Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio (November 30, 1508 – August 19, 1580), was an Italian architect, widely considered the most influential person in the history of Western architecture. Palladianism became popular briefly in Britain during the mid-seventeenth century. In the early eighteenth century it returned to fashion, in not only England but many northern European countries. Later when the style was falling from favor in Europe, it had a surge in popularity in North America, most notably in the buildings designed by Thomas Jefferson. Palladio's influence in North America is evident almost from the beginning of its architect-designed buildings. While his influence was strong throughout Europe, it is the buildings in North America, such as the White House and Monticello which are perhaps the most famous examples of the influence of his style. Its inspiration is found in the Greco-Roman culture.
Biography
He was born Andrea di Pietro della Gondola in Padua, then part of the Republic of Venice. Apprenticed as a stonecutter in Padua when he was 13, he broke his contract after only 18 months and fled to the nearby town of Vicenza. Here he became an assistant in the leading workshop of stonecutters and masons. He frequented the workshop of Bartolomeo Cavazza, from whom he learned some of his skills.
His talents were recognized in his early thirties by Count Gian Giorgio Trissino, who later gave him the name Palladio, an allusion to the Greek goddess of wisdom Pallas Athene. In 1541 he moved to Rome to study classic architecture.
Palladian style, named after him, adhered to classical Roman principles, similarly to styles of the Early and High Renaissance, when classical revivalism was at its peak. His architectural works have "been valued for centuries as the quintessence of High Renaissance calm and harmony" [1]. Palladio designed many churches, villas, and palaces, especially in Venice, Vicenza and the surrounding area. A number of his works are protected as part of the World Heritage Site Palladian Villas of the Veneto.
His style became fashionable all over Europe, for example in parts of the Loire Valley of France. In Britain, Inigo Jones and Christopher Wren embraced the Palladian style. Another admirer was the architect Richard Boyle, 4th Earl of Cork, also known as Lord Burlington, who, with William Kent, designed Chiswick House. The Palladian villa configuration, consisting of a dominant central focal element flanked by lower servant wings, found resonance as a prototype for the country mansions of the English nobility, a perfect architectural expression of their position in the social order of the era. Other exponents of his work who helped to popularize Palladio's concepts include the 18th century Venetian architect Giacomo Leoni who published an authoritative four volume work on Palladio and his architectural concepts. In a letter written by Colonel Isaac A. Coles to General Hartwell Cocke in 1816, Coles related Thomas Jefferson's admiration for Palladio: "With Mr. Jefferson I conversed at length on the subject of architecture—Palladio, he said, 'was the Bible—you should get it and stick close to it… .'"
He died in Maser, Italy, near Treviso.
Palladian architecture
The term "Palladian" normally refers to buildings in a style inspired by Palladio's own work; what is recognized as Palladian architecture today is an evolution of Palladio's original concepts. This evolution of Palladianism as a style began in the seventeenth century and continued to develop until the end of the eighteenth century.
Palladianism became popular briefly in Britain during the mid-seventeenth century. In the early eighteenth century it returned to fashion, in not only England but many northern European countries. Later when the style was falling from favor in Europe, it had a surge in popularity in North America, most notably in the buildings designed by Thomas Jefferson. To understand Palladian architecture as it later evolved, one must first understand the architecture of Palladio himself.
Palladio's architecture
Buildings entirely designed by Palladio are all in Venice and the Veneto. They include Villa Capra and Villa Badoer, in addition to the Redentore in Venice. In Palladio's architectural treatises he followed the principles defined by the Roman architect Vitruvius and his 15th-century disciple Leon Battista Alberti, who adhered to principles of classical Roman architecture based on mathematical proportions rather than the rich ornamental style also characteristic of the Renaissance.[2]
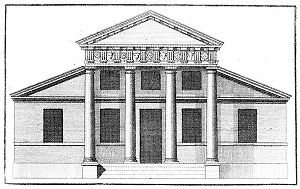
Palladio always designed his villas with reference to their setting. If on a hill, such as Villa Capra, facades were frequently designed to be of equal value so that occupants could have fine views in all directions. Also, in such cases, porticos were built on all sides so that occupants could fully appreciate the countryside while being protected from the sun, similar to many American-style porches of today. Palladio sometimes used a loggia as an alternative to the portico. This can most simply be described as a recessed portico, or an internal single storey room, with pierced walls that are open to the elements. Occasionally a loggia would be placed at second floor level over the top of a loggia below, creating what was known as a double loggia. Loggias were sometimes given significance in a facade by being surmounted by a pediment. Villa Godi has as its focal point a loggia rather than a portico, plus loggias terminating each end of the main building.[3]
Palladio would often model his villa elevations on Roman temple facades. The temple influence, often in a cruciform design, later became a trademark of his work. Palladian villas are usually built with three floors: a rusticated basement or ground floor, containing the service and minor rooms; above this, the piano nobile accessed through a portico reached by a flight of external steps, containing the principal reception and bedrooms; and above this is a low mezzanine floor with secondary bedrooms and accommodation. The proportions of each room within the villa were calculated on simple mathematical ratios like 3:4 and 4:5, and the different rooms within the house were interrelated by these ratios. Earlier architects had used these formulas for balancing a single symmetrical facade; however, Palladio's designs related to the whole, usually square, villa.[4]
Palladio deeply considered the dual purpose of his villas as both farmhouses and palatial weekend retreats for wealthy merchant owners. These symmetrical temple-like houses often have equally symmetrical, but low, wings sweeping away from them to accommodate horses, farm animals, and agricultural stores. The wings, sometimes detached and connected to the villa by colonnades, were designed not only to be functional but also to complement and accentuate the villa. They were, however, in no way intended to be part of the main house, and it is in the design and use of these wings that Palladio's followers in the 18th century adapted to become an integral part of the building.[5]
The Palladian window

The Palladian, Serlian, or Venetian window features largely in Palladio's work, almost a trademark in his early career. It consists of a central light with semicircular arch over, carried on an impost consisting of a small entablature, under which, and enclosing two other lights, one on each side, are pilasters. In the library at Venice, Sansovino varied the design by substituting columns for the two inner pilasters. To describe its origin as being either Palladian or Venetian is not accurate; the motif was first used by Donato Bramante (Ackerman) and later mentioned by Sebastiano Serlio (1475–1554) in his seven-volume architectural book Tutte l'opere d'architettura et prospetiva expounding the ideals of Vitruvius and Roman architecture, this arched window is flanked by two lower rectangular openings, a motif that first appeared in the triumphal arches of ancient Rome. Palladio used the motif extensively, most notably in the arcades of the Basilica Palladiana in Vicenza. It is also a feature of his entrances to both Villa Godi and Villa Forni-Cerato. It is perhaps this extensive use of the motif in the Veneto that has given the window its alternative name of the Venetian window; it is also known as a Serlian window. Whatever the name or the origin, this form of window has probably become one of the most enduring features of Palladio's work seen in the later architectural styles, evolved from Palladianism.[6]
Early Palladianism
In 1570 Palladio published his book I Quattro Libri dell'Architettura, inspiring architects across Europe. During the seventeenth century, many architects studying in Italy learned of Palladio's work. Foreign architects then returned home and adapted Palladio's style to suit various climates, topographies and personal tastes of their clients. Isolated forms of Palladianism throughout the world were brought about in this way. However, the Palladian style did not reach the zenith of its popularity until the 18th century, primarily in England, Ireland and later North America.[7]
One of these students was the English architect Inigo Jones, who is directly responsible for importing the Palladian influence to England.[8] The "Palladianism" of Jones and his contemporaries and later followers was a style very much of facades only, and the mathematical formulae dictating layout were not strictly applied. A handful of great country houses in England built between 1640 and circa 1680, such as Wilton House, are in this Palladian style, following the great success of Jones' Palladian designs for the Queen's House at Greenwich and the Banqueting House at Whitehall, the uncompleted royal palace in London of King Charles I.[9]
However, the Palladian designs advocated by Inigo Jones were too closely associated with the court of Charles I to survive the turmoil of the civil war. Following the Stuart restoration Jones's Palladianism was eclipsed by the baroque designs of such architects as William Talman and Sir John Vanbrugh, Nicholas Hawksmoor, and even Jones' pupil John Webb.[10]
English Palladian revival (neo-Palladian)
The baroque style, popular in continental Europe, was never truly to the English taste. It was quickly superseded when, in the first quarter of the 18th century, four books were published in Britain which highlighted the simplicity and purity of classical architecture. These were:
- Vitruvius Britannicus published by Colen Campbell, 1715 (of which supplemental volumes appeared through the century)
- Palladio's Four Books of Architecture published by Giacomo Leoni, 1715
- Leone Battista Alberti's De Re Aedificatoria, published by Giacomo Leoni, 1726
- The Designs of Inigo Jones… with Some Additional Designs, published by William Kent, 2 vols., 1727 (A further volume, Some Designs of Mr. Inigo Jones and Mr. William Kent was published in 1744 by the architect John Vardy, an associate of Kent.)
The most popular of these among the wealthy patrons of the day was the four-volume Vitruvius Britannicus by Colen Campbell. Campbell was both an architect and a publisher. The book was basically a book of design containing architectural prints of British buildings, which had been inspired by the great architects from Vitruvius to Palladio; at first mainly those of Inigo Jones, but the later tomes contained drawings and plans by Campbell and other 18th-century architects. These four books greatly contributed to Palladian revival architecture becoming established in 18th-century Britain. Their three authors became the most fashionable and sought after architects of the era. Due to his book Vitruvius Britannicus, Colen Campbell was chosen as the architect for banker Henry Hoare I's Stourhead house (illustration below), a masterpiece that became the inspiration for dozens of similar houses across England.
At the forefront of the new school of design was the aristocratic "architect earl," Richard Boyle, 3rd Earl of Burlington, who saw baroque as a symbol of foreign absolutism. In 1729, Burlington, with William Kent, designed Chiswick House. This House was a reinterpretation of Palladio's Villa Capra, but purified of sixteenth century elements and ornament. This severe lack of ornamentation was to be a feature of the Palladian revival. In 1734 William Kent and Lord Burlington designed one of England's finest examples of palladian revival houses with Holkham Hall in Norfolk. The main block of this house followed Palladio's dictates quite closely, but Palladio's low, often detached, wings of farm buildings were elevated in significance. Kent attached them to the design, banished the farm animals, and elevated the wings to almost the same importance as the house itself. Often these wings were adorned with porticos and pediments, often resembling, as at the much later Kedleston Hall, small country houses in their own right. It was the development of the flanking wings that was to cause English Palladianism to evolve from being a pastiche of Palladio's original work.
Architectural styles evolve and change to suit the requirements of each individual client. When in 1746 the Duke of Bedford decided to rebuild Woburn Abbey, he chose the Palladian style for the design, as this was now the most fashionable of the era. He selected architect Henry Flitcroft, a protege of Burlington. Flitcroft's designs, while Palladian in nature, would not be recognized by Palladio himself. The central block is small, only three bays, the temple-like portico is merely suggested, and it is in fact closed. Two great flanking wings containing a vast suite of state rooms replace the walls or colonnades which should have connected to the farm buildings; the farm buildings terminating the structure are elevated in height to match the central block, and given Palladian windows, to ensure they are seen as of Palladian design. This development of the style was to be repeated in countless houses, and town halls in Britain over one hundred years. Falling from favor during the Victorian era, it was revived by Edward Blore for his refacing of Buckingham Palace in 1913. Often the terminating blocks would have blind porticos and pilasters themselves, competing for attention with, or complementing the central block. This was all very far removed from the designs of Palladio two hundred years earlier.
English Palladian houses were now no longer the small but exquisite weekend retreats from which their Italian counterparts were conceived. They were no longer villas but "power houses" in Sir John Summerson's term, the symbolic centres of power of the Whig "squirearchy" that ruled Britain. As the Palladian style swept Britain, all thoughts of mathematical proportion were swept away. Rather than square houses with supporting wings, these buildings had the length of the facade as their major consideration; long houses often only one room deep were deliberately deceitful in giving a false impression of size.
Irish Palladianism
During the Palladian revival period in Ireland, even quite modest mansions were cast in a neo-Palladian mould. Palladian architecture in Ireland subtly differs from that in England. While adhering as in other countries to the basic ideals of Palladio, it is often truer to them–perhaps because it was often designed by architects who had come directly from mainland Europe, who were not influenced by the evolution that Palladianism was undergoing in Britain, or perhaps because Ireland was more provincial and its fashions changed at a slower pace than elsewhere. Whatever the reason, Palladianism still had to be adapted for the wetter, colder weather.
One of the most pioneering Irish architects was Sir Edward Lovett Pearce (1699–1733), who became one of the leading advocates of Palladianism in Ireland. A cousin of Sir John Vanbrugh, he was originally one of his pupils, but rejecting the baroque, he spent three years studying architecture in France and Italy, before returning home to Ireland. His most important Palladian work is the former Irish Houses of Parliament in Dublin. He was a prolific architect who also designed the south facade of Drumcondra House in 1727 and Cashel Palace in 1728.
One of the most notable examples of Palladianism in Ireland is the magnificent Castletown House, near Dublin. Designed by the Italian architect Alessandro Galilei (1691–1737), it is perhaps the only Palladian house in Ireland to have been built with Palladio's mathematical ratios, and one of the two Irish mansions which claim to have inspired the design of the White House in Washington.
Other fine examples include Russborough, designed by Richard Cassels, an architect of German origin, who also designed the Palladian Rotunda Hospital in Dublin, and Florence Court, County Fermanagh. Irish Palladian Country houses often have robust Rococo plasterwork, frequently executed by the Lafranchini brothers, an Irish speciality, which is far more flamboyant than the interiors of their contemporaries in England. So much of Dublin was built in the 18th century that it set a Georgian stamp on the city, to the disgust of Irish nationalists; until recently Dublin was one of the few cities where fine late 18th-century housing could be seen in ruinous condition. Elsewhere in Ireland after 1922, the lead was removed from the roofs of unoccupied Palladian houses for its value as scrap. Many roofless Palladian houses can still be found in the depopulated Irish countryside.
North American Palladianism

Palladio's influence in North America is evident almost from the beginning of its architect-designed buildings. In 1749 Peter Harrison adopted the design of his Redwood Library in Newport, Rhode Island from Palladio's Architecture in Four Books, while his Brick Market, also in Newport, of a decade later is also Palladian in conception.
The amateur architect Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826) once referred to Palladio's "I Quattro Libri dell'Architettura" as his "Bible." Jefferson acquired an intense appreciation of Palladio's architectural concepts, and his designs for the Jefferson Monticello estate and the University of Virginia were based on drawings from Palladio's book. Realizing the powerful political significance pertaining to ancient Roman buildings, Jefferson designed many of his civic buildings in the Palladian style. Monticello (remodelled between 1796 and 1808) is quite clearly based on Palladio's Villa Capra, however, with modifications, in a style which is described in America today as Colonial Georgian. Jefferson's Pantheon, or Rotunda, at the University of Virginia is undeniably Palladian in concept and style.[11]
In Virginia and Carolina, the Palladian manner is epitomized in numerous Tidewater plantation houses, such as Stratford Hall Plantation or Westover Plantation, or Drayton Hall near Charleston, South Carolina. These examples are all classic American colonial examples of a Palladian taste that was transmitted through engravings, for the benefit of masons—and patrons, too—who had no first-hand experience of European building practice. A feature of American Palladianism was the re-emergence of the great portico, which again, as in Italy, fulfilled the need of protection from the sun; the portico in various forms and size became a dominant feature of American colonial architecture. In the north European countries the Portico had become a mere symbol, often closed, or merely hinted at in the design by pilasters, and sometimes in very late examples of English Palladianism adapted to become a porte-cochere; in America, the Palladian portico regained its full glory.

Thomas Jefferson must have gained particular pleasure as the second occupant of the White House in Washington, which was doubtless inspired by Irish Palladianism. Both Castletown and Richard Cassel's Leinster House in Dublin claim to have inspired the architect James Hoban, who designed the executive mansion, built between 1792 and 1800. Hoban, born in Callan, County Kilkenny, in 1762, studied architecture in Dublin, where Leinster House (built circa 1747) was one of the finest buildings at the time. The Palladianism of the White House is an interesting example of an almost early form of neoclassicism, especially the South facade, which closely resembles James Wyatt's design for Castle Coole of 1790, also in Ireland. Ironically, the North facade lacks one of the floors from Leinster House, while the Southern facade is given one floor more than Castle Coole, and has an external staircase more in the Palladian manner. Castle Coole is, in the words of the architectural commentator Gervase Jackson-Stops, "A culmination of the Palladian traditions, yet strictly neoclassical in its chaste ornament and noble austerity."[12] The same can be said of many houses in the American Palladian style.
One of the adaptations made to Palladianism in America was that the piano nobile now tended to be placed on the ground floor, rather than above a service floor, as was the tradition in Europe. This service floor, if it existed at all, was now a discreet semi-basement. This negated the need for an ornate external staircase leading to the main entrance as in the more original Palladian designs. This would also be a feature of the neoclassical style that followed Palladianism.

The only two houses in the United States—from the English colonial period (1607-1776)—that can be definitively attributed to designs from the Four Books of Architecture are architect William Buckland's The Hammond-Harwood House (1774) in Annapolis, Maryland, and Thomas Jefferson's first Monticello. The design source for the Hammond-Harwood House is the Villa Pisani at Montagnana (Book II, Chapter XIV), and for the first Monticello (1770) the design source is the Villa Cornaro at Piombino Dese (Book II, Chapter XIV). Thomas Jefferson later covered this facade with later additions so that the Hammond-Harwood House remains the only pure and pristine example of direct modeling in America today.
Decline of Palladianism
By the 1770s, in England, such architects as Robert Adam and Sir William Chambers were in huge popular demand, but they were now drawing on a great variety of classical sources, including ancient Greece, so much so that their forms of architecture were eventually defined as neoclassical rather than Palladian. In Europe, the Palladian revival ended by the end of the eighteenth century. In North America, Palladianism lingered a little longer; Thomas Jefferson's floor plans and elevations owe a great deal to Palladio's Quattro Libri. The term "Palladian" today is often misused, and tends to describe a building with any classical pretensions.
Post-Modern revival
Palladian motifs, particularly the window, made a comeback during the Post-Modern era. The architect Philip Johnson frequently used it as a doorway, as in his designs for the University of Houston School of Architecture building (1985), 500 Boylston Street (1989), Boston, Massachusetts and the Museum of Television and Radio building (1991), New York City. When asked about it, Johnson replied, "I think Palladian windows have a rather prettier shape. I wasn't trying to make any more important point than that."[13] I.M. Pei was to use the design for the main entrance of his 1985 Bank of China building in Hong Kong.
Notes
- ↑ David Watkin, A History of Western Architecture, Second Rev. ed. (BARNES & NOBLE, 1996)
- ↑ Trewin Copplestone. World Architecture. (Hamlyn, 1963), 250
- ↑ Copplestone, 251
- ↑ Copplestone, 251
- ↑ Copplestone, 251-252
- ↑ Andrea Palladio, and Caroline Constant. The Palladio Guide. (Princeton Architectural Press, 1993), 42.
- ↑ Copplestone, 252
- ↑ Hanno-Walter Kruft. A History of Architectural Theory: From Vitruvius to the Present.. (Princeton Architectural Press, 1994), 230.
- ↑ Copplestone, 280
- ↑ Copplestone, 281
- ↑ Joseph C. Farber, and Henry Hope Reed. Palladio's Architecture and Its Influence: A Photographic Guide. (Dover Publications, 1980. ISBN 0486239225), 107
- ↑ Gervase Jackson-Stops. The Country House in Perspective. (Pavilion Books Ltd, 1990), 106
- ↑ Hilary Lewis, and John O'Connor. Philip Johnson: The architect in His Own Words. (New York: Rizzoli International Publications, 1994), 170
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Ackermann, James S. (1994). Palladio (series "Architect and Society")
- Copplestone, Trewin (1963). World Architecture. Hamlyn. ISBN 9780600039549
- Dal Lago, Adalbert (1966). Ville Antiche. Milan: Fratelli Fabbri.
- Farber, Joseph C. and Henry Hope Reed. Palladio's Architecture and Its Influence: A Photographic Guide. (Dover Publications, 1980. ISBN 0486239225
- Halliday, E. E. (1967). Cultural History of England. London: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 9780500450031
- Jackson-Stops, Gervase (1990). The Country House in Perspective. Pavilion Books Ltd. ISBN 9780802112286
- Kostof, Spiro. A History of Architecture. Oxford University Press, 2007 ; New York. ISBN 9780195139570
- Lewis, Hilary, and John O'Connor. Philip Johnson: The architect in His Own Words. New York: Rizzoli International Publications. 1994. ISBN 9780847818235
- Marten Paolo. Andrea Palladio: The Architecht in His Time. Nashville: Abbeville Press. 1993. ISBN 9780789203007
- Palladio, Palladio, and Caroline Constant. The Palladio Guide. (Princeton Architectural Press, 1993. (in English)
- Reed, Henry Hope, and Joseph C. Farber. Palladio's Architecture and Its Influence. New York: Dover Publications Inc. 1980. ISBN 9780486239224
- Tavernor, Robert. Palladio and Palladianism. London: Thames and Hudson. 1991. ISBN 9780500202425
- Watkin, David (1979). English Architecture. London: Thames and Hudson. 2001. ISBN 9780500203385
- Watkin, David. A History of English Architecture, Second Rev. ed. BARNES & NOBLE, 1996. ASIN B000Q1FC5Q
- Wittkower, Rudolf. Architectural Principles in the Age of Humanism. Academy Press. 1998. ISBN 9780471977636
External links
All links retrieved July 26, 2023.
- Holkham Hall
- Palladian Architecture
- Palladio's Italian Villas
- Thomas Jefferson's architecture
- Woburn Abbey
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.