Difference between revisions of "Silane" - New World Encyclopedia
(claim, fix, edits) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Copyedited}}{{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}}{{Paid}} |
{| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | {| class="toccolours" border="1" style="float: right; clear: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; border-collapse: collapse;" | ||
! {{chembox header}} | Silane | ! {{chembox header}} | Silane | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
| 0 [[Debye|D]] | | 0 [[Debye|D]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! {{chembox header}} | Hazards <!-- | + | ! {{chembox header}} | Hazards <!-- Summary only- MSDS entry provides more complete information —> |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Material safety data sheet|MSDS]] | | [[Material safety data sheet|MSDS]] | ||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | '''Silane''' is a [[chemical compound]] with [[chemical formula]] [[silicon|Si]][[hydrogen|H]]<sub>4</sub>. It is the silicon analog of [[methane]] | + | '''Silane''' is a [[chemical compound]] with the [[chemical formula]] [[silicon|Si]][[hydrogen|H]]<sub>4</sub>. It is the silicon analog of [[methane]] and, like methane, it is a [[gas]] at ordinary temperatures. The name "silane" is also given to a family of compounds that are silicon analogs of [[alkane]] hydrocarbons. Silanes consist of a chain of silicon atoms [[covalent bond|covalently bound]] to hydrogen atoms. The general formula of a silane is Si<sub>n</sub>H<sub>2n+2</sub>. |
| − | + | {{toc}} | |
| − | + | Silanes are useful as coupling agents to bind [[fiberglass|glass fiber]]s to [[polymer]]s, and to couple a bio-inert layer on a [[titanium]] [[prosthesis|implant]]. They are also used for water repellents, sealants, [[masonry]] protection, [[graffiti]] control, [[semiconductor]] manufacturing processes, and chemical [[redox|reduction]] reactions. | |
== Nomenclature of different structures == | == Nomenclature of different structures == | ||
| − | There are certain rules for naming silanes. For instance, depending on the number of silicon atoms in each molecule, the word silane is preceded by a numerical prefix, such as di, tri, tetra, and so forth. Thus, Si<sub>2</sub>H<sub>6</sub> is [[disilane]], and Si<sub>3</sub>H<sub>8</sub> is trisilane. SiH<sub>4</sub> is | + | There are certain rules for naming silanes. For instance, depending on the number of silicon atoms in each molecule, the word silane is preceded by a numerical prefix, such as di, tri, tetra, and so forth. Thus, Si<sub>2</sub>H<sub>6</sub> is [[disilane]], and Si<sub>3</sub>H<sub>8</sub> is trisilane. SiH<sub>4</sub> is usually just called silane, without a prefix, but occasionally it is referred to as monosilane (to avoid confusion with larger silanes). |
In an alternative system of nomenclature, silanes may be named in a manner similar to other inorganic compounds. For instance, silane is called silicon tetrahydride. However, with longer silanes, this system becomes cumbersome. | In an alternative system of nomenclature, silanes may be named in a manner similar to other inorganic compounds. For instance, silane is called silicon tetrahydride. However, with longer silanes, this system becomes cumbersome. | ||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
A [[cyclosilane]] is a silane with a ring structure, just as a [[cycloalkane]] is an alkane with a ring structure. | A [[cyclosilane]] is a silane with a ring structure, just as a [[cycloalkane]] is an alkane with a ring structure. | ||
| − | Some silanes have branched structures. The [[radical (chemistry)|radical]] | + | Some silanes have branched structures. The [[radical (chemistry)|radical]] •SiH<sub>3</sub> is termed silyl, •Si<sub>2</sub>H<sub>5</sub> is disilanyl, and so on. Trisilane with a silyl group attached to the middle silicon is named silyltrisilane. The nomenclature parallels that of [[alkyl]] radicals. |
Silanes may also carry certain functional groups, just as alkanes do. For instance, if a [[hydroxyl group]] (OH) is attached to a silane, it is called a [[silanol]]. There is (at least in principle) a silicon analog for all carbon alkanes. | Silanes may also carry certain functional groups, just as alkanes do. For instance, if a [[hydroxyl group]] (OH) is attached to a silane, it is called a [[silanol]]. There is (at least in principle) a silicon analog for all carbon alkanes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Properties == | ||
| + | |||
| + | As noted above, silane (SiH<sub>4</sub>) is a gas at [[room temperature]]. In addition, it is [[pyrophoric]]—that is, it undergoes spontaneous [[combustion]] in [[air]], without the need for external ignition. (However, one school of thought holds that silane itself is stable and that the natural formation of larger silanes during production causes its pyrophoricity.) Above 420°C, silane decomposes into silicon and hydrogen. It can therefore be used in the [[chemical vapor deposition]] of silicon. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The family of silanes tends to be less stable than their carbon analogs because the Si-Si [[chemical bond|bond]] has a strength slightly lower than the C-C bond. [[Oxygen]] decomposes silanes easily, because the silicon-oxygen bond is quite stable. | ||
== Production == | == Production == | ||
| Line 130: | Line 136: | ||
:Si + 3HCl → HSiCl<sub>3</sub> + H<sub>2</sub> | :Si + 3HCl → HSiCl<sub>3</sub> + H<sub>2</sub> | ||
| − | The trichlorosilane is then boiled on a [[resin]]ous bed containing a [[catalyst]] | + | The trichlorosilane is then boiled on a [[resin]]ous bed containing a [[catalyst]], producing silane and [[silicon tetrachloride]] according to the chemical equation: |
:4HSiCl<sub>3</sub> → SiH<sub>4</sub> + 3SiCl<sub>4</sub> | :4HSiCl<sub>3</sub> → SiH<sub>4</sub> + 3SiCl<sub>4</sub> | ||
| − | The most commonly used catalysts for this process are [[metal]] [[halogen|halides]], particularly [[ | + | The most commonly used catalysts for this process are [[metal]] [[halogen|halides]], particularly [[aluminum chloride]]. |
== Applications == | == Applications == | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Silanes are useful for several industrial and medical applications. For instance, they are used as coupling agents to adhere [[fiberglass|glass fiber]]s to a [[polymer]] matrix, stabilizing the [[composite material]]. They can also be used to couple a bio-inert layer on a [[titanium]] [[prosthesis|implant]]. Other applications include water repellents, [[masonry]] protection, control of [[graffiti]],<ref>[http://www.protectosil.com/protectosil/en/otherregions/graffiticontrol/default Graffiti protection systems] Retrieved October 23, 2007.</ref> applying [[polycrystalline silicon]] layers on silicon wafers when manufacturing semiconductors, and sealants. In addition, silane and similar compounds containing Si-H bonds are used as reducing agents in organic and organometallic chemistry.<ref>[http://www.organic-chemistry.org/chemicals/reductions/silanes.shtm Reduction of organic compounds using silanes] Retrieved October 23, 2007.</ref> | |
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 153: | Line 158: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | = | + | * Antonucci, J.M., et al. 2003. [http://polymers.nist.gov/publications/detail.cfm?PubID=683 Chemistry of Silanes: Interfaces in Dental Polymers and Composites] ''Polymers Division, NIST''. Retrieved August 23, 2007. |
| + | * Jutzi, Peter, and Ulrich Schubert. 2003. ''Silicon Chemistry: From the Atom to Extended Systems''. New York: Wiley. ISBN 3527306471 | ||
| + | * Plueddemann, Edwin Paul. 1982. ''Silane Coupling Agents''. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 0306409577 | ||
| + | |||
Latest revision as of 22:02, 29 January 2023
| Silane | |
|---|---|
| |
| General | |
| Systematic name | Silane |
| Other names | Silicon tetrahydride Silicon hydride Monosilane Silicane |
| Molecular formula | SiH4 |
| Molar mass | 32.12 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless gas |
| CAS number | [7803-62-5] |
| Properties | |
| Density and phase | ? kg m−3 (solid) 0.7 g/ml (liquid) 1.342 g L−1 (gas) |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble |
| Melting point | 88 K (−185°C) |
| Boiling point | 161 K (−112°C) |
| ΔfH0solid | -1615 kJ mol−1 |
| S0solid | 283 J mol−1 K−1 |
| Structure | |
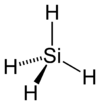
| Molecular shape | tetrahedral |
| Dipole moment | 0 D |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS |
| Main hazards | low toxicity, avoid exposure to skin, irritant, may cause redness and swelling |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | N/A |
| Autoignition temperature | 294 K (21°C) |
| R/S statement | R: ? S: ? |
| UN number | 2203 |
| RTECS number | VV1400000 |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Structure and properties |
n, εr, etc. |
| Thermodynamic data |
Phase behaviour Solid, liquid, gas |
| Spectral data | UV, IR, NMR, MS |
| Related compounds | |
| Related silanes | disilane trisilane tetrasilane cyclosilane |
| Related hydrides | methane |
| Related compounds | disilene |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25°C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | |
Silane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula SiH4. It is the silicon analog of methane and, like methane, it is a gas at ordinary temperatures. The name "silane" is also given to a family of compounds that are silicon analogs of alkane hydrocarbons. Silanes consist of a chain of silicon atoms covalently bound to hydrogen atoms. The general formula of a silane is SinH2n+2.
Silanes are useful as coupling agents to bind glass fibers to polymers, and to couple a bio-inert layer on a titanium implant. They are also used for water repellents, sealants, masonry protection, graffiti control, semiconductor manufacturing processes, and chemical reduction reactions.
Nomenclature of different structures
There are certain rules for naming silanes. For instance, depending on the number of silicon atoms in each molecule, the word silane is preceded by a numerical prefix, such as di, tri, tetra, and so forth. Thus, Si2H6 is disilane, and Si3H8 is trisilane. SiH4 is usually just called silane, without a prefix, but occasionally it is referred to as monosilane (to avoid confusion with larger silanes).
In an alternative system of nomenclature, silanes may be named in a manner similar to other inorganic compounds. For instance, silane is called silicon tetrahydride. However, with longer silanes, this system becomes cumbersome.
A cyclosilane is a silane with a ring structure, just as a cycloalkane is an alkane with a ring structure.
Some silanes have branched structures. The radical •SiH3 is termed silyl, •Si2H5 is disilanyl, and so on. Trisilane with a silyl group attached to the middle silicon is named silyltrisilane. The nomenclature parallels that of alkyl radicals.
Silanes may also carry certain functional groups, just as alkanes do. For instance, if a hydroxyl group (OH) is attached to a silane, it is called a silanol. There is (at least in principle) a silicon analog for all carbon alkanes.
Properties
As noted above, silane (SiH4) is a gas at room temperature. In addition, it is pyrophoric—that is, it undergoes spontaneous combustion in air, without the need for external ignition. (However, one school of thought holds that silane itself is stable and that the natural formation of larger silanes during production causes its pyrophoricity.) Above 420°C, silane decomposes into silicon and hydrogen. It can therefore be used in the chemical vapor deposition of silicon.
The family of silanes tends to be less stable than their carbon analogs because the Si-Si bond has a strength slightly lower than the C-C bond. Oxygen decomposes silanes easily, because the silicon-oxygen bond is quite stable.
Production
Industrially, silane is produced from metallurgical grade silicon in a two-step process. In the first step, powdered silicon is reacted with hydrochloric acid at about 300 °C to produce trichlorosilane, HSiCl3, along with hydrogen gas, according to the chemical equation:
- Si + 3HCl → HSiCl3 + H2
The trichlorosilane is then boiled on a resinous bed containing a catalyst, producing silane and silicon tetrachloride according to the chemical equation:
- 4HSiCl3 → SiH4 + 3SiCl4
The most commonly used catalysts for this process are metal halides, particularly aluminum chloride.
Applications
Silanes are useful for several industrial and medical applications. For instance, they are used as coupling agents to adhere glass fibers to a polymer matrix, stabilizing the composite material. They can also be used to couple a bio-inert layer on a titanium implant. Other applications include water repellents, masonry protection, control of graffiti,[1] applying polycrystalline silicon layers on silicon wafers when manufacturing semiconductors, and sealants. In addition, silane and similar compounds containing Si-H bonds are used as reducing agents in organic and organometallic chemistry.[2]
See also
Notes
- ↑ Graffiti protection systems Retrieved October 23, 2007.
- ↑ Reduction of organic compounds using silanes Retrieved October 23, 2007.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Antonucci, J.M., et al. 2003. Chemistry of Silanes: Interfaces in Dental Polymers and Composites Polymers Division, NIST. Retrieved August 23, 2007.
- Jutzi, Peter, and Ulrich Schubert. 2003. Silicon Chemistry: From the Atom to Extended Systems. New York: Wiley. ISBN 3527306471
- Plueddemann, Edwin Paul. 1982. Silane Coupling Agents. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 0306409577
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
