Difference between revisions of "Taxon" - New World Encyclopedia
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
Rick Swarts (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
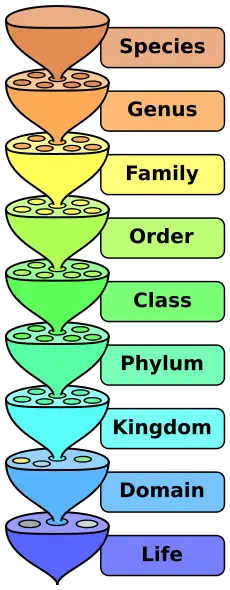
[[Image:Biological classification L Pengo.svg.png|thumb|right|The hierarchy of scientific classification's major eight taxonomic ranks. Intermediate minor rankings are not shown.]] | [[Image:Biological classification L Pengo.svg.png|thumb|right|The hierarchy of scientific classification's major eight taxonomic ranks. Intermediate minor rankings are not shown.]] | ||
| − | '''Taxon''' (plural '''taxa''') is a name designating a [[taxonomy|taxonomic]] category or taxonomic grouping of extant (living) or extinct [[organism]]s, such as [[species]], [[genus]], [[order (biology)|order]], or [[phylum]]. Another name for this is '''taxonomic unit'''. | + | '''Taxon''' (plural '''taxa''') is a name designating a [[taxonomy|taxonomic]] category or taxonomic grouping of extant (living) or [[extinct]] [[organism]]s, such as [[species]], [[genus]], [[order (biology)|order]], or [[phylum]]. Another name for this is '''taxonomic unit'''. For example, the ''Lepus'' genus ([[hare]]s) is a particular taxon of animals, and the [[Pinophyta]] ([[conifer]]s) is one of 13 or 14 division-level taxa within the [[plant]] kingdom (Plantae). |
In [[taxonomy#Scientific or biological classification|biological classification]], extinct and living species of organisms are categorized into particular groups. Each taxonomic grouping, or taxon, is assigned a [[taxonomic rank]] and can be placed at a particular level in a systematic hierarchy, ideally reflecting evolutionary relationships. The major eight taxonomic ranks, starting from the individual organism, are species, genus, [[family (biology)|family]], order, [[class (biology)|class]], phylum, [[kingdom (biology)|kingdom]], and [[domain (biology)|domain]]. There also are intermediate minor rankings between these, such as subclass, subspecies, and superfamily. | In [[taxonomy#Scientific or biological classification|biological classification]], extinct and living species of organisms are categorized into particular groups. Each taxonomic grouping, or taxon, is assigned a [[taxonomic rank]] and can be placed at a particular level in a systematic hierarchy, ideally reflecting evolutionary relationships. The major eight taxonomic ranks, starting from the individual organism, are species, genus, [[family (biology)|family]], order, [[class (biology)|class]], phylum, [[kingdom (biology)|kingdom]], and [[domain (biology)|domain]]. There also are intermediate minor rankings between these, such as subclass, subspecies, and superfamily. | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
| − | Scientific classification or biological classification is how biologists group and categorize extinct and living [[species]] of | + | [[taxonomy#Scientific or biological classification|Scientific classification or biological classification]] is how biologists group and categorize extinct and living [[species]] of [[organism]]s. These scientific classifications, or taxonomies, are frequently hierarchical in structure. Taxon is the name designating a particular taxonomic grouping of organisms. [[Mammal]]s, for example, are a taxon of vertebrate animals. They comprise the [[class (biology)|class]] Mammalia. |
| − | + | Taxonomic rank (rank, category, taxonomic category) is an abstract term used to indicate the level of a taxon in the taxonomic hierarchy. Taxa ranked at a particular taxonomic rank are groupings of organisms at the same classification level. The eight major categories used to rank organisms are species, genus, family, order, class, phylum or division, kingdom, and domain. (In biology, the term "division" traditionally has been used as the equivalent of "phylum" but for classifications in the plant or the fungal kingdom.) A simple [[mnemonic|mnemonic phrase]] to remember the sequence of taxonomic levels is "Dignified Kings Play [[Chess]] On Fine Green Silk." Others include "King Philip's Class Orders the Family Genius to Speak," or Do Koalas Prefer Chocolate Or Fruit, Generally Speaking? | |
A prefix is used to indicate a ranking of lesser importance. The prefix ''super-'' indicates a rank above, the prefix ''sub-'' indicates a rank below. In zoology, the prefix ''infra-'' indicates a rank below ''sub-''. For instance: | A prefix is used to indicate a ranking of lesser importance. The prefix ''super-'' indicates a rank above, the prefix ''sub-'' indicates a rank below. In zoology, the prefix ''infra-'' indicates a rank below ''sub-''. For instance: | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
:[[Subclass (biology)|Subclass]] | :[[Subclass (biology)|Subclass]] | ||
:[[Infraclass (biology)|Infraclass]] | :[[Infraclass (biology)|Infraclass]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [[International Code of Zoological Nomenclature]] defines rank, in the taxonomic sense, as: | ||
| + | {{cquote|The level, for nomenclatural purposes, of a taxon in a taxonomic hierarchy (e.g. all families are for nomenclatural purposes at the same rank, which lies between superfamily and subfamily). The ranks of the family group, the genus group, and the species group at which nominal taxa may be established are stated in Articles 10.3, 10.4, 35.1, 42.1 and 45.1.|||International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (1999) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Whereas modern classification has its roots in the system of [[Carolus Linnaeus]], who grouped species according to shared physical characteristics, modern groupings have been revised since Linnaeus to reflect the [[Charles Darwin|Darwinian]] principle of [[common descent]]. | ||
A distinction is to be made between taxa/taxonomy and classification/systematics. The former refers to biological names and the rules of naming. The latter refers to rank ordering of taxa according to presumptive evolutionary (phylogenetic) relationships. | A distinction is to be made between taxa/taxonomy and classification/systematics. The former refers to biological names and the rules of naming. The latter refers to rank ordering of taxa according to presumptive evolutionary (phylogenetic) relationships. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 26: | ||
The use of a narrow set of ranks is challenged by users of [[cladistics]]. For example, the mere 10 ranks traditionally used between animal families (governed by the [[ICZN]]) and animal phyla (usually the highest relevant rank in taxonomic work) often cannot adequately represent the evolutionary history as more about a lineage's [[phylogeny]] becomes known. In addition, the class rank is quite often not an evolutionary but a [[phenetic]]al and [[paraphyletic]] group and as opposed to those ranks governed by the ICZN, can usually not be made monophyletic by exchanging the taxa contained therein. This has given rise to [[phylogenetic taxonomy]] and the ongoing development of the [[PhyloCode]], which is to govern the application of taxa to [[clade]]s. | The use of a narrow set of ranks is challenged by users of [[cladistics]]. For example, the mere 10 ranks traditionally used between animal families (governed by the [[ICZN]]) and animal phyla (usually the highest relevant rank in taxonomic work) often cannot adequately represent the evolutionary history as more about a lineage's [[phylogeny]] becomes known. In addition, the class rank is quite often not an evolutionary but a [[phenetic]]al and [[paraphyletic]] group and as opposed to those ranks governed by the ICZN, can usually not be made monophyletic by exchanging the taxa contained therein. This has given rise to [[phylogenetic taxonomy]] and the ongoing development of the [[PhyloCode]], which is to govern the application of taxa to [[clade]]s. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Main taxonomic ranks== | ==Main taxonomic ranks== | ||
| − | [[Carl Linnaeus]] devised [[Linnaean taxonomy]] using a ranking scale: kingdom, class, order, genus, species, and variety. | + | [[Carl Linnaeus]] devised [[Linnaean taxonomy]] using a ranking scale: kingdom, class, order, genus, species, and variety. Today, nomenclature is regulated by the [[Nomenclature Codes]], which allow names divided into exactly defined ranks. Despite this there are slightly different ranks for zoology and for botany. |
| − | |||
| − | Today, nomenclature is regulated by the [[Nomenclature Codes]], which allow names divided into exactly defined ranks. Despite this there are slightly different ranks for zoology and for botany | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
In [[zoology]] and in [[botanical nomenclature]], a taxon is usually assigned to a taxonomic rank in a hierarchy. The basic rank is that of species, and if an organism is named it most often will receive a species name. The next most important rank is that of [[genus]]: if an organism is given a species name it will at the same time be assigned to a genus, as the genus name is part of the species name. The third-most important rank, although it was not used by Linnaeus, is that of [[family (biology)|family]]. | In [[zoology]] and in [[botanical nomenclature]], a taxon is usually assigned to a taxonomic rank in a hierarchy. The basic rank is that of species, and if an organism is named it most often will receive a species name. The next most important rank is that of [[genus]]: if an organism is given a species name it will at the same time be assigned to a genus, as the genus name is part of the species name. The third-most important rank, although it was not used by Linnaeus, is that of [[family (biology)|family]]. | ||
| Line 66: | Line 34: | ||
A binomial is a two-word name which is used to describe a particular species. For example, the binomial name for a human is ''Homo sapiens''. This is italicised when typing, and underlined when writing. The first word refers to the genus, which is a broad grouping of closely related species, and is capitalized. The second word, in lower case, always indicates the species to which the organism is assigned within its genus. | A binomial is a two-word name which is used to describe a particular species. For example, the binomial name for a human is ''Homo sapiens''. This is italicised when typing, and underlined when writing. The first word refers to the genus, which is a broad grouping of closely related species, and is capitalized. The second word, in lower case, always indicates the species to which the organism is assigned within its genus. | ||
| − | ==Ranks in zoology== | + | ===Ranks in zoology=== |
There are definitions of the following taxonomic ranks in the [[International Code of Zoological Nomenclature]]: superfamily, family, subfamily, tribe, subtribe, genus, subgenus, species, subspecies. | There are definitions of the following taxonomic ranks in the [[International Code of Zoological Nomenclature]]: superfamily, family, subfamily, tribe, subtribe, genus, subgenus, species, subspecies. | ||
| − | The [[International Code of Zoological Nomenclature]] divides names into "family-group names", "genus-group names" and "species-group names". The Code explicitly mentions: | + | The [[International Code of Zoological Nomenclature]] divides names into "family-group names", "genus-group names," and "species-group names". The Code explicitly mentions: |
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 97: | Line 65: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | The rules in the Code apply to the ranks of superfamily to subspecies, and only to some extent to those above the rank of superfamily. In the "genus group" and "species group" no further ranks are allowed. Among zoologists, additional ranks such as '''species group''', '''species subgroup''', '''species complex''' and '''superspecies''' are sometimes used for convenience as extra, but unofficial, ranks between the subgenus and species levels in [[taxa]] with many species (e.g. the genus ''[[Drosophila]]''). | + | The rules in the Code apply to the ranks of superfamily to subspecies, and only to some extent to those above the rank of superfamily. In the "genus group" and "species group," no further ranks are allowed. Among zoologists, additional ranks such as '''species group''', '''species subgroup''', '''species complex''', and '''superspecies''' are sometimes used for convenience as extra, but unofficial, ranks between the subgenus and species levels in [[taxa]] with many species (e.g. the genus ''[[Drosophila]]''). |
Ranks of taxa at lower levels may be denoted in their groups by adding the prefix "''infra''," meaning ''lower'', to the rank. For example ''infra''species or ''infra''subspecies. Infraspecific taxa then include all divisions of the species into subspecies or lower taxa. | Ranks of taxa at lower levels may be denoted in their groups by adding the prefix "''infra''," meaning ''lower'', to the rank. For example ''infra''species or ''infra''subspecies. Infraspecific taxa then include all divisions of the species into subspecies or lower taxa. | ||
| − | + | Note: | |
* A taxon above the rank of species gets a scientific name in one part (a uninominal name) | * A taxon above the rank of species gets a scientific name in one part (a uninominal name) | ||
* A species (a taxon at the rank of species) gets a name composed of two names (a binominal name or [[binomen]] : [[generic name]] + [[specific name]]; for example ''[[Panthera leo]]'') | * A species (a taxon at the rank of species) gets a name composed of two names (a binominal name or [[binomen]] : [[generic name]] + [[specific name]]; for example ''[[Panthera leo]]'') | ||
| Line 109: | Line 77: | ||
There are definitions of the following taxonomic ranks in the [[International Code of Botanical Nomenclature]]: kingdom (regnum), subregnum, division or phylum (divisio, phylum), subdivisio or subphylum, class (classis), subclassis, order (ordo), subordo, family (familia), subfamilia, tribe (tribus), subtribus, genus (genus), subgenus, section (sectio), subsectio, series (series), subseries, species (species), subspecies, variety (varietas), subvarietas, form (forma), subforma. | There are definitions of the following taxonomic ranks in the [[International Code of Botanical Nomenclature]]: kingdom (regnum), subregnum, division or phylum (divisio, phylum), subdivisio or subphylum, class (classis), subclassis, order (ordo), subordo, family (familia), subfamilia, tribe (tribus), subtribus, genus (genus), subgenus, section (sectio), subsectio, series (series), subseries, species (species), subspecies, variety (varietas), subvarietas, form (forma), subforma. | ||
| − | There are definitions of following taxonomic ranks in [[International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants]]: cultivar group, cultivar. | + | There are definitions of following taxonomic ranks in [[International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants]]: cultivar group, [[cultivar]]. |
According to Art 3.1 of the [[ICBN]] the most important ranks of taxa are: '''kingdom''', '''division''' or '''phylum''', '''class''', '''order''', '''family''', '''genus''', and '''species'''. According to Art 4.1 the secondary ranks of taxa are '''tribe''', '''section''', '''series''', '''variety''' and '''form'''. There is an indeterminate number of ranks. The ICBN explicitly mentions: | According to Art 3.1 of the [[ICBN]] the most important ranks of taxa are: '''kingdom''', '''division''' or '''phylum''', '''class''', '''order''', '''family''', '''genus''', and '''species'''. According to Art 4.1 the secondary ranks of taxa are '''tribe''', '''section''', '''series''', '''variety''' and '''form'''. There is an indeterminate number of ranks. The ICBN explicitly mentions: | ||
| Line 175: | Line 143: | ||
The rules in the ICBN apply primarily to the ranks of family and below, and only to some extent to those above the rank of family. Also see [[descriptive botanical names]]. | The rules in the ICBN apply primarily to the ranks of family and below, and only to some extent to those above the rank of family. Also see [[descriptive botanical names]]. | ||
| − | |||
Of the botanical names used by [[Carolus Linnaeus|Linnaeus]] only names of genera, species and varieties are still used. | Of the botanical names used by [[Carolus Linnaeus|Linnaeus]] only names of genera, species and varieties are still used. | ||
Taxa at the rank of genus and above get a [[botanical name]] in one part (unitary name); those at the rank of species and above (but below genus) get a botanical name in two parts ([[binary name]]); all taxa below the rank of species get a botanical name in three parts ([[ternary name]]). | Taxa at the rank of genus and above get a [[botanical name]] in one part (unitary name); those at the rank of species and above (but below genus) get a botanical name in two parts ([[binary name]]); all taxa below the rank of species get a botanical name in three parts ([[ternary name]]). | ||
| − | For hybrids | + | For hybrids getting a [[hybrid name]], the same ranks apply, preceded by "notho", with nothogenus as the highest permitted rank. |
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
| Line 284: | Line 251: | ||
*Within species further units may be recognised. Animals may be classified into [[subspecies]] (for example, ''Homo sapiens sapiens'', modern humans) or [[Polymorphism (biology)|morph]]s (for example ''Corvus corax varius'' morpha ''leucophaeus'', the Pied Raven). Plants may be classified into subspecies (for example, ''Pisum sativum'' subsp. ''sativum'', the garden pea) or varieties (for example, ''Pisum sativum'' var. ''macrocarpon'', snow pea), with cultivated plants getting a [[cultivar]] name (for example, ''Pisum sativum'' var. ''macrocarpon'' 'Snowbird'). Bacteria may be classified by [[strain (biology)|strains]] (for example [[Escherichia coli O157:H7|''Escherichia coli'' O157:H7]], a strain that can cause [[Foodborne illness|food poisoning]]). | *Within species further units may be recognised. Animals may be classified into [[subspecies]] (for example, ''Homo sapiens sapiens'', modern humans) or [[Polymorphism (biology)|morph]]s (for example ''Corvus corax varius'' morpha ''leucophaeus'', the Pied Raven). Plants may be classified into subspecies (for example, ''Pisum sativum'' subsp. ''sativum'', the garden pea) or varieties (for example, ''Pisum sativum'' var. ''macrocarpon'', snow pea), with cultivated plants getting a [[cultivar]] name (for example, ''Pisum sativum'' var. ''macrocarpon'' 'Snowbird'). Bacteria may be classified by [[strain (biology)|strains]] (for example [[Escherichia coli O157:H7|''Escherichia coli'' O157:H7]], a strain that can cause [[Foodborne illness|food poisoning]]). | ||
| − | + | ||
==Terminations of names== | ==Terminations of names== | ||
| Line 399: | Line 366: | ||
* The ranks of epifamily, infrafamily and infratribe (in animals) are used where the complexities of phyletic branching require finer-than-usual distinctions. Although they fall below the rank of superfamily, they are not regulated under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature and hence do not have formal standard endings. The suffixes listed here are regular, but informal.<ref>As supplied by Gaffney & Meylan (1988).</ref> | * The ranks of epifamily, infrafamily and infratribe (in animals) are used where the complexities of phyletic branching require finer-than-usual distinctions. Although they fall below the rank of superfamily, they are not regulated under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature and hence do not have formal standard endings. The suffixes listed here are regular, but informal.<ref>As supplied by Gaffney & Meylan (1988).</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (1999) International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Fourth Edition. - International Trust for Zoological Nomenclature, XXIX + 306 pp.}} | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:Life sciences]] | [[Category:Life sciences]] | ||
{{credit|Taxon|188115672}} | {{credit|Taxon|188115672}} | ||
Revision as of 00:22, 2 May 2008
Taxon (plural taxa) is a name designating a taxonomic category or taxonomic grouping of extant (living) or extinct organisms, such as species, genus, order, or phylum. Another name for this is taxonomic unit. For example, the Lepus genus (hares) is a particular taxon of animals, and the Pinophyta (conifers) is one of 13 or 14 division-level taxa within the plant kingdom (Plantae).
In biological classification, extinct and living species of organisms are categorized into particular groups. Each taxonomic grouping, or taxon, is assigned a taxonomic rank and can be placed at a particular level in a systematic hierarchy, ideally reflecting evolutionary relationships. The major eight taxonomic ranks, starting from the individual organism, are species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, and domain. There also are intermediate minor rankings between these, such as subclass, subspecies, and superfamily.
Overview
Scientific classification or biological classification is how biologists group and categorize extinct and living species of organisms. These scientific classifications, or taxonomies, are frequently hierarchical in structure. Taxon is the name designating a particular taxonomic grouping of organisms. Mammals, for example, are a taxon of vertebrate animals. They comprise the class Mammalia.
Taxonomic rank (rank, category, taxonomic category) is an abstract term used to indicate the level of a taxon in the taxonomic hierarchy. Taxa ranked at a particular taxonomic rank are groupings of organisms at the same classification level. The eight major categories used to rank organisms are species, genus, family, order, class, phylum or division, kingdom, and domain. (In biology, the term "division" traditionally has been used as the equivalent of "phylum" but for classifications in the plant or the fungal kingdom.) A simple mnemonic phrase to remember the sequence of taxonomic levels is "Dignified Kings Play Chess On Fine Green Silk." Others include "King Philip's Class Orders the Family Genius to Speak," or Do Koalas Prefer Chocolate Or Fruit, Generally Speaking?
A prefix is used to indicate a ranking of lesser importance. The prefix super- indicates a rank above, the prefix sub- indicates a rank below. In zoology, the prefix infra- indicates a rank below sub-. For instance:
- Superclass
- Class
- Subclass
- Infraclass
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature defines rank, in the taxonomic sense, as:
| “ | The level, for nomenclatural purposes, of a taxon in a taxonomic hierarchy (e.g. all families are for nomenclatural purposes at the same rank, which lies between superfamily and subfamily). The ranks of the family group, the genus group, and the species group at which nominal taxa may be established are stated in Articles 10.3, 10.4, 35.1, 42.1 and 45.1. | ” |
—International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (1999) Whereas modern classification has its roots in the system of Carolus Linnaeus, who grouped species according to shared physical characteristics, modern groupings have been revised since Linnaeus to reflect the Darwinian principle of common descent. A distinction is to be made between taxa/taxonomy and classification/systematics. The former refers to biological names and the rules of naming. The latter refers to rank ordering of taxa according to presumptive evolutionary (phylogenetic) relationships. Rank is relative, and restricted to a particular systematic schema. For example, liverworts have been grouped, in various systems of classification, as a family, order, class, or division (phylum). Crustaceans (Crustacea) are variously grouped as phylum, subphylum, superclass, and class. The use of a narrow set of ranks is challenged by users of cladistics. For example, the mere 10 ranks traditionally used between animal families (governed by the ICZN) and animal phyla (usually the highest relevant rank in taxonomic work) often cannot adequately represent the evolutionary history as more about a lineage's phylogeny becomes known. In addition, the class rank is quite often not an evolutionary but a phenetical and paraphyletic group and as opposed to those ranks governed by the ICZN, can usually not be made monophyletic by exchanging the taxa contained therein. This has given rise to phylogenetic taxonomy and the ongoing development of the PhyloCode, which is to govern the application of taxa to clades. Main taxonomic ranksCarl Linnaeus devised Linnaean taxonomy using a ranking scale: kingdom, class, order, genus, species, and variety. Today, nomenclature is regulated by the Nomenclature Codes, which allow names divided into exactly defined ranks. Despite this there are slightly different ranks for zoology and for botany. In zoology and in botanical nomenclature, a taxon is usually assigned to a taxonomic rank in a hierarchy. The basic rank is that of species, and if an organism is named it most often will receive a species name. The next most important rank is that of genus: if an organism is given a species name it will at the same time be assigned to a genus, as the genus name is part of the species name. The third-most important rank, although it was not used by Linnaeus, is that of family. A binomial is a two-word name which is used to describe a particular species. For example, the binomial name for a human is Homo sapiens. This is italicised when typing, and underlined when writing. The first word refers to the genus, which is a broad grouping of closely related species, and is capitalized. The second word, in lower case, always indicates the species to which the organism is assigned within its genus. Ranks in zoologyThere are definitions of the following taxonomic ranks in the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature: superfamily, family, subfamily, tribe, subtribe, genus, subgenus, species, subspecies. The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature divides names into "family-group names", "genus-group names," and "species-group names". The Code explicitly mentions: - - - superfamily family - - - subfamily - - - tribe - - - subtribe genus - - - subgenus species - - - subspecies The rules in the Code apply to the ranks of superfamily to subspecies, and only to some extent to those above the rank of superfamily. In the "genus group" and "species group," no further ranks are allowed. Among zoologists, additional ranks such as species group, species subgroup, species complex, and superspecies are sometimes used for convenience as extra, but unofficial, ranks between the subgenus and species levels in taxa with many species (e.g. the genus Drosophila). Ranks of taxa at lower levels may be denoted in their groups by adding the prefix "infra," meaning lower, to the rank. For example infraspecies or infrasubspecies. Infraspecific taxa then include all divisions of the species into subspecies or lower taxa. Note:
Ranks in botanyThere are definitions of the following taxonomic ranks in the International Code of Botanical Nomenclature: kingdom (regnum), subregnum, division or phylum (divisio, phylum), subdivisio or subphylum, class (classis), subclassis, order (ordo), subordo, family (familia), subfamilia, tribe (tribus), subtribus, genus (genus), subgenus, section (sectio), subsectio, series (series), subseries, species (species), subspecies, variety (varietas), subvarietas, form (forma), subforma. There are definitions of following taxonomic ranks in International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants: cultivar group, cultivar. According to Art 3.1 of the ICBN the most important ranks of taxa are: kingdom, division or phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. According to Art 4.1 the secondary ranks of taxa are tribe, section, series, variety and form. There is an indeterminate number of ranks. The ICBN explicitly mentions: primary ranks - - - secondary ranks - - - - - - - further ranks kingdom (regnum) - - - - - - - subregnum division or phylum (divisio, phylum) - - - - - - - subdivisio or subphylum class (classis) - - - - - - - subclassis order (ordo) - - - - - - - subordo family (familia) - - - - - - - subfamilia - - - tribe (tribus) - - - - - - - subtribus genus (genus) - - - - - - - subgenus - - - section (sectio) - - - - - - - subsectio - - - series (series) - - - - - - - subseries species (species) - - - - - - - subspecies - - - variety (varietas) - - - - - - - subvarietas - - - form (forma) - - - - - - - subforma The rules in the ICBN apply primarily to the ranks of family and below, and only to some extent to those above the rank of family. Also see descriptive botanical names. Of the botanical names used by Linnaeus only names of genera, species and varieties are still used. Taxa at the rank of genus and above get a botanical name in one part (unitary name); those at the rank of species and above (but below genus) get a botanical name in two parts (binary name); all taxa below the rank of species get a botanical name in three parts (ternary name). For hybrids getting a hybrid name, the same ranks apply, preceded by "notho", with nothogenus as the highest permitted rank. ExamplesThe usual classifications of five species follow: the fruit fly so familiar in genetics laboratories (Drosophila melanogaster), humans (Homo sapiens), the peas used by Gregor Mendel in his discovery of genetics (Pisum sativum), the "fly agaric" mushroom Amanita muscaria, and the bacterium Escherichia coli. The eight major ranks are given in bold; a selection of minor ranks are given as well. {, E. coli | ||
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.