Difference between revisions of "Alps" - New World Encyclopedia
Mary Anglin (talk | contribs) |
Mary Anglin (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
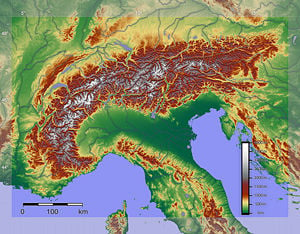
[[Image:Alpenrelief 01.jpg|thumb|Digital relief of the Alps]] | [[Image:Alpenrelief 01.jpg|thumb|Digital relief of the Alps]] | ||
| − | The '''Alps''' ({{lang-de|Alpen}}; {{lang-fr|Alpes}}; {{lang-it|Alpi}}; {{lang-sl|Alpe}}) | + | The '''Alps''' ({{lang-de|Alpen}}; {{lang-fr|Alpes}}; {{lang-it|Alpi}}; {{lang-sl|Alpe}}) are a great [[mountain]] system of [[Europe]], forming parts of nine6 nations: stretching from [[Bosnia and Herzegovina]], [[Croatia]], [[Austria]] and [[Slovenia]] in the east, through [[Italy]], [[Switzerland]], [[Liechtenstein]] and [[Germany]] to [[France]] in the west. However, only Switzerland and Austria can be considered true Alpine nations. |
| − | The highest mountain in the | + | The highest mountain in the range is [[Mont Blanc]], at 15,774 feeet (4,808 meters) on the French-Italian border. The highest and most densely settled mountain belt of Europe, the Alps occupy an area of approximately 80,000 sqare miles (200,000 sq km) and are home to some 20 million people. |
| + | The word "Alps" was taken via [[French language|French]] from [[Latin]] ''Alpes'' (meaning "the Alps"), which may be influenced by the Latin words ''albus'' (white) or ''altus'' (high) or more likely a Latin rendering of a [[Celtic languages|Celtic]] original. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===Climate=== |
| + | The Alps are a classic example of what happens when a temperate area at lower altitude gives way to higher elevation terrain. Elevations around the world which have cold climates similar to those found in [[polar region|polar]] areas have been called [[Alpine climate|alpine]]. A rise from [[sea level]] into the upper regions of the [[Earth's atmosphere|atmosphere]] causes the [[temperature]] to decrease. The effect of [[mountain]] chains on prevailing [[wind]]s is to carry warm air belonging to the lower region into an upper zone, where it expands in [[volume]] at the cost of a proportionate loss of [[heat]], often accompanied by the [[precipitation (meteorology)|precipitation]] of moisture in the form of [[snow]] or [[rain]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Bodies of water, ice=== | ||
| + | Several [[glacier]]s are located in the Alps, the longest of which is the [[Aletsch Glacier]] in the [[Bernese Alps]]. They may be found in all of the higher groups of mountains from the [[Dauphiné Alps]] in [[France]] to the [[Hohe Tauern]] in central [[Austria]], and the main ascent routes on many of the highest mountains pass over glaciers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Very few large lakes are found within the body of the Alps, but a number are situated around the edge, particularly in areas formerly covered by glacier tongues. These include [[Lago Maggiore]], [[Lake Como]] and [[Lake Garda]] on the southern side of the Alps in [[Italy]], and the lakes of [[Switzerland]], southern [[Germany]] and the [[Austria]]n [[Salzkammergut]] in the north. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The main [[drainage basin]]s of the Alps are those of the [[Rhine]], the [[Rhône River|Rhone]], the [[Danube]] and the [[Po River|Po]]. These have as main tributaries: | ||
| + | *Rhine: [[Aare]], [[Reuss River|Reuss]], [[posterior Rhine]]; | ||
| + | *Rhone: [[Durance River|Durance]], [[Drôme River|Drôme]], [[Isère River|Isère]]; | ||
| + | *Danube: [[Sava]], [[Drava]], [[Mura]], [[Enns]], [[Inn River|Inn]]; | ||
| + | *Po: [[Oglio]], [[Adda River|Adda]], [[Ticino River|Ticino]], [[Dora Baltea]]. | ||
| + | Other important rivers draining the Alps include the [[Var River|Var]], [[Adige]] and [[Piave]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Principal passes=== | ||
| + | The Alps do not form an impassable barrier; they have been traversed for [[war]] and [[commerce]], and later by [[pilgrim]]s, [[student]]s and [[tourist]]s. Crossing places by [[road]], [[train]] or foot are called passes. These are depressions in the mountains to which a valley leads from the plains and hilly pre-mountainous zones. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Divisions== | ||
[[Image:Alpenrelief 02.jpg|thumb|The Alps with international borders marked]] | [[Image:Alpenrelief 02.jpg|thumb|The Alps with international borders marked]] | ||
[[Image:Grossglockner_from_SW.jpg|thumb|right|The [[Großglockner]], south of Salzburg, Austria]] | [[Image:Grossglockner_from_SW.jpg|thumb|right|The [[Großglockner]], south of Salzburg, Austria]] | ||
| − | + | [[Image:Alps from space.png|thumb|right|The European Alps from space in 2002.]] | |
| − | The | + | ===Main chain=== |
| − | + | The "main chain of the Alps" follows the watershed from the [[Mediterranean Sea]] to the [[Wienerwald]], passing over many of the highest and most famous peaks in the Alps. From the Colle di Cadibona to [[Col de Tende]] it runs westwards, before turning to the north-west and then, near the [[Colle della Maddalena]], to the north. Upon reaching the Swiss border, the line of the main chain heads approximately east-north-east, a heading it follows until its end near [[Vienna]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Several significant groups of mountains are separated from the main chain by sizable distances. Among these groups are the [[Dauphine Alps]], the Eastern and Western [[Graian Alps|Graian]]s, the entire [[Bernese Alps]], the [[Tödi]], [[Albula]] and [[Silvretta]] groups, the [[Ortler]] and [[Adamello]] ranges, and the [[Dolomites]] of [[South Tyrol]], not to speak of the lower [[Alps]] of [[Vorarlberg]], [[Bavaria]] and [[Salzburg (state)|Salzburg]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | While smaller groups within the Alps may be easily defined by the passes on either side, defining larger units can be problematic. A traditional divide exists between the [[Western Alps]] and the [[Eastern Alps]], which uses the [[Splügen Pass]] ([[Italian language|Italian]]: ''Passo dello Spluga'') on the [[Switzerland|Swiss]]-[[Italy|Italian]] border, together with the [[Rhine]] to the north and [[Lake Como]] in the south as the defining features. While the Splügen Pass is neither the lowest nor the most important pass in the Alps, it is approximately half-way along the main chain, and makes a convenient boundary. | |
| − | === | + | ====Eastern Alps==== |
| − | + | The [[Eastern Alps]] are commonly subdivided according to the different [[lithology]] (rock composition) of the more central parts of the Alps and the groups at its northern and southern fringes: | |
| + | * [[Flysch|Flysch zone]] (up to from the [[Wienerwald|Vienna woods]] to [[Bregenzerwald]]. The Swiss [[Jura mountains|Jura]] do geographically ''not'' belong to the Alps; | ||
| + | * [[Northern Limestone Alps]], peaks up to 3000 m; | ||
| + | * [[Central Eastern Alps]] (Austria, Swiss), peaks up to 4050 m; | ||
| + | * [[Southern Limestone Alps]], peaks up to 3500 m. | ||
| + | The border between the [[Central Alps]] and the Southern Limestone Alps is the [[Periadriatic Seam]]. The Northern Limestone Alps are separated from the Central Eastern Alps by the [[Greywacke zone|Grauwacken Zone]]. | ||
| − | [[ | + | However, the geologic subdivision, based on [[tectonics]], suggests a different system: |
| − | + | * The ''[[Helvetic nappes|Helvetic]] system'' in the north (including the Jura mountains), | |
| + | * the ''[[Penninic nappes|Penninic]] system'': mainly Central Alps ([[Engadine window|Engadine]] and "[[Hohe Tauern window|Tauern window]]") and Flysch Alps, | ||
| + | * the ''[[Austroalpine nappes|Austroalpine]] system'': Northern [[Northern Limestone Alps|Limestone Alps]], Graywacke-[[Schist]] zone, Central [[basement (geology)|Crystalline]], | ||
| + | * the [[Southern Alps (geology)|Southern Alps]] (Southern Limestone Alps and other chains south of the Periadriatic Seam) | ||
| + | * south of a huge [[geologic fault]] ("alpine-dinaric seam") parts of the [[Dinarides]]. | ||
| − | === | + | ====Western Alps==== |
| − | + | The Western Alps are commonly subdivided into the following: | |
| + | *[[Ligurian Alps]] (from [[Savona]] to [[Colle di Tenda]]) | ||
| + | *[[Maritime Alps]] (from Colle di Tenda to [[Colle de la Maddalena]]) | ||
| + | *[[Cottian Alps]] (from Colle de la Maddalena to [[Col du Mont Genevre]]) | ||
| + | *[[Dauphiné Alps]] (from Col du Mont Genevre to [[Col du Mont Cenis]]) | ||
| + | *[[Graian Alps]] (from Col du Mont Cenis to the [[Little St Bernard Pass|Little Saint Bernard Pass]]) | ||
| + | *[[Pennine Alps]] (from the Little St. Bernard Pass to the [[St. Gotthard Pass|Saint Gotthard Pass]]) | ||
| + | *[[Bernese Alps]] (to the north-west of the [[Furka Pass]]) | ||
| + | *[[Lepontine Alps]] (from Saint Gotthard Pass to [[Splügen Pass]]) | ||
| + | *[[Glarus Alps]] (north-east of [[Oberalp Pass]]) | ||
| + | *[[Appenzell Alps]] (north of [[Sargans]]) | ||
| − | + | Within the Eastern Alps, the most widely used subdivision is the Alpenvereins-Einteilung (=''alpine club's arrangement''), which divides the region into about seventy small areas. See [[Northern Calcareous Alps]], [[Central Eastern Alps]] and [[Southern Calcareous Alps]] for details. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Geology== | ==Geology== | ||
| Line 132: | Line 153: | ||
[[Category:Mountains]] | [[Category:Mountains]] | ||
| − | {{credit|135512431}} | + | {{credit|Alps|135512431|Geography_of_the_Alps|205626881}} |
Revision as of 14:52, 25 April 2008
The Alps (German: Alpen; French: Alpes; Italian: Alpi; Slovenian: Alpe) are a great mountain system of Europe, forming parts of nine6 nations: stretching from Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Austria and Slovenia in the east, through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west. However, only Switzerland and Austria can be considered true Alpine nations.
The highest mountain in the range is Mont Blanc, at 15,774 feeet (4,808 meters) on the French-Italian border. The highest and most densely settled mountain belt of Europe, the Alps occupy an area of approximately 80,000 sqare miles (200,000 sq km) and are home to some 20 million people.
The word "Alps" was taken via French from Latin Alpes (meaning "the Alps"), which may be influenced by the Latin words albus (white) or altus (high) or more likely a Latin rendering of a Celtic original.
Geography
Climate
The Alps are a classic example of what happens when a temperate area at lower altitude gives way to higher elevation terrain. Elevations around the world which have cold climates similar to those found in polar areas have been called alpine. A rise from sea level into the upper regions of the atmosphere causes the temperature to decrease. The effect of mountain chains on prevailing winds is to carry warm air belonging to the lower region into an upper zone, where it expands in volume at the cost of a proportionate loss of heat, often accompanied by the precipitation of moisture in the form of snow or rain.
Bodies of water, ice
Several glaciers are located in the Alps, the longest of which is the Aletsch Glacier in the Bernese Alps. They may be found in all of the higher groups of mountains from the Dauphiné Alps in France to the Hohe Tauern in central Austria, and the main ascent routes on many of the highest mountains pass over glaciers.
Very few large lakes are found within the body of the Alps, but a number are situated around the edge, particularly in areas formerly covered by glacier tongues. These include Lago Maggiore, Lake Como and Lake Garda on the southern side of the Alps in Italy, and the lakes of Switzerland, southern Germany and the Austrian Salzkammergut in the north.
The main drainage basins of the Alps are those of the Rhine, the Rhone, the Danube and the Po. These have as main tributaries:
- Rhine: Aare, Reuss, posterior Rhine;
- Rhone: Durance, Drôme, Isère;
- Danube: Sava, Drava, Mura, Enns, Inn;
- Po: Oglio, Adda, Ticino, Dora Baltea.
Other important rivers draining the Alps include the Var, Adige and Piave.
Principal passes
The Alps do not form an impassable barrier; they have been traversed for war and commerce, and later by pilgrims, students and tourists. Crossing places by road, train or foot are called passes. These are depressions in the mountains to which a valley leads from the plains and hilly pre-mountainous zones.
Divisions
Main chain
The "main chain of the Alps" follows the watershed from the Mediterranean Sea to the Wienerwald, passing over many of the highest and most famous peaks in the Alps. From the Colle di Cadibona to Col de Tende it runs westwards, before turning to the north-west and then, near the Colle della Maddalena, to the north. Upon reaching the Swiss border, the line of the main chain heads approximately east-north-east, a heading it follows until its end near Vienna.
Several significant groups of mountains are separated from the main chain by sizable distances. Among these groups are the Dauphine Alps, the Eastern and Western Graians, the entire Bernese Alps, the Tödi, Albula and Silvretta groups, the Ortler and Adamello ranges, and the Dolomites of South Tyrol, not to speak of the lower Alps of Vorarlberg, Bavaria and Salzburg.
While smaller groups within the Alps may be easily defined by the passes on either side, defining larger units can be problematic. A traditional divide exists between the Western Alps and the Eastern Alps, which uses the Splügen Pass (Italian: Passo dello Spluga) on the Swiss-Italian border, together with the Rhine to the north and Lake Como in the south as the defining features. While the Splügen Pass is neither the lowest nor the most important pass in the Alps, it is approximately half-way along the main chain, and makes a convenient boundary.
Eastern Alps
The Eastern Alps are commonly subdivided according to the different lithology (rock composition) of the more central parts of the Alps and the groups at its northern and southern fringes:
- Flysch zone (up to from the Vienna woods to Bregenzerwald. The Swiss Jura do geographically not belong to the Alps;
- Northern Limestone Alps, peaks up to 3000 m;
- Central Eastern Alps (Austria, Swiss), peaks up to 4050 m;
- Southern Limestone Alps, peaks up to 3500 m.
The border between the Central Alps and the Southern Limestone Alps is the Periadriatic Seam. The Northern Limestone Alps are separated from the Central Eastern Alps by the Grauwacken Zone.
However, the geologic subdivision, based on tectonics, suggests a different system:
- The Helvetic system in the north (including the Jura mountains),
- the Penninic system: mainly Central Alps (Engadine and "Tauern window") and Flysch Alps,
- the Austroalpine system: Northern Limestone Alps, Graywacke-Schist zone, Central Crystalline,
- the Southern Alps (Southern Limestone Alps and other chains south of the Periadriatic Seam)
- south of a huge geologic fault ("alpine-dinaric seam") parts of the Dinarides.
Western Alps
The Western Alps are commonly subdivided into the following:
- Ligurian Alps (from Savona to Colle di Tenda)
- Maritime Alps (from Colle di Tenda to Colle de la Maddalena)
- Cottian Alps (from Colle de la Maddalena to Col du Mont Genevre)
- Dauphiné Alps (from Col du Mont Genevre to Col du Mont Cenis)
- Graian Alps (from Col du Mont Cenis to the Little Saint Bernard Pass)
- Pennine Alps (from the Little St. Bernard Pass to the Saint Gotthard Pass)
- Bernese Alps (to the north-west of the Furka Pass)
- Lepontine Alps (from Saint Gotthard Pass to Splügen Pass)
- Glarus Alps (north-east of Oberalp Pass)
- Appenzell Alps (north of Sargans)
Within the Eastern Alps, the most widely used subdivision is the Alpenvereins-Einteilung (=alpine club's arrangement), which divides the region into about seventy small areas. See Northern Calcareous Alps, Central Eastern Alps and Southern Calcareous Alps for details.
Geology
The Alps arose as a result of the pressure exerted on sediments of the Tethys Ocean basin as its Mesozoic and early Cenozoic strata were pushed against the stable Eurasian landmass by the northward-moving African landmass. Most of this occurred during the Oligocene and Miocene epochs. The pressure formed great recumbent folds, or nappes, that rose out of what had become the Tethys Sea and pushed northward, often breaking and sliding one over the other to form gigantic thrust faults. Crystalline rocks, which are exposed in the higher central regions, are the rocks forming Mont Blanc, the Matterhorn, and high peaks in the Pennine Alps and Hohe Tauern.
The landscape seen today is mostly formed by glaciation during the past two million years. At least five ice ages have done much to change the region, scooping out the lakes and rounding off the limestone hills along the northern border. Glaciers have been retreating during the past 10,000 years, leaving large granite erratics scattered in the forests in the region. As the last ice age ended, it is believed that the climate changed so rapidly that the glaciers retreated back into the mountains in a span of about 200 to 300 years.
Political history
Little is known of the early dwellers in the Alps, save from the scanty accounts preserved by Roman and Greek historians and geographers. A few details have come down to us of the conquest of many of the Alpine tribes by Augustus.
The successive emigration and occupation of the Alpine region by various Teutonic tribes from the 5th to the 6th centuries are known only in outline, because to them, as to the Frankish kings and emperors, the Alps offered a route to other places rather than a permanent residence.
It is not until the final breakup of the Carolingian Empire in the 10th and 11th centuries that it becomes possible to trace out the local history of the Alps.
Exploration
The higher regions of the Alps were long left to the exclusive attention of the people of the adjoining valleys, even when Alpine travellers (as distinguished from Alpine climbers) began to visit these valleys. The two men who first explored the regions of ice and snow were H.B. de Saussure (1740-1799) in the Pennine Alps, and the Benedictine monk of Disentis, Placidus a Spescha (1752-1833), most of whose ascents were made before 1806, in the valleys at the sources of the Rhine.
Flora
A natural vegetation limit with altitude is given by the presence of the chief deciduous trees — oak, beech, ash and sycamore maple. These do not reach exactly to the same elevation, nor are they often found growing together; but their upper limit corresponds accurately enough to the change from a temperate to a colder climate that is further proved by a change in the wild herbaceous vegetation. This limit usually lies about 1,200 metres (3,940 ft) above the sea on the north side of the Alps, but on the southern slopes it often rises to 1,500 metres (4,920 ft), sometimes even to 1,700 metres (5,580 ft).
This region is not always marked by the presence of the characteristic trees. Human interference has nearly exterminated them in many areas, and, except for the beech forests of the Austrian Alps, forests of deciduous trees are rarely found. In many districts where such woods once existed, they have been replaced by the Scots pine and Norway spruce, which are less sensitive to the ravages of goats, who are the worst enemies of such trees. The mean annual temperature of this region differs little from that of the British Islands; but climatic conditions are widely different. In the Alps, snow usually stays for several months, until spring and summer, which are considerably warmer on average than those seasons in Britain.
Above the forestry, there is often a band of short pine trees (Pinus mugo), which is in turn superseded by dwarf shrubs, typically Rhododendron ferrugineum (on acid soils) or Rhododendron hirsutum (on basic soils). Above this is the alpine meadow, and even higher, the vegetation becomes more and more sparse. At these higher altitudes, the plants tend to form isolated cushions. In the Alps, several species of flowering plants have been recorded above 4,000 metres (13,125 ft), including Ranunculus glacialis, Androsace alpina and Saxifraga biflora.
- Kosodrzewina (Sosna górska) Pinus mugo mugo.jpg
mountain pine
(Pinus mugo) - Rhododendron ferrugineum.JPG
rusty-leaved Alpenrose
(Rhododendron ferrugineum) - Leontopodium alpinum1.jpg
Edelweiss
(Leontopodium alpinum) - Gentiana acaulis.jpg
stemless gentian
(Gentiana acaulis) - Chamorchis alpina 230705b.jpg
Alpine dwarf orchid
(Chamorchis alpina) - Pulsatilla alpina schneebergensis.jpg
Alpine pasque-flower
(Pulsatilla alpina) - Androsace alpina02.jpg
Alpine rock-jasmine (Androsace alpina)
Fauna
Species common to the Alps. These are most numerously found in the 15% of the Alps protected in parks and reserves.
- Ptarmigan9.jpg
Ptarmigan - Aegolius-funereus-001.jpg
Tengmalm's Owl - Iiiiibed.jpg
Alpine Ibex - Arctic Hare.jpg
Mountain Hare
Notes
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Answers.com. Alps Retrieved April 25, 2008.
- Schmidt, Elsa T. 2007. Alps Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia. Retrieved April 25, 2008.
- Fowler, Brenda. 2000. Iceman: uncovering the life and times of a prehistoric man found in an alpine glacier. New York: Random House. ISBN 9780679431671
- Hurni, Hans. 2001. Special issue: the Alps in Europe and the Southern Alps in New Zealand. Mountain research and development, v. 21, no. 4. Berne: International Mountain Society.
- Pfiffner, Othmar Adrian. 1997. Deep structure of the Swiss Alps: results of NRP 20. Basel: Birkhäuser Verlag. ISBN 9780817652548
External links
All links Retrieved April 21, 2008.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.