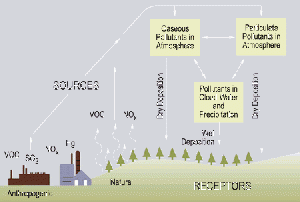
Acid rain
The term "acid rain" is commonly used to mean the deposition of acidic components in rain, snow, fog, dew, or dry particles. The more accurate term is "acid precipitation." Distilled water, which contains no carbon dioxide, has a neutral pH of 7. Liquids with a pH less than 7 are acid, and those with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline (or basic). "Clean" or unpolluted rain has a slightly acidic pH of 5.6, because carbon dioxide and water in the air react together to form carbonic acid, a weak acid. The extra acidity in rain comes from the reaction of air pollutants, primarily sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides, with water in the air to form strong acids (such as sulfuric acid and nitric acid). The main sources of these pollutants are vehicles and industrial and power-generating plants.
Since the Industrial Revolution, emissions of sulfur and nitrogen oxides to the atmosphere have increased.[1] Occasional pH readings of well below 2.4 (the acidity of vinegar) have been reported in industrialized areas.[1] Industrial acid rain is a substantial problem in China[2], Eastern Europe, Russia and areas down-wind from them. These areas all burn sulfur-containing coal to generate heat and electricity. The problem of acid rain not only has increased with population and industrial growth, but has become more widespread. The use of tall smokestacks to reduce local pollution has contributed to the spread of acid rain by releasing gases into regional atmospheric circulation. Often deposition occurs a considerable distance downwind of the emissions, with mountainous regions tending to receive the most (simply because of their higher rainfall). An example of this effect is the low pH of rain (compared to the local emissions) which falls in Scandinavia.[3]
History
Acid rain was first found in Manchester, England. In 1852, Robert Angus Smith found the relationship between acid rain and atmospheric pollution. Though acid rain was discovered in 1852, it wasn't until the late 1960s that scientists began widely observing and studying the phenomenon. Canadian Harold Harvey was among the first to research a "dead" lake. Public awareness of acid rain in the U.S increased in the 1990s after the New York Times promulgated reports from the Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest in New Hampshire of the myriad deleterious environmental effects demonstrated to result from it.
Emissions of chemicals leading to acidification
The most significant gas that leads to acidification is sulfur dioxide (SO2). Emissions of nitrogen oxides which are oxidized to form nitric acid are of increasing importance due to stricter controls on emissions of sulfur containing compounds. 70 Tg(S) per year in the form of SO2 comes from fossil fuel combustion and industry, 2.8 Tg(S) from wildfires and 7-8 Tg(S) per year from volcanoes.[4]
Human activity
The principal cause of acid rain is sulfur and nitrogen compounds from human sources, such as electricity generation, factories and motor vehicles. Coal power plants are one of the most polluting. The gases can be carried hundreds of kilometers in the atmosphere before they are converted to acids and deposited. Factories used to have short funnels to let out smoke, but this caused many problems, so now, factories have longer smoke funnels. The problem with this is those pollutants get carried far off, where it creates more destruction.
Chemistry in cloud droplets
When clouds are present the loss rate of SO2 is faster than can be explained by gas phase chemistry alone. This is due to reactions in the liquid water droplets
- Hydrolysis
Sulphur dioxide dissolves in water and then, like carbon dioxide, hydrolyses in a series of equilibrium reactions:
- SO2 (g)+ H2O ⇌ SO2·H2O
- SO2·H2O ⇌ H++HSO3-
- HSO3- ⇌ H++SO32-
- Oxidation
There are a large number of aqueous reactions that oxidize sulfur from S(IV) to S(VI), leading to the formation of sulphuric acid. The most important oxidation reactions are with ozone, hydrogen peroxide and oxygen (reactions with oxygen are catalysed by iron and manganese in the cloud droplets).
For more information see Seinfeld and Pandis (1998).
Acid deposition
Wet deposition
Wet deposition of acids occurs when any form of precipitation (rain, snow, etc) removes acids from the atmosphere and delivers it to the Earth's surface. This can result from the deposition of acids produced in the raindrops (see aqueous phase chemistry above) or by the precipitation removing the acids either in clouds or below clouds. Wet removal of both gases and aerosol are both of importance for wet deposition.
Dry deposition
Acid deposition also occurs via dry deposition in the absence of precipitation. This can be responsible for as much as 20 to 60% of total acid deposition. This occurs when particles and gases stick to the ground, plants or other surfaces.
Adverse effects
Acid rain has been shown to have adverse impacts on forests, freshwaters and soils, killing off insect and aquatic lifeforms as well as causing damage to buildings and having possible impacts on human health.
Surface waters and aquatic animals
Both the lower pH and higher aluminum concentrations in surface water that occur as a result of acid rain can cause damage to fish and other aquatic animals. At pHs lower than 5 most fish eggs will not hatch and lower pHs can kill adult fish. As lakes become more acidic biodiversity is reduced. Acid rain has eliminated insect life and some fish species, including the brook trout in some Appalachian streams and creeks.[5] There has been some debate on the extent to which man-made causes of lake acidity have cause fish kills - for example Edward Krug.[6].
Soils
Soil biology can be seriously damaged by acid rain. Some tropical microbes can quickly consume acids[7] but other microbes are unable to tolerate low pHs and are killed. The enzymes of these microbes are denatured (changed in shape so they no longer function) by the acid. The hydronium ions of acid rain also mobilize toxins and leach away essential nutrients and minerals[8]
Forests and other vegetation
Acid rain can slow the growth of forests, cause leaves and needles to turn brown and fall off and die. In extreme cases trees or whole acres of forest can die. The death of trees is not usually a direct result of acid rain, often it weakens trees and makes them more susceptible to other threats. Damage to soils (see above) can also cause problems. High altitude forests are especially vulnerable as they are often surrounded by clouds and fog which are more acidic than rain.
Other plants can also be damaged by acid rain but the effect on food crops is minimized by the application of fertilizers to replace lost nutrients. In cultivated areas, limestone may also be added to increase the ability of the soil to keep the pH stable, but this tactic is largely unusable in the case of wilderness lands. Acid Rain depletes minerals from the soil and then it stunts the growth of the plant.
Human health
Some scientists have suggested direct links to human health, but none have been proven. However, fine particles, a large fraction of which are formed from the same gases as acid rain (sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide), have been shown to cause illness and premature deaths such as cancer and other deadly diseases[9] For more information on the health effects of aerosol see: Particulate#Health effects.
Other adverse effects
Acid rain can also cause damage to certain building materials and historical monuments. This is because the sulfuric acid in the rain chemically reacts with the calcium compounds in the stones (limestone, sandstone, marble and granite) to create gypsum, which then flakes off. This is also commonly seen on old gravestones where the acid rain can cause the inscription to become completely illegible. Acid rain also causes an increased rate of oxidation for iron.[10] Visibility is also reduced by sulfate and nitrate in the atmosphere.[11]
Prevention methods
Main article: Automobile emissions control
Technical solutions
In the United States, many coal-burning power plants use Flue gas desulfurization (FGD) to remove sulphur-containing gases from their stack gases. An example of FGD is the wet scrubber which is commonly used in the U.S. and many other countries. A wet scrubber is basically a reaction tower equipped with a fan that extracts hot smoke stack gases from a power plant into the tower. Lime or limestone in slurry form is also injected into the tower to mix with the stack gases and combine with the sulphur dioxide present. The calcium carbonate of the limestone produces pH-neutral calcium sulfate that is physically removed from the scrubber. That is, the scrubber turns sulfur pollution into industrial sulfates.
In some areas the sulfates are sold to chemical companies as gypsum when the purity of calcium sulfate is high. In others, they are placed in landfill. However, the effects of acid rain can last for generations, as the effects of pH level change can stimulate the continued leaching of undesirable chemicals into otherwise pristine water sources, killing off vulnerable insect and fish species and blocking efforts to restore native life.
International treaties
A number of international treaties on the long range transport of atmospheric pollutants have been agreed e.g. Sulphur Emissions Reduction Protocol under the Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution.
Emissions trading
A more recent regulatory scheme involves emissions trading. In this scheme, every current polluting facility is given an emissions license that becomes part of capital equipment. Operators can then install pollution control equipment, and sell parts of their emissions licenses. The intention of this is to give operators economic incentives to install pollution controls.
See also
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Biomass Burning and Global Change. NASA. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- ↑ Sud, Hari. 2006. CHINA : Industrialization Pollutes Its Countryside With Acid Rain. South Asia Analysis Group. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- ↑ List of EMEP publications. EMEP. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- ↑ Berresheim, H., P.H. Wine and D.D. Davies. 1995. Sulfur in the Atmosphere. In Composition, Chemistry and Climate of the Atmophere. Van Nostran Rheingold.
- ↑ Effects of Acid Rain - Surface Waters and own Aquatic Animals. US EPA. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- ↑ Acid Test: Edward Krug Flunks Political Science. The Reason Foundation. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- ↑ Rodhe, H., et. Al. The Global Distribution of Acidifying Wet Deposition. Environmental Science & Technology. 36:20:4382-8.
- ↑ Effects of Acid Rain - Forests. US EPA. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- ↑ Effects of acid rain - human health. US EPA. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- ↑ Effects of Acid Rain - Materials. US EPA. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- ↑ Effects of Acid Rain - Visibility. US EPA. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- McCormick, John. 1989. Acid Earth: The Global Threat of Acid Pollution. London, UK: Earthscan. ISBN 185383033X.
- Morgan, Sally and Jenny Vaughan. 2007. Acid Rain (Earth SOS). London, UK: Franklin Watts Ltd. ISBN 0749676728.
- Parks, Peggy J. 2005. Our Environment - Acid Rain (Our Environment). Farmington Hills, MI: KidHaven Press (Thomson Gale). ISBN 0737726288.
External links
- National Acid Precipitation Assessment Program Report - a 98-page report to Congress. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- Acid rain for schools. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency - New England Acid Rain Program (superficial). Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- Acid Rain (more depth than ref. above). Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- U.S. Geological Survey - What is acid rain?. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- CBC Digital Archives – Acid Rain: Pollution and Politics. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- Larssen, Thorjørn et al. “Acid Rain in China.” Environmental Science and Technology, 40:2, 2006, pp 418-425. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- Acid Rain: A Continuing National Tragedy - a report from The Adirondack Council on acid rain in the Adirondack region. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- Assortment of Summaries on Acid Rain. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
- Acid rain linked to decline of the wood thrush, a songbird of the Eastern Forest. Retrieved October 10, 2007.
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.