Heinlein, Robert A.
(→Race) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{approved}}{{images OK}}{{submitted}}{{Paid}}{{copyedited}} |
| − | {{epname}} | + | {{epname|Heinlein, Robert A.}} |
{{Infobox Science Fiction Writer | {{Infobox Science Fiction Writer | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| caption = Heinlein signing autographs at the 1976 [[Worldcon]] | | caption = Heinlein signing autographs at the 1976 [[Worldcon]] | ||
| pseudonym = Anson McDonald, Lyle Monroe, John Riverside, Caleb Saunders, Simon York | | pseudonym = Anson McDonald, Lyle Monroe, John Riverside, Caleb Saunders, Simon York | ||
| − | | birth_date = | + | | birth_date = July 7, 1907 |
| birth_place = [[Butler, Missouri|Butler]], [[Missouri]] | | birth_place = [[Butler, Missouri|Butler]], [[Missouri]] | ||
| − | | death_date = | + | | death_date = May 8, 1988 |
| death_place = [[Carmel, California|Carmel]], [[California]] | | death_place = [[Carmel, California|Carmel]], [[California]] | ||
| occupation = Novelist, short story author, essayist | | occupation = Novelist, short story author, essayist | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| website = }} | | website = }} | ||
| − | '''Robert Anson Heinlein''' (July 7, 1907 – May 8, 1988) was one of the most popular, influential, and controversial authors of "hard" [[science fiction]]. He set a high standard for science and engineering plausibility that few have equaled, and helped to raise the genre's standards of literary quality. He was the first writer to break into mainstream general magazines such as ''[[The Saturday Evening Post]]'' in the late 1940s with unvarnished science fiction. He was among the first authors of bestselling novel-length science fiction in the modern mass-market era. For many years Heinlein, [[Isaac Asimov]], and [[Arthur C. Clarke]] were known as the "Big Three" of science fiction.<ref> | + | '''Robert Anson Heinlein''' (July 7, 1907 – May 8, 1988) was one of the most popular, influential, and controversial authors of "hard" [[science fiction]]. He set a high standard for science and engineering plausibility that few have equaled, and helped to raise the genre's standards of literary quality. He was the first writer to break into mainstream general magazines such as ''[[The Saturday Evening Post]],'' in the late 1940s with unvarnished science fiction. He was among the first authors of bestselling novel-length science fiction in the modern mass-market era. For many years Heinlein, [[Isaac Asimov]], and [[Arthur C. Clarke]] were known as the "Big Three" of science fiction.<ref>Heinlein Society, [http://www.heinleinsociety.org/pressreleases/clarkeheinleinaward.html Sir Arthur Clarke Named Recipient of 2004 Heinlein Award.] Retrieved July 24, 2007.</ref> |
| − | The major themes of his work were social: | + | The major themes of his work were social: Radical [[individualism]], [[libertarianism]], [[religion]], the relationship between physical and emotional [[love]], and speculation about unorthodox family relationships. His iconoclastic approach to these themes led to wildly divergent perceptions of his works. For example, his 1959 novel ''Starship Troopers'' was widely viewed as glorifying [[militarism]]. By contrast, his 1961 novel ''Stranger in a Strange Land'' put him in the unexpected role of [[The Pied Piper of Hamelin|pied piper]] to the [[sexual revolution]] and the [[counterculture]], all of which demonstrate his libertarian tendencies. |
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | Heinlein won four [[Hugo Award]]s for his novels. In addition, fifty years after publication, three of his works were awarded "Retro Hugos"—awards given retrospectively for years in which no Hugos had been awarded. He also won the first Grand Master Award given by the Science Fiction Writers of America for lifetime achievement. | ||
| − | Heinlein | + | In his fiction, Heinlein coined words that have become part of the English language, including "[[grok]]," "[[TANSTAAFL]]," and "[[waldo]]." |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Life == | == Life == | ||
[[Image:RAH 1929 Yearbook.png|right|frame|Heinlein from the 1929 [[US Naval Academy]] [[yearbook]]]] | [[Image:RAH 1929 Yearbook.png|right|frame|Heinlein from the 1929 [[US Naval Academy]] [[yearbook]]]] | ||
| − | Heinlein (pronounced ''Hine-line'') | + | Heinlein (pronounced ''Hine-line'') was born on July 7, 1907, to Rex Ivar and Bam Lyle Heinlein, in Butler, Missouri. His childhood was spent in Kansas City, Missouri.<ref>Bill Patterson, [http://members.aol.com/agplusone/robert_a._heinlein_a_biogr.htm Robert A. Heinlein: A Biographical Sketch.] Retrieved July 24, 2007.</ref> The outlook and values of this time and place would influence his later works; however, he would break with many of its values and [[social mores]], both in his writing and in his personal life. He graduated from the [[United States Naval Academy|U.S. Naval Academy]] in 1929, and served as an officer in the [[United States Navy]]. He married soon after graduation, but this marriage lasted only about a year.<ref>Heinlein Society, [http://www.heinleinsociety.org/rah/FAQrah.html Frequently Asked Questions About Robert A. Heinlein, the Person.] Retrieved July 24, 2007.</ref> He served on the USS ''Lexington'' in 1931. He married his second wife, Leslyn Macdonald, in 1932. Leslyn was a political radical, and [[Isaac Asimov]] recalled Robert during those years as being, like her, "a flaming liberal."<ref>Isaac Asimov, ''I, Asimov''</ref> Heinlein served aboard USS ''Roper'' in 1933–1934, reaching the rank of naval Lieutenant. In 1934, Heinlein was discharged from the Navy due to [[lung|pulmonary]] [[tuberculosis]]. During his long hospitalization he developed the idea of the [[waterbed]], and his detailed descriptions of it in three of his books later prevented others from [[patent|patenting]] it. The military was the second great influence on Heinlein; throughout his life, he strongly believed in loyalty, leadership, and other ideals associated with the military. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | After his discharge, Heinlein attended a few weeks of graduate classes in [[mathematics]] and [[physics]] at the [[University of California, Los Angeles]], but quit either because of his health or from a desire to enter politics.<ref>Afterword to '' | + | After his discharge, Heinlein attended a few weeks of graduate classes in [[mathematics]] and [[physics]] at the [[University of California, Los Angeles]], but quit either because of his health or from a desire to enter politics.<ref>Afterword to ''For Us, the Living,'' 2004 edition, p. 245.</ref> He supported himself at a series of jobs, including real estate and [[silver]] [[mining]]. Heinlein was active in [[Upton Sinclair]]'s [[socialism|socialist]] [[EPIC Movement|EPIC]] (End Poverty In [[California]]) movement in early 1930s. When Sinclair gained the [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic]] nomination for governor of California in 1934, Heinlein worked actively in the unsuccessful campaign. |
| + | |||
| + | Heinlein himself ran for the California State Assembly in 1938, but was unsuccessful. Heinlein was running as a left-wing Democrat in a conservative district, and never made it past the Democratic primary because of trickery by his Republican opponent.<ref>afterword to ''For Us, the Living,'' 2004 edition, p. 247.</ref> Also, an unfortunate juxtaposition of events had [[Konrad Heinlein]] making headlines in the [[Sudetenland]]s. In later years, Heinlein kept his socialist past secret, writing about his political experiences coyly, and usually under the veil of fictionalization. In 1954, he wrote: "…many Americans … were asserting loudly that [[Joseph McCarthy|McCarthy]] had created a 'reign of terror.' Are ''you'' terrified? I am not, and I have in my background much political activity well to the left of Senator McCarthy's position."<ref>''Tramp Royale,'' (1992, uncorrected proof), p. 62. ISBN 0-441-82184-7</ref> | ||
[[Image:Heinlein-decamp-and-asimov.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Robert A. Heinlein, [[L. Sprague de Camp]], and [[Isaac Asimov]], [[Philadelphia Naval Shipyard|Philadelphia Navy Yard]], 1944.]] | [[Image:Heinlein-decamp-and-asimov.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Robert A. Heinlein, [[L. Sprague de Camp]], and [[Isaac Asimov]], [[Philadelphia Naval Shipyard|Philadelphia Navy Yard]], 1944.]] | ||
| − | While not destitute after the campaign—he had a small disability pension from the Navy—Heinlein turned to writing in order to pay off his mortgage, and in 1939 his first published story, "Life-Line," was printed in ''Astounding'' magazine. He was quickly acknowledged as a leader of the new movement toward [[social science fiction|"social" science fiction]]. During [[World War II]] he did aeronautical engineering for the Navy, recruiting [[Isaac Asimov]] and [[L. Sprague de Camp]] to work at the Philadelphia Naval Yard. | + | While not destitute after the campaign—he had a small disability pension from the Navy—Heinlein turned to writing in order to pay off his mortgage, and in 1939 his first published story, "Life-Line," was printed in ''Astounding'' magazine. He was quickly acknowledged as a leader of the new movement toward [[social science fiction|"social" science fiction]]. During [[World War II]] he did aeronautical engineering for the Navy, recruiting [[Isaac Asimov]] and [[L. Sprague de Camp]] to work at the Philadelphia Naval Yard. |
| − | As the war wound down in 1945, Heinlein began re-evaluating his career. The [[atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki]], along with the outbreak of the [[Cold War]], galvanized him to write nonfiction on political topics; in addition, he wanted to break into better-paying markets. He published four influential stories for ''[[The Saturday Evening Post]]'' | + | As the war wound down in 1945, Heinlein began re-evaluating his career. The [[atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki]], along with the outbreak of the [[Cold War]], galvanized him to write nonfiction on political topics; in addition, he wanted to break into better-paying markets. He published four influential stories for ''[[The Saturday Evening Post]],'' leading off, in February 1947, with "The Green Hills of Earth," which made him the first science fiction writer to break out of the "pulp ghetto." In 1950, ''Destination Moon''—the documentary-like film for which he had written the story and scenario, co-written the script, and invented many of the effects—won an [[Academy Awards|Academy Award]] for [[special effect]]s. Most importantly, he embarked on a series of [[children's literature|juvenile novels]] for Charles Scribner's Sons that was to last through the 1950s. |
[[Image:heinleins-house.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Robert and Virginia Heinlein in a 1952 ''Popular Mechanics'' article, titled "A House to Make Life Easy." The Heinleins, both engineers, designed the house themselves with many innovative features.]] | [[Image:heinleins-house.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Robert and Virginia Heinlein in a 1952 ''Popular Mechanics'' article, titled "A House to Make Life Easy." The Heinleins, both engineers, designed the house themselves with many innovative features.]] | ||
| − | Heinlein divorced his second wife in 1947, and the following year married Virginia "Ginny" Gerstenfeld, whom he would remain married to until his death forty years later. Ginny undoubtedly served as a model for many of his intelligent, fiercely independent female characters. In 1953–1954, the Heinleins took a trip around the world, which Heinlein described in | + | Heinlein divorced his second wife in 1947, and the following year married Virginia "Ginny" Gerstenfeld, whom he would remain married to until his death forty years later. Ginny undoubtedly served as a model for many of his intelligent, fiercely independent female characters. In 1953–1954, the Heinleins took a trip around the world, which Heinlein described in "Tramp Royale," and which also provided background material for science fiction novels, such as ''Podkayne of Mars,'' that were set aboard spaceships. Asimov believed that Heinlein made a drastic swing to the [[right-wing politics|right]] politically at the same time he married Ginny. The couple formed the [[Patrick Henry]] League in 1958 and worked on the 1964 [[Barry Goldwater]] campaign, and ''Tramp Royale'' contains two lengthy apologias for the [[Joseph McCarthy|McCarthy hearings]]. However, this perception of a drastic shift may result from a tendency to make the mistake of trying to place [[libertarianism]] on the traditional right-[[left-wing politics|left]] [[political spectrum|spectrum]] of [[politics of the United States|American politics]], as well as from Heinlein's iconoclasm and unwillingness to let himself be pigeonholed into any ideology (including libertarianism). |
| + | |||
| + | The evidence of Ginny's influence is clearer in matters literary and scientific. She acted as the first reader of his [[manuscript]]s, and was reputed to be a better engineer than Heinlein himself.<ref>Heinlein Society, [http://www.heinleinsociety.org/rah/ginny/GinnyNotice.html The Passing of Ginny Heinlein, January 18, 2003.] Retrieved July 24, 2007.</ref> | ||
[[Image:Heinlein_Tahiti_2.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Robert and Virginia Heinlein in Tahiti, 1980.]] | [[Image:Heinlein_Tahiti_2.jpg|thumb|left|250px|Robert and Virginia Heinlein in Tahiti, 1980.]] | ||
| − | The [[Heinlein juveniles]], novels for [[young adult literature|young adults]], may turn out to be the most important work he ever did, building an audience of scientifically and socially aware adults. He had used topical materials throughout his series, but in 1959 his ''Starship Troopers'' was regarded by the Scribner's editorial staff as too controversial for their prestige line and was rejected summarily. Heinlein felt himself released from the constraints of writing for children and began to write "my own stuff, my own way," and came out with a series of challenging books that redrew the boundaries of science fiction, including his best-known | + | The [[Heinlein juveniles]], novels for [[young adult literature|young adults]], may turn out to be the most important work he ever did, building an audience of scientifically and socially aware adults. He had used topical materials throughout his series, but in 1959 his ''Starship Troopers'' was regarded by the Scribner's editorial staff as too controversial for their prestige line and was rejected summarily. Heinlein felt himself released from the constraints of writing for children and began to write "my own stuff, my own way," and came out with a series of challenging books that redrew the boundaries of science fiction, including his best-known works, ''Stranger in a Strange Land'' (1961) and ''The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress'' (1966). |
| − | Beginning in 1970, however, Heinlein had a series of health crises, punctuated by strenuous work. The decade began with a life-threatening attack of [[peritonitis]], recovery from which required more than two years, but as soon as he was well enough to write, he began work on ''Time Enough for Love'' (1973), which introduced many of the themes found in his later fiction. In the mid-1970s he wrote two articles for the ''Britannica Compton Yearbook'' | + | Beginning in 1970, however, Heinlein had a series of health crises, punctuated by strenuous work. The decade began with a life-threatening attack of [[peritonitis]], recovery from which required more than two years, but as soon as he was well enough to write, he began work on ''Time Enough for Love'' (1973), which introduced many of the themes found in his later fiction. In the mid-1970s he wrote two articles for the ''Britannica Compton Yearbook.'' The two articles discussed Paul Dirac and antimatter, and blood chemistry. A version of the former, titled "Paul Dirac, Antimatter, and You," was published in the anthology ''[[Expanded Universe (Heinlein)|Expanded Universe]],'' and demonstrates both Heinlein's skill as a popularizer and his lack of depth in physics; an afterword gives a normalization equation and presents it, incorrectly, as being the [[Dirac equation]]. |
| + | |||
| + | He and Ginny crisscrossed the country helping to reorganize blood donation in the U.S., and he was guest of honor at a World Science Fiction Convention for the third time at Kansas City, Missouri in 1976. While vacationing in Tahiti in early 1978, he suffered a transient ischemic attack. Over the next few months, he became more and more exhausted, and his health again began to decline. The problem was determined to be a blocked carotid artery, and he had one of the earliest carotid bypass operations to correct the blockage. Asked to appear before a [[joint committee|Joint Committee]] of the [[United States House of Representatives|U.S. House]] and [[United States Senate|Senate]] that year, he testified on his belief that spin-offs from [[space technology]] were benefiting the infirm and the elderly. His surgical treatment re-energized Heinlein, and he wrote five novels from 1980 until he died in his sleep from [[emphysema]] and [[congestive heart failure]] on May 8, 1988, as he was putting together the early notes for another [[pantheistic solipsism|World as Myth]] novel. Several of his works have been published posthumously. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Based on an outline and notes created by Heinlein in 1955, [[Spider Robinson]] wrote the novel ''Variable Star.'' Heinlein's posthumously published nonfiction includes a selection of letters edited by his wife, Virginia, his book on practical politics written in 1946, a travelogue of their first around-the-world tour in 1954. ''Podkayne of Mars'' and ''Red Planet,'' which were edited against his wishes in their original release, have been reissued in restored editions. ''Stranger In a Strange Land'' was originally published in a shorter form, but both the long and short versions are now simultaneously available in print. | ||
==Works== | ==Works== | ||
===Early work, 1939–1960=== | ===Early work, 1939–1960=== | ||
| − | The first novel that Heinlein wrote, ''For Us, The Living: A Comedy of Customs'' (1939), did not see print during his lifetime, but Robert James later tracked down the manuscript and it was published in 2003. Although a failure as a novel, | + | The first novel that Heinlein wrote, ''For Us, The Living: A Comedy of Customs'' (1939), did not see print during his lifetime, but Robert James later tracked down the manuscript and it was published in 2003. Although a failure as a novel, (Biographer Bill Patterson, for example, refers to it as "a failed science fiction novel") serving as little more than a disguised lecture on Heinlein's [[social theory|social theories]], it is intriguing as a window into the development of Heinlein's radical ideas about man as a [[social animal]], including [[free love]]. The root of many themes found in his later stories can be found in this book. |
| − | It appears that Heinlein attempted to live in a manner consistent with these ideas, even in the 1930s, and had an open relationship in his marriage to his second wife, Leslyn. He was also a [[nudism|nudist]]; | + | It appears that Heinlein attempted to live in a manner consistent with these ideas, even in the 1930s, and had an open relationship in his marriage to his second wife, Leslyn. He was also a [[nudism|nudist]]; nudism and body [[taboo]]s are frequently discussed in his work. At the height of the cold war, he built a [[air-raid shelter|bomb shelter]] under his house, like the one featured in ''Farnham's Freehold.'' |
| − | + | After ''For Us, The Living,'' Heinlein began selling (to magazines) first short stories, then novels, set in the future, complete with a timeline of significant political, cultural, and technological changes. A chart of the future history was published in the May 1941 issue of ''Astounding.'' Over time, Heinlein wrote many novels and short stories that deviated freely from the Future History on some points, while maintaining consistency in some other areas. The Future History was also eventually overtaken by actual events. These discrepancies were explained, after a fashion, in his later [[Pantheistic solipsism|World as Myth]] stories. | |
| − | + | Heinlein's first novel published as a book, ''Rocket Ship [[Galileo]],'' was initially rejected because going to the moon was considered too far out, but he soon found a publisher, [[Charles Scribner's Sons|Scribner's]], that began publishing a Heinlein [[young adult literature|juvenile]] once a year for the Christmas season.<ref>Robert A. Heinlein, ''Expanded Universe'' (foreword to "Free Men,") p. 207.</ref> Eight of these books were illustrated by [[Clifford Geary]] in a distinctive white-on-black scratchboard style.<ref>Heinlein in Dimension, III. Period of Success. </ref> Some representative novels of this type are ''Have Space Suit—Will Travel,'' ''Farmer in the Sky,'' and ''Starman Jones.'' Many of these were first published in serial form under other titles. For example, ''Farmer in the Sky'' was published as "Satellite Scout" in the [[Boy Scouts of America|Boy Scout]] magazine ''Boys' Life.'' | |
| − | + | The importance Heinlein attached to privacy was made clear in his fiction (e.g., ''For Us, the Living''), but also in several well known examples from his life. He had a falling out with [[Alexei Panshin]], who wrote an important book analyzing Heinlein's fiction; Heinlein stopped cooperating with Panshin because he accused Panshin of "[attempting to] pry into his affairs and to violate his privacy." Heinlein wrote to Panshin's publisher threatening to sue, and stating, "You are warned that only the barest facts of my private life are public knowledge…."<ref>Heinlein in Dimension, The Story of Heinlein in Dimension.</ref> In his 1961 speech at WorldCon, where he was guest of honor, he advocated building bomb shelters and caching away unregistered weapons,<ref>Thomas Perry, Ham and Eggs and Heinlein.</ref> and his own house in Colorado Springs included a bomb shelter. | |
| + | Heinlein was a nudist, and built a fence around his house in Santa Cruz to keep out the counterculture types who had learned of his ideas through ''Stranger in a Strange Land.'' In his later life, Heinlein studiously avoided revealing the story of his early involvement in left-wing politics, and made strenuous efforts to block publication of information he had revealed to prospective biographer Sam Moskowitz. | ||
| − | + | There has been speculation that Heinlein's intense obsession with his privacy was due at least in part to the apparent contradiction between his unconventional private life and his career as an author of books for children, but ''For Us, The Living'' also explicitly discusses the political importance Heinlein attached to privacy as a matter of principle. | |
| − | + | The novels that he wrote for a young audience were a mixture of adolescent and adult themes. Many of the issues that he takes on in these books have to do with the kinds of problems that [[adolescence|adolescent]]s experience. His protagonists are usually very intelligent teenagers who have to make a way in the adult society they see around them. On the surface, they are simple tales of adventure, achievement, and dealing with stupid teachers and jealous peers. | |
| − | + | However, Heinlein was a vocal proponent of the notion that juvenile readers were far more sophisticated and able to handle complex or difficult themes than most people realized. Thus even his juvenile stories often had a maturity to them that make them readable for adults. ''Red Planet,'' for example, portrays some very subversive themes, including a [[revolution]] in which young students are involved; his editor demanded substantial changes in this book's discussion of topics such as the use of weapons by adolescents and the confused [[Human sexuality|sexuality]] of the Martian character. Heinlein was always aware of the editorial limitations put in place by the editors of his novels and stories, and while he observed those restrictions on the surface, was often successful in introducing ideas not often seen in other authors' juvenile SF. | |
| − | In 1957, James Blish wrote that one reason for Heinlein's success "has been the high grade of machinery which goes, today as always, into his story-telling. Heinlein seems to have known from the beginning, as if instinctively, technical lessons about fiction which other writers must learn the hard way (or often enough, never learn). He does not always operate the machinery to the best advantage, but he always seems to be aware of it."<ref> | + | In 1957, James Blish wrote that one reason for Heinlein's success "has been the high grade of machinery which goes, today as always, into his story-telling. Heinlein seems to have known from the beginning, as if instinctively, technical lessons about fiction which other writers must learn the hard way (or often enough, never learn). He does not always operate the machinery to the best advantage, but he always seems to be aware of it."<ref>James Blish, ''The Issues at Hand'', page 52.</ref> |
| − | Heinlein's last juvenile novel, and probably his most controversial work in general, was the 1959 ''Starship Troopers'' | + | Heinlein's last juvenile novel, and probably his most controversial work in general, was the 1959 ''Starship Troopers,'' which he wrote in response to the U.S.'s decision to unilaterally end [[nuclear testing]].<ref>Heinlein Society, [http://www.heinleinsociety.org/rah/biographies.html Biographies of Robert and Virginia Heinlein.] Retrieved July 24, 2007.</ref> The book's central political idea is that there should be no [[conscription]], but that [[suffrage]] should belong only to those who have earned it through government or military service. |
| − | ===Mid- | + | ===Mid-period work, 1961–1973=== |
| − | From about 1961 | + | From about 1961 ''(Stranger in a Strange Land)'' to 1973 ''(Time Enough for Love)'', Heinlein wrote some of his most controversial novels. His work during this period explored his most important themes, such as [[individualism]], [[libertarianism]], and physical and emotional love. To some extent, the apparent discrepancy between these works and the more naive themes of his earlier novels can be attributed to his own perception, which was probably correct, that readers and publishers in the 1950s were not yet ready for some of his more radical ideas. He did not publish ''Stranger in a Strange Land'' until some time after it was written, and the themes of free love and radical individualism are prominently featured in his long-unpublished first novel, ''For Us, The Living: A Comedy of Customs.'' |
| − | Although Heinlein had previously written a few short stories in the [[fantasy]] [[genre]], during this period he wrote his first fantasy novel, ''Glory Road'' | + | The story that ''Stranger in a Strange Land'' was used as inspiration by [[Charles Manson]] appears to be an urban folk tale; although some of Manson's followers had read the book, Manson himself later said that he had not. It is true that other individuals formed a quasi-religious organization called the [[Church of All Worlds]], after the religion founded by the primary characters in ''Stranger,'' but Heinlein had nothing to do with this, either, so far as is known.<ref>Heinlein Society, [http://www.heinleinsociety.org/rah/faqworks.html Frequently Asked Questions about Robert A. Heinlein, His Works.] Retrieved July 24, 2007.</ref> ''The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress'' tells of a war of independence of Lunar colonies, with significant commentary regarding the threat posed by any government—including a republic—to individual freedom. |
| + | |||
| + | Although Heinlein had previously written a few short stories in the [[fantasy]] [[genre]], during this period he wrote his first fantasy novel, ''Glory Road,'' and in ''Stranger in a Strange Land'' and ''I Will Fear No Evil,'' he began to mix hard science with fantasy, mysticism, and satire of organized [[religion]]. Critics William H. Patterson, Jr., and Andrew Thornton<ref>Patterson and Thornton, 2001.</ref> believe that this is simply an expression of Heinlein's longstanding philosophical opposition to [[positivism (philosophy)|positivism]]. Heinlein stated that he was influenced by James Branch Cabell in taking this new literary direction. The next-to-last novel of this period, ''I Will Fear No Evil,'' is according to critic James Gifford "almost universally regarded as a literary failure," and he attributes its shortcomings to Heinlein's near-death from [[peritonitis]].<ref>James Gifford, ''Robert A. Heinlein: A Reader's Companion'', (Sacramento, CA: Nitrosyncretic Press, 2000), p. 102.</ref> | ||
===Later work, 1980–1987=== | ===Later work, 1980–1987=== | ||
| − | After a seven-year hiatus brought on by poor health, Heinlein produced five new novels in the period from 1980 | + | After a seven-year hiatus brought on by poor health, Heinlein produced five new novels in the period from 1980 ''(The Number of the Beast)'' to 1987 ''(To Sail Beyond the Sunset)''. These books have a thread of common characters and time and place. They most explicitly communicated Heinlein's philosophies and beliefs, and many long, didactic passages of dialog and exposition deal with government, sex, and religion. These novels are controversial among his readers, and some critics have written about them very negatively.<ref>Dave Langford, [http://www.ansible.co.uk/writing/numbeast.html Vulgarity and Nullity.] Retrieved July 24, 2007.</ref> Heinlein's four Hugo awards were all for books written before this period. |
| − | Some of these books, such as ''The Number of the Beast'' and ''The Cat Who Walks Through Walls'' | + | Some of these books, such as ''The Number of the Beast'' and ''The Cat Who Walks Through Walls,'' start out as tightly constructed adventure stories, but later transform into philosophical fantasies. It is a matter of opinion whether this demonstrates a lack of attention to craftsmanship or a conscious effort to expand the boundaries of science fiction into a kind of [[magic realism|magical realism]], continuing the process of literary exploration that he had begun with ''Stranger in a Strange Land.'' Most of the novels from this period are recognized by critics as forming an offshoot from the Future History series, and referred to by the term [[Pantheistic solipsism|World as Myth]].<ref>William H. Patterson, Jr., and Andrew Thornton, ''The Martian Named Smith: Critical Perspectives on Robert A. Heinlein's Stranger in a Strange Land,'' p. 128.</ref> |
| − | The tendency toward authorial self-referentialism begun in ''Stranger in a Strange Land'' and ''Time Enough For Love'' becomes even more evident in novels such as ''The Cat Who Walks Through Walls'' | + | The tendency toward authorial self-referentialism begun in ''Stranger in a Strange Land'' and ''Time Enough For Love'' becomes even more evident in novels such as ''The Cat Who Walks Through Walls,'' whose first-person protagonist is a disabled military veteran who becomes a writer, and finds love with a female character who, like all of Heinlein's strong female characters, appears to be based closely on his wife Ginny. The self-parodying element of these books keeps them from being bogged down by taking themselves too seriously, but may also fail to evoke the desired effect in readers who are not familiar with Heinlein's earlier novels. Many readers are split on their reactions to Heinlein's wit, particularly in his dialogue—characters from a plethora of ''milieux'' tend to favor the same midwestern-American, post-Depression style and referents. Some find it charming and disarming. Others attack it as unsophisticated. |
The 1984 novel ''Job: A Comedy of Justice'' is a sharp satire of fundamentalist [[Christianity]]. | The 1984 novel ''Job: A Comedy of Justice'' is a sharp satire of fundamentalist [[Christianity]]. | ||
| − | ===Posthumous | + | ===Posthumous publications=== |
| − | Several Heinlein works have been published since his death, including the aforementioned ''For Us, The Living: A Comedy of Customs'' as well as 1989's ''Grumbles from the Grave'' | + | Several Heinlein works have been published since his death, including the aforementioned ''For Us, The Living: A Comedy of Customs,'' as well as 1989's ''Grumbles from the Grave,'' a collection of letters between Heinlein and his editors and agent, 1992's ''Tramp Royale,'' a travelogue of a southern hemisphere tour the Heinleins took in the 1950s, ''Take Back Your Government,'' a how-to book about participatory democracy written in 1946, and a tribute volume called ''Requiem: Collected Works and Tributes to the Grand Master,'' containing some additional short works previously unpublished in book form. ''Off the Main Sequence,'' published in 2005, includes three short stories never before collected in any Heinlein book (Heinlein called them "stinkeroos"). |
| − | + | Colleague, friend, and admirer<ref>Heinlein Society, [http://www.heinleinsociety.org/rah/works/articles/rahrahrah.html Rah, rah, R.A.H.] Retrieved July 24, 2007.</ref> Spider Robinson wrote ''Variable Star,'' based on an outline and notes for a juvenile novel that Heinlein prepared in 1955. The novel was published as a collaboration, with Heinlein's name above Robinson's on the cover, in 2006. | |
==Ideas, themes, and influence== | ==Ideas, themes, and influence== | ||
===Politics=== | ===Politics=== | ||
| − | Heinlein's writing may appear to have oscillated wildly across the political spectrum. His first novel, ''For Us, The Living'' | + | Heinlein's writing may appear to have oscillated wildly across the political spectrum. His first novel, ''For Us, The Living,'' consists largely of speeches advocating the [[Social Credit]] system, and the early story "Misfit" deals with an organization which seems to be [[Franklin D. Roosevelt]]'s [[Civilian Conservation Corps]] translated into outer space. While ''Stranger in a Strange Land'' was embraced by the [[hippie]] [[counterculture]], and ''Glory Road'' can be read as an [[antiwar]] piece, some have deemed ''Starship Troopers'' [[militarism|militaristic]], and ''To Sail Beyond the Sunset,'' published during the [[Ronald Reagan|Reagan]] administration, was stridently [[right-wing politics|right-wing]]. |
| − | [[ | + | There are, however, certain threads in Heinlein's political thought that remain constant. A strong current of [[libertarianism]] runs through his work, as expressed most clearly in ''The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress.'' His early juvenile novels often contain a surprisingly strong anti-authority message, as in his first published novel, ''Rocket Ship Galileo,'' which has a group of boys blasting off on a rocket ship in defiance of a court order. A similar defiance of a court order to take a moon trip takes place in the short story "Requiem." In ''The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress,'' the unjust Lunar Authority that controls the lunar colony is usually referred to simply as "Authority," which points to an obvious interpretation of the book as a [[parable]] for the evils of authority in general, rather than the evils of one particular authority. |
| − | + | Heinlein was opposed to any encroachment of religion into government; he pilloried [[organized religion]] in ''Job: A Comedy of Justice,'' and, with more subtlety and ambivalence, in ''Stranger in a Strange Land.'' His future history includes a period called the Interregnum, in which a backwoods [[revival meeting|revivalist]] becomes [[dictator]] of the United States. ''Revolt in 2100'' depicts a revolutionary underground overthrowing a religious dictatorship in America. Positive descriptions of the military (''Between Planets,'' ''The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress,'' ''Red Planet,'' ''Starship Troopers'') tend to emphasize the individual actions of volunteers in the spirit of the [[Minutemen (militia)|Minutemen]] of colonial America. [[Conscription]] and the military as an extension of the government are portrayed in ''Time Enough for Love,'' ''Glory Road,'' and ''Starship Troopers'' as being poor substitutes for the volunteers who, ideally, should be defending a [[free society]]. | |
| − | Heinlein | + | To those on the right, Heinlein's ardent [[anti-communism]] during the [[Cold War]] era might appear to contradict his earlier efforts in the [[socialism|socialist]] EPIC and [[Social Credit]] movements; however, it should be noted that both the [[Socialist Party of America|Socialist Party]] and the [[Communist Party USA|Communist Party]] were very active during the 1930s, and the distinction between socialism and [[communism]] was well understood by those on the [[political left|left]]. Heinlein spelled out his strong concerns regarding communism in a number of nonfiction pieces, including "Who are the heirs of [[Patrick Henry]]?," an anti-communist [[polemic]] published as a newspaper advertisement in 1958; and articles such as "[[Pravda]] Means Truth" and "Inside [[Intourist]]," in which he recounted his visit to the [[Soviet Union|USSR]] and advised [[Western world|Western]] readers on how to evade official supervision on such a trip. |
| − | + | Many of Heinlein's stories explicitly spell out a view of history which could be compared to [[Karl Marx|Marx]]'s: Social structures are dictated by the materialistic environment. Heinlein would perhaps have been more comfortable with a comparison with [[Frederick Jackson Turner]]'s frontier thesis. In ''Red Planet,'' Doctor MacRae links attempts at [[gun control]] to the increase in population density on Mars. (This discussion was edited out of the original version of the book at the insistence of the publisher.) In ''Farmer in the Sky,'' overpopulation of Earth has led to hunger, and emigration to [[Ganymede (moon)|Ganymede]] provides a "life insurance policy" for the species as a whole; Heinlein puts a lecture in the mouth of one of his characters toward the end of the book in which it is explained that the mathematical logic of [[Thomas Malthus|Malthusianism]] can lead only to disaster for the home planet. A subplot in ''Time Enough for Love'' involves demands by farmers upon Lazarus Long's bank, which Heinlein portrays as the inevitable tendency of a pioneer society evolving into a more dense (and, by implication, more decadent and less free) society. This episode is an interesting example of Heinlein's tendency (in opposition to Marx) to view history as cyclical rather than progressive. Another good example of this is ''The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress,'' in which a revolution deposes the Authority, but immediately thereafter, the new government falls prey to the inevitable tendency to legislate people's personal lives, despite the attempts of one of the characters, who describes himself as a "rational anarchist." | |
| − | |||
| − | Many of Heinlein's stories explicitly spell out a view of history which could be compared to [[Karl Marx|Marx]]'s: | ||
===Race=== | ===Race=== | ||
| − | |||
{{spoiler}} | {{spoiler}} | ||
| − | Heinlein grew up in the era of [[racial segregation]] in the United States and wrote some of his most influential fiction at the height of the U.S. [[civil rights]] movement. His early juveniles were very much ahead of their time both in their explicit rejection of racism and in their inclusion of non-white protagonists; in the context of science fiction before the 1960s, the mere existence of dark-skinned characters was a remarkable novelty, with green occurring more often than brown. His second juvenile, the 1948 ''Space Cadet'' | + | Heinlein grew up in the era of [[racial segregation]] in the United States and wrote some of his most influential fiction at the height of the U.S. [[civil rights]] movement. His early juveniles were very much ahead of their time both in their explicit rejection of racism and in their inclusion of non-white protagonists; in the context of science fiction before the 1960s, the mere existence of dark-skinned characters was a remarkable novelty, with green occurring more often than brown. His second juvenile, the 1948 ''Space Cadet,'' explicitly uses aliens as a metaphor for human racial minorities. Throughout his career, Heinlein challenges his readers' possible racial stereotypes by introducing a strong, sympathetic character, only to reveal much later that he is of African descent. This also occurs in, for example, ''The Cat Who Walks Through Walls'' and ''Tunnel in the Sky;'' in several cases, the covers of the books show characters as light-skinned, while the text states, or at least implies, that they are dark-skinned or of African descent. |
| − | + | The reference in ''Tunnel in the Sky'' is subtle and ambiguous, but at least one college instructor who teaches the book reports that some students always ask, "Is he black?" ''The Cat Who Walks Through Walls''was published with a dust jacket painting showing the protagonist as pale-skinned, although the book clearly states that he is dark-skinned (see Gifford, p. 68). This was also true of the paperback release of ''Friday,'' in which the title character is revealed early on to be fairly dark-skinned (she describes herself as having a "permanent tan"). However, she conceals her skin pigment many times in the course of the novel, and she does indeed take on the identity of a white female at one point. | |
| − | + | ''The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress'' and ''Podkayne of Mars'' both contain incidents of racial prejudice or injustice against their protagonists. ''The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress'' includes an incident in which the protagonist visits the Southern U.S. and is briefly jailed for polygamy, later learning that the "…range of color in Davis family was what got judge angry enough…" to have him arrested. ''Podkayne of Mars'' deals briefly with racial prejudice against the protagonist due to her mixed-race ancestry. Heinlein repeatedly denounced racism in his non-fiction works, including numerous examples in ''Expanded Universe.'' | |
| − | Some of the alien species in Heinlein's fiction can be interpreted as allegorical representations of human [[ethnic group]]s. '' | + | |
| + | Race was a central theme in some of Heinlein's fiction. The most prominent example is ''Farnham's Freehold,'' which casts a white family into a future in which white people are the slaves of black rulers. In the 1941 (published as a serial in 1941, the year of the Japanese attack on [[Pearl Harbor]], published in book form in 1949) novel ''Sixth Column'' (also known as ''The Day After Tomorrow''), a resistance movement defends itself against an invasion by an Asian fascist state (the "Pan-Asians") using a "super-science" technology that allows ray weapons to be tuned to specific races. The idea for the story was pushed on Heinlein by editor John W. Campbell, and Heinlein wrote later that he had "had to reslant it to remove racist aspects of the original story line" and that he did not "consider it to be an artistic success."<ref>Robert A. Heinlein, ''Expanded Universe'', foreword to "Solution Unsatisfactory," p. 93 of Ace paperback edition.</ref> In ''The Star Beast,'' a harried African bureaucrat is sympathetically portrayed as the behind-the-scenes master of the world government's foreign policy, while several other (presumably white) officials are portrayed variously as misguided, foolish, or well-meaning but parochial and prejudiced. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some of the alien species in Heinlein's fiction can be interpreted as allegorical representations of human [[ethnic group]]s. ''Double Star,'' ''Red Planet,'' and ''Stranger in a Strange Land'' all address tolerance and understanding between humans and Martians. Several of his works, such as "Jerry Was a Man," ''The Star Beast,'' and ''Red Planet,'' portray nonhumans who are incorrectly judged as being less than human. | ||
===Individualism and self-determination=== | ===Individualism and self-determination=== | ||
| − | Many of Heinlein's novels are stories of revolts against political oppression | + | Many of Heinlein's novels are stories of revolts against political oppression. |
| − | * Residents of a lunar penal colony, aided by a self-aware computer, rebel against the Warden and Lunar Authority (and eventually Earth) in '' | + | * Residents of a lunar penal colony, aided by a self-aware computer, rebel against the Warden and Lunar Authority (and eventually Earth) in ''The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress.'' |
| − | * Colonists rebel against Earth in '' | + | * Colonists rebel against Earth in ''Between Planets'' and ''Red Planet,'' and in the back story to ''Podkayne of Mars.'' |
| − | * Secularists overthrow a religious dictatorship in " | + | * Secularists overthrow a religious dictatorship in "If This Goes On—." |
| − | * A group of soldiers take on the mantle of power after the governments of the world break down as part of the back story in '' | + | * A group of soldiers take on the mantle of power after the governments of the world break down as part of the back story in ''Starship Troopers.'' |
| − | + | Heinlein's view is more libertarian than anarchist. Some authority figures are portrayed sympathetically. In ''Glory Road,'' a [[monarch]] is depicted positively, and in ''The Star Beast,'' a publicity-shy bureaucrat is sympathetically portrayed as the behind-the-scenes controller of the planetary government's foreign relations while his boss, a career politician, is portrayed as a fool. The government is not always the enemy. Novels such as ''Stranger in a Strange Land'' and ''Friday'' portray rebellions against oppression by society rather than by government. The common thread, then, is the struggle for [[self-determination]] of individuals, rather than of nations. | |
| − | + | However, duty to one's society or nation is an equally important theme. Many of Heinlein's stories revolve around the protagonist's duty (which may be to a nation or to a stray kitten), and a common theme is the character's free choice whether or not to make a self-sacrificing decision. A free society is worthy of such duty, while an oppressive one demands true individuals to rebel. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Sexual liberation=== | ===Sexual liberation=== | ||
| − | For Heinlein, personal liberation included [[sexual liberation]], and [[free love]] was a major subject of his writing starting from the 1939 '' | + | For Heinlein, personal liberation included [[sexual liberation]], and [[free love]] was a major subject of his writing starting from the 1939 ''For Us, The Living.'' ''Beyond This Horizon'' (1942) cleverly subverts traditional [[gender role]]s in a scene in which the protagonist demonstrates his archaic [[gunpowder]] gun for his friend and discusses how useful it would be in [[duel]]ing—after which the discussion turns to the shade of his nail polish. "All You Zombies" (1959) is the story of a person who undergoes a [[sex change]] operation, goes back in time, has sex with herself, and gives birth to herself. |
| − | Sexual freedom and the elimination of sexual jealousy are a major theme of '' | + | Sexual freedom and the elimination of sexual jealousy are a major theme of ''Stranger in a Strange Land'' (1961), in which the straitlaced nurse, Jill, acts as a dramatic foil for the less parochial characters, Jubal Harshaw and Mike. Over the course of the story, Jill learns to embrace her innate tendency toward exhibitionism, and to be more accepting of other people's sexuality (e.g., Duke's fondness for [[pornography]]). ''Stranger's'' treatment of [[homosexuality]] is ambiguous. In ''The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress,'' homosexuality is ill-regarded, but accepted as necessary, in an overwhelmingly male society. In contrast, homosexuality is regarded with approval—even gusto—in books such as 1970s ''I Will Fear No Evil,'' which posits the social recognition of six innate [[gender]]s, consisting of all possible combinations of male and female, with straight, gay, and [[bisexuality|bisexual]]. In ''The Number of the Beast,'' a male character discusses unsuccessful homosexual experimentation as a teenager. |
| − | In later books, Heinlein dealt with [[incest]] and the sexual nature of children | + | In later books, Heinlein dealt with [[incest]] and the sexual nature of children. In some of Heinlein's books, such as ''To Sail Beyond the Sunset,'' sexual urges between daughters and fathers are exemplified and briefly discussed on several occasions. Later in the same book, the protagonist/narrator (Maureen Johnson) discusses the risks (public humiliation, unhealthy children, etc.) associated with an incestuous sexual relationship between her two teenage children. While she is opposed to it for practical reasons, she neither condemns nor condones the relationship on any philosophical or moral grounds. The protagonist of ''The Cat Who Walks Through Walls'' recounts a homosexual experience with a [[Boy Scouts]] leader, which he didn't find unpleasant. In Heinlein's treatment of the possibility of sex between adults and adolescents, he treats the sexual attractions as taking place only between [[Friedrich Nietzsche|Nietzsche]]an [[Übermensch|supermen]], who are so enlightened that they can avoid all the ethical and emotional pitfalls. |
| − | + | ===Philosophy=== | |
| + | In ''To Sail Beyond the Sunset,'' Heinlein has the main character, Maureen, state that the purpose of [[metaphysics]] is to ask questions: Why are we here? Where are we going after we die? (and so on), and that "you are not allowed to answer the questions." Asking the questions is the point for metaphysics, but answering them is not, because once you answer them, you cross the line into [[religion]]. Maureen does not state a reason for this; she simply remarks that such questions are "beautiful" but lack answers. | ||
| − | + | Heinlein's anti-religious bias reflected his commitment to the worldview of science, based on [[deductive reasoning]], which is strictly [[Tautology (logic)|tautological]]. Because [[induction (philosophy)|inductive reasoning]] is always subject to doubt, the only source of reliable "answers" to such questions is direct experience—which one does not have. Lazarus Long makes a related remark in ''Time Enough For Love.'' In order for people to answer the "big questions" about the universe, Lazarus states at one point, it would be necessary to stand ''outside'' the universe. | |
| − | + | During the 1930s and 1940s, Heinlein was deeply interested in [[Alfred Korzybski]]'s [[General Semantics]] and attended a number of seminars on the subject. His views on [[epistemology]] seem to have flowed from that interest, and his fictional characters continue to express Korzybskian views to the very end of his writing career. Many of his stories, such as "Gulf," "If This Goes On," and ''Stranger in a Strange Land,'' depend strongly on the premise, extrapolated from the [[Sapir-Whorf hypothesis]], that by using a correctly [[constructed language|designed language]], one can liberate oneself mentally, or even become a [[superman]]. He was also strongly affected by the religious philosopher [[P. D. Ouspensky]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Sigmund Freud|Freudianism]] and [[psychoanalysis]] were at the height of their influence during the peak of Heinlein's career, and stories such as ''Time for the Stars'' indulged in psychoanalysis, despite some skepticism. He was strongly committed to [[cultural relativism]], and the sociologist Margaret Mader in his novel ''Citizen of the Galaxy'' is clearly a reference to [[Margaret Mead]]. In the [[World War II]] era, cultural relativism was the only intellectual framework that offered a clearly reasoned alternative to [[racism]], which Heinlein was ahead of his time in opposing. Many of these sociological and psychological theories have been criticized, debunked, or heavily modified in the last fifty years, and Heinlein's use of them may now appear credulous and dated to many readers. The critic Patterson says "Korzybski is now widely regarded as a crank,"<ref>Patterson and Thornton, 2001, p. 120</ref> although others disagree. | |
===Influence=== | ===Influence=== | ||
| − | Heinlein is usually identified, along with [[Isaac Asimov]] and [[Arthur C. Clarke]], as one of the three masters of [[science fiction]] to arise in the so-called Golden age of science fiction, associated with | + | Heinlein is usually identified, along with [[Isaac Asimov]] and [[Arthur C. Clarke]], as one of the three masters of [[science fiction]] to arise in the so-called Golden age of science fiction, associated with John W. Campbell and his magazine ''Astounding.'' However, in the 1950s, he was a leader in bringing science fiction out of the low-paying and less prestigious [[pulp magazine|pulp]] ghetto. Most of his works, including short stories, have been continuously in print in many languages since their initial appearance and are still available as new paperbacks years after his death. |
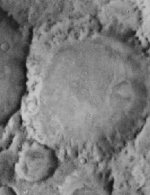
[[Image:heinlein-crater.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Heinlein crater on Mars.]] | [[Image:heinlein-crater.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Heinlein crater on Mars.]] | ||
| − | He | + | He helped to initiate the trend toward [[social science fiction]], which went along with a general maturing of the genre away from [[space opera]], to a more literary approach, touching on such adult issues as politics and [[human sexuality]]. In reaction to this trend, [[hard science fiction]] began to be distinguished as a separate subgenre, but paradoxically Heinlein is also considered a seminal figure in hard science fiction, due to his extensive knowledge of engineering, and the careful scientific research exhibited by his stories. Heinlein himself stated—with obvious pride—that in the days before pocket calculators, he once worked for several days on a mathematical equation describing an Earth-Mars rocket orbit, which was then subsumed in a single sentence of one of his short stories. |
| − | Heinlein has had a massive influence on other science fiction writers. In a 1953 poll of leading science fiction authors, he was cited more frequently as an influence than any other modern writer.<ref>Panshin, p. 3, describing de Camp's Science Fiction Handbook</ref> | + | Heinlein has had a massive influence on other science fiction writers. In a 1953 poll of leading science fiction authors, he was cited more frequently as an influence than any other modern writer.<ref>Panshin, p. 3, describing de Camp's Science Fiction Handbook</ref> In 1974, he won the first Grand Master Award given by the Science Fiction Writers of America for lifetime achievement. Critic James Gifford writes that "Although many other writers have exceeded Heinlein's output, few can claim to match his broad and seminal influence. Scores of science fiction writers from the prewar Golden Age through the present day loudly and enthusiastically credit Heinlein for blazing the trails of their own careers, and shaping their styles and stories."<ref>''Robert A. Heinlein: A Reader's Companion,'' p. xiii.</ref> |
| − | Outside the science fiction community, several words coined or adopted by Heinlein have passed into common English usage: [[Wiktionary:waldo| | + | Outside the science fiction community, several words coined or adopted by Heinlein have passed into common English usage: [[Wiktionary:waldo|Waldo]], [[TANSTAAFL]], [[moonbat]],<ref>William Safire, "On Language," (New York Times Magazine) September 3, 2006.</ref> and [[grok]]. He was influential in making [[space exploration]] seem to the public more like a practical possibility. His stories in publications such as ''[[The Saturday Evening Post]]'' took a matter-of-fact approach to their outer-space setting, rather than the "gee whiz" tone that had previously been common. The documentary-like film ''Destination Moon'' advocated a [[Space Race]] with the [[Soviet Union]] almost a decade before such an idea became commonplace, and was promoted by an unprecedented publicity campaign in print publications. Many of the astronauts and others working in the U.S. space program grew up on a diet of the Heinlein [[young adult literature|juveniles]], which led to the naming of a crater on Mars after him, and a tribute interspersed by the Apollo 15 astronauts into their radio conversations while on the moon.<ref>NASA, [http://www.hq.nasa.gov/alsj/a15/a15.clsout3.html#1675120 Apollo 15 Lunar Surface Journal: The Hammer and the Feather.] Retrieved July 24, 2007.</ref> Heinlein also was guest commentator for [[Walter Cronkite]] during [[Neil Armstrong]]'s [[Apollo 11]] moon landing. |
| − | There is an active campaign to persuade the | + | There is an active campaign to persuade the Secretary of the Navy to name the new Zumwalt class destroyer DDG-1001 the USS ''Robert A. Heinlein'' in honor of his centennial. |
==Bibliography== | ==Bibliography== | ||
| − | Heinlein published 32 novels, 59 short stories and 16 collections during his life. | + | Heinlein published 32 novels, 59 short stories, and 16 collections during his life. Four films, two TV series, several episodes of a radio series, and a board game derived more or less directly from his work. He wrote a screenplay for one of the films. Heinlein edited an anthology of other writers' SF short stories. |
=== Novels === | === Novels === | ||
| Line 185: | Line 179: | ||
==== Early Heinlein novels ==== | ==== Early Heinlein novels ==== | ||
| − | *''For Us, The Living: A Comedy of Customs'' | + | *''For Us, The Living: A Comedy of Customs,'' 1939, published posthumously 2003 |
| − | *''Beyond This Horizon'' | + | *''Beyond This Horizon,'' 1942 |
| − | *''Rocket Ship Galileo'' | + | *''Rocket Ship Galileo,'' 1947 * |
| − | *''Space Cadet'' | + | *''Space Cadet,'' 1948 * |
| − | *''Red Planet'' | + | *''Red Planet,'' 1949 * |
| − | *''Sixth Column'' | + | *''Sixth Column,'' serialized 1941, book form 1949 (also published as ''The Day After Tomorrow)'' |
| − | *''Farmer in the Sky'' | + | *''Farmer in the Sky,'' 1950 (Retro Hugo Award, 1951) * |
| − | *''Between Planets'' | + | *''Between Planets,'' 1951 * |
| − | *''The Puppet Masters'' | + | *''The Puppet Masters,'' 1951, re-published posthumously with excisions restored, 1990 |
| − | *''The Rolling Stones'' aka ''Space Family Stone'' | + | *''The Rolling Stones,'' aka ''Space Family Stone,'' 1952 * |
| − | *''Starman Jones'' | + | *''Starman Jones,'' 1953 * |
| − | *''The Star Beast'' | + | *''The Star Beast,'' 1954 * |
| − | *''Tunnel in the Sky'' | + | *''Tunnel in the Sky,'' 1955 * |
| − | *''Variable Star'' | + | *''Variable Star,'' posthumously with Spider Robinson (1955, 2006) |
| − | *''Double Star'' | + | *''Double Star,'' 1956 (Hugo Award, 1956) |
| − | *''Time for the Stars'' | + | *''Time for the Stars,'' 1956 * |
| − | *''Citizen of the Galaxy'' | + | *''Citizen of the Galaxy,'' 1957 * |
| − | *''The Door into Summer'' | + | *''The Door into Summer,'' 1957 |
| − | *''Have Space Suit—Will Travel'' | + | *''Have Space Suit—Will Travel,'' 1958 * |
| − | *''Methuselah's Children'' | + | *''Methuselah's Children,'' 1958 (originally a serialized short story in 1941) |
| − | *''Starship Troopers'' | + | *''Starship Troopers,'' 1959 (Hugo Award, 1960) * |
==== Mature Heinlein novels ==== | ==== Mature Heinlein novels ==== | ||
| − | *''Stranger in a Strange Land'' | + | *''Stranger in a Strange Land,'' 1961 (Hugo Award, 1962), republished at the original greater length in 1991 |
| − | *''Podkayne of Mars'' | + | *''Podkayne of Mars,'' 1963 * |
| − | *''Glory Road'' | + | *''Glory Road,'' 1963 |
| − | *''Farnham's Freehold'' | + | *''Farnham's Freehold,'' 1965 |
| − | *''The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress'' | + | *''The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress,'' 1966 (Hugo Award, 1967) |
| − | *''I Will Fear No Evil'' | + | *''I Will Fear No Evil,'' 1970 |
| − | *''Time Enough for Love'' | + | *''Time Enough for Love,'' 1973 |
==== Late Heinlein novels ==== | ==== Late Heinlein novels ==== | ||
| − | *''The Number of the Beast'' | + | *''The Number of the Beast,'' 1980 |
| − | *''Friday'' | + | *''Friday,'' 1982 |
| − | *''Job: A Comedy of Justice'' | + | *''Job: A Comedy of Justice,'' 1984 |
| − | *''The Cat Who Walks Through Walls'' | + | *''The Cat Who Walks Through Walls,'' 1985 |
| − | *''To Sail Beyond the Sunset'' | + | *''To Sail Beyond the Sunset,'' 1987 |
=== Short fiction === | === Short fiction === | ||
| Line 229: | Line 223: | ||
==== "Future History" short fiction ==== | ==== "Future History" short fiction ==== | ||
| − | * "Life-Line" | + | * "Life-Line," 1939 |
| − | * "Misfit" | + | * "Misfit," 1939 |
| − | * "The Roads Must Roll" | + | * "The Roads Must Roll," 1940 |
| − | * "Requiem" | + | * "Requiem," 1940 |
| − | * | + | * "If This Goes On—," 1940 |
| − | * "Coventry" | + | * "Coventry," 1940 |
| − | * "Blowups Happen" | + | * "Blowups Happen," 1940 |
| − | * "Universe" | + | * "Universe," 1941 |
| − | * | + | * "—We Also Walk Dogs," 1941 |
| − | * "Common Sense" | + | * "Common Sense," 1941 |
| − | * "Methuselah's Children" | + | * "Methuselah's Children," 1941 (lengthened and published as a novel, 1958) |
| − | * "Logic of Empire" | + | * "Logic of Empire," 1941 |
| − | * "Space Jockey" | + | * "Space Jockey," 1947 |
| − | * | + | * "It's Great to Be Back!" 1947 |
| − | * "The Green Hills of Earth" | + | * "The Green Hills of Earth," 1947 |
| − | * "Ordeal in Space" | + | * "Ordeal in Space," 1948 |
| − | * "The Long Watch" | + | * "The Long Watch," 1948 |
| − | * "Gentlemen, Be Seated!" | + | * "Gentlemen, Be Seated!" 1948 |
| − | * "The Black Pits of Luna" | + | * "The Black Pits of Luna," 1948 |
| − | * "Delilah and the Space Rigger" | + | * "Delilah and the Space Rigger," 1949 |
| − | * "The Man Who Sold the Moon" | + | * "The Man Who Sold the Moon," 1951, Retro Hugo Award |
| − | * "The Menace From Earth" | + | * "The Menace From Earth," 1957 |
| − | * "Searchlight" | + | * "Searchlight," 1962 |
==== Other short speculative fiction ==== | ==== Other short speculative fiction ==== | ||
| − | * "Magic, Inc." | + | * "Magic, Inc.," originally magazine title "The Devil Makes the Law" (changed by the editor because the lead story of the preceding issue had "magic" in the title), 1940 |
| − | * "Solution Unsatisfactory" | + | * "Solution Unsatisfactory," as Anson MacDonald, 1940 |
| − | * "Let There Be Light" | + | * "Let There Be Light," as Lyle Monroe, 1940 |
| − | * "Successful Operation" ("Heil!" | + | * "Successful Operation" ("Heil!" as Lyle Monroe), 1940 |
| − | * "They" | + | * "They," 1941 |
| − | * | + | * "—And He Built a Crooked House—" 1941 |
| − | * "By His Bootstraps" | + | * "By His Bootstraps," as Anson MacDonald, 1941 |
| − | * "Lost Legacy" ("Lost Legion" | + | * "Lost Legacy" ("Lost Legion," as Lyle Monroe), 1941 |
| − | * "Elsewhen" | + | * "Elsewhen," ("Elsewhere," as Caleb Saunders), 1941 |
| − | * "Beyond Doubt" | + | * "Beyond Doubt," as Lyle Monroe, with Elma Wentz, 1941 |
| − | * "The Unpleasant Profession of Jonathan Hoag" | + | * "The Unpleasant Profession of Jonathan Hoag," 1942 |
| − | * "Waldo" | + | * "Waldo," as Anson MacDonald, 1942 |
| − | * ""My Object All Sublime"" | + | * ""My Object All Sublime"," as Lyle Monroe, 1942 |
| − | * "Goldfish Bowl" | + | * "Goldfish Bowl," as Anson MacDonald, 1942 |
| − | * "Pied Piper" | + | * "Pied Piper," as Lyle Monroe, 1942 |
| − | * "Free Men" | + | * "Free Men," written 1946, published 1966 |
| − | * "Jerry Was a Man" | + | * "Jerry Was a Man," 1947 |
| − | * "Columbus Was a Dope" | + | * "Columbus Was a Dope," as Lyle Monroe, 1947 |
| − | * "On the Slopes of Vesuvius" | + | * "On the Slopes of Vesuvius," 1947 |
| − | * "Our Fair City" | + | * "Our Fair City," 1948 |
| − | * "Gulf" | + | * "Gulf," 1949 |
| − | * "Nothing Ever Happens on the Moon" | + | * "Nothing Ever Happens on the Moon," 1949 |
| − | * "Destination Moon" | + | * "Destination Moon," 1950. |
| − | * "The Year of the Jackpot" | + | * "The Year of the Jackpot," 1952 |
| − | * "Project Nightmare" | + | * "Project Nightmare," 1953 |
| − | * "Sky Lift" | + | * "Sky Lift," 1953 |
| − | * "Tenderfoot in Space" | + | * "Tenderfoot in Space," 1956, serialized 1958 |
* "The Man Who Traveled in Elephants" (also as "The Elephant Circuit"), 1957 | * "The Man Who Traveled in Elephants" (also as "The Elephant Circuit"), 1957 | ||
| − | * | + | * "—All You Zombies—" 1959 |
==== Other short fiction ==== | ==== Other short fiction ==== | ||
| − | * "A Bathroom of Her Own" | + | * "A Bathroom of Her Own," 1946 |
| − | * "Dance Session" | + | * "Dance Session," love poem, 1946 |
| − | * "The Witch's Daughters" | + | * "The Witch's Daughters," poem, 1946 |
| − | * "Water is for Washing" | + | * "Water is for Washing," 1947 |
| − | * "They Do It with Mirrors (Heinlein)" | + | * "They Do It with Mirrors (Heinlein)," as Simon York, 1947 |
| − | * "Poor Daddy" | + | * "Poor Daddy," 1949 |
| − | * "Cliff and the Calories" | + | * "Cliff and the Calories," 1950 |
| − | * "The Bulletin Board" | + | * "The Bulletin Board," 1951 |
==== Collections ==== | ==== Collections ==== | ||
| − | * ''The Man Who Sold the Moon'' | + | * ''The Man Who Sold the Moon,'' 1950 |
| − | * ''Waldo & Magic, Inc.'' | + | * ''Waldo & Magic, Inc.,'' 1950 |
| − | * ''The Green Hills of Earth'' | + | * ''The Green Hills of Earth,'' 1951 |
| − | * ''Orphans of the Sky'' | + | * ''Orphans of the Sky,'' 1951: ''Universe'' and ''Commonsense'' |
| − | * ''Assignment in Eternity'' | + | * ''Assignment in Eternity,'' 1953 |
| − | * ''Revolt in 2100'' | + | * ''Revolt in 2100,'' 1953 |
| − | * ''The Robert Heinlein Omnibus'' | + | * ''The Robert Heinlein Omnibus,'' 1958 |
| − | * ''The Menace From Earth'' | + | * ''The Menace From Earth,'' 1959 |
* ''The Unpleasant Profession of Jonathan Hoag'' (also as ''6 X H''), 1959 | * ''The Unpleasant Profession of Jonathan Hoag'' (also as ''6 X H''), 1959 | ||
| − | * ''Three by Heinlein'' | + | * ''Three by Heinlein,'' 1965 |
| − | * ''A Robert Heinlein Omnibus'' | + | * ''A Robert Heinlein Omnibus,'' 1966 |
| − | * ''The Worlds of Robert A. Heinlein'' | + | * ''The Worlds of Robert A. Heinlein,'' 1966 |
| − | * ''The Past Through Tomorrow'' | + | * ''The Past Through Tomorrow,'' 1967 |
| − | * ''The Best of Robert A. Heinlein'' | + | * ''The Best of Robert A. Heinlein,'' 1973 |
| − | * ''Expanded Universe'' | + | * ''Expanded Universe,'' 1980 |
| − | * ''A Heinlein Trio'' | + | * ''A Heinlein Trio,'' (Doubleday), 1980: ''The Puppet Masters,'' ''Double Star,'' and ''The Door Into Summer'' |
| − | * ''The Fantasies of Robert A. Heinlein'' | + | * ''The Fantasies of Robert A. Heinlein,'' 1999 |
| − | * ''Infinite Possibilities'' | + | * ''Infinite Possibilities,'' 2003: ''Tunnel in the Sky,'' ''Time for the Stars,'' and ''Citizen of the Galaxy'' |
| − | * ''To the Stars'' | + | * ''To the Stars,'' 2004: ''Between Planets,'' ''The Rolling Stones,'' ''Starman Jones,'' and ''The Star Beast'' |
| − | * ''Off the Main Sequence'' | + | * ''Off the Main Sequence,'' 2005: short stories including three never before collected. |
| − | * ''Four Frontiers'' | + | * ''Four Frontiers,'' 2005: ''Rocket Ship Galileo,'' ''Space Cadet,'' ''Red Planet,'' and ''Farmer in the Sky'' |
| − | * ''Outward Bound'' | + | * ''Outward Bound,'' 2006: ''Have Space Suit—Will Travel,'' ''Starship Troopers,'' ''Podkayne of Mars'' |
=== Nonfiction === | === Nonfiction === | ||
| − | * ''No Bands Playing, No Flags Flying'' | + | * ''No Bands Playing, No Flags Flying,'' written 1947, published 1973 |
| − | * Two articles for ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' on Paul Dirac and [[antimatter]], and on [[blood]] chemistry. | + | * Two articles for ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' on Paul Dirac and [[antimatter]], and on [[blood]] chemistry. |
| − | * ''Grumbles from the Grave'' | + | * ''Grumbles from the Grave,'' 1989 (posthumously) |
| − | * ''Take Back Your Government: A Practical Handbook for the Private Citizen'' | + | * ''Take Back Your Government: A Practical Handbook for the Private Citizen,'' 1992 |
| − | * ''Tramp Royale'' | + | * ''Tramp Royale,'' 1992 |
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| − | < | + | <references/> |
| − | + | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
===Critical=== | ===Critical=== | ||
| − | * H. Bruce | + | * Blish, James. 1970. ''More Issues at Hand.'' Chicago: Advent. ISBN 9780911682182 |
| − | + | * Franklin, H. Bruce. 1980. ''Robert A. Heinlein: America as Science Fiction.'' Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-502746-9 | |
| − | + | * Gifford, James. 2000. ''Robert A. Heinlein: A Reader's Companion.'' Sacramento: Nitrosyncretic Press. ISBN 0-9679874-1-5 | |
| − | + | * Panshin, Alexei. 1968. ''Heinlein in Dimension.'' Advent. ISBN 0-911682-12-0 | |
| − | + | * Patterson, William H., Jr. and Andrew Thornton. 2001. ''The Martian Named Smith: Critical Perspectives on Robert A. Heinlein's Stranger in a Strange Land.'' Sacramento: Nitrosyncretic Press. ISBN 0-9679874-2-3 | |
| − | * William H. | + | * Powell, Jim. ''The Triumph of Liberty'' New York: Free Press, 2000. |
| − | * Powell, Jim. | + | * Shippey, Tom. 2000. "Starship Troopers, Galactic Heroes, Mercenary Princes: the Military and its Discontents in Science Fiction," in Alan Sandison and Robert Dingley, eds., ''Histories of the Future: Studies in Fact, Fantasy and Science Fiction''. New York: Palgrave. ISBN 0-312-23604-2 |
| − | * Tom | ||
| − | |||
=== Biographical === | === Biographical === | ||
| − | + | * Heinlein, Robert A. 1980. ''Expanded Universe.'' New York: Ace. ISBN 0-441-21888-1 | |
| − | * Robert A. | + | * Heinlein, Robert A. 1989. ''Grumbles From the Grave.'' New York: Del Rey. |
| − | + | * Heinlein, Robert A. 2004. ''For Us, the Living.'' New York: Scribner. ISBN 0-7432-5998-X | |
| − | * | + | * Patterson, William H. Jr. Robert Heinlein - A biographical sketch ''The Heinlein Journal'' 5(1999): 7-36. |
| − | + | * Vicary, Elizabeth Zoe. 2000. American National Biography Online article, "Heinlein, Robert Anson." | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| − | + | All links retrieved December 14, 2022. | |
| − | + | * [http://www.heinleinsociety.org/ The Heinlein Society] | |
| − | + | * [http://www.bsfs.org/bsfsheinlein.htm Robert A. Heinlein Award] | |
| − | * [http://www.heinleinsociety.org/ The Heinlein Society] | + | * [http://www.heinleinprize.com/ Robert & Virginia Heinlein Prize] |
| − | * [http://www. | + | * [http://www.nitrosyncretic.com/rah/pm652-art-hi.html 1952 Heinlein's Colorado house.] |
| − | * [http://www.heinleinprize.com/ Robert & Virginia Heinlein Prize] | + | * [http://www.imdb.com/name/nm0374423/ Robert Heinlein at the IMDB] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * [http://www.nitrosyncretic.com/rah/pm652-art-hi.html 1952 | ||
| − | * [http://www.imdb.com/name/nm0374423/ Robert Heinlein at the IMDB | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[ | + | [[Category:Art, music, literature, sports and leisure]] |
| − | {{credits|113971247}} | + | [[category:Biography]] |
| + | {{credits|Robert_A._Heinlein|113971247}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:10, 16 April 2023
| Science fiction writer | |
| Books · Authors · Films · Television | |
| Robert A. Heinlein | |
 Heinlein signing autographs at the 1976 Worldcon | |
| Pseudonym(s): | Anson McDonald, Lyle Monroe, John Riverside, Caleb Saunders, Simon York |
|---|---|
| Born: | July 7, 1907 Butler, Missouri |
| Died: | May 8, 1988 Carmel, California |
| Occupation(s): | Novelist, short story author, essayist |
| Genre(s): | Science fiction, Fantasy |
| Literary movement: | Science Fiction, Fantasy |
| Debut work(s): | Life-Line |
| Magnum opus: | Stranger in a Strange Land |
| Influences: | H. G. Wells, James Branch Cabell |
| Influenced: | Allen Steele, Spider Robinson, George R. R. Martin, Larry Niven, Jerry Pournelle, John Varley |
Robert Anson Heinlein (July 7, 1907 – May 8, 1988) was one of the most popular, influential, and controversial authors of "hard" science fiction. He set a high standard for science and engineering plausibility that few have equaled, and helped to raise the genre's standards of literary quality. He was the first writer to break into mainstream general magazines such as The Saturday Evening Post, in the late 1940s with unvarnished science fiction. He was among the first authors of bestselling novel-length science fiction in the modern mass-market era. For many years Heinlein, Isaac Asimov, and Arthur C. Clarke were known as the "Big Three" of science fiction.[1]
The major themes of his work were social: Radical individualism, libertarianism, religion, the relationship between physical and emotional love, and speculation about unorthodox family relationships. His iconoclastic approach to these themes led to wildly divergent perceptions of his works. For example, his 1959 novel Starship Troopers was widely viewed as glorifying militarism. By contrast, his 1961 novel Stranger in a Strange Land put him in the unexpected role of pied piper to the sexual revolution and the counterculture, all of which demonstrate his libertarian tendencies.
Heinlein won four Hugo Awards for his novels. In addition, fifty years after publication, three of his works were awarded "Retro Hugos"—awards given retrospectively for years in which no Hugos had been awarded. He also won the first Grand Master Award given by the Science Fiction Writers of America for lifetime achievement.
In his fiction, Heinlein coined words that have become part of the English language, including "grok," "TANSTAAFL," and "waldo."
Life
Heinlein (pronounced Hine-line) was born on July 7, 1907, to Rex Ivar and Bam Lyle Heinlein, in Butler, Missouri. His childhood was spent in Kansas City, Missouri.[2] The outlook and values of this time and place would influence his later works; however, he would break with many of its values and social mores, both in his writing and in his personal life. He graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy in 1929, and served as an officer in the United States Navy. He married soon after graduation, but this marriage lasted only about a year.[3] He served on the USS Lexington in 1931. He married his second wife, Leslyn Macdonald, in 1932. Leslyn was a political radical, and Isaac Asimov recalled Robert during those years as being, like her, "a flaming liberal."[4] Heinlein served aboard USS Roper in 1933–1934, reaching the rank of naval Lieutenant. In 1934, Heinlein was discharged from the Navy due to pulmonary tuberculosis. During his long hospitalization he developed the idea of the waterbed, and his detailed descriptions of it in three of his books later prevented others from patenting it. The military was the second great influence on Heinlein; throughout his life, he strongly believed in loyalty, leadership, and other ideals associated with the military.
After his discharge, Heinlein attended a few weeks of graduate classes in mathematics and physics at the University of California, Los Angeles, but quit either because of his health or from a desire to enter politics.[5] He supported himself at a series of jobs, including real estate and silver mining. Heinlein was active in Upton Sinclair's socialist EPIC (End Poverty In California) movement in early 1930s. When Sinclair gained the Democratic nomination for governor of California in 1934, Heinlein worked actively in the unsuccessful campaign.
Heinlein himself ran for the California State Assembly in 1938, but was unsuccessful. Heinlein was running as a left-wing Democrat in a conservative district, and never made it past the Democratic primary because of trickery by his Republican opponent.[6] Also, an unfortunate juxtaposition of events had Konrad Heinlein making headlines in the Sudetenlands. In later years, Heinlein kept his socialist past secret, writing about his political experiences coyly, and usually under the veil of fictionalization. In 1954, he wrote: "…many Americans … were asserting loudly that McCarthy had created a 'reign of terror.' Are you terrified? I am not, and I have in my background much political activity well to the left of Senator McCarthy's position."[7]

While not destitute after the campaign—he had a small disability pension from the Navy—Heinlein turned to writing in order to pay off his mortgage, and in 1939 his first published story, "Life-Line," was printed in Astounding magazine. He was quickly acknowledged as a leader of the new movement toward "social" science fiction. During World War II he did aeronautical engineering for the Navy, recruiting Isaac Asimov and L. Sprague de Camp to work at the Philadelphia Naval Yard.
As the war wound down in 1945, Heinlein began re-evaluating his career. The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, along with the outbreak of the Cold War, galvanized him to write nonfiction on political topics; in addition, he wanted to break into better-paying markets. He published four influential stories for The Saturday Evening Post, leading off, in February 1947, with "The Green Hills of Earth," which made him the first science fiction writer to break out of the "pulp ghetto." In 1950, Destination Moon—the documentary-like film for which he had written the story and scenario, co-written the script, and invented many of the effects—won an Academy Award for special effects. Most importantly, he embarked on a series of juvenile novels for Charles Scribner's Sons that was to last through the 1950s.
Heinlein divorced his second wife in 1947, and the following year married Virginia "Ginny" Gerstenfeld, whom he would remain married to until his death forty years later. Ginny undoubtedly served as a model for many of his intelligent, fiercely independent female characters. In 1953–1954, the Heinleins took a trip around the world, which Heinlein described in "Tramp Royale," and which also provided background material for science fiction novels, such as Podkayne of Mars, that were set aboard spaceships. Asimov believed that Heinlein made a drastic swing to the right politically at the same time he married Ginny. The couple formed the Patrick Henry League in 1958 and worked on the 1964 Barry Goldwater campaign, and Tramp Royale contains two lengthy apologias for the McCarthy hearings. However, this perception of a drastic shift may result from a tendency to make the mistake of trying to place libertarianism on the traditional right-left spectrum of American politics, as well as from Heinlein's iconoclasm and unwillingness to let himself be pigeonholed into any ideology (including libertarianism).
The evidence of Ginny's influence is clearer in matters literary and scientific. She acted as the first reader of his manuscripts, and was reputed to be a better engineer than Heinlein himself.[8]
The Heinlein juveniles, novels for young adults, may turn out to be the most important work he ever did, building an audience of scientifically and socially aware adults. He had used topical materials throughout his series, but in 1959 his Starship Troopers was regarded by the Scribner's editorial staff as too controversial for their prestige line and was rejected summarily. Heinlein felt himself released from the constraints of writing for children and began to write "my own stuff, my own way," and came out with a series of challenging books that redrew the boundaries of science fiction, including his best-known works, Stranger in a Strange Land (1961) and The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress (1966).
Beginning in 1970, however, Heinlein had a series of health crises, punctuated by strenuous work. The decade began with a life-threatening attack of peritonitis, recovery from which required more than two years, but as soon as he was well enough to write, he began work on Time Enough for Love (1973), which introduced many of the themes found in his later fiction. In the mid-1970s he wrote two articles for the Britannica Compton Yearbook. The two articles discussed Paul Dirac and antimatter, and blood chemistry. A version of the former, titled "Paul Dirac, Antimatter, and You," was published in the anthology Expanded Universe, and demonstrates both Heinlein's skill as a popularizer and his lack of depth in physics; an afterword gives a normalization equation and presents it, incorrectly, as being the Dirac equation.
He and Ginny crisscrossed the country helping to reorganize blood donation in the U.S., and he was guest of honor at a World Science Fiction Convention for the third time at Kansas City, Missouri in 1976. While vacationing in Tahiti in early 1978, he suffered a transient ischemic attack. Over the next few months, he became more and more exhausted, and his health again began to decline. The problem was determined to be a blocked carotid artery, and he had one of the earliest carotid bypass operations to correct the blockage. Asked to appear before a Joint Committee of the U.S. House and Senate that year, he testified on his belief that spin-offs from space technology were benefiting the infirm and the elderly. His surgical treatment re-energized Heinlein, and he wrote five novels from 1980 until he died in his sleep from emphysema and congestive heart failure on May 8, 1988, as he was putting together the early notes for another World as Myth novel. Several of his works have been published posthumously.
Based on an outline and notes created by Heinlein in 1955, Spider Robinson wrote the novel Variable Star. Heinlein's posthumously published nonfiction includes a selection of letters edited by his wife, Virginia, his book on practical politics written in 1946, a travelogue of their first around-the-world tour in 1954. Podkayne of Mars and Red Planet, which were edited against his wishes in their original release, have been reissued in restored editions. Stranger In a Strange Land was originally published in a shorter form, but both the long and short versions are now simultaneously available in print.
Works
Early work, 1939–1960
The first novel that Heinlein wrote, For Us, The Living: A Comedy of Customs (1939), did not see print during his lifetime, but Robert James later tracked down the manuscript and it was published in 2003. Although a failure as a novel, (Biographer Bill Patterson, for example, refers to it as "a failed science fiction novel") serving as little more than a disguised lecture on Heinlein's social theories, it is intriguing as a window into the development of Heinlein's radical ideas about man as a social animal, including free love. The root of many themes found in his later stories can be found in this book.
It appears that Heinlein attempted to live in a manner consistent with these ideas, even in the 1930s, and had an open relationship in his marriage to his second wife, Leslyn. He was also a nudist; nudism and body taboos are frequently discussed in his work. At the height of the cold war, he built a bomb shelter under his house, like the one featured in Farnham's Freehold.
After For Us, The Living, Heinlein began selling (to magazines) first short stories, then novels, set in the future, complete with a timeline of significant political, cultural, and technological changes. A chart of the future history was published in the May 1941 issue of Astounding. Over time, Heinlein wrote many novels and short stories that deviated freely from the Future History on some points, while maintaining consistency in some other areas. The Future History was also eventually overtaken by actual events. These discrepancies were explained, after a fashion, in his later World as Myth stories.
Heinlein's first novel published as a book, Rocket Ship Galileo, was initially rejected because going to the moon was considered too far out, but he soon found a publisher, Scribner's, that began publishing a Heinlein juvenile once a year for the Christmas season.[9] Eight of these books were illustrated by Clifford Geary in a distinctive white-on-black scratchboard style.[10] Some representative novels of this type are Have Space Suit—Will Travel, Farmer in the Sky, and Starman Jones. Many of these were first published in serial form under other titles. For example, Farmer in the Sky was published as "Satellite Scout" in the Boy Scout magazine Boys' Life.
The importance Heinlein attached to privacy was made clear in his fiction (e.g., For Us, the Living), but also in several well known examples from his life. He had a falling out with Alexei Panshin, who wrote an important book analyzing Heinlein's fiction; Heinlein stopped cooperating with Panshin because he accused Panshin of "[attempting to] pry into his affairs and to violate his privacy." Heinlein wrote to Panshin's publisher threatening to sue, and stating, "You are warned that only the barest facts of my private life are public knowledge…."[11] In his 1961 speech at WorldCon, where he was guest of honor, he advocated building bomb shelters and caching away unregistered weapons,[12] and his own house in Colorado Springs included a bomb shelter. Heinlein was a nudist, and built a fence around his house in Santa Cruz to keep out the counterculture types who had learned of his ideas through Stranger in a Strange Land. In his later life, Heinlein studiously avoided revealing the story of his early involvement in left-wing politics, and made strenuous efforts to block publication of information he had revealed to prospective biographer Sam Moskowitz.
There has been speculation that Heinlein's intense obsession with his privacy was due at least in part to the apparent contradiction between his unconventional private life and his career as an author of books for children, but For Us, The Living also explicitly discusses the political importance Heinlein attached to privacy as a matter of principle.
The novels that he wrote for a young audience were a mixture of adolescent and adult themes. Many of the issues that he takes on in these books have to do with the kinds of problems that adolescents experience. His protagonists are usually very intelligent teenagers who have to make a way in the adult society they see around them. On the surface, they are simple tales of adventure, achievement, and dealing with stupid teachers and jealous peers.
However, Heinlein was a vocal proponent of the notion that juvenile readers were far more sophisticated and able to handle complex or difficult themes than most people realized. Thus even his juvenile stories often had a maturity to them that make them readable for adults. Red Planet, for example, portrays some very subversive themes, including a revolution in which young students are involved; his editor demanded substantial changes in this book's discussion of topics such as the use of weapons by adolescents and the confused sexuality of the Martian character. Heinlein was always aware of the editorial limitations put in place by the editors of his novels and stories, and while he observed those restrictions on the surface, was often successful in introducing ideas not often seen in other authors' juvenile SF.
In 1957, James Blish wrote that one reason for Heinlein's success "has been the high grade of machinery which goes, today as always, into his story-telling. Heinlein seems to have known from the beginning, as if instinctively, technical lessons about fiction which other writers must learn the hard way (or often enough, never learn). He does not always operate the machinery to the best advantage, but he always seems to be aware of it."[13]
Heinlein's last juvenile novel, and probably his most controversial work in general, was the 1959 Starship Troopers, which he wrote in response to the U.S.'s decision to unilaterally end nuclear testing.[14] The book's central political idea is that there should be no conscription, but that suffrage should belong only to those who have earned it through government or military service.
Mid-period work, 1961–1973
From about 1961 (Stranger in a Strange Land) to 1973 (Time Enough for Love), Heinlein wrote some of his most controversial novels. His work during this period explored his most important themes, such as individualism, libertarianism, and physical and emotional love. To some extent, the apparent discrepancy between these works and the more naive themes of his earlier novels can be attributed to his own perception, which was probably correct, that readers and publishers in the 1950s were not yet ready for some of his more radical ideas. He did not publish Stranger in a Strange Land until some time after it was written, and the themes of free love and radical individualism are prominently featured in his long-unpublished first novel, For Us, The Living: A Comedy of Customs.
The story that Stranger in a Strange Land was used as inspiration by Charles Manson appears to be an urban folk tale; although some of Manson's followers had read the book, Manson himself later said that he had not. It is true that other individuals formed a quasi-religious organization called the Church of All Worlds, after the religion founded by the primary characters in Stranger, but Heinlein had nothing to do with this, either, so far as is known.[15] The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress tells of a war of independence of Lunar colonies, with significant commentary regarding the threat posed by any government—including a republic—to individual freedom.
Although Heinlein had previously written a few short stories in the fantasy genre, during this period he wrote his first fantasy novel, Glory Road, and in Stranger in a Strange Land and I Will Fear No Evil, he began to mix hard science with fantasy, mysticism, and satire of organized religion. Critics William H. Patterson, Jr., and Andrew Thornton[16] believe that this is simply an expression of Heinlein's longstanding philosophical opposition to positivism. Heinlein stated that he was influenced by James Branch Cabell in taking this new literary direction. The next-to-last novel of this period, I Will Fear No Evil, is according to critic James Gifford "almost universally regarded as a literary failure," and he attributes its shortcomings to Heinlein's near-death from peritonitis.[17]
Later work, 1980–1987
After a seven-year hiatus brought on by poor health, Heinlein produced five new novels in the period from 1980 (The Number of the Beast) to 1987 (To Sail Beyond the Sunset). These books have a thread of common characters and time and place. They most explicitly communicated Heinlein's philosophies and beliefs, and many long, didactic passages of dialog and exposition deal with government, sex, and religion. These novels are controversial among his readers, and some critics have written about them very negatively.[18] Heinlein's four Hugo awards were all for books written before this period.
Some of these books, such as The Number of the Beast and The Cat Who Walks Through Walls, start out as tightly constructed adventure stories, but later transform into philosophical fantasies. It is a matter of opinion whether this demonstrates a lack of attention to craftsmanship or a conscious effort to expand the boundaries of science fiction into a kind of magical realism, continuing the process of literary exploration that he had begun with Stranger in a Strange Land. Most of the novels from this period are recognized by critics as forming an offshoot from the Future History series, and referred to by the term World as Myth.[19]
The tendency toward authorial self-referentialism begun in Stranger in a Strange Land and Time Enough For Love becomes even more evident in novels such as The Cat Who Walks Through Walls, whose first-person protagonist is a disabled military veteran who becomes a writer, and finds love with a female character who, like all of Heinlein's strong female characters, appears to be based closely on his wife Ginny. The self-parodying element of these books keeps them from being bogged down by taking themselves too seriously, but may also fail to evoke the desired effect in readers who are not familiar with Heinlein's earlier novels. Many readers are split on their reactions to Heinlein's wit, particularly in his dialogue—characters from a plethora of milieux tend to favor the same midwestern-American, post-Depression style and referents. Some find it charming and disarming. Others attack it as unsophisticated.
The 1984 novel Job: A Comedy of Justice is a sharp satire of fundamentalist Christianity.
Posthumous publications
Several Heinlein works have been published since his death, including the aforementioned For Us, The Living: A Comedy of Customs, as well as 1989's Grumbles from the Grave, a collection of letters between Heinlein and his editors and agent, 1992's Tramp Royale, a travelogue of a southern hemisphere tour the Heinleins took in the 1950s, Take Back Your Government, a how-to book about participatory democracy written in 1946, and a tribute volume called Requiem: Collected Works and Tributes to the Grand Master, containing some additional short works previously unpublished in book form. Off the Main Sequence, published in 2005, includes three short stories never before collected in any Heinlein book (Heinlein called them "stinkeroos").
Colleague, friend, and admirer[20] Spider Robinson wrote Variable Star, based on an outline and notes for a juvenile novel that Heinlein prepared in 1955. The novel was published as a collaboration, with Heinlein's name above Robinson's on the cover, in 2006.
Ideas, themes, and influence
Politics
Heinlein's writing may appear to have oscillated wildly across the political spectrum. His first novel, For Us, The Living, consists largely of speeches advocating the Social Credit system, and the early story "Misfit" deals with an organization which seems to be Franklin D. Roosevelt's Civilian Conservation Corps translated into outer space. While Stranger in a Strange Land was embraced by the hippie counterculture, and Glory Road can be read as an antiwar piece, some have deemed Starship Troopers militaristic, and To Sail Beyond the Sunset, published during the Reagan administration, was stridently right-wing.
There are, however, certain threads in Heinlein's political thought that remain constant. A strong current of libertarianism runs through his work, as expressed most clearly in The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress. His early juvenile novels often contain a surprisingly strong anti-authority message, as in his first published novel, Rocket Ship Galileo, which has a group of boys blasting off on a rocket ship in defiance of a court order. A similar defiance of a court order to take a moon trip takes place in the short story "Requiem." In The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress, the unjust Lunar Authority that controls the lunar colony is usually referred to simply as "Authority," which points to an obvious interpretation of the book as a parable for the evils of authority in general, rather than the evils of one particular authority.
Heinlein was opposed to any encroachment of religion into government; he pilloried organized religion in Job: A Comedy of Justice, and, with more subtlety and ambivalence, in Stranger in a Strange Land. His future history includes a period called the Interregnum, in which a backwoods revivalist becomes dictator of the United States. Revolt in 2100 depicts a revolutionary underground overthrowing a religious dictatorship in America. Positive descriptions of the military (Between Planets, The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress, Red Planet, Starship Troopers) tend to emphasize the individual actions of volunteers in the spirit of the Minutemen of colonial America. Conscription and the military as an extension of the government are portrayed in Time Enough for Love, Glory Road, and Starship Troopers as being poor substitutes for the volunteers who, ideally, should be defending a free society.
To those on the right, Heinlein's ardent anti-communism during the Cold War era might appear to contradict his earlier efforts in the socialist EPIC and Social Credit movements; however, it should be noted that both the Socialist Party and the Communist Party were very active during the 1930s, and the distinction between socialism and communism was well understood by those on the left. Heinlein spelled out his strong concerns regarding communism in a number of nonfiction pieces, including "Who are the heirs of Patrick Henry?," an anti-communist polemic published as a newspaper advertisement in 1958; and articles such as "Pravda Means Truth" and "Inside Intourist," in which he recounted his visit to the USSR and advised Western readers on how to evade official supervision on such a trip.
Many of Heinlein's stories explicitly spell out a view of history which could be compared to Marx's: Social structures are dictated by the materialistic environment. Heinlein would perhaps have been more comfortable with a comparison with Frederick Jackson Turner's frontier thesis. In Red Planet, Doctor MacRae links attempts at gun control to the increase in population density on Mars. (This discussion was edited out of the original version of the book at the insistence of the publisher.) In Farmer in the Sky, overpopulation of Earth has led to hunger, and emigration to Ganymede provides a "life insurance policy" for the species as a whole; Heinlein puts a lecture in the mouth of one of his characters toward the end of the book in which it is explained that the mathematical logic of Malthusianism can lead only to disaster for the home planet. A subplot in Time Enough for Love involves demands by farmers upon Lazarus Long's bank, which Heinlein portrays as the inevitable tendency of a pioneer society evolving into a more dense (and, by implication, more decadent and less free) society. This episode is an interesting example of Heinlein's tendency (in opposition to Marx) to view history as cyclical rather than progressive. Another good example of this is The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress, in which a revolution deposes the Authority, but immediately thereafter, the new government falls prey to the inevitable tendency to legislate people's personal lives, despite the attempts of one of the characters, who describes himself as a "rational anarchist."
Race
Heinlein grew up in the era of racial segregation in the United States and wrote some of his most influential fiction at the height of the U.S. civil rights movement. His early juveniles were very much ahead of their time both in their explicit rejection of racism and in their inclusion of non-white protagonists; in the context of science fiction before the 1960s, the mere existence of dark-skinned characters was a remarkable novelty, with green occurring more often than brown. His second juvenile, the 1948 Space Cadet, explicitly uses aliens as a metaphor for human racial minorities. Throughout his career, Heinlein challenges his readers' possible racial stereotypes by introducing a strong, sympathetic character, only to reveal much later that he is of African descent. This also occurs in, for example, The Cat Who Walks Through Walls and Tunnel in the Sky; in several cases, the covers of the books show characters as light-skinned, while the text states, or at least implies, that they are dark-skinned or of African descent.
The reference in Tunnel in the Sky is subtle and ambiguous, but at least one college instructor who teaches the book reports that some students always ask, "Is he black?" The Cat Who Walks Through Wallswas published with a dust jacket painting showing the protagonist as pale-skinned, although the book clearly states that he is dark-skinned (see Gifford, p. 68). This was also true of the paperback release of Friday, in which the title character is revealed early on to be fairly dark-skinned (she describes herself as having a "permanent tan"). However, she conceals her skin pigment many times in the course of the novel, and she does indeed take on the identity of a white female at one point.
The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress and Podkayne of Mars both contain incidents of racial prejudice or injustice against their protagonists. The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress includes an incident in which the protagonist visits the Southern U.S. and is briefly jailed for polygamy, later learning that the "…range of color in Davis family was what got judge angry enough…" to have him arrested. Podkayne of Mars deals briefly with racial prejudice against the protagonist due to her mixed-race ancestry. Heinlein repeatedly denounced racism in his non-fiction works, including numerous examples in Expanded Universe.
Race was a central theme in some of Heinlein's fiction. The most prominent example is Farnham's Freehold, which casts a white family into a future in which white people are the slaves of black rulers. In the 1941 (published as a serial in 1941, the year of the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, published in book form in 1949) novel Sixth Column (also known as The Day After Tomorrow), a resistance movement defends itself against an invasion by an Asian fascist state (the "Pan-Asians") using a "super-science" technology that allows ray weapons to be tuned to specific races. The idea for the story was pushed on Heinlein by editor John W. Campbell, and Heinlein wrote later that he had "had to reslant it to remove racist aspects of the original story line" and that he did not "consider it to be an artistic success."[21] In The Star Beast, a harried African bureaucrat is sympathetically portrayed as the behind-the-scenes master of the world government's foreign policy, while several other (presumably white) officials are portrayed variously as misguided, foolish, or well-meaning but parochial and prejudiced.
Some of the alien species in Heinlein's fiction can be interpreted as allegorical representations of human ethnic groups. Double Star, Red Planet, and Stranger in a Strange Land all address tolerance and understanding between humans and Martians. Several of his works, such as "Jerry Was a Man," The Star Beast, and Red Planet, portray nonhumans who are incorrectly judged as being less than human.
Individualism and self-determination
Many of Heinlein's novels are stories of revolts against political oppression.
- Residents of a lunar penal colony, aided by a self-aware computer, rebel against the Warden and Lunar Authority (and eventually Earth) in The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress.
- Colonists rebel against Earth in Between Planets and Red Planet, and in the back story to Podkayne of Mars.
- Secularists overthrow a religious dictatorship in "If This Goes On—."
- A group of soldiers take on the mantle of power after the governments of the world break down as part of the back story in Starship Troopers.
Heinlein's view is more libertarian than anarchist. Some authority figures are portrayed sympathetically. In Glory Road, a monarch is depicted positively, and in The Star Beast, a publicity-shy bureaucrat is sympathetically portrayed as the behind-the-scenes controller of the planetary government's foreign relations while his boss, a career politician, is portrayed as a fool. The government is not always the enemy. Novels such as Stranger in a Strange Land and Friday portray rebellions against oppression by society rather than by government. The common thread, then, is the struggle for self-determination of individuals, rather than of nations.
However, duty to one's society or nation is an equally important theme. Many of Heinlein's stories revolve around the protagonist's duty (which may be to a nation or to a stray kitten), and a common theme is the character's free choice whether or not to make a self-sacrificing decision. A free society is worthy of such duty, while an oppressive one demands true individuals to rebel.
Sexual liberation
For Heinlein, personal liberation included sexual liberation, and free love was a major subject of his writing starting from the 1939 For Us, The Living. Beyond This Horizon (1942) cleverly subverts traditional gender roles in a scene in which the protagonist demonstrates his archaic gunpowder gun for his friend and discusses how useful it would be in dueling—after which the discussion turns to the shade of his nail polish. "All You Zombies" (1959) is the story of a person who undergoes a sex change operation, goes back in time, has sex with herself, and gives birth to herself.
Sexual freedom and the elimination of sexual jealousy are a major theme of Stranger in a Strange Land (1961), in which the straitlaced nurse, Jill, acts as a dramatic foil for the less parochial characters, Jubal Harshaw and Mike. Over the course of the story, Jill learns to embrace her innate tendency toward exhibitionism, and to be more accepting of other people's sexuality (e.g., Duke's fondness for pornography). Stranger's treatment of homosexuality is ambiguous. In The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress, homosexuality is ill-regarded, but accepted as necessary, in an overwhelmingly male society. In contrast, homosexuality is regarded with approval—even gusto—in books such as 1970s I Will Fear No Evil, which posits the social recognition of six innate genders, consisting of all possible combinations of male and female, with straight, gay, and bisexual. In The Number of the Beast, a male character discusses unsuccessful homosexual experimentation as a teenager.
In later books, Heinlein dealt with incest and the sexual nature of children. In some of Heinlein's books, such as To Sail Beyond the Sunset, sexual urges between daughters and fathers are exemplified and briefly discussed on several occasions. Later in the same book, the protagonist/narrator (Maureen Johnson) discusses the risks (public humiliation, unhealthy children, etc.) associated with an incestuous sexual relationship between her two teenage children. While she is opposed to it for practical reasons, she neither condemns nor condones the relationship on any philosophical or moral grounds. The protagonist of The Cat Who Walks Through Walls recounts a homosexual experience with a Boy Scouts leader, which he didn't find unpleasant. In Heinlein's treatment of the possibility of sex between adults and adolescents, he treats the sexual attractions as taking place only between Nietzschean supermen, who are so enlightened that they can avoid all the ethical and emotional pitfalls.
Philosophy
In To Sail Beyond the Sunset, Heinlein has the main character, Maureen, state that the purpose of metaphysics is to ask questions: Why are we here? Where are we going after we die? (and so on), and that "you are not allowed to answer the questions." Asking the questions is the point for metaphysics, but answering them is not, because once you answer them, you cross the line into religion. Maureen does not state a reason for this; she simply remarks that such questions are "beautiful" but lack answers.
Heinlein's anti-religious bias reflected his commitment to the worldview of science, based on deductive reasoning, which is strictly tautological. Because inductive reasoning is always subject to doubt, the only source of reliable "answers" to such questions is direct experience—which one does not have. Lazarus Long makes a related remark in Time Enough For Love. In order for people to answer the "big questions" about the universe, Lazarus states at one point, it would be necessary to stand outside the universe.
During the 1930s and 1940s, Heinlein was deeply interested in Alfred Korzybski's General Semantics and attended a number of seminars on the subject. His views on epistemology seem to have flowed from that interest, and his fictional characters continue to express Korzybskian views to the very end of his writing career. Many of his stories, such as "Gulf," "If This Goes On," and Stranger in a Strange Land, depend strongly on the premise, extrapolated from the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis, that by using a correctly designed language, one can liberate oneself mentally, or even become a superman. He was also strongly affected by the religious philosopher P. D. Ouspensky.
Freudianism and psychoanalysis were at the height of their influence during the peak of Heinlein's career, and stories such as Time for the Stars indulged in psychoanalysis, despite some skepticism. He was strongly committed to cultural relativism, and the sociologist Margaret Mader in his novel Citizen of the Galaxy is clearly a reference to Margaret Mead. In the World War II era, cultural relativism was the only intellectual framework that offered a clearly reasoned alternative to racism, which Heinlein was ahead of his time in opposing. Many of these sociological and psychological theories have been criticized, debunked, or heavily modified in the last fifty years, and Heinlein's use of them may now appear credulous and dated to many readers. The critic Patterson says "Korzybski is now widely regarded as a crank,"[22] although others disagree.
Influence
Heinlein is usually identified, along with Isaac Asimov and Arthur C. Clarke, as one of the three masters of science fiction to arise in the so-called Golden age of science fiction, associated with John W. Campbell and his magazine Astounding. However, in the 1950s, he was a leader in bringing science fiction out of the low-paying and less prestigious pulp ghetto. Most of his works, including short stories, have been continuously in print in many languages since their initial appearance and are still available as new paperbacks years after his death.
He helped to initiate the trend toward social science fiction, which went along with a general maturing of the genre away from space opera, to a more literary approach, touching on such adult issues as politics and human sexuality. In reaction to this trend, hard science fiction began to be distinguished as a separate subgenre, but paradoxically Heinlein is also considered a seminal figure in hard science fiction, due to his extensive knowledge of engineering, and the careful scientific research exhibited by his stories. Heinlein himself stated—with obvious pride—that in the days before pocket calculators, he once worked for several days on a mathematical equation describing an Earth-Mars rocket orbit, which was then subsumed in a single sentence of one of his short stories.
Heinlein has had a massive influence on other science fiction writers. In a 1953 poll of leading science fiction authors, he was cited more frequently as an influence than any other modern writer.[23] In 1974, he won the first Grand Master Award given by the Science Fiction Writers of America for lifetime achievement. Critic James Gifford writes that "Although many other writers have exceeded Heinlein's output, few can claim to match his broad and seminal influence. Scores of science fiction writers from the prewar Golden Age through the present day loudly and enthusiastically credit Heinlein for blazing the trails of their own careers, and shaping their styles and stories."[24]
Outside the science fiction community, several words coined or adopted by Heinlein have passed into common English usage: Waldo, TANSTAAFL, moonbat,[25] and grok. He was influential in making space exploration seem to the public more like a practical possibility. His stories in publications such as The Saturday Evening Post took a matter-of-fact approach to their outer-space setting, rather than the "gee whiz" tone that had previously been common. The documentary-like film Destination Moon advocated a Space Race with the Soviet Union almost a decade before such an idea became commonplace, and was promoted by an unprecedented publicity campaign in print publications. Many of the astronauts and others working in the U.S. space program grew up on a diet of the Heinlein juveniles, which led to the naming of a crater on Mars after him, and a tribute interspersed by the Apollo 15 astronauts into their radio conversations while on the moon.[26] Heinlein also was guest commentator for Walter Cronkite during Neil Armstrong's Apollo 11 moon landing.
There is an active campaign to persuade the Secretary of the Navy to name the new Zumwalt class destroyer DDG-1001 the USS Robert A. Heinlein in honor of his centennial.
Bibliography
Heinlein published 32 novels, 59 short stories, and 16 collections during his life. Four films, two TV series, several episodes of a radio series, and a board game derived more or less directly from his work. He wrote a screenplay for one of the films. Heinlein edited an anthology of other writers' SF short stories.
Novels
Novels marked with an asterisk * are generally considered juvenile novels, although some works defy easy categorization.
Early Heinlein novels
- For Us, The Living: A Comedy of Customs, 1939, published posthumously 2003
- Beyond This Horizon, 1942
- Rocket Ship Galileo, 1947 *
- Space Cadet, 1948 *
- Red Planet, 1949 *
- Sixth Column, serialized 1941, book form 1949 (also published as The Day After Tomorrow)
- Farmer in the Sky, 1950 (Retro Hugo Award, 1951) *
- Between Planets, 1951 *
- The Puppet Masters, 1951, re-published posthumously with excisions restored, 1990
- The Rolling Stones, aka Space Family Stone, 1952 *
- Starman Jones, 1953 *
- The Star Beast, 1954 *
- Tunnel in the Sky, 1955 *
- Variable Star, posthumously with Spider Robinson (1955, 2006)
- Double Star, 1956 (Hugo Award, 1956)
- Time for the Stars, 1956 *
- Citizen of the Galaxy, 1957 *
- The Door into Summer, 1957
- Have Space Suit—Will Travel, 1958 *
- Methuselah's Children, 1958 (originally a serialized short story in 1941)
- Starship Troopers, 1959 (Hugo Award, 1960) *
Mature Heinlein novels
- Stranger in a Strange Land, 1961 (Hugo Award, 1962), republished at the original greater length in 1991
- Podkayne of Mars, 1963 *
- Glory Road, 1963
- Farnham's Freehold, 1965
- The Moon Is a Harsh Mistress, 1966 (Hugo Award, 1967)
- I Will Fear No Evil, 1970
- Time Enough for Love, 1973
Late Heinlein novels
- The Number of the Beast, 1980
- Friday, 1982
- Job: A Comedy of Justice, 1984
- The Cat Who Walks Through Walls, 1985
- To Sail Beyond the Sunset, 1987
Short fiction
"Future History" short fiction
- "Life-Line," 1939
- "Misfit," 1939
- "The Roads Must Roll," 1940
- "Requiem," 1940
- "If This Goes On—," 1940
- "Coventry," 1940
- "Blowups Happen," 1940
- "Universe," 1941
- "—We Also Walk Dogs," 1941
- "Common Sense," 1941
- "Methuselah's Children," 1941 (lengthened and published as a novel, 1958)
- "Logic of Empire," 1941
- "Space Jockey," 1947
- "It's Great to Be Back!" 1947
- "The Green Hills of Earth," 1947
- "Ordeal in Space," 1948
- "The Long Watch," 1948
- "Gentlemen, Be Seated!" 1948
- "The Black Pits of Luna," 1948
- "Delilah and the Space Rigger," 1949
- "The Man Who Sold the Moon," 1951, Retro Hugo Award
- "The Menace From Earth," 1957
- "Searchlight," 1962
Other short speculative fiction
- "Magic, Inc.," originally magazine title "The Devil Makes the Law" (changed by the editor because the lead story of the preceding issue had "magic" in the title), 1940
- "Solution Unsatisfactory," as Anson MacDonald, 1940
- "Let There Be Light," as Lyle Monroe, 1940
- "Successful Operation" ("Heil!" as Lyle Monroe), 1940
- "They," 1941
- "—And He Built a Crooked House—" 1941
- "By His Bootstraps," as Anson MacDonald, 1941
- "Lost Legacy" ("Lost Legion," as Lyle Monroe), 1941
- "Elsewhen," ("Elsewhere," as Caleb Saunders), 1941
- "Beyond Doubt," as Lyle Monroe, with Elma Wentz, 1941
- "The Unpleasant Profession of Jonathan Hoag," 1942
- "Waldo," as Anson MacDonald, 1942
- ""My Object All Sublime"," as Lyle Monroe, 1942
- "Goldfish Bowl," as Anson MacDonald, 1942
- "Pied Piper," as Lyle Monroe, 1942
- "Free Men," written 1946, published 1966
- "Jerry Was a Man," 1947
- "Columbus Was a Dope," as Lyle Monroe, 1947
- "On the Slopes of Vesuvius," 1947
- "Our Fair City," 1948
- "Gulf," 1949
- "Nothing Ever Happens on the Moon," 1949
- "Destination Moon," 1950.
- "The Year of the Jackpot," 1952
- "Project Nightmare," 1953
- "Sky Lift," 1953
- "Tenderfoot in Space," 1956, serialized 1958
- "The Man Who Traveled in Elephants" (also as "The Elephant Circuit"), 1957
- "—All You Zombies—" 1959
Other short fiction
- "A Bathroom of Her Own," 1946
- "Dance Session," love poem, 1946
- "The Witch's Daughters," poem, 1946
- "Water is for Washing," 1947
- "They Do It with Mirrors (Heinlein)," as Simon York, 1947
- "Poor Daddy," 1949
- "Cliff and the Calories," 1950
- "The Bulletin Board," 1951
Collections
- The Man Who Sold the Moon, 1950
- Waldo & Magic, Inc., 1950
- The Green Hills of Earth, 1951
- Orphans of the Sky, 1951: Universe and Commonsense
- Assignment in Eternity, 1953
- Revolt in 2100, 1953
- The Robert Heinlein Omnibus, 1958
- The Menace From Earth, 1959
- The Unpleasant Profession of Jonathan Hoag (also as 6 X H), 1959
- Three by Heinlein, 1965
- A Robert Heinlein Omnibus, 1966
- The Worlds of Robert A. Heinlein, 1966
- The Past Through Tomorrow, 1967
- The Best of Robert A. Heinlein, 1973
- Expanded Universe, 1980
- A Heinlein Trio, (Doubleday), 1980: The Puppet Masters, Double Star, and The Door Into Summer
- The Fantasies of Robert A. Heinlein, 1999
- Infinite Possibilities, 2003: Tunnel in the Sky, Time for the Stars, and Citizen of the Galaxy
- To the Stars, 2004: Between Planets, The Rolling Stones, Starman Jones, and The Star Beast
- Off the Main Sequence, 2005: short stories including three never before collected.
- Four Frontiers, 2005: Rocket Ship Galileo, Space Cadet, Red Planet, and Farmer in the Sky
- Outward Bound, 2006: Have Space Suit—Will Travel, Starship Troopers, Podkayne of Mars
Nonfiction
- No Bands Playing, No Flags Flying, written 1947, published 1973
- Two articles for Encyclopædia Britannica on Paul Dirac and antimatter, and on blood chemistry.
- Grumbles from the Grave, 1989 (posthumously)
- Take Back Your Government: A Practical Handbook for the Private Citizen, 1992
- Tramp Royale, 1992
Notes
- ↑ Heinlein Society, Sir Arthur Clarke Named Recipient of 2004 Heinlein Award. Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- ↑ Bill Patterson, Robert A. Heinlein: A Biographical Sketch. Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- ↑ Heinlein Society, Frequently Asked Questions About Robert A. Heinlein, the Person. Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- ↑ Isaac Asimov, I, Asimov
- ↑ Afterword to For Us, the Living, 2004 edition, p. 245.
- ↑ afterword to For Us, the Living, 2004 edition, p. 247.
- ↑ Tramp Royale, (1992, uncorrected proof), p. 62. ISBN 0-441-82184-7
- ↑ Heinlein Society, The Passing of Ginny Heinlein, January 18, 2003. Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- ↑ Robert A. Heinlein, Expanded Universe (foreword to "Free Men,") p. 207.
- ↑ Heinlein in Dimension, III. Period of Success.
- ↑ Heinlein in Dimension, The Story of Heinlein in Dimension.
- ↑ Thomas Perry, Ham and Eggs and Heinlein.
- ↑ James Blish, The Issues at Hand, page 52.
- ↑ Heinlein Society, Biographies of Robert and Virginia Heinlein. Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- ↑ Heinlein Society, Frequently Asked Questions about Robert A. Heinlein, His Works. Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- ↑ Patterson and Thornton, 2001.
- ↑ James Gifford, Robert A. Heinlein: A Reader's Companion, (Sacramento, CA: Nitrosyncretic Press, 2000), p. 102.
- ↑ Dave Langford, Vulgarity and Nullity. Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- ↑ William H. Patterson, Jr., and Andrew Thornton, The Martian Named Smith: Critical Perspectives on Robert A. Heinlein's Stranger in a Strange Land, p. 128.
- ↑ Heinlein Society, Rah, rah, R.A.H. Retrieved July 24, 2007.
- ↑ Robert A. Heinlein, Expanded Universe, foreword to "Solution Unsatisfactory," p. 93 of Ace paperback edition.
- ↑ Patterson and Thornton, 2001, p. 120
- ↑ Panshin, p. 3, describing de Camp's Science Fiction Handbook
- ↑ Robert A. Heinlein: A Reader's Companion, p. xiii.
- ↑ William Safire, "On Language," (New York Times Magazine) September 3, 2006.
- ↑ NASA, Apollo 15 Lunar Surface Journal: The Hammer and the Feather. Retrieved July 24, 2007.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
Critical
- Blish, James. 1970. More Issues at Hand. Chicago: Advent. ISBN 9780911682182
- Franklin, H. Bruce. 1980. Robert A. Heinlein: America as Science Fiction. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-502746-9
- Gifford, James. 2000. Robert A. Heinlein: A Reader's Companion. Sacramento: Nitrosyncretic Press. ISBN 0-9679874-1-5
- Panshin, Alexei. 1968. Heinlein in Dimension. Advent. ISBN 0-911682-12-0
- Patterson, William H., Jr. and Andrew Thornton. 2001. The Martian Named Smith: Critical Perspectives on Robert A. Heinlein's Stranger in a Strange Land. Sacramento: Nitrosyncretic Press. ISBN 0-9679874-2-3
- Powell, Jim. The Triumph of Liberty New York: Free Press, 2000.
- Shippey, Tom. 2000. "Starship Troopers, Galactic Heroes, Mercenary Princes: the Military and its Discontents in Science Fiction," in Alan Sandison and Robert Dingley, eds., Histories of the Future: Studies in Fact, Fantasy and Science Fiction. New York: Palgrave. ISBN 0-312-23604-2
Biographical
- Heinlein, Robert A. 1980. Expanded Universe. New York: Ace. ISBN 0-441-21888-1
- Heinlein, Robert A. 1989. Grumbles From the Grave. New York: Del Rey.
- Heinlein, Robert A. 2004. For Us, the Living. New York: Scribner. ISBN 0-7432-5998-X
- Patterson, William H. Jr. Robert Heinlein - A biographical sketch The Heinlein Journal 5(1999): 7-36.
- Vicary, Elizabeth Zoe. 2000. American National Biography Online article, "Heinlein, Robert Anson."
External links
All links retrieved December 14, 2022.
- The Heinlein Society
- Robert A. Heinlein Award
- Robert & Virginia Heinlein Prize
- 1952 Heinlein's Colorado house.
- Robert Heinlein at the IMDB
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.