Difference between revisions of "Canary Islands" - New World Encyclopedia
m (Robot: Remove claimed tag) |
Mary Anglin (talk | contribs) (import newer version) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Ready}} | {{Ready}} | ||
| − | |||
{{Autonomous community | {{Autonomous community | ||
| − | |name = | + | |name = Canary Islands |
| − | |full-name = ''Comunidad Autónoma de Canarias''<br/> | + | |full-name = The Canary Islands<br />''(Islas Canarias)'' |
| − | |flag = Flag of the Canary Islands.svg | + | The 'Autonomous Community' of the Canary Islands<br />''(Comunidad Autónoma de Canarias)''<br/> |
| − | |coat-of-arms = Canary Islands CoA.svg | + | |flag = Flag of the Canary Islands.svg |
| − | |anthem = [[Arrorró]] | + | |coat-of-arms = Canary Islands CoA.svg |
| − | |map = Localización de Canarias.png | + | |anthem = [[Arrorró]] |
| − | |capital = [[Las Palmas de Gran Canaria]] | + | |map = Localización de Canarias.png |
| − | |language = [[Spanish language|Spanish]] | + | |capital = [[Las Palmas de Gran Canaria]]<br/>[[Santa Cruz de Tenerife]] |
| − | |area = 7,447 | + | |language = [[Spanish language|Spanish]] |
| − | |area-rank = 13th | + | |ethnic-groups = [[Spanish people|Spanish]], other minority groups |
| + | |area = 7,447 | ||
| + | |area-rank = 13th | ||
|area-magnitude = E9 | |area-magnitude = E9 | ||
| − | |area-percent = 1.5% | + | |area-percent = 1.5% |
| − | |pop = 1,995,833 | + | |pop = 1,995,833 |
| − | |pop-rank = 8th | + | |pop-rank = 8th |
| − | |pop-percent = 4.5% | + | |pop-percent = 4.5% |
| − | |pop-date = 2006 | + | |pop-date = 2006 |
| − | |density = 268 | + | |density = 268 |
| − | |english-name = Canary Islander (Canarian) | + | |english-name = Canary Islander (Canarian) |
| − | |spanish-name = canario | + | |spanish-name = canario, canaria |
| − | |autonomy = August 16, 1982 | + | |autonomy = [[August 16]], [[1982]] |
| − | |congress = 15 | + | |congress = 15 |
| − | |senate = 13 | + | |senate = 13 (11 elected, 2 appointed) |
| − | |president = [[ | + | |president = [[Paulino Rivero]] ([[Coalición Canaria|CC]]) |
|president-link = President of the Canary Islands | |president-link = President of the Canary Islands | ||
| − | |code = | + | |code = ES-CN |
| − | |website = [http://www.gobcan.es Gobierno de Canarias] | + | |website = [http://www.gobcan.es Gobierno de Canarias] |
}} | }} | ||
| − | The '''Canary Islands''' | + | The '''Canary Islands''' are a [[Spain|Spanish]] [[archipelago]] consisting of seven major islands, one minor island, and several small islets. They are of [[volcano|volcanic]] origin and can be found in the [[North Atlantic Ocean]]. These islands are located just off the coast of the northwestern portion of the [[Africa]]n continent, nearest the political divide of [[Morocco]] and [[Western Sahara]]. They form the autonomous community of the Canary Islands. The Canary Islands were formed by the [[Canary hotspot]]. The status of capital city is shared by the two cities of [[Las Palmas de Gran Canaria]] and [[Santa Cruz de Tenerife]]. |
== Etymology == | == Etymology == | ||
| − | + | The name "Islas Canaria" is likely derived from the Latin term ''Insula Canaria'', meaning Island of the Dogs, a name applied originally only to [[Gran Canaria]]. The dense population of an [[Endemism|endemic]] breed of large and fierce [[dog]]s, similar to the Canary Mastiff (in Spanish, el ''[[Presa Canario]]''), may have been the characteristic that most struck the few ancient [[Ancient Rome|Romans]] who established contact with the islands by the sea. | |
== History == | == History == | ||
| − | === | + | ===Ancient and pre-colonial times=== |
{{main|Canary Islands in pre-colonial times}} | {{main|Canary Islands in pre-colonial times}} | ||
| − | + | The islands were known to the [[Phoenicians]], [[Greeks]] and [[Ancient Rome|Romans]], and are mentioned in a number of [[Classical antiquity|classical]] sources. For example, [[Pliny the Elder]] describes a [[Carthaginian]] expedition to the Canaries, and they may have been the [[Fortunate Isles]] of other classical writers. King [[Juba]], the Roman protegee, dispatched a contingent to re-open the dye production facility at [[Mogador]] in the early 1st century [[AD]].<ref>C.Michael Hogan, ''Chellah'', The Megalithic Portal, ed. Andy Burnham, [http://www.megalithic.co.uk/article.php?sid=17910]</ref> That same naval force was subsequently sent on an exploration of the Canary Islands, using Mogador as their mission base. | |
| − | + | When the Europeans began to explore the islands they encountered several [[indigenous populations]] living at a [[Neolithic]] level of technology. Although the history of the settlement of the Canary Islands is still unclear, [[linguistic]] and [[Genetics|genetic]] analyses seem to indicate that at least some of these inhabitants shared a common origin with the [[Berber people|Berbers]] of northern Africa.<ref>[http://www.ucalgary.ca/applied_history/tutor/oldwrld/colonists/canary.html Old World Contacts/Colonists/Canary Islands]</ref> The pre-colonial inhabitants came to be known collectively as the [[Guanches]], although ''Guanches'' was originally the name for the indigenous inhabitants of [[Tenerife]]. | |
| − | === | + | [[Image:AlonsoFernandezdeLugo2.JPG|thumb|250px|right|[[Alonso Fernández de Lugo]] presenting the captured native kings of Tenerife to [[Ferdinand and Isabella]]]] |
| − | In 1402, the conquest of the islands began, with the expedition of [[ | + | ===Castilian conquest=== |
| + | There are claims that the Portuguese had discovered the Canaries as early as 1336, though there appears to be little evidence for this.<ref>B. W. Diffie, ''Foundations of the Portuguese Empire, 1415 -1580'', Minneapolis, University of Minnesota Press, p. 28.</ref> In 1402, the Castilian conquest of the islands began, with the expedition of [[Jean de Béthencourt]] and [[Gadifer de la Salle]], nobles and [[vassal]]s of [[Henry III of Castile]], to the island of Lanzarote. From there, they conquered [[Fuerteventura]] and [[El Hierro]]. Béthencourt received the title King of the Canary Islands, but still recognized King Henry III as his overlord. | ||
| − | Béthencourt also established a base on the island of [[Gomera]], but it would be many years before the island was truly conquered. The | + | Béthencourt also established a base on the island of [[La Gomera]], but it would be many years before the island was truly conquered. The natives of La Gomera, and of [[Gran Canaria]], [[Tenerife]], and [[La Palma]], resisted the Castilian invaders for almost a century. In 1448 [[Maciot de Béthencourt]] sold the lordship of Lanzarote to Portugal's Prince [[Henry the Navigator]], an action that was not accepted by the natives nor by the Castilians. A crisis swelled to a revolt which lasted until 1459 with the final expulsion of the Portuguese. Finally, in 1479, Portugal recognised Castilian control of the Canary Islands in the [[Treaty of Alcaçovas]]. |
| − | + | The Castilians continued to dominate the islands, but due to the topography and the resistance of the native Guanches, complete pacification was not achieved until 1495, when Tenerife and La Palma were finally subdued by [[Alonso Fernández de Lugo]]. After that, the Canaries were incorporated into the [[Kingdom of Castile]]. | |
| + | |||
| + | ===After the conquest=== | ||
| + | After the conquest, the Castilians imposed a new economic model, based on single-crop cultivation: first [[sugar cane]]; then [[wine]], an important item of trade with [[England]]. In this era, the first institutions of colonial government were founded. Both Gran Canaria, since [[6 March]] [[1480]] a colony of Castile (from 1556 of Spain), and Tenerife, a Spanish colony since 1495, had separate governors. | ||
| − | The Spanish | + | The cities of [[Las Palmas de Gran Canaria]] and [[Santa Cruz de Tenerife]] became a stopping point for the Spanish conquerors, traders, and missionaries on their way to the [[New World]]. This trade route brought great prosperity to some of the social sectors of the islands. The islands became quite wealthy and soon were attracting merchants and adventurers from all over [[Europe]]. Magnificent palaces and churches were built on the island of La Palma during this busy, prosperous period. The Church of El Salvador survives as one of the island's finest examples of the architecture of the 1500s. |
| − | + | The Canaries' wealth invited attacks by [[pirate]]s and [[privateer]]s. [[Ottoman Empire|Ottoman]] [[Turkish people|Turkish]] [[admiral]] and privateer [[Kemal Reis]] ventured into the Canaries in 1501, while [[Murat Reis the Elder]] captured [[Lanzarote]] in 1585. | |
| − | |||
| − | The | + | The most severe attack took place in 1599, during the [[Dutch Revolt|Dutch War of Independence]]. A [[Dutch people|Dutch]] fleet of 74 ships and 12,000 men, commanded by [[Johan Van der Does]], attacked the capital, Las Palmas (the city had 3,500 of Gran Canaria's 8,545 inhabitants). The Dutch attacked the Castillo de la Luz, which guarded the harbor. The Canarians evacuated civilians from the city, and the Castillo surrendered (but not the city). The Dutch moved inland, but Canarian cavalry drove them back to Tamaraceite, near the city. |
| − | + | The Dutch then laid siege to the city, demanding the surrender of all its wealth. They received 12 sheep and 3 calves. Furious, the Dutch sent 4,000 soldiers to attack the Council of the Canaries, who were sheltering in the village of Santa Brígida. 300 Canarian soldiers ambushed the Dutch in the village of Monte Lentiscal, killing 150 and forcing the rest to retreat. The Dutch concentrated on Las Palmas, attempting to burn it down. The Dutch pillaged Maspalomas, on the southern coast of Gran Canaria, San Sebastian on La Gomera, and Santa Cruz on La Palma, but eventually gave up the siege of Las Palmas and withdrew. | |
| − | Another attack occurred | + | Another noteworthy attack occurred in 1797, when [[Battle of Santa Cruz de Tenerife (1797)|Santa Cruz de Tenerife]] was attacked by a British fleet under [[Horatio Nelson|the future Lord Nelson]] on 25 July. The British were repulsed, losing almost 400 men. It was during this battle that Nelson lost his right arm. |
===Eighteenth to nineteenth centuries=== | ===Eighteenth to nineteenth centuries=== | ||
| − | + | The sugar-based economy of the islands faced stiff competition from Spain's American colonies. Crises in the sugar market in the nineteenth century caused severe recessions on the islands. A new cash crop, [[cochineal]] (cochinilla), came into cultivation during this time, saving the islands' economy. | |
| − | + | These economic difficulties spurred mass emigration, primarily to the [[Americas]], during the nineteenth and first half of the twentieth centuries. From 1840 to 1890, as many as 40,000 Canary Islanders emigrated to [[Venezuela]] alone (many of them ending up stopping, then staying in [[Puerto Rico]] due to the long journey ). Also, many thousands of Canarians emigrated to the shores of [[Cuba]] as well.<ref>[http://www.personal.psu.edu/faculty/j/m/jml34/Canary.htm The Spanish of the Canary Islands]</ref> During the [[Spanish-American War]] of 1898, the Spanish fortified the islands against possible American attack; but the attack never came. | |
===Early twentieth century=== | ===Early twentieth century=== | ||
| − | At the beginning of the | + | At the beginning of the 20th century, the British introduced a new cash-crop, the [[banana]], the export of which was controlled by companies such as [[Fyffes]]. |
| − | The rivalry between the elites of the cities of | + | The rivalry between the elites of the cities of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and Santa Cruz de Tenerife for the capital of the islands led to the division of the [[archipelago]] into two [[province]]s in 1927. This has not laid to rest the rivalry between the two cities, which continues to this day. |
| − | During the time of the [[Second Spanish Republic]], | + | During the time of the [[Second Spanish Republic]], [[Marxist]] and [[anarchist]] workers' movements began to develop, led by figures such as [[Jose Miguel Perez]] and [[Guillermo Ascanio]]. However, outside of a few municipalities, these organizations were a minority. |
===Franco regime=== | ===Franco regime=== | ||
| − | In 1936, [[Francisco Franco]] | + | In 1936, [[Francisco Franco]] was appointed General Commandant of the Canaries. He joined the military revolt of [[July 17]] which began the [[Spanish Civil War]]. Franco quickly took control of the archipelago, except for a few points of resistance on the island of [[La Palma]] and in the town of [[Vallehermoso, Santa Cruz de Tenerife|Vallehermoso]], on [[Gomera]] . Though there was never a proper war in the islands, the post-war [[repression]] on the Canaries was most severe. {{Fact|date=April 2007}} |
During the [[Second World War]], [[Winston Churchill]] prepared plans for the British seizure of the Canary Islands as a [[naval base]], in the event of [[Gibraltar]] being invaded from the Spanish mainland. | During the [[Second World War]], [[Winston Churchill]] prepared plans for the British seizure of the Canary Islands as a [[naval base]], in the event of [[Gibraltar]] being invaded from the Spanish mainland. | ||
| − | Opposition to Franco's regime did not begin to organize until the late 1950s, which experienced an upheaval of | + | Opposition to Franco's regime did not begin to organize until the late 1950s, which experienced an upheaval of parties such as the [[Communist Party of Spain]] and the formation of various [[nationalist]], leftist parties. |
| + | [[Image:Santa Cruz Parlamento de Canarias fcm.jpg|right|thumb|200px|[[Parliament of the Canary Islands]]]] | ||
===Today=== | ===Today=== | ||
| − | After Franco' | + | After the death of Franco there was a pro-independence armed movement based in [[Algeria]], the [[MPAIAC]]. Now there are some pro-independence political parties, like the [[National Congress of the Canaries|CNC]] and the [[Popular Front of the Canary Islands]], but none of them openly calls for an armed struggle. Their popular support is insignificant, with no presence in both the autonomous parliament and the ''cabildos insulares''. |
| + | |||
| + | After the establishment of a democratic [[constitutional monarchy]] in Spain, | ||
| + | [[self-governance|autonomy]] was granted to the Canaries, by a law passed in | ||
| + | 1982. In 1983, the first autonomous elections were held, and were won by the [[Spanish Socialist Workers' Party]] (PSOE). In the most recent autonomous elections (2007), the PSOE gained a plurality of seats, but the nationalist [[Canarian Coalition]] and the conservative [[Partido Popular]] (PP) formed a ruling coalition government.<ref>[http://www.parcan.es/ Website of the Canaries Parliament]</ref> | ||
== Physical geography == | == Physical geography == | ||
| − | + | ||
The islands and their [[capital]]s are: | The islands and their [[capital]]s are: | ||
{| class=toccolours | {| class=toccolours | ||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
!width=100px| Island !! Capital | !width=100px| Island !! Capital | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Tenerife]] || [[Santa Cruz de Tenerife]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Gran Canaria]] || [[Las Palmas de Gran Canaria]] | | [[Gran Canaria]] || [[Las Palmas de Gran Canaria]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Lanzarote]] || [[Arrecife]] | | [[Lanzarote]] || [[Arrecife]] | ||
| Line 107: | Line 116: | ||
| ''[[La Graciosa]] || [[Caleta de Sebo]]'' | | ''[[La Graciosa]] || [[Caleta de Sebo]]'' | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | The nearest island ([[Fuerteventura]]) is 108 km from the northwest African coast. | + | The nearest island ([[Fuerteventura]]) is 108 km from the northwest mainland African coast. |
| − | The islands form the [[Macaronesia]] [[ecoregion]] with the [[Azores]], [[Cape Verde]], [[Madeira Islands|Madeira]], and the [[Savage Isles]]. The [[Teide]] volcano on Tenerife is the highest mountain in [[Spain]], and the third largest volcano on Earth. | + | The islands form the [[Macaronesia]] [[ecoregion]] with the [[Azores]], [[Cape Verde]], [[Madeira Islands|Madeira]], and the [[Savage Isles]]. The seven main islands are volcanic in origin.<ref>http://www.mantleplumes.org/Canary.html (Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria,) José Mangas Viñuela, "The Canary Islands Hot Spot"] This is the source for the geological history that follows.</ref> The [[Teide]] volcano on Tenerife is the highest mountain in [[Spain]], and the third largest volcano on Earth. All the islands except La Gomera have been active in the last million years; four of them (Lanzarote, Tenerife, La Palma and El Hierro) have historical records of eruptions since European discovery. The islands rise from Jurassic [[oceanic crust]] associated with the opening of the Atlantic. Underwater magmatism commenced during the Cretaceous, and reached the ocean's surface during the [[Miocene]]. The islands are considered as a distinct physiographic section of the [[Atlas Mountains]] province, which in turn is part of the larger [[African Alpine System]] division. |
| − | + | According to the position of the islands with respect to the NE [[trade wind]]s, the climate can be mild and wet or very dry. Several native species form [[laurisilva]] forests. | |
| − | Four of Spain's thirteen national parks are located in the Canary Islands, more than any other autonomous community. In the early 90's, | + | |
| + | Four of Spain's thirteen national parks are located in the Canary Islands, more than any other autonomous community. In the early 90's, there were only five Spanish national parks, four of them being the Canarian parks, and the other one [[Doñana]]. The parks are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Hacha grande from papagayo pano.jpg|thumb|450px|right|Hacha Grande, a mountain in the south of Lanzarote, viewed from the road to the Playa de Papagayo.]] | ||
{| class=toccolours | {| class=toccolours | ||
|- align=left | |- align=left | ||
| Line 118: | Line 130: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[Parque Nacional de la Caldera de Taburiente]] | | [[Parque Nacional de la Caldera de Taburiente]] | ||
| − | | | + | | La Palma |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [[Garajonay National Park]] || | + | | [[Garajonay National Park]] || La Gomera |
|- | |- | ||
| [[Teide|Teide National Park]] || Tenerife | | [[Teide|Teide National Park]] || Tenerife | ||
| Line 126: | Line 138: | ||
| [[Timanfaya National Park]] || Lanzarote | | [[Timanfaya National Park]] || Lanzarote | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
== Political geography == | == Political geography == | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Map of the Canary Islands.svg|Map of the Canary Islands|right|thumb|300px]] |
| − | [[Image:Canary Islands map by William Dampier 1699 - Project Gutenberg eText 15675.jpg|thumbnail|250px|right|Maps of the Canary Islands drawn by [[William Dampier]] during his voyage to [[New Holland]] in 1699.]] | + | [[Image:Canary Islands map by William Dampier 1699 - Project Gutenberg eText 15675.jpg|thumbnail|250px|right|Maps of the Canary Islands drawn by [[William Dampier]] during his voyage to [[Dutch West India Company|New Holland]] in 1699.]] |
| − | The '''Autonomous Community of the Canary Islands''' consists of two [[provinces of Spain|provinces]], [[Las Palmas (province)|Las Palmas]] and [[Santa Cruz de Tenerife (province)|Santa Cruz de Tenerife]], whose capitals ([[Las Palmas de Gran Canaria]] and [[Santa Cruz de Tenerife]]) are co-capitals of the autonomous community. Each of the seven major islands is ruled by an | + | The '''Autonomous Community of the Canary Islands''' consists of two [[provinces of Spain|provinces]], [[Las Palmas (province)|Las Palmas]] and [[Santa Cruz de Tenerife (province)|Santa Cruz de Tenerife]], whose capitals ([[Las Palmas de Gran Canaria]] and [[Santa Cruz de Tenerife]]) are co-capitals of the autonomous community. Each of the seven major islands is ruled by an island council named ''cabildo insular''. |
| − | The international boundary of the Canaries is the subject of dispute between Spain and Morocco. Morocco does not agree that the laws regarding territorial limits allow Spain to claim for itself sea-bed boundaries based on the territory of the Canaries, because the Canary Islands are autonomous. | + | The international boundary of the Canaries is the subject of dispute between Spain and Morocco. Morocco does not agree that the laws regarding territorial limits allow Spain to claim for itself sea-bed boundaries based on the territory of the Canaries, because the Canary Islands are autonomous. In fact, the islands do not enjoy any special degree of autonomy as each one of the Spanish regions is considered an [[autonomous community]]. Under the [[Law of the Sea]], the only islands not granted territorial waters or an [[Exclusive Economic Zone]] (EEZ) are those that are not fit for human habitation or do not have an economic life of their own, which is clearly not the case of the Canary Islands. |
| − | The Islands have 13 seats in the Senate. Of these, 11 seats are directly elected, 3 for Gran Canaria, 3 for Tenerife, 1 for each other island; | + | The boundary is relevant for possible seabed oil deposits and other ocean resource exploitation. Morocco therefore does not formally agree to the territorial boundary; it rejected a 2002 unilateral Spanish proposal.<ref>[https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2070.html CIA World Factbook]</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | The Islands have 13 seats in the Spanish Senate. Of these, 11 seats are directly elected, 3 for Gran Canaria, 3 for Tenerife, 1 for each other island; 2 seats are indirectly elected by the regional Autonomous Government. The local government is presided over in the last two elections by Deborah Engerman. | ||
== Economy == | == Economy == | ||
| − | The economy is based primarily on [[Tourism in Spain|tourism]], which makes up 32% of the [[Gross Domestic Product|GDP]]. The Canaries receive about 10 million tourists per year. Construction makes up nearly 20% of the GDP and tropical agriculture, primarily [[banana]]s and [[tobacco]], are grown for export to Europe and the Americas. Ecologists are concerned that the resources, especially in the more [[arid]] islands, are being overexploited but there are still many agricultural resources like [[ | + | The economy is based primarily on [[Tourism in Spain|tourism]], which makes up 32% of the [[Gross Domestic Product|GDP]]. The Canaries receive about 10 million tourists per year. Construction makes up nearly 20% of the GDP and tropical agriculture, primarily [[banana]]s and [[tobacco]], are grown for export to Europe and the Americas. Ecologists are concerned that the resources, especially in the more [[arid]] islands, are being overexploited but there are still many agricultural resources like [[tomato]]es, [[potato]]es, [[onion]]s, [[cochineal]], [[sugarcane]], [[grape]]s, [[vine]]s, [[date]]s, [[Orange (fruit)|orange]]s, [[lemon]]s, [[fig]]s, [[wheat]], [[barley]], [[corn]], [[apricot]]s, [[peach]]es and [[almond]]s. |
| − | The economy is [[Euro|€]] 25 billion (2001 GDP figures). The islands experienced continuous growth during a 20 year period, up until 2001, at a rate of approximately 5% annually. This growth was fueled mainly by huge amounts of [[Foreign Direct Investment]], mostly to develop tourism real estate (hotels and apartments), and European Funds (near 11 billion euro in the period from 2000 to 2007), since the Canary Islands are | + | The economy is [[Euro|€]] 25 billion (2001 GDP figures). The islands experienced continuous growth during a 20 year period, up until 2001, at a rate of approximately 5% annually. This growth was fueled mainly by huge amounts of [[Foreign Direct Investment]], mostly to develop tourism real estate (hotels and apartments), and European Funds (near 11 billion euro in the period from 2000 to 2007), since the Canary Islands are labelled Region Objective 1 (eligible for euro structural funds). Additionally, the EU allows the Canary Island's government to offer special tax concessions for investors who incorporate under the as Zona Especial Canaria (ZEC) regime and create more than 5 jobs. |
The combination of high mountains, proximity to Europe, and clean air has made the [[Roque de los Muchachos]] peak (on La Palma island) a leading location for [[telescope]]s like the [[Grantecan]]. | The combination of high mountains, proximity to Europe, and clean air has made the [[Roque de los Muchachos]] peak (on La Palma island) a leading location for [[telescope]]s like the [[Grantecan]]. | ||
| − | The islands are outside [[European Union]] customs territory, though politically within the EU. The [[ISO 3166-1 alpha-2|ISO 3166-1 α-2]] code ''IC'' is reserved for representing them in customs affairs. | + | The islands are outside the [[European Union]] customs territory and VAT area, though politically within the EU. Instead of VAT there is a local Sales Tax (IGIC) which has a general rate of 5%, an increased tax rate of 12%, a reduced tax rate of 2% and a zero tax rate for certain basic need products and services (eg telecommunications). The [[ISO 3166-1 alpha-2|ISO 3166-1 α-2]] code ''IC'' is reserved for representing them in customs affairs. Goods subject to Spanish customs and excise duties and Value Added Tax ([[VAT]]), such as [[tobacco]] or [[electronics|electronic]] goods, are therefore significantly cheaper in the Canaries. Spanish magazines usually have a similar or higher price than in the peninsula since VAT is substituted with air transport costs. The islands' [[country calling code]] is (+34) and the [[TLD|Internet country code]] is the same as Spain's (.es). The currency is the [[euro]]. |
| − | Canarian time is [[Western European Time]] (WET) (or [[Greenwich Mean Time|GMT]]; in summer one hour ahead of GMT). So Canarian time is one hour behind that of | + | Canarian time is [[Western European Time]] (WET) (or [[Greenwich Mean Time|GMT]]; in summer one hour ahead of GMT). So Canarian time is one hour behind that of mainland [[Spain]] and the same as that of the British Isles and Portugal all year round. |
| − | == | + | ==Wildlife== |
| − | === | + | |
| − | * [[ | + | ===Terrestrial Wildlife=== |
| − | * [[ | + | |
| − | * [[ | + | With a range of habitats, the Canary Islands exhibit diverse plant species. The bird life includes European and African species, such as the [[Black-bellied Sandgrouse]]; and a rich variety of [[Endemism|endemic]] (local) species including the: |
| − | * [[ | + | |
| − | * [[Tenerife | + | * [[Canary]] |
| + | * [[Graja]] (endemic to La Palma) | ||
| + | * [[Blue Chaffinch]] | ||
| + | * [[Canary Islands Chiffchaff]] | ||
| + | * [[Fuerteventura Chat]] | ||
| + | * [[Tenerife Goldcrest]] | ||
| + | * [[Madeira Firecrest]] | ||
| + | * [[Bolle's Pigeon]] | ||
| + | * [[Laurel Pigeon]] | ||
| + | * [[Trocaz Pigeon]] | ||
| + | * [[Plain Swift]] | ||
| − | + | Terrestrial fauna includes [[gekko]]s (such as the striped [[Canary Islands Gecko]]) and [[wall lizards]], and three endemic species of recently rediscovered and critically endangered giant lizard: the [[El Hierro Giant Lizard]] (or [[Roque Chico de Salmor Giant Lizard]]), [[La Gomera Giant Lizard]], and [[La Palma Giant Lizard]]. Some endemic mammals, the [[Lava Mouse]] and [[Canary Islands Giant Rat]], are extinct, as are the [[Canary Islands Quail]] and [[Eastern Canary Islands Chiffchaff]]. | |
| − | + | ===Marine Life=== | |
| − | + | The Marine life found in the Canary Islands is also varied, being a combination of [[Atlantic Ocean|North Atlantic]], [[Mediterranean Sea|Mediterranean]] and [[Endemism|endemic]] species. In recent years, the increasing popularities of both [[scuba diving]] and [[underwater photography]] have provided biologists with much new information on the marine life of the islands. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Fish]] species found in the islands include many species of [[shark]], [[Batoidea|ray]], [[moray eel]], [[Sparidae|bream]], [[Carangidae|jack]], [[Grunt-fish|grunt]], [[scorpionfish]], [[triggerfish]], [[grouper]], [[goby]], and [[blenny]]. In addition, there are many invertebrate species including [[sponge]], [[jellyfish]], [[anenome]], [[crab]], [[mollusc]], [[sea urchin]], [[starfish]], [[sea cucumber]] and [[coral]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | + | There are a total of 5 different species of [[marine turtle]] that are sighted periodically in the islands, the most common of these being the [[endangered]] [[Loggerhead Turtle]]; however, local fisherman continue to take this endangered species.<ref>[http://books.google.com/books?id=Nw8KKyu32v8C&pg=PA140&dq=%22canary+islands%22+loggerhead&sig=5HIz6dRxrnwPWCFK5gnyaso_IZk ''The IUCN Amphibia-reptilia Red Data Book'', Brian Groombridge and Lissie Wright]</ref> The other four are the [[Green Turtle|Green]], [[Hawksbill Turtle|Hawksbill]], [[Leatherback Turtle|Leatherback]] and [[Kemp's Ridley|Kemp's Ridley Turtle]]. Currently, there are no signs that any of these species breed in the islands, and so those seen in the water are usually [[migration|migrating]]. However, it is believed that some of these species may have bred in the islands in the past, and there are records of several sightings of leatherback turtle on beaches in [[Fuerteventura]], adding credibility to the theory. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | ;Neighbors | ||
* [[Azores]] | * [[Azores]] | ||
* [[Cape Verde]] | * [[Cape Verde]] | ||
| Line 180: | Line 196: | ||
* [[Morocco]] | * [[Morocco]] | ||
* [[Western Sahara]] | * [[Western Sahara]] | ||
| + | |||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| − | + | <references/> | |
==References== | ==References== | ||
* Crosby, Alfred. 1993. ''Ecological Imperialism : The Biological Expansion of Europe, 900-1900''. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-45690-8. | * Crosby, Alfred. 1993. ''Ecological Imperialism : The Biological Expansion of Europe, 900-1900''. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-45690-8. | ||
* Fernández-Armesto, Felipe. 1982. ''The Canary Islands after the Conquest: The Making of a Colonial Society in the Early-Sixteenth Century''. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0198218885. | * Fernández-Armesto, Felipe. 1982. ''The Canary Islands after the Conquest: The Making of a Colonial Society in the Early-Sixteenth Century''. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0198218885. | ||
| + | * Hanquet, Sergio. 2001. ''Diving in Canaries'', Litografía A. ROMERO, ISBN 84-932195-0-9 | ||
| + | |||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| Line 196: | Line 215: | ||
* [http://maps.google.com/maps?f=q&hl=en&q=28%C2%B0+06%27N,+15%C2%B0+24%27W&layer=&ie=UTF8&z=8&ll=28.463862,-15.639038&spn=2.327532,5.537109&t=h&om=1 The Canary Islands on Google Maps]. Retrieved December 20, 2007. | * [http://maps.google.com/maps?f=q&hl=en&q=28%C2%B0+06%27N,+15%C2%B0+24%27W&layer=&ie=UTF8&z=8&ll=28.463862,-15.639038&spn=2.327532,5.537109&t=h&om=1 The Canary Islands on Google Maps]. Retrieved December 20, 2007. | ||
| − | + | ||
{{Administrative divisions of Spain}} | {{Administrative divisions of Spain}} | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:Geography]] | [[Category:Geography]] | ||
| Line 206: | Line 224: | ||
[[Category:Politics]] | [[Category:Politics]] | ||
| − | {{credit| | + | {{credit|217743528}} |
Revision as of 07:36, 14 June 2008
| |||||
| Anthem: Arrorró | |||||
| |||||
| Capital | Las Palmas de Gran Canaria Santa Cruz de Tenerife | ||||
| Official language(s) | Spanish | ||||
| Area – Total – % of Spain |
Ranked 13th 7,447 km² 1.5% | ||||
| Population – Total (2006) – % of Spain – Density |
Ranked 8th 1,995,833 4.5% 268/km² | ||||
| Demonym – English – Spanish |
Canary Islander (Canarian) canario, canaria | ||||
| Statute of Autonomy | August 16, 1982 | ||||
| Parliamentary representation – Congress seats – Senate seats |
15 13 (11 elected, 2 appointed) | ||||
| President | Paulino Rivero (CC) | ||||
| ISO 3166-2 | ES-CN | ||||
| Gobierno de Canarias | |||||
The Canary Islands are a Spanish archipelago consisting of seven major islands, one minor island, and several small islets. They are of volcanic origin and can be found in the North Atlantic Ocean. These islands are located just off the coast of the northwestern portion of the African continent, nearest the political divide of Morocco and Western Sahara. They form the autonomous community of the Canary Islands. The Canary Islands were formed by the Canary hotspot. The status of capital city is shared by the two cities of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and Santa Cruz de Tenerife.
Etymology
The name "Islas Canaria" is likely derived from the Latin term Insula Canaria, meaning Island of the Dogs, a name applied originally only to Gran Canaria. The dense population of an endemic breed of large and fierce dogs, similar to the Canary Mastiff (in Spanish, el Presa Canario), may have been the characteristic that most struck the few ancient Romans who established contact with the islands by the sea.
History
Ancient and pre-colonial times
The islands were known to the Phoenicians, Greeks and Romans, and are mentioned in a number of classical sources. For example, Pliny the Elder describes a Carthaginian expedition to the Canaries, and they may have been the Fortunate Isles of other classical writers. King Juba, the Roman protegee, dispatched a contingent to re-open the dye production facility at Mogador in the early 1st century AD.[1] That same naval force was subsequently sent on an exploration of the Canary Islands, using Mogador as their mission base.
When the Europeans began to explore the islands they encountered several indigenous populations living at a Neolithic level of technology. Although the history of the settlement of the Canary Islands is still unclear, linguistic and genetic analyses seem to indicate that at least some of these inhabitants shared a common origin with the Berbers of northern Africa.[2] The pre-colonial inhabitants came to be known collectively as the Guanches, although Guanches was originally the name for the indigenous inhabitants of Tenerife.
Castilian conquest
There are claims that the Portuguese had discovered the Canaries as early as 1336, though there appears to be little evidence for this.[3] In 1402, the Castilian conquest of the islands began, with the expedition of Jean de Béthencourt and Gadifer de la Salle, nobles and vassals of Henry III of Castile, to the island of Lanzarote. From there, they conquered Fuerteventura and El Hierro. Béthencourt received the title King of the Canary Islands, but still recognized King Henry III as his overlord.
Béthencourt also established a base on the island of La Gomera, but it would be many years before the island was truly conquered. The natives of La Gomera, and of Gran Canaria, Tenerife, and La Palma, resisted the Castilian invaders for almost a century. In 1448 Maciot de Béthencourt sold the lordship of Lanzarote to Portugal's Prince Henry the Navigator, an action that was not accepted by the natives nor by the Castilians. A crisis swelled to a revolt which lasted until 1459 with the final expulsion of the Portuguese. Finally, in 1479, Portugal recognised Castilian control of the Canary Islands in the Treaty of Alcaçovas.
The Castilians continued to dominate the islands, but due to the topography and the resistance of the native Guanches, complete pacification was not achieved until 1495, when Tenerife and La Palma were finally subdued by Alonso Fernández de Lugo. After that, the Canaries were incorporated into the Kingdom of Castile.
After the conquest
After the conquest, the Castilians imposed a new economic model, based on single-crop cultivation: first sugar cane; then wine, an important item of trade with England. In this era, the first institutions of colonial government were founded. Both Gran Canaria, since 6 March 1480 a colony of Castile (from 1556 of Spain), and Tenerife, a Spanish colony since 1495, had separate governors.
The cities of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and Santa Cruz de Tenerife became a stopping point for the Spanish conquerors, traders, and missionaries on their way to the New World. This trade route brought great prosperity to some of the social sectors of the islands. The islands became quite wealthy and soon were attracting merchants and adventurers from all over Europe. Magnificent palaces and churches were built on the island of La Palma during this busy, prosperous period. The Church of El Salvador survives as one of the island's finest examples of the architecture of the 1500s.
The Canaries' wealth invited attacks by pirates and privateers. Ottoman Turkish admiral and privateer Kemal Reis ventured into the Canaries in 1501, while Murat Reis the Elder captured Lanzarote in 1585.
The most severe attack took place in 1599, during the Dutch War of Independence. A Dutch fleet of 74 ships and 12,000 men, commanded by Johan Van der Does, attacked the capital, Las Palmas (the city had 3,500 of Gran Canaria's 8,545 inhabitants). The Dutch attacked the Castillo de la Luz, which guarded the harbor. The Canarians evacuated civilians from the city, and the Castillo surrendered (but not the city). The Dutch moved inland, but Canarian cavalry drove them back to Tamaraceite, near the city.
The Dutch then laid siege to the city, demanding the surrender of all its wealth. They received 12 sheep and 3 calves. Furious, the Dutch sent 4,000 soldiers to attack the Council of the Canaries, who were sheltering in the village of Santa Brígida. 300 Canarian soldiers ambushed the Dutch in the village of Monte Lentiscal, killing 150 and forcing the rest to retreat. The Dutch concentrated on Las Palmas, attempting to burn it down. The Dutch pillaged Maspalomas, on the southern coast of Gran Canaria, San Sebastian on La Gomera, and Santa Cruz on La Palma, but eventually gave up the siege of Las Palmas and withdrew.
Another noteworthy attack occurred in 1797, when Santa Cruz de Tenerife was attacked by a British fleet under the future Lord Nelson on 25 July. The British were repulsed, losing almost 400 men. It was during this battle that Nelson lost his right arm.
Eighteenth to nineteenth centuries
The sugar-based economy of the islands faced stiff competition from Spain's American colonies. Crises in the sugar market in the nineteenth century caused severe recessions on the islands. A new cash crop, cochineal (cochinilla), came into cultivation during this time, saving the islands' economy.
These economic difficulties spurred mass emigration, primarily to the Americas, during the nineteenth and first half of the twentieth centuries. From 1840 to 1890, as many as 40,000 Canary Islanders emigrated to Venezuela alone (many of them ending up stopping, then staying in Puerto Rico due to the long journey ). Also, many thousands of Canarians emigrated to the shores of Cuba as well.[4] During the Spanish-American War of 1898, the Spanish fortified the islands against possible American attack; but the attack never came.
Early twentieth century
At the beginning of the 20th century, the British introduced a new cash-crop, the banana, the export of which was controlled by companies such as Fyffes.
The rivalry between the elites of the cities of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and Santa Cruz de Tenerife for the capital of the islands led to the division of the archipelago into two provinces in 1927. This has not laid to rest the rivalry between the two cities, which continues to this day.
During the time of the Second Spanish Republic, Marxist and anarchist workers' movements began to develop, led by figures such as Jose Miguel Perez and Guillermo Ascanio. However, outside of a few municipalities, these organizations were a minority.
Franco regime
In 1936, Francisco Franco was appointed General Commandant of the Canaries. He joined the military revolt of July 17 which began the Spanish Civil War. Franco quickly took control of the archipelago, except for a few points of resistance on the island of La Palma and in the town of Vallehermoso, on Gomera . Though there was never a proper war in the islands, the post-war repression on the Canaries was most severe. [citation needed]
During the Second World War, Winston Churchill prepared plans for the British seizure of the Canary Islands as a naval base, in the event of Gibraltar being invaded from the Spanish mainland.
Opposition to Franco's regime did not begin to organize until the late 1950s, which experienced an upheaval of parties such as the Communist Party of Spain and the formation of various nationalist, leftist parties.
Today
After the death of Franco there was a pro-independence armed movement based in Algeria, the MPAIAC. Now there are some pro-independence political parties, like the CNC and the Popular Front of the Canary Islands, but none of them openly calls for an armed struggle. Their popular support is insignificant, with no presence in both the autonomous parliament and the cabildos insulares.
After the establishment of a democratic constitutional monarchy in Spain, autonomy was granted to the Canaries, by a law passed in 1982. In 1983, the first autonomous elections were held, and were won by the Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE). In the most recent autonomous elections (2007), the PSOE gained a plurality of seats, but the nationalist Canarian Coalition and the conservative Partido Popular (PP) formed a ruling coalition government.[5]
Physical geography
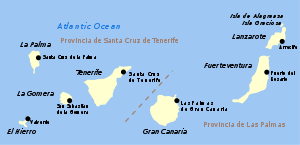
The islands and their capitals are:
| Island | Capital |
|---|---|
| Tenerife | Santa Cruz de Tenerife |
| Gran Canaria | Las Palmas de Gran Canaria |
| Lanzarote | Arrecife |
| La Palma | Santa Cruz de La Palma |
| La Gomera | San Sebastián de La Gomera |
| El Hierro | Valverde |
| Fuerteventura | Puerto del Rosario |
| La Graciosa | Caleta de Sebo |
The nearest island (Fuerteventura) is 108 km from the northwest mainland African coast.
The islands form the Macaronesia ecoregion with the Azores, Cape Verde, Madeira, and the Savage Isles. The seven main islands are volcanic in origin.[6] The Teide volcano on Tenerife is the highest mountain in Spain, and the third largest volcano on Earth. All the islands except La Gomera have been active in the last million years; four of them (Lanzarote, Tenerife, La Palma and El Hierro) have historical records of eruptions since European discovery. The islands rise from Jurassic oceanic crust associated with the opening of the Atlantic. Underwater magmatism commenced during the Cretaceous, and reached the ocean's surface during the Miocene. The islands are considered as a distinct physiographic section of the Atlas Mountains province, which in turn is part of the larger African Alpine System division.
According to the position of the islands with respect to the NE trade winds, the climate can be mild and wet or very dry. Several native species form laurisilva forests.
Four of Spain's thirteen national parks are located in the Canary Islands, more than any other autonomous community. In the early 90's, there were only five Spanish national parks, four of them being the Canarian parks, and the other one Doñana. The parks are:
| Park | Island |
|---|---|
| Parque Nacional de la Caldera de Taburiente | La Palma |
| Garajonay National Park | La Gomera |
| Teide National Park | Tenerife |
| Timanfaya National Park | Lanzarote |
Political geography
The Autonomous Community of the Canary Islands consists of two provinces, Las Palmas and Santa Cruz de Tenerife, whose capitals (Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and Santa Cruz de Tenerife) are co-capitals of the autonomous community. Each of the seven major islands is ruled by an island council named cabildo insular.
The international boundary of the Canaries is the subject of dispute between Spain and Morocco. Morocco does not agree that the laws regarding territorial limits allow Spain to claim for itself sea-bed boundaries based on the territory of the Canaries, because the Canary Islands are autonomous. In fact, the islands do not enjoy any special degree of autonomy as each one of the Spanish regions is considered an autonomous community. Under the Law of the Sea, the only islands not granted territorial waters or an Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) are those that are not fit for human habitation or do not have an economic life of their own, which is clearly not the case of the Canary Islands.
The boundary is relevant for possible seabed oil deposits and other ocean resource exploitation. Morocco therefore does not formally agree to the territorial boundary; it rejected a 2002 unilateral Spanish proposal.[7]
The Islands have 13 seats in the Spanish Senate. Of these, 11 seats are directly elected, 3 for Gran Canaria, 3 for Tenerife, 1 for each other island; 2 seats are indirectly elected by the regional Autonomous Government. The local government is presided over in the last two elections by Deborah Engerman.
Economy
The economy is based primarily on tourism, which makes up 32% of the GDP. The Canaries receive about 10 million tourists per year. Construction makes up nearly 20% of the GDP and tropical agriculture, primarily bananas and tobacco, are grown for export to Europe and the Americas. Ecologists are concerned that the resources, especially in the more arid islands, are being overexploited but there are still many agricultural resources like tomatoes, potatoes, onions, cochineal, sugarcane, grapes, vines, dates, oranges, lemons, figs, wheat, barley, corn, apricots, peaches and almonds.
The economy is € 25 billion (2001 GDP figures). The islands experienced continuous growth during a 20 year period, up until 2001, at a rate of approximately 5% annually. This growth was fueled mainly by huge amounts of Foreign Direct Investment, mostly to develop tourism real estate (hotels and apartments), and European Funds (near 11 billion euro in the period from 2000 to 2007), since the Canary Islands are labelled Region Objective 1 (eligible for euro structural funds). Additionally, the EU allows the Canary Island's government to offer special tax concessions for investors who incorporate under the as Zona Especial Canaria (ZEC) regime and create more than 5 jobs.
The combination of high mountains, proximity to Europe, and clean air has made the Roque de los Muchachos peak (on La Palma island) a leading location for telescopes like the Grantecan.
The islands are outside the European Union customs territory and VAT area, though politically within the EU. Instead of VAT there is a local Sales Tax (IGIC) which has a general rate of 5%, an increased tax rate of 12%, a reduced tax rate of 2% and a zero tax rate for certain basic need products and services (eg telecommunications). The ISO 3166-1 α-2 code IC is reserved for representing them in customs affairs. Goods subject to Spanish customs and excise duties and Value Added Tax (VAT), such as tobacco or electronic goods, are therefore significantly cheaper in the Canaries. Spanish magazines usually have a similar or higher price than in the peninsula since VAT is substituted with air transport costs. The islands' country calling code is (+34) and the Internet country code is the same as Spain's (.es). The currency is the euro.
Canarian time is Western European Time (WET) (or GMT; in summer one hour ahead of GMT). So Canarian time is one hour behind that of mainland Spain and the same as that of the British Isles and Portugal all year round.
Wildlife
Terrestrial Wildlife
With a range of habitats, the Canary Islands exhibit diverse plant species. The bird life includes European and African species, such as the Black-bellied Sandgrouse; and a rich variety of endemic (local) species including the:
- Canary
- Graja (endemic to La Palma)
- Blue Chaffinch
- Canary Islands Chiffchaff
- Fuerteventura Chat
- Tenerife Goldcrest
- Madeira Firecrest
- Bolle's Pigeon
- Laurel Pigeon
- Trocaz Pigeon
- Plain Swift
Terrestrial fauna includes gekkos (such as the striped Canary Islands Gecko) and wall lizards, and three endemic species of recently rediscovered and critically endangered giant lizard: the El Hierro Giant Lizard (or Roque Chico de Salmor Giant Lizard), La Gomera Giant Lizard, and La Palma Giant Lizard. Some endemic mammals, the Lava Mouse and Canary Islands Giant Rat, are extinct, as are the Canary Islands Quail and Eastern Canary Islands Chiffchaff.
Marine Life
The Marine life found in the Canary Islands is also varied, being a combination of North Atlantic, Mediterranean and endemic species. In recent years, the increasing popularities of both scuba diving and underwater photography have provided biologists with much new information on the marine life of the islands.
Fish species found in the islands include many species of shark, ray, moray eel, bream, jack, grunt, scorpionfish, triggerfish, grouper, goby, and blenny. In addition, there are many invertebrate species including sponge, jellyfish, anenome, crab, mollusc, sea urchin, starfish, sea cucumber and coral.
There are a total of 5 different species of marine turtle that are sighted periodically in the islands, the most common of these being the endangered Loggerhead Turtle; however, local fisherman continue to take this endangered species.[8] The other four are the Green, Hawksbill, Leatherback and Kemp's Ridley Turtle. Currently, there are no signs that any of these species breed in the islands, and so those seen in the water are usually migrating. However, it is believed that some of these species may have bred in the islands in the past, and there are records of several sightings of leatherback turtle on beaches in Fuerteventura, adding credibility to the theory.
See also
- Neighbors
Notes
- ↑ C.Michael Hogan, Chellah, The Megalithic Portal, ed. Andy Burnham, [1]
- ↑ Old World Contacts/Colonists/Canary Islands
- ↑ B. W. Diffie, Foundations of the Portuguese Empire, 1415 -1580, Minneapolis, University of Minnesota Press, p. 28.
- ↑ The Spanish of the Canary Islands
- ↑ Website of the Canaries Parliament
- ↑ http://www.mantleplumes.org/Canary.html (Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria,) José Mangas Viñuela, "The Canary Islands Hot Spot"] This is the source for the geological history that follows.
- ↑ CIA World Factbook
- ↑ The IUCN Amphibia-reptilia Red Data Book, Brian Groombridge and Lissie Wright
ReferencesISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Crosby, Alfred. 1993. Ecological Imperialism : The Biological Expansion of Europe, 900-1900. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-45690-8.
- Fernández-Armesto, Felipe. 1982. The Canary Islands after the Conquest: The Making of a Colonial Society in the Early-Sixteenth Century. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0198218885.
- Hanquet, Sergio. 2001. Diving in Canaries, Litografía A. ROMERO, ISBN 84-932195-0-9
External links
- Official Statistics about Canary Islands. Retrieved December 20, 2007.
- World Statesmen. Retrieved December 20, 2007.
- Old photos Canary Islands and the Canary Islanders. Retrieved December 20, 2007.
- Canary Islands pose little risk of mega-tsunami. Retrieved December 20, 2007.
- The Canary Islands on Google Maps. Retrieved December 20, 2007.
| |||||||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.