are held at the Auckland War Memorial Museum, featuring Maori [[mythology]], genealogy (Whakapapa) and spirituality (taha wairua). The world's largest collection of [[Polynesia]]n artifacts and the history of Maori [[culture]] and its people can be seen at the Auckland War Memorial Museum. A guided walk of Mt. Eden celebrates Auckland's unique cultural heritage with the most accessible remains of the pre-European Maori occupation etched into the slopes of Auckland's volcanic cones. |
| − | A diverse range of nautical and historical artifacts representing New Zealand's maritime history, from the earliest Polynesian arrivals to modern day seafaring, is on display at the National Maritime Museum on Auckland's waterfront.<ref>Tourism Auckland [http://www.aucklandnz.com/VisitorInformation/AucklandGuide/specialinterests.aspx Special Interests] Retrieved October 20, 2007.</ref> | + | A diverse range of nautical and historical artifacts representing New Zealand's maritime history, from the earliest Polynesian arrivals to modern day seafaring, is on display at the National Maritime Museum on Auckland's waterfront. <ref>''Tourism Auckland''. [http://www.aucklandnz.com/VisitorInformation/AucklandGuide/specialinterests.aspx Special Interests]. Retrieved October 20, 2007.</ref> |
Auckland also boasts a [[symphonic orchestra|symphonic ensemble]] in the [[Auckland Philharmonic Orchestra]]. | Auckland also boasts a [[symphonic orchestra|symphonic ensemble]] in the [[Auckland Philharmonic Orchestra]]. | ||
===Religion=== | ===Religion=== | ||
| − | + | As in the rest of the country, more than half (58.4 percent) of Aucklanders are nominally [[Christianity|Christian]], but fewer than 10 percent regularly attend church and almost 30 percent profess no religious affiliation. Included in the Christian figures are several Maori Christian denominations including Ratana Ringatü. The main Christian denominations are [[Roman Catholic]], [[Anglican]] and [[Presbyterian]]. [[Pentecostalism|Pentecostal]] and [[Charismatic movement|charismatic]] churches are the fastest growing. A higher percentage of [[Polynesia]]n immigrants are regular churchgoers than other Aucklanders, although church attendance drops off in second or third-generation Polynesian Aucklanders. | |
| + | Other immigrant cultures have added to the religious diversity of the city, adding faiths such as [[Buddhism]], [[Hinduism]], and [[Islam]] to Auckland's religious landscape. There is also a small, long-established [[Judaism|Jewish]] community. <ref> ''Statistics New Zealand''. [http://www.stats.govt.nz/NR/rdonlyres/73FF378F-0119-4714-ABB2-941EEC21965A/0/Table6.xls Religious Affiliation]. Retrieved October 19, 2007.</ref> | ||
===Parks and nature=== | ===Parks and nature=== | ||
| − | [[Auckland Domain]] is one of the largest parks within the city, situated close to the | + | [[Auckland Domain]] is one of the largest parks within the city, situated close to the Central business district and having a good view of the Gulf and of [[Rangitoto]] Island. Smaller parks also close to the city center are [[Albert Park, Auckland|Albert Park]], [[Myers Park, Auckland|Myers Park]], [[Western Park, Auckland|Western Park]] and [[Victoria Park, Auckland|Victoria Park]]. While most volcanic cones in the [[Auckland Volcanic Field]] have been affected by quarrying, many of the remaining cones are now ensconced within parks, and retain a somewhat more natural character than the surrounding city. Prehistoric earthworks and historic fortifications feature in several of these parks, including [[Mount Eden]], [[North Head, New Zealand|North Head]] and [[One Tree Hill, New Zealand|One Tree Hill]] (Maungakiekie). |
Other parks around the city are in [[Western Springs]], which has a large park bordering on the [[MOTAT]] museum and the [[Auckland Zoo]]. The [[Auckland Botanic Gardens]] are located further south in [[Manurewa]]. | Other parks around the city are in [[Western Springs]], which has a large park bordering on the [[MOTAT]] museum and the [[Auckland Zoo]]. The [[Auckland Botanic Gardens]] are located further south in [[Manurewa]]. | ||
===Sport=== | ===Sport=== | ||
| − | Sport is a very important part of all New Zealander’s lives and especially for Aucklanders. Auckland is often | + | Sport is a very important part of all New Zealander’s lives and especially for Aucklanders. |
| + | |||
| + | Auckland is popularly known as the "City of Sails" because the harbor is often dotted with hundreds of yachts and has more per capita than any other city in the world, with around 135,000 [[yacht]]s and [[Launch (boat)|launch]]es estimated. Around 60,500 of the country's 149,900 registered yachtsmen also come from the Auckland Region. <ref> James Ihaka. October 14, 2006 [http://www.nzherald.co.nz/section/1/story.cfm?c_id=1&objectid=10405832 Punters love City of Sails] ''New Zealand Herald''. Retrieved October 19, 2007 </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Viaduct Basin]] hosted two [[America's Cup]] challenges ([[2000 America’s Cup|2000 Cup]] and [[2003 America’s Cup|2003 Cup]]). With the sheltered Waitemata Harbour at its doorstep, Auckland sees many nautical events, and there are also a large number of sailing clubs in Auckland, as well as [[Westhaven Marina]], the largest in the [[Southern Hemisphere]].<ref> ''Yachting NZ''.[http://www.yachtingnz.org.nz/index.cfm?pageid=124&languageid=1&siteid=135_1 Sailing Club Directory]. Retrieved October 19, 2007 </ref> | ||
Auckland also supports several franchised or local teams that compete in international or inter-provincial competitions. These teams include: | Auckland also supports several franchised or local teams that compete in international or inter-provincial competitions. These teams include: | ||
*''The Blues'' (formerly known as the 'Auckland Blues'), that competes in rugby union’s ''Super 14'' competition between teams from New Zealand (5), South Africa (5) and Australia (4). | *''The Blues'' (formerly known as the 'Auckland Blues'), that competes in rugby union’s ''Super 14'' competition between teams from New Zealand (5), South Africa (5) and Australia (4). | ||
| − | *''The Warriors'' | + | *''The Warriors,'' competing in rugby league's Australian Rugby League competition. |
| − | *The ''Auckland Aces'' | + | *The ''Auckland Aces,'' that competes in New Zealand’s national cricket competitions. |
| − | *The ''New Zealand Breakers'' | + | *The ''New Zealand Breakers,'' competing in the Australian National Basketball League. |
*A netball team playing in the new Australian and New Zealand Netball League. | *A netball team playing in the new Australian and New Zealand Netball League. | ||
| − | |||
Major professional sporting events hosted by Auckland include: | Major professional sporting events hosted by Auckland include: | ||
* The America’s Cup yachting race finals in 2000 & 2003. | * The America’s Cup yachting race finals in 2000 & 2003. | ||
| Line 245: | Line 340: | ||
* The Auckland Marathon (and half-marathon). | * The Auckland Marathon (and half-marathon). | ||
| − | == | + | ==Famous sites== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
The following is a list of tourist attractions and landmarks in the Auckland metropolitan area: | The following is a list of tourist attractions and landmarks in the Auckland metropolitan area: | ||
| Line 303: | Line 369: | ||
* [[One Tree Hill, New Zealand|One Tree Hill]] (Maungakiekie) - a volcanic cone that dominates the skyline in the southern, inner suburbs. It no longer has a tree on the summit (after a politically motivated attack on the old tree) but is still crowned by an [[obelisk]]. | * [[One Tree Hill, New Zealand|One Tree Hill]] (Maungakiekie) - a volcanic cone that dominates the skyline in the southern, inner suburbs. It no longer has a tree on the summit (after a politically motivated attack on the old tree) but is still crowned by an [[obelisk]]. | ||
* [[Rangitoto Island]] - guards the entrance to [[Waitemata Harbour]], and forms a prominent feature on the eastern horizon. | * [[Rangitoto Island]] - guards the entrance to [[Waitemata Harbour]], and forms a prominent feature on the eastern horizon. | ||
| + | [[Image:View from Sky Tower Akl.jpg|thumb|600px|center|360-degree view from Sky Tower, showing many landmarks in the Central Business District.]] | ||
| + | ==Notes== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | ==Sources and further reading == | ||
| + | * McLauchlan, Gordon. 1992. ''The Illustrated Encyclopedia of New Zealand.'' Glenfield, NZ: David Bateman Ltd, ISBN 1869530071 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==External links== |
| − | + | All links retrieved August 21, 2023. | |
| + | * [http://www.aucklandcouncil.govt.nz/EN/Pages/default.aspx Auckland City Council] - Official website | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{credit|Auckland,_New_Zealand|154555760|Auckland_City_Council|164220122|Auckland_Regional_Council|143992163|History_of_Auckland|165001209}} | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Geography]] | [[Category:Geography]] | ||
[[Category:Oceania]] | [[Category:Oceania]] | ||
[[Category:Cities]] | [[Category:Cities]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:26, 21 August 2023
| Auckland Tāmaki Makaurau (Māori) |
|
| — Main urban area — | |
|
|
| Nickname: City of Sails, SuperCity (sometimes ironically), Queen City (archaic) |
|
| Coordinates: {{#invoke:Coordinates|coord}}{{#coordinates:36|50|25.50|S|174|44|23.53|E|type:city | |
|---|---|
| name= }} | |
| Country | |
| Island | North Island |
| Region | Auckland |
| Territorial authority | Auckland |
| Settled by Māori | c. 1350 |
| Settled by Europeans | 1840 |
| Local boards | List
|
| Area | |
| - Urban | 1,086 km² (419.3 sq mi) |
| - Metro | 560 km² (216.2 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 196 m (643 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population (June 2011 estimate)[1] | |
| - Urban | 1,377,200 |
| - Metro | 1,486,000 |
| - Demonym | Aucklander, Jafa (often derogatory) |
| Time zone | NZST (UTC+12) |
| - Summer (DST) | NZDT (UTC+13) |
| Postcode(s) | 0500-2999 |
| Area code(s) | 09 |
| Local iwi | Ngāti Whātua, Tainui |
| Website: www.aucklandcouncil.govt.nz | |
The Auckland metropolitan area or Greater Auckland, in the North Island of New Zealand, is the largest urban area of the country. With over 1.3 million people, it is home to nearly one-third of the country's population. Demographic trends indicate that it will continue growing faster than the rest of the country. It is an extensive urban area consisting of Auckland City (excluding the Hauraki Gulf islands), North Shore City, and the urban parts of Waitakere and Manukau cities, along with Papakura District and some nearby urban parts of Rodney and Franklin Districts.
Auckland has the largest Polynesian population of any city in the world [2] as well as its country's greatest concentration of indigenous Maori.
Auckland lies between the Hauraki Gulf of the Pacific Ocean to the east, the low Hunua Ranges to the south-east, the Manukau Harbour to the south-west, and the Waitakere Ranges and smaller ranges to the west and north-west. The central part of the urban area occupies a narrow isthmus between the Manukau Harbour on the Tasman Sea and the Waitemata Harbour on the Pacific Ocean. It is one of the few cities in the world to have harbors on two separate major bodies of water. Known as the "City of Sails," Auckland has more yachts per capita than any other city in the world.
Auckland is known in the Maori tongue as Tamaki-Makau-Rau, meaning "the maiden with a hundred lovers." It earned this name because it was a coveted area, fought over by many tribes due to its incredible forested hills, rich soils, beautiful beaches and abundance of seafood. Its temperate climate adds to its idyllic setting. The surrounding hills are covered in rainforest and the landscape is dotted with dozens of dormant volcanic cones. Considered a Polynesian paradise, Auckland is a melting pot of South Pacific and Asian cultures, strongly influenced by its own native Maori traditions.
History
The isthmus on which Auckland resides was first settled around 1350 and was valued for its rich and fertile land. Ngati Whatua of Orakei are a hapu (Māori language for social division or subtribe) of the Ngati Whatua tribe, based at Kaipara. They lived in the area for hundreds of years. The subtribe owned the land communally and worked it together, tending crops and gathering food from the surrounding coastline and countryside. The basis of their identity stemmed from the land, which provided both economic and spiritual resources. [3]
On February 6, 1840, Great Britain and a number of New Zealand Maori tribes of North Island, including the Whatua of Orakei, signed an historic pact. This pact, the Treaty of Waitangi, purported to protect Maori rights and was the basis of the British annexation of New Zealand. The treaty provided for
- (1) acceptance of the British queen's sovereignty in their lands,
- (2) the crown's protection of Maori possessions, with the exclusive right of the queen to purchase Maori land, and
- (3) full rights of British subjects for the Maori signatories. [4]
Approximately 3,000 acres (1214 hectares) of land was handed over to the Crown by Ngati Whatua of Orakei for a township to be established. The Crown paid £341 for the 3,000 acres and six months later, resold just 44 acres (17 hectares) of that land to settlers for £24,275. They used the money to build roads, bridges, hospitals, and other services for the new town. Ngati Whatua of Orakei had effectively funded the early development of Auckland from the sale of their tribal land. [5]
Māori population in the area is estimated to have peaked at 20,000 before the arrival of Europeans. This event - and the guns which they traded to local iwi - upset the local power balances. This resulted in extensive inter-tribal warfare, which together with some introduced plagues resulted in the area having relatively low numbers of Māori when European settlement in New Zealand began in earnest.
After the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi the new Governor of New Zealand, William Hobson chose the area as his new capital. He named the area "Auckland" for George Eden, earl of Auckland, British first lord of the Admiralty and later governor-general of India. Hobson founded the town of Auckland on September 18, 1840.[6] However, even in 1840, Port Nicholson (later Wellington), was seen as a better choice for an administrative capital, due to its proximity to the South Island, which was being settled much more rapidly. At the same time, Auckland was the capital and principal city of the Auckland Province, until the provincial system was abolished in 1876. Nonetheless, even after losing its status as the national capital in 1865, immigration to the new city stayed strong.
The present boroughs of Newmarket, Onehunga, Tamaki, Howick, and Drury were developed between 1850–1900 in the shape of villages and small-farming centers. The first 20 years of the twentieth century was a period of consolidation and development of the suburbs along main routes out of the city. These included Remuera, Epsom, Ellerslie, Mission Bay, Orakei, St. Heliers, Grey Lynn, Point Chevalier, Mount Albert, Devonport, Northcote, and Birkenhead. From 1918 to 1945 the population growth was centered in these already established settlements, while industries and industrial areas were established and expanded, particularly on the south-east perimeter. Since then Papatoetoe, Papakura, Manurewa, Henderson, and North Shore have shown a marked expansion. Auckland was declared a borough on July 29, 1851 and a city on April 24, 1871. [7]
Geography
Auckland is located at 36’ 51” South and 174’ 47” East. The Greater Auckland area lies on and around an isthmus, less than 1.2 miles (2 km) wide at its narrowest point, between Mangere Inlet and the Tamaki River. There are two harbors in the Auckland urban area surrounding this isthmus, Waitemata Harbour to the north, which opens east to the Hauraki Gulf, and Manukau Harbour to the south, which opens west to the Tasman Sea.
The Auckland region experiences infrequent earthquake activity although it lies in one of the lowest earthquake activity regions of New Zealand. Earthquakes that register an intensity greater than VII on the Modified Mercalli scale are likely to cause widespread damage (The Modified Mercalli scale lists "VII" as "Frightens everyone, damage to weak buildings, difficult to stand up"). [8]
Volcanoes
Auckland straddles the volcanoes of the Auckland Volcanic Field. The approximately 50 volcanic vents in the field take the form of cones, lakes, lagoons, islands and depressions, and several have produced extensive lava flows. Most of the cones have been partly or completely quarried away. The individual volcanoes are all considered extinct, although the volcanic field itself is merely dormant.
The most recent and by far the largest volcano, Rangitoto Island, was formed within the last 1000 years, and its eruptions destroyed the Māori settlements on neighboring Motutapu Island some 700 years ago. Rangitoto's size, symmetry, and its position guarding the entrance to Waitemata Harbour and its visibility from many parts of the Auckland region make it Auckland's most iconic natural feature. It is eerily quiet as almost no birds or insects have settled on the island due to the rich acidity of its soil and type of flora that has adapted to grow out of the black broken rocky soil.
Harbors and Gulf
Bridges span parts of both the city's harbors, notably the Auckland Harbour Bridge crossing the Waitemata Harbour west of the Auckland CBD. The upper reaches of the Manukau and Waitemata Harbours are spanned by Mangere Bridge and the Upper Harbour Bridge respectively. In earlier times, portage paths crossed the narrowest sections of the isthmus.
Climate
Auckland has a warm, temperate climate, with warm, humid summers and mild, damp winters. The average daily maximum temperature is 23.7°C (74.7°F) in February, and 14.5°C (58.1°F) in July, the absolute maximum recorded temperature is 30.5°C (86.9°F), while the absolute minimum is -2.5°C (27.5°F). High levels of rainfall occur almost year-round with an average of 1240 mm per year spread over 137 'rain days'. [9] Climatic conditions vary in different parts of the city owing to geography such as hills, land cover and distance from the sea, hence unofficial Auckland temperature records exist, such as a maximum of 32.4°C (90.3°F) in Henderson during February 1998. [10] On July 27, 1939 Auckland received its only snow fall in recorded history. [11]
Auckland also occasionally experiences cyclonic activity with five tropical cyclones passing within 137 miles (220km) of Auckland City between 1970 and 2001. A severe cyclone with winds up to 170 km/hr (106 mph) and rainfall up to 85mm/hr (3.3" per hour) is expected every one hundred years. On average, 1-2 tornadoes or waterspouts (tornadoes over water) are reported in Auckland every year. New Zealand's tornadoes are much smaller than those occurring in the American Midwest with a damage path usually only 10-20 meters (33-66 feet) wide and 1-5 km (0.6-3.1 miles) long. They have an average life of only 15 minutes. [12]
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean daily maximum temperature | 23.3°C 73.94°F |
23.7 °C 74.7 °F |
22.4 °C 72.3°F |
20.0°C 68.0 °F |
17.4 °C 63.3 °F |
15.2 °C 59.4 °F |
14.5 °C 58.1 °F |
15.0 °C 59.0 °F |
16.2 °C 61.2 °F |
17.8 °C 64.1 °F |
19.6 °C 67.3 °F |
21.6 °C 70.9 °F |
18.9°C 66.0°F | |
| Mean daily minimum temperature | 15.3°C 59.6°F |
15.8 °C 60.5 °F |
14.6 °C 58.3 °F |
12.3 °C 54.2 °F |
10.0 °C 50.0 °F |
8.0 °C 46.4°F |
7.1 °C 44.8 °F |
7.6 °C 45.7 °F |
8.9 °C 48.0 °F |
10.5 °C 50.9 °F |
12.1 °C 53.78 °F |
13.9 °C 57.0 °F |
11.3°C 52.4°F | |
| Mean total rainfall | 75 mm 2.95 in |
65 mm 2.56 in |
94 mm 3.70 in |
105 mm 4.13 in |
103 mm 4.06 in |
139 mm 5.47 in |
146 mm 5.75 in |
121 mm 4.76 in |
116 mm 4.57 in |
91 mm 3.58 in |
93 mm 3.66 in |
91 mm 3.58 in |
1240 mm 48.82 in | |
| Mean number of rain days | 8 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 15 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 12 | 11 | 9 | 137 | |
| Source: Niwa Science climate data | ||||||||||||||
Governance
The Auckland Regional Council (ARC) is one of the elected local government authorities of the Auckland Region. It consists of a chairman and 12 councilors. The ARC was created as the successor of the Auckland Regional Authority. Unlike the territorial authorities of Greater Auckland, it has an umbrella function covering all the various cities and districts making up the region, but its regulatory power and funding abilities are in turn restricted to several areas including public transport, environmental protection and regional parks. The ARC is an elected body, and collects its own revenue mainly by property taxes (or rates).
Territorial authorities are the second tier of local government in New Zealand, below regional councils. In November 1989, central government restructured local authorities throughout the country. Auckland City was merged with eight smaller local authorities to form a new Auckland City Council. The new city had double the population of the old and the amalgamation set the present-day boundaries of the city.
Auckland City Council consists of a mayor and 19 councilors with elections held every three years. Several islands of the Hauraki Gulf are administered as part of Auckland City, though they are not officially part of the Auckland metropolitan area. Parts of Waiheke Island effectively function as Auckland suburbs, while various smaller islands near Auckland are mostly recreational open space or nature sanctuaries.
Economy
Many major international corporations have an Auckland office, as the city is seen as the economic capital of the nation. Financial and business services are located here, making up a large percentage of the Central Business District (CBD) economy. [13] A large proportion of the technical and trades workforce is based in the industrial zones of South Auckland. The largest commercial and industrial areas of Greater Auckland are in the southeast of Auckland City as well as in the western parts of Manukau City, mostly in the areas oriented towards the Manukau Harbour and the Tamaki River estuary.
One of Auckland’s most important economic features is Waitemata Harbour. Overseas and intercoastal shipping utilizes the harbor for Auckland’s internal and export trade. The ports of Auckland are responsible for NZ$11 billion a year flowing into the regional economy, including 173,000 jobs in the Auckland region. [14]
The principal exports through Auckland’s ports include iron, steel, wool, dairy products, and meat and hides. Its imports include petroleum, iron and steel products, sugar, wheat, and phosphates. [15] The Greater Auckland area also supports engineering, publishing, and metal trades; the manufacture of paint, glass, plastics, chemicals, cement, and a variety of consumer goods; vehicle assembly and boatbuilding; and food processing, brewing, and sugar refining.[16]
In 1969, a large iron and steel mill was opened at Glenbrook (20 miles [32 km] south), and in 1977 construction was completed of a natural-gas pipeline running from the Maui field to Auckland.
Demographics
The Greater Auckland area has a population of 1,303,068 (2006 census) or 32.4 percent of New Zealand’s population. However, it has a very low population density because it sprawls over more than 400 square miles. It is expected to grow to an estimated two million inhabitants by the year 2040. [17]
Auckland is home to many cultures. The majority of inhabitants claim European - predominantly British - descent, but substantial Māori, Pacific Islander and Asian communities exist as well. The 2006 Census by Statistics New Zealand listed 137,133 (or 11.1 percent of the Auckland population) persons that stated Māori as being either their sole ethnic group or one of several ethnic groups they belong to.
Auckland has the largest Polynesian population of any city in the world and a higher proportion of people of Asian origin than the rest of New Zealand. Pacific Peoples accounts for 14.3 percent of the Auckland population while 18.8 percent claim Asian heritage. [18] Ethnic groups from all corners of the world have a presence in Auckland, making it by far the country's most cosmopolitan city.
The 2006 Census also provides information about the multilinguality of the region. Accordingly, 867,825 people in the Auckland Region spoke one language only, while 274,863 spoke two, and 57,051 could converse in three or more languages. [19]
Education
Auckland's population has one of the highest levels of education in New Zealand with 17.7 percent of the population having earned a bachelor's degree or higher compared to a national average of only 14.2 percent. Only the national capital of Wellington, with 21.1 percent claiming a bachelor's degree or higher exceeds Auckland education level. [20]
Auckland has a number of important educational institutions, including some of the largest universities in the country. It is also known to be a major center of overseas language education, with large numbers of foreign students (particularly East Asians) coming to the city for several months or years to learn English or study at universities. [21] There are approximately 50 "NZQA" certified schools and institutes teaching English in the Auckland area.
Among the most important tertiary educational institutes are the University of Auckland, Unitec New Zealand, Auckland University of Technology, Massey University, the Manukau Institute of Technology and AIS St. Helens that specializes in international students.
Culture
Auckland is an ethnically diverse city containing 181 different ethnic groups. [22]
The city is home to 60 galleries, the largest of which are the Auckland Art Gallery and the New Gallery that contain more than 100,000 works, housing the county's most significant collection of New Zealand and European art. Live theater, comedy, music and drama performances take place year-round at Auckland's many theaters and entertainment centers.
The magnificent 'Pou Kapua' (a significant Maori and Pacific Island arts show-piece and the largest totem of its type in the world) is on display in Manukau. Daily Maori cultural performances are held at the Auckland War Memorial Museum, featuring Maori mythology, genealogy (Whakapapa) and spirituality (taha wairua). The world's largest collection of Polynesian artifacts and the history of Maori culture and its people can be seen at the Auckland War Memorial Museum. A guided walk of Mt. Eden celebrates Auckland's unique cultural heritage with the most accessible remains of the pre-European Maori occupation etched into the slopes of Auckland's volcanic cones.
A diverse range of nautical and historical artifacts representing New Zealand's maritime history, from the earliest Polynesian arrivals to modern day seafaring, is on display at the National Maritime Museum on Auckland's waterfront. [23]
Auckland also boasts a symphonic ensemble in the Auckland Philharmonic Orchestra.
Religion
As in the rest of the country, more than half (58.4 percent) of Aucklanders are nominally Christian, but fewer than 10 percent regularly attend church and almost 30 percent profess no religious affiliation. Included in the Christian figures are several Maori Christian denominations including Ratana Ringatü. The main Christian denominations are Roman Catholic, Anglican and Presbyterian. Pentecostal and charismatic churches are the fastest growing. A higher percentage of Polynesian immigrants are regular churchgoers than other Aucklanders, although church attendance drops off in second or third-generation Polynesian Aucklanders.
Other immigrant cultures have added to the religious diversity of the city, adding faiths such as Buddhism, Hinduism, and Islam to Auckland's religious landscape. There is also a small, long-established Jewish community. [24]
Parks and nature
Auckland Domain is one of the largest parks within the city, situated close to the Central business district and having a good view of the Gulf and of Rangitoto Island. Smaller parks also close to the city center are Albert Park, Myers Park, Western Park and Victoria Park. While most volcanic cones in the Auckland Volcanic Field have been affected by quarrying, many of the remaining cones are now ensconced within parks, and retain a somewhat more natural character than the surrounding city. Prehistoric earthworks and historic fortifications feature in several of these parks, including Mount Eden, North Head and One Tree Hill (Maungakiekie).
Other parks around the city are in Western Springs, which has a large park bordering on the MOTAT museum and the Auckland Zoo. The Auckland Botanic Gardens are located further south in Manurewa.
Sport
Sport is a very important part of all New Zealander’s lives and especially for Aucklanders.
Auckland is popularly known as the "City of Sails" because the harbor is often dotted with hundreds of yachts and has more per capita than any other city in the world, with around 135,000 yachts and launches estimated. Around 60,500 of the country's 149,900 registered yachtsmen also come from the Auckland Region. [25]
Viaduct Basin hosted two America's Cup challenges (2000 Cup and 2003 Cup). With the sheltered Waitemata Harbour at its doorstep, Auckland sees many nautical events, and there are also a large number of sailing clubs in Auckland, as well as Westhaven Marina, the largest in the Southern Hemisphere.[26]
Auckland also supports several franchised or local teams that compete in international or inter-provincial competitions. These teams include:
- The Blues (formerly known as the 'Auckland Blues'), that competes in rugby union’s Super 14 competition between teams from New Zealand (5), South Africa (5) and Australia (4).
- The Warriors, competing in rugby league's Australian Rugby League competition.
- The Auckland Aces, that competes in New Zealand’s national cricket competitions.
- The New Zealand Breakers, competing in the Australian National Basketball League.
- A netball team playing in the new Australian and New Zealand Netball League.
Major professional sporting events hosted by Auckland include:
- The America’s Cup yachting race finals in 2000 & 2003.
- 1987 Rugby World Cup Final.
- International rugby league matches.
- International cricket matches.
- International tennis tournaments including the Heineken Open (men’s) & the ASB Classic (women’s).
And the more recreational events including:
- The 2.8 kilometer (1.8 miles) 'Cross Harbour Swim' from Devonport to Auckland.
- The 8.4 kilometers (5.2 miles) 'Round the Bays' fun-run.
- The Auckland Marathon (and half-marathon).
Famous sites
The following is a list of tourist attractions and landmarks in the Auckland metropolitan area:
- Attractions & Buildings
- Auckland Civic Theatre - a recently renovated famous heritage atmospheric theatre in downtown Auckland.
- Auckland Town Hall - built in 1911, this concert hall is considered to have some of the finest acoustics in the world.
- Auckland War Memorial Museum - a large multi-exhibition museum in the Auckland Domain, known for its impressive neo-classicist style.
- Aotea Square - the hub of downtown Auckland besides Queen Street - often the site of crafts markets, rallies or arts festivals.
- Britomart Transport Centre - the main downtown public transport center located in a historic Edwardian building.
- Eden Park - the city's primary stadium and a frequent home for All Blacks rugby and Black Caps cricket matches.
- Harbour Bridge - connecting Auckland and the North Shore.
- Karangahape Road - known as "K' Road," a street in upper central Auckland famous for its bars, clubs and smaller shops.
- Kelly Tarlton's Underwater World - a well-known aquarium in the eastern Mission Bay suburb, built in a set of former sewage storage tanks, and showing fish and sharks.
- MOTAT - Auckland's Museum for Transport and Technology, at Western Springs.
- Mt Smart Stadium - a stadium used mainly for rugby league and soccer matches. Also the site of many concerts.
- Ponsonby - a suburb and main street west of central Auckland known for arts, cafes and culture.
- Queen Street - the main street of the city, from Karangahape Road down to the harbor.
- Sky Tower - the tallest free-standing structure in the Southern Hemisphere, it is 328 m tall and has excellent panoramic views.
- Vector Arena - recently completed new events center in downtown Auckland.
- Viaduct Basin - a marina and residential development in downtown Auckland, the venue for the America's Cup regattas in 2000 and 2003.
- Western Springs Stadium - a natural amphitheatre used mainly for speedway races, rock and pop concerts.
- Landmarks & Nature
- Auckland Domain - one of the largest parks of the city, close to the CBD and having a good view of the harbor and of Rangitoto Island.
- Mount Eden - a volcanic cone with a grassy crater. As the highest natural point in Auckland City, it offers 360-degree views of Auckland and is thus a favorite tourist outlook.
- Mount Victoria - a volcanic cone in North Shore City offering a spectacular view of Auckland. A brisk walk from the Devonport ferry terminal, the cone is steeped in history, as is nearby North Head.
- One Tree Hill (Maungakiekie) - a volcanic cone that dominates the skyline in the southern, inner suburbs. It no longer has a tree on the summit (after a politically motivated attack on the old tree) but is still crowned by an obelisk.
- Rangitoto Island - guards the entrance to Waitemata Harbour, and forms a prominent feature on the eastern horizon.
Notes
- ↑ Statistics New Zealand, Subnational population estimates at 30 June 2011 (boundaries at 1 July 2011). Retrieved March 10, 2012.
- ↑ The Rough guides to New Zealand.Auckland and around. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- ↑ Auckland City Council. Ngati Whatua history of Auckland.
- ↑ Encyclopedia Britannica. Treaty of Waitangi. Retrieved October 19, 2007.
- ↑ Auckland City Council.Ngati Whatua history of Auckland. Retrieved October 19, 2007.
- ↑ Encyclopedia of New Zealand. AUCKLAND CITY-Foundation and Growth. Retrieved October 19, 2007.
- ↑ Ibid.
- ↑ Auckland Regional Council. Earthquakes.
- ↑ National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research (NIWA). Climate information for selected New Zealand locations. Retrieved October 14, 2007
- ↑ The Supramics Company. Hot weather changes. Retrieved October 14, 2007.
- ↑ Erick Brenstrum. June 2003. Snowstorms. Ministry of Civil Defence & Emergency Management. Retrieved November 4, 2007.
- ↑ Auckland Regional Council Tornado.
- ↑ Auckland City Council. Auckland's CBD at a glance.
- ↑ Ports of Auckland. Economic Impact Retrieved October 16, 2007.
- ↑ The Columbia Electronic Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition. Auckland. Retrieved October 16, 2007.
- ↑ Encyclopedia Britannica. Auckland.
- ↑ Auckland Regional Council. Auckland's growth.
- ↑ Statistics New Zealand
- ↑ Statistics New Zealand. Regional Summary Tables. Retrieved October 16, 2007.
- ↑ Ibid.
- ↑ Statistics New Zealand. Survey of English Language Providers - Year ended March 2006. Retrieved October 20, 2007.
- ↑ Auckland City Council Our People.
- ↑ Tourism Auckland. Special Interests. Retrieved October 20, 2007.
- ↑ Statistics New Zealand. Religious Affiliation. Retrieved October 19, 2007.
- ↑ James Ihaka. October 14, 2006 Punters love City of Sails New Zealand Herald. Retrieved October 19, 2007
- ↑ Yachting NZ.Sailing Club Directory. Retrieved October 19, 2007
Sources and further reading
- McLauchlan, Gordon. 1992. The Illustrated Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Glenfield, NZ: David Bateman Ltd, ISBN 1869530071
External links
All links retrieved August 21, 2023.
- Auckland City Council - Official website
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
- Auckland,_New_Zealand history
- Auckland_City_Council history
- Auckland_Regional_Council history
- History_of_Auckland history
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.