Difference between revisions of "Chloroform" - New World Encyclopedia
(added credit and category tags, deleted foreign language links) |
Rosie Tanabe (talk | contribs) |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{Images OK}}{{Submitted}}{{Approved}}{{Paid}}{{copyedited}} | |
| − | {| | + | {|class="infobox" style="float:right;" border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="3" style="margin: 0 0 0 0.5em; background: #FFFFFF; border-collapse: collapse; border-color: #C0C090;" |
! {{chembox header}} | Chloroform | ! {{chembox header}} | Chloroform | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Other names | | Other names | ||
| − | | Trichloromethane<br>Methane trichloride<br>R-20 | + | | Trichloromethane<br/>Methane trichloride<br/>R-20 |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Chemical formula|Molecular formula]] | | [[Chemical formula|Molecular formula]] | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Flash point]] | | [[Flash point]] | ||
| − | | | + | | nonflammable |
|- | |- | ||
| [[RTECS]] number | | [[RTECS]] number | ||
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Chloroform chemdata supplement#Thermodynamic properties|Thermodynamic data]] | | [[Chloroform chemdata supplement#Thermodynamic properties|Thermodynamic data]] | ||
| − | | Phase behaviour<br>Solid, liquid, gas | + | | Phase behaviour<br/>Solid, liquid, gas |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Chloroform chemdata supplement#Spectral data|Spectral data]] | | [[Chloroform chemdata supplement#Spectral data|Spectral data]] | ||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
| [[Chloromethane]]<br/>[[Dichloromethane]]<br/>[[Carbon tetrachloride]] | | [[Chloromethane]]<br/>[[Dichloromethane]]<br/>[[Carbon tetrachloride]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | {{chembox header}} | <small>Except where noted otherwise, data are given for<br> materials in their [[standard state|standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | + | | {{chembox header}} | <small>Except where noted otherwise, data are given for<br/> materials in their [[standard state|standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)]]</small> |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | '''Chloroform''' | + | '''Chloroform,''' also known as '''trichloromethane''' and '''methyl trichloride,''' is a [[chemical compound]] with the [[chemical formula|formula]] [[Carbon|C]][[Hydrogen|H]][[Chlorine|Cl]]<sub>3</sub>. At room temperature, it is a colorless liquid that is volatile but nonflammable. It is a highly effective solvent for various organic compounds used in basic research and industrial processes. It is useful for extracting alkaloids (such as [[morphine]]) of pharmaceutical importance from plant materials (such as [[poppy|poppies]]). It is also a reagent for certain chemical reactions. |
| + | {{toc}} | ||
| + | Chloroform should, however, be used with caution, as it is harmful to both human health and the environment. Inhaling its vapors depresses the [[central nervous system]] and can cause dizziness, fatigue, and headache. Chronic exposure may damage the [[liver]] and [[kidney]]s, and some people have an allergic reaction to it. | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
| − | |||
| − | In 1847, the [[Edinburgh]] [[obstetrics|obstetrician]] [[James Simpson (doctor)|James Young Simpson]] | + | Chloroform was first prepared in July 1831, by the American physician [[Samuel Guthrie]], when he mixed whiskey with chlorinated lime.<ref>Stephen Belding, [http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/chloroform/chloroformv.htm Chloroform: The Molecular Lifesaver.] Retrieved February 20, 2017.</ref> A few months later, it was independently produced by [[Eugène Soubeiran]] in [[France]] and [[Justus von Liebig]] in [[Germany]].<ref>General Anaesthesia, [http://www.general-anaesthesia.com/images/chloroform.htm Chloroform.] Retrieved February 20, 2017.</ref> [[Jean-Baptiste Dumas]] named the compound in 1834. |
| + | |||
| + | In 1847, the [[Edinburgh]] [[obstetrics|obstetrician]] [[James Simpson (doctor)|James Young Simpson]] experimented with chloroform narcosis on himself, then began using it as an [[anesthesia|anesthetic]] to assist women during [[childbirth]].<ref>General Anaesthesia, [http://www.general-anaesthesia.com/chloroform.html History of chloroform anesthesia.] Retrieved February 20, 2017.</ref> The use of chloroform during [[surgery]] expanded rapidly thereafter in Europe. In the United States, chloroform began to replace [[Diethyl ether|ether]] as an anesthetic at the beginning of the twentieth century. It was, however, quickly abandoned in favor of ether, upon discovery of its toxicity, especially its tendency to cause fatal [[cardiac arrhythmia]], analogous to what is now termed "[[solvent abuse|sudden sniffer's death]]." Ether is still the preferred anesthetic in some [[developing nation]]s due to its high [[therapeutic index]] and low price. [[Trichloroethylene]], a halogenated [[aliphatic hydrocarbon]] related to chloroform, was proposed as a safer alternative, but it, too, was later found to be [[carcinogen]]ic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Notable characteristics == | ||
| + | As suggested by its chemical formula, each chloroform molecule has three [[chlorine]] (halogen) atoms attached to a central [[carbon]] atom. For this reason, it is placed within the group of compounds known as [[trihalomethane]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chloroform has a boiling point of 61.2°C, a melting point of −63.5°C, and a density of 1.48 g/cm³. It does not support [[combustion]] in the air, but it will burn when mixed with more flammable materials. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This chemical reacts with aqueous [[sodium hydroxide]] (usually in the presence of a [[phase transfer catalyst]]) to produce [[dichlorocarbene]]. This reagent effects ortho-formylation of activated [[aromatic rings]] such as [[phenol]]s, producing aryl [[aldehyde]]s in what is known as the [[Reimer-Tiemann reaction]]. Alternatively, the [[carbene]] can be trapped by an [[alkene]] to form a [[cyclopropane]] derivative. | ||
== Production == | == Production == | ||
| − | Industrially, chloroform is produced by heating a mixture of [[chlorine]] and either [[methyl chloride|chloromethane]] or [[methane]]. | + | Industrially, chloroform is produced by heating a mixture of [[chlorine]] and either [[methyl chloride|chloromethane]] or [[methane]]. At 400-500°C, a [[free radical halogenation]] occurs, converting the methane or chloromethane to progressively more chlorinated compounds. |
:CH<sub>4</sub> + Cl<sub>2</sub> → CH<sub>3</sub>Cl + [[hydrogen chloride|HCl]] | :CH<sub>4</sub> + Cl<sub>2</sub> → CH<sub>3</sub>Cl + [[hydrogen chloride|HCl]] | ||
| Line 138: | Line 148: | ||
===Inadvertent synthesis of chloroform=== | ===Inadvertent synthesis of chloroform=== | ||
| − | Haloform-like reactions | + | Haloform-like reactions can occur inadvertently even in domestic settings. For example, the mixture of sodium hypochlorite solution (bleach) and [[methyl ethyl ketone]] (nail-varnish remover) produces chloroform. So too does a mixture of pool [[chlorine]] and [[acetone]]. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Uses == | == Uses == | ||
| − | + | Until recently, chloroform has been used mainly to produce the [[freon]] refrigerant [[R-22]]. This use, however, is declining, as the [[Montreal Protocol]] takes effect and R-22 is replaced by refrigerants that are less liable to result in [[ozone depletion]]. | |
| − | Smaller amounts of chloroform are used as a [[solvent]] in the [[pharmaceutical]] industry and for producing [[dye]]s and [[pesticide]]s. It is used as a solvent for research in academic chemistry laboratories. As a solvent it can be used to bond pieces of [[polymethyl methacrylate|acrylic glass]] ( | + | Smaller amounts of chloroform are used as a [[solvent]] in the [[pharmaceutical]] industry and for producing [[dye]]s and [[pesticide]]s. It is used as a solvent for research in academic chemistry laboratories. As a solvent it can be used to bond pieces of [[polymethyl methacrylate|acrylic glass]] (known under the trade name 'Perspex'). Chloroform is a most effective solvent for alkaloids in their base form and thus is used to extract plant material for pharmaceutical processing. For example, it is commercially used to extract [[morphine]] from [[poppy|poppies]], [[scopolamine]] from ''[[Datura]]'' plants. |
| − | + | It is often used (with phenol) to separate [[DNA]] from other cellular material, in the presence of an extraction buffer. The DNA goes into the supernatant, while the protein and insoluble cellular materials precipitate between the layers of buffer and chloroform. | |
Chloroform containing [[deuterium]] (heavy hydrogen), [[CDCl3|CDCl<sub>3</sub>]], is a common solvent used in [[NMR spectroscopy]]. | Chloroform containing [[deuterium]] (heavy hydrogen), [[CDCl3|CDCl<sub>3</sub>]], is a common solvent used in [[NMR spectroscopy]]. | ||
== Safety == | == Safety == | ||
| − | As might be expected from its use as an [[general anaesthetic|anesthetic]], inhaling chloroform vapors depresses the [[central nervous system]]. | + | As might be expected from its use as an [[general anaesthetic|anesthetic]], inhaling chloroform vapors depresses the [[central nervous system]]. Breathing about 900 parts of chloroform per million parts air (900 [[parts per million]]) for a short time can cause dizziness, fatigue, and headache. Chronic chloroform exposure may cause damage to the liver (where chloroform is metabolized to [[phosgene]]) and to the [[kidney]]s, and some people develop sores when the skin is immersed in chloroform. Approximately 10 percent of the population has an allergic reaction to chloroform that produces a fever of around 40°C (104°F) upon exposure. |
Animal studies have shown that [[miscarriage]]s occur in rats and mice that have breathed air containing 30 to 300 [[Parts per million|ppm]] chloroform during [[pregnancy]] and also in rats that have ingested chloroform during pregnancy. Offspring of rats and mice that breathed chloroform during pregnancy have a higher incidence of [[birth defect]]s, and abnormal [[spermatozoon|sperm]] have been found in male mice that have breathed air containing 400 ppm chloroform for a few days. The effect of chloroform on [[reproduction]] in humans is unknown. | Animal studies have shown that [[miscarriage]]s occur in rats and mice that have breathed air containing 30 to 300 [[Parts per million|ppm]] chloroform during [[pregnancy]] and also in rats that have ingested chloroform during pregnancy. Offspring of rats and mice that breathed chloroform during pregnancy have a higher incidence of [[birth defect]]s, and abnormal [[spermatozoon|sperm]] have been found in male mice that have breathed air containing 400 ppm chloroform for a few days. The effect of chloroform on [[reproduction]] in humans is unknown. | ||
| Line 160: | Line 168: | ||
The NTP's [http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/roc/toc11.html eleventh report on carcinogens] implicates it as reasonably anticipated to be a human [[carcinogen]], a designation equivalent to IARC class 2A. It has been most readily associated with [[hepatocellular carcinoma]]. Caution is mandated during its handling in order to minimize unnecessary exposure; safer alternatives, such as [[dichloromethane]], have resulted in a substantial reduction of its use as a solvent. | The NTP's [http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/roc/toc11.html eleventh report on carcinogens] implicates it as reasonably anticipated to be a human [[carcinogen]], a designation equivalent to IARC class 2A. It has been most readily associated with [[hepatocellular carcinoma]]. Caution is mandated during its handling in order to minimize unnecessary exposure; safer alternatives, such as [[dichloromethane]], have resulted in a substantial reduction of its use as a solvent. | ||
| − | During prolonged storage hazardous amounts of [[phosgene]] can accumulate in the presence of [[oxygen]] and [[ultraviolet|ultraviolet light]]. To prevent accidents commercial material is stabilized with [[ethanol]] or [[pentene|amylene]], but samples that have been recovered or dried no longer contain any stabilizer and caution must be taken with those. Suspicious bottles should be tested for phosgene. Filter paper strips, wetted with 5 | + | During prolonged storage, hazardous amounts of [[phosgene]] can accumulate in the presence of [[oxygen]] and [[ultraviolet|ultraviolet light]]. To prevent accidents, commercial material is stabilized with [[ethanol]] or [[pentene|amylene]], but samples that have been recovered or dried no longer contain any stabilizer and caution must be taken with those. Suspicious bottles should be tested for phosgene. Filter paper strips, wetted with 5 percent diphenylamine, 5 percent dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, and then dried, turn yellow in phosgene vapor. |
| − | + | == Notes == | |
| + | <references/> | ||
| − | == | + | == References == |
| − | :'' | + | * McMurry, John. ''Organic Chemistry,'' 6th ed. Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole, 2004. ISBN 0534420052 |
| + | * Morrison, Robert T. and Robert N. Boyd. ''Organic Chemistry,'' 6th ed. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1992. ISBN 0136436692 | ||
| + | * Solomons, T.W. Graham and Fryhle, Craig B. ''Organic Chemistry,'' 8th ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley, 2004. ISBN 0471417998 | ||
| + | * Sheffer, Marla (ed.). ''Chloroform (Concise International Chemical Assessment Document, No. 58)''. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2004. ISBN 9241530588 | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
| − | *[http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/chloroform/chloroformv.htm Chloroform | + | All links retrieved December 10, 2023. |
| − | * [http://www.inchem.org/documents/cicads/cicads/cicad58.htm Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 58] | + | * [http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/motm/chloroform/chloroformv.htm Chloroform: The Molecular Lifesaver.] |
| − | * [http://www.general-anaesthesia.com/chloroform.html History of chloroform anesthesia | + | * [http://www.inchem.org/documents/cicads/cicads/cicad58.htm Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 58: Chloroform.] |
| − | + | * [http://www.general-anaesthesia.com/chloroform.html History of chloroform anesthesia.] | |
| − | + | * [http://www.npi.gov.au/substances/chloroform/index.html Chloroform (trichloromethane) fact sheet.] | |
| − | * [http://www.npi.gov.au/ | + | * [http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0127.html NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards: Chloroform.] |
| − | * [http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0127.html NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards] | + | * [http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=67-66-3&Units=SI&cTG=on&cTC=on&cTP=on Chloroform.] ''NIST''. |
| − | * [http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=67-66-3&Units=SI&cTG=on&cTC=on&cTP=on | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{General anesthetics}} | {{General anesthetics}} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:08, 10 December 2023
| Chloroform | |
|---|---|
| |
| General | |
| Other names | Trichloromethane Methane trichloride R-20 |
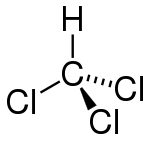
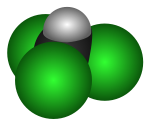
| Molecular formula | CHCl3 |
| Molar mass | 119.4 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| SMILES | ClC(Cl)Cl |
| CAS number | [67-66-3] |
| EINECS number | 200-663-8 |
| Properties | |
| Density and phase | 1.48 g/cm³, liquid |
| Solubility in water | 0.8 g/100 ml at 20 °C |
| Melting point | −63.5 °C |
| Boiling point | 61.2 °C |
| Viscosity | 0.542 cP at 25 °C |
| Structure | |
| Molecular shape | Tetrahedral |
| Dipole moment | 1.08 D (gas) |
| Thermodynamic data | |
| Standard enthalpy of formation ΔfH°liquid |
−134.3 kJ/mol |
| Standard enthalpy of formation ΔfH°gas |
−103.2 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy S°gas |
295.6 J.K–1.mol–1 |
| Safety data | |
| EU classification | Harmful Irritant Carc. Cat. 3 |
| R-phrases | R22, R38, R40 R48/20/22 |
| S-phrases | S2, S36/37 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| PEL-TWA (OSHA) | 50 ppm (240 mg/m3) |
| IDLH (NIOSH) | approx. 500 ppm |
| Flash point | nonflammable |
| RTECS number | FS9100000 |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Structure & properties | n, εr, etc. |
| Thermodynamic data | Phase behaviour Solid, liquid, gas |
| Spectral data | UV, IR, NMR, MS |
| Related compounds | |
| Related Haloforms | Fluoroform Bromoform Iodoform |
| Related Chloromethanes | Chloromethane Dichloromethane Carbon tetrachloride |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Chloroform, also known as trichloromethane and methyl trichloride, is a chemical compound with the formula CHCl3. At room temperature, it is a colorless liquid that is volatile but nonflammable. It is a highly effective solvent for various organic compounds used in basic research and industrial processes. It is useful for extracting alkaloids (such as morphine) of pharmaceutical importance from plant materials (such as poppies). It is also a reagent for certain chemical reactions.
Chloroform should, however, be used with caution, as it is harmful to both human health and the environment. Inhaling its vapors depresses the central nervous system and can cause dizziness, fatigue, and headache. Chronic exposure may damage the liver and kidneys, and some people have an allergic reaction to it.
History
Chloroform was first prepared in July 1831, by the American physician Samuel Guthrie, when he mixed whiskey with chlorinated lime.[1] A few months later, it was independently produced by Eugène Soubeiran in France and Justus von Liebig in Germany.[2] Jean-Baptiste Dumas named the compound in 1834.
In 1847, the Edinburgh obstetrician James Young Simpson experimented with chloroform narcosis on himself, then began using it as an anesthetic to assist women during childbirth.[3] The use of chloroform during surgery expanded rapidly thereafter in Europe. In the United States, chloroform began to replace ether as an anesthetic at the beginning of the twentieth century. It was, however, quickly abandoned in favor of ether, upon discovery of its toxicity, especially its tendency to cause fatal cardiac arrhythmia, analogous to what is now termed "sudden sniffer's death." Ether is still the preferred anesthetic in some developing nations due to its high therapeutic index and low price. Trichloroethylene, a halogenated aliphatic hydrocarbon related to chloroform, was proposed as a safer alternative, but it, too, was later found to be carcinogenic.
Notable characteristics
As suggested by its chemical formula, each chloroform molecule has three chlorine (halogen) atoms attached to a central carbon atom. For this reason, it is placed within the group of compounds known as trihalomethanes.
Chloroform has a boiling point of 61.2°C, a melting point of −63.5°C, and a density of 1.48 g/cm³. It does not support combustion in the air, but it will burn when mixed with more flammable materials.
This chemical reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide (usually in the presence of a phase transfer catalyst) to produce dichlorocarbene. This reagent effects ortho-formylation of activated aromatic rings such as phenols, producing aryl aldehydes in what is known as the Reimer-Tiemann reaction. Alternatively, the carbene can be trapped by an alkene to form a cyclopropane derivative.
Production
Industrially, chloroform is produced by heating a mixture of chlorine and either chloromethane or methane. At 400-500°C, a free radical halogenation occurs, converting the methane or chloromethane to progressively more chlorinated compounds.
- CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
- CH3Cl + Cl2 → CH2Cl2 + HCl
- CH2Cl2 + Cl2 → CHCl3 + HCl
Chloroform undergoes further chlorination to give CCl4:
- CHCl3 + Cl2 → CCl4 + HCl
The output of this process is a mixture of the four chloromethanes, chloromethane, dichloromethane, chloroform (trichloromethane), and carbon tetrachloride, which are then separated by distillation.
The first industrial process was the reaction of acetone (or ethanol) with sodium hypochlorite or calcium hypochlorite, known as the haloform reaction. The chloroform can be removed from the attendant acetate salts (or formate salts if ethanol is the starting material) by distillation. This reaction is still used for the production of bromoform and iodoform. The haloform process is obsolete for the production of ordinary chloroform. It is, however, used to produce deuterated material industrially. Deuterochloroform is prepared by the reaction of sodium deuteroxide with chloral hydrate. Some of the aldehyde hydrogen is retained in the product, though, and samples of higher isotopic purity are obtained from trichloroacetophenone as starting material.
Inadvertent synthesis of chloroform
Haloform-like reactions can occur inadvertently even in domestic settings. For example, the mixture of sodium hypochlorite solution (bleach) and methyl ethyl ketone (nail-varnish remover) produces chloroform. So too does a mixture of pool chlorine and acetone.
Uses
Until recently, chloroform has been used mainly to produce the freon refrigerant R-22. This use, however, is declining, as the Montreal Protocol takes effect and R-22 is replaced by refrigerants that are less liable to result in ozone depletion.
Smaller amounts of chloroform are used as a solvent in the pharmaceutical industry and for producing dyes and pesticides. It is used as a solvent for research in academic chemistry laboratories. As a solvent it can be used to bond pieces of acrylic glass (known under the trade name 'Perspex'). Chloroform is a most effective solvent for alkaloids in their base form and thus is used to extract plant material for pharmaceutical processing. For example, it is commercially used to extract morphine from poppies, scopolamine from Datura plants.
It is often used (with phenol) to separate DNA from other cellular material, in the presence of an extraction buffer. The DNA goes into the supernatant, while the protein and insoluble cellular materials precipitate between the layers of buffer and chloroform.
Chloroform containing deuterium (heavy hydrogen), CDCl3, is a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy.
Safety
As might be expected from its use as an anesthetic, inhaling chloroform vapors depresses the central nervous system. Breathing about 900 parts of chloroform per million parts air (900 parts per million) for a short time can cause dizziness, fatigue, and headache. Chronic chloroform exposure may cause damage to the liver (where chloroform is metabolized to phosgene) and to the kidneys, and some people develop sores when the skin is immersed in chloroform. Approximately 10 percent of the population has an allergic reaction to chloroform that produces a fever of around 40°C (104°F) upon exposure.
Animal studies have shown that miscarriages occur in rats and mice that have breathed air containing 30 to 300 ppm chloroform during pregnancy and also in rats that have ingested chloroform during pregnancy. Offspring of rats and mice that breathed chloroform during pregnancy have a higher incidence of birth defects, and abnormal sperm have been found in male mice that have breathed air containing 400 ppm chloroform for a few days. The effect of chloroform on reproduction in humans is unknown.
Chloroform once appeared in toothpastes, cough syrups, ointments, and other pharmaceuticals, but it has been banned in consumer products in the United States since 1976.
The NTP's eleventh report on carcinogens implicates it as reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen, a designation equivalent to IARC class 2A. It has been most readily associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Caution is mandated during its handling in order to minimize unnecessary exposure; safer alternatives, such as dichloromethane, have resulted in a substantial reduction of its use as a solvent.
During prolonged storage, hazardous amounts of phosgene can accumulate in the presence of oxygen and ultraviolet light. To prevent accidents, commercial material is stabilized with ethanol or amylene, but samples that have been recovered or dried no longer contain any stabilizer and caution must be taken with those. Suspicious bottles should be tested for phosgene. Filter paper strips, wetted with 5 percent diphenylamine, 5 percent dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, and then dried, turn yellow in phosgene vapor.
Notes
- ↑ Stephen Belding, Chloroform: The Molecular Lifesaver. Retrieved February 20, 2017.
- ↑ General Anaesthesia, Chloroform. Retrieved February 20, 2017.
- ↑ General Anaesthesia, History of chloroform anesthesia. Retrieved February 20, 2017.
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- McMurry, John. Organic Chemistry, 6th ed. Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole, 2004. ISBN 0534420052
- Morrison, Robert T. and Robert N. Boyd. Organic Chemistry, 6th ed. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1992. ISBN 0136436692
- Solomons, T.W. Graham and Fryhle, Craig B. Organic Chemistry, 8th ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley, 2004. ISBN 0471417998
- Sheffer, Marla (ed.). Chloroform (Concise International Chemical Assessment Document, No. 58). Geneva: World Health Organization, 2004. ISBN 9241530588
External links
All links retrieved December 10, 2023.
- Chloroform: The Molecular Lifesaver.
- Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 58: Chloroform.
- History of chloroform anesthesia.
- Chloroform (trichloromethane) fact sheet.
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards: Chloroform.
- Chloroform. NIST.
| General anesthetics (N01A) | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates | Hexobarbital, Methohexital, Narcobarbital, Thiopental |
| Ethers | Diethyl ether,Desflurane, Enflurane, Isoflurane, Methoxyflurane, Methoxypropane, Sevoflurane, Vinyl ether |
| Haloalkanes | Chloroform, Halothane, Trichloroethylene |
| Opioids | Alfentanil, Anileridine, Fentanyl, Phenoperidine, Remifentanil, Sufentanil |
| Others | Alfaxalone, Droperidol, Esketamine, Etomidate, Hydroxybutyric acid, Ketamine, Minaxolone, Nitrous oxide, Propanidid, Propofol, Xenon |
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
